Abstract
Carboxylate (TCNF) and sulfonated (SCNC) cellulose nanofibers were synthesized and used as adsorbents for metallic cations in aqueous solutions: Na+ and Hg2+ (SCNC); Mg2+ and Hg2+ (TCNF). ICP-OES analysis of the liquid phase revealed metal removal efficiencies at room temperature of 89.3% (Hg2+) and 100% (Mg2+) for TCNF, 35.2% (Hg2+) and 63.3% (Na+) for SCNC after 3 h of contact. Interestingly, the nanofibers exhibited a distinct thermal degradation profile (characterized by two main events) compared to that of cellulose, suggesting that their nanostructured morphology and surface functionalization may enhance thermal instability. Additionally, the presence of metals at its surface notably altered the thermal degradation kinetics, as observed for mercury and magnesium in TCNF. Finally, the results for SCNC strongly suggest that the mechanism for thermal degradation can also change, as observed for mercury and sodium, expressed through the appearance of a new DTG peak located around 300 °C.
1. Introduction
Saline effluents mainly originate from industries such as agro-food, oil and gas, tannery, chlor-alkali, and pulp and paper, as well as from acid mine drainage and desalination plants. Food processing discharges brines rich in sodium chloride, while desalination brines often exceed 5 wt% salts and contain pre-treatment chemicals and heavy metals from equipment corrosion [1].
Mercury (Hg) is a persistent global pollutant cycling through the atomosphere, land, and water, with significant natural and anthropogenic sources. Key fluxes include oceanic evasion of elemental Hg (Hg) at 7950 kg/day, vegetation deposition via litterfall (2795–3370 kg/day), and inland inputs from artisanal gold mining (2410 kg/day), industrial discharges (603 kg/day), and terrestrial mobilization (465–820 kg/day) [2]. Mercury concentrations in contaminated groundwater can reach up to 94.4 µg/L, whereas industrial wastewaters, particularly from chlor-alkali industries, can have greater levels of up to 10 mg/L [3]. Sodium concentrations in industrial effluents and salty streams range from 20 to 80,000 mg/L [4,5].
Magnesium (Mg) is increasingly released by industry because of demand from electric vehicles, aluminum alloys, batteries, fertilizers, and water treatment. For example, China discharges 54,800 tons of magnesium chloride daily from fertilizer production, affecting the quality of water and soil. Magnesium concentrations in seawater can reach approximately 1300 mg/L, while in desalination brines, they may increase up to 4200 mg/L [6]. Magnesium concentrations have been reported to reach 183 mg/L in municipal drain water samples from Faisalabad, Pakistan [7], and up to 377.3 mg/L in raw effluent from the stainless steel industry [8]. Although Mg toxicity is low, high wastewater concentrations harm soil structure and plant growth. Recovery of Mg can mitigate impacts and provide valuable resources, highlighting the role of adsorption in the management of metal contaminants [9].
Adsorption has gained attention for its versatility and efficiency. Governed by mass transfer in liquids, adsorption in organic solids is used both to synthesize metal and nanostructured oxide catalysts [10,11] for green processes such as biodiesel production and dye degradation and as a sustainable method for removing metal ions from contaminated waters [12,13,14,15,16,17]. Adsorption can also be used as a way to remove metals from aqueous effluents [18,19,20,21] and, in this context, as a viable alternative compared to hydrometallurgical strategies for wastewater treatment.
As adsorption of metallic cations contained in aqueous solutions involves mass transfer from the liquid phase to the surface of solid particles in suspension and can involve the establishment of chemical bonds with the adsorbent surface molecular groups, it is desirable that the solid particles, for example, biomass fibers, have dimensions in the nanometric range, and also that the chemical structure of the molecules present in the particle surface is amenable to functionalization, or, in other words, substitution of specific groups by others to which the metals can build a much more stable interaction. In this context, it should be noted that nanocellulose is a type of nanomaterial, which is a good complement to both stated requirements.
Nanocellulose can be considered a future material, as it derives from both sustainable nature and the multiple applications of nanofibers, which range from additives in composites to wastewater treatment [22]. Sustainability is practiced, as nanocellulose can be produced practically from all types of lignocellulosic biomass raw material or residue, including sugarcane bagasse, seed shells, or wood. Among the several properties of nanocellulose that justify its application in different fields, its reduced particle size in the nanometric range and the possible insertion of specific organic units (functionalization) can both considerably enhance the desired physical or chemical property. Concerning adsorption, high selectivity and adsorptive capacities can be achieved through proper functionalization and size control [19].
The interaction of various types of nanocellulose with metal cations has been extensively investigated in literature, particularly in the context of adsorption processes [23,24,25,26,27,28]. Sulfonated cellulose nanocrystals (SCNC), prepared by acid hydrolysis with sulfuric acid, have been applied as adsorbents for different metal cations, Pb2+, Ni2+, and Cd2+, reaching an adsorption capacity of 9.4, 8.5, and 9.7 mg·g−1, respectively, in pH 6.5 [29]. For the same functionalization type, SCNC was also tested as an adsorbent for Ag+, Cu2+, and Fe3+. The adsorptive capacity reached values of 56, 2, and 6.5 mg·g−1, respectively [30]. Singh et al. 2014 [31] also employed SCNC which was funcionalized with succinic acid under the presence of ethylenediamine for both Cr (III) and Cr (VI) removal from aqueous solutions at room temperature. The metal recovery reached values equal to 94.8% for Cr (III) at pH 6.5 and 98.3% for Cr (VI) at pH 3.5. Recently, Teixeira et al. [32] investigated the use of SCNC nanofibers for Co2+ removal from aqueous solutions at pH 6.0. After 40 min of contact time, cobalt concentration in solution remained constant, suggesting that equilibrium was achieved, with metal recovery and adsorptive capacity respectively equal to 87% and 87 mg·g−1.
Cellulose nanofibers oxidized by TEMPO (TCNF) have already been used as adsorbents for Cr (III), Ni (II), Zn (II), and Cu (II) cations. The adsorptive capacity was equal to 0.167 g·g−1 for Cr (III), 1.104 g·g−1 for Ni (II), 0.065 g·g−1 for Zn (II), and 0.143 g·g−1 for Cu (II) [33]. Moreover, it was observed that TCNF thin films can act as adsorbent of radioactive complex cations, for example, UO22+, suggesting a significant correlation between the presence of carboxylate units, which is typical for TCNF nanofibers, and the observed adsorbent potential for metallic cations or complexes. In the case of UO22+ cations, the adsorptive capacity reached the expressive value of 167 mg·g−1 [34]. Teixeira et al. [32] also used TCNF nanofibers as adsorbents for Co2+ present in aqueous solutions, and a 90% metal removal was reported after 30 min of contact time at pH 6, as well as a maximum equilibrium adsorptive capacity of 90 mg·g−1.
The examples mentioned so far clearly illustrate the significant potential of both cellulose nanofibers (TCNF and SCNC) as adsorbents for metals cations or complexes present in aqueous solutions. The diversity of the metals already tested suggests that nanocellulose, once properly functionalized, could be viewed as a possible solution to treat real industrial waste. It is worthwhile to mention that after saturation (equilibrium) achievement under the desired operational conditions, the solid nanofibers containing the removed metals could possibly be employed as an additive for enhancing either mechanical or thermal properties of technologically relevant composites [35,36,37].
In this context, it is generally understood that the desired positive effect associated with the presence of the nanocellulose fibers can be limited by their thermal degradation, which should be evaluated prior to their incorporation into the final composite. In the case of cellulose, literature data strongly suggest a correlation between the raw material used and the thermal behavior observed. For example, in the case of cellulose extracted from maze straw and soybean hull, the peak for DTG for both celluloses were located around 300–400 °C and 270–390 °C, respectively, for heating rates varying between 5 and 20 °C·min−1 [35]. In addition to the raw material nature, nanofiber dimensions can appreciably influence the observed thermal behavior. For TCNF, its thermal degradation should start at 222 °C, whereas for cellulose, at 275 °C. Moreover, two thermal events should be observed in the case of nanocellulose, and only one for cellulose, as clearly evidenced by DTG data [36].
Additionally, the nanofibers’ stability has been demonstrated to be strongly dependent on the type and amount of functionalization, as observed for SCNC [37], suggesting that as the sulfonated groups’ concentration gets higher, the nanofibers’ stability shrinks, and the observed initial degradation temperature shifts to lower values. For example, in the case of bacterial cellulose (BC), thermal degradation under air atmosphere should start around 250 °C, while with the substitution of hydroxyl for sulfonated groups (66 mmol·g−1), thermal degradation starts around 150 °C. In both cases, the temperature varied between 110 and 500 °C, and the heating rate was fixed at 2 °C·min−1 [37].
On the topic of the effect of metal presence on nanofiber thermal behavior, only a few studies can be found in the literature, most of which are associated with the oxidation or thermal degradation of nanocomposites in which nanocellulose comprises the matrix, and noble metallic nanoparticles are embedded in it. Results so far point out that nanocellulose thermal behavior should strongly depend on the chemical nature of the nanoparticles present.
For palladium adsorbed in SCNC (Pd-SCNC), for example, the TGA profile did not change at all, with mass loss starting at 230 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C·min−1 and air atmosphere. In the end, the remaining mass of the Pd-SCNC sample is attributed to the residue of noble metals [38]. Moreover, Cirtiu et al. [39] investigated the thermal degradation of a nanocellulose matrix nanocomposite containing Pd nanoparticles and concluded that the presence of the nanoparticle did not change the thermal degradation profile, which was measured under a heating rate of 10 °C·min−1 and N2) atmosphere.
In the case of the Ag and Au nanoparticle presence over a SCNC matrix, both the initial degradation temperature and the thermal events observed by mass loss measurements are different from the thermal behavior of the pure nanofibers. Both metal-containing samples showed an initial degradation temperature around 110 °C, which was much lower than that of the pure SCNC sample, 220 °C. Also, the presence of metal appears to have a strong influence over the degradation mechanism, as three main thermal events can be attributed to Au-SCNC and Ag-SCNC, whereas in the case of pure SCNC, there are only two. The last thermal event of all samples appears to be unaffected by the presence of metallic particles [40].
The purpose of the present article is to contribute knowledge on both the use of two nanocelluloses types (SCNC and TCNF) as adsorbents for cations contained in aqueous solutions, to which, till the present date, no data are available in literature (Na+ and Hg2+ for SCNC; Mg2+ and Hg2+ for TCNF). In addition, the effect of the presence of metal on the nanofibers’ thermal behavior is explored, a topic that, despite its technological implications, is also very poorly covered in literature. Moreover, results obtained are of significant technological value, reinforcing the potential use of nanocellulose suspensions as an alternative strategy for removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. They also show the significant impact that the metallic cation presence can have on the observed thermal behavior.
Considering the application of nanocellulose as an adsorbent for effluent treatment and, subsequently, its potential use as an additive in composites, the present study addresses a critical gap in the literature by investigating the thermal degradation behavior of nanocellulose (TCNF and SCNC) following the adsorption of selected metal cations such as Mg2+, Hg2+, and Na+. These cations were selected due to their relevance to water potability, particularly with respect to toxicity, salinity, and hardness. This work distinctively examines the influence of adsorbed metallic species over the thermal stability of nanocellulose, a topic of considerable technological importance but poorly explored in scientific literature. The present findings provide meaningful information on the potential use of nanocellulose suspensions as an effective and sustainable strategy for the removal of heavy metals from industrial effluents, while also elucidating the significant impact of metal presence on the thermal properties of the nanofibers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of SCNC and TCNF
In this study, two types of nanocellulose were prepared: SCNC and TCNF. SCNC was obtained via acid hydrolysis using an aqueous H2SO4 solution, whereas TCNF was synthesized using an aqueous oxidizing solution containing NaOCl, NaOH, and the TEMPO catalyst. In both cases, a high-purity cellulose sample (99%, Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) served as the raw material. Detailed synthesis procedures are described by Teixeira et al. [32]. Prior to FT-IR characterization, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and metal adsorption the synthesized nanocelulloses were thoroughly washed with deionized water and centrifuged four times (15 min at 5800 rpm).
2.2. Adsorption Tests
For both nanocellulose suspensions, the pH was previously adjusted to 6.0 ± 0.5, where the surface charge of the fiber can reach a maximum negative value [32], thus contributing to the effectiveness of cation adsorption. The system (nanofibers suspension together with the cationic solution), comprising a total volume of 100 mL, was continuously stirred at 150 rpm at room temperature (CIENTEC CT-712RNT, São Paulo, Brazil). After a contact time of 3 h, the liquid phase was separated through centrifugation, under conditions similar to those employed during nanocellulose synthesis. Next, the remaining cation concentration was then quantitatively evaluated using ICP-OES (Optima 7300 DV, Perkin Elmer, Inc. Shelton, CT, USA).
In order to evaluate the adsorptive capacity, Equation (1) was employed, where represents the final concentration after 3 h contact time and the initial concentration, both expressed in mg·L−1, V the total solution volume in L, and is the adsorbent dose (g).
Metal recovery values were also evaluated, according to Equation (2). The adsorbent doses, cationic precursors, and initial metal concentrations of the tests are shown in Table 1

Table 1.
Adsorbent dose, cationic precursor, and initial metal concentration during adsorption tests.
The initial conditions for the adsorption tests are listed in Table 1, which, besides each metallic precursor used, describes the adsorbent dose employed and each metallic cation concentration after establishing contact with the nanocellulose suspension. After the desired contact time, the nanofibers impregnated with metallic cations were next washed/centrifuged four times and stored in vacuum before TGA analysis. To provide context for the experimental design, it is necessary to consider the normal concentrations of these metal ions in real-world effluents. Our adsorption studies used high initial concentrations of mercury (500–1000 mg/L), sodium (1000 mg/L), and magnesium (2.4 mg/L), as reported in Table 1, to ensure that the nanocellulose adsorbents were saturated. It should be mentioned that the low initial concentration of magnesium hydroxide is justified by its low aqueous solubility at room temperature. After adsorption process, the impact of the metal cations presence over the nanofibers thermal degradation profile could be studied, which was the core focus of present research.
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
For evaluating the nature of the main functional groups found in the nanocellulose molecular chains, 2 mg of each vacuum dried samples (TCNF, SCNC and Sigma Aldrich alfa-cellulose), was characterized through FT-IR (PERKIN ELMER Frontier, Waltham, MA, USA). During sample preparation, the dried nanocellulose was mixed with 0.198 g of KBr (inert dilutant) and pressed in form of small pellets.
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS)
The TCNF sample containing mercury (TCNF-Hg) was further characterized through SEM (TM3000 HITACHI, Tokyo, Japan) coupled with EDS analysis (SWIFT ED3000, Oxford Instruments, Abingdon, UK), in order to qualitatively evaluate the metals composition over the nanofibers surface. The obtained EDS signal was processed and analyzed by SWIFT ED 1.7.3.0 software, and elemental maps were constructed.
2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
The thermal degradation pattern of each nanocellulose dried sample (10 mg) before and after metal adsorption was evaluated at 20 °Cmin−1 through dynamic TGA under inert atmosphere (high purity N2) in the temperature range between 25 and 600 °C (Netzsch Jupiter STA 449 F3, Selb, Germany).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR
In Figure 1, the characteristic FTIR spectra of pure cellulose (Sigma Aldrich) and of both nanocellulose samples in the range between 500 cm−1 and 4000 cm−1 can be observed. The obtained FTIR spectra were compared with previous literature data. The IR bands of interest to the present discussion and their corresponding positions in spectra according to the literature are presented in Table 2.
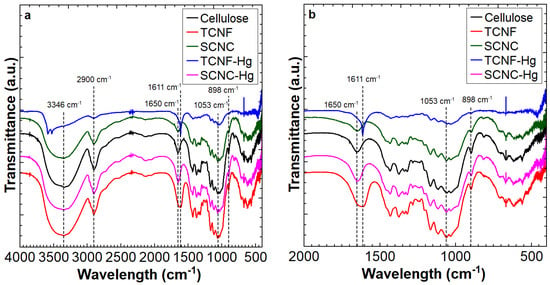
Figure 1.
FT-IR spectra of cellulose, SCNC, and TCNF samples (a), and the detailed region between 2000 and 400 cm−1 (b).

Table 2.
Bands and related groups identified on the FTIR spectra.
It is important to note that the necessity of dilution of the solid to be analyzed with KBr, as explained in the Section 2, does not allow a quantitative comparison of the transmittance measured. Therefore, the analysis of the obtained FTIR signal focused on the identification of each band and associated wave number, which has been compared with literature data (Table 2). As expected, the FT-IR spectra of TCNF and SCNC samples exhibited typical absorption bands corresponding to stretching vibrations of O–H, C–H, and C–O–C bonds (Table 2). Notably, the band at 898 cm−1, attributed to glycosidic bond vibrations, appeared with lower intensity in the TCNF and SCNC samples compared to that of the cellulose reference. This observation may be attributed to a reduction in the length of the polymer chain resulting from the nanocellulose synthesis process [41,42].
For TCNF spectra, a new band was evidenced (1611 cm−1), which corresponds to C=O stretching in carboxylate groups (COO−) asymmetric stretching vibration, confirming the introduction of carboxylate units during TEMPO oxidation [43,44]. After mercury adsorption, the sample was subjected to FTIR analysis, and a change in the FTIR peak corresponding to carboxylate groups presence can be observed, suggesting a measurable chemical or physical interaction with the inserted COO- units. This interaction may involve electrostatic forces, complexation, or ion exchange, which can alter the electron density and, consequently, the peak shape and vibrational characteristics [45]. In contrast, sulfate group stretching bands were not identified within the precision limits of the applied method; however, it should be noted that the presence of sulfur in SCNC samples synthesized under the same conditions, as applied in the present work, was already reported in the literature by SEM/EDS analysis [32]. Furthermore, a very evident band can be observed in the spectra of SCNC and cellulose at a wave number of 1650 cm−1, which, according to the literature, should be associated with O-H stretching vibrations from adsorbed water molecules. In the case of TCNF, the mentioned vibration band was not observed, although all samples have been submitted to the same vacuum drying procedure before analysis. Therefore, the authors believe that the absence of this signal, in this case, can be attributed to a convolution with the C=O band, which can be viewed as a TCNF fingerprint.
3.2. Adsorption Tests
In Table 3, adsorption test results are shown for both nanocellulose fibers employed as adsorbents (TCNF and SCNC), together with an estimation of the uncertainties involved based on the expected variances of mass, volume, and concentration (ICP-OES) measurements.

Table 3.
Metal recovery and adsorptive capacity for SCNC and TCNF samples after 3 h of contact time.
Table 3 shows substantial metal recovery values for Hg2+ (89.3%, TCNF), Mg2+ (100%, TCNF), and Na+ (63.3%, SCNC), indicating the strong potential of nanocellulose fibers as adsorbents in aqueous systems. Notably, the efficiency of metal removal appears to be influenced by the type of surface functionalization. For instance, mercury exhibited significantly greater adsorption onto TCNF than onto SCNC, despite the use of a smaller adsorbent mass (0.5 g of TCNF vs. 1 g of SCNC). The final concentration of Mg2+ was close to zero, which may be considered a limitation due to the extremely low initial concentration. For future studies, the authors suggest the use of a more soluble magnesium precursor, such as MgCl2.
It is worth mentioning that the adsorptive capacity achieved for mercury using TCNF fibers in the present work is higher than previous reported for other functionalization groups, as in the case of L-cysteine functionalized nanocellulose (TCNF) produced from sugarcane bagasse [46], where an adsorptive capacity equal to 80 mgg−1 was observed at pH equal to 6.0 and ambient temperature for a contact time of 30 min. The authors employed an initial concentration of Hg2+ equal to 100 ppm, which is also much lower than the one explored in the present article, and an adsorbent dose of 0.01 g. Lei et al. [47] investigated mercury removal employing a nanocomposite containing a TCNF matrix and gold nanoclusters as adsorbent, at pH equal to 6.0 and ambient temperature. For an initial Hg2+ concentration of 10 mg·L−1, equilibrium was established only after a contact time of 240 min, and a final adsorptive capacity of approximately 55 mg·g−1 was achieved. Kandile and Mohamed [48] also investigated Hg2+ adsorption, but using chitosan hydrogel. For an adsorbent dose of 0.1 g and an initial concentration of 4 mgL−1, an adsorptive capacity of 35 mgg−1 was measured under pH 5.0.
Finally, in the work of Kozemy et al. [49], Hg2+ removal from aqueous solutions was investigated using a wheat flour-derived hydrogel at 30 °C, with 0.04 g adsorbent dose. At pH 6 and for an initial concentration of Hg2+ of 50 ppm, equilibrium was achieved after 600 min, and a final adsorptive capacity equal to 13 mgg−1 has been evidenced. It is important to note that the 3 h contact time considered in the present investigation should indeed be much higher than the minimum time required for equilibrium to be achieved. Previous work employing the same sort of adsorbents (TCNF and SCN) [32] demonstrated that cobalt equilibrium can be achieved after approximately 30 min at pH 6.0. A detailed study of the kinetics associated with Hg2+ adsorption using both TCNF and SCN should indeed be considered in a future publication, as well as the possibility of reuse of TCNF nanofibers.
The higher adsorptive capacity for Hg2+ removal can be associated with the presence of -COOH groups in the surface of TCNF fibers, as suggested by the FT-IR pattern around 1600 cm−1 (Figure 1). It is interesting to observe that TCNF nanofibers also show appreciable adsorptive potential for other metallic cations, such as, Co2+ [32] (90 mg·g−1 and 90% recovery), Cr3+ (167 mg·g−1), Ni2+ (1104 mg·g−1) and Cu2+ (143 mg·g−1) [33], reinforcing that nanocellulose, once proper functionalized, for example, through insertion of -COOH groups, as in the case of TCNF, can be seen as promising adsorbent for heavy metals present in aqueous media, such process could be seen as complementary for the typical hydrometallurgical pathways. Comparative data from different studies on metal ion adsorption using TCNF and SCNC are summarized in Table 4.

Table 4.
Summary of studies on metal ion adsorption using TCNF and related adsorbents.
It is important to point out that the degree of functionalization and defibrillation could be even more stimulated through enhancing NaOCl concentration during TCNF production, which works in the regeneration of the TEMPO catalyst [50]. With this approach, a much higher functionalization degree and lower nanofiber size could be achieved, considerably contributing to both the adsorption driving force and kinetics. This topic, although very interesting for a future publication, lies outside the present scope, which focuses on the effect of the metal’s presence over nanofiber TGA behavior, but will also be a part of a future publication.
3.3. SEM-EDS
Considering the higher toxicity associated with mercury in water and the fact that the highest recovery was achieved for its adsorption over TCNF nanofibers; the TCNF-Hg sample was characterized through SEM analysis (Figure 2 and Figure 3). The EDS map and corresponding sample area are depicted in Figure 2, and the associated characteristic electromagnetic spectra in Figure 3. The EDS mapping (Figure 2) and corresponding spectra for the TCNF-Hg sample (Figure 3) confirmed the presence of carbon and oxygen, the primary constituents of cellulose, along with detectable amounts of sodium, chlorine, and mercury. The sodium signal suggests the formation of carboxylate groups via oxidation, subsequently activated through carbonate formation. Chlorine detection is attributed to the adsorption of Cl− ions originating from the chlorinated precursors used during synthesis (NaClO and HgCl2). The identification of a significant contrast associated to mercury in the EDS map, as well as a clear contribution of this element to the EDS spectra (peak between 2 and 2.5 keV in Figure 3) strongly suggest that mercury has adsorbed into the nanofibers surface, as expected by the significant recovery reported in Table 2. Figure 4 and Figure 5 show, respectively, the TEMPO-mediated oxidation of cellulose and the acid hydrolysis reaction used to produce SCNC.
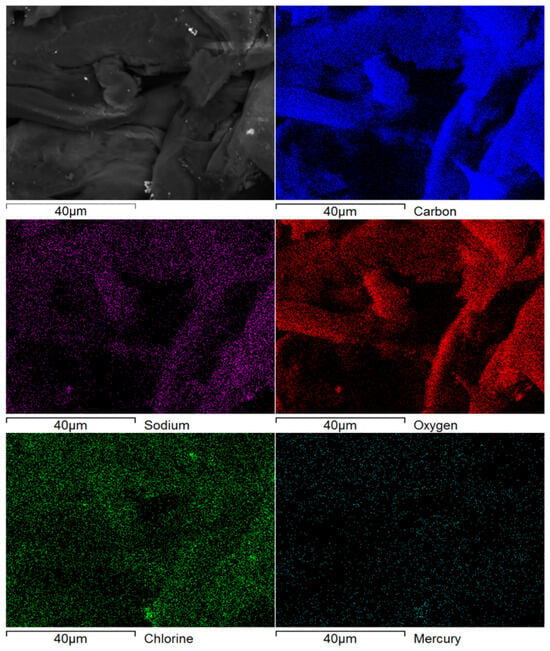
Figure 2.
SEM image and elemental EDS map for TCNF-Hg sample.
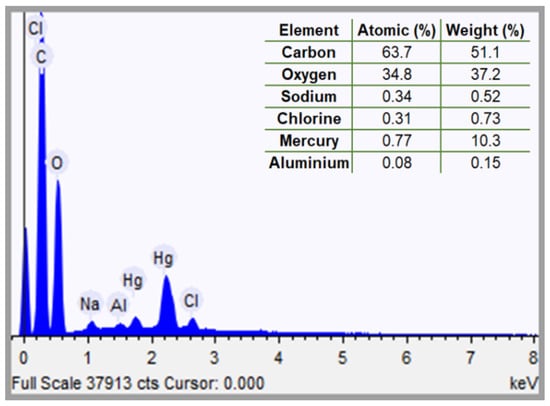
Figure 3.
EDS spectra for TCNF-Hg sample for sample area depicted in Figure 2.
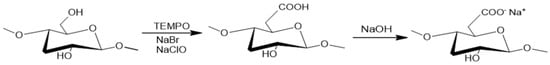
Figure 4.
Activation and carboxylate group formation in the cellulose surface.
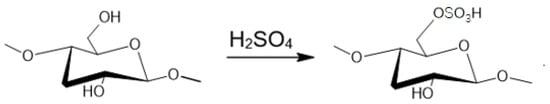
Figure 5.
Acid hydrolysis of cellulose resulting in SCNC.
It should also be pointed out that the low mercury concentration evidenced by the EDS signal can be explained by the lixiviation of part of the adsorbed metal during the washing cycles. Finally, the bright particles depicted in the SEM image in Figure 2 could be associated with some residual presence of the reaction media (inefficient centrifugation and washing), resulting in the formation of HgCl2 and or NaCl crystals.
3.4. TGA
The TGA analysis results, along with the corresponding DTG signals for cellulose and both synthesized nanocellulose samples, are shown in Figure 6. The thermal behavior of TCNF and SCNC after mercury adsorption is presented in Figure 7, the results for Na+ and Mg2+ adsorption are shown in Figure 8.
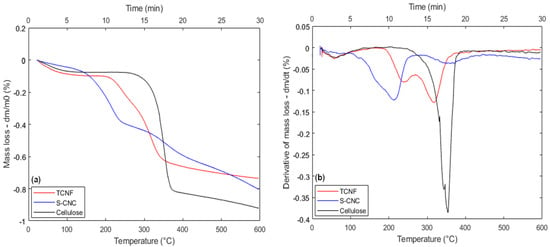
Figure 6.
Thermal behavior for cellulose, SCNC, and TCNF samples: (a) TGA; (b) DTG.
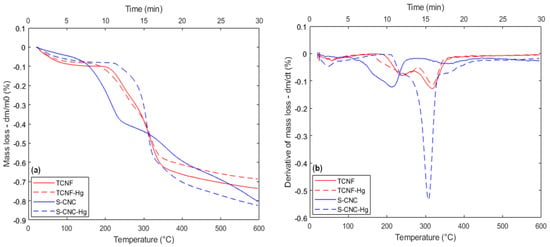
Figure 7.
Thermal behavior for SCNC and TCNF samples after mercury adsorption, with 3 h of contact time and temperature range from 25 to 600 Celsius: (a) TGA; (b) DTG.
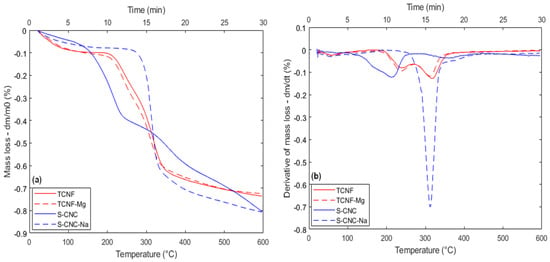
Figure 8.
Thermal behavior for SCNC sample after sodium adsorption and TCNF sample after magnesium adsorption, with 3 h of contact time and temperature range from 25 to 600 Celsius: (a) TGA; (b) DTG.
In Figure 6, both the TGA signal (Figure 6a) and associated DTG curves (Figure 6b) are depicted for pure cellulose and the two nanocellulose samples synthesized (SCNC and TCNF). According to the data, thermal decomposition of cellulose occurs at around 260 °C, which is in accordance with previous results from the literature. In the case of cellulose extracted from maize straw, for example, degradation should start at a temperature around 250 °C in N2) atmosphere (5 °C·min−1) [35], 275 °C in air atmosphere (4 °C·min−1) for softwood bleached Kraft cellulose [36], and 280 °C in N2) atmosphere (10 °C·min−1) for rice straw cellulose [43].
The observed differences can be attributed to energy transport effects (convection and/or conduction within the TGA system), sample composition (e.g., residues from prior treatments), crucible material, gas flow and composition, and the applied heating rate. Lower heating rates shift decomposition temperatures to lower values, as previously noted for maize straw cellulose (250 °C; 5 °C·min−1). In contrast, higher onset temperatures in other cases likely result from the remaining factors.
The DTG signal for cellulose (black curve in Figure 5b) shows a single major mass loss near 350 °C, indicating one dominant thermal event. This is consistent with reported values in the literature (339 °C at 4 °C·min−1 [35]; 361 °C at 10 °C·min−1 [43]).
The ratio of amorphous to crystalline domains in nanocelluloses appears to influence both adsorption capability and thermal stability. Amorphous regions, being less ordered and more flexible, tend to enhance adsorption by increasing molecular mobility and providing more accessible active sites. Conversely, crystalline domains, although less accessible, contribute to thermal resistance due to their compact and well-organized structure, which limits molecular motion and delays thermal degradation. Previous XRD analysis [32] with Rietveld refinement indicated crystallinity degrees of 66.3% for TCNF and 72.3% for SCNC, with average crystallite sizes between 4.2 and 4.6 nm. These structural differences may directly affect thermal behavior: SCNC is expected to exhibit greater thermal resistance, while TCNF may begin degrading at lower temperatures due to its higher amorphous content and less stable molecular arrangement.
Compared to cellulose, both nanocelluloses (TCNF and SCNC) exhibit much lower decomposition onset temperatures—approximately 200 °C and 116 °C, respectively—due to their nanoscale structure and presence of functional groups, which increase thermal instability.
Nanoscale materials possess higher molar Gibbs energy than bulk counterparts, leading to reduced thermal stability. SCNC, with dimensions of 10 nm (thickness) and 20–100 nm (length) [32], presents a greater surface area than TCNF (5.6 nm thickness, micrometric length), accelerating heat-induced degradation. Additionally, larger functional groups such as –COOH and –OSO3H further destabilize the nanofibers [36,51].
Thus, the lower thermal stability of SCNC arises from both its sulfonate content and nanoscale dimensions, which increase surface exposure to heat. Acid hydrolysis shortens cellulose chains and may disrupt crystallinity, reducing thermal resistance [52,53]. The higher surface area enhances thermal interaction, explaining the faster degradation of SCNC compared to the fibrillar, less exposed structure of TCNF [54]. This lower dimension also contributes to an earlier initiation of heat breakdown, as smaller nanoparticles have a greater surface area and reactivity. However, SCNC’s increased crystallinity allows for a more thermally stable degradation peak, surpassing that of TCNF. As a result, the SCNC degradation profile shows a balance of early thermal activation due to particle size and increased thermal resistance due to crystalline domains.
Another key distinction in thermal behavior between the nanofibers and micrometric cellulose lies in the DTG profiles. While cellulose exhibits a single thermal event, both functionalized nanocellulose samples show two distinct DTG peaks (240 and 310 °C for TCNF and 210 and 350 °C for SCNC). The literature suggests that this dual-peak pattern may result from partial functionalization, where the first peak corresponds to the functionalized regions of the nanofibers and the second to the unmodified regions [36,50].
Indeed, this explanation appears to be reasonable in the case of SCNC because the DTG peak of the second thermal event is almost coincident with the sole peak identified for the cellulose sample. However, in the case of TCNF, the temperature interval of the second thermal event is very different than the one found for SCNC.
Therefore, it could be suggested that a change in the functionalization type can not only affect the thermal instability but also stimulate considerable modifications in the thermal decomposition mechanism involved. It is also interesting to note that the presence of two DTG peaks has already been reported before for nanocellulose fibers, and the temperature range in which both thermal events are observed in the present work is consistent with these previous results. For TCNF, Fukuzumi et al. [36] cited two peaks; the first one is around 233 °C and the second around 282 °C. Regarding the metal presence effect over the observed nanofiber thermal degradation pattern, the obtained results suggest that the adsorbed metal cations can influence not only the velocity (kinetics) in which a specific thermal event takes place, but also in some cases completely change the thermal degradation mechanism involved, extending the behavior already pointed out in literature for the effect of metallic nanoparticles in TCNF [38,39,40].
In the case of mercury, for example (Figure 7a,b), the effect observed for TCNF is much less pronounced in comparison to the SCNC nanofibers, as in the case of TCNF, the same number of thermal events are evidenced after Hg2+ adsorption, with a measurable difference in the starting temperature of the first DTG peak, which reduces from 200 °C (before adsorption) to 170 °C after adsorption. For the second thermal event, such an effect is not observed (Figure 7b). It is also interesting to observe that the presence of mercury did not appear to have a measurable influence on each DTG peak magnitude.
In contrast to TCNF, SCNC presents a huge difference in thermal behavior after the adsorption of mercury. The associated DTG signal clearly shows that in the presence of mercury cations, the SCNC nanofibers should now decompose in three consecutive thermal events, the first one starting at a higher temperature (210 °C) in comparison to the first DTG peak of SCNC before metal incorporation. Also, the peak intensity appears to be of much lower intensity in the presence of mercury as compared to the one found in the sample without the metal. The third peak, which, as was said before, in the case of the SCNC sample, should be related to the non-functionalized part, has almost the same intensity and shape as compared with the condition before metal adsorption. This is consistent with the expectation that mercury should preferentially adsorb in regions where -O3SOH groups had been previously inserted. Finally, between the two mentioned thermal events, a new one is observed, with a maximum DTG peak intensity of around 305 °C. This last DTG peak strongly suggests that in the case of SCNC, the presence of mercury can indeed induce a change in the mechanism associated with the thermal degradation of the nanofibers. The possible change in the degradation mechanism associated with the adsorption of specific metallic cations over nanocellulose fibers was also evidenced in the case of sodium when SCNC fibers are used as adsorbents (Figure 8a,b).
According to the data, the presence of sodium completely changes the intensity and temperature range of the first thermal degradation event observed, the initial temperature varying from around 116 °C (without sodium) to almost 280 °C in the presence of the metal. It is worthwhile to mention that again, for the second thermal event, the presence of the cation did not appear to have any influence at all, again corroborating the hypothesis that this part of the thermal behavior should involve the non-functionalized part of the material, which, as in the case of mercury, should not be appreciably involved in the metal’s adsorption. In the case of magnesium, no effect at all over the TCNF thermal behavior was evidenced. This fact could be explained by the low concentration used in initial solution of MgOH, which was limited by the very low solubility of the cation precursor (Mg(OH)2) at ambient temperature (25 °C). Consequentially, even after a contact time of 3 h, a very low adsorptive capacity was achieved (0.48 mgg−1), although with full cationic removal. The reduced cation concentration over the nanofibers surface should then explain why the thermal behavior was almost identical to the one found for the TCNF nanofibers without the metal presence.
4. Conclusions
Based on the findings of this study, both TCNF and SCNC nanofibers demonstrated considerable potential as adsorbents for removing metal cations from aqueous media. SCNC effectively removed mercury (Hg2+) and magnesium (Mg2+), while TCNF performed well in adsorbing sodium (Na+) and especially mercury. In all cases, metal recovery exceeded 55%, with TCNF showing superior performance. Notably, TCNF achieved mercury recovery and adsorption capacity values of 86% and 172 mgg−1, respectively.
Therefore, it can be suggested that the carboxylate groups generated during TCNF synthesis have a very high affinity to the Hg2+ cations available in solution. Regarding the thermal behavior studied, nanocellulose appears to be much more unstable in comparison to the bulk sample. While bulk cellulose starts to decompose at 260 °C at a heating rate of 20 °Cmin−1, TCNF and SCNC samples start to decompose much earlier, with the initial temperatures respectively equal to 200 °C and 160 °C. In addition to that, the decomposition mechanism of TCNF appears to be very different from the bulk cellulose sample, with two very distinct thermal events and DTG peaks. In the case of SCNC, two thermal events can also be observed, with the second one occurring in a similar region as the DTG peak of bulk cellulose, although of less intensity. Therefore, it is proposed that the second event, in this case, is associated with the part of the nanocellulose that is not functionalized through the insertion of sulfate units (-O3SOH), whose presence stimulates thermal instability.
Finally, regarding the effect of metals presence over each nanofiber’s thermal behavior, it can be said that it is influenced by both cation nature and nanocellulose type. In the case of SCNC, the presence of mercury leads to a strong modification of the decomposition pattern, resulting in the incorporation of a third thermal event, with a dominant DTG peak, when compared with the other two thermal events observed. In the case of sodium, the first thermal event shifts to a much higher initial temperature (around 306 °C; 20 °Cmin−1), and also the DTG peak intensity exhibits a significant increase. Therefore, binding of both cations (Hg2+ and Na+) with the previously inserted sulfonic units (-O3SOH) stimulates, in the case of SCNC, with a significant modification of the thermal degradation mechanism.
In the case of TCNF, the effect is less significant. For mercury, two main thermal events were also observed; the second event exhibited a DTG profile very similar to that of the same sample before metal adsorption, while the first event was shifted to a higher temperature range (initial temperature around 250 °C), with peak intensity remaining nearly unchanged. These results suggest that the effect of mercury should not be associated with a significant change in mechanism, as in the case of sodium and mercury over SCNC nanofibers. Finally, in the case of Mg2+ over TCNF nanofibers, no effect at all was observed, which can be explained by the very low adsorptive capacity achieved after 3 h contact time (0.48 mgg−1). Although the metal recovery was very prominent (99.6%), the initial concentration of magnesium (2.4 gL−1) was much lower than that of mercury (1000 gL−1), which is understood to be based on the low solubility of the cationic precursor (Mg(OH)2) at ambient temperature (20–25 °C).
Author Contributions
Methodology, W.F.B., L.T.T. and R.N.; Software, O.G.P.; Validation, W.F.B., L.T.T. and R.N.; Formal analysis, O.G.P.; Investigation, R.N. and O.G.P.; Resources, L.T.T.; Data curation, O.G.P.; Writing—original draft, L.T.T. and O.G.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support of Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ-SEI-260003/015222/2021/E-26/201.315/2021), and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brazil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001 (CAPES Portaria nº206, de 4 de setembro de 2018). L.T.T. acknowledge CNPq.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| TCNF | TEMPO-oxidized Cellulose Nanofiber |
| SCNC | Sulfonated Cellulose Nanocrystals |
| TEMPO | 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| DTG | Derivative Thermogravimetry |
| SEM-EDS | Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy |
| ICP-OES | Inductively Coupled Plasma - Optical Emission Spectrometry |
References
- Sahu, P. A comprehensive review of saline effluent disposal and treatment: Conventional practices, emerging technologies, and future potential. Water Reuse 2021, 11, 33–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrist, D.; Kirk, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Sunderland, E.M.; Jiskra, M.; Selin, N.E. A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: Changes of emissions, climate, and land use. Ambio 2018, 47, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner-Döbler, I.; Von Canstein, H.; Li, Y.; Timmis, K.N.; Deckwer, W.D. Removal of mercury from chemical wastewater by microoganisms in technical scale. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4628–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, A. Study and evaluation of the characteristics of saline wastewater (brine) produced by desalination and industrial plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 23736–23749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appiah-Brempong, M.; Essandoh, H.M.K.; Asiedu, N.Y.; Dadzie, S.K.; Momade, F.W.Y. Artisanal tannery wastewater: Quantity and characteristics. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkh, B.A.; Al-Amoudi, A.A.; Farooque, M.; Fellows, C.M.; Ihm, S.; Lee, S.; Li, S.; Voutchkov, N. Seawater desalination concentrate—a new frontier for sustainable mining of valuable minerals. npj Clean Water 2022, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quddoos, A.; Muhmood, K.; Naz, I.; Aslam, R.W.; Usman, S.Y. Geospatial insights into groundwater contamination from urban and industrial effluents in Faisalabad. Discov. Water 2024, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsido, T.T.; McCrindle, R.I.; Maree, J.; Monyatsi, L. Removal of Al, Ba and Mg from industrial wastewater using EAFDS and lime. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.G.; Vo, D.V.N.; Tran, H.T.; Duy Dat, N.; Luu, S.D.; Rahman, M.M.; Huang, Y.H.; Vu, C.T. Recovery of magnesium from industrial effluent and its implication on carbon capture and storage. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 6732–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.F.; Paulista, A.P.F.; Torres, M.A.M.; Braga, T.P. Synthesis of the Fe–Co alloy from hybrid spheres using carboxymethylcellulose as template and its application in catalysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 242, 122550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataee-Esfahani, H.; Nemoto, Y.; Imura, M.; Yamauchi, Y. Facile synthesis of nanoporous Pt-Ru alloy spheres with various compositions toward highly active electrocatalysts. Chem.-An Asian J. 2012, 7, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaprakash, G.; Mohanrasu, K.; Obeth, J.; Bora, A.; Yuvakkumar, R.; Mahmoud, A.H.; El-Abedein, A.I.Z.; Saravanan, S.; Arun, A. Zinc based iron mixed oxide catalyst for biodiesel production from Entermorpha intestinalis, Caulerpa racemosa and Hypnea musicoformisis and antibiofilm analysis using leftover catalyst after transesterification. J. King Saud-Univ.-Sci. 2020, 32, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, G.; Soumiya, S. Production of biodiesel from castor oil using iron (II) doped zinc oxide nanocatalyst. Renew. Energy 2016, 98, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghetti, S.M.P.; Meneghetti, M.R.; Wolf, C.R.; Silva, E.C.; Lima, G.E.; de Lira Silva, L.; Serra, T.M.; Cauduro, F.; de Oliveira, L.G. Biodiesel from castor oil: A comparison of ethanolysis versus methanolysis. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 2262–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeprasanth, P.; Srivastava, R.; Srinivas, D.; Ratnasamy, P. Hydrophobic, solid acid catalysts for production of biofuels and lubricants. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 314, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahemed, J.; Rao D, V.; Pasha, J.; Kore, R.; Gade, R.; Bhongiri, Y.; Chetti, P.; Pola, S. Synthesis of new Zn (II) complexes for photo decomposition of organic dye pollutants, industrial wastewater and photo-oxidation of methyl arenes under visible-light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 419, 113455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Guo, Y.Q.; Zuo, L.Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, L.L.; Yu, J.J.; Feng, X.; Li, B.; Wang, L.Y. Synthesis of zinc-based metal–organic framework as highly efficient photocatalyst for decomposition of organic dyes in aqueous solution. Rare Met. 2023, 42, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norfarhana, A.; Ilyas, R.; Ngadi, N. A review of nanocellulose adsorptive membrane as multifunctional wastewater treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfoudhi, N.; Boufi, S. Nanocellulose as a novel nanostructured adsorbent for environmental remediation: A review. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1171–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, G.K.; Sen Gupta, S.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Nanomaterials as versatile adsorbents for heavy metal ions in water: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6245–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I. New generation adsorbents for water treatment. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5073–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehaqui, H.; Zhou, Q.; Berglund, L.A. High-porosity aerogels of high specific surface area prepared from nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC). Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Saini, D.; Sonkar, S.; Sonker, A.; Westman, G. Sunlight Promoted Removal of Toxic Hexavalent Chromium by Cellulose Derived Photocative Carbon Dots. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Wu, S.; Zhou, J. Preparation and Modification of Nanocellulose and Its Application to Heavy Metal Adsorption: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 236, 123916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshmy, R.; Philip, E.; Madhavan, A.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Sindhu, R.; Sirohi, R.; Awasthi, M.; Pandey, A.; Binod, P. Nanocellulose as Green Material for Remediation of Hazardous Heavy Metal Contaminants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Borja Oiembarrena, F.; Hullebusch, E.; Marsac, R.; Merayo, N.; Blanco, A.; Negro, C. Selective Recovery of Co(II), Mn(II), Cu(II), and Ni(II) by Multiple Step Batch Treatments with Nanocellulose Products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 66725–66741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobi, M.; Kumar, A.; Singh, J.; Singh, S.; Ramamurthy, P. Nanocellulose-Based Adsorption for the Removal of Heavy Metal from Wastewater—A Review. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2024, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejje, F.; Matshwele, J.; Obuseng, V.; Nareetsile, F. Nanocellulose Chemical Treatment Reactions and Their Influence on the Adsorption of Aqueous Transition Metal Ions—A Review. Chem. Rev. Lett. 2023, 6, 245–255. [Google Scholar]
- Kardam, A.; Raj, K.R.; Srivastava, S.; Srivastava, M.M. Nanocellulose fibers for biosorption of cadmium, nickel, and lead ions from aqueous solution. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Borrell, P.F.; Božič, M.; Kokol, V.; Oksman, K.; Mathew, A.P. Nanocelluloses and their phosphorylated derivatives for selective adsorption of Ag+, Cu2+ and Fe3+ from industrial effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 294, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Arora, J.K.; Sinha, T.J.M.; Srivastava, S. Functionalization of nanocrystalline cellulose for decontamination of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) from aqueous system: Computational modeling approach. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.T.; Braz, W.F.; de Siqueira, R.N.C.; Pandoli, O.G.; Geraldes, M.C. Sulfated and carboxylated nanocellulose for Co+2 adsorption. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehaqui, H.; De Larraya, U.P.; Liu, P.; Pfenninger, N.; Mathew, A.P.; Zimmermann, T.; Tingaut, P. Enhancing adsorption of heavy metal ions onto biobased nanofibers from waste pulp residues for application in wastewater treatment. Cellulose 2014, 21, 2831–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Ultrafine cellulose nanofibers as efficient adsorbents for removal of UO22+ in water. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, M.; Bica, C.; Nachtigall, S.; Rehman, N.; Rosa, S. Kinetical thermal degradation study of maize straw and soybean hull celluloses by simultaneous DSC–TGA and MDSC techniques. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 565, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzumi, H.; Saito, T.; Okita, Y.; Isogai, A. Thermal stabilization of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.; Winter, W.T. Effect of Sulfate Groups from Sulfuric Acid Hydrolysis on the Thermal Degradation Behavior of Bacterial Cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebali, Z.; Granados, A.; Nabili, A.; Boufi, S.; do Rego, A.M.B.; Majdoub, H.; Vallribera, A. Cationic cellulose nanofibrils as a green support of palladium nanoparticles: Catalyst evaluation in Suzuki reactions. Cellulose 2018, 25, 6963–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirtiu, C.M.; Dunlop-Briere, A.F.; Moores, A. Cellulose nanocrystallites as an efficient support for nanoparticles of palladium: Application for catalytic hydrogenation and Heck coupling under mild conditions. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisa, W.H.; Abdelgawad, A.M.; Rojas, O.J. Solid-state synthesis of metal nanoparticles supported on cellulose nanocrystals and their catalytic activity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madivoli, E.S.; Kareru, P.G.; Gachanja, A.N.; Mugo, S.; Murigi, M.K.; Kairigo, P.; Kipyegon, C.; Mutembei, J.K.; Njonge, F.K. Adsorption of selected heavy metals on modified nano cellulose. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, D.; Patel, B.H. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Nano Cellulose for Enhanced Performance of Textiles. J. Text. Sci. Eng. 2016, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Hsieh, Y.L. Chemically and mechanically isolated nanocellulose and their self-assembled structures. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of Infrared Spectra, A Practical Approach. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2000; pp. 10815–10837. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, H.R.; Bera, M.K.; Macke, N.; Rowan, S.J.; Tirrell, M.V. Quantitative Determination of Metal Ion Adsorption on Cellulose Nanocrystals Surfaces. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, M.; Ram, B.; Chauhan, G.S.; Kaushik, A. L-Cysteine functionalized bagasse cellulose nanofibers for mercury(II) ions adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Li, H.; Luo, Y.; Sun, X.; Guo, X.; Hu, Y.; Wen, R. Novel fluorescent nanocellulose hydrogel based on gold nanoclusters for the effective adsorption and sensitive detection of mercury ions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 123, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandile, N.G.; Mohamed, H.M. Chitosan nanoparticle hydrogel based sebacoyl moiety with remarkable capability for metal ion removal from aqueous systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khozemy, E.E.; Nasef, S.M.; Mohamed, T.M. Radiation synthesis of superabsorbent hydrogel (wheat flour/acrylamide) for removal of mercury and lead ions from waste solutions. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 1669–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogai, A.; Saito, T.; Fukuzumi, H. TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De M. Teixeira, E.; De Oliveira, C.; Mattoso, L.; Corrêa, A.; Paladin, P. Cotton nanofibers obtained by different hydrolytic acid conditions | Nanofibras de algodão obtidas sob diferentes condições de hidrólise ácida. Polimeros 2010, 20, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, Y.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose nanocrystals: Chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Dhar, N.; Liu, H.; Tam, K.C. Chemistry and applications of nanocrystalline cellulose and its derivatives: A nanotechnology perspective. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 96, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Kimura, S.; Nishiyama, Y.; Isogai, A. Cellulose nanofibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).