The Effect of Mg Content on the Microstructure and Open Porosity of a Porous FeAl Intermetallic Compound
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
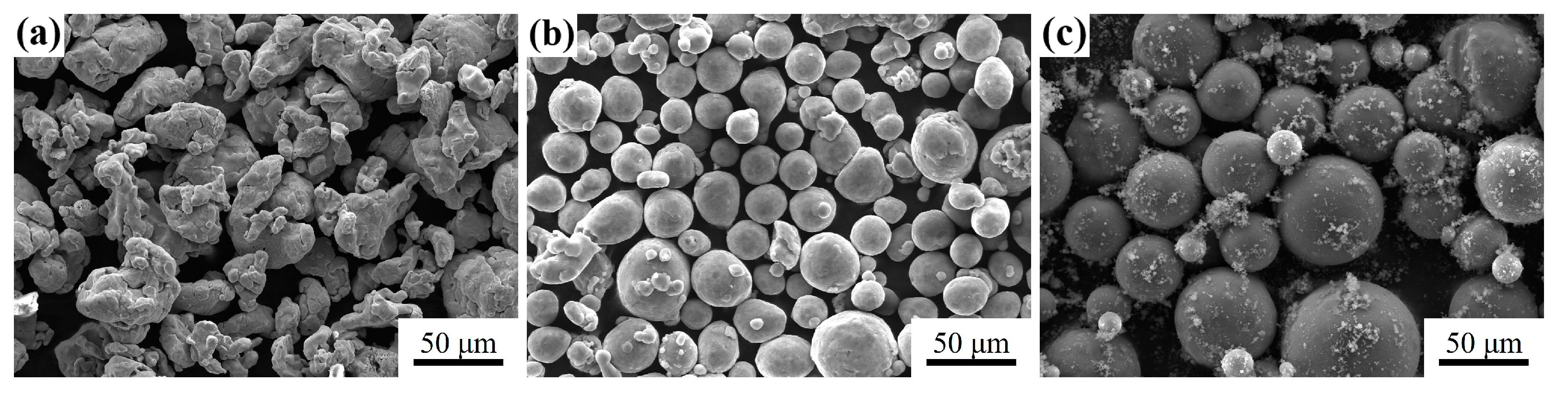
2.1. Powder Preparation
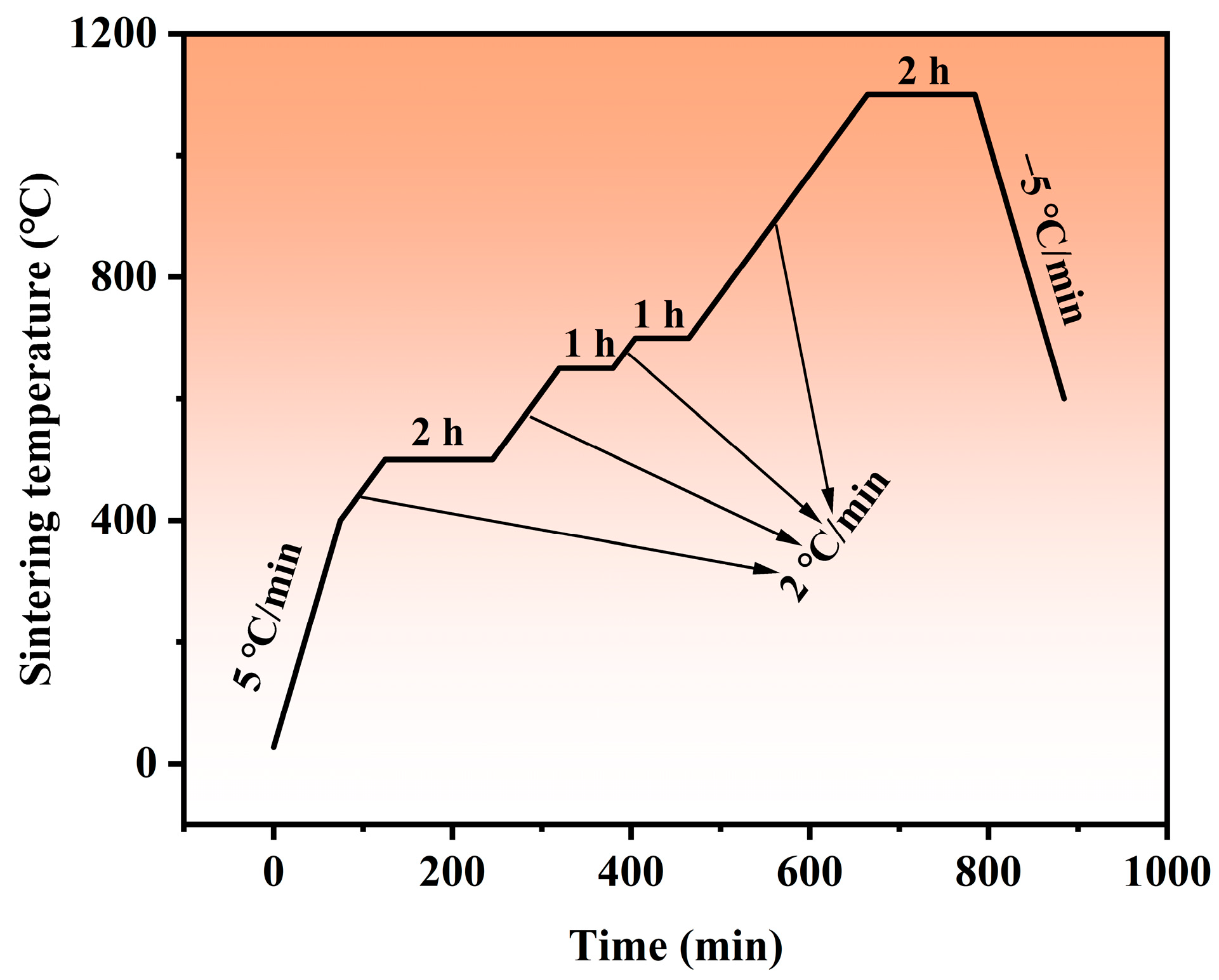
2.2. Press and Sinter
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
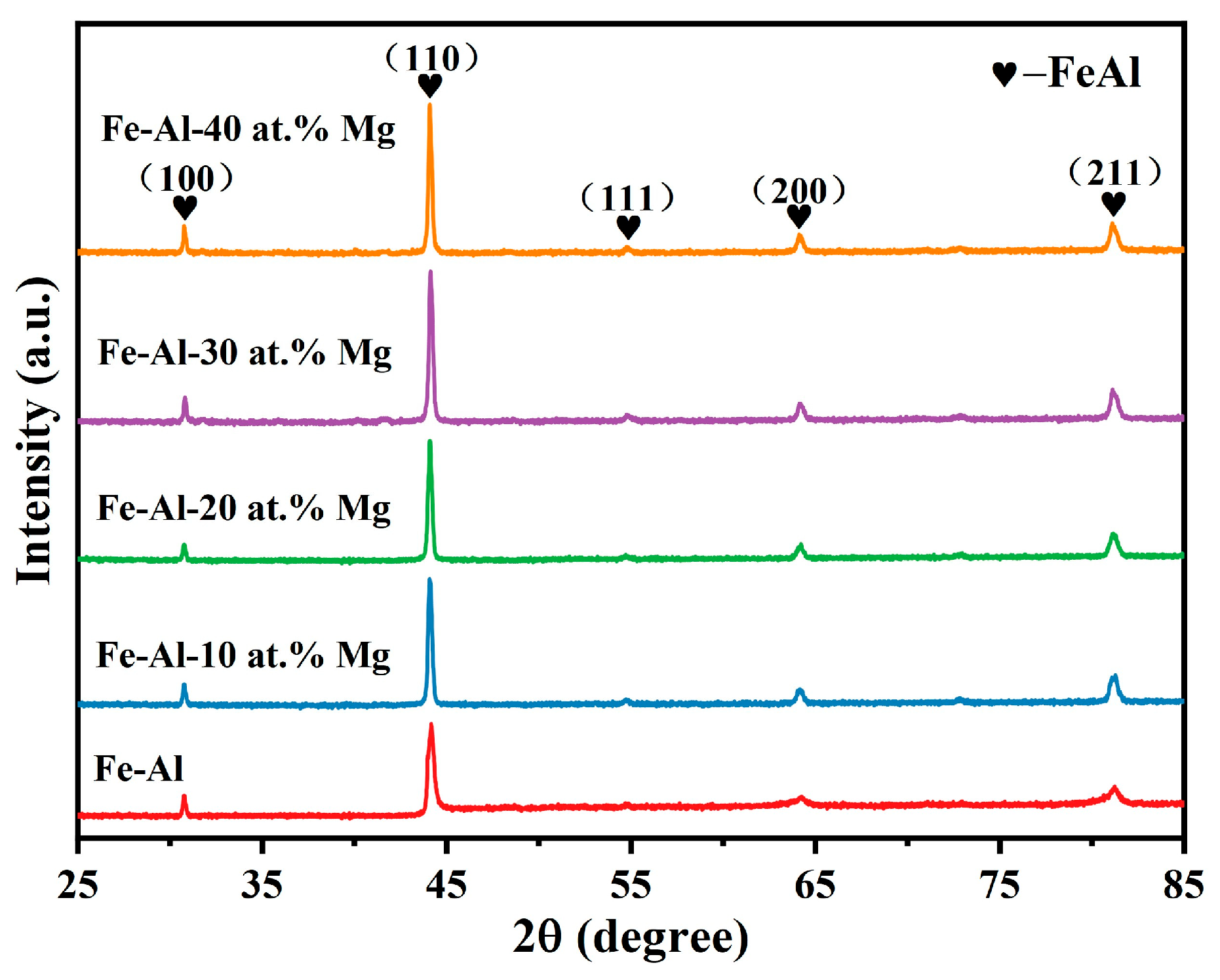
3.1. Influence of Mg Content on Phase Composition
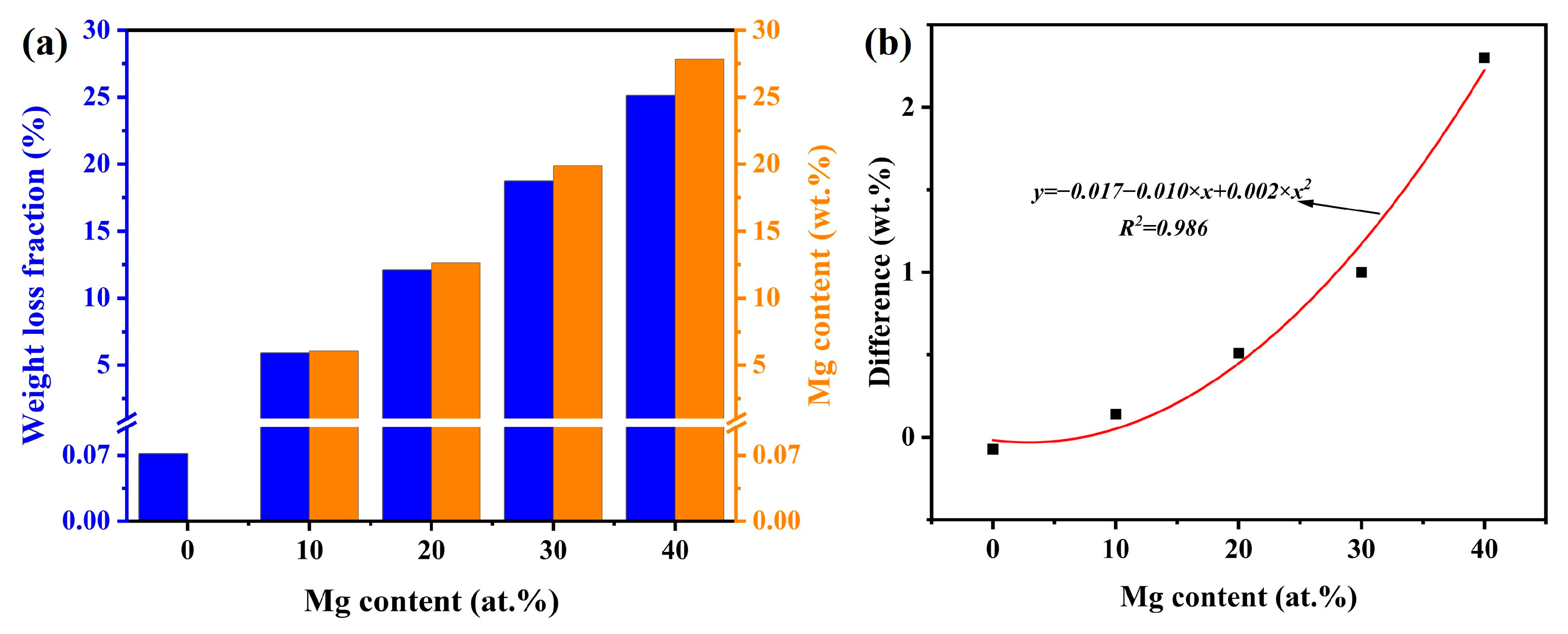
3.2. Influence of Mg Content on Weight Loss Rate
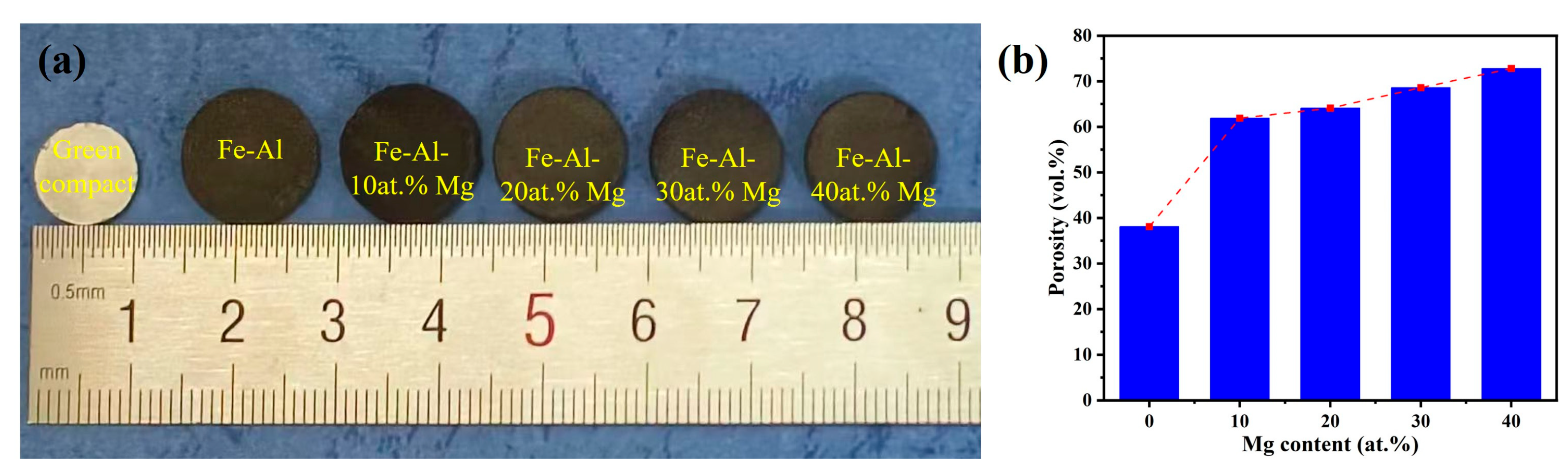
3.3. Influence of Mg Content on Macroscopic Characteristics and Open Porosity
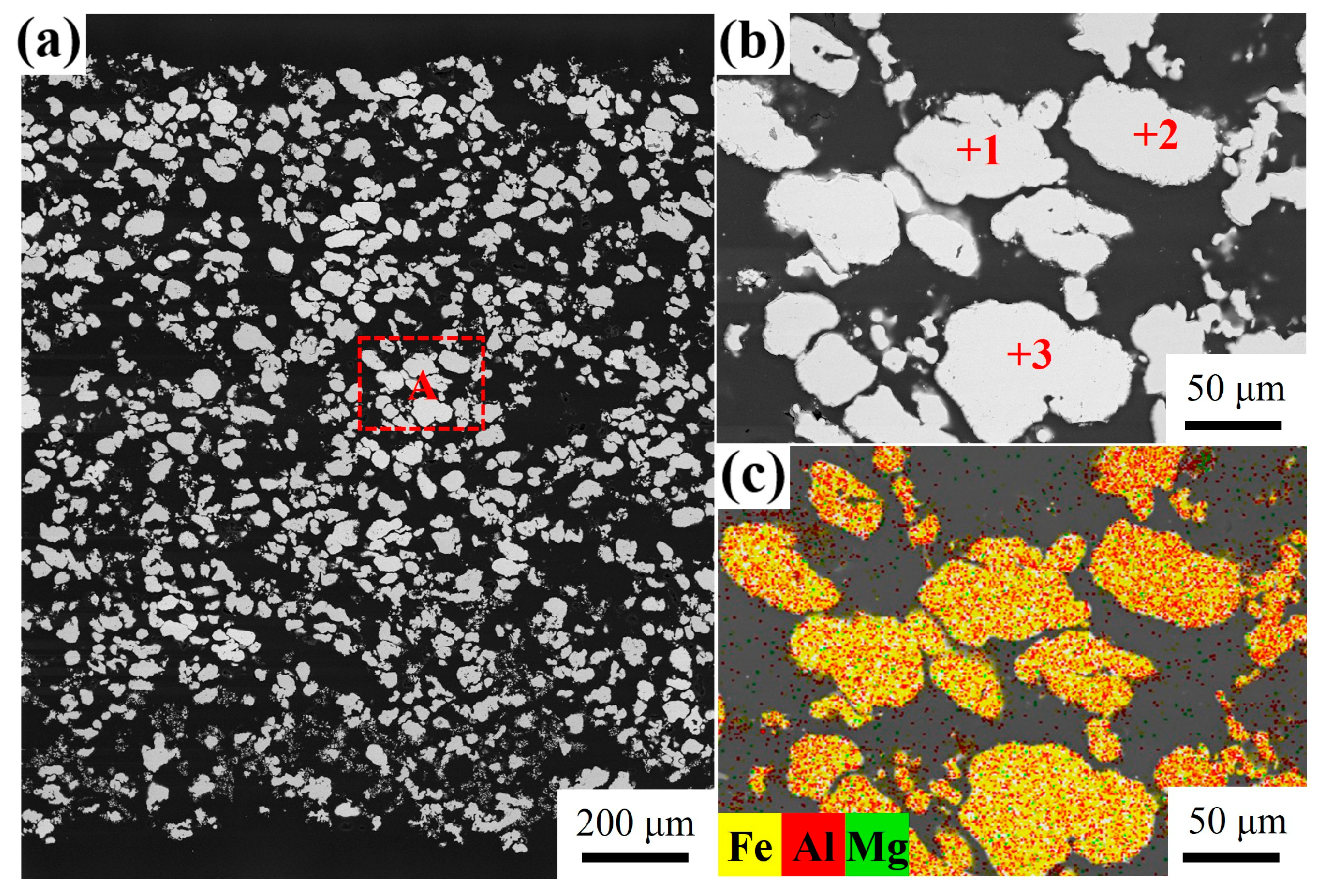
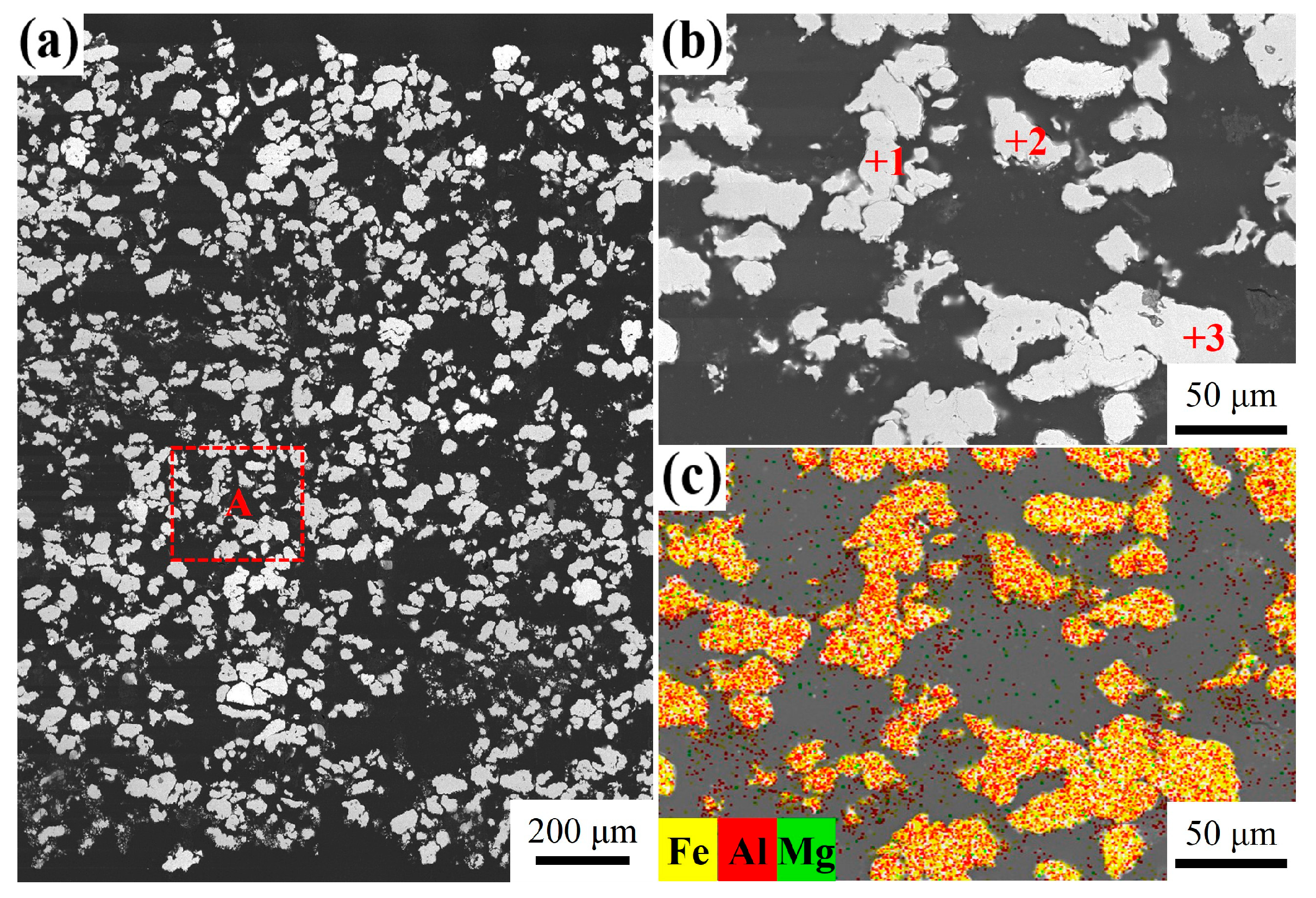
3.4. Influence of Mg Content on Microstructure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lang, F.; Yu, Z.; Gedevanishvili, S.; Deevi, S.C.; Hayashi, S.; Narita, T. Sulfidation behavior of Fe-40Al sheet in H2-H2S mixtures at high temperatures. Intermetallics 2004, 12, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deevi, S.C.; Sikka, V.K.; Liu, C.T. Processing, properties, and applications of nickel and iron aluminides. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1997, 42, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudina, D.V.; Bokhonov, B.B.; Legan, M.A.; Novoselov, A.N.; Skovorodin, I.N.; Bulina, N.V.; Esikov, M.A.; Mali, V.I. Analysis of the formation of FeAl with a high open porosity during electric current-assisted sintering of loosely packed Fe-Al powder mixtures. Vacuum 2017, 146, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, D. Porous Iron Aluminide: Innovative Filtration Technology for Refineries and Clean Coal Applications. Adv. Mater. Process. 2011, 169, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, S.; Zheng, G. Improving oxidation resistance of porous FeAl-based intermetallics with high boron/yttrium alloying. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 32, 2620–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Rao, Q.; He, Y.; Xie, W. Effects of porosity on tensile mechanical properties of porous FeAl intermetallics. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 2757–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; He, Y.; Zou, J.; Xu, N.; Liu, C. Pore structure control for porous FeAl intermetallics. Intermetallics 2013, 32, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; He, Y.; Shen, P.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, C. Effect of pressure on pore structure of porous FeAl intermetallics. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; He, Y.; Gao, H.; Zou, J.; Xu, N.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, B.; Liu, C. Development of a new graded-porosity FeAl alloy by elemental reactive synthesis. Desalination 2009, 249, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudina, D.V.; Legan, M.A.; Fedorova, N.V.; Novoselov, A.N.; Anisimov, A.G.; Esikov, M.A. Structural and mechanical characterization of porous iron aluminide FeAl obtained by pressureless Spark Plasma Sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 695, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liss, K.D.; Chen, C.; He, Y.; Qu, X.; Cao, P. Porous FeAl alloys via powder sintering: Phase transformation, microstructure and aqueous corrosion behavior. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 86, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łazińska, M.; Durejko, T.; Lipiński, S.; Polkowski, W.; Czujko, T.; Varin, R.A. Porous graded FeAl intermetallic foams fabricated by sintering process using NaCl space holders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 636, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, K.; Stȩpniowski, W.J.; Jóźwiak, S. Highly-porous FeAl intermetallic foams formed via sintering with Eosin Y as a gas releasing agent. Mater. Lett. 2016, 178, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, K.; Stepniowski, W.J.; Chojnacki, M.; Jozwiak, S. Crystalline oxalic acid aided FeAl intermetallic alloy sintering. Fabrication of intermetallic foam with porosity above 45% %. Mater. Lett. 2016, 164, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Cai, X.; Jiao, X.; Feng, P. Fabrication of porous FeAl-based intermetallics via thermal explosion. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2018, 28, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipek Nakaş, G.; Dericioǧlu, A.F.; Bor, T. Monotonic and cyclic compressive behavior of superelastic TiNi foams processed by sintering using magnesium space holder technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 582, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydoǧmuş, T.; Bor, S. Superelasticity and compression behavior of porous TiNi alloys produced using Mg spacers. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 15, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aşık, E.E.; Bor, Ş. Fatigue behavior of Ti–6Al–4V foams processed by magnesium space holder technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 621, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W. Diffusion mechanism of immiscible Fe-Mg system induced by high-density defects at the steel/Mg composite interface. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 144, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayeb-Hashemi, A.A.; Clark, J.B.; Swartzendruber, L.J. The Fe-Mg (Iron-Magnesium) System. J. Phase Equilibria 1985, 6, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shen, D.; Wang, K.; He, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Cao, P.; Huang, S.; Peng, J.; Shen, Q.; et al. Synthesis of a novel Al foam with a periodic architecture by introducing hollow Al tubes and Al/Mg powders. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 148, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Guo, E.; Shen, D.; Yang, Z.; Xie, C.; Peng, J.; Shen, Q.; Wang, C. Sintering temperature dependence of microstructure evolution and compression performance of a novel circular Al honeycomb fabricated via powder sintering. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 35, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Shen, Q.; Wang, C. Fabrication of a Porous Fe-Al Intermetallic Alloy with Ultrahigh Open Porosity. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM B0962-23; Standard Test Methods for Density of Compacted or Sintered Powder Metallurgy (PM) Products Using Archimedes Principle. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023; p. 7.
- Yang, C.; Tian, Y.; Qu, T.; Yang, B.; Xu, B.; Dai, Y. Magnesium vapor nucleation in phase transitions and condensation under vacuum conditions. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Fu, D.; Guo, J.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, T.a. Volatilization and condensation behavior of magnesium vapor during magnesium production via a silicothermic process with magnesite. Vacuum 2021, 189, 110227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanzade, M.; Barnoush, A.; Motz, C. A review on the properties of iron aluminide intermetallics. Crystals 2016, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmanf, J.A. Mechanism of pore formation associated with the Kirkendall effect. Acta Metall. 1955, 3, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Supplemental Literature Review of Binary Phase Diagrams: Al-Mg, Bi-Sr, Ce-Cu, Co-Nd, Cu-Nd, Dy-Pb, Fe-Nb, Nd-Pb, Pb-Pr, Pb-Tb, Pd-Sb, and Si-W. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2015, 36, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
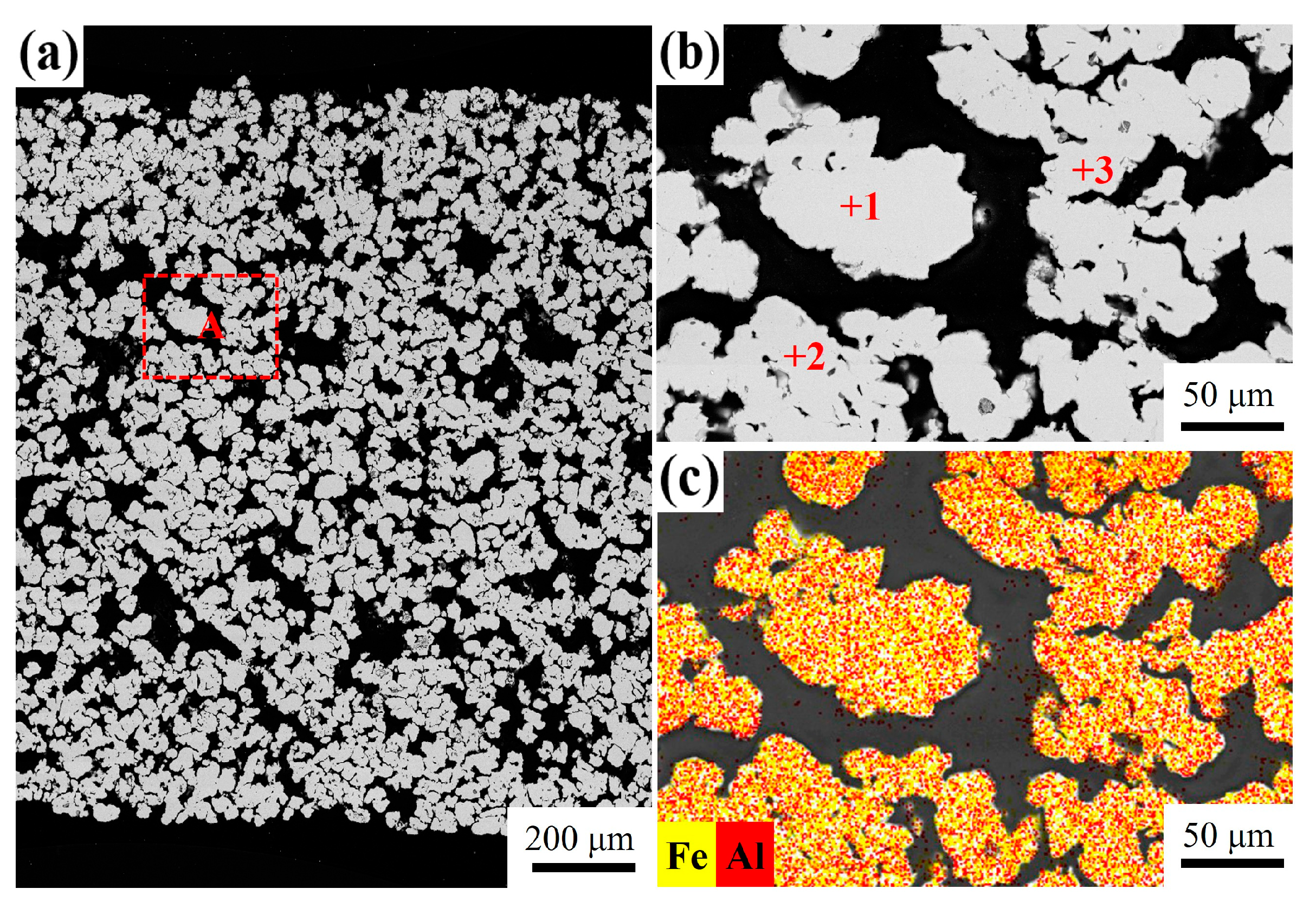
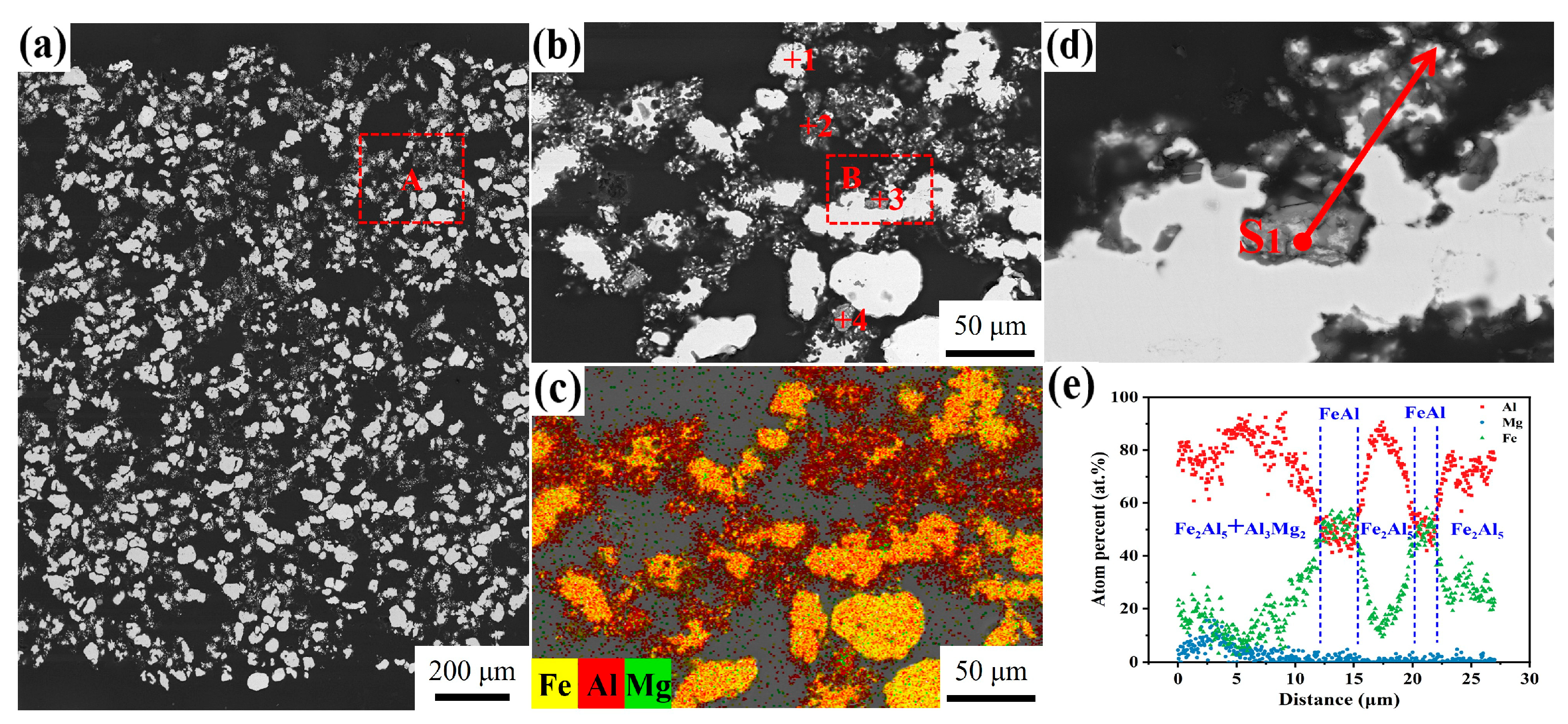

| Point | Fe (at.%) | Al (at.%) | Possible Phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 53.53 | 46.47 | FeAl |
| 2 | 55.91 | 44.09 | FeAl |
| 3 | 56.39 | 43.61 | FeAl |
| Point | Fe (at.%) | Al (at.%) | Mg (at.%) | Possible Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 64.65 | 35.31 | 0.04 | FeAl |
| 2 | 60.67 | 39.32 | 0.01 | FeAl |
| 3 | 63.11 | 36.87 | 0.02 | FeAl |
| Point | Fe (at.%) | Al (at.%) | Mg (at.%) | Possible Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 55.78 | 44.22 | 0 | FeAl |
| 2 | 55.51 | 44.43 | 0.06 | FeAl |
| 3 | 60.84 | 38.99 | 0.17 | FeAl |
| Point | Fe (at.%) | Al (at.%) | Mg (at.%) | Possible Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 54.71 | 45.29 | 0 | FeAl |
| 2 | 34.47 | 65.40 | 0.13 | Fe2Al5 |
| 3 | 20.32 | 74.82 | 4.86 | Fe2Al5 + Al3Mg2 |
| 4 | 18.72 | 69.44 | 11.83 | Fe2Al5 + Al3Mg2 |
| Point | Fe (at.%) | Al (at.%) | Mg (at.%) | Possible Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 65.52 | 34.48 | 0 | Fe + FeAl |
| 2 | 16.76 | 66.23 | 17.01 | Fe2Al5 + Al3Mg2 |
| 3 | 18.61 | 67.33 | 14.06 | FeAl + Al3Mg2 |
| 4 | 19.78 | 19.73 | 60.49 | FeAl + Mg + Al3Mg2 |
| 5 | 56.78 | 42.91 | 0.32 | FeAl |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, D.; Xu, Z. The Effect of Mg Content on the Microstructure and Open Porosity of a Porous FeAl Intermetallic Compound. Metals 2025, 15, 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060628
Xue W, Liu Z, Liu D, Xu Z. The Effect of Mg Content on the Microstructure and Open Porosity of a Porous FeAl Intermetallic Compound. Metals. 2025; 15(6):628. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060628
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Weilun, Zhuoxuan Liu, Dongming Liu, and Zhigang Xu. 2025. "The Effect of Mg Content on the Microstructure and Open Porosity of a Porous FeAl Intermetallic Compound" Metals 15, no. 6: 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060628
APA StyleXue, W., Liu, Z., Liu, D., & Xu, Z. (2025). The Effect of Mg Content on the Microstructure and Open Porosity of a Porous FeAl Intermetallic Compound. Metals, 15(6), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060628





