Performance Study of CaO-CaF2- and CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-Based High-Efficiency Desulfurizers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methods
2.1. Thermodynamic Calculation
2.2. Melting Temperature Test
2.3. Slag–Steel Contact Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. RH Desulfurizer Component Design
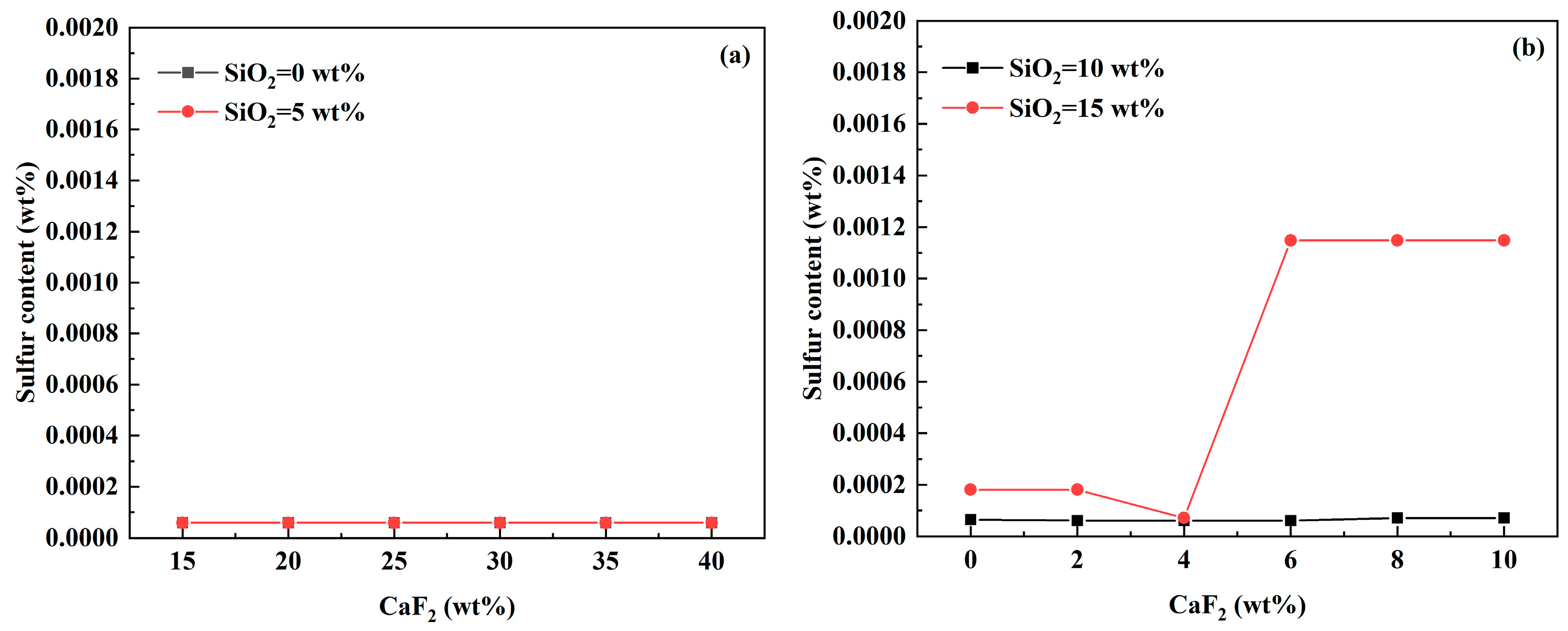
3.2. Influence of RH Desulfurizer Compositions on S Content of Molten Steel
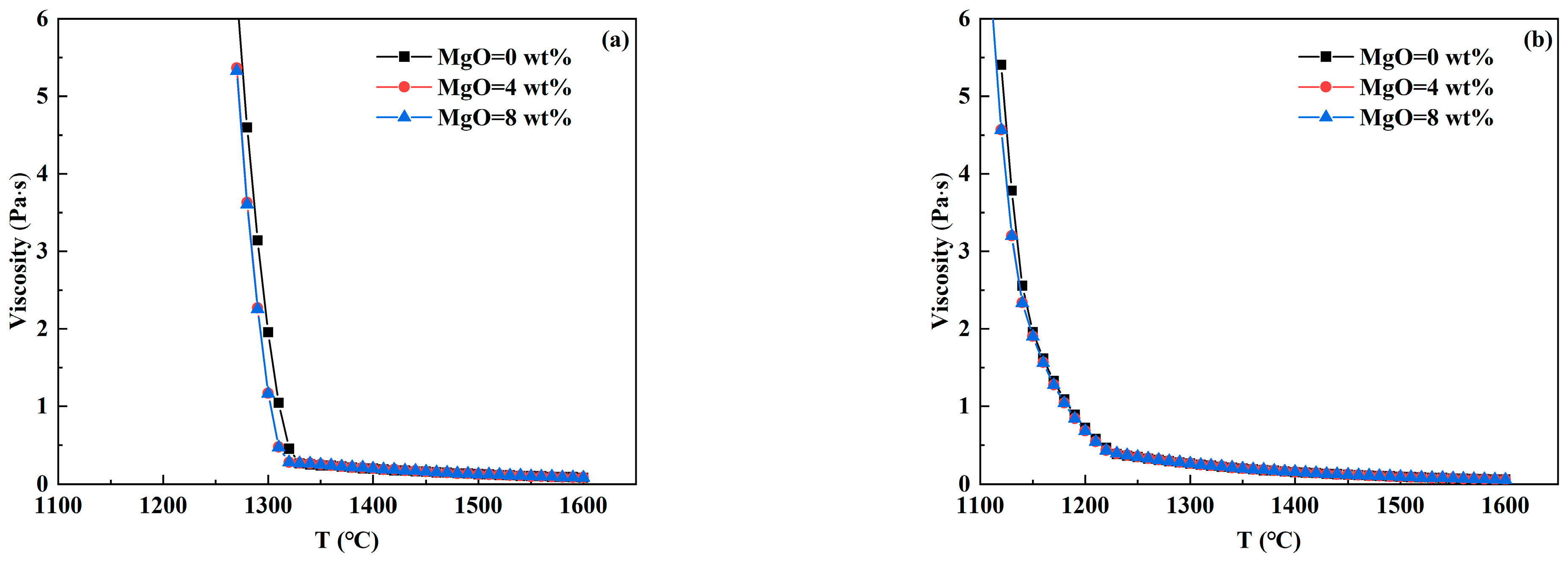
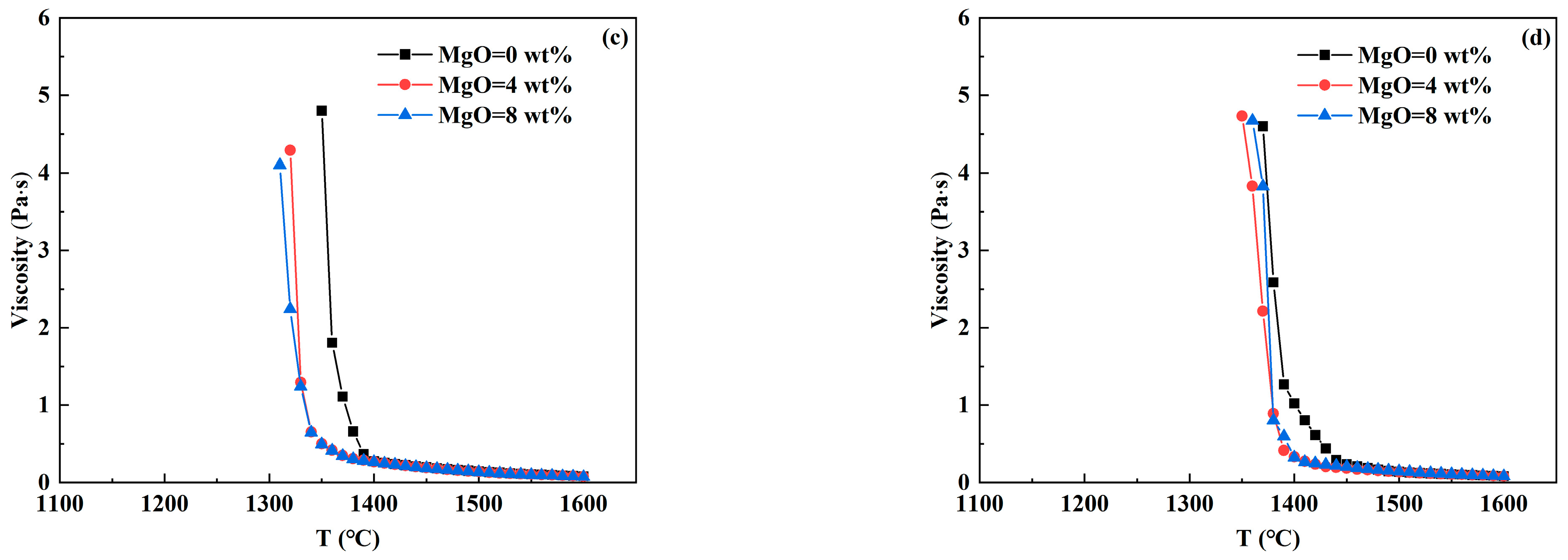
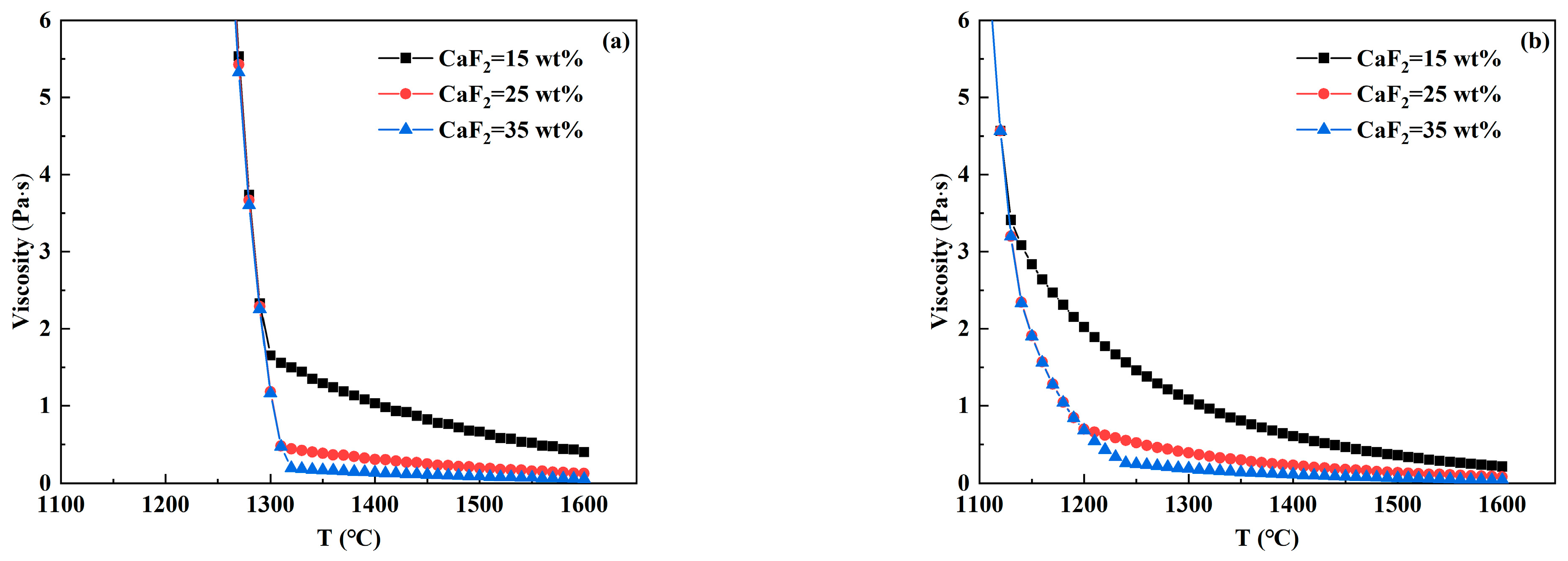
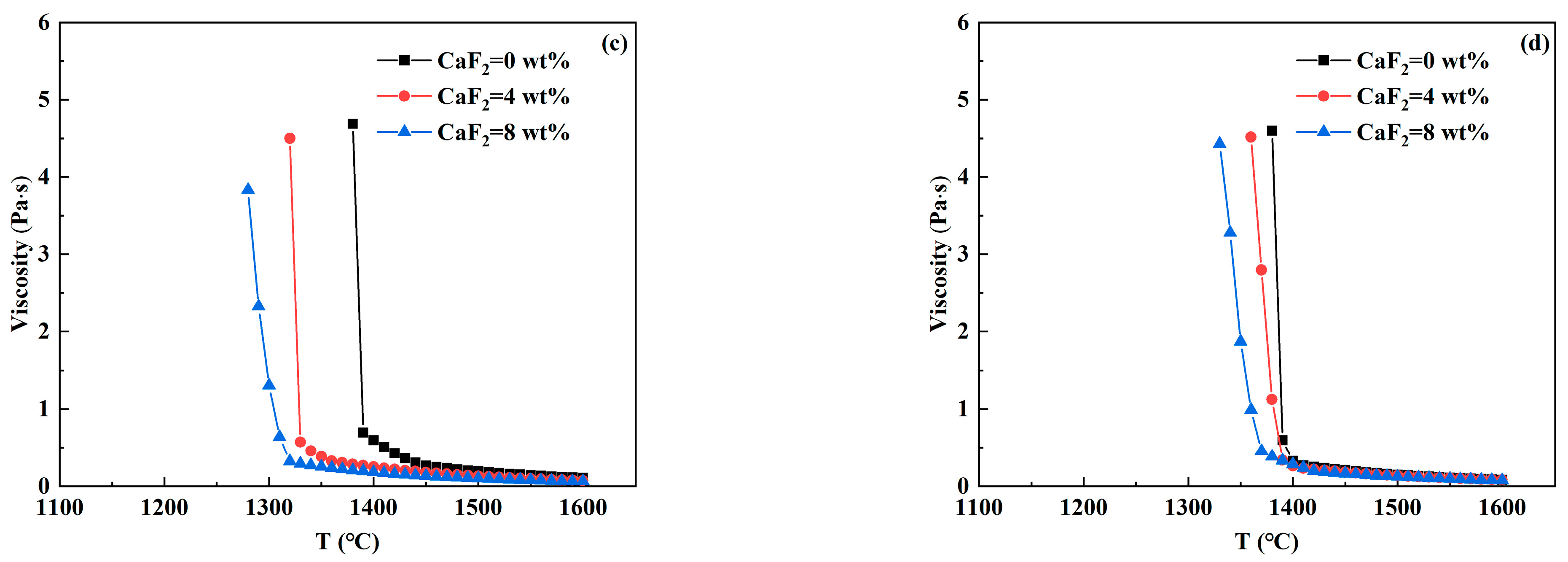
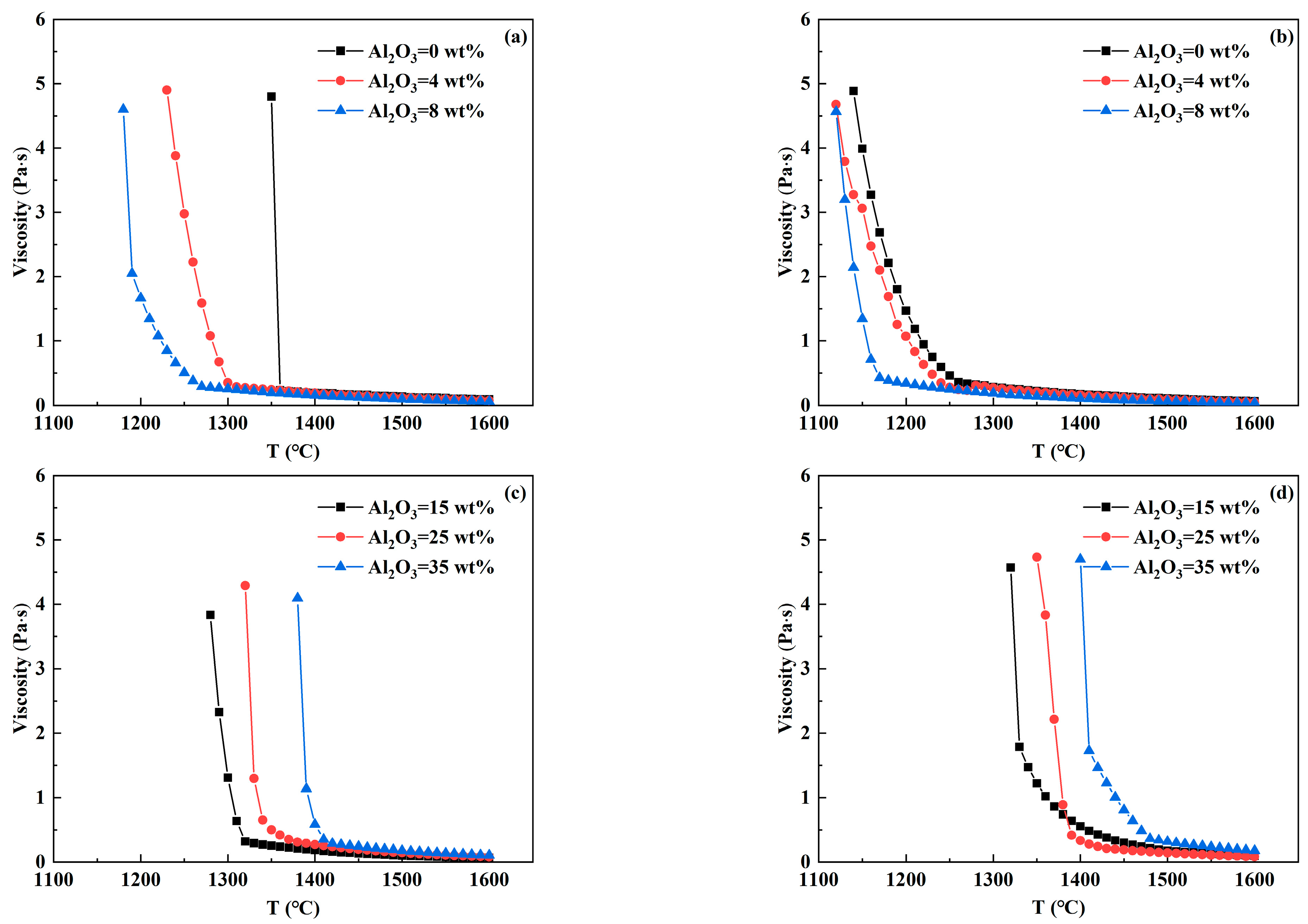
3.3. Analysis of Viscosity—Temperature Curve of RH Desulfurizer
3.4. Desulfurization Experiment of RH Desulfurizer
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- By comprehensive thermodynamic calculation of liquidus temperature and sulfur capacity of the desulfurizer, it is obtained that the CaO-CaF2-based desulfurizer compositions with high liquidus temperature and sulfur capacity are concentrated in areas with low Al2O3 content and high CaO and CaF2 content, and the CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-based desulfurizer compositions with low liquidus temperature and sulfur capacity have a wide range of CaO = 30–60 wt%, CaF2 = 5–50 wt%, Al2O3 = 0–40 wt%, and MgO ≤ 6 wt%.
- (2)
- In CaO-CaF2- and CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 based-desulfurizers, when the content of SiO2 is low, the change in CaF2, MgO, and Al2O3 contents has little effect on the equilibrium S content of molten steel, whereas, when the content of SiO2 is high, the equilibrium S content of molten steel increased significantly when the content of CaF2, MgO, and Al2O3 are greater than a certain value.
- (3)
- In CaO-CaF2- and CaO-Al2O3-SiO2- based desulfurizers, the increase in CaF2 and MgO content reduces the high-temperature viscosity and breaking temperature to varying degrees, so that the slag system has better fluidity and is beneficial to prevent crust formation. With the increase in Al2O3 and SiO2 contents, the breaking temperature of the CaO-CaF2-based desulfurizer decreases significantly, which is beneficial to preventing crust. However, when the breaking temperature of the CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-based desulfurizer increases, part of the slag has solidified at 1400 °C, which is prone to leading to slag crust when the temperature drops.
- (4)
- The melting temperatures of CaO-CaF2- and CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-based desulfurizers in the present work is lower than the RH desulfurization process temperature, so the desulfurization kinetics conditions will not be worsened. In summary, for the CaO-CaF2-based desulfurizer, CaO = 60 wt%, CaF2 = 30 wt%, SiO2 = 0–5 wt%, with a small amount of Al2O3 and MgO added, the desulfurization effect is significant. For the CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-based desulfurizer, CaO = 39–57 wt%, Al2O3 = 20–35 wt%, SiO2 = 10–15 wt%, MgO = 4 wt%, and CaF2 = 4–8 wt%, its desulfurization effect meets the demand, and this desulfurizer can reduce equipment erosion and environmental pollution.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, X.Y. Research and practice of optimization feeding technology and equipment for KR method. Metall. Equip. 2016, 3, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, Y.F.; Li, C.Y.; Liu, P.; Xu, G.J. Effect of RH desulfurization on inclusions in non-oriented electrical steel. SteelMak 2019, 35, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.S.; Tang, X. The kinetics of desulfurization of hot metal by CaO-CaF2 based fluxes. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 1081–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, C.H.; Jo, S.K.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.R.; Kim, J.T. The effect of CaF2 on thermodynamics of CaO-CaF2-SiO2-(MgO) slags. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2004, 35, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Utagawa, K.; Shibata, H.; Kitamura, S.Y.; Kikuchi, N.; Kishimoto, Y. Influence of solid CaO and liquid slag on hot metal desulfurization. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.J.; Lai, Z.B.; Qing, Z.; Chou, S.T. Review of RH desulfurization. Nonferrous Met. Sci. Eng. 2013, 4, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.X. Experimental Study on Deep Desulfurization for Ultra-Low Carbon Steel in Pansteel. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 16 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.C.; Guo, X.L.; Huang, S.G. Desulphurisation of stainless steel by using CaO-Al2O3 based slags during secondary metallurgy. ISIJ Int. 2013, 53, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.M.; Sun, L.J.; Li, G.J.; Zeng, J.H.; Zhang, M.; He, S.P.; Wang, Q. Effect of constituents of BaO, Na2O bearing refining slag series on sulfur distribution ratio. SteelMak 2008, 24, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Sano, N.; Seetharaman, S. Sulphide capacities of CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-MgO-MnO slags in the temperature range 1673–1773 K. ISIJ Int. 2009, 49, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsuro, S.; Takashi, N.; Takeshi, N.; Mitsunori, E.; Hideyuki, I.; Tomio, T. Evaluation of desulfurization flux in CaO-Al2O3-BaO-Ce2O-MgO system. Steel Res. Int. 2004, 54, 308–313. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, W. Study on desulfurization ability of CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 and CaO-CaF2 slags at 1600 °C. Steel Res. Int. 2016, 86, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.C.; Huang, S.G.; Joris, V.D. Desulphurisation and inclusion behaviour of stainless steel refining by using CaO-Al2O3 based slag at low sulphur levels. ISIJ Int. 2014, 54, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.B.; Shi, Q.L.; Chen, Q.Q.; Huang, C.H.; Li, J.Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, T.Y. Development of new type desulfurizer for RH vacuum treatment. SteelMak 2006, 22, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, L.Q.; Cai, K.K. Desulfurization technology for molten steel in RH treatment process. SteelMak 2001, 17, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.H.; Xue, Z.L.; Gao, J.B. Study on the melting point of desulfurization refining slag. Res. Iron Steel. 2007, 35, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.B.; Pelton, A.D. Thermodynamic model and database for sulfides dissolved in molten oxide slags. Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 2009, 40, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, T.; Lei, J.; Wang, H.C.; Wang, Q. First-principles calculation of CaO-Al2O3-CaF2 slag. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2024, 55, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, T.S.; Park, J.H. Effect of fluorspar and industrial wastes (red mud and ferromanganese slag) on desulfurization efficiency of molten steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Component | CaO | CaF2 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | MgO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | 30–80 | 0–50 | 0–50 | 0–30 | 0–12 |
| Step | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 |
| Desulfurizer. | CaO | SiO2 | CaF2 | Al2O3 | MgO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaO-CaF2 based | 51~66 | 0, 5 | 30 | 4 | 0~10 |
| 47~77 | 0, 5 | 15~40 | 4 | 4 | |
| 51~66 | 0, 5 | 30 | 0~10 | 4 | |
| CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 based | 41~56 | 10, 15 | 4 | 30 | 0~10 |
| 41~56 | 10, 15 | 0~10 | 30 | 4 | |
| 37~67 | 10, 15 | 4 | 15~40 | 4 |
| Number | CaO | SiO2 | MgO | Al2O3 | CaF2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise RH desulfurizer | 64.08 | 4.92 | 2.66 | 0.46 | 27.88 | |
| CaO-CaF2-based desulfurizer | 1 | 62 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 30 |
| 2 | 57 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 30 | |
| CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-based desulfurizer | 3 | 52 | 10 | 4 | 30 | 4 |
| 4 | 48 | 10 | 4 | 30 | 8 | |
| 5 | 48 | 10 | 8 | 30 | 4 | |
| 6 | 47 | 10 | 4 | 35 | 4 | |
| 7 | 57 | 10 | 4 | 25 | 4 | |
| 8 | 43 | 15 | 4 | 30 | 8 | |
| 9 | 39 | 15 | 8 | 30 | 8 | |
| 10 | 53 | 15 | 4 | 20 | 8 | |
| Number | S0 | S5 | S10 | Tm1 | Tm2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise RH desulfurizer | 0.039 | 0.003 | <0.002 | 1450 | 1457 | |
| CaO-CaF2-based desulfurizer | 1 | 0.025 | <0.002 | 1465 | 1460 | |
| 2 | 0.035 | <0.002 | 1458 | 1424 | ||
| CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-based desulfurizer | 3 | 0.022 | <0.002 | 1371 | 1355 | |
| 4 | 0.025 | <0.002 | 1364 | 1348 | ||
| 5 | 0.028 | 0.007 | <0.002 | 1389 | 1372 | |
| 6 | 0.017 | <0.002 | 1368 | 1354 | ||
| 7 | 0.017 | <0.002 | 1396 | 1386 | ||
| 8 | 0.025 | <0.002 | 1353 | 1358 | ||
| 9 | 0.023 | 0.005 | <0.002 | 1344 | 1328 | |
| 10 | 0.034 | <0.002 | 1360 | 1350 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, R.; Qiu, S.; Wu, T.; Wang, H. Performance Study of CaO-CaF2- and CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-Based High-Efficiency Desulfurizers. Metals 2025, 15, 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050550
Cao R, Qiu S, Wu T, Wang H. Performance Study of CaO-CaF2- and CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-Based High-Efficiency Desulfurizers. Metals. 2025; 15(5):550. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050550
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Ruihong, Shengtao Qiu, Ting Wu, and Haijun Wang. 2025. "Performance Study of CaO-CaF2- and CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-Based High-Efficiency Desulfurizers" Metals 15, no. 5: 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050550
APA StyleCao, R., Qiu, S., Wu, T., & Wang, H. (2025). Performance Study of CaO-CaF2- and CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-Based High-Efficiency Desulfurizers. Metals, 15(5), 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15050550







