Effect of Sintering Temperature and Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
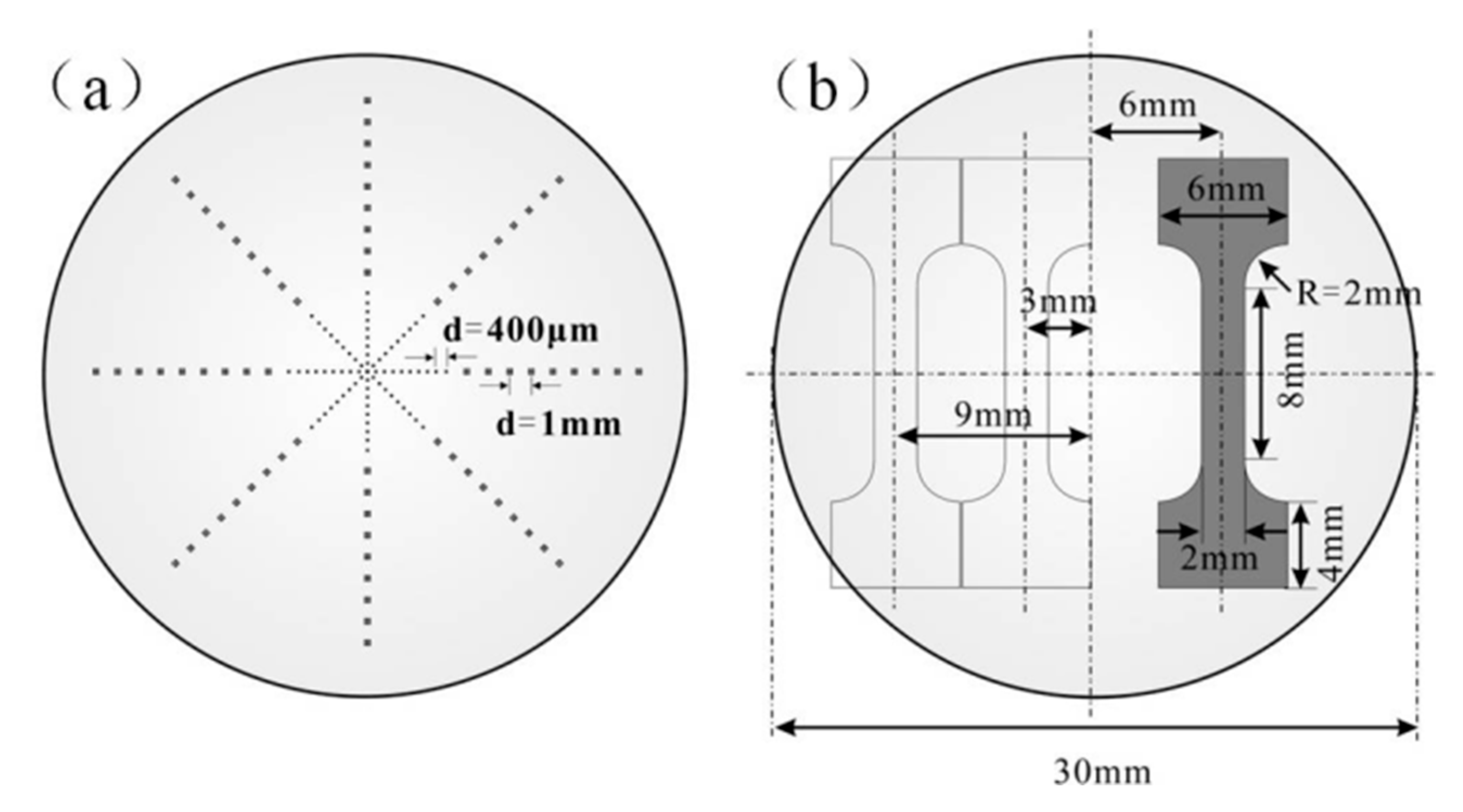
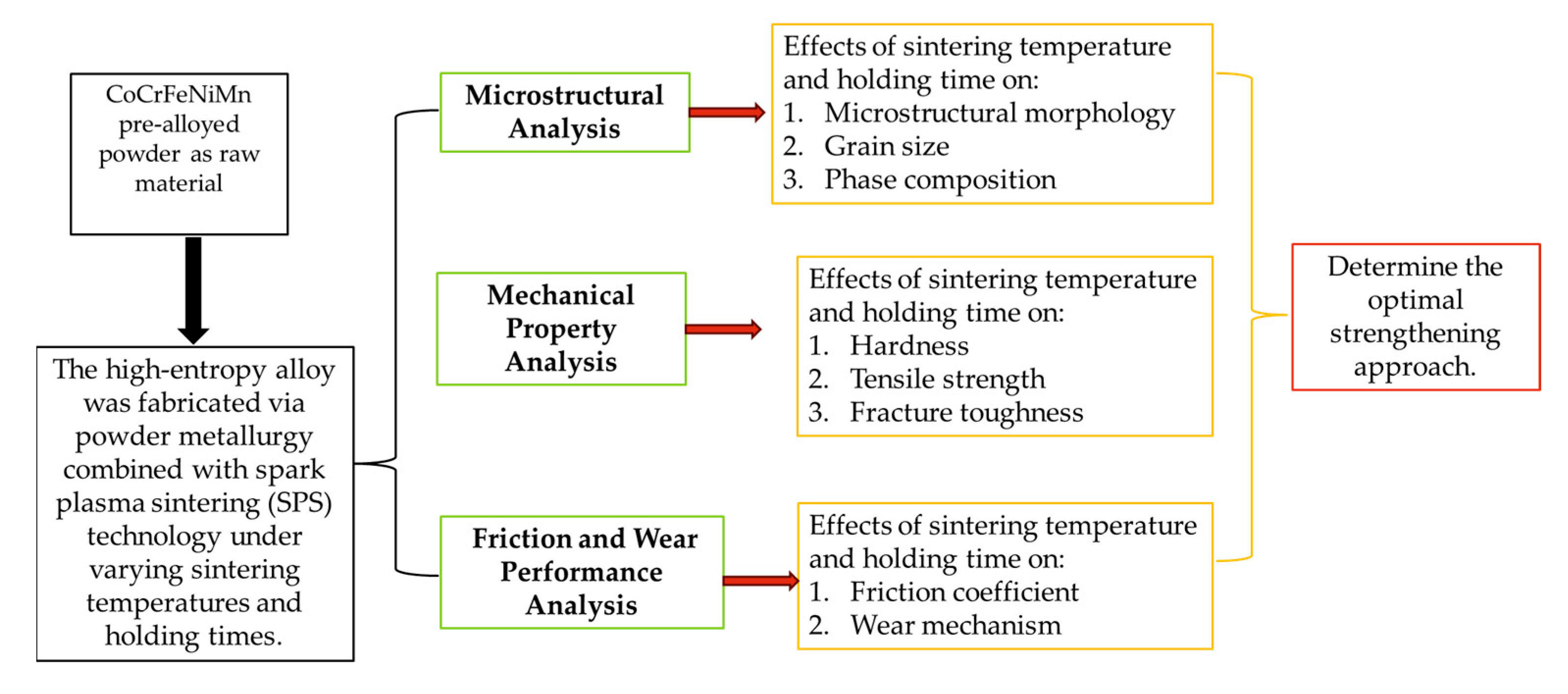
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
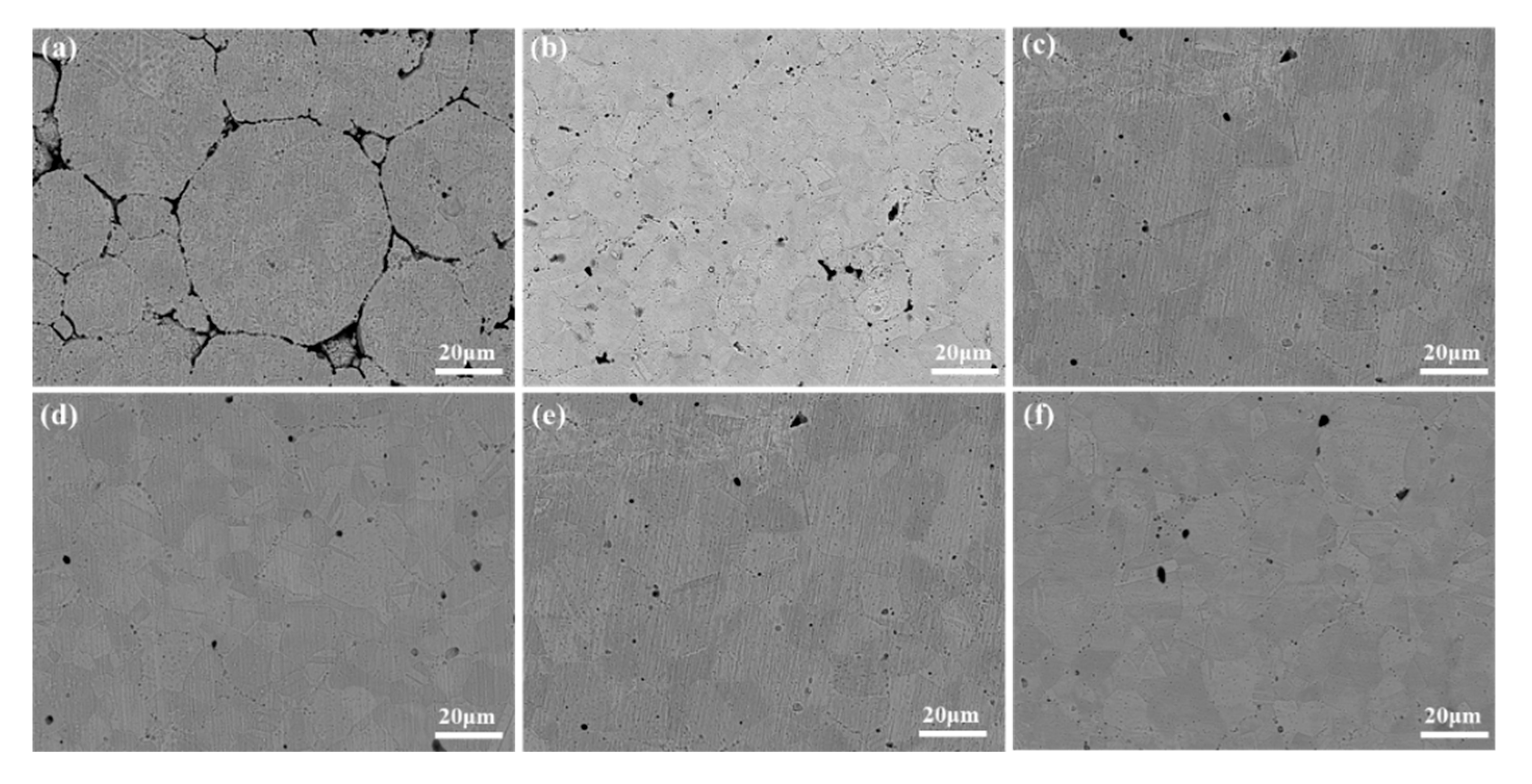
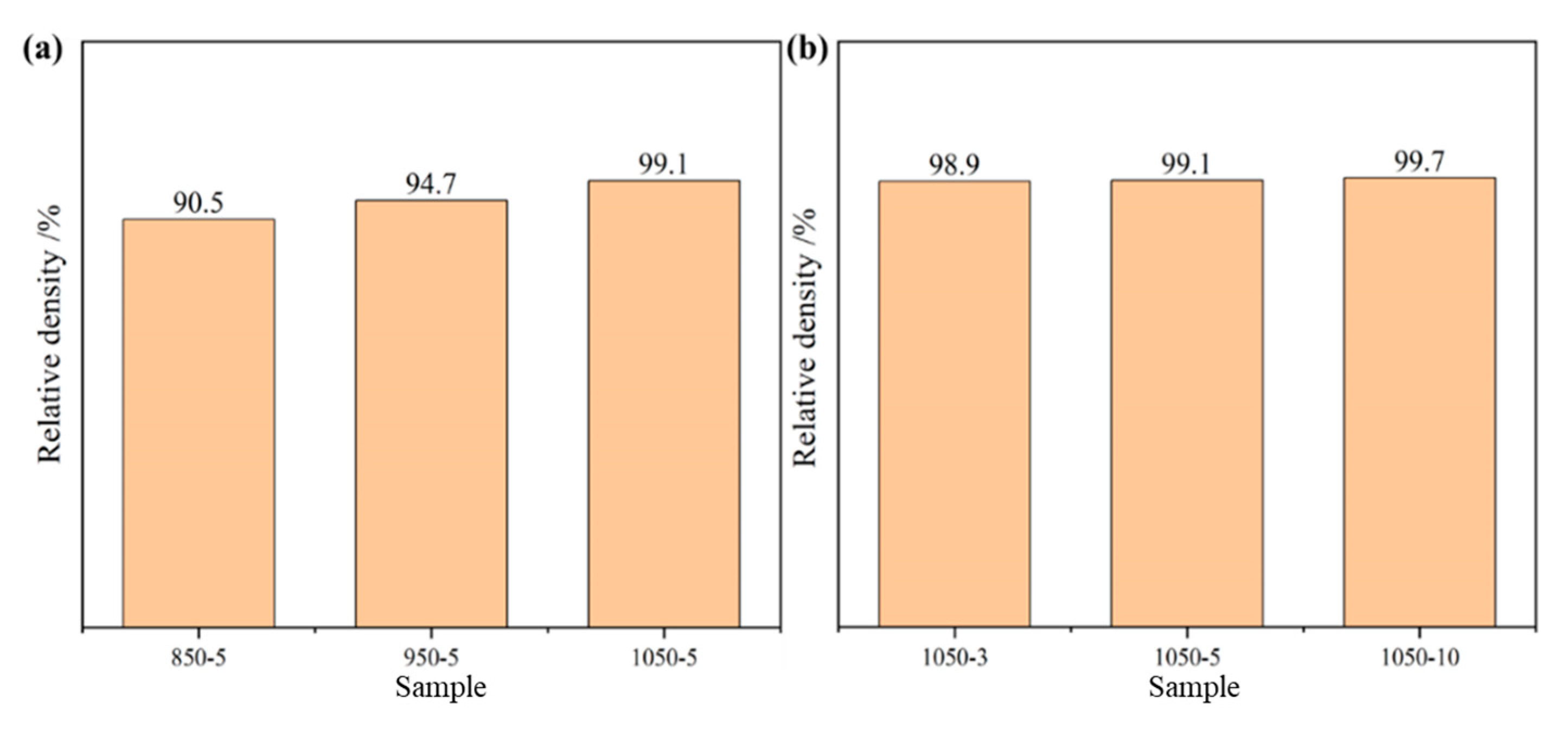
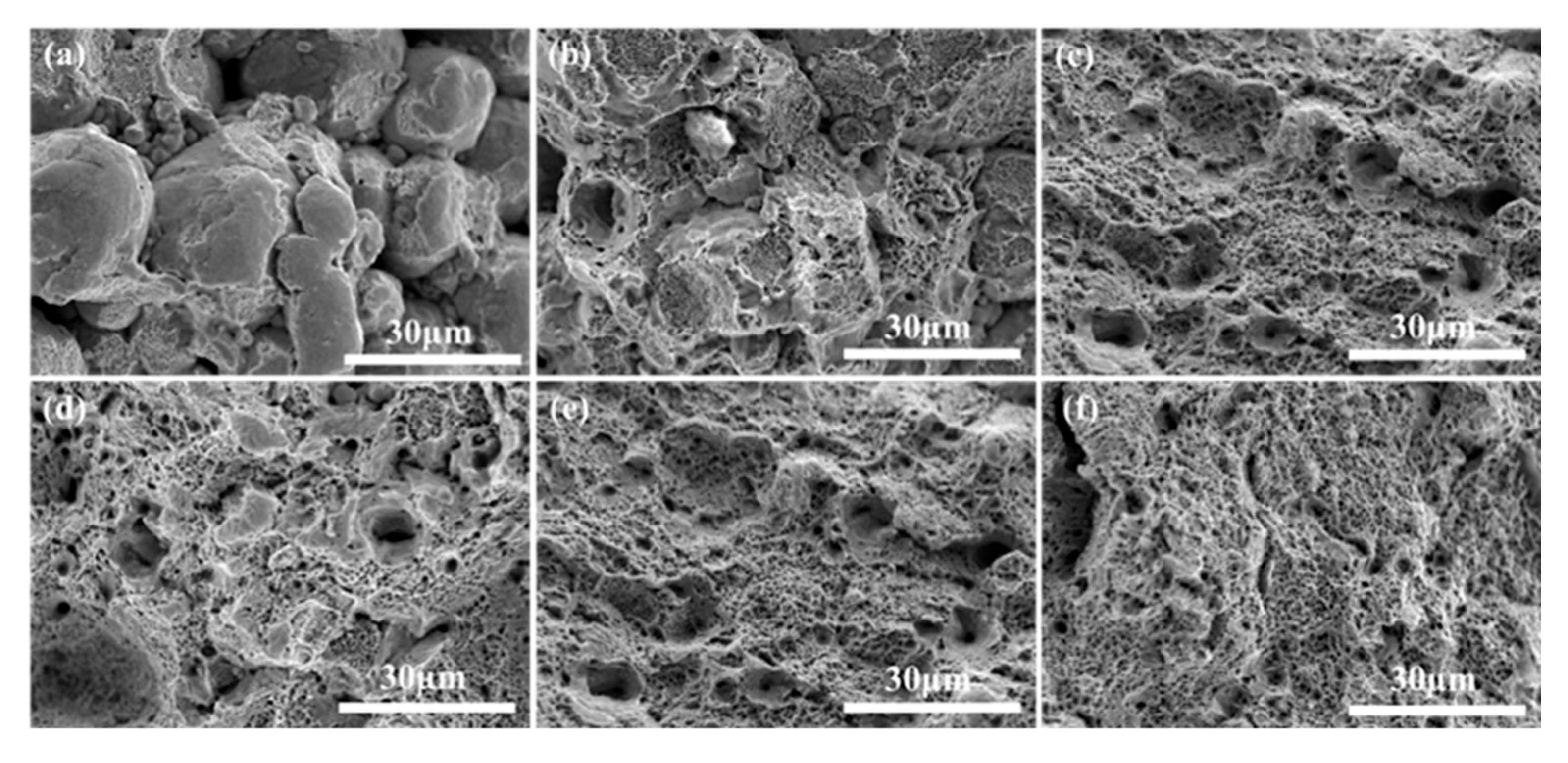
3.1. Microstructure
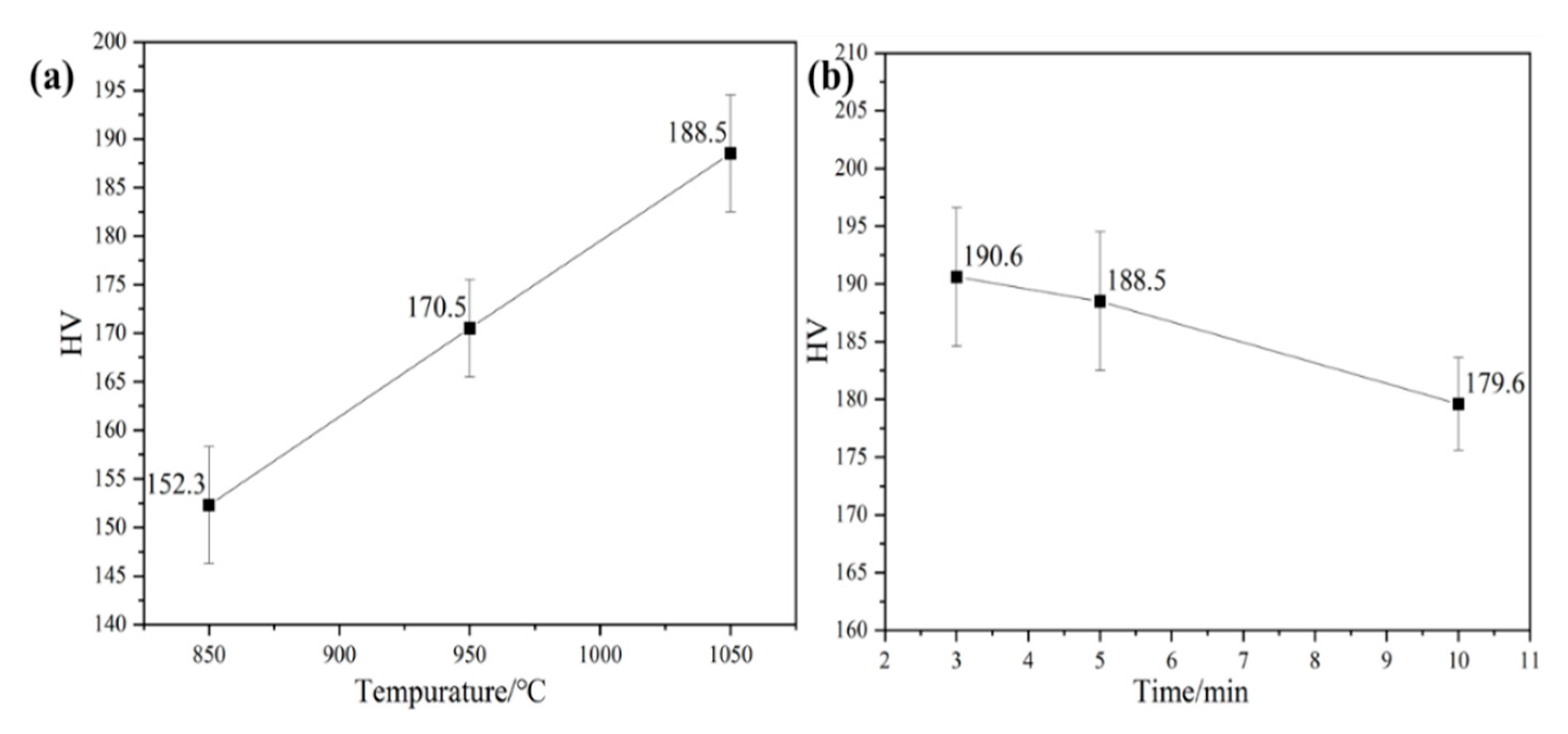
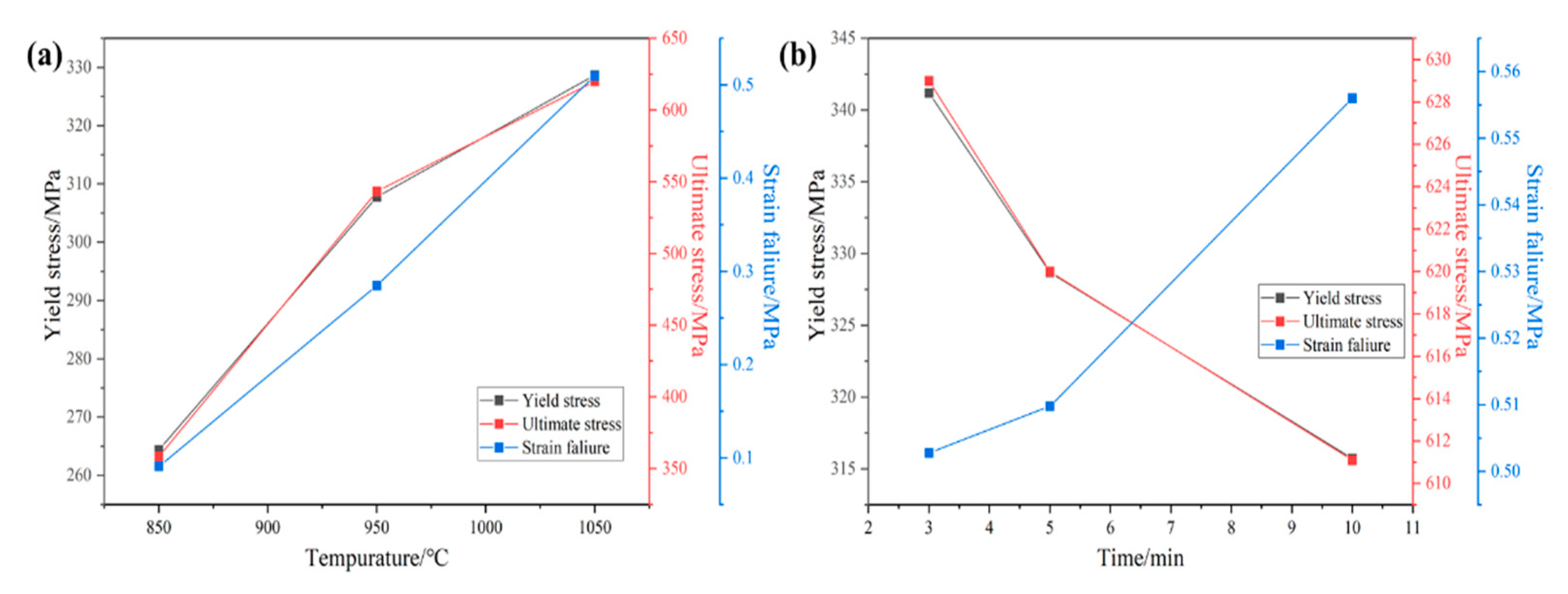
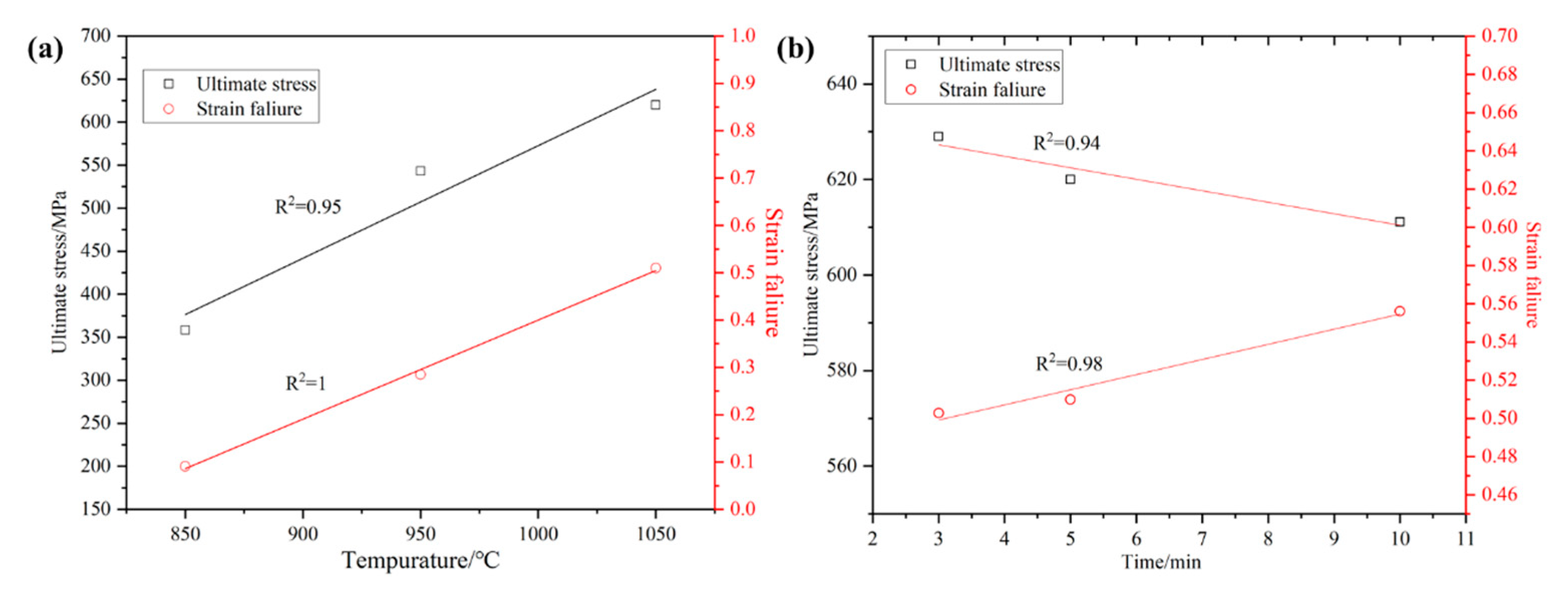
3.2. Mechanical Properties
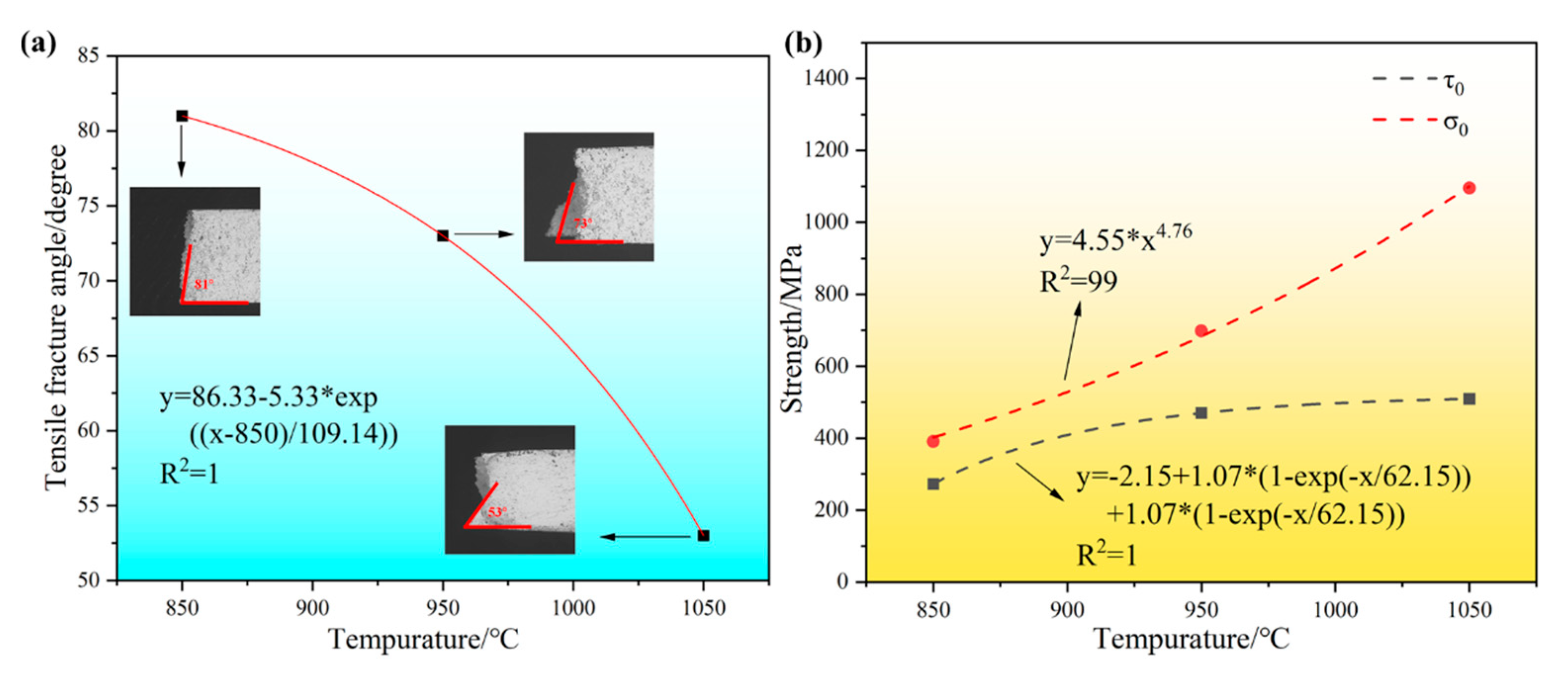
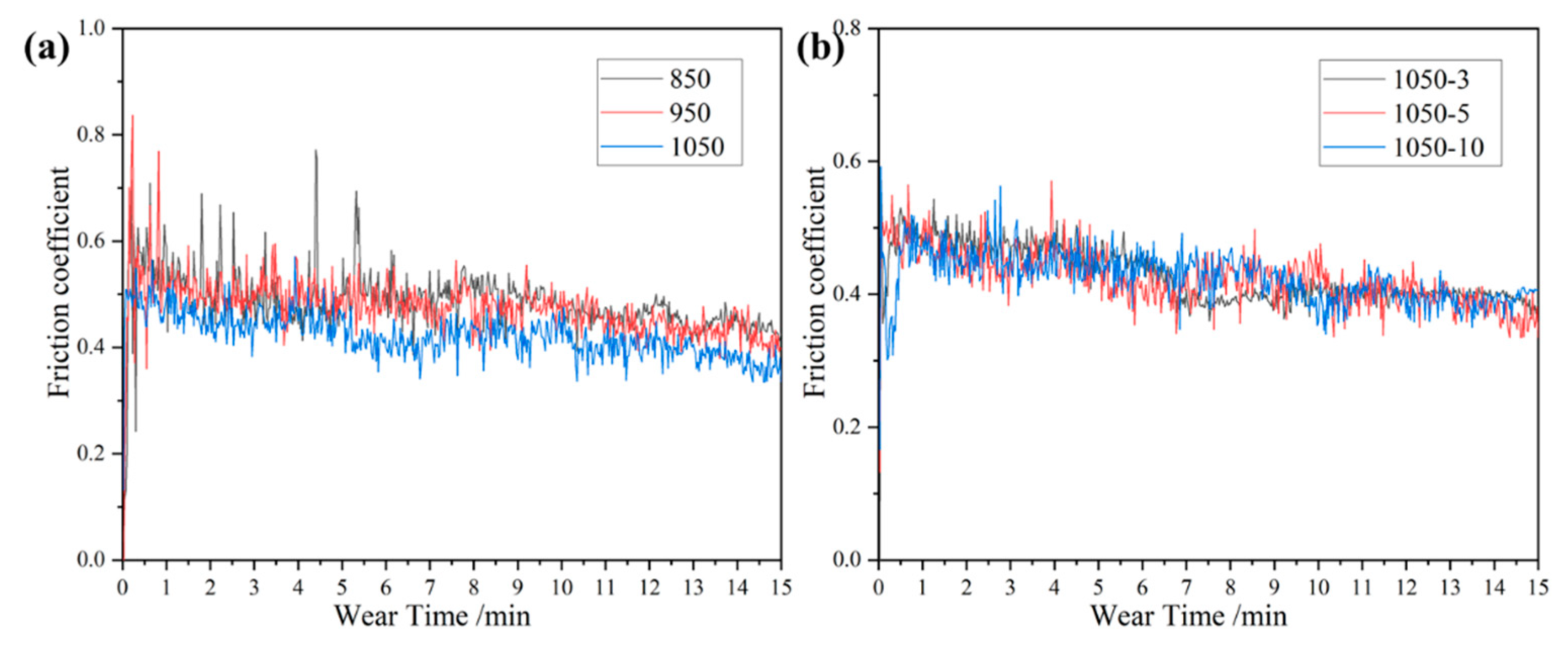
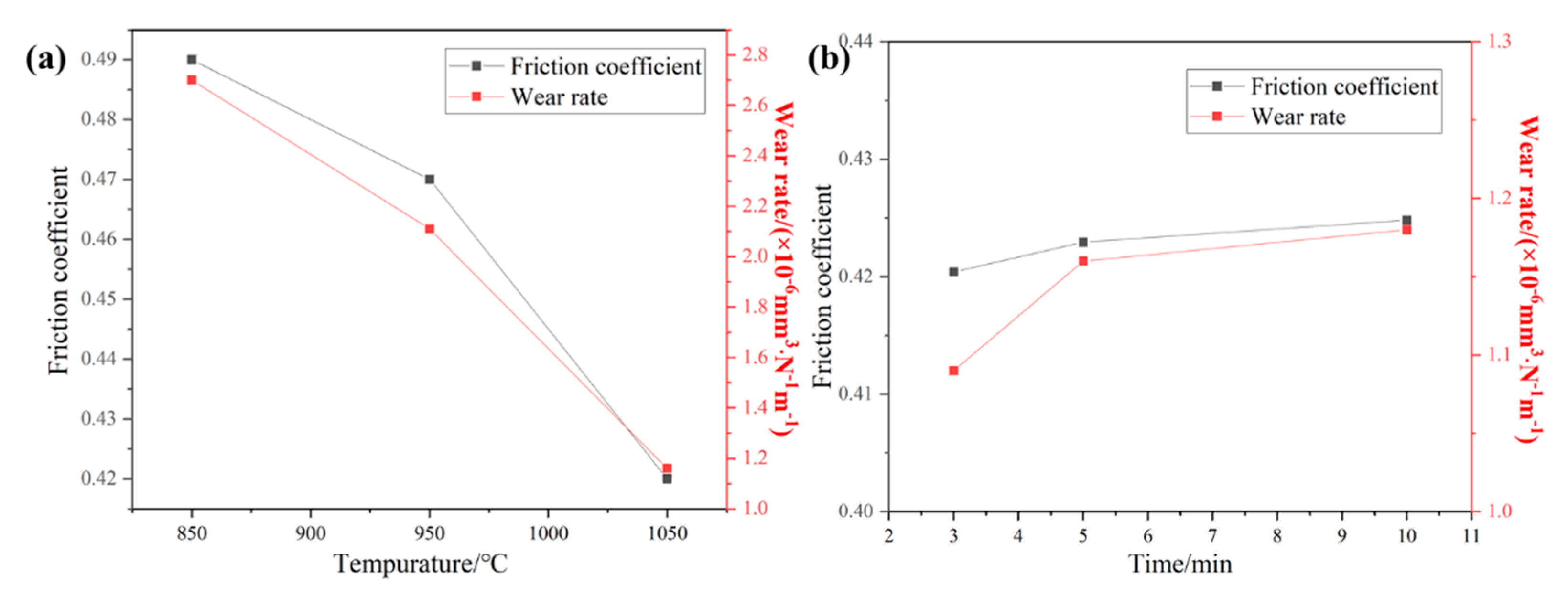
3.3. Wear Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
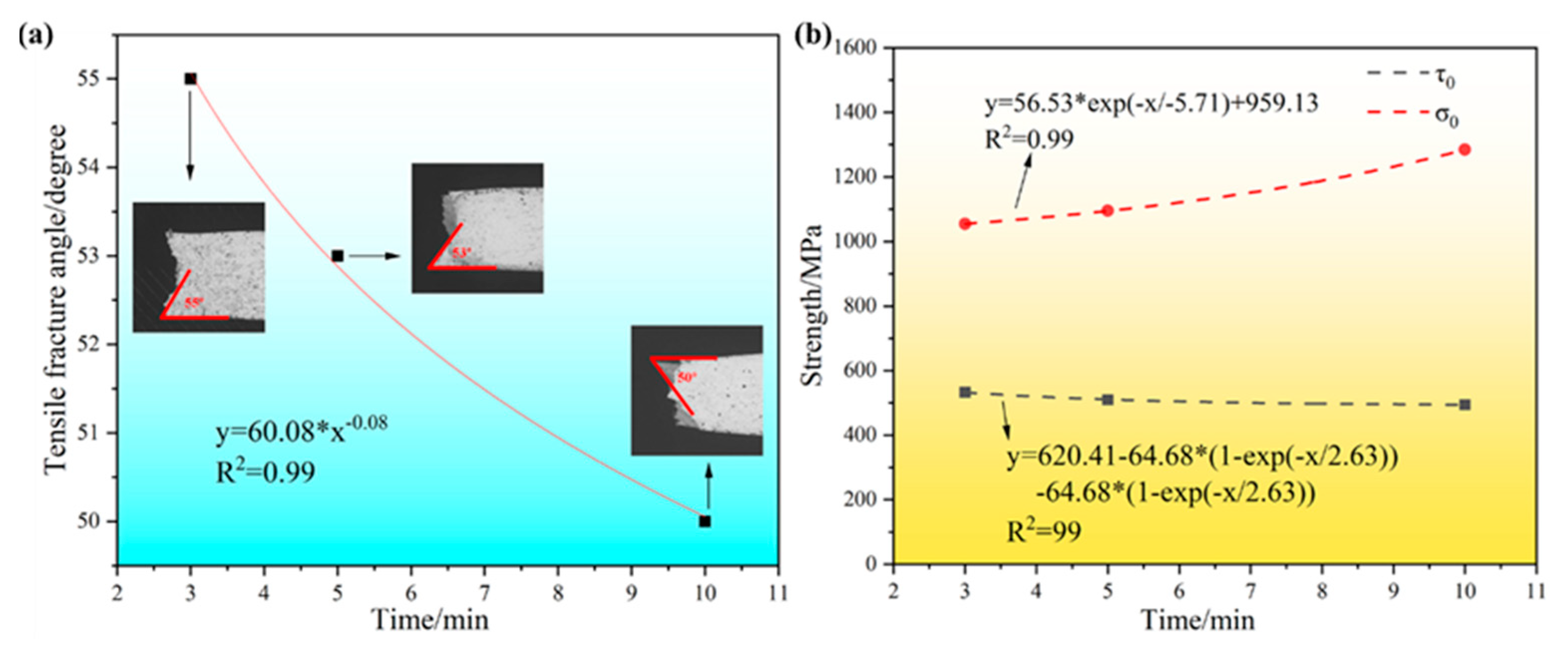
- The alloy sintered at 1050 °C and held for 3 min has the highest tensile strength of 629.0 MPa, and the alloy sintered at 1050 °C and held for 10 min has the best ductility of 55.6%. The fracture mechanism was ductile.
- (2)
- As the sintering temperature increases, the porosity of the alloy decreases and the tensile properties and ductility increase. With the increase in the holding time, the tensile strength of the alloy decreases, the grain size increases, and the ductility rises.
- (3)
- With the increase in the sintering temperature, the critical normal fracture strength σ0 shows an obvious rising trend, and when the sintering temperature reaches a certain temperature, the shear fracture strength τ0 no longer rises. With the increase in the holding time, the critical normal fracture strength σ0 shows a clear rising trend, and the shear fracture strength τ0 shows a gradual decline. The alloy fracture form is gradually changed from the normal fracture to shear fracture mode.
- (4)
- The alloy sintered at 1050 °C and held for 3 min has the highest hardness and the best wear resistance, and the wear mechanism is mainly adhesive wear and abrasive wear.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Li, C.; Feng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Sha, G.; Lewandowski, J.J.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. High-entropy Al0.3CoCrFeNi alloy fibers with high tensile strength and ductility at ambient and cryogenic temperatures. Acta Mater. 2017, 123, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, G.L. Solid solution alloys of AlCoCrFeNiTix with excellent room-temperature mechanical properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 181904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Lv, Y.; Yang, W.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y. A review on fundamental of high entropy alloys with promising high–temperature properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 760, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, T.E.; Pickering, E.J.; Owen, L.R.; Senkov, O.N.; Miracle, D.B.; Stone, H.J.; Jones, N.G. An assessment of the thermal stability of refractory high entropy superalloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 857, 157583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.-H.; Tsai, M.-H.; Wang, W.-R.; Lin, S.-J.; Yeh, J.-W. Microstructure and wear behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6308–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill, M.; Yuan, T.; Wang, G.; Yeh, J.; Tsai, C.; Chuang, A.; Liaw, P. Fatigue behavior of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 5723–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.; Muñoz-Moreno, R.; Stone, H.; Jones, N. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, F.; Yang, Y.; Bei, H.; George, E. Relative effects of enthalpy and entropy on the phase stability of equiatomic high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 2628–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.; Muñoz-Moreno, R.; Stone, H.; Jones, N. Precipitation in the equiatomic high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi. Scr. Mater. 2016, 113, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Dlouhý, A.; Somsen, C.; Bei, H.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 5743–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yao, Z.; Huang, X.; Du, F.; Li, C.; Chen, A.; Wu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCoxCrFeNi3-x eutectic high-entropy-alloy system. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 823, 153886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, T. Effects of annealing treatment on microstructure and hardness of bulk AlCrFeNiMo0.2 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 82, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Xie, Y.C.; Tang, Q.H.; Cong, R.A.; Dai, P.Q. Microstructure and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNiMn high-entropy alloy produced by mechanical alloying and vacuum hot pressing sintering. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2018, 28, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Eckert, J. Unified Tensile Fracture Criterion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 094301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Perozziello, G.; Boccazzi, P.; Sinskey, A.J.; Geschke, O.; Jensen, K.F. Microbioreactors for Bioprocess Development. JALA J. Assoc. Lab. Autom. 2007, 12, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Zhang, P.; Pang, J.; Ren, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Z. Strength, damage and fracture behaviors of high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel processed by high-pressure torsion. Scr. Mater. 2015, 96, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, N.; Du, G.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, H.; Wu, J. High-temperature oxidation resistance, mechanical and wear resistance properties of Ti(C,N)-based cermets with Al0.3CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy as a metal binder. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 815, 152486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Haghdadi, N.; Shamlaye, K.; Hodgson, P.; Barnett, M.; Fabijanic, D. The sliding wear behaviour of CoCrFeMnNi and AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys at elevated temperatures. Wear 2019, 428–429, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lan, L.; Shi, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, M.; Qiao, J. The tribological properties of Al0.6CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy with the sigma phase precipitation at elevated temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 180–189. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.-M.; Lin, S.-J.; Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.-K.; Huang, Y.-S.; Chen, H.-C. Adhesive wear behavior of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloys as a function of aluminum content. Wear 2006, 261, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
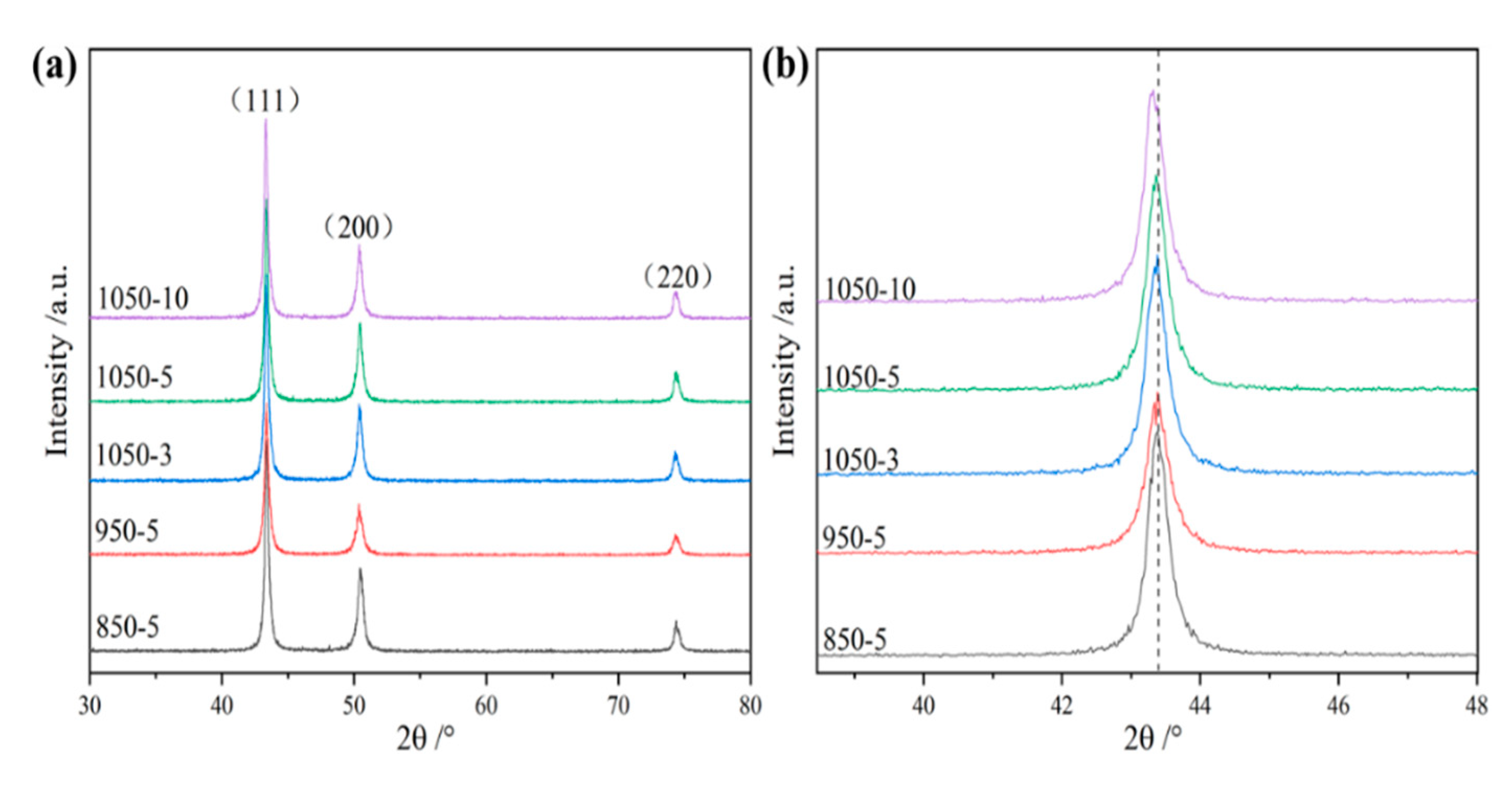



| Sample | α/(Å) | FWHM |
|---|---|---|
| 850 | 0.3882 | 0.40395 |
| 950 | 0.3883 | 0.41390 |
| 1050-3 | 0.3884 | 0.43123 |
| 1050-5 | 0.3885 | 0.42526 |
| 1050-10 | 0.3887 | 0.42302 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, N.; Wu, C.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Hou, J.; Dong, F. Effect of Sintering Temperature and Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2025, 15, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060591
Li N, Wu C, Wu Z, Jiang M, Hou J, Dong F. Effect of Sintering Temperature and Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloys. Metals. 2025; 15(6):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060591
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ning, Chengbo Wu, Zhennan Wu, Mengyuan Jiang, Junfeng Hou, and Fuyuan Dong. 2025. "Effect of Sintering Temperature and Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloys" Metals 15, no. 6: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060591
APA StyleLi, N., Wu, C., Wu, Z., Jiang, M., Hou, J., & Dong, F. (2025). Effect of Sintering Temperature and Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloys. Metals, 15(6), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15060591






