Thermal Demercurization of Coal Sorbents
Abstract
1. Introduction
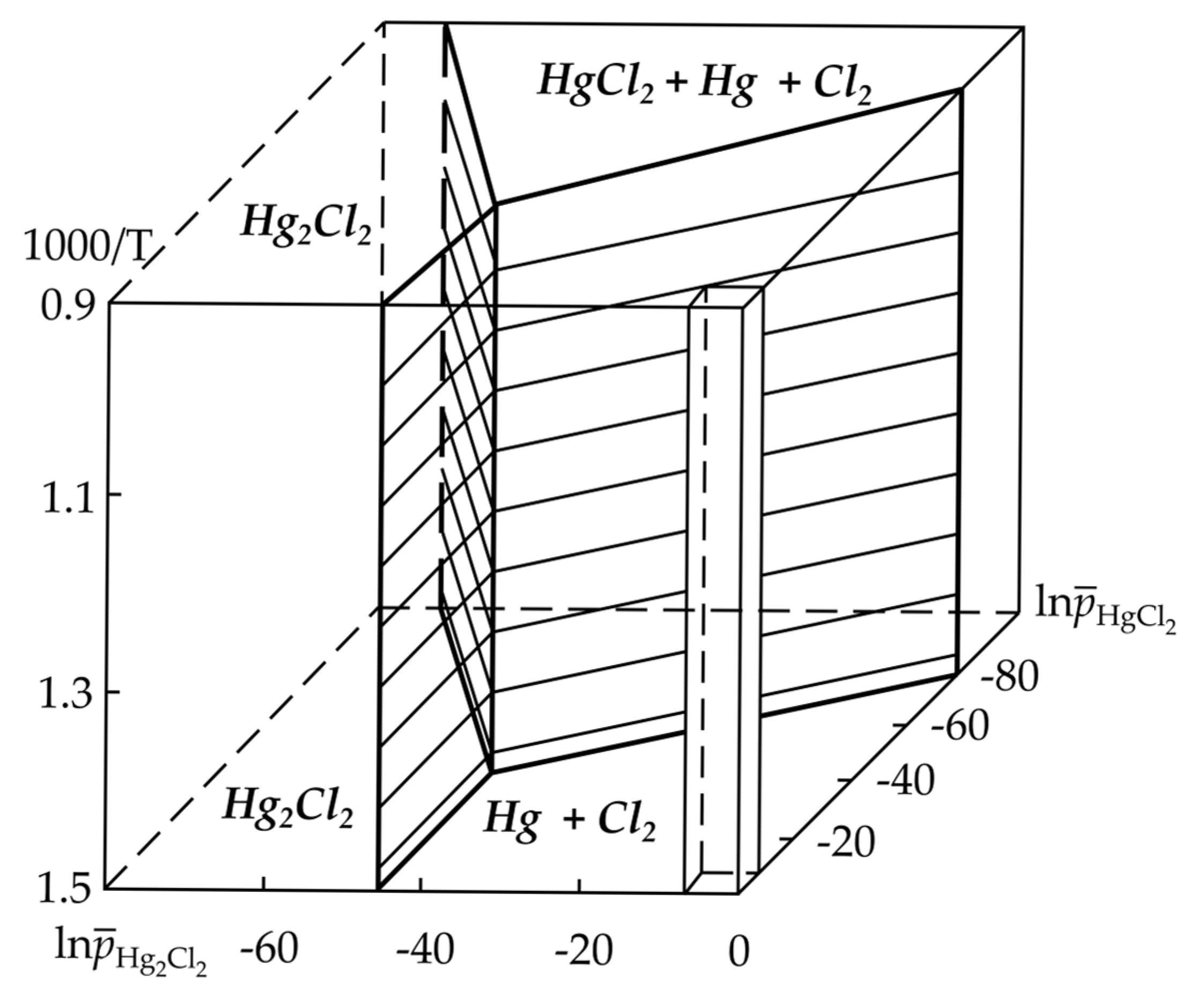
2. Behavior of Mercury Compounds During Thermal Desorption
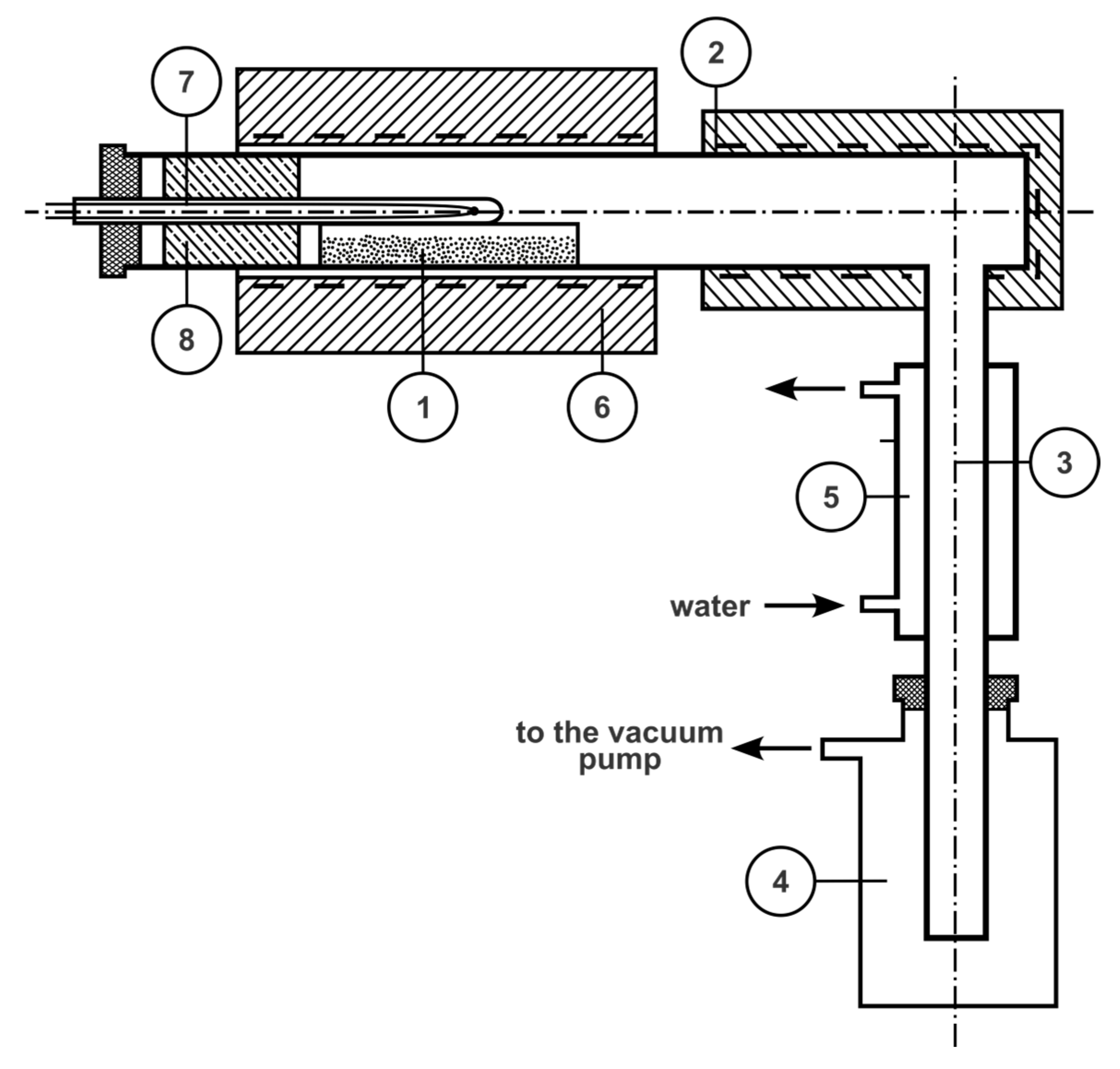
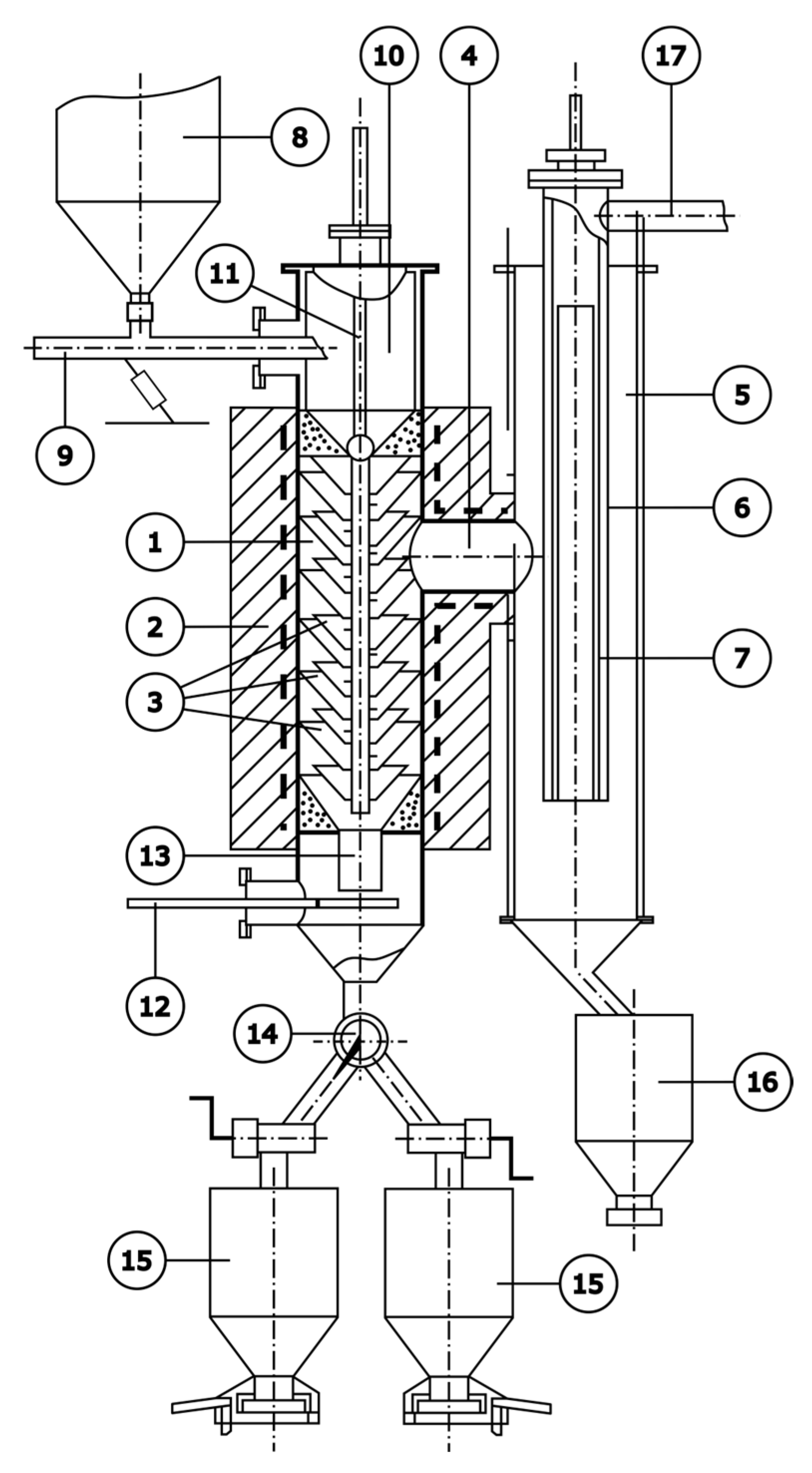
3. Technological Studies on Demercurization of Coal Sorbents
4. Determination of the Sorption Capacity of the Sorbent After Demercurization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yudovich, Y.E.; Ketris, M.P. Mercury in coal: A review: Part 1. Geochemistry. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2005, 62, 107–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudovich, Y.E.; Ketris, M.P. Mercury in coal: A review: Part 2. Geochemistry. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2005, 62, 135–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayev, F.F. Nomenclature of Mercury-Containing Production and Consumption Waste. Available online: https://www.waste.ru/modules/section/item.php?itemid=318 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Gayev, F.F. Processing and Disposal of Mercury-Containing Waste. Available online: https://www.waste.ru/modules/section/item.php?itemid=319 (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Kenzhaliyev, B.K. Innovative technologies providing enhancement of non-ferrous, precious, rare and rare earth metals extraction. Kompleks. Ispolzovanie Miner. Syra Complex Use Miner. Resour. 2019, 310, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yessengarayev, Y.K.; Surimbayev, B.N.; Baimbetov, B.S.; Mamyachenkov, S.V.; Kanaly, T.S. Ore treatment hydrogen peroxide during heap leaching of gold. Kompleks. Ispolzovanie Miner. Syra Complex Use Miner. Resour. 2021, 316, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Hu, C.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Stability of mercury on three activated carbon sorbents. Fuel Proc. Technol. 2006, 87, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shi, N.; Yan, B.; Wang, T.; Pan, W. Removal of elementary mercury by solid sorbents at different temperatures: Variation of the desorption activation energy through thermal desorption analysis. Fuel 2022, 307, 121889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Lee, J. Adsorption kinetic and equilibrium study for removal of mercuric chloride by CuCl2–impregnated activated carbon sorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252–253, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Wu, D.; Gu, C.; Zhang, Z. Elemental mercury removal from syngas by porous carbon-supported CuCl2sorbents. Fuel 2019, 239, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Perez, J.; López-Antón, M.A.; Diaz-Somano, M.; Garcia, R.; Martinez-Tarazona, M.R. Regenerable sorbents for mercury capture in simulated coal combustion flue gas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Giménez, C.; Izquierdo, M.T.; de las Obras-Loscertales, M.; de Diego, L.F.; Garcial-Labiano, F.; Adanez, J. Mercury capture by a structured Au/C regenerable sorbent under oxycoal combustion representative and real conditions. Fuel 2017, 207, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Giménez, C.; Ballestero, D.; Ferrer, N.; Rubio, B.; Izquierdo, M.T. Influence of crystal/particle size and gold content of a structured Au/C based sorbent on mercury capture. J. Phys. Chem. Solid. 2017, 110, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huo, Q.; Chen, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Chang, L.; Bao, W. High organic sulfur coal derived carbon-based sorbent for Hg capture from coal–fired flue gas. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 287, 119703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, G.; Hu, H.; Huang, Y. Investigation of elemental mercury removal performance and mechanism of rice straw biochars from a fluidized bed pyrolysis system impregnated by NH4Br. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 492, 152069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebukhov, S.A.; Marki, I.A.; Nitsenko, A.V.; Trebukhov, A.A. Vacuum–thermal demercurization of spent coal sorbents from gold mining enterprises. Non-Ferr. Met. 2016, 9, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Dazhuang, L. The loss rate by sublimation of mercuric chloride adsorbed on activated carbon. Carbon 1993, 31, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Yungman, V.S.; Glushko, V.P. Thermal Constants of Substances, Reference Book; Glushko, V.P.M., Ed.; VINITI: Moscow, Russia, 1973; Volume 6, 466pp. [Google Scholar]
- Babichev, N.A.; Babushkina, A.M.; Bratkovsky, A.M. Physical Quantities. Reference Book; Grigoriev, I.S., Meilikhov, E.Z., Eds.; Energoatomizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1991; 1232p. [Google Scholar]
- Yaws, C.L.; Nijhawan, S.; Bu, L. Handbook of Vapor Pressure; Gulf Pub. Co.: Houston, TX, USA, 1995; Volume 4, pp. 352–357. [Google Scholar]
- Karyakin, Y.V.; Angelov, I.I. Pure Chemical Substances; Khimiya: Moscow, Russia, 1974; p. 407. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation (EU) 2017/852 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 May 2017 on Mercury, and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 1102/2008 (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1531231211865&uri=CELEX:32017R0852 (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Barchenkov, V.V.; Gaidukov, I.V. How to restore the sorption properties of activated carbon. Zolotodobycha 2017, 221. Available online: https://zolotodb.ru/article/11622 (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Volodin, V.N.; Trebukhov, S.A.; Kenzhaliyev, B.K.; Nitsenko, F.V.; Burabayeva, N.M.; Trebukhov, A.A.; Tuleutai, F.K. Vacuum Electric Furnace for Processing Bulk Materials. Patent of the Republic of Kazakhstan No. 36160 7 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Trebukhov, S.; Volodin, V.; Nitsenko, A.; Linnik, X.; Kilibayev, E.; Kolesnikova, O.; Liseitsev, Y. Dearsenation of Gold-Bearing Composite Concentrates without Forced Displacement in a Sublimator. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pressure | Temperatures, K | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.33 kPa (10 mm Hg) | 514 | 521 | 519 | 522 |
| 40 kPa (300 mm Hg) | 615 | 620 | 614 | 628 |
| No. | Reaction | Equilibrium Constant | Values of ln Kp at Temperature, K | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 673 | 1073 | |||
| 1 | Hg2Cl2 = Hg + HgCl2 | 14.625 | 17.015 | |
| 2 | Hg2Cl2 = 2Hg + Cl2 | 46.496 | 48.675 | |
| 3 | HgCl2 = Hg + Cl2 | 35.311 | 32.729 | |
| 4 | 2Hg2Cl2 = 3Hg + HgCl2 + Cl2 | 57.678 | 62.248 | |
| 5 | Hg2Cl2 + Cl2 = 2HgCl2 | −6.780 | 32.174 | |
| 6 | Hg2Cl2 + HgCl2 = 3Hg + 2Cl2 | 80.876 | 83.777 | |
| Fraction size, mm | +2.5 | −2.5 + 2.0 | −2.0 + 1.0 | −1.0 |
| Quantity, wt.% | 13.6 ÷ 19.5 | 34.7 ÷ 39.6 | 50.7 ÷ 40.6 | 1.0 ÷ 0.3 |
| Temperature, °C | Content in Residue and Extraction of Mercury at Pressure, kPa: | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.13 | 1.33 | 13.33 | 91.99 | |||||
| Content, % | Extraction, % | Content, % | Extraction, % | Content, % | Extraction, % | Content, % | Extraction, % | |
| 300 | 8 × 10−4 | 99.94 | 1 × 10−3 | 99.92 | 8 × 10−3 | 99.40 | 8.7 × 10−2 | 93.43 |
| 400 | 5 × 10−4 | 99.96 | 6 × 10−4 | 99.95 | 6 × 10−3 | 99.55 | 5.0 × 10−2 | 96.22 |
| 500 | 5 × 10−4 | 99.96 | 6 × 10−4 | 99.95 | 2 × 10−3 | 99.85 | 1.6 × 10−2 | 98.79 |
| 600 | 3 × 10−4 | 99.98 | 5 × 10−4 | 99.96 | 3.4 × 10−3 | 99.74 | 3 × 10−3 | 99.77 |
| 800 | 4 × 10−4 | 99.97 | 3 × 10−4 | 99.98 | 1.9 × 10−3 | 99.97 | 2 × 10−3 | 99.85 |
| Temperature, °C | Time, min | Content in Residue and Extraction of Mercury at Pressure, kPa: | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.33 | 91.99 | ||||
| Content, % | Extraction, % | Content, % | Extraction, % | ||
| 600 | 30 | 3 × 10−3 | 99.77 | 3 × 10−3 | 99.77 |
| 600 | 60 | 1 × 10−3 | 99.92 | 1 × 10−3 | 99.92 |
| 600 | 120 | 3 × 10−4 | 99.98 | 1 × 10−4 | 99.98 |
| 800 | 30 | 3 × 10−3 | 99.77 | 2 × 10−3 | 99.85 |
| 800 | 60 | 3 × 10−4 | 99.98 | 1 × 10−3 | 99.92 |
| 800 | 120 | 1 × 10−4 | 99.99 | 1 × 10−4 | 99.99 |
| No. | Temperature, °C | Pressure, kPa | Sorbent Output, % | Hg Content in Residue, % | Hg Recovery Rate, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 400 | 1.33 | 98.34 | 7.0 × 10−4 | 99.94 |
| 2 | 400 | 91.99 | 96.77 | 5.0 × 10−2 | 96.00 |
| 3 | 600 | 1.33 | 97.64 | 6.0 × 10−4 | 99.95 |
| 4 | 600 | 91.99 | 96.31 | 3.0 × 10−3 | 99.76 |
| 5 | 800 | 1.33 | 97.13 | 3.0 × 10−4 | 99.98 |
| 6 | 800 | 91.99 | 95.43 | 3.0 × 10−3 | 99.76 |
| Carbon Sorbent | Au Content in Initial Solution, mg/L | Au Content in Solution After Sorption, mg/L | Au Recovery, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| After thermal demercurization | 2.564 | 0.202 | 92.12 |
| Original “Norit” | 2.564 | 0.198 | 92.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kenzhaliyev, B.; Volodin, V.; Trebukhov, S.; Nitsenko, A.; Linnik, X.; Magomedov, D.; Kilibayev, Y. Thermal Demercurization of Coal Sorbents. Metals 2025, 15, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060662
Kenzhaliyev B, Volodin V, Trebukhov S, Nitsenko A, Linnik X, Magomedov D, Kilibayev Y. Thermal Demercurization of Coal Sorbents. Metals. 2025; 15(6):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060662
Chicago/Turabian StyleKenzhaliyev, Bagdaulet, Valeriy Volodin, Sergey Trebukhov, Alina Nitsenko, Xeniya Linnik, David Magomedov, and Yerkebulan Kilibayev. 2025. "Thermal Demercurization of Coal Sorbents" Metals 15, no. 6: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060662
APA StyleKenzhaliyev, B., Volodin, V., Trebukhov, S., Nitsenko, A., Linnik, X., Magomedov, D., & Kilibayev, Y. (2025). Thermal Demercurization of Coal Sorbents. Metals, 15(6), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060662






