Physical Model of Liquid Steel Jets Impacting on Solid-Rigid Surfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Steel [1550 °C] | Water [20 °C] | |
|---|---|---|
| Density [kg/m3] | 7000 | 1000 |
| Viscosity [Pa·s] | 0.0065 | 0.001 |
| Kinematic viscosity [m2/s] | 0.928 × 10−6 | 1.0 × 10−6 |
| surface tension [N/m] | 1.8 | 0.0728 |
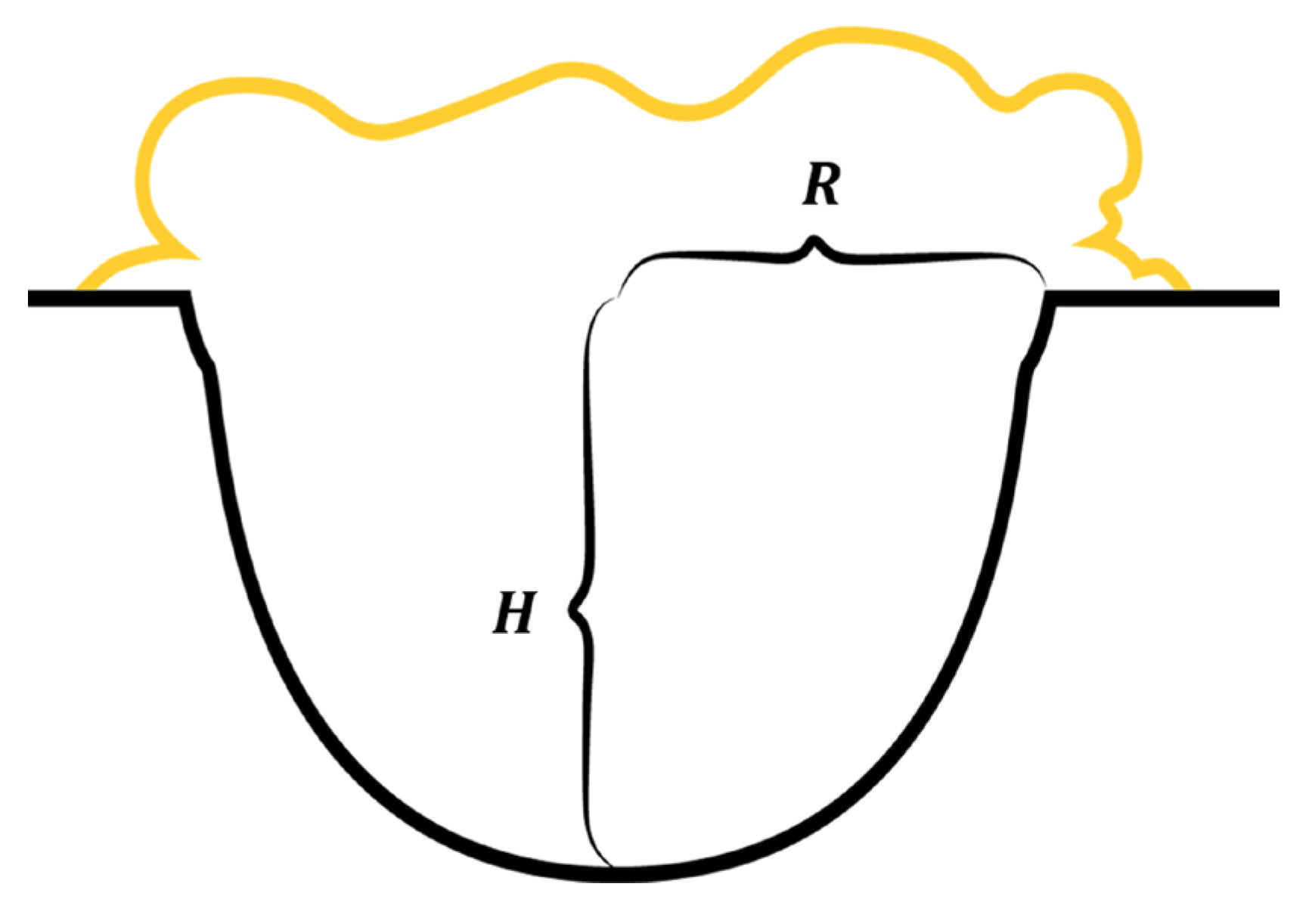
2. Physical Model
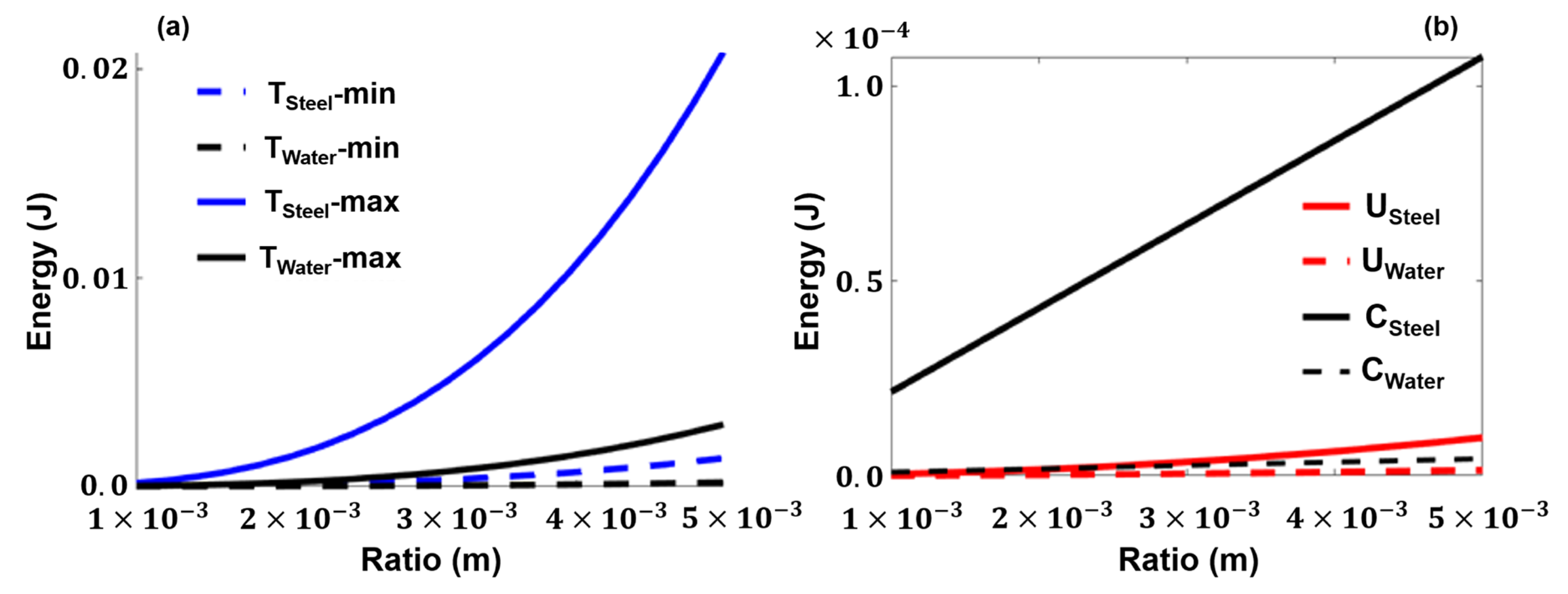
3. Results and Discussion
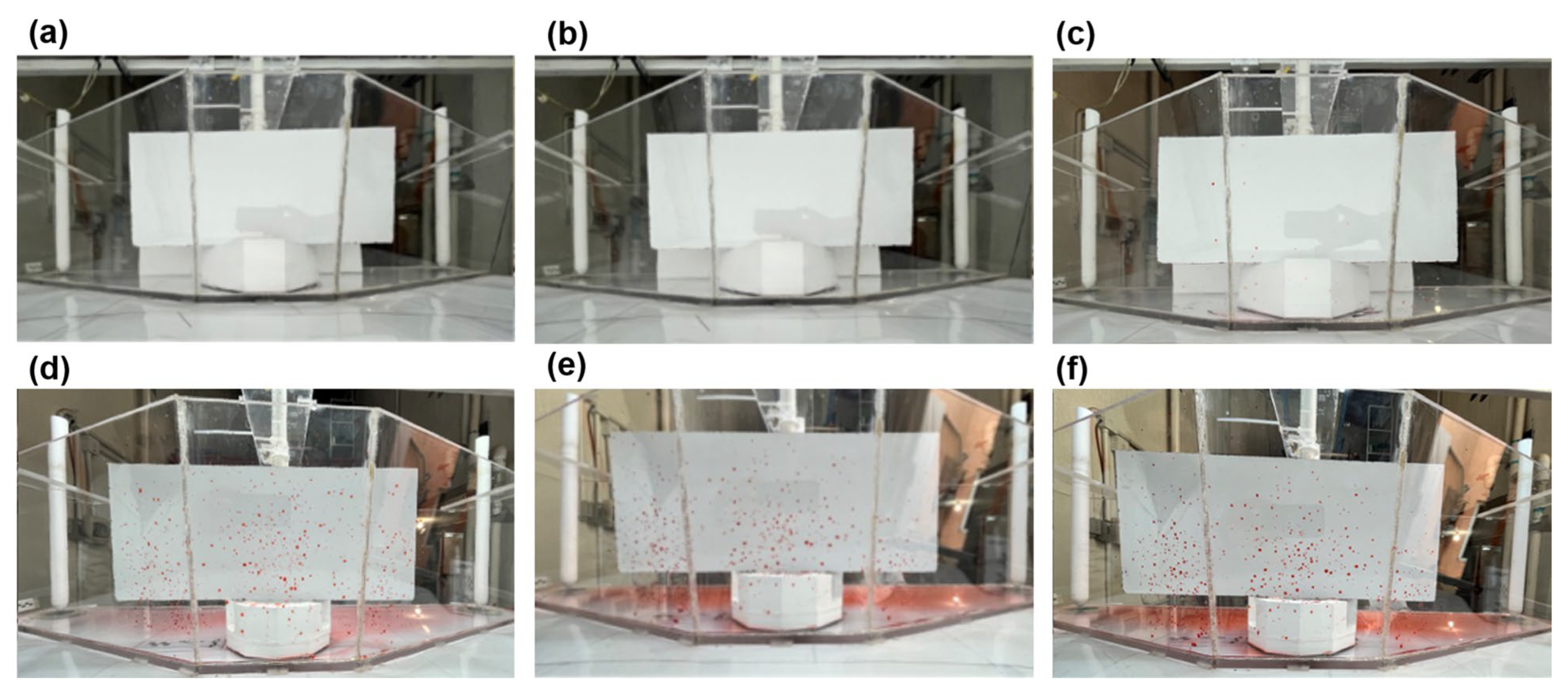
3.1. Initial Flow Patterns
3.2. Drop and Splashing Dynamics
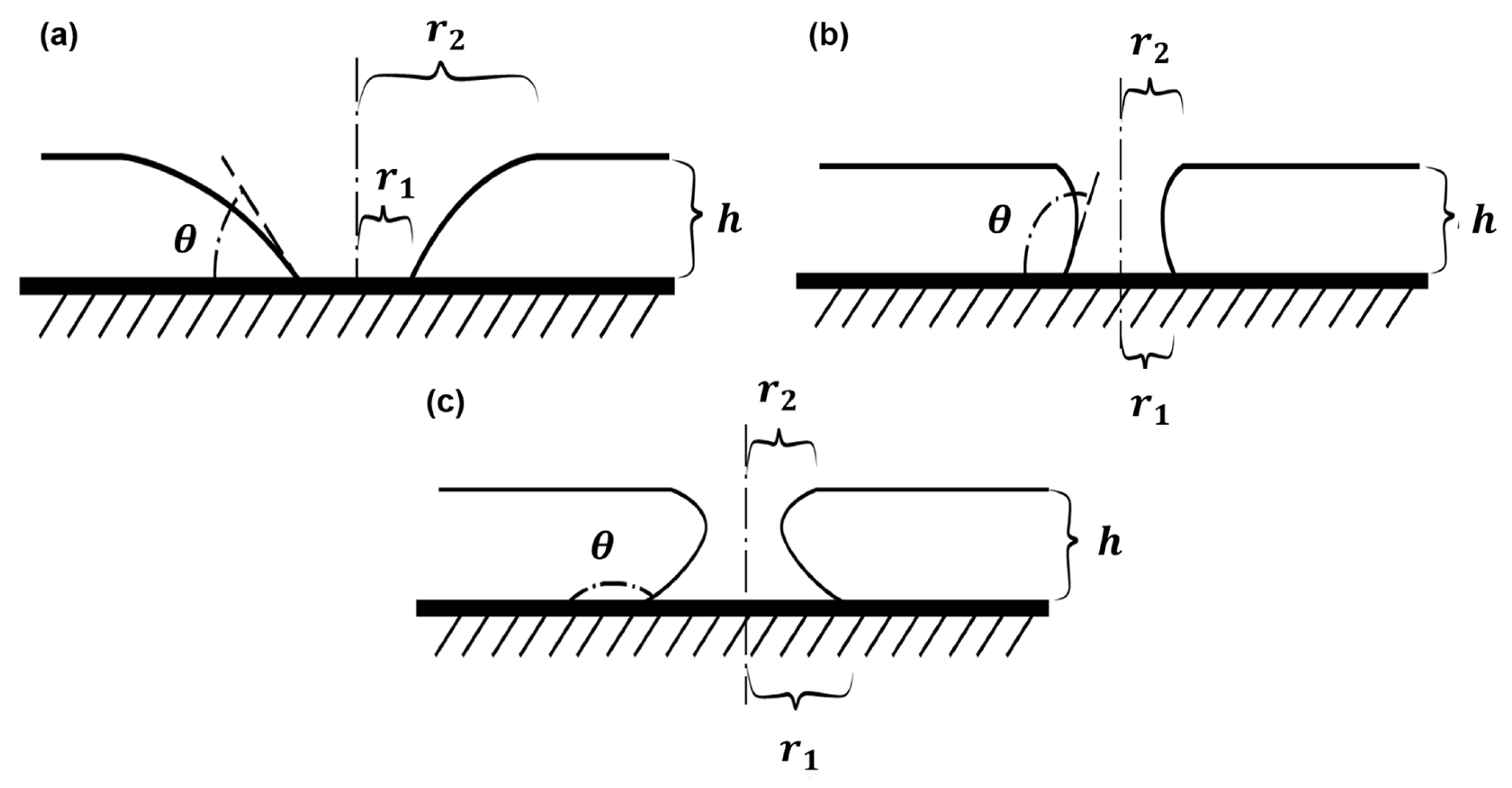
3.3. Splat Dynamics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Worthington, A. On the Forms Assumed by Drops of Liquids Falling Vertically on a Horizontal Plate. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1876, 25, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzegorz, T.; Jerzy, P.; Tadeusz, W.; Mariusz, P. Druk Strumieniowy Jako Metoda Wytwarzania Elastycznych Obwodów Drukowanych. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference of IMAPS-CPMT, Rzeszów-Czarna, Poland, 21–24 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, D.; Su, H.; Vaidya, A. Splash Dynamics of Paint on Dry, Wet, and Cooled Surfaces. Fluids 2016, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandalahalli, M.M.; Wagner, E.C.; Portela, L.M.; Mudde, R.F. Electrolyte Effects on Recirculating Dense Bubbly Flow: An Experimental Study Using X-Ray Imaging. AIChE J. 2020, 66, e16696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josserand, C.; Thoroddsen, S.T. Drop Impact on a Solid Surface. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2016, 48, 365–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Foltyn, P.; Geppert, A.; Weigand, B. Air Entrapment and Bubble Formation During Droplet Impact onto a Single Cubic Pillar. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Socolofsky, S.A.; Breier, J.A.; Seewald, J.S. Observations of Bubbles in Natural Seep Flares at MC 118 and GC 600 Using in Situ Quantitative Imaging. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 2203–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, O.J.; Coronado, R.M.C.; Morales, R.D.; Guarneros, J.; Rodriguez, J.; Nájera, A.B.; Servín, R.C. Comparative Analysis of Liquid Steel Fluid Dynamics, Including Spillage and Spreading on the Bottom of a Three-Strand Tundish Between Two Turbulence Inhibitors at the Start of the Casting Sequence. Metals 2024, 14, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalesk, K.; Gryc, K.; Socha, L.; Tkadleckova, M.; Satermus, M.; Pieprzyca, J.; Merder, T.; Pindor, L. Study of Tundish Slag Entrainment Using Physical Modelling. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2016, 61, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnsihacacha, A.; Piyapaneekoon, A.; Kowitwarangkul, P. Physical Water Model and CFD Studies of Fluid Flow in a Single Strand Tundish. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 9220–9228. [Google Scholar]
- Sujata, D.; Rajeev, K.S.; Amitava, P. Role of Tundish Argon Diffuser in Steelmaking Tundish to Improve Inclusion Flotation with CFD and Water Modelling Studies. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2015, 4, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, P.; Zuo, X.; Wu, D.; Wu, D. Optimization of the Liquid Steel Flow Behavior in the Tundish through Water Model Experiment, Numerical Simulation and Industrial Trial. Metals 2022, 12, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koria, S.C.; Singh, S. Physical Modeling of the Effects of the Flow Modifier on the Dynamics of Molten Steel Flowing in a Tundish Satish. ISIJ Int. 1994, 34, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwudziński, A. Numerical, Physical, and Industrial Experiments of Liquid Steel Mixture in One Strand Slab Tundish with Flow Control Devices. Steel Res Int. 2014, 85, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.-Y.; Chen, D. Comparison of Fluid Flow and Temperature Distribution in a Single-Strand Tundish with Different Flow Control Devices. Metals 2021, 11, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Bao, Y.P.; Sun, Q.S.; Wang, L.F. Optimization of Flow Control Devices in a Single-Strand Slab Continuous Casting Tundish. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2011, 18, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkadlečková, M.; Walek, J.; Michalek, K.; Huczala, T. Numerical Analysis of RTD Curves and Inclusions Removal in a Multi-Strand Asymmetric Tundish with Different Configuration of Impact Pad. Metals 2020, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Y.; Fang, W.; Yang, W.; Shao, S.; Yang, J.; Mao, W. Transient Behavior of Inclusions During Reoxidation of Si-Killed Stainless Steels in Continuous Casting Tundish. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruehan, R.J. (Ed.) Surface Tension (Sec. 2.4.7). In The Making, Shaping, and Treating of Steel: Steelmaking and Refining Volume; The AISE Steel Foundation: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1998; pp. 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Michon, G.; Josserand, C.; Seon, T. Jet Dynamics Post Drop Impact on A Deep Pool. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2017, 2, 023601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Zhu, P. Asymmetric Jetting During the Impact of Liquid Drops on Superhydrophobic Concave Surfaces. Micromachines 2022, 3, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, G. Splashing and Breaking of Droplets Impacting on a Solid Surface. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Young, T. An Essay on The Cohesion of Fluids. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 1805, 95, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkonen, L. Young’s Equation Revisited. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2016, 28, 135001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Ruckenstein, E. Dewetting of Solids by the Formation of Holes in Macroscopic Liquid Films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 133, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasandideh, F.M.; Qiao, Y.M.; Chandra, S.; Mostaghimi, J. Capillary Effects During Droplet Impact on a Solid Surface. Phys. Fluids 1996, 8, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
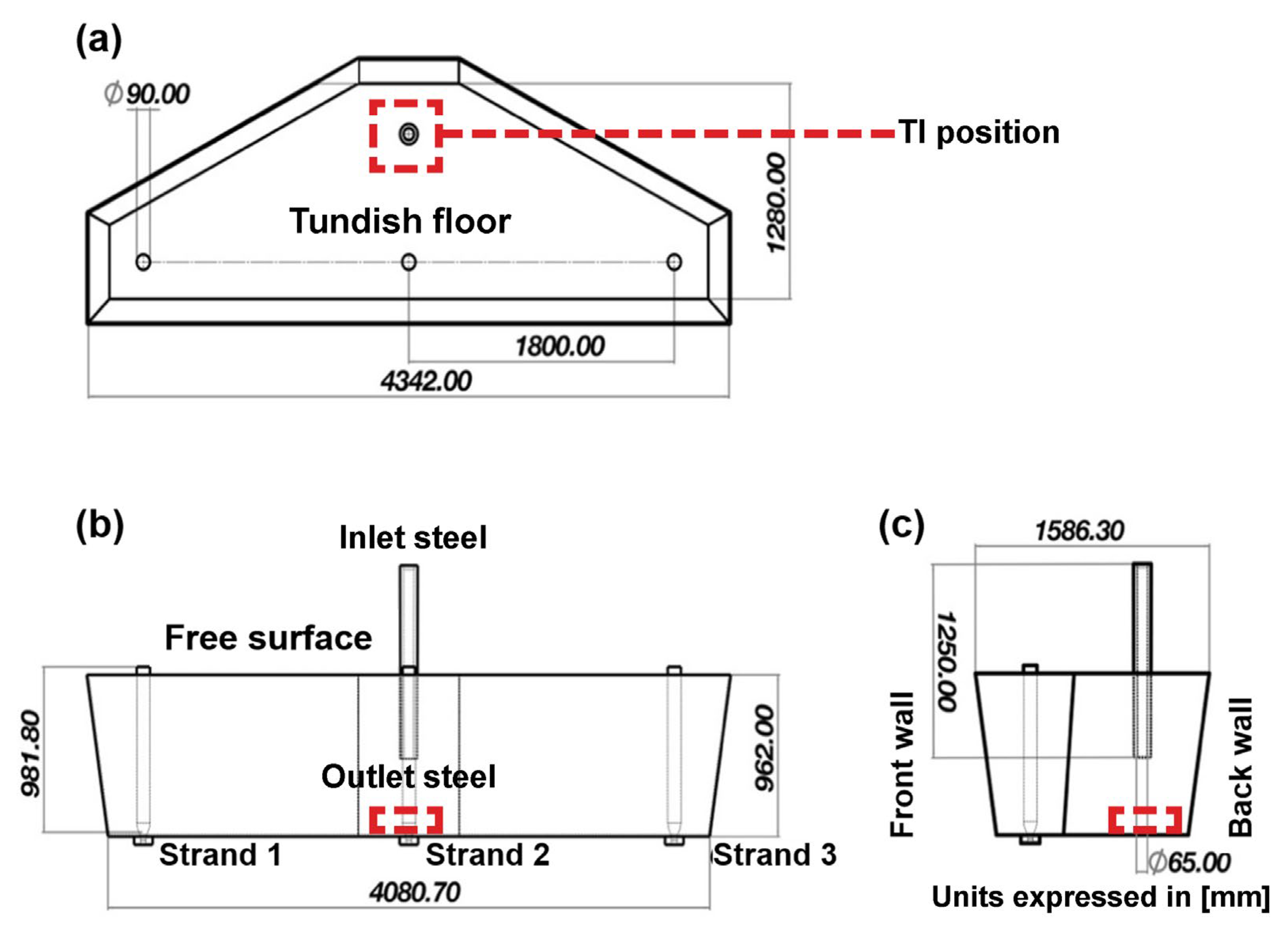
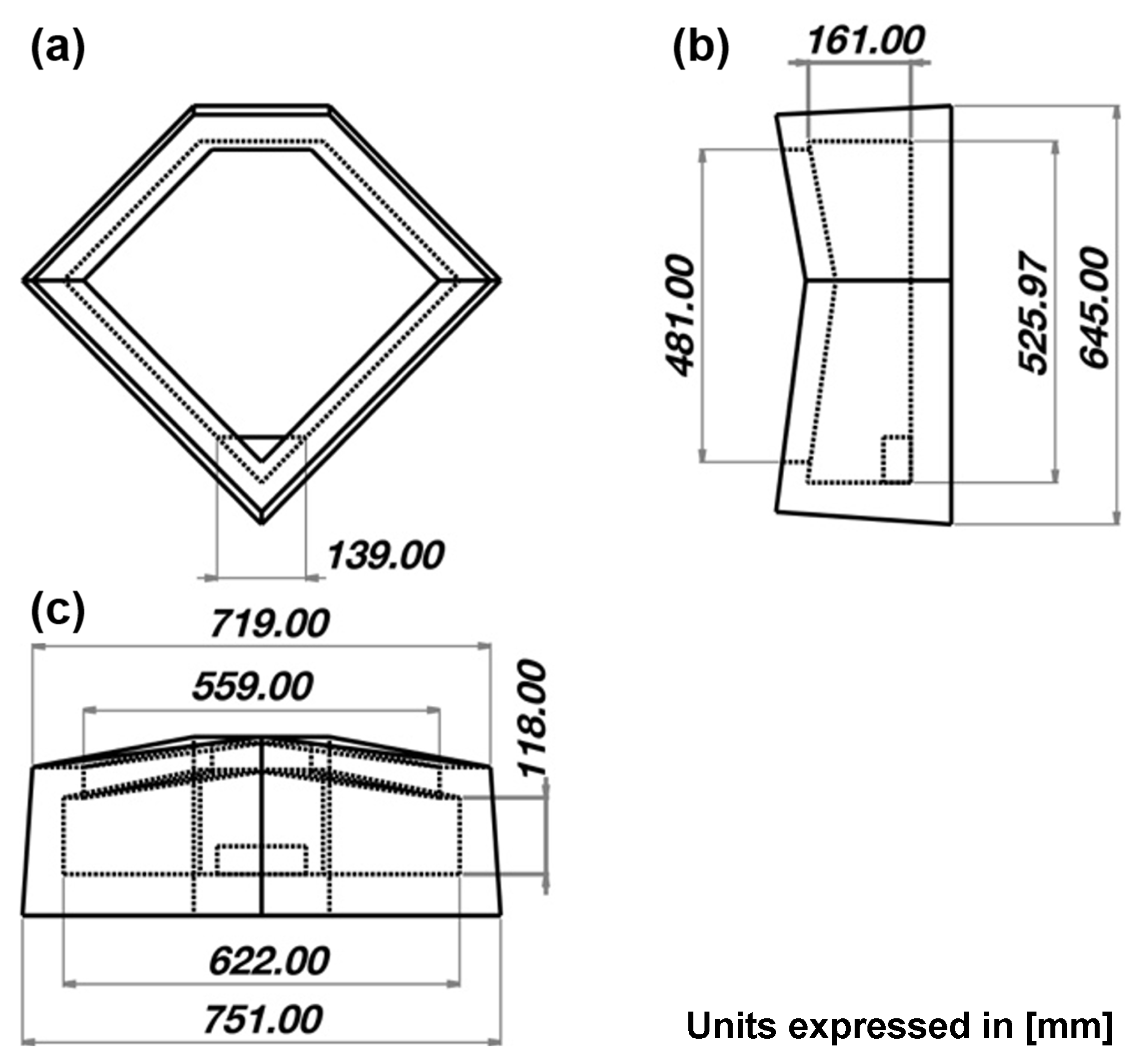


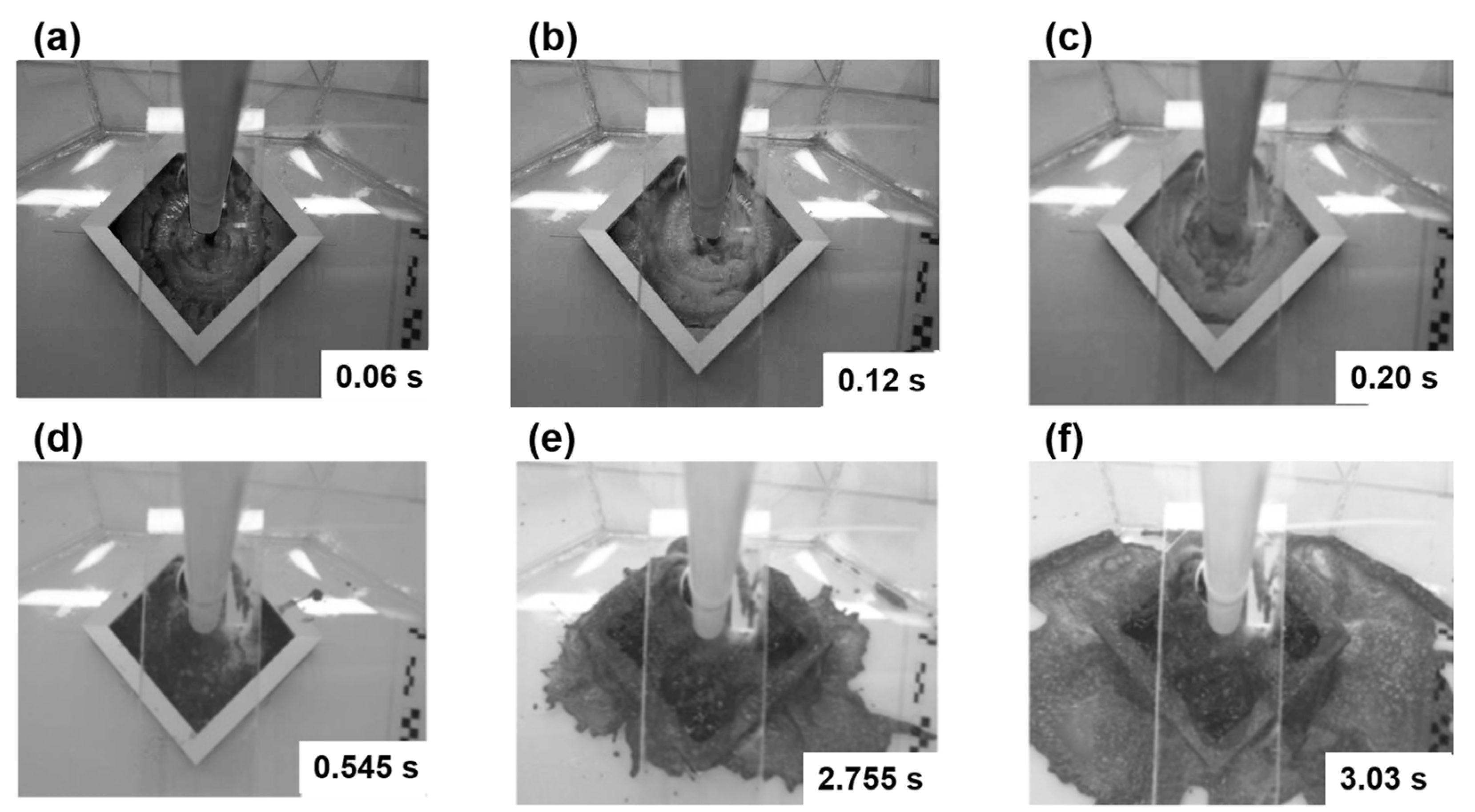
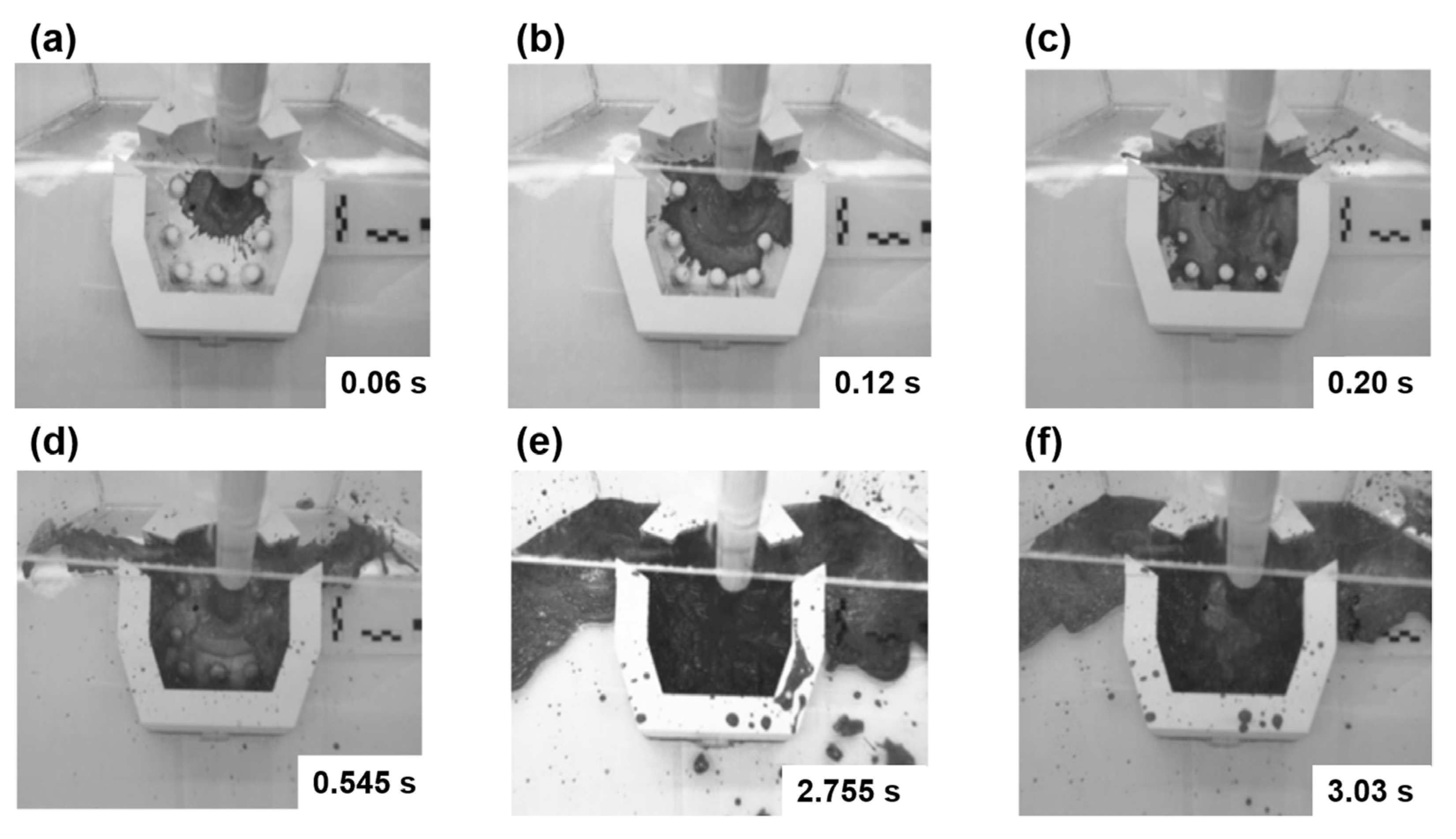
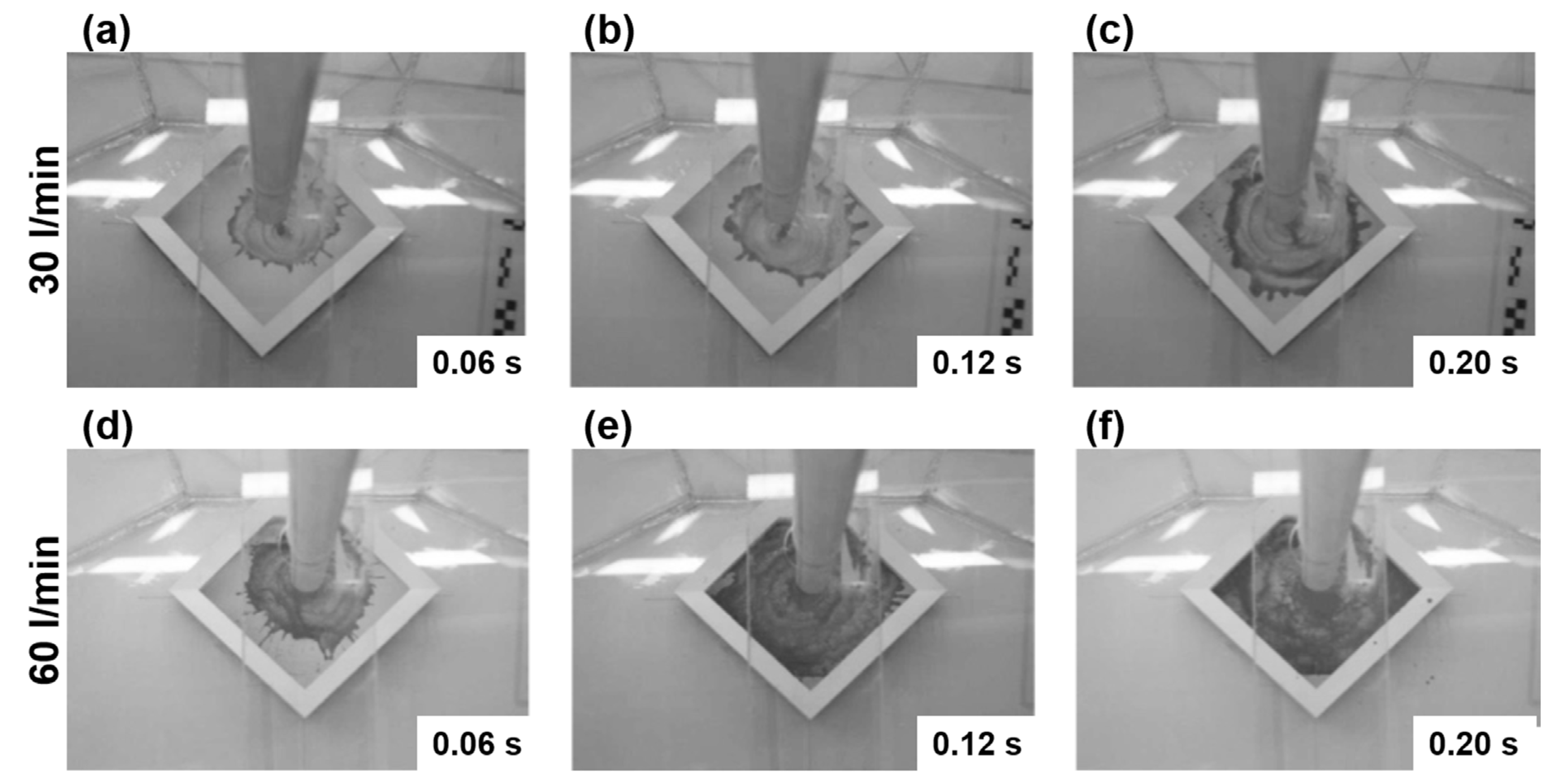
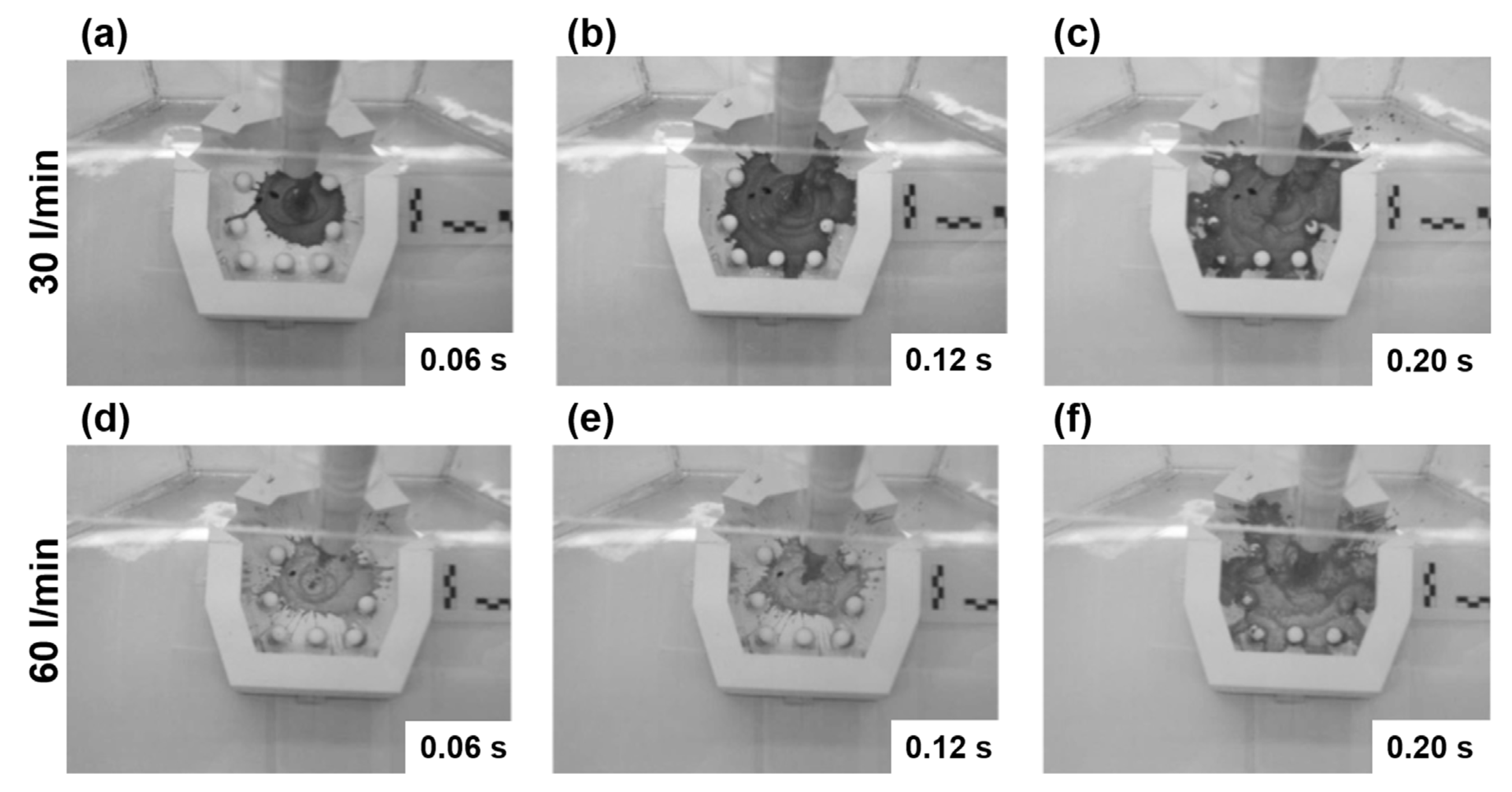
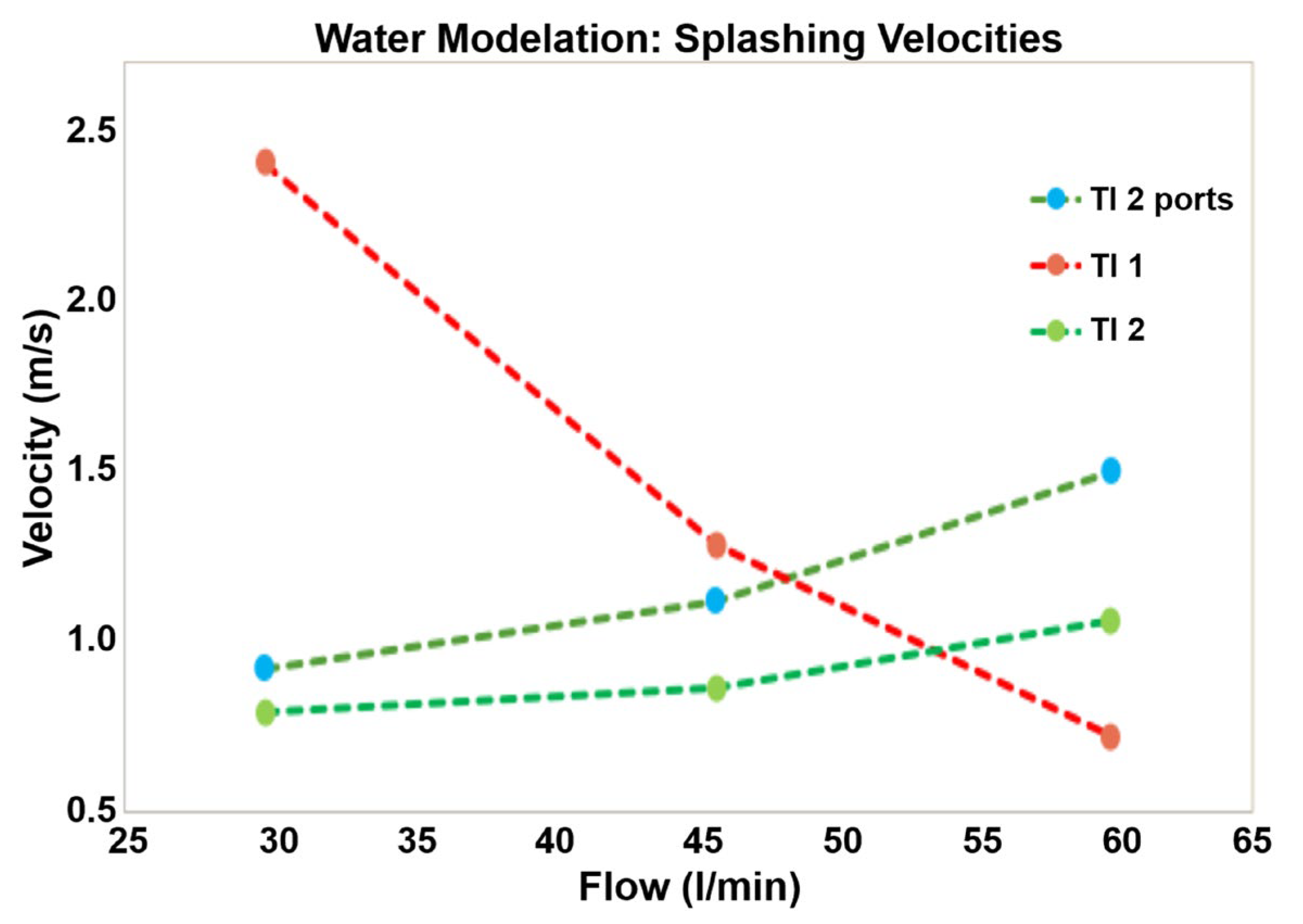
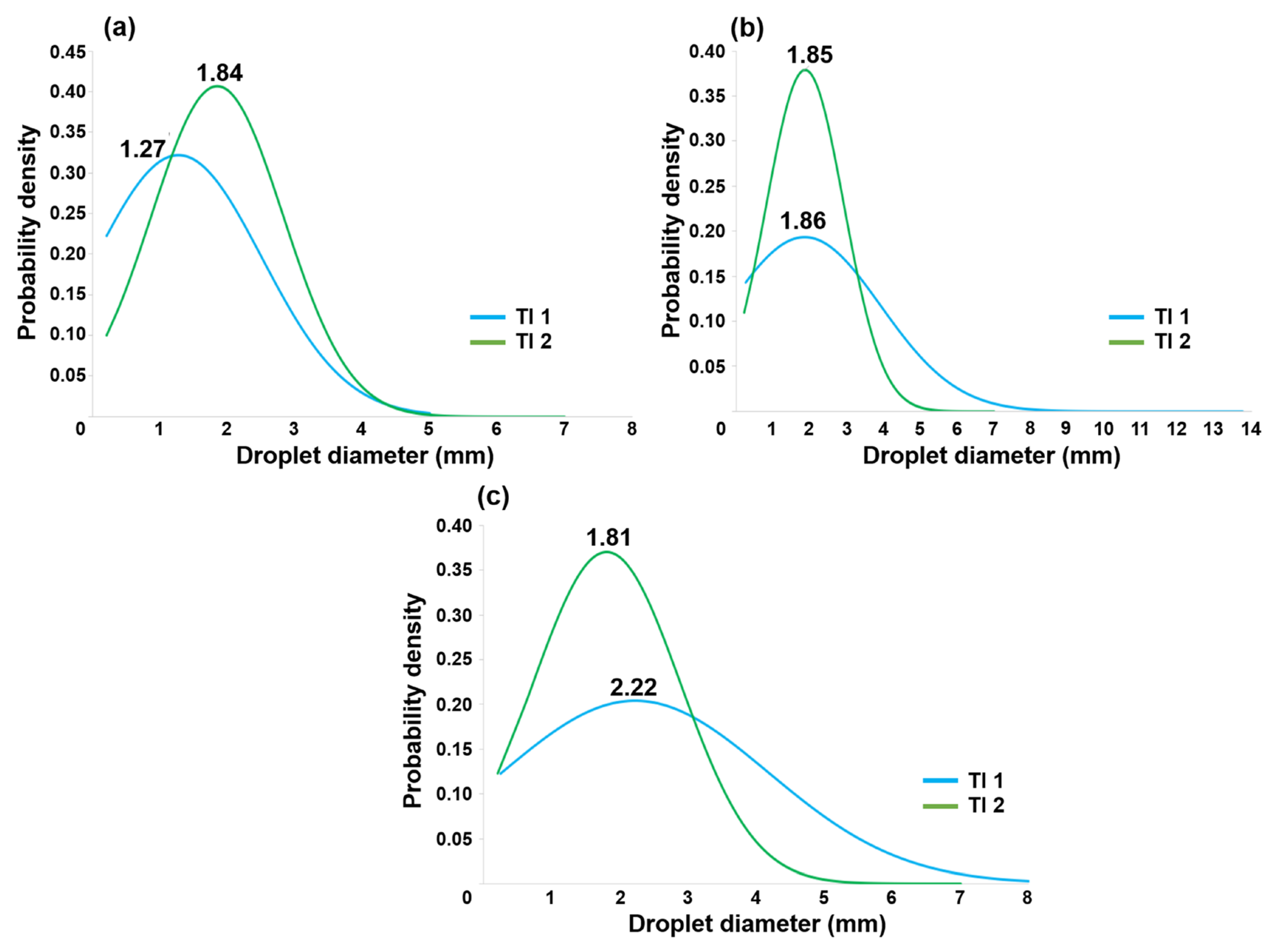


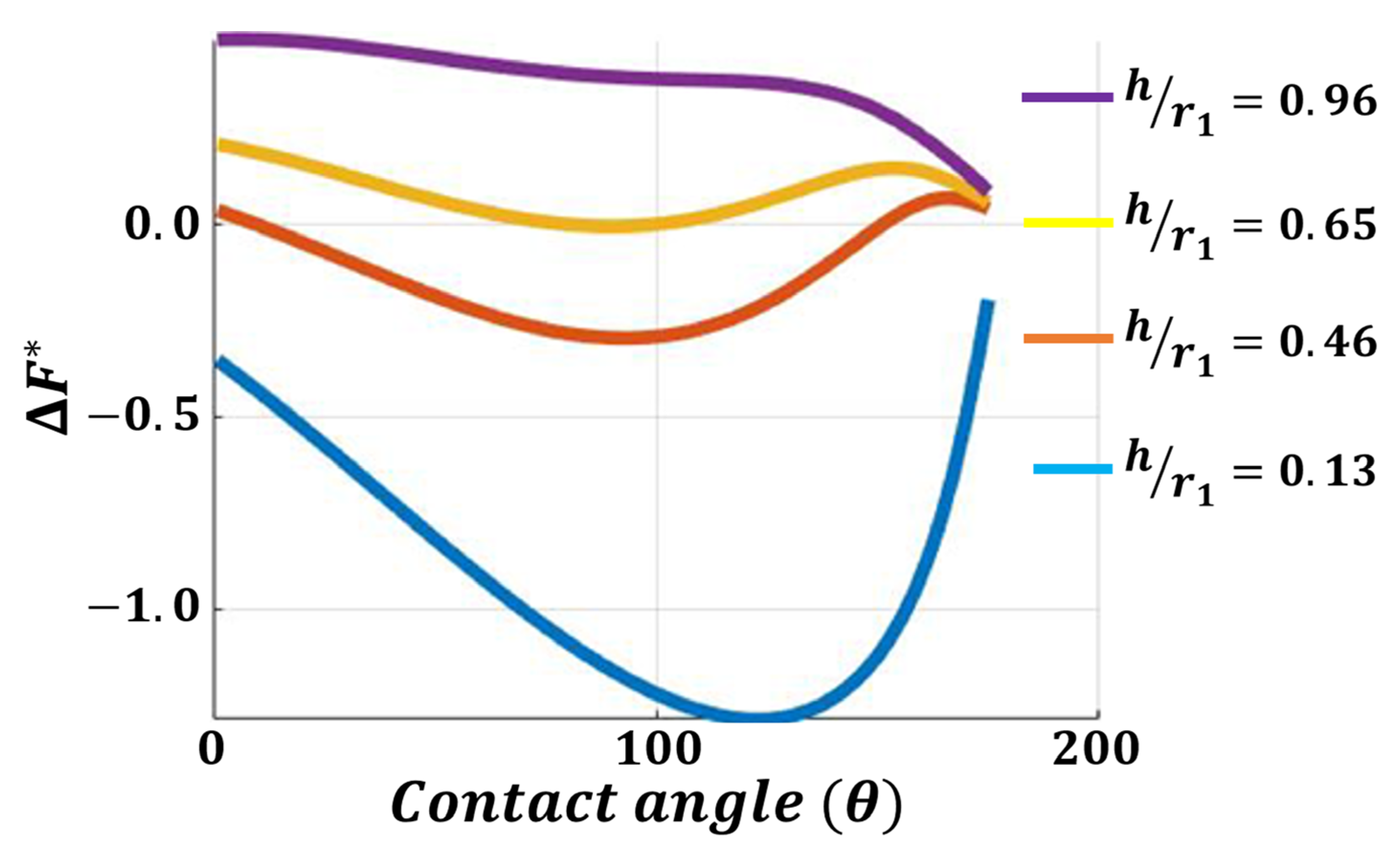
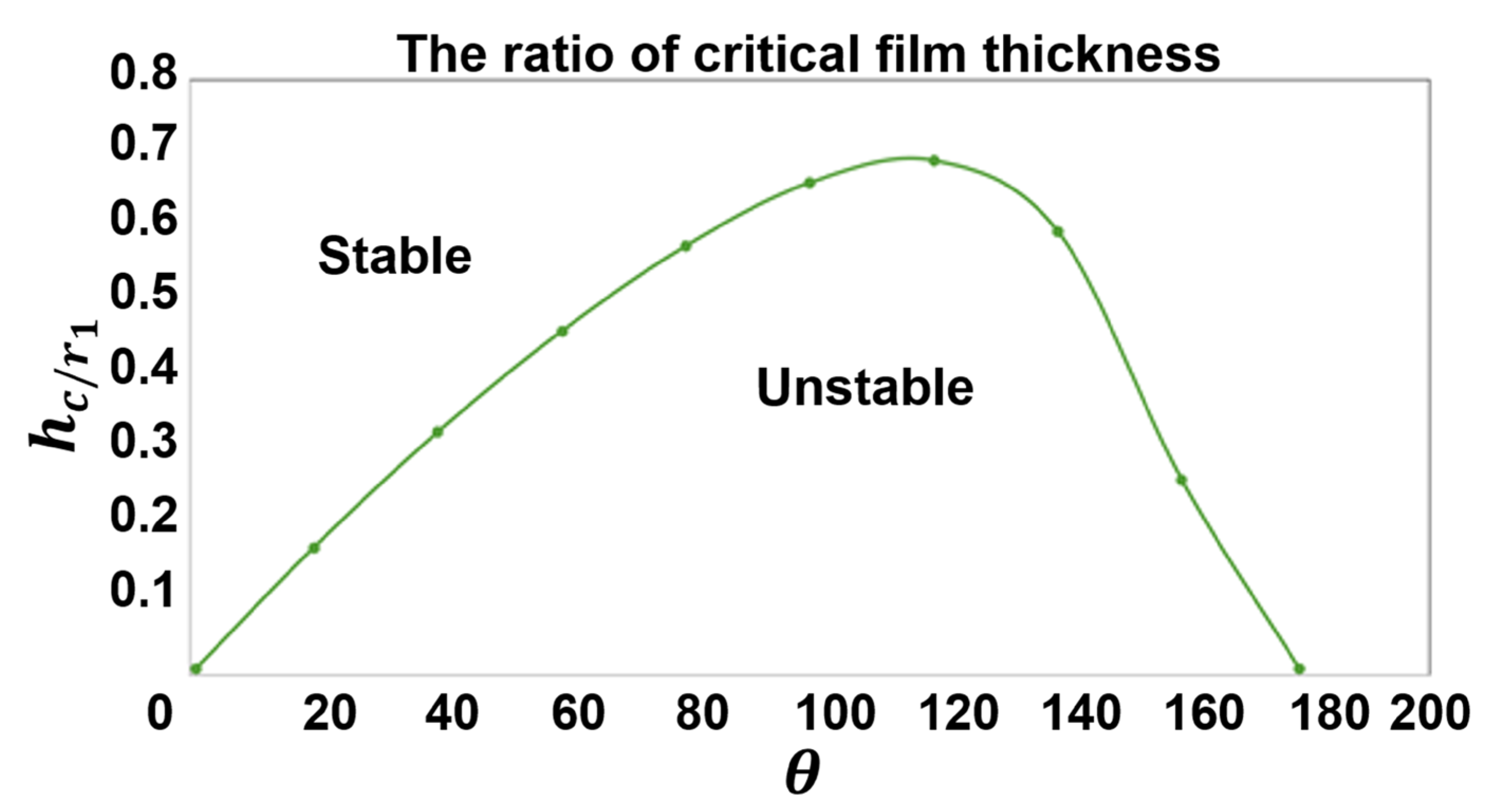


| Steel [L/min] | Water [L/min] | |
|---|---|---|
| IT1 | 467 | 30 |
| 717 | 46 | |
| 935 | 60 | |
| IT2 | 467 | 30 |
| 717 | 46 | |
| 935 | 60 |
| Dimensionless Number | Equation | Meaning | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reynolds | (1) | Inertial forces/viscous forces | |
| Weber | (2) | Inertial forces/tensile forces | |
| Ohnesorge | (3) | Viscous forces/surface tension forces | |
| Capilar | (4) | Viscous forces/surface forces | |
| Stokes | (5) | Gas viscous forces/liquid viscous forces |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores Jazmín, O.; Rodriguez, J.; Martinez Villafañe, J.F.; Morales Davila, R.; Guarneros, J.; Nájera-Bastida, A. Physical Model of Liquid Steel Jets Impacting on Solid-Rigid Surfaces. Metals 2025, 15, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040339
Flores Jazmín O, Rodriguez J, Martinez Villafañe JF, Morales Davila R, Guarneros J, Nájera-Bastida A. Physical Model of Liquid Steel Jets Impacting on Solid-Rigid Surfaces. Metals. 2025; 15(4):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040339
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores Jazmín, Octavio, Jafeth Rodriguez, Jesus Fernando Martinez Villafañe, Rodolfo Morales Davila, Javier Guarneros, and Alfonso Nájera-Bastida. 2025. "Physical Model of Liquid Steel Jets Impacting on Solid-Rigid Surfaces" Metals 15, no. 4: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040339
APA StyleFlores Jazmín, O., Rodriguez, J., Martinez Villafañe, J. F., Morales Davila, R., Guarneros, J., & Nájera-Bastida, A. (2025). Physical Model of Liquid Steel Jets Impacting on Solid-Rigid Surfaces. Metals, 15(4), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040339







