Optimized Ammonia Leaching and Energy-Efficient Stripping for Lithium and Cobalt Recovery from Spent LiCoO2 Cathodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Source and Pretreatment of Spent LIB Cathodes
3.2. Characterization of Cathode Material
3.3. Ammonia Leaching of Cathode Material
3.4. Ammonia Distillation and Recovery of Li and Co
4. Results and Discussion
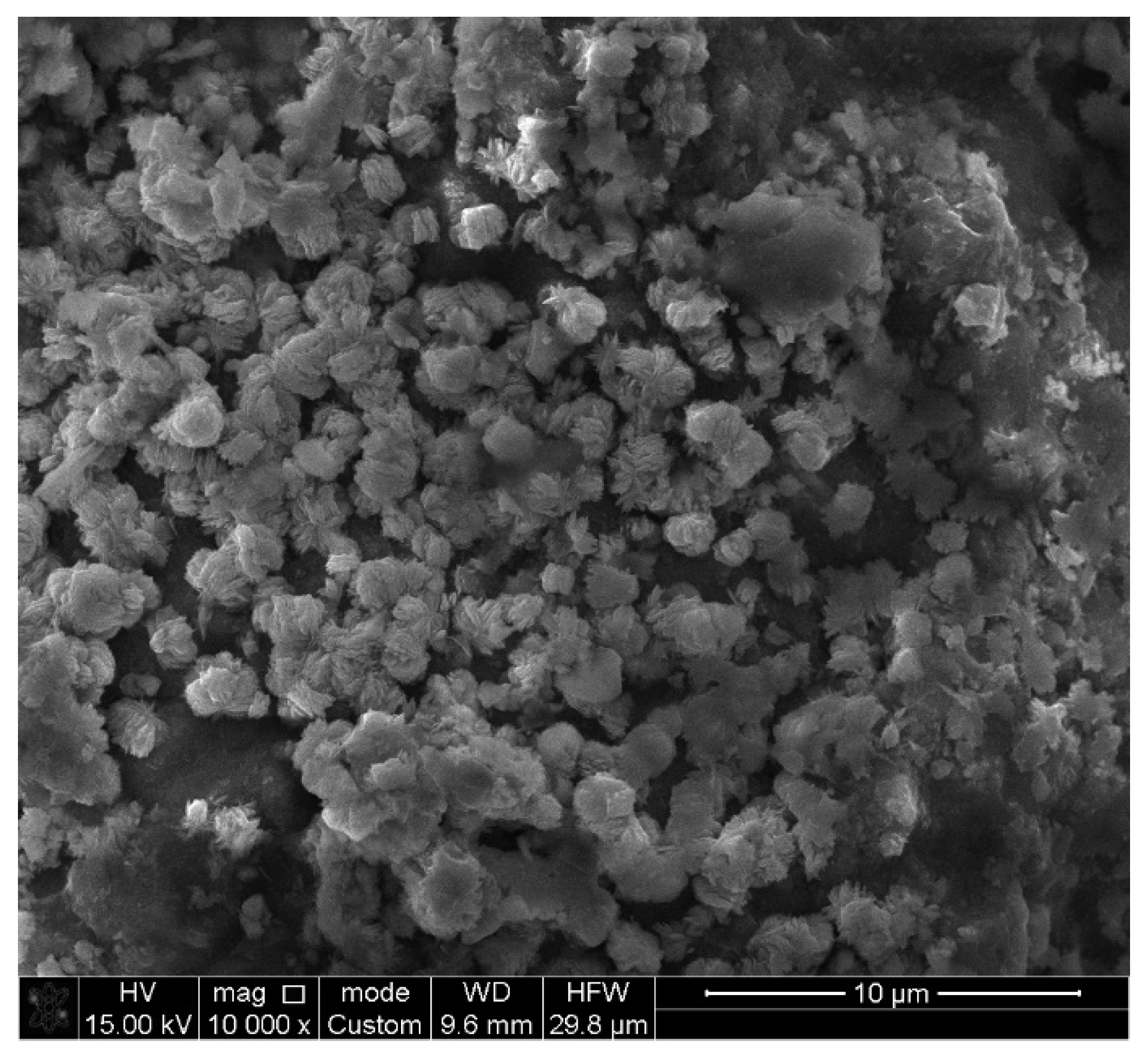
4.1. Characterization of Spent Cathode Sample
4.2. Kinetic Analysis of Ammonia Leaching Process
5. Ammonia Leaching Process Optimization
6. Lithium and Cobalt Precipitation: Optimization of Ammonia Stripping for Energy Efficiency
- temperature control—higher temperatures enhance ammonia volatilization but increase energy consumption;
- pH adjustment—since NH3 exists in equilibrium with NH4+, raising the pH shifts the equilibrium towards volatile NH3 gas, facilitating its removal.
7. Conclusions
- Kinetic analysis revealed that both lithium and cobalt extraction follow pseudo-first-order kinetics, indicating a chemically controlled process. The activation energies (76.54 kJ/mol for Li and 97.22 kJ/mol for Co) confirm the reaction-controlled nature of the leaching.
- Optimal leaching conditions were established at 6 M NH3, 1.5 M (NH4)2CO3, L:S ratio of 10:1, and 70 °C for 5 h, achieving 82.5% lithium and 96.1% cobalt recovery.
- The ammonia stripping process was optimized for energy efficiency, with operations at 95–98 °C providing the best balance between rapid NH3 removal and energy consumption. At 98 °C, energy demand was reduced to ~282 kJ/mol, a sevenfold improvement over lower temperature operations.
- A stepwise separation strategy was developed, involving selective lithium precipitation at pH 10.7–10.8, followed by controlled ammonia stripping to precipitate cobalt at pH 8.8–9.0.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, E.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Chen, R.; Wu, F. Sustainable recycling technology for Li-ion batteries and beyond: Challenges and future prospects. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 7020–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Mu, D.; Lu, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tian, S.; Dai, C. A comprehensive review on the recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries: Urgent status and technology advances. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Aravindan, V. An urgent call to spent LIB recycling: Whys and wherefores for graphite recovery. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2002238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hh Du, M.; Du, K.D.; Guo, J.Z.; Liu, Y.; Aravindan, V.; Yang, J.L.; Zhang, K.-Y.; Gu, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.-T.; Wu, X.L. Direct reuse of oxide scrap from retired lithium-ion batteries: Advanced cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Rare Met. 2023, 42, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.-H.; Wang, X.-T.; Gu, Z.-Y.; Lü, H.-Y.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Cao, J.-M.; Guo, J.-Z.; Deng, X.-T.; Wu, Z.-T.; Zeng, R.-H.; et al. Direct and rapid regeneration of spent LiFePO4 cathodes via a high-temperature shock strategy. J. Power Sources 2023, 587, 233697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Lü, H.; Du, K.; Zheng, S.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; Zeng, R.; Wu, X. Upcycling the spent graphite/LiCoO2 batteries for high-voltage graphite/LiCoPO4-co-workable dual-ion batteries. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2024, 31, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. Pyrometallurgical technology in the recycling of a spent lithium ion battery: Evolution and the challenge. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 1, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, A.; Windisch-Kern, S.; Ponak, C.; Raupenstrauch, H. A novel pyrometallurgical recycling process for lithium-ion batteries and its application to the recycling of LCO and LFP. Metals 2021, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.S.; Sohn, I.L. Fundamental thermokinetic study of a sustainable lithium-ion battery pyrometallurgical recycling process. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 158, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuza, B.; Tian, Q.; Guo, X.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Yu, D. Pyrometallurgical options for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries: A comprehensive review. J. Power Sources 2021, 491, 229622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larouche, F.; Tedjar, F.; Amouzegar, K.; Houlachi, G.; Bouchard, P.; Demopoulos, G.P.; Zaghib, K. Progress and status of hydrometallurgical and direct recycling of Li-ion batteries and beyond. Materials 2020, 13, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi Dalini, E.; Karimi, G.; Zandevakili, S.; Goodarzi, M. A review on environmental, economic and hydrometallurgical processes of recycling spent lithium-ion batteries. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2021, 42, 451–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo-Gonzalez, M.D.M.; Villen-Guzman, M.; Vereda-Alonso, C.; Rodriguez-Maroto, J.M.; Paz-Garcia, J.M. Towards sustainable lithium-ion battery recycling: Advancements in circular hydrometallurgy. Processes 2024, 12, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.; Hyde, C.; Hartley, J.M.; Abbott, A.P.; Anderson, P.A.; Harper, G.D. To shred or not to shred: A comparative techno-economic assessment of lithium ion battery hydrometallurgical recycling retaining value and improving circularity in LIB supply chains. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 175, 105741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B. Recovery and recycling of lithium: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 172, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Tong, B.; Fan, Y.; Hua, Z. Hydrometallurgical processes for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries: A critical review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 13611–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, Z.J.; Bird, R.E.; Yu, X.; Ma, J. Lithium-ion battery recycling—Overview of techniques and trends. ACS Energy Lett. 2022, 7, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saim, A.K. Ammoniacal leaching for the extraction of valuable metals from secondary resources: A review. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2025, 46, 284–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Senanayake, G. A review of ammoniacal thiosulfate leaching of gold: An update useful for further research in non-cyanide gold lixiviants. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2016, 37, 385–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, B.; Zheng, S.; Wang, S.; Du, H.; Dreisinger, D.B.; Zhang, Y. A cleaner vanadium extraction method featuring non-salt roasting and ammonium bicarbonate leaching. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Zhang, R.; He, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wu, M.; Xu, Z.; Chi, R.; Yang, H. Research progress on leaching technology and theory of weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ore. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 193, 105295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Meng, F.; Yi, X.; Shu, J.; Chen, M.; Sun, Z.; Sun, S.; Xiu, F.R. A novel and efficient ammonia leaching method for recycling waste lithium ion batteries. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, H.; Jung, Y.; Jo, M.; Park, S.; Kim, S.; Yang, D.; Rhee, K.; An, E.-M.; Sohn, J.; Kwon, K. Recycling of spent lithium-ion battery cathode materials by ammoniacal leaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 313, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Li, B.; Yuan, C.; Ni, S.; Li, L. Recycling valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries by ammonium sulfite-reduction ammonia leaching. Waste Manag. 2019, 93, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, N.; Hu, F.; Ye, L.; Xi, Y.; Yang, S. Thermal treatment and ammoniacal leaching for the recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, B.; Ou, X.; Zhang, J.; Meng, K.; Ji, G.; Li, P.; Xu, J. Ammonia leaching mechanism and kinetics of LiCoO2 material from spent lithium-ion batteries. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2333–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Lai, F.; Yan, F.; Zhang, Z. Reduction-ammoniacal leaching to recycle lithium, cobalt, and nickel from spent lithium-ion batteries with a hydrothermal method: Effect of reductants and ammonium salts. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Yan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Z. Recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries: Selective ammonia leaching of valuable metals and simultaneous synthesis of high-purity manganese carbonate. Waste Manag. 2020, 114, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, H.; Zhang, J.; Shen, A.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. A simplified method for the recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries via manganese selective recovery by anoxic ammonia leaching and spontaneous precipitation. J. Power Sources 2024, 590, 233799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daminescu, D.; Duteanu, N.; Ciopec, M.; Negrea, A.; Negrea, P.; Nemeş, N.S.; Pascu, B.; Lazău, R.; Berbecea, A. Kinetic Modelling the Solid–Liquid Extraction Process of Scandium from Red Mud: Influence of Acid Composition, Contact Time and Temperature. Materials 2023, 16, 6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, J.; Tanda, S.; Liu, J.C. Subcritical water extraction of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. Molecules 2020, 25, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, J.; Liu, J.C. Closed-vessel microwave leaching of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) using dual-function leaching agent: Ascorbic acid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 266, 118458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Chan, W.P.; Dou, X.; Lisak, G.; Chang, V.W.C. Kinetics and modeling of trace metal leaching from bottom ashes dominated by diffusion or advection. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, P.; Xu, H.; Zeng, G.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Deng, C.; He, J. Oriented conversion of spent LiCoO2-lithium battery cathode materials to high-value products via thermochemical reduction with common ammonium oxalate. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 190, 106782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Azimi, G. Process analysis and study of factors affecting the lithium carbonate crystallization from sulfate media during lithium extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 199, 105532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.G.; Sun, S.Y. Preparation of battery-grade lithium carbonate with lithium-containing desorption solution. Metals 2021, 11, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinov, V.; Klimko, J.; Takáčová, Z.; Pirošková, J.; Miškufová, A.; Sommerfeld, M.; Dertmann, C.; Friedrich, B.; Oráč, D. Lithium production and recovery methods: Overview of lithium losses. Metals 2023, 13, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallmeister, C.; Friedrich, B. Holistic investigation of the inert thermal treatment of industrially shredded NMC 622 lithium-ion batteries and its influence on selective lithium recovery by water leaching. Metals 2023, 13, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becci, A.; Amato, A.; Rodríguez Maroto, J.M.; Beolchini, F. Prediction model for Cu chemical leaching from printed circuit boards. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 20585–20591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashifana, T.; Ntuli, F.; Okonta, F. Leaching kinetics on the removal of phosphorus from waste phosphogypsum by application of shrinking core model. South Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidler, K.J. The development of the Arrhenius equation. J. Chem. Educ. 1984, 61, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Liang, J.; Yan, H.; Liu, J. Leaching kinetics of secondary zinc oxide in a NH3–NH4HCO3–H2O System. Crystals 2021, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindo, S.Y.; Omoniyi, K.I.; Raji, M.A. Chalcopyrite leaching in ammonia-ammonium chloride solutions: Insight into the dissolution kinetic studies. J. Sustain. Mater. Process. Manag. 2022, 2, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueye, R.S.; Gaye, N.; Baldé, M.; Diedhiou, A.; Diouf, N.; Awa, S.G.; Ndoye, I.; Tine, Y.; Seck, M.; Fall, D.; et al. Review of Research on Li-Ion Batteries Waste Management. Open J. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 12, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Zhu, W.; Ruan, Z.; Xie, M.; Chen, J.; Ren, X. Recycling of lithium batteries—A review. Energies 2022, 15, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, K.; Xiong, H.; Dong, H. Ammoniacal leaching process for the selective recovery of value metals from waste lithium-ion batteries. Environ. Technol. 2023, 44, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asselin, E. Thermochemistry of the Fe, Ni and Co-NH 3-H 2 O systems as they relate to the Caron process: A review. Min. Metall. Explor. 2011, 28, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Formica, M.; Fusi, V.; Micheloni, M.; Pontellini, R.; Romani, P. Cryptand ligands for selective lithium coordination. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 184, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mani, R.; Louhi-Kultanen, M. Process monitoring of cobalt carbonate precipitation by reactions between cobalt sulfate and sodium carbonate solutions to control product morphology and purity. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 224, 106232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
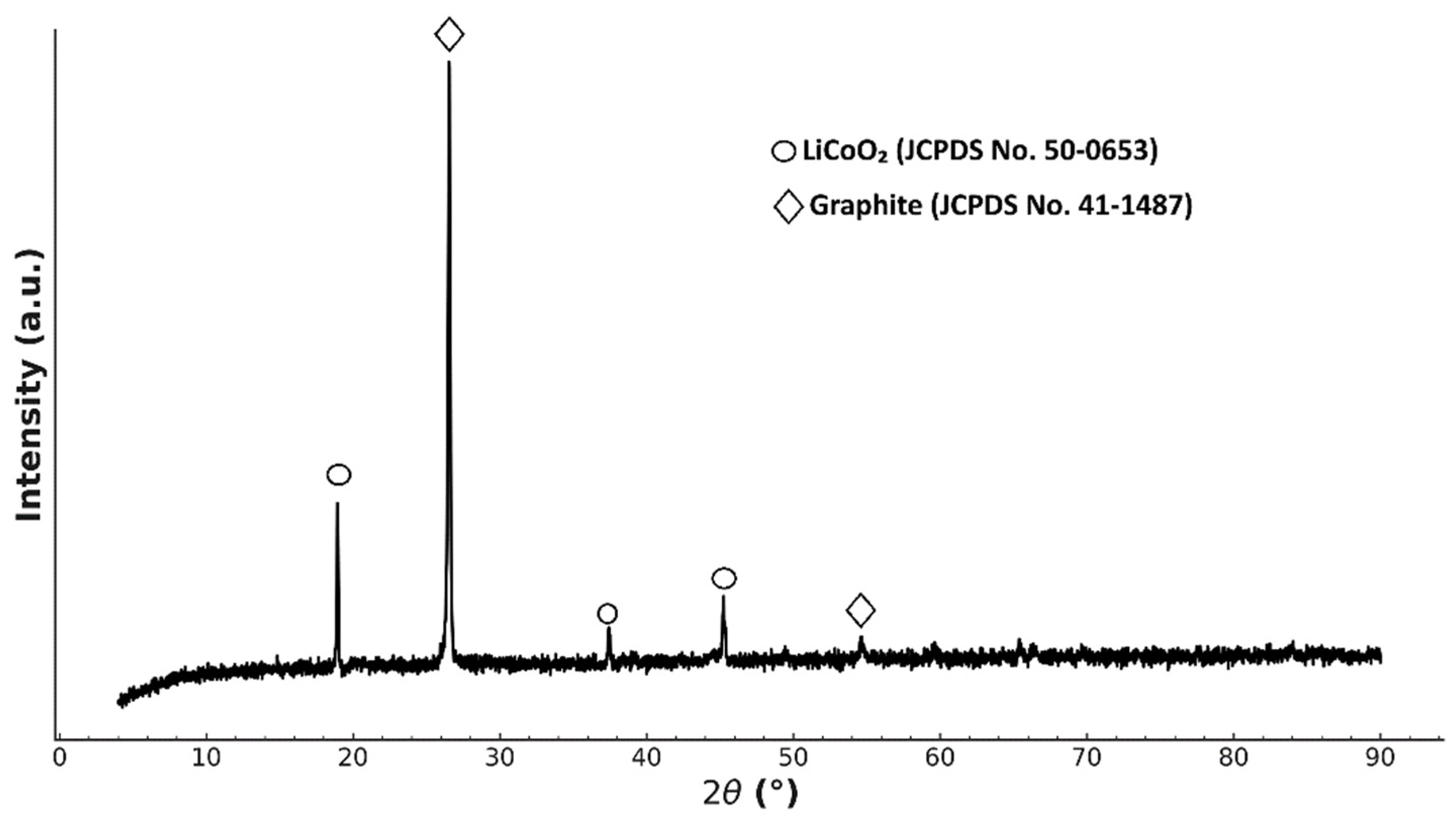


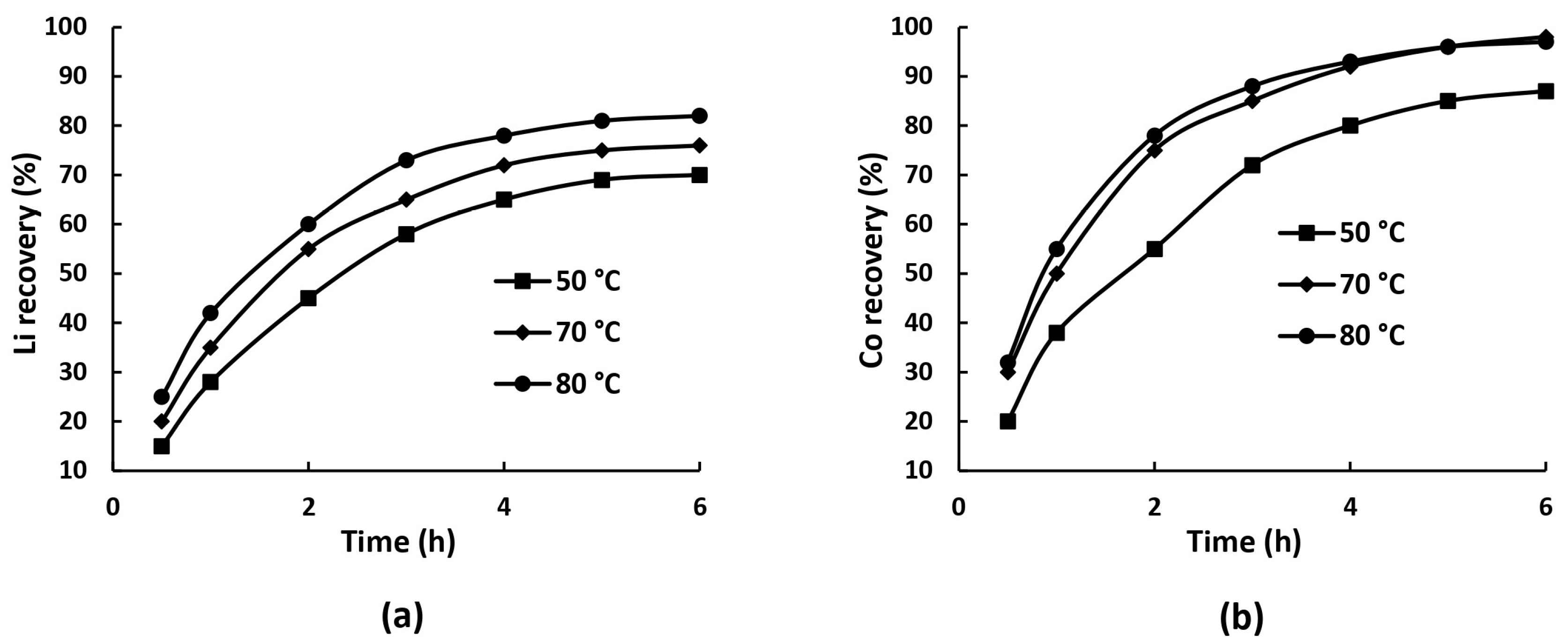
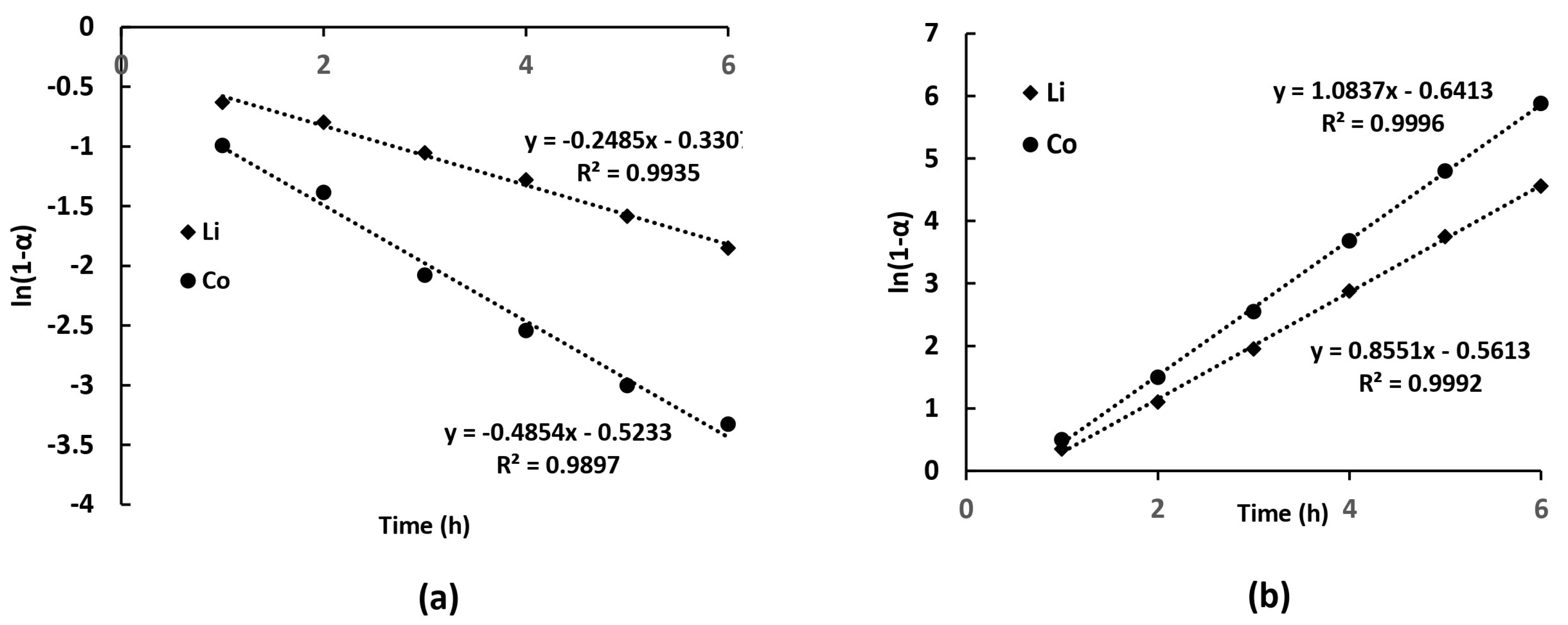

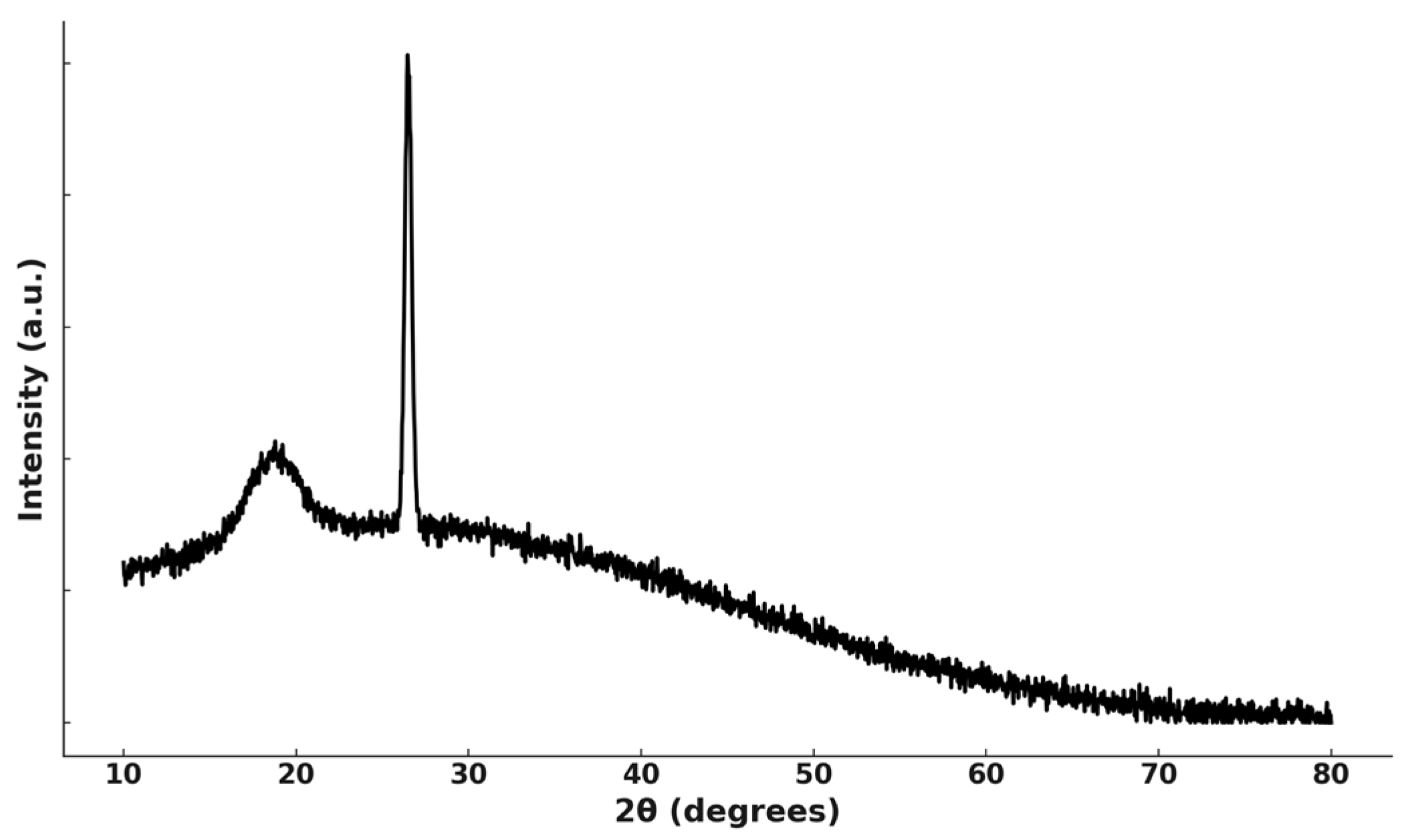

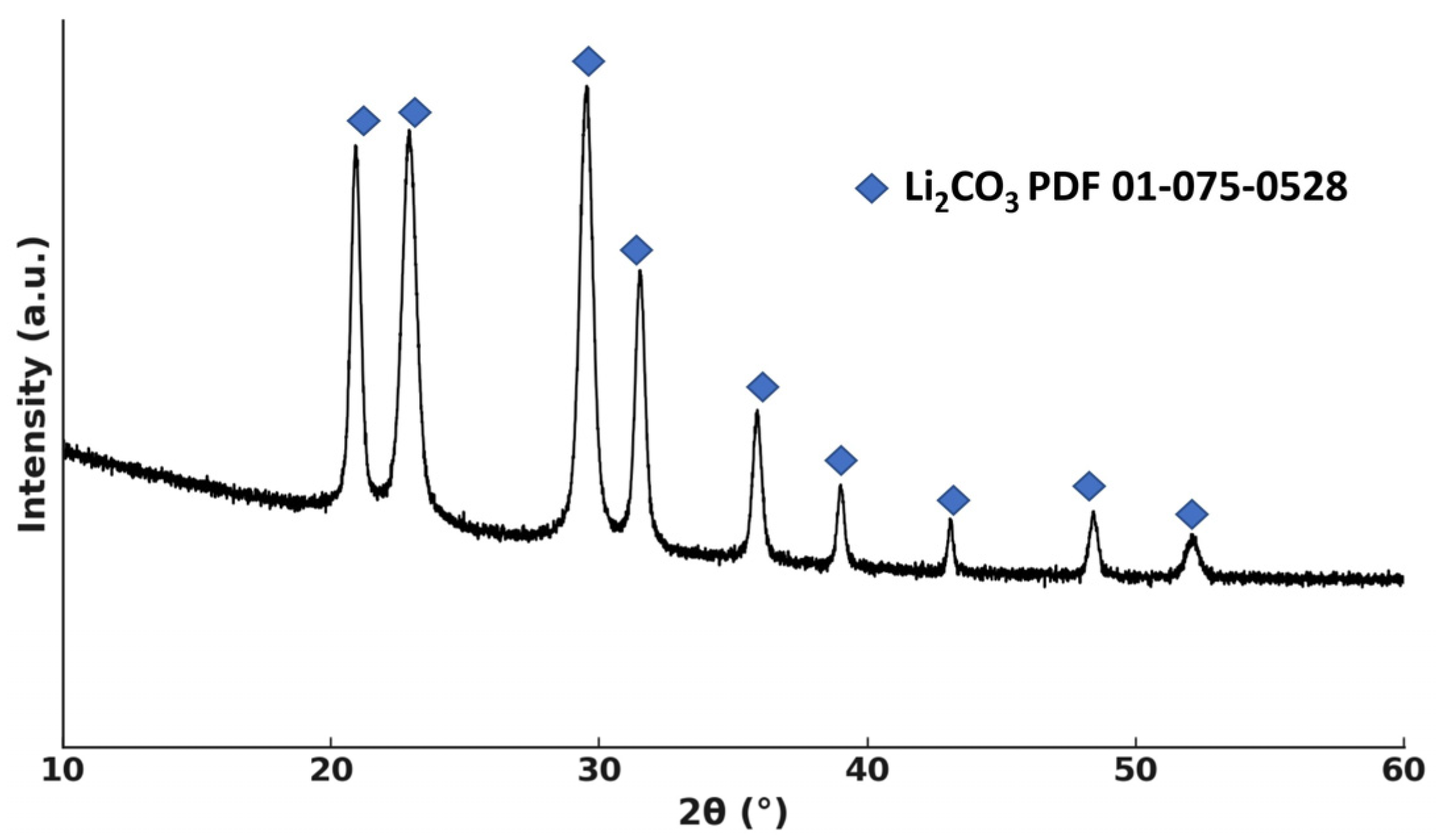
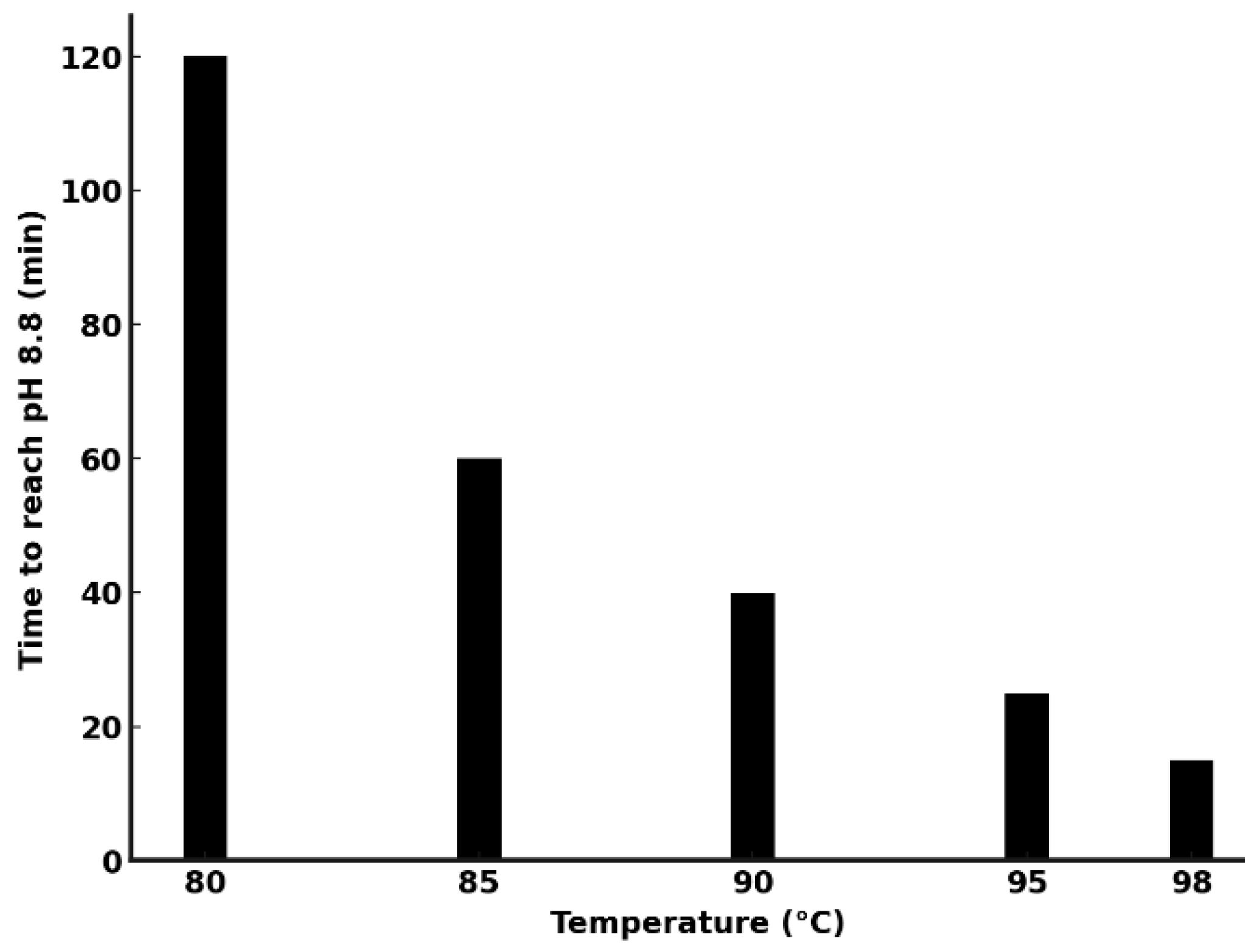
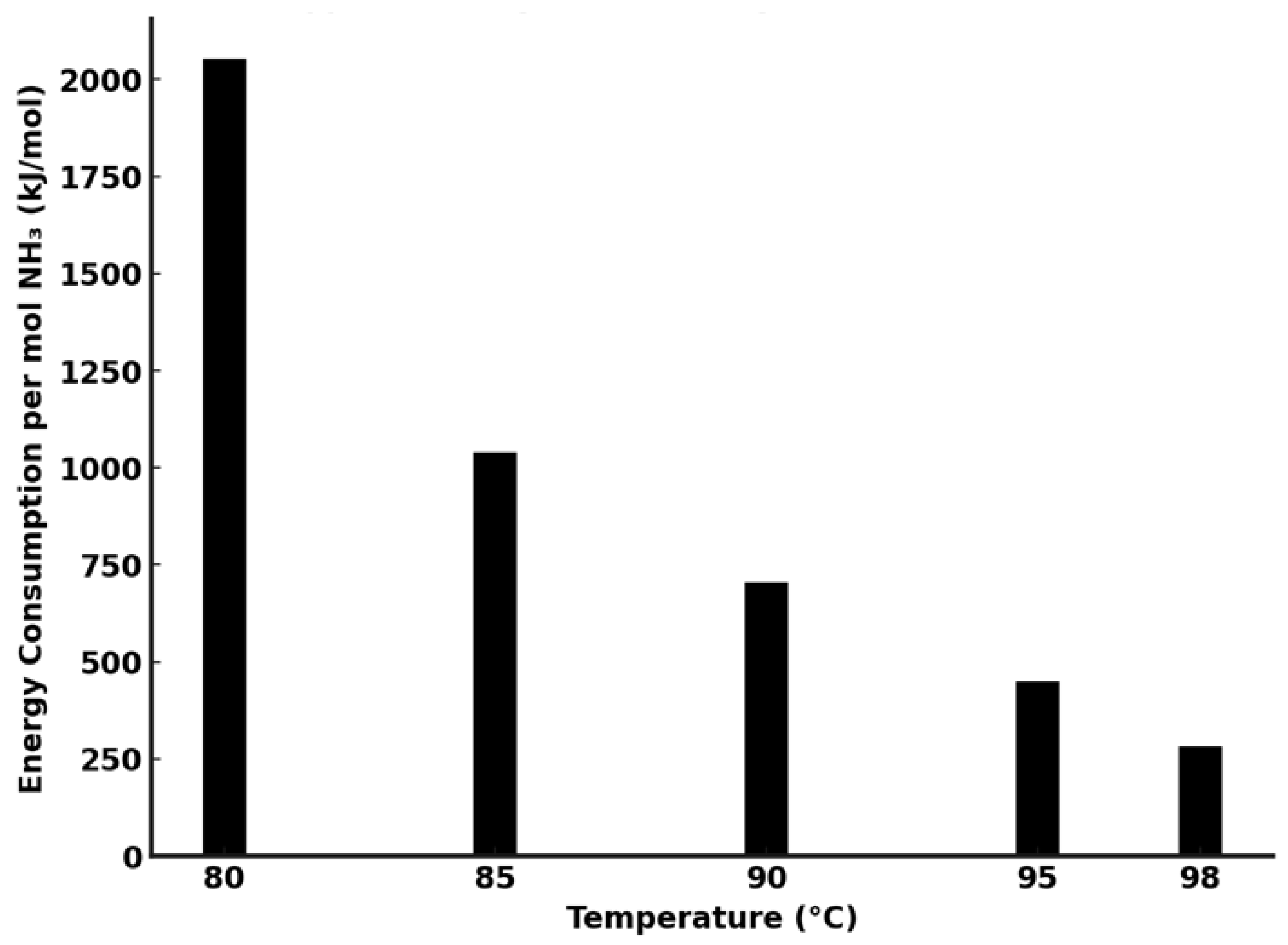
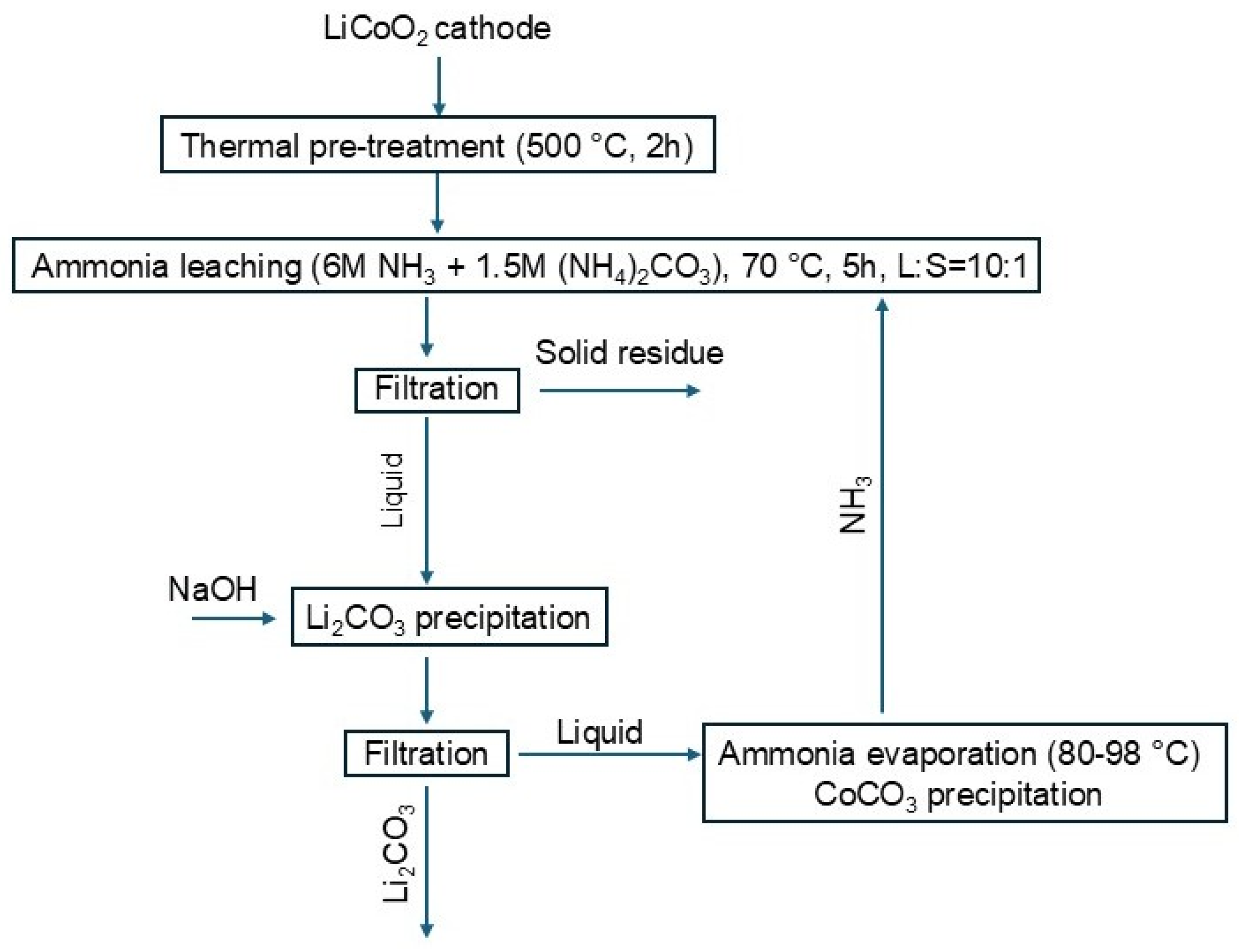
| Cathode | Leaching System | Optimal Conditions | Leaching Efficiency, % Li/Ni/Co/Mn, % | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiCoO2/NCM | NH3 + (NH4)2SO3 + (NH4)HCO3 | ≥60 °C, 3 h, S/L 20 g L−1 | 60.5 (Li), ≈100 (Ni), 81.0 (Co) | [24] |
| LiCoO2 | (NH4)2SO4 + (NH4)2SO3 | 90 °C, 2 h, S/L 10 g L−1 | 98 (Li), 98 (Ni), 81 (Co) | [25] |
| LiCoO2 | 6 M NH3 + 0.5 M NH4Cl + 0.5 M Na2SO3 | 60 °C, 4 h, S/L 10 g L−1 | 88.9 (Li), ≈64 (Ni), 98.2 (Co) | [26] |
| NCM111 | 4 M NH3 + 1.5 M (NH4)2SO4 + 0.5 M Na2SO3 | 90 °C, 3 h, S/L 10 g L−1 | 96.2 (Li), 90.1 (Ni), 89.9 (Co) | [25] |
| Mixed NCM | 0.61 M NH3·H2O + 3.56 M (NH4)2SO3 + 0.92 M (NH4)2CO3 | 80 °C, 5 h, S/L 10 g L−1 | 90.3 (Li), 64.1 (Ni), 84.6 (Co) | [26] |
| Li (wt%) | Co (wt%) | Al (wt%) | Cu (wt%) | Ni (ppm) | Mn (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.6 | 58.3 | 0.9 | 0.4 | <50 | <50 |
| Metal | Temperature (°C) | k1 (h−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Li | 50 | 0.1073 | 0.9875 |
| Li | 70 | 0.2485 | 0.9897 |
| Li | 80 | 0.3126 | 0.9912 |
| Co | 50 | 0.1786 | 0.9932 |
| Co | 70 | 0.4854 | 0.9941 |
| Co | 80 | 0.6281 | 0.9953 |
| Experiment No. | NH3 (mol/L) | (NH4)2CO3 (mol/L) | L:S Ratio (mL/g) | Li Recovery (%) | Co Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | 1 | 5:1 | 65.4 | 85.5 |
| 2 | 4 | 1.5 | 10:1 | 72.3 | 90.1 |
| 3 | 4 | 2 | 15:1 | 74.5 | 91.5 |
| 4 | 6 | 1 | 5:1 | 76.1 | 92.8 |
| 5 | 6 | 1.5 | 10:1 | 82.5 | 96.1 |
| 6 | 6 | 2 | 15:1 | 82.6 | 96.2 |
| 7 | 8 | 1 | 5:1 | 82.7 | 96.3 |
| 8 | 8 | 1.5 | 10:1 | 82.4 | 96.7 |
| 9 | 8 | 2 | 15:1 | 82.5 | 96.7 |
| L:S Ratio (mL/g) | Initial Leaching Rate of Li (%/h) | Initial Leaching Rate of Co (%/h) |
|---|---|---|
| 5:1 | 34.9 ± 0.3 | 47.8 ± 0.5 |
| 10:1 | 35.2 ± 0.3 | 49.8 ± 0.5 |
| 15:1 | 35.0 ± 0.3 | 50.3 ± 0.5 |
| NH3 (mol/L) | (NH4)2CO3 (mol/L) | Li Recovery After 1 h (%) | Co Recovery After 1 h (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 1.0 | 36.7 ± 0.4 | 47.9 ± 0.5 |
| 6 | 1.0 | 35.9 ± 0.3 | 48.3 ± 0.5 |
| 8 | 1.0 | 36.2 ± 0.5 | 47.1 ± 0.4 |
| 4 | 1.5 | 35.1 ± 0.3 | 49.0 ± 0.5 |
| 6 | 1.5 | 35.2 ± 0.3 | 49.8 ± 0.5 |
| 8 | 1.5 | 37.0 ± 0.5 | 50.2 ± 0.5 |
| 4 | 2.0 | 36.8 ± 0.3 | 48.7 ± 0.3 |
| 6 | 2.0 | 37.2 ± 0.4 | 50.4 ± 0.5 |
| 8 | 2.0 | 36.3 ± 0.4 | 49.7 ± 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batkal, A.; Kamunur, K.; Mussapyrova, L.; Milikhat, B.; Nadirov, R. Optimized Ammonia Leaching and Energy-Efficient Stripping for Lithium and Cobalt Recovery from Spent LiCoO2 Cathodes. Metals 2025, 15, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070690
Batkal A, Kamunur K, Mussapyrova L, Milikhat B, Nadirov R. Optimized Ammonia Leaching and Energy-Efficient Stripping for Lithium and Cobalt Recovery from Spent LiCoO2 Cathodes. Metals. 2025; 15(7):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070690
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatkal, Aisulu, Kaster Kamunur, Lyazzat Mussapyrova, Bagdatgul Milikhat, and Rashid Nadirov. 2025. "Optimized Ammonia Leaching and Energy-Efficient Stripping for Lithium and Cobalt Recovery from Spent LiCoO2 Cathodes" Metals 15, no. 7: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070690
APA StyleBatkal, A., Kamunur, K., Mussapyrova, L., Milikhat, B., & Nadirov, R. (2025). Optimized Ammonia Leaching and Energy-Efficient Stripping for Lithium and Cobalt Recovery from Spent LiCoO2 Cathodes. Metals, 15(7), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15070690






