Electrochemical Noise Analysis in Passivated Martensitic Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steels in H2SO4 and NaCl Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Microstructure of Martensitic PHSS
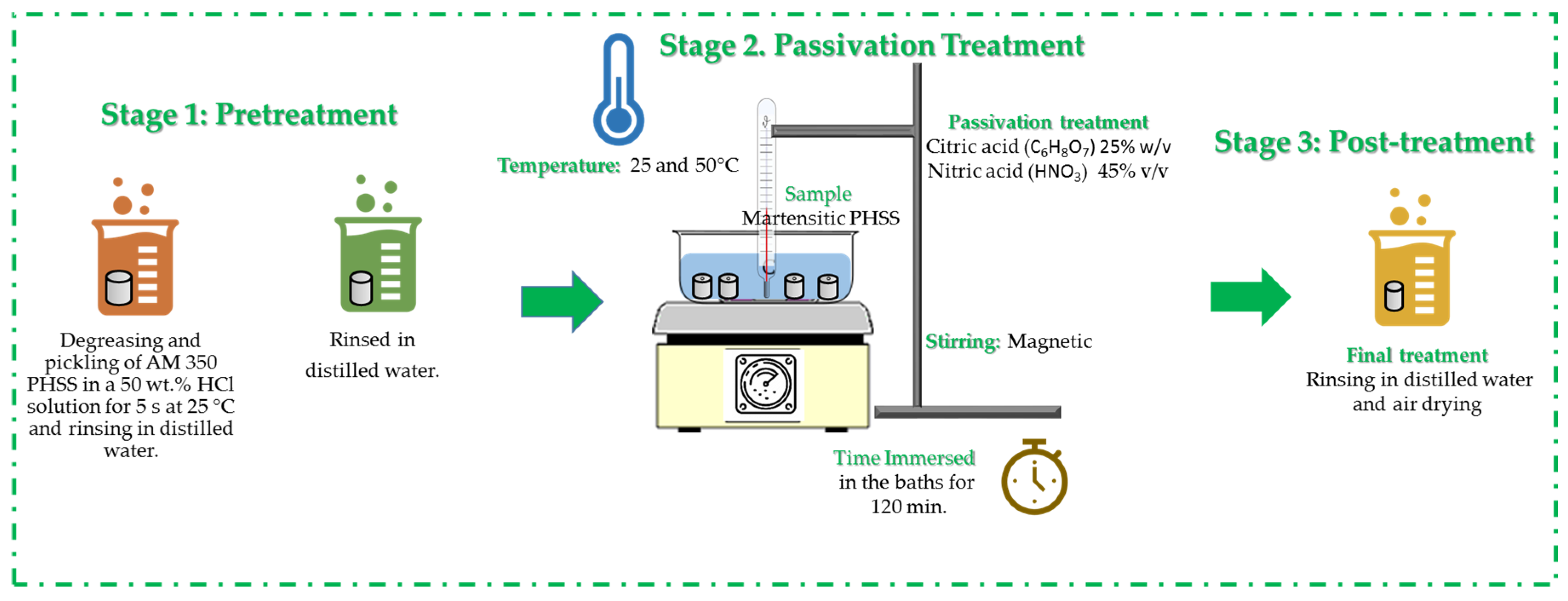
2.3. Chemical Passivation Treatment
2.4. Corrosion Measurement
2.5. Microstructural Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
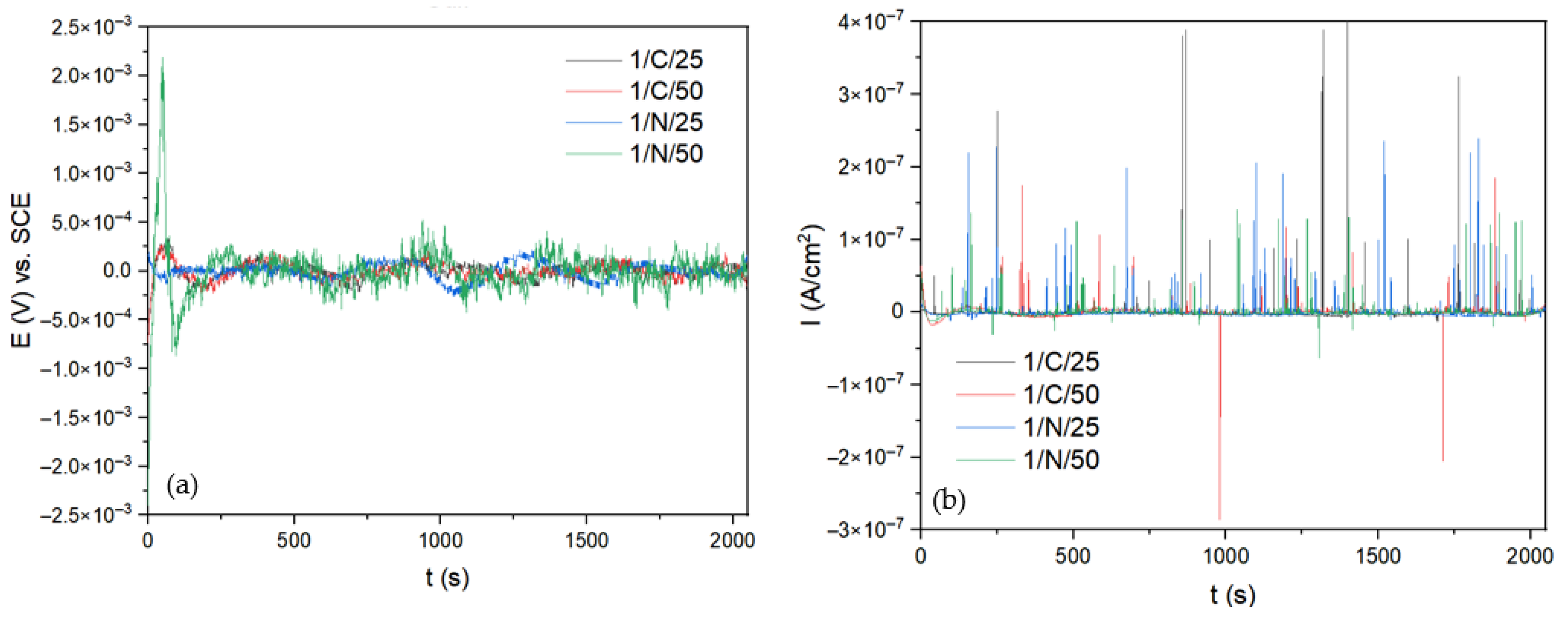
3.1. Corrosion Measurements
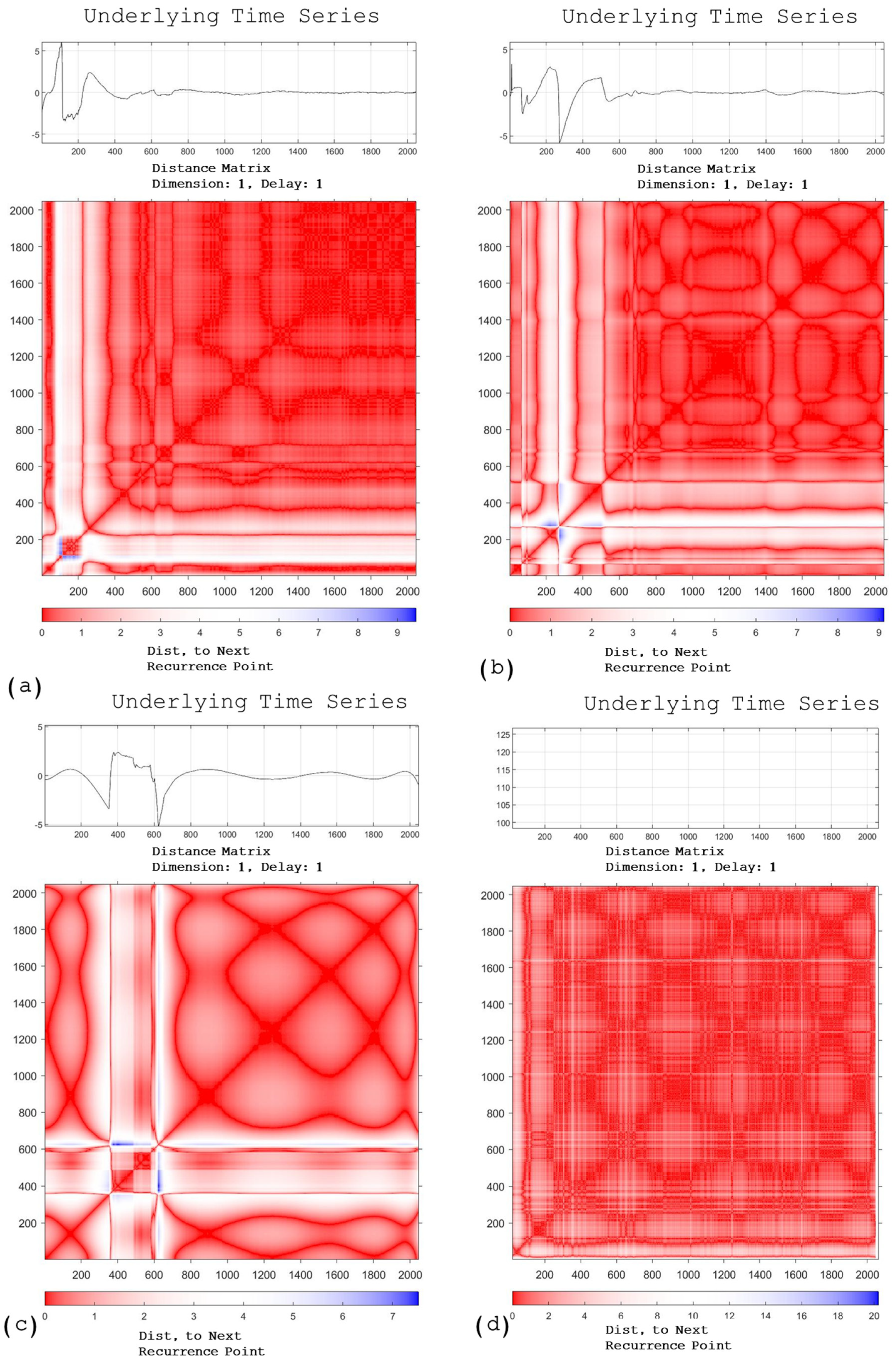
Electrochemical Noise
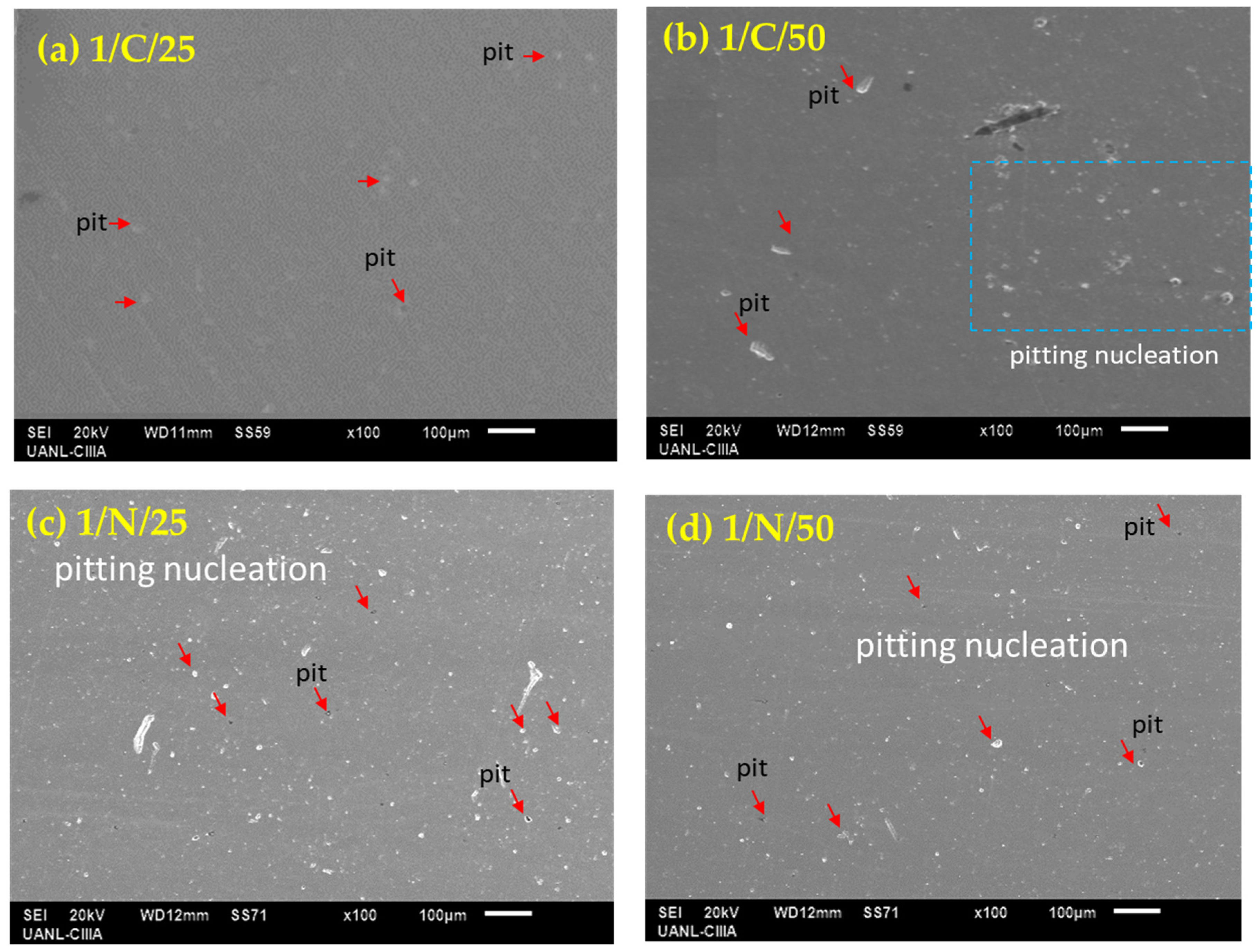
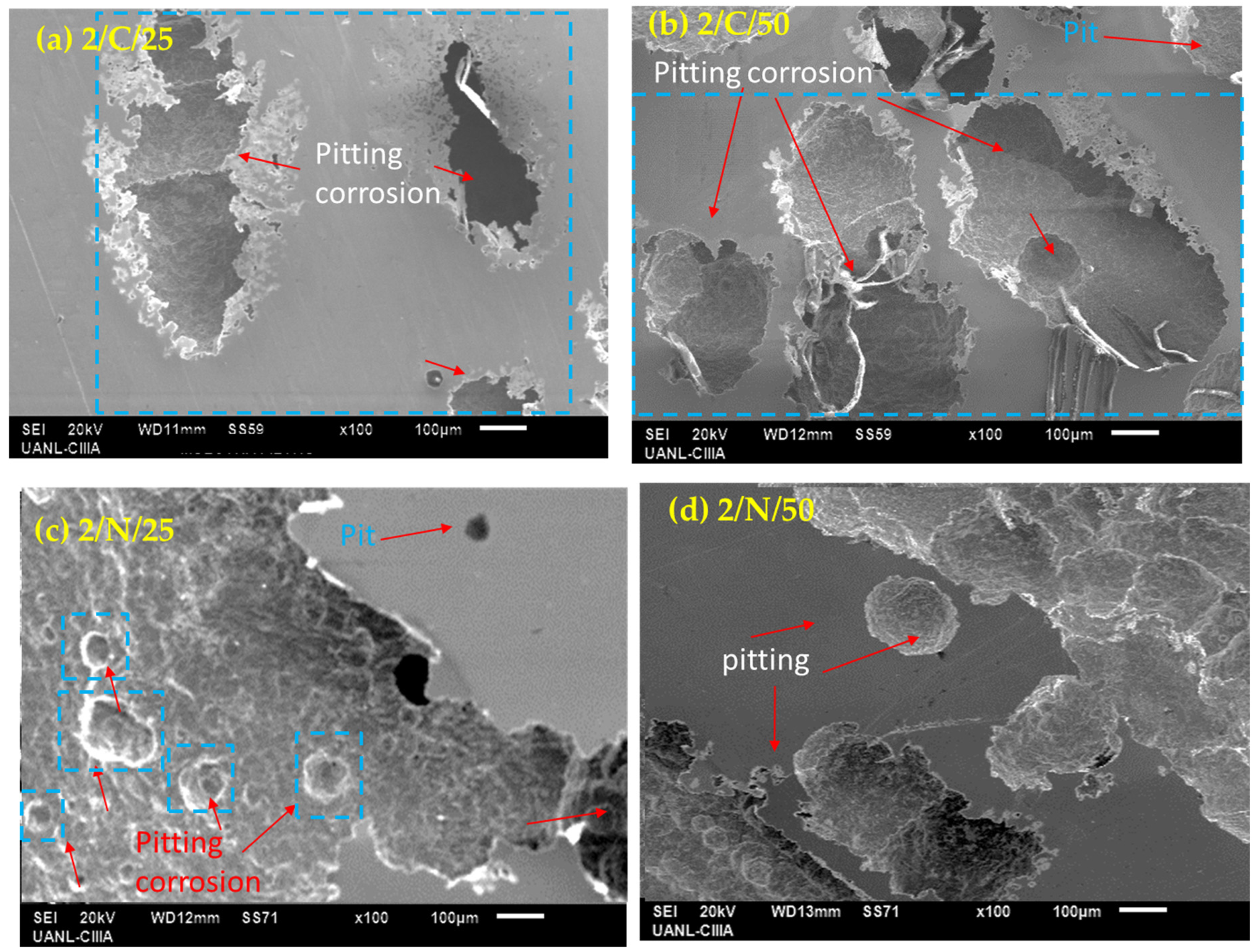
3.2. SEM Characterization of PHSS After Electrochemical Corrosion Measurements
4. Conclusions
- The electrochemical noise results indicated that the martensitic precipitation-hardening stainless steel samples exposed to H2SO4 presented uniform pitting corrosion attacks.
- The samples exposed to NaCl presented pitting corrosion attacks. It is due to the susceptibility of PHSS to pitting generated by Cl− ions in preference zones due to the presence of two phases.
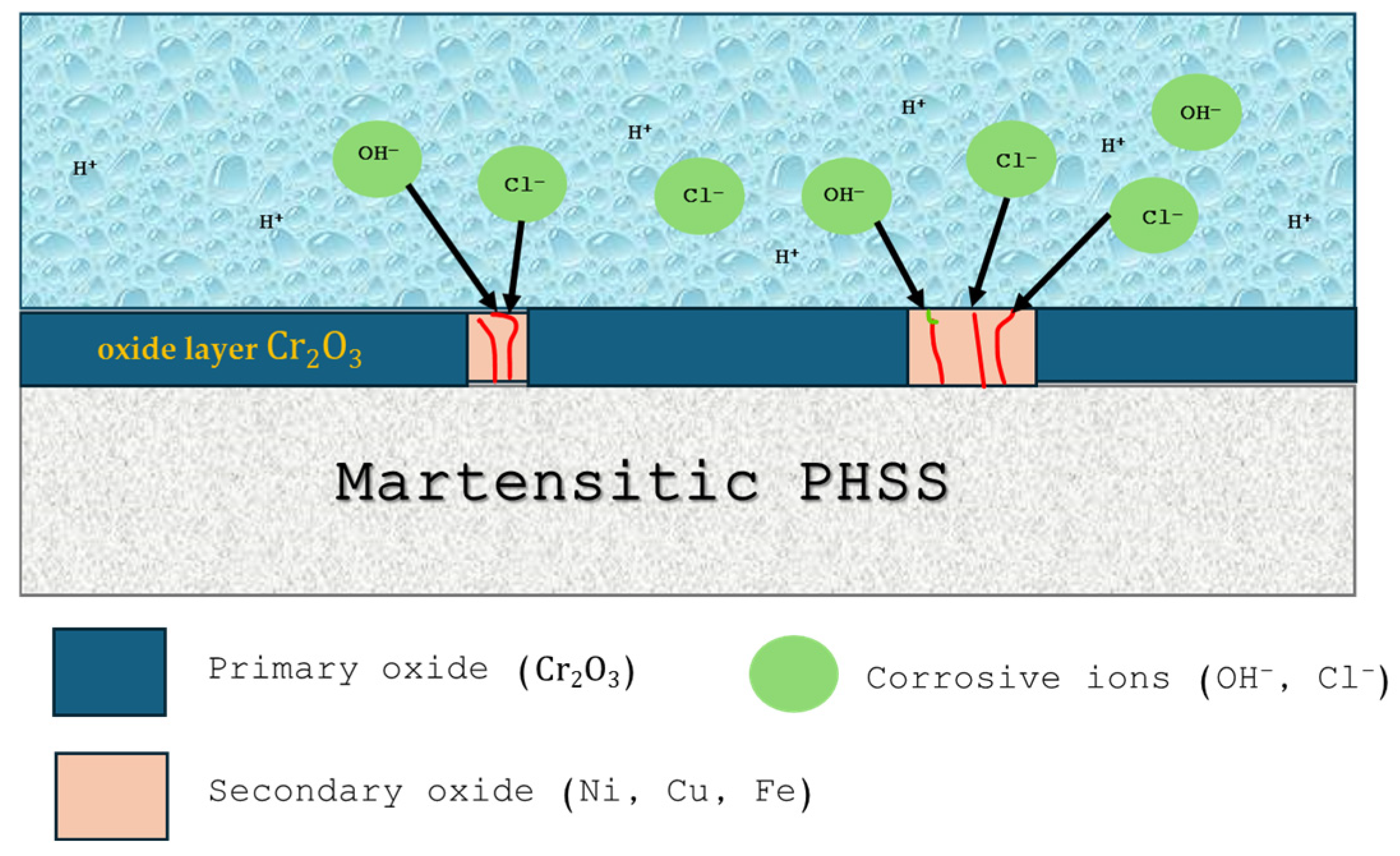
- The passivation of martensitic PHSS samples increased the corrosion resistance; however, the susceptibility to localized corrosion increased for passivated samples.
- Localized attacks occurred due to secondary oxide formation that facilitated surface differences, attacking in preference zones.
- Surface morphologies obtained by SEM indicate that the passivated martensitic precipitation-hardening stainless steel samples exhibit pitting corrosion, which is more intense when the steels are exposed to NaCl solution due to the aggressivity of Cl− ion.
- The best performance of passivation in nitric acid at 50 °C relates to the exothermic properties of the solution.
- The citric acid passivation process on stainless steels could be an environmentally friendly alternative to the frequently used nitric acid passivation process; however, it is necessary to increase research. The corrosion resistance increases, but the efficiency in comparison to nitric acid is lower.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mouritz, P.A. Introduction to Aerospace Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Villegas-Tovar, J.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Lara-Banda, M.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Baltazar-Zamora, M.A.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Olguin-Coca, J.; Estupiñan-Lopez, F.; Almeraya-Calderón, F. Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Passivated Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steels for Aerospace Applications. Metals 2023, 13, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gialanella, S.; Malandruccolo, A. Aerospace Alloys. In Topics in Mining, Metallurgy and Materials Engineering; Bergmann, C.P., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISSN 2364-3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaniego-Gámez, O.; Almeraya-Calderón, F.; Chacón-Nava, J.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Flores-De los Rios, J.P.; Jáquez-Muñoz, J.M.; Delgado, A.D.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C. Corrosion Behavior of Passivated CUSTOM450 and AM350 Stainless Steels For Aeronautical Applications. Metals 2022, 12, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, H.M. The History of Stainless Steel; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, J.C. Material selection for aeronautical structural application. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mat. 2008, 20, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Farrar, J. The Alloy Tree—A Guide to Low-Alloy Steels, Stainless Steels and Nickel-Base Alloys; Woodhead Publishing Limited and CRC Press: Sawston, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Almeraya-Calderón, F.; Samaniego-Gámez, O.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Olguín-Coca, J.; Jáquez-Muñoz, J.M.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; Flores-De los Rios, J.P.; Bautista-Margulis, R.G.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C. Corrosion Behavior of Passivated Martensitic and Semi-Austenitic Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASM International. Introduction to Stainless Steel. In Alloy Digest Sourcebook—Stainless Steel, 3rd ed.; David, J.R., Davis & Associates, Eds.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2000; pp. 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Villafañe, A.; Almeraya-Calderón, M.F.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J.G.; Porcayo-Calderón, J. High-Temperature Degradation and Protection of Ferritic and Austenitic Steels in Steam Generators. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 1998, 7, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Shironita, S.; Souma, K.; Umeda, M. Effect of chromium content on the corrosion resistance of ferritic stainless steels in sulfuric acid solution. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, S. Corrosion Control in the Aerospace Industry; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, P.; Kolody, M. Alternative to Nitric Acid Passivation of Stainless Steel Alloys. In Technology Evaluation for Environmental Risk Mitigation Compendium, Proceedings of the NASA Technology Evaluation for Environmental Risk Mitigation Principal Center (TEERM); Department of Defense (DoD) and NASA, Kennedy Space Center: Merritt Island, FL, USA, 13 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Samaniego-Gámez, O.; Jáquez-Muñoz, J.M.; Baltazar-Zamora, M.A.; Landa-Ruiz, L.; Lira-Martínez, A.; los Rios, J.P.F.-D.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; Estupinán-López, F.; Almeraya-Calderon, F. Frequency-Time Domain Analysis of Electrochemical Noise of Passivated AM350 Stainless Steel for Aeronautical Applications. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 220950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM A967-17; Standard Specification for Chemical Passivation Treatments for Stainless Steel Parts. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999.
- Outokumpu. Handbook of Stainless Steel; Outokumpu Oyj: Helsinki, Finland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.K.; Tsai, W.J. Corrosion fatigue behaviour of a 15Cr-6Ni precipitation-hardening stainless steel in different tempers. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2000, 23, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollapour, Y.; Poursaeidi, E. Experimental and numerical analysis of Pitting Corrosion in CUSTOM 450 Stainless Steel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 128, 105589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.K.; Chu, C.C. Mean stress effects on low-cycle fatigue for a precipitation-hardening martensitic stainless steel in different tempers. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2000, 23, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeraya-Calderon, F.; Villegas-Tovar, M.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Lara-Banda, M.; Baltazar-Zamora, M.A.; Santiago-Hurtado, G.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Lopez-Leon, L.D.; Jaquez-Muñoz, J.M.; Estupiñán-López, F.; et al. Use of Electrochemical Noise for the Study of Corrosion by Passivated CUSTOM 450 and AM 350 Stainless Steels. Metals 2024, 14, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasensky, D.; Reali, J.; Larson, C.; Carl, C. Citric acid passivation of stainless steel. In Proceedings of the Aircraft Airworthiness and Sustainment Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.; Feng, S.; Ding, C.; Gu, M.; Yu, P.; Huang, M. A Sequential Dual-Passivation Strategy for Designing Stainless Steel Used above Water Oxidation. Mater. Today 2023, 70, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, K.; Kim, D.I.; Chung, W.; Shin, B.H. The Effect of Surface Roughness on Re-Passivation and Pitting Corrosion of Super Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S 32760. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2023, 18, 100351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z. The Influence of Cr and Mo on the Formation of the Passivation Film on the Surface of Ferritic Stainless Steel. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 108221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.P.; Chen, X.L.; Ye, K.Q.; Huang, M.X. Counterintuitive Passivation Role of Manganese in Stainless Steel under High Potential in Neutral NaCl Solution. Corros. Sci. 2025, 246, 112756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukkum, V.B.; Christudasjustus, J.; Darwish, A.A.; Storck, S.M.; Gupta, R.K. Enhanced Corrosion Resistance of Additively Manufactured Stainless Steel by Modification of Feedstock. npj Mater. Degrad. 2022, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.H.; Park, J.; Jeon, J.; Heo, S.b.o.; Chung, W. Effect of Cooling Rate after Heat Treatment on Pitting Corrosion of Super Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S 32750. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 2018, 65, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, C. Effect of Heat Input and Post Weld Heat Treatment on the Texture, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser Beam Welded AISI 317L Austenitic Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 855, 143966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, C.; Dong, C.; Cui, Z.; Xiao, K.; Yu, Q.; Li, X. A comparative study of primary and secondary passive films formed on AM355 stainless steel in 0.1 M NaOH. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojinov, M.; Betova, I.; Fabricius, G.; Laitinen, T.; Saario, T. The stability of the passive state of iron–chromium alloys in sulphuric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 1999, 41, 1557–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Jaquez, R.E.; Buelna-Rodríguez, J.E.; Barrios-Durstewitz, C.P.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Almeraya-Calderón, F. Corrosion of modified concrete with sugar cane bagasse ash. Int. J. Corros. 2012, 2012, 451864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeraya-Calderón, F.; Villegas-Tovar, M.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Lara-Banda, M.; Baltazar-Zamora, M.A.; Landa-Ruiz, L.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Jaquez-Muñoz, J.M.; Estupiñan-Lopez, F.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; et al. Localized Corrosion of CUSTOM 450 and AM 350 Stainless Steels in H2SO4 and NaCl Solutions. Materials 2025, 18, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alireza, R.; Abdolreza, F.; Avni, B.; Alireza, S.; Mikhail, A.V.; Valbonë, M.; Zhong, X.; Samira, Y.; Richard, D. Novel sucrose derivative as a thermally stable inhibitor for mild steel corrosion in 15% HCl medium: An experimental and computational study. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, G.U.; Kamachi, M.S. Electrochemical Noise Analysis of Pitting Corrosion of Type 304L Stainless Steel. Corrosion 2014, 70, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Banda, M.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Zambrano-Robledo, P.; Delgado-E, M.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Estupiñan-Lopez, F.; Chacón-Nava, J.; Almeraya-Calderón, F. Alternative to Nitric Acid Passivation of 15-5 and 17-4PH Stainless Steel Using Electrochemical Techniques. Materials 2020, 13, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragaglia, M.; Cherubini, V.; Cacciotti, I.; Rinaldi, M.; Mori, S.; Soltani, P.; Nanni, F.; Kaciulis, S.; Montesperelli, G. Citric Acid Aerospace Stainless Steel Passivation: A Green Approach. In Proceedings of the CEAS Aerospace Europe Conference 2015, Delft, The Netherlands, 7–11 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Marcelin, S.; Pébèrea, N.; Régnierb, S. Electrochemical characterisation of a martensitic stainless steel in a neutral chloride solution. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 87, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Taib Heakal, F.; Ghoneim, A.; Fekry, A. Stability of spontaneous passive films on high strength Mo-containing stainless steels in aqueous solutions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2007, 37, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Taib Heakal, F.; Ameer, M.A.; El-Aziz, A.M.; Fekry, A.M. Electrochemical behavior of Mo-containing austenitic stainless steel in buffer solutions. Mater. Sci. Eng. Tecnol. 2004, 35, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakić, B.; Ćubela, D. Review of the Development of Research in the Design of Semi Austenitic Stainless Steel 17-7PH. In Proceedings of the 17th International Research/Expert Conference “Trends in the Development of Machinery and Associated Technology” TMT 2013, Istanbul, Turkey, 10–11 September 2013; pp. 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, J.; Wei, D.Y. The low cycle fatigue behavior of the controlled transformation stainless steel alloy AM355 at 121, 204 and 315 °C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 475, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ma, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Ren, J.; Jiang, Z.; Fan, G.; Han, P. Effects of B and Ce Grain Boundary Segregation on Precipitates in Super Austenitic Stainless Steel. Metals 2023, 13, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Bai, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Han, P. Effect of boron on dissolution and repairing behavior of passive film on S31254 super-austenitic stainless steel immersed in H2SO4 solution. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2022, 29, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, H.; George, G.; Khatak, H.S. Failure analysis of an AM 350 steel bellows. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2001, 8, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaquez-Muñoz, J.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Lira-Martinez, A.; Zambrano-Robledo, P.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Samaniego-Gamez, O.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Olguin-Coca, J.; Estupiñan-Lopez, F.; Almeraya-Calderon, F. Susceptibility to pitting corrosion of Ti-CP2, Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo, and Ti-6Al-4V alloys for aeronautical applications. Metals 2021, 11, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.S.; Ramanujam, R.; Vignesh, M.; Rohith, D.; Manoj, V.; Sankar, P.H. Comparative machining studies on custom 450 alloy with TiCN, TiAlN coated and uncoated carbide tools using Taguchi-Fuzzy logic approach. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 066411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jáquez-Muñoz, J.M.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Méndez-Ramírez, C.T.; Baltazar-Zamora, M.Á.; Estupinán-López, F.; Bautista-Margulis, R.G.; Cuevas-Rodríguez, J.; Flores-De los Rios, J.P.; Almeraya-Calderón, F. Corrosion of Titanium Alloys Anodized Using Electrochemical Techniques. Metals 2023, 13, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custom 450® Stainless Steel. Available online: https://www.ulbrich.com/uploads/data-sheets/Custom-450-Stainless-Steel-Wire-UNS-S45000.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- ASTM G199-90; Standard Guide for Electrochemical Noise Measurement. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1995.
- ASTM E3-95; Standard Practice for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1995.
- Gallego-Juárez, J.A.; Graff, K.F. Power Ultrasonics-Applications of High-Intensity Ultrasound; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- The British Stainless Steel Association. 2022. Available online: https://bssa.org.uk/bssa_articles/calculation-of-pren/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Lara-Banda, M.; Ortiz, D.; Gaoan-Tiburcio, C.; Zambrano, P.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.C.; Almeraya- Calderon, F. Citric Acid Passivation of 15-5PH and 17-4PH Stainless Steel Used in the Aeronautical Industry. In International Materials Research Congress; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM A380-17; Standard Practice for Cleaning, Descaling and Passivation of Stainless-Steel Parts, Equipment, and Systems. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999.
- SAE AMS 2700F; Passivation of Corrosion Resistant Steels. Aerospace Material Specification. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018.
- ASTM G199-09; Standard Guide for Electrochemical Noise Measurement. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Cottis, R. Interpretation of Electrochemical Noise Data. Corrosion 2001, 57, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, B.; Tiburcio, C.G.; Bastidas, D.; Lara-Banda, M.; Samaniego, O.; Calderon, F.A. Electrochemical Evaluation of 15-5PH Stainless Steel Passivated in Citric Acid. ECS Trans. 2022, 106, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, D.C. Tutorial on Cyclic Potentiodynamic Polarization Technique. In Proceedings of the CORROSION 98, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–27 March 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, D.C. Practical Corrosion Prediction Using Electrochemical Techniques. In Uhlig’s Corrosion Handbook, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1129–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STP1277-EB; Electrochemical Noise Measurement for Corrosion Applications. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Sanchez-Amaya, J.M.; Cottis, R.A.; Botana, F.J. Shot Noise and Statistical Parameters for the Estimation of Corrosion Mechanisms. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 3280–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgoose, S.; Cottis, R.A. Electrochemical Impedance and Noise; NACE International: Houston, TX, USA, 2009; ISBN 1575900939. [Google Scholar]
- Galvan-Martinez, R.; Orozco-Cruz, R.; Torres-Sanchez, R.; Martinez, E.A. Corrosion Study of the X52 Steel Immersed in Seawater with a Corrosion Inhibitor Using a Rotating Cylinder Electrode. Mater. Corros. 2010, 61, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocci, U.; Huet, F. Noise Analysis Applied to Electrochemical Systems. Corrosion 1995, 51, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocci, U.; Kruger, J. Studies of Passive Film Breakdown by Detection and Analysis of Electrochemical Noise. Surf. Sci. 1980, 101, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zanki, I.A.; Gill, J.S.; Dawson, J.L. Electrochemical Noise Measurements on Mild Steel in 0.5 M Sulphuric Acid. Mater. Sci. Forum 1986, 8, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eden, D.A.; Rothwell, A.N. Electrochemical Noise Data: Analysis, Interpretation and Presentation; NACE International: Houston, TX, USA, 1992; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bertocci, U.; Gabrielli, C.; Huet, F.; Keddam, M.; Rousseau, P. Noise Resistance Applied to Corrosion Measurements: II. Experimental Tests. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eden, D.A.; John, D.G.; Dawson, J.L. International Patent WO 87/07022, 19 November 1987.
- Mansfeld, F.; Sun, Z.; Hsu, C.H.; Nagiub, A. Concerning Trend Removal in Electrochemical Noise Measurements. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Mansfeld, F. Analysis of Electrochemical Noise Data for a Passive System in the Frequency Domain. Corros. Sci. 1998, 40, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homborg, A.M.; Tinga, T.; Van Westing, E.P.M.; Zhang, X.; Ferrari, G.M.; De Wit, J.H.W.; Mol, J.M.C. A Critical Appraisal of the Interpretation of Electrochemical Noise for Corrosion Studies. Corrosion 2014, 70, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Cao, F.; Liao, X.; Liu, W.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Cao, C. Study of Pitting Corrosion on Mild Steel during Wet–Dry Cycles by Electrochemical Noise Analysis Based on Chaos Theory. Corros. Sci. 2013, 66, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfeld, F.; Sun, Z. Technical Note: Localization Index Obtained from Electrochemical Noise Analysis. Corrosion 1999, 55, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.A.; Eden, D.A. Assessment of Corrosion. U.S. Patent US9264824B1, 24 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Eden, D.A. Electrochemical Noise—The First Two Octaves. In Proceedings of the NACE—International Corrosion Conference Series; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, D.L. Electrochemical Noise Measurement: The definitive In-Situ Technique for Corrosion Applications? In Electrochemical Noise Measurement for Corrosion Applications STP 1277; Kearns, J.R., Scully, J.R., Roberge, P.R., Reirchert, D.L., Dawson, L., Eds.; ASTM International, Materials Park: Russell, OH, USA, 1996; pp. 3–39. [Google Scholar]
- Almeraya-Calderón, F.; Jáquez-Muñoz, J.M.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Olgui-Coca, J.; Lopez-Leon, L.D.; Estupiñán-López, F.; Lira-Martínez, A.; Gaona Tiburcio, C. Corrosion Resistance of Titanium Alloys Anodized in Alkaline Solutions. Metals 2023, 13, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Guan, L.; Li, Y.; Zhong, J.; Liao, L.; Xia, D.; Huang, J. Understanding the Galvanic Corrosion of Cu-Ni Alloy/2205 DSS Couple Using Electrochemical Noise and Microelectrochemical Studies. Corros. Sci. 2023, 224, 111512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojinov, M.; Fabricius, G.; Kinnunen, P.; Laitinen, T.; Mäkelä, K.; Saario, T.; Sundholm, G. The mechanism of transpassive dissolution of Ni–Cr alloys in sulphate solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 2791–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, X.; Han, E.H. Electrochemical properties and growth mechanism of passive films on Alloy 690 in high-temperature alkaline environments. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3444–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calinski, C.; Strehblow, H.H. ISS depth profiles of the passive layer on Fe/Cr alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1989, 36, 1328–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.-H.; Song, S.; Behnamian, Y.; Hu, W.; Cheng, Y.F.; Luo, J.-L.; Huet, F. Review—Electrochemical Noise Applied in Corrosion Science: Theoretical and Mathematical Models towards Quantitative Analysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 081507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah-alhosseini, A.; Taheri Shoja, S.; Heydari Zebardast, B.; Mohamadian Samim, P. An Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopic Study of the Passive State on AISI 304 Stainless Steel. Int. J. Electrochem. 2011, 2011, 152143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, B.E.; Vilche, R.J. Investigation of passive layers on iron and iron-chromium alloys by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 1993, 38, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wan, S.; Song, L.F.; Liao, B.K.; Guo, X.P. Modified nano-lignin as a novel biomass-derived corrosion inhibitor for enhanced corrosion resistance of carbon steel. Corrs. Sci. 2024, 227, 111705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Arteaga, C.; Porcayo-Calderón, J. Electrochemical noise analysis in the frequency domain and determination of corrosion rates for SS-304 stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 435–436, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Aparicio, B.; Martínez-Bastidas, D.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Martin, U.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; Almeraya-Calderón, F. Localized corrosion of 15–5 PH and 17–4 PH stainless steel in NaCl solution. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2023, 11, 2993–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Du, L.; Pei, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J. Citric Acid Enhances the Ignition and Combustion Performance of Aluminum: Coating and Etching. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 689, 133628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ochoa, E.; Maldonado, P.; Corvo, F. Non-linear Dynamics of Potassium Iodide Adsorption on the Interface of Carbon Steel in Acidic Medium. Mater. Corros. 2020, 71, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwan, N.; Webber, C.L.; Macau, E.E.N.; Viana, R.L. Introduction to Focus Issue: Recurrence Quantification Analysis for Understanding Complex Systems. Chaos 2018, 28, 85601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanis, D.; Spanoudaki, D.; Gkili, C.; Sazou, D. Using Recurrence Plots for the Analysis of the Non-linear Dynamical Response of Iron Passivation-Corrosion Processes. Chaos 2018, 28, 085708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ramos, C.; Olguin-Coca, J.; Lopez-Leon, L.D.; Gaona-Tiburcio, C.; Lara-Banda, M.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Castañeda-Robles, I.; Jaquez-Muñoz, J.M.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; et al. Electrochemical Noise Analysis Using Experimental Chaos Theory, Power Spectral Density and Hilbert–Huang Transform in Anodized Aluminum Alloys in Tartaric–Phosphoric–Sulfuric Acid Solutions. Metals 2023, 13, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünleitner, T.; Henning, A.; Bissolo, M.; Zengerle, M.; Gregoratti, L.; Amati, M.; Zeller, P.; Eichhorn, J.; Stier, A.V.; Holleitner, A.W.; et al. Real-Time Investigation of Sulfur Vacancy Generation and Passivation in Monolayer Molybdenum Disulfide via in Situ X-Ray Photoelectron Spectromicroscopy. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 20364–20375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Di-Franco, F.; Seyeux, A.; Zanna, S.; Maurice, V.; Marcus, P. Passivation-Induced Physicochemical Alterations of the Native Surface Oxide Film on 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, C3376–C3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chong, K.; Qiao, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Guo, F.; Wu, D.; Zou, Y. Synthesis and Corrosion Behavior of Mo15Nb20Ta10Ti35V20 Refractory High Entropy Alloy. Mater. Des. 2023, 228, 111820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Peng, S.; Ma, C.; Yu, C.; Wu, D. Redox Behavior of Secondary Solid Iron Species and the Corresponding Effects on Hydroxyl Radical Generation during the Pyrite Oxidation Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 12635–12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Tong, H.; Li, Y.; Tan, Q.; Zhu, Y. Passivation Behavior of S136H Steel in Neutral Electrolytes Composed of NaClO3 and NaNO3 and Its Influence on Micro Electrochemical Machining Performance. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 29, 102762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.R.; Yao, J.T.; Dong, H.; Chen, Z.L.; Liu, X.G. Enhancing the Corrosion Resistance of Passivation Films via the Synergistic Effects of Graphene Oxide and Epoxy Resin. Coatings 2025, 15, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botona Pedemonte, F.J.; Aballe Villero, A.; Marcos Bárcena, M. Ruido Electroquímico. Métodos de Análisis; Septem Ediciones, S.L.: Oviedo, Spain, 2002; ISBN 84-95687-33-X. [Google Scholar]



| Element | Martensitic PHSS |
|---|---|
| Cr | 14.0–16.0 |
| Ni | 5.0–7.0 |
| Mo | 0.50–1.0 |
| Mn | 1.00 max |
| Cu | 1.25–1.75 |
| Nb | 0.35–0.75 |
| N | ≤0.1 |
| Si | 1.00 max |
| S | 0.030 |
| C | ≤0.05 |
| Fe | Balance |
| Electrolyte | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Passivation Baths | Nomenclature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2SO4 (1) | 25 | 120 | Citric Acid C6H8O7 (25% w/v) | 1/C/25 |
| 50 | 1/C/50 | |||
| 25 | 120 | Nitric Acid HNO3 (45% v/v) | 1/N/25 | |
| 50 | 1/N/50 | |||
| NaCl (2) | 25 | 120 | Citric Acid C6H8O7 (25% w/v) | 2/C/25 |
| 50 | 2/C/50 | |||
| 25 | 120 | Nitric Acid HNO3 (45% v/v) | 2/N/25 | |
| 50 | 2/N/50 |
| Corrosion Type | Potential | Current | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skewness | Kurtosis | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
| Uniform | <±1 | <3 | <±1 | <3 |
| Pitting | <−2 | >>3 | >±2 | >>3 |
| Transgranular (SCC) | 4 | 20 | −4 | 20 |
| Intergranular (SCC #1) | −6.6 | 18 to 114 | 1.5 to 3.2 | 6.4 to 15.6 |
| Intergranular (SCC #2) | −2 to −6 | 5 to 45 | 3 to 6 | 10 to 60 |
| Electrolyte | Parameters | Samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/C/25 | 1/C/50 | 1/N/25 | 1/N/50 | ||
| H2SO4 | Rn (Ω·cm2) | 4060 ± 9 | 7027 ± 5 | 4734 ± 4 | 22146 ± 6 |
| LI | 0.07 ± 0.002 | 0.1 ± 0.002 | 0.2 ± 0.002 | 0.4 ± 0.002 | |
| Kurtosis | 258 ± 3 | 240 ± 2 | 116 ± 2 | 83 ± 2 | |
| Skewness | 15 ± 2.1 | −3.7 ± 0.5 | 9.9 ± 0.6 | 8.1 ± 0.2 | |
| NaCl | Rn (Ω·cm2) | 716 ± 7 | 1716 ± 11 | 2102 ± 13 | 44985 ± 16 |
| LI | 0.06 ± 0.002 | 0.02 ± 0.001 | 0.1 ±0.001 | 0.06 ± 0.001 | |
| Kurtosis | 12 ± 0.01 | 13 ± 0.004 | 8 ± 0.005 | 49 ± 0.006 | |
| Skewness | —1.5 ± 0.04 | 1.1 ± 0.01 | —1.5 ± 0.05 | 3.2 ± 0.04 | |
| Electrolyte | Parameters | Samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/C/25 | 1/C/50 | 1/N/25 | 1/N/50 | ||
| H2SO4 | RR | 0.606 ± 0.006 | 0.211 ± 0.005 | 0.5 ± 0.01 | 0.295 ± 0.006 |
| Det | 0.937 ± 0.003 | 0.827 ± 0.002 | 0.871 ± 0.002 | 0.856 ± 0.008 | |
| L | 7.72 ± 0.004 | 4.682 ± 0.006 | 4.468 ± 0.005 | 4.204 ± 0.004 | |
| LAM | 0.962 ± 0.005 | 0.902 ± 0.002 | 0.932 ± 0.002 | 0.924 ± 0.005 | |
| TT | 12.5 ± 0.01 | 7.14 ± 0.01 | 6.85 ± 0.01 | 6.34 ± 0.01 | |
| NaCl | RR | 0.196 ± 0.002 | 0.255 ± 0.001 | 0.113 ± 0.004 | 0.096 ± 0.004 |
| Det | 0.992 ± 0.006 | 0.992 ± 0.008 | 0.986 ± 0.005 | 0.386 ± 0.004 | |
| L | 20.82 ± 0.05 | 20.46 ± 0.02 | 24.61 ± 0.03 | 2.33 ± 0.02 | |
| LAM | 0.996 ± 0.002 | 0.996 ± 0.001 | 0.993 ± 0.002 | 0.493 ± 0.004 | |
| TT | 30.905 ± 0.002 | 32.635 ± 0.002 | 31.327 ± 0.002 | 2.576 ± 0.002 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almeraya-Calderon, F.; Villegas-Tovar, M.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Méndez-Ramírez, C.T.; Baltazar-Zamora, M.A.; Olguín-Coca, J.; Lopez-Leon, L.D.; Santiago-Hurtado, G.; Almaguer-Cantu, V.; et al. Electrochemical Noise Analysis in Passivated Martensitic Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steels in H2SO4 and NaCl Solutions. Metals 2025, 15, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080837
Almeraya-Calderon F, Villegas-Tovar M, Maldonado-Bandala E, Nieves-Mendoza D, Méndez-Ramírez CT, Baltazar-Zamora MA, Olguín-Coca J, Lopez-Leon LD, Santiago-Hurtado G, Almaguer-Cantu V, et al. Electrochemical Noise Analysis in Passivated Martensitic Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steels in H2SO4 and NaCl Solutions. Metals. 2025; 15(8):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080837
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmeraya-Calderon, Facundo, Miguel Villegas-Tovar, Erick Maldonado-Bandala, Demetrio Nieves-Mendoza, Ce Tochtli Méndez-Ramírez, Miguel Angel Baltazar-Zamora, Javier Olguín-Coca, Luis Daimir Lopez-Leon, Griselda Santiago-Hurtado, Verónica Almaguer-Cantu, and et al. 2025. "Electrochemical Noise Analysis in Passivated Martensitic Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steels in H2SO4 and NaCl Solutions" Metals 15, no. 8: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080837
APA StyleAlmeraya-Calderon, F., Villegas-Tovar, M., Maldonado-Bandala, E., Nieves-Mendoza, D., Méndez-Ramírez, C. T., Baltazar-Zamora, M. A., Olguín-Coca, J., Lopez-Leon, L. D., Santiago-Hurtado, G., Almaguer-Cantu, V., Jaquez-Muñoz, J. M., & Gaona-Tiburcio, C. (2025). Electrochemical Noise Analysis in Passivated Martensitic Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steels in H2SO4 and NaCl Solutions. Metals, 15(8), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080837













