Microstructure and Properties of Resistance Element Welded Joints of DP780 Steel and 6061 Aluminum Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
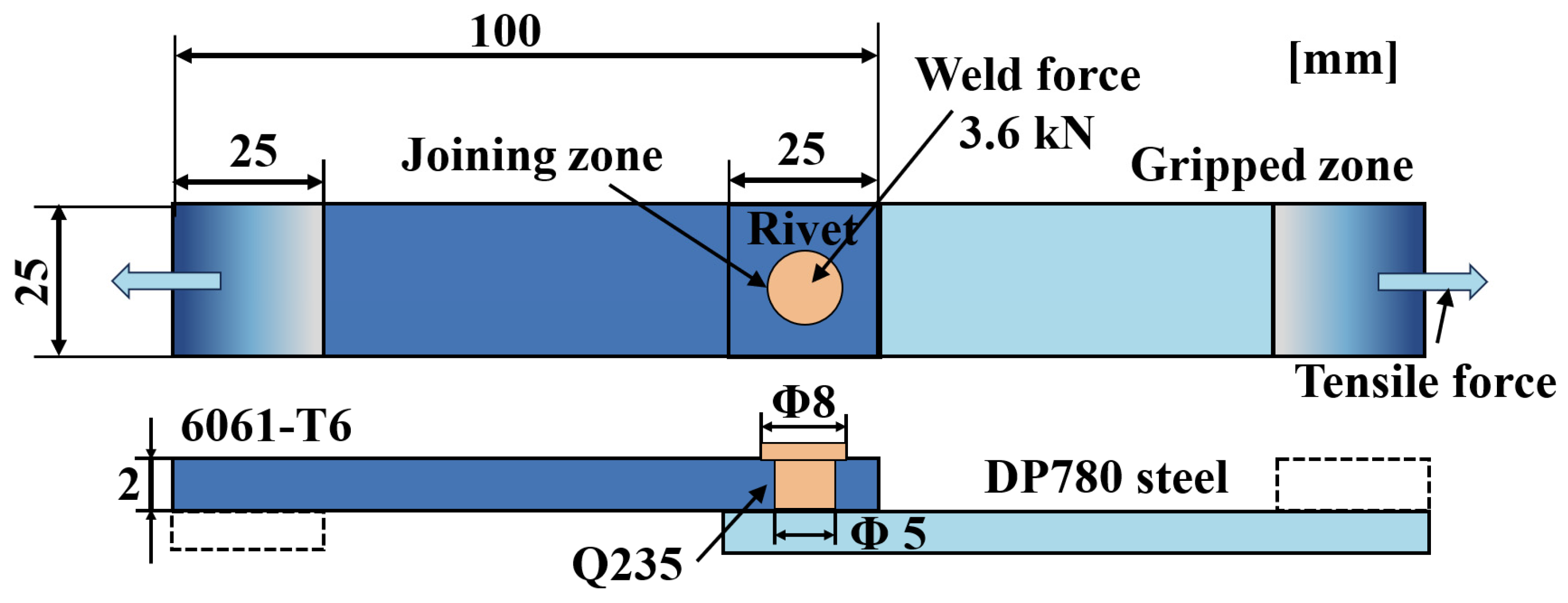
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Metallographic Observation
2.4. Mechanical Properties
3. Result
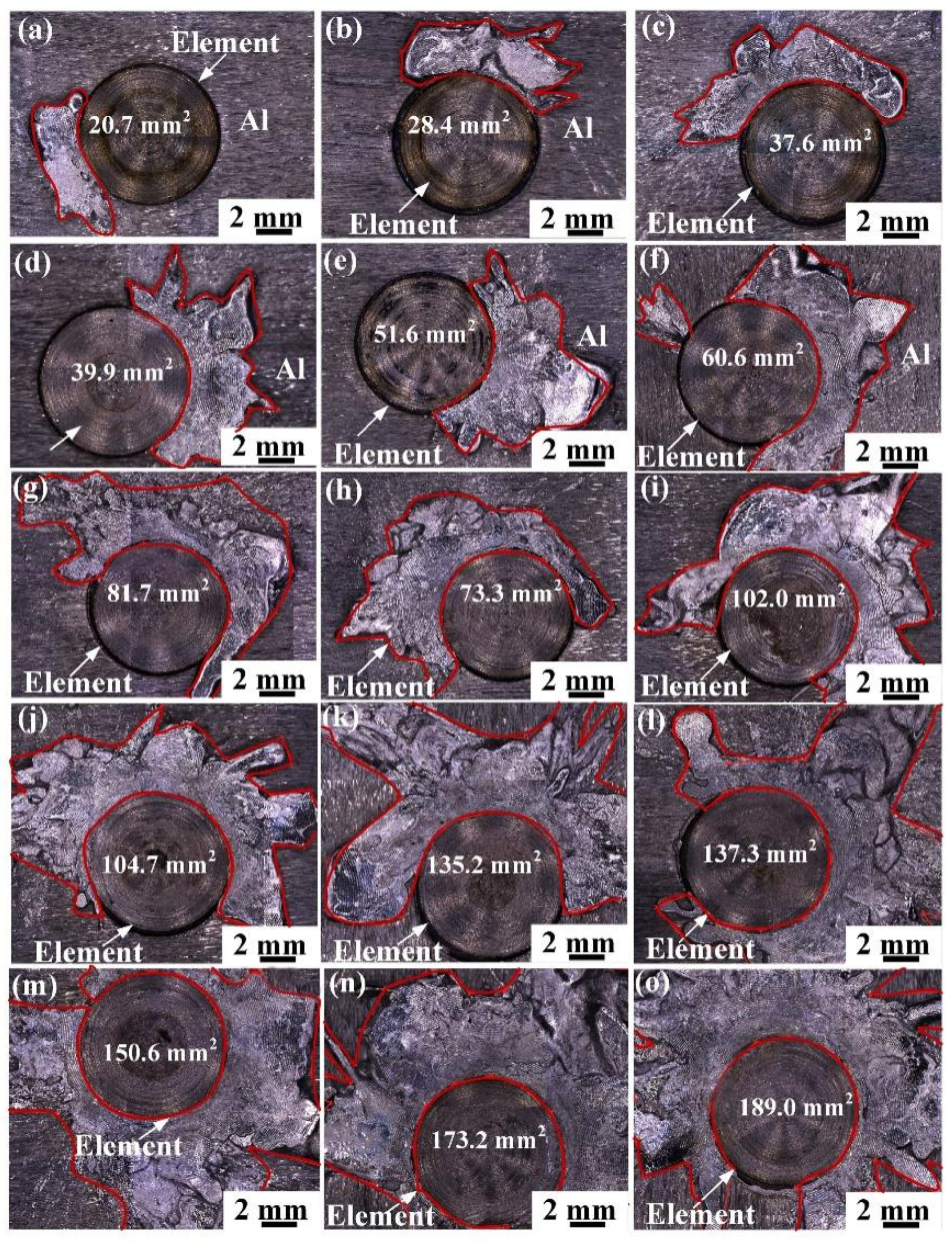
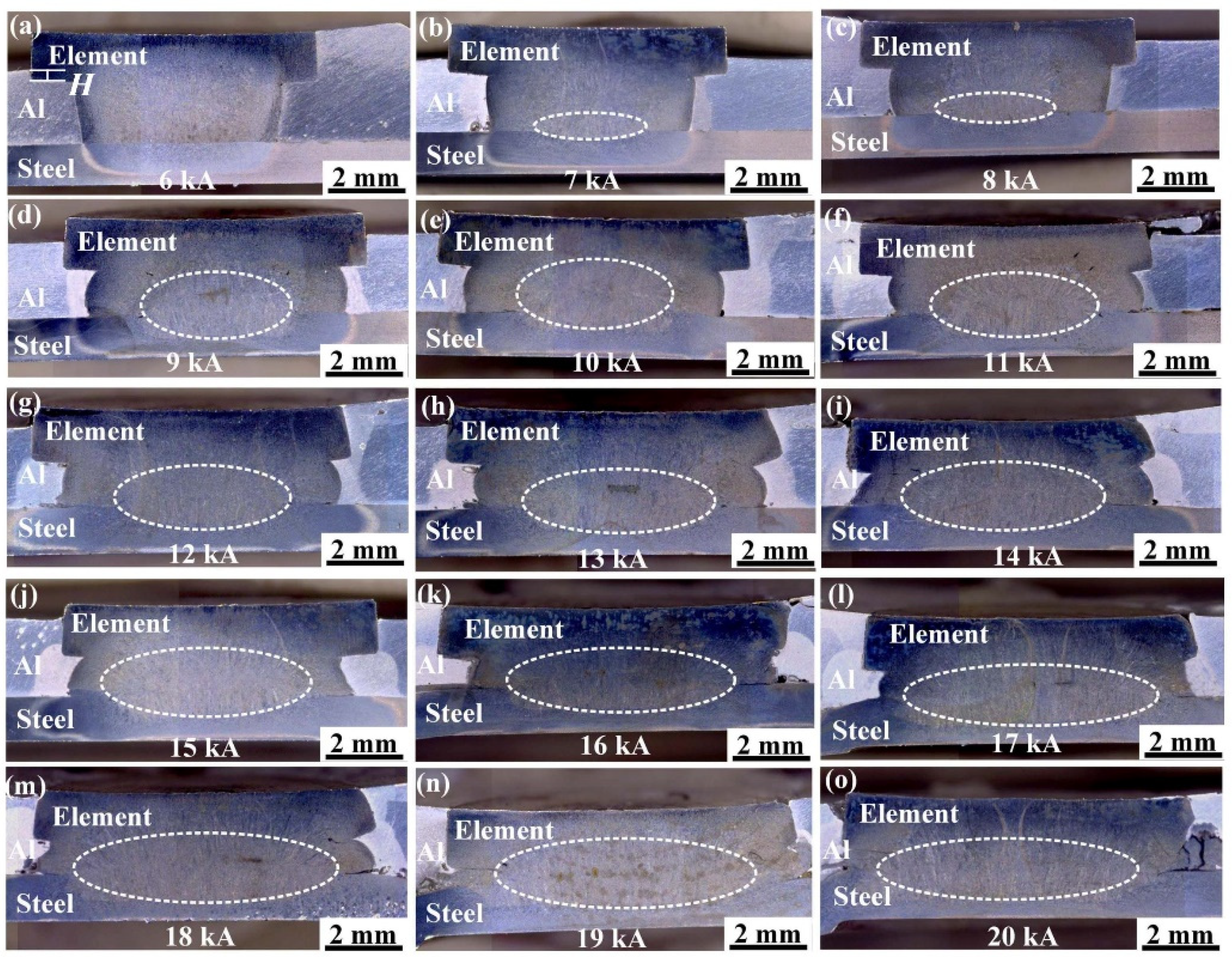
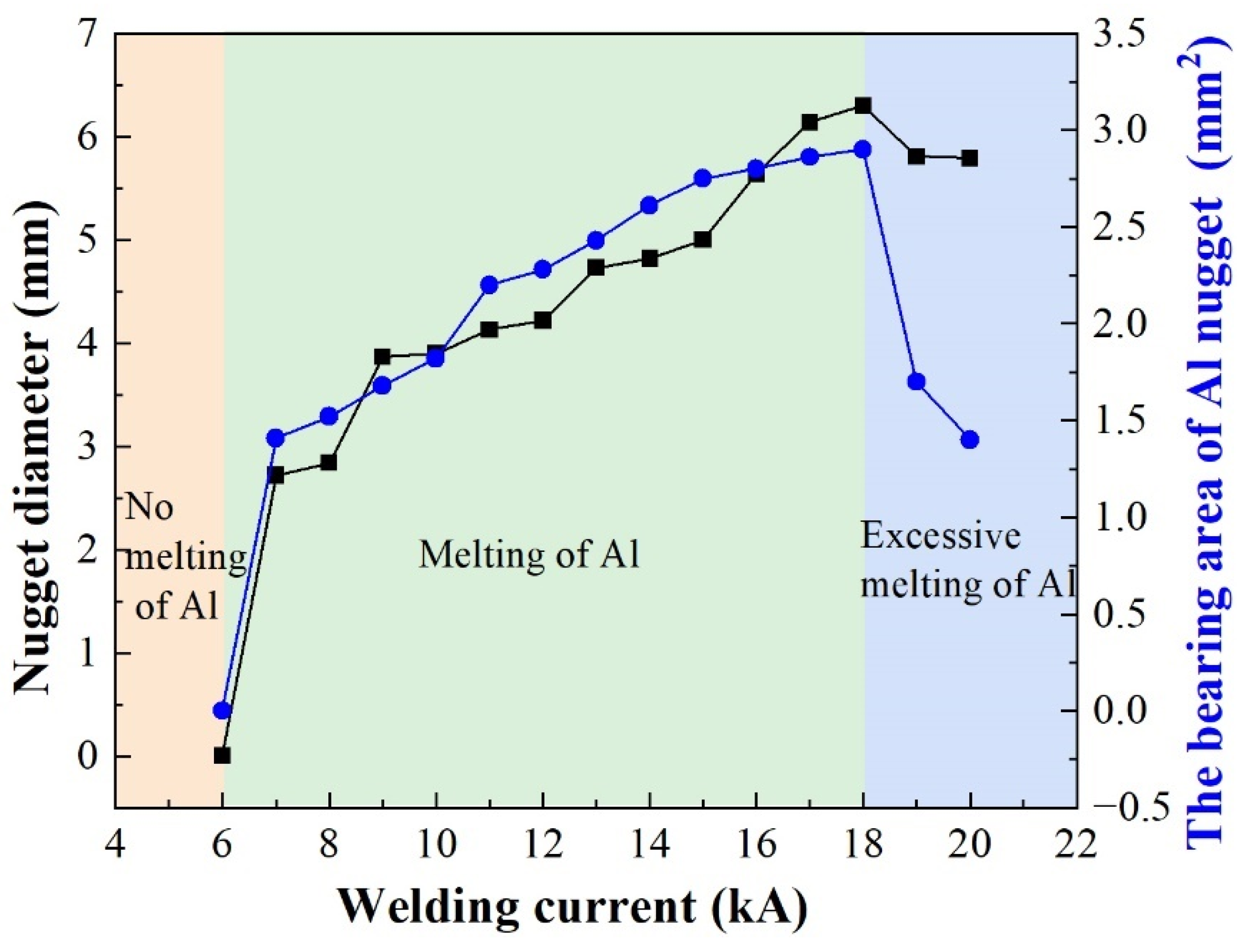
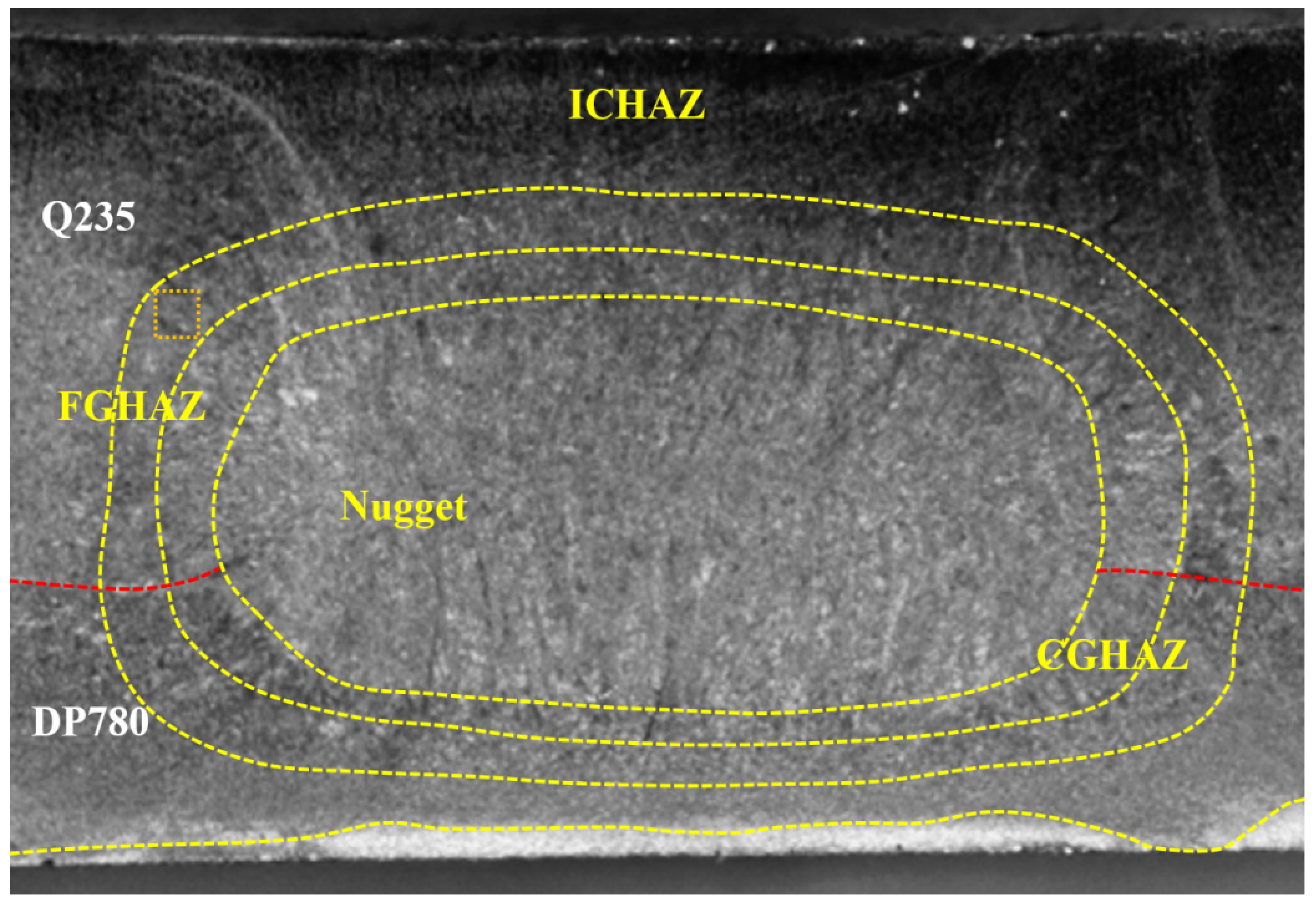
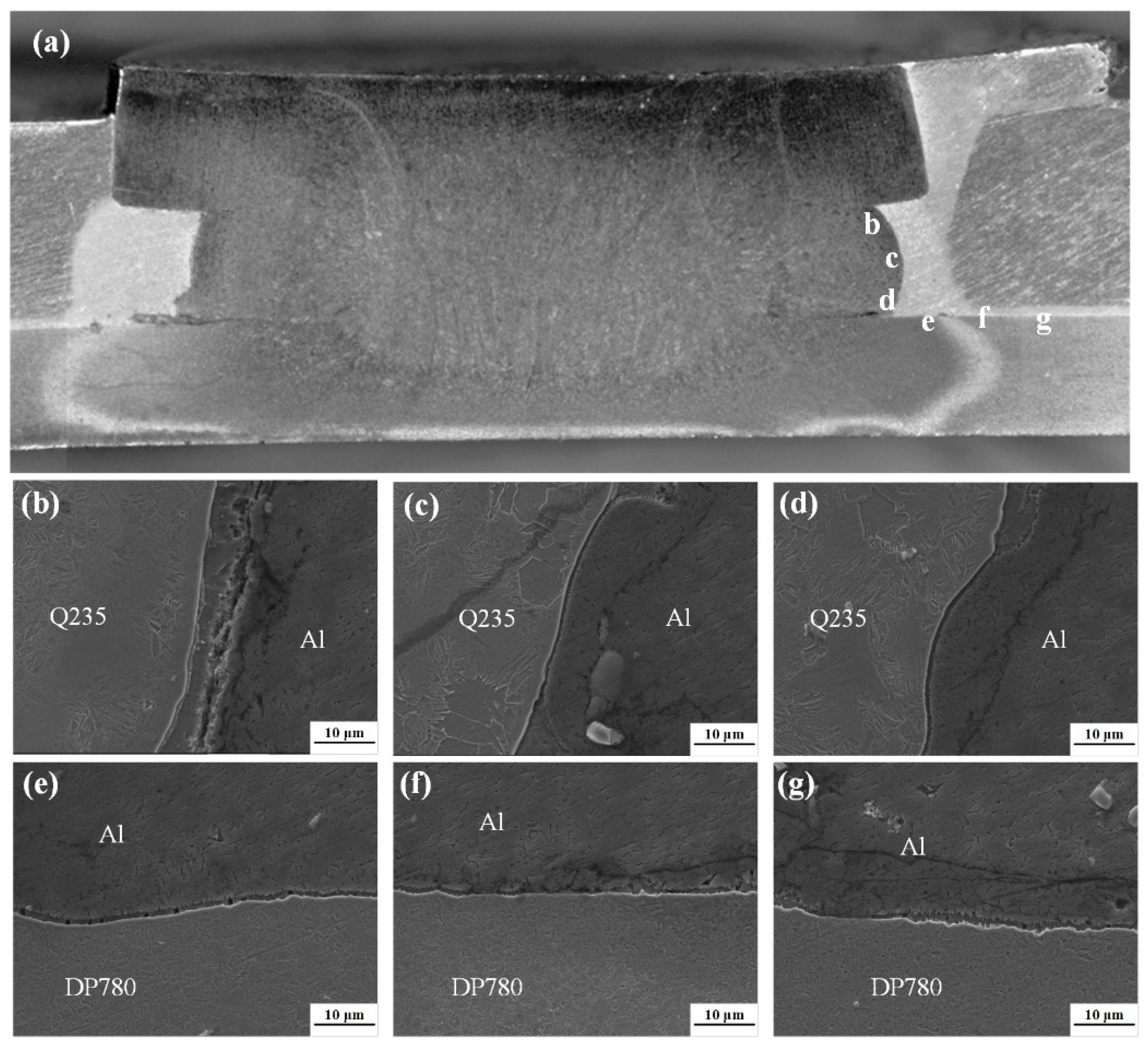
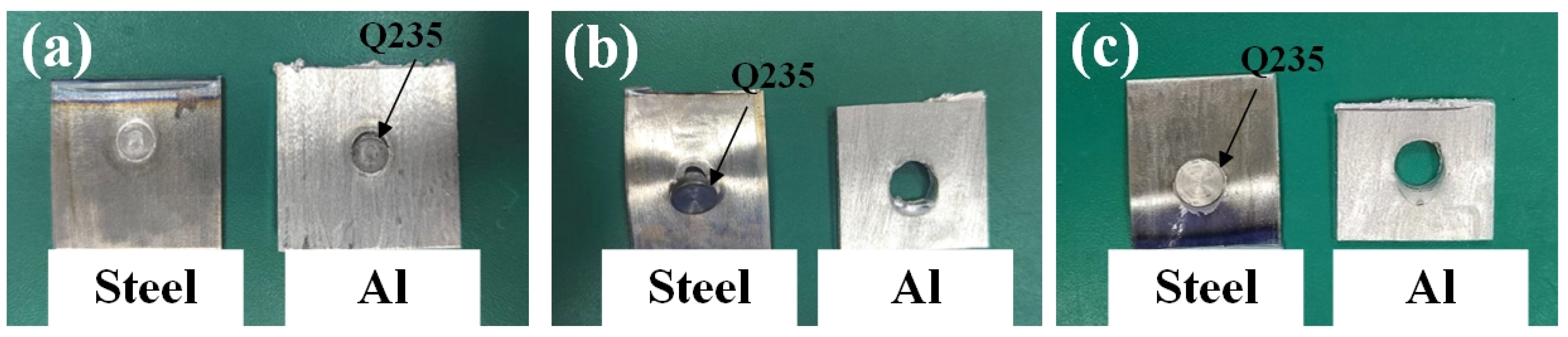
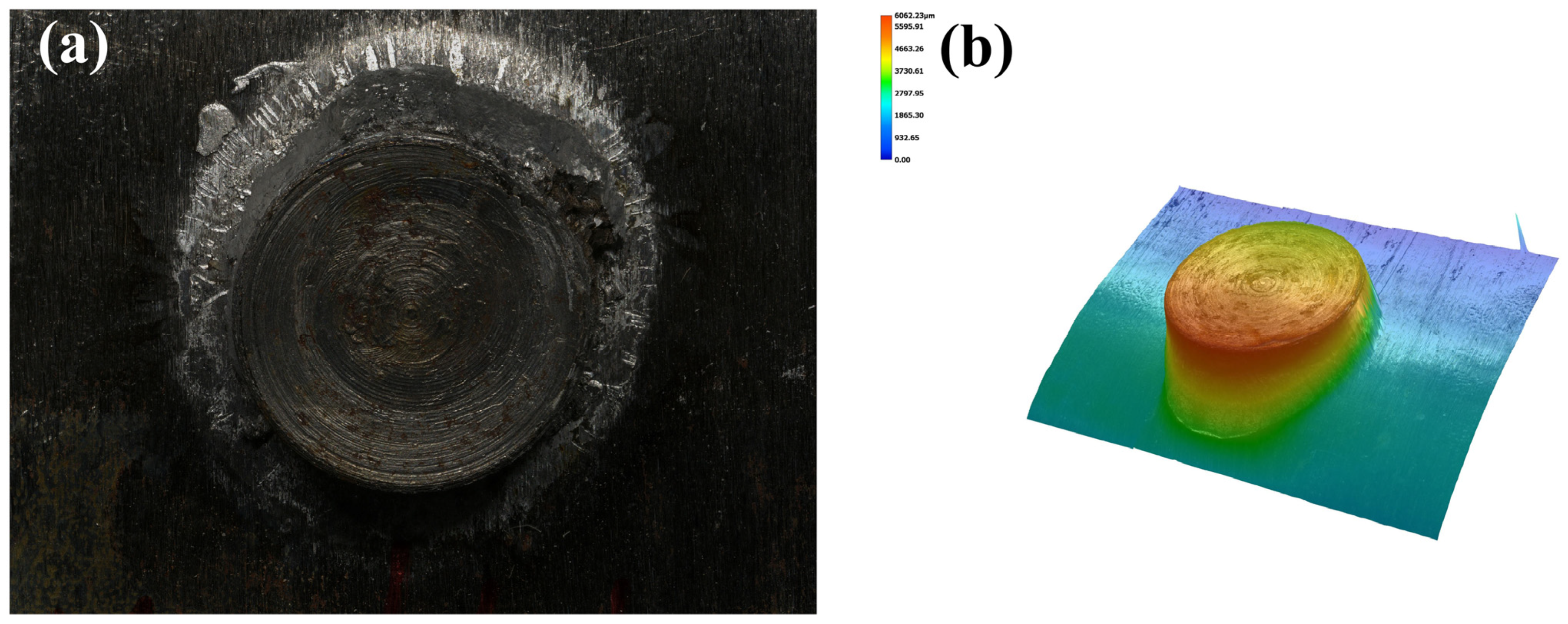
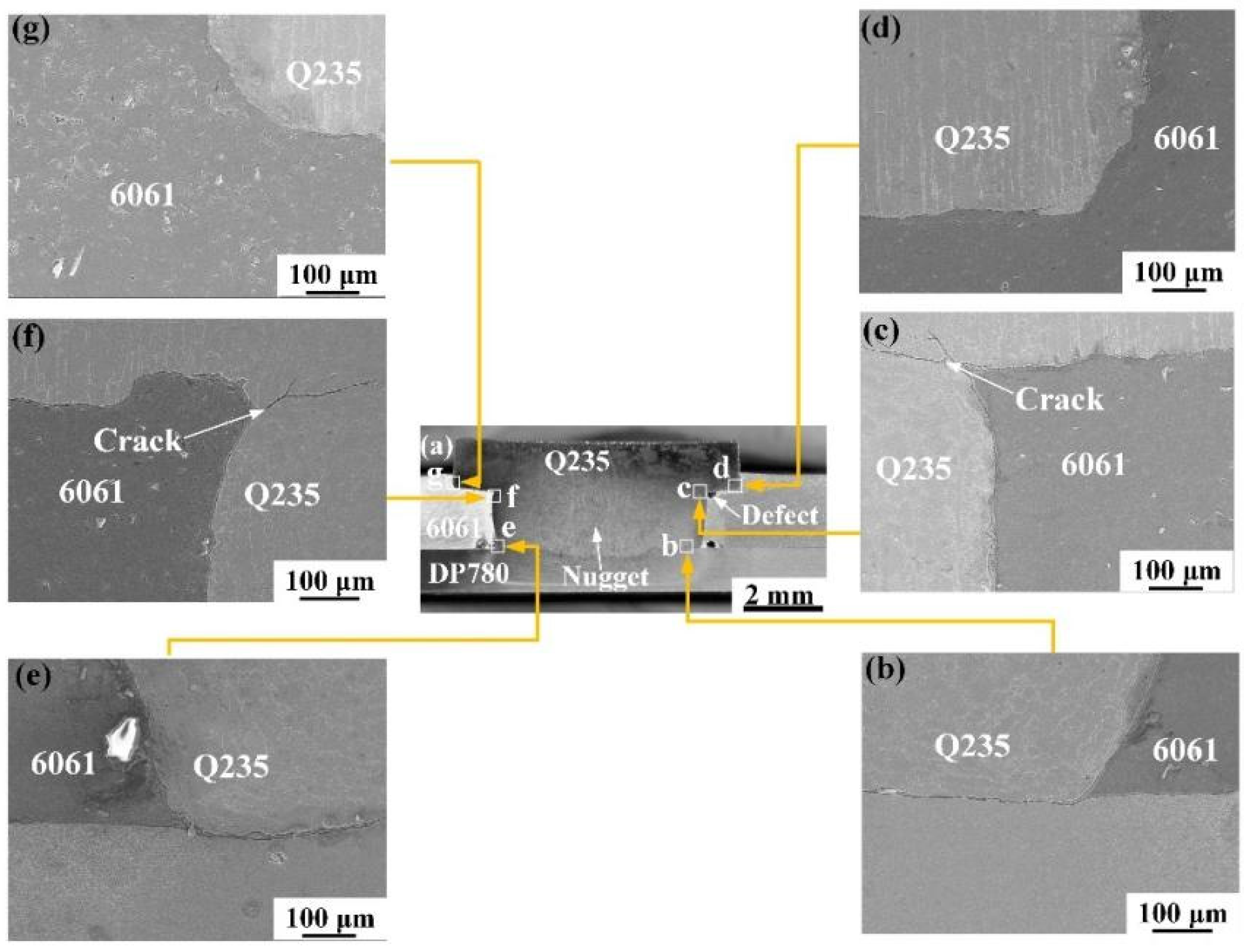
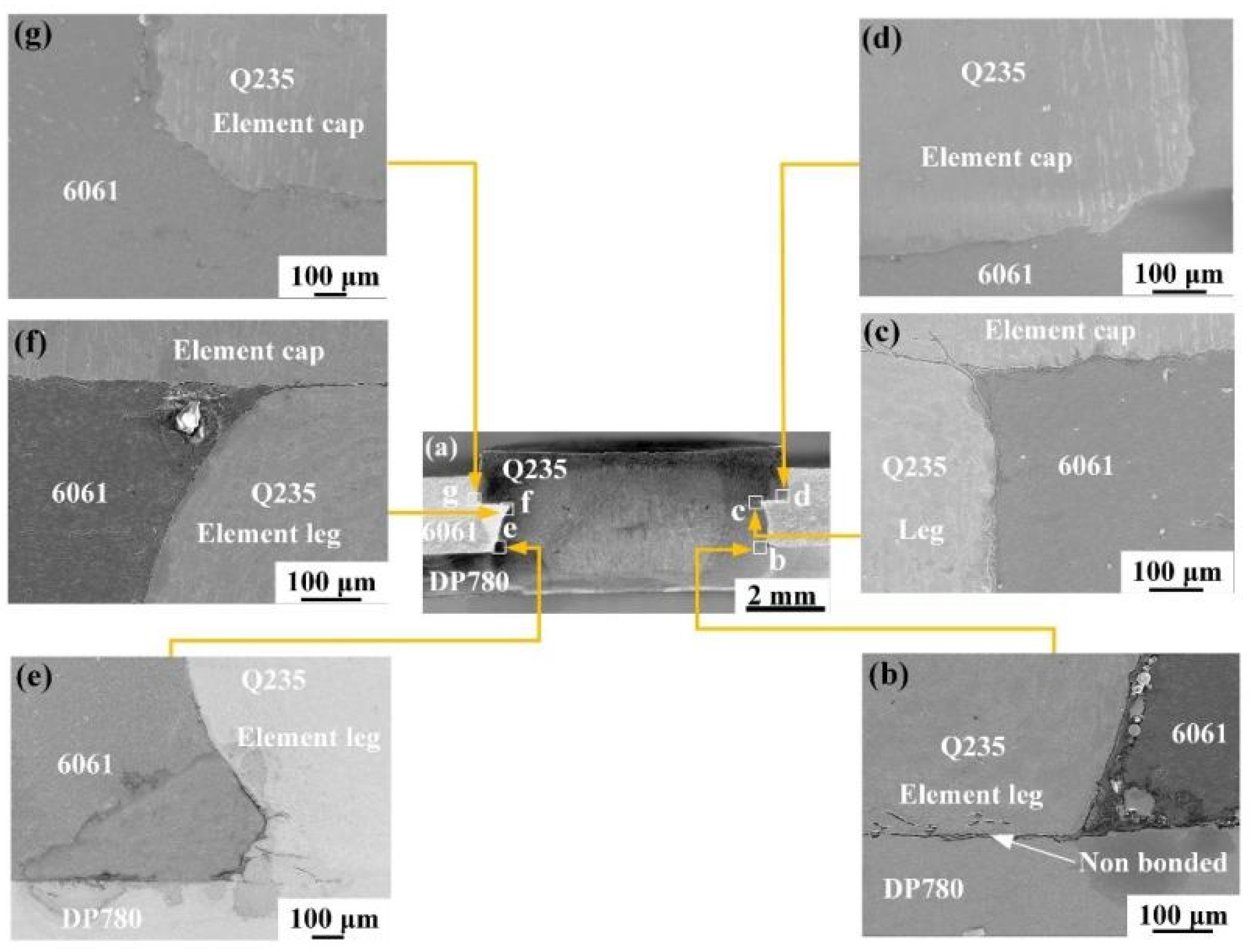
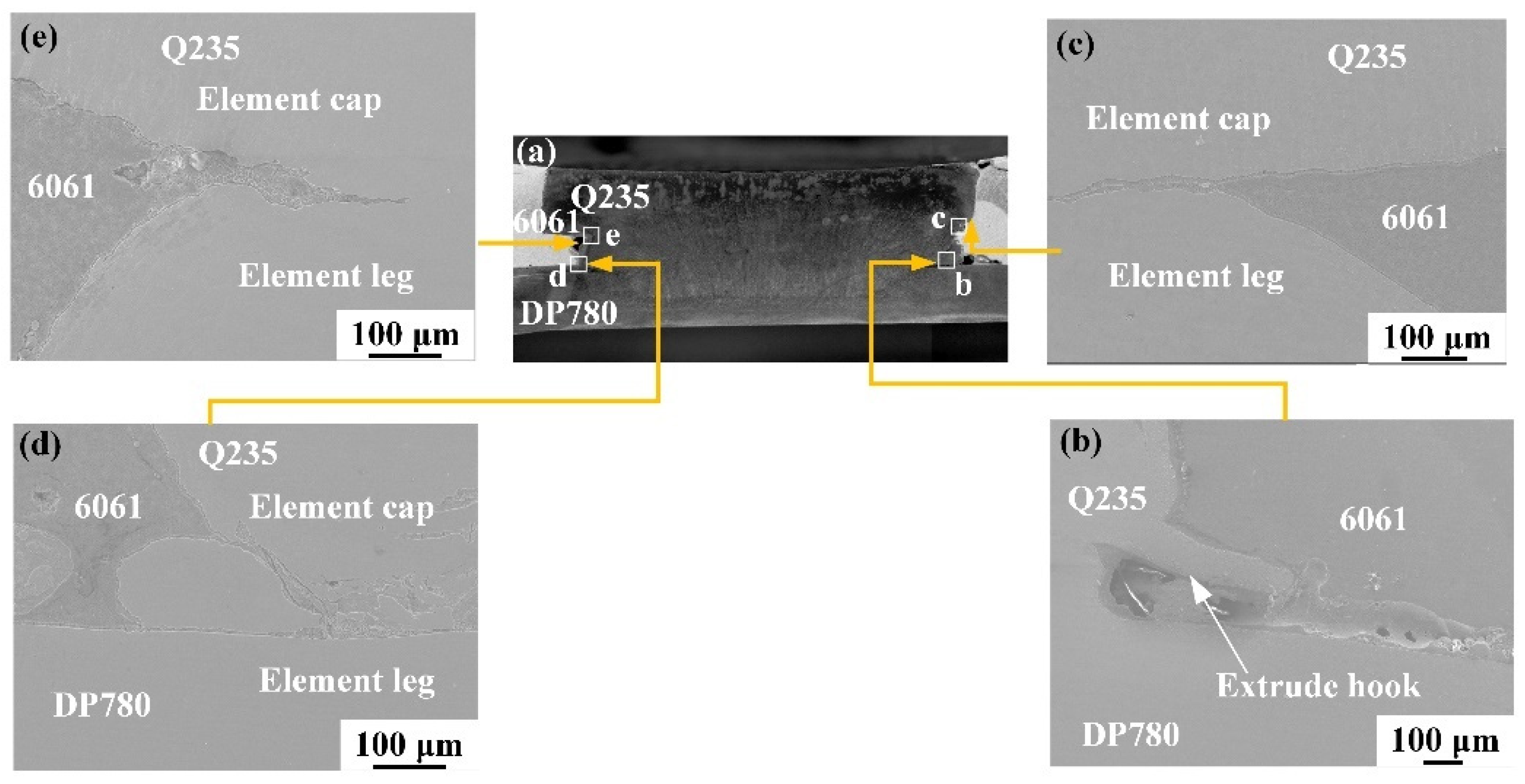
3.1. Macroscopic Morphology of the Joint Surface and Cross-Section
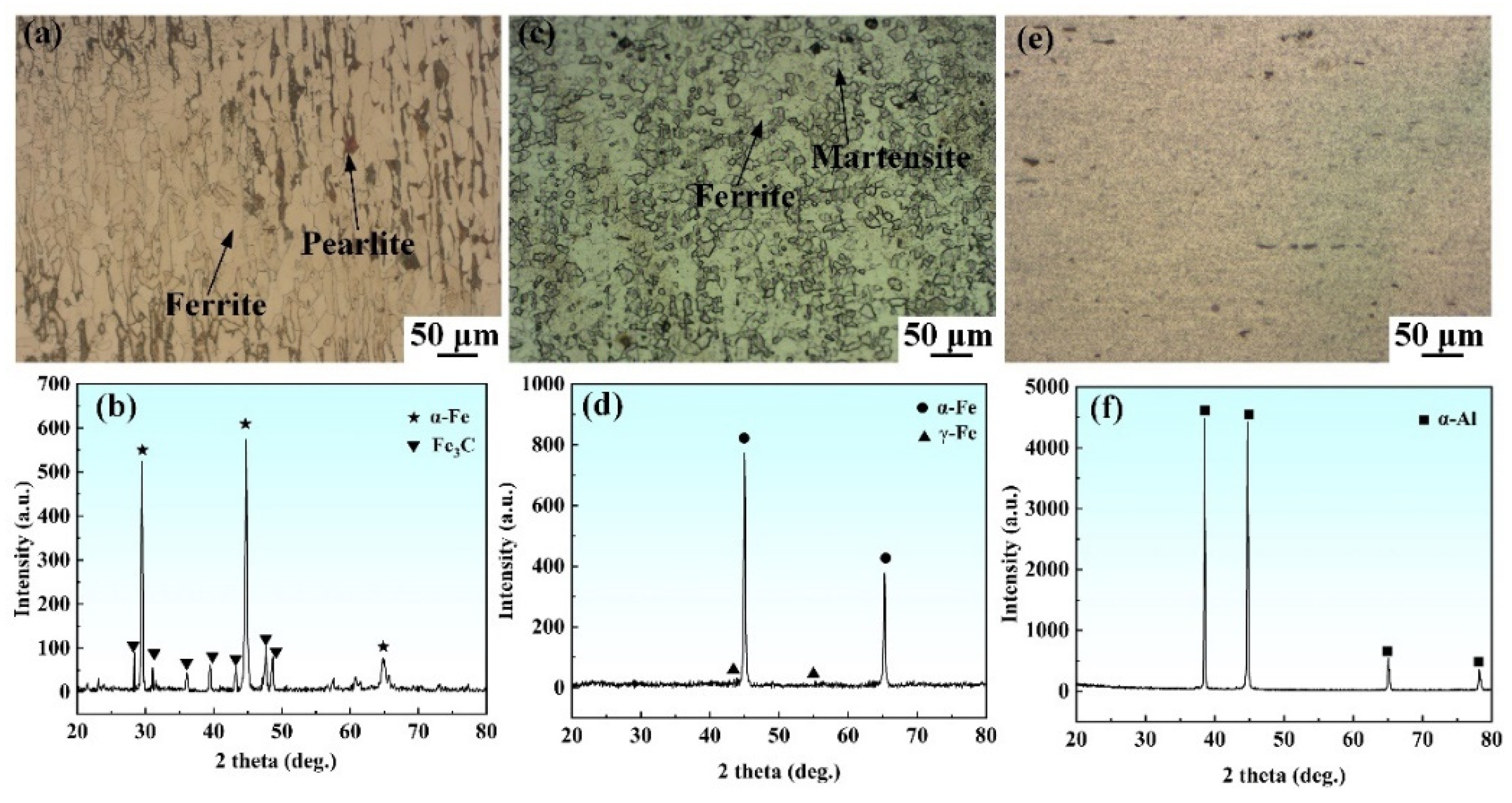
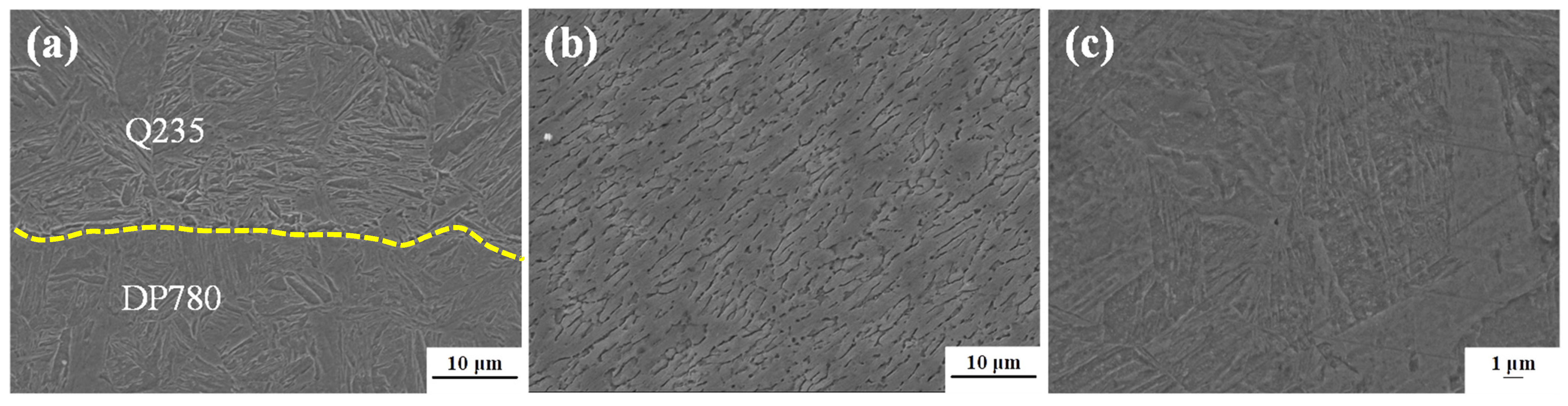
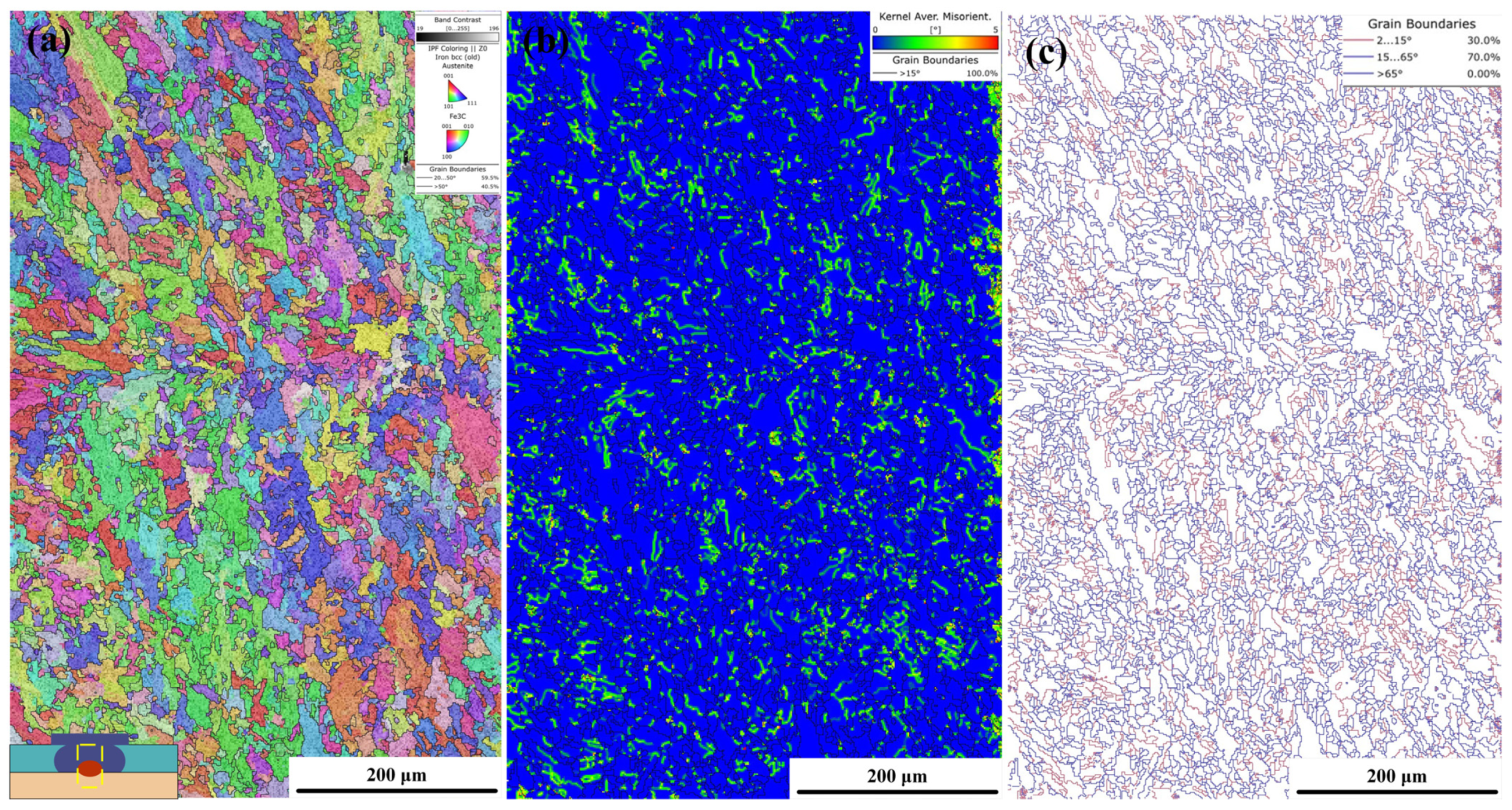
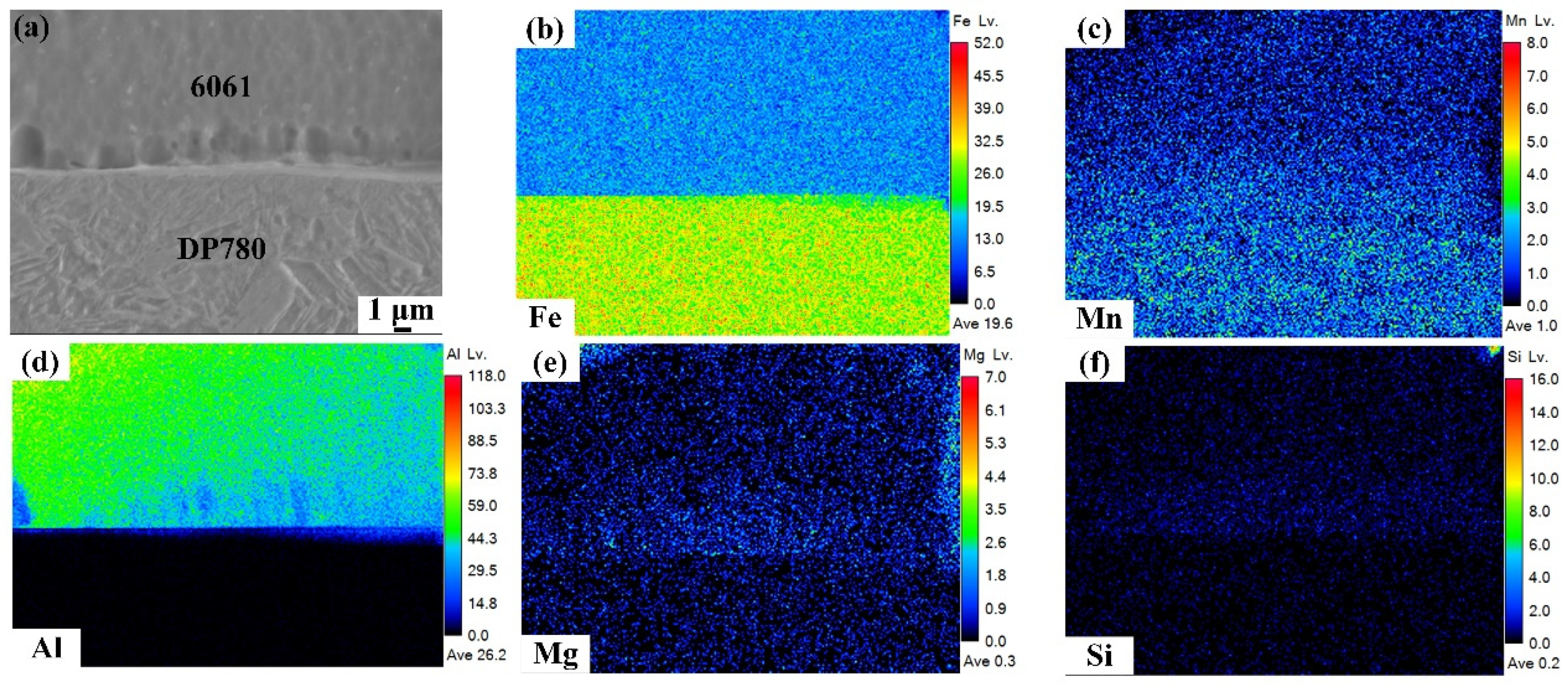
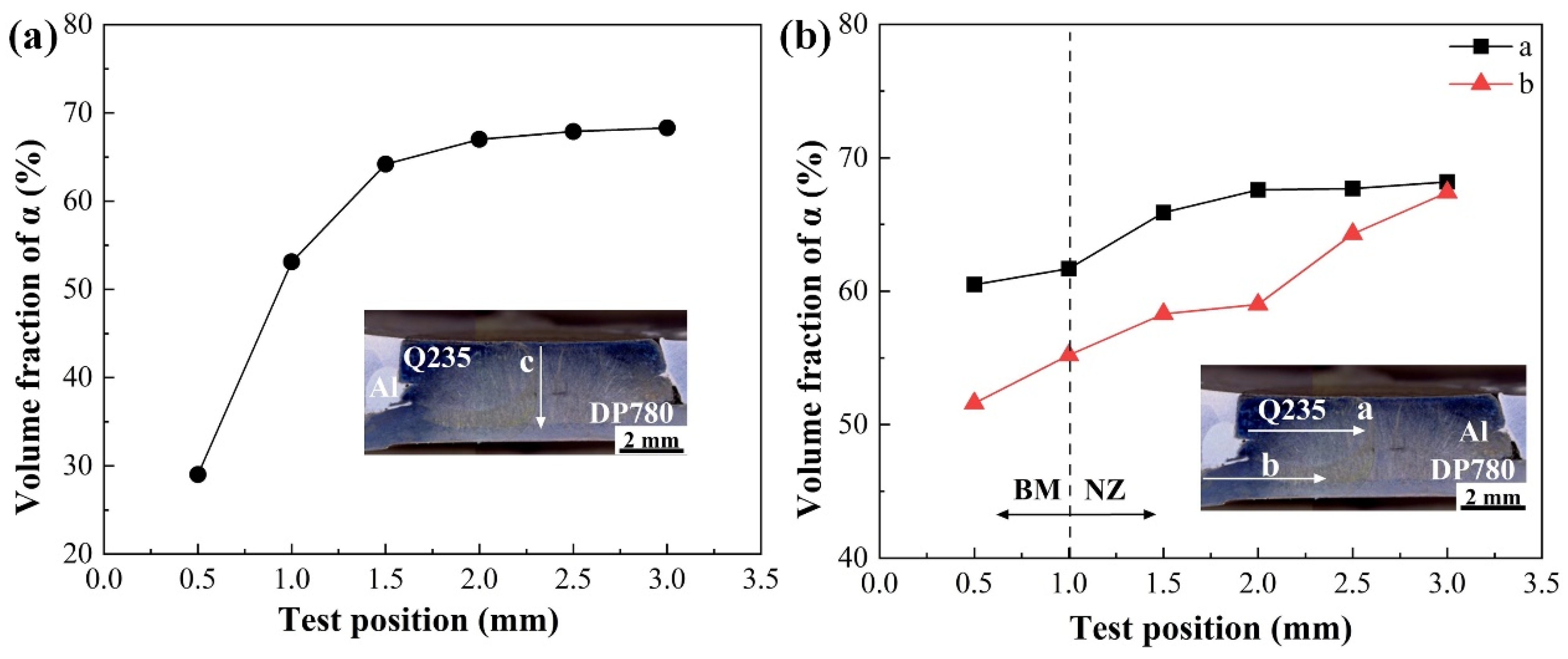
3.2. Grain Structure and Element Distribution in the Steel Fusion Zone
3.3. Intermetallic Compound Layer
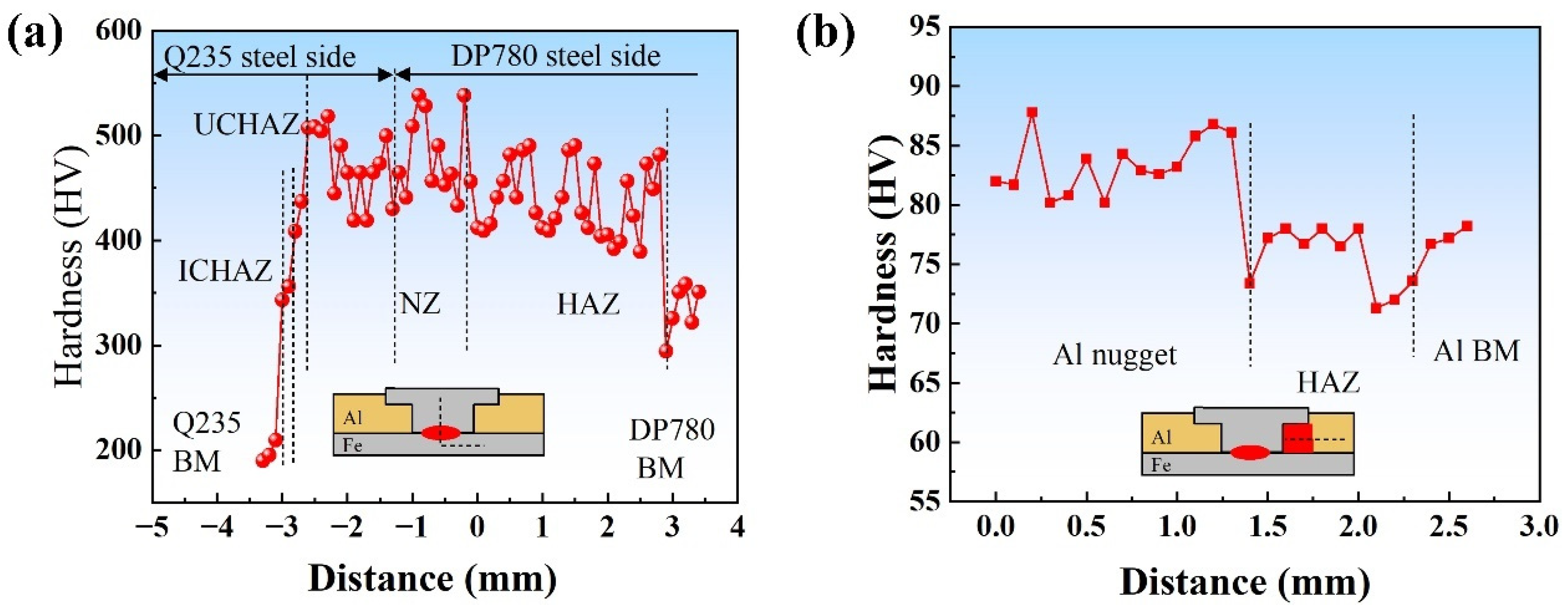
3.4. Microhardness of the Joint
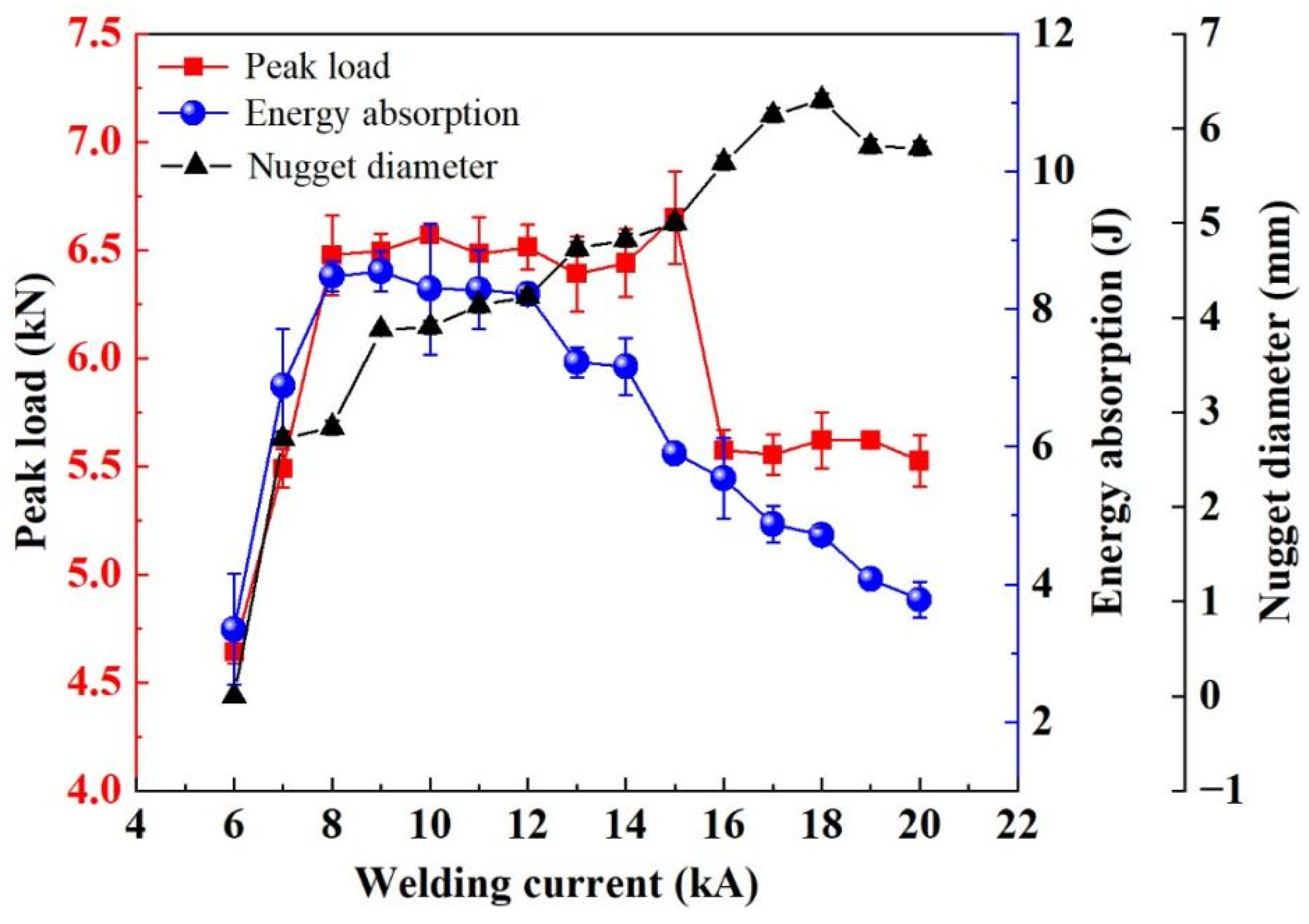
3.5. Mechanical Properties and Failure Modes
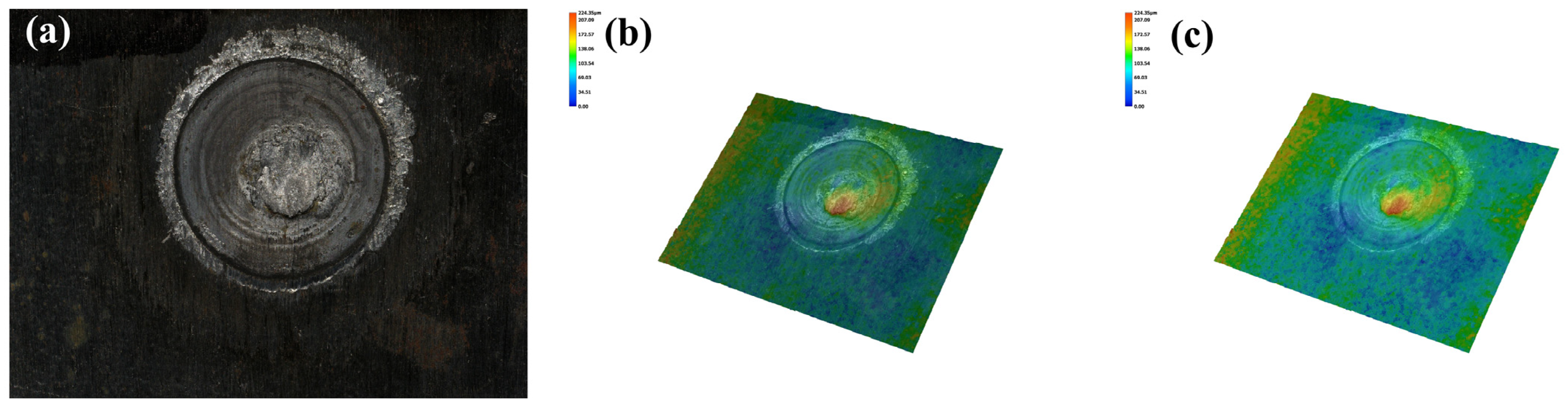
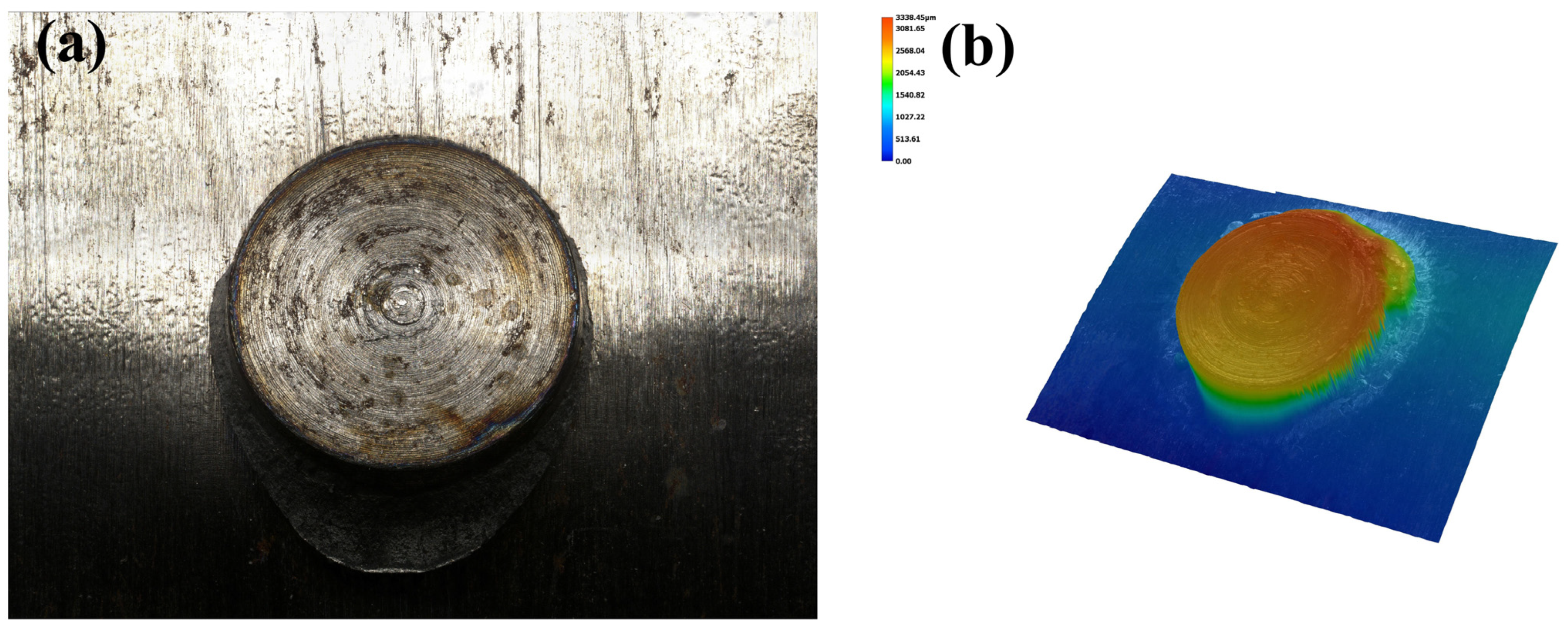
3.6. Fracture Morphology of the Joint
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The REW joint between 6061 aluminum and DP780 steel can be divided into NZ, HAZ, and BM. The NZ structure is entirely martensite. The CGHAZ on both sides of Q235 steel and DP780 steel is mainly composed of lath martensite and coarse bainite, and the FGHAZ is mainly composed of fine martensite and contains some fine ferrite inclusion.
- (2)
- The IMC layer is composed of tongue Fe2Al5 adjacent to the steel side and needle Fe4Al13 adjacent to the aluminum alloy side. Fe2Al5 layer thickens toward the base of the rivet. The layers of the two interfacial compounds are thin and discontinuous.
- (3)
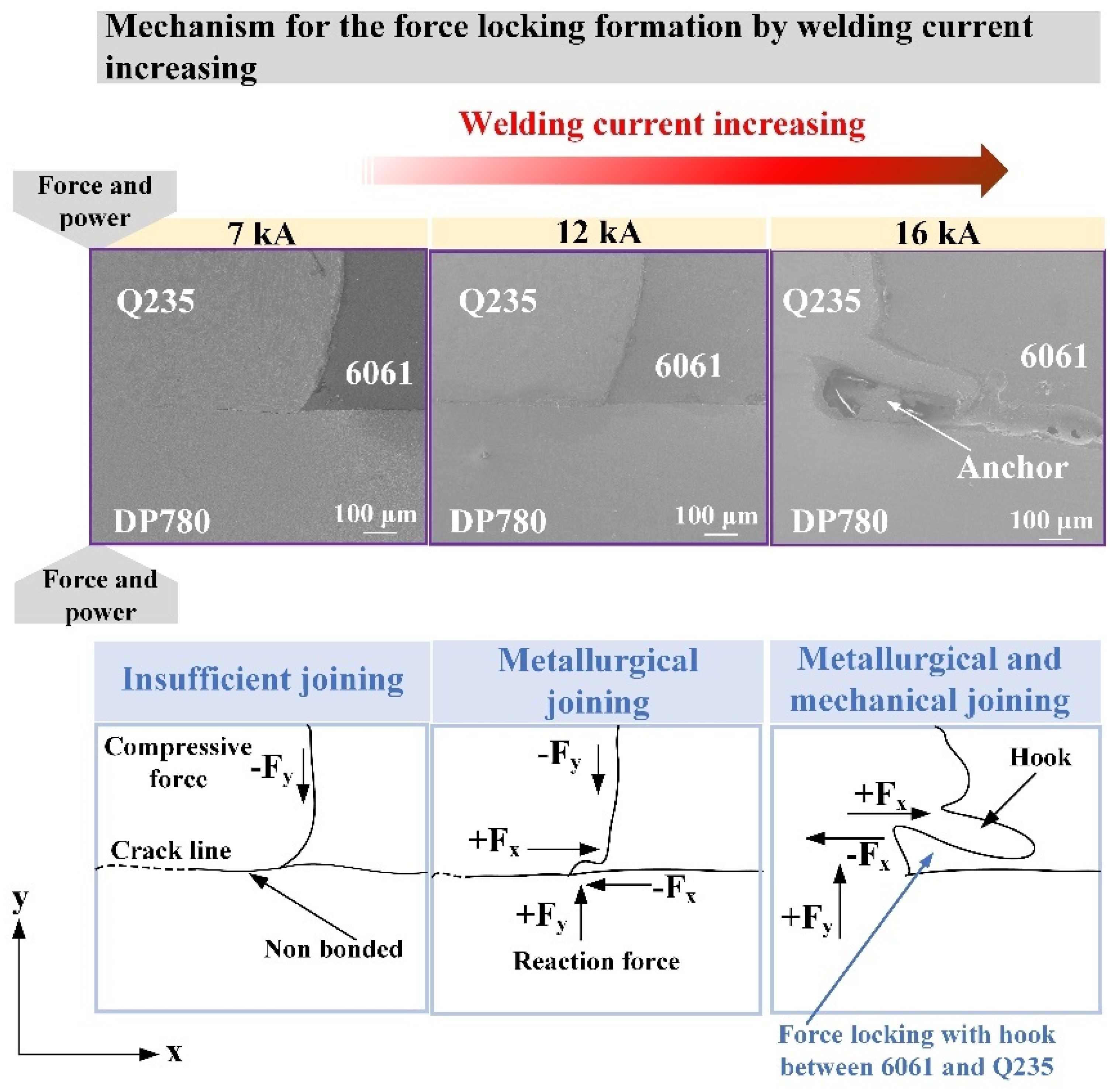
- As the welding current increases, the structure of the REW joint evolves into a hooklike structure, which improves the bearing capacity of the joint. When the welding current is less than 7 kA, the failure mode of the REW joint is IF mode. Between 7 and 15 kA, it shows POF mode. Above 15 kA, it shows BPF mode. The maximum core diameter, peak load, and energy absorption of the joint are 5.05 mm, 6.91 kN, and 8.47 J, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akhshik, M.; Panthapulakkal, S.; Tjong, J.; Sain, M. The effect of lightweighting on greenhouse gas emissions and life cycle energy for automotive composite parts. Clean. Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Sidhar, H.; Mishra, R.S.; Hovanski, Y.; Upadhyay, P.; Carlson, B. Evaluation of intermetallic compound layer at aluminum/steel interface joined by friction stir scribe technology. Mater. Des. 2019, 174, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Zhou, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, H.S. Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of direct laser welding 7075 super hard aluminum alloy/D6AC ultra-high strength alloy structural steel. Mater. Lett. 2021, 287, 129312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Hu, T.H.; Wu, T.H.; Dong, W.F.; Zhu, P.; Wang, S.J.; Pan, H.; Gao, Y.L. Role of the position of the laser spot in the failure transition during the tensile test for the laser welding-brazing of galvanized CRRA1000 steel to 5754 aluminum alloy in an overlapped joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 880, 145314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meschut, G.; Janzen, V.; Olfermann, T. Innovative and Highly Productive Joining Technologies for Multi-Material Lightweight Car Body Structures. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.Z. Hybrid joining of a modular multi-material body-in-white structure. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 275, 116351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.B.; Yuan, X.J.; Hu, Z.; Li, T.; Wu, K.L.; Li, C. Improvement of resistance-spot-welded joints for DP600 steel and A5052 aluminum alloy with Zn slice interlayer. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 30, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Ye, T.; Li, Y.Z.; Pei, X.J.; Sun, Z. Quasi-in-situ characterization of microstructure evolution in friction stir welding of aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 6380–6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bi, J.; Liu, H.W.; Li, Y.; Li, M.Y.; Ao, S.S.; Luo, Z. Research progress on the microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded Al-Li alloy joints. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 82, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebizadehsardari, P.; Musharavati, F.; Khan, A.; Sebaey, T.A.; Derazkola, H.A. Underwater friction stir welding of Al-Mg alloy: Thermo-mechanical modeling and validation. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 101965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Singh, G.; Singh, H. Investigation on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a dissimilar friction stir welded joint of magnesium alloys. J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2019, 233, 2444–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Su, J.H.; Gao, C.K.; Zhao, Y.X.; Liu, H.B.; Oliveira, J.P.; Tan, C.W.; Yu, Z.S. Effect of heat input on interfacial microstructure, tensile and bending properties of dissimilar Al/steel lap joints by laser welding-brazing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 142, 107218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.W.; Long, Y.H.; Li, Z.Y. Research progress of transition layer and filler wire for laser welding of steel and aluminum dissimilar metals. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 4149–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, G.L.; Li, F.N.; Wang, G.; Wei, H.Y. The interface control of butt joints in laser braze welding of aluminium-steel with coaxial powder feeding. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2017, 246, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.P.; Ponder, K.; Brizes, E.; Abke, T.; Ramirez, A.J. Combining resistance spot welding and friction element welding for dissimilar joining of aluminum to high strength steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 273, 116192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Absar, S.; Ruszkiewicz, B.J.; Skovron, J.D.; Mears, L.; Abke, T.; Xin, Z.; Choi, H. Temperature measurement in friction element welding process with micro thin film thermocouples. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 26, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.; Nassiri, A.; Mears, L.; Choi, H.; Xin, Z. Numerical study of chipping during friction element welding. Manuf. Lett. 2022, 34, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Han, R.B.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhu, M.L.; Liu, L.M. Riveting-welding hybrid bonding of high-strength steel and aluminum alloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2019, 34, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.B.; Wang, H.Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, L.M.; Zhu, M.L. Research on riveting-laser arc welding hybrid joining mechanism of aluminum alloy and high strength steel. J. Mech. Eng. 2020, 56, 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.S.; Dong, Y.C.; Liu, L.M.; Zhu, M.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, C.B. Effect of pulsed laser and laser-arc hybrid on aluminum/steel riveting-welding hybrid bonding technology. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Haghshenas, M.; Gerlich, A.P. Role of welding parameters on interfacial bonding in dissimilar steel/aluminum friction stir welds. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 18, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Shamsolhodaei, A.; Ghatei-Kalashami, A.; Oliveira, J.P.; Zang, C.; Schell, N.; Li, J.; Midawi, A.R.H.; Lopes, J.G.; Yan, J.; et al. Revealing microstructural evolutions and mechanical properties of resistance spot welded NiTi-stainless steel with Ni or Nb interlayer. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 180, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, B.; Kishore, K.; Mishra, V. Investigation of a novel TIG-spot welding vis-à-vis resistance spot welding of dual-phase 590 (DP590) steel: Processing-microstructure-mechanical properties correlation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 296, 127254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.F.; Iwamoto, C.; Satonaka, S. Interfacial microstructure and strength of steel/aluminum alloy joints welded by resistance spot welding with cover plate. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 4186–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.N.; Wang, H.P.; Wang, M.; Carlson, B.E.; Sigler, D.R. Schedule and electrode design for resistance spot weld bonding Al to steels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 265, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Q.; Ma, Y.W.; Li, Y.B.; Lin, Z.Q.; Haselhuhn, A.S.; CarlSon, B.E. Comparison of the resistance spot weldability of AA5754 and AA6022 aluminum to steels. Weld. J. 2020, 99, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seungyeop, B.; Jongho, S.; Lee, H.; Park, S.; Song, K.-H.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.-J.; Chen, C.T.; Kim, D. Robust bonding and microstructure behavior of aluminum/high-strength steel lap joints using resistance element welding process for lightweight vehicles: Experimental and numerical investigation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 833, 142378. [Google Scholar]
- Manladan, S.M.; Zhang, Y.; Ramesh, S.; Cai, Y.; Ao, S.S.; Luo, Z. Resistance element welding of magnesium alloy and austenitic stainless steel in three-sheet configurations. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 274, 116292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Go, G.Y.; Park, J.-W.; Jongho, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, S.; Chen, C.T.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, D. Microstructural and interface geometrical influence on the mechanical fatigue property of aluminum/high-strength steel lap joints using resistance element welding for lightweight vehicles: Experimental and computational investigation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günter, H.; Meschut, G. Joining of ultra-high-strength steels using resistance element welding on conventional resistance spot welding guns. Weld. World 2021, 65, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Ou, L.; Liu, J.W. Preventing nugget shifting in joining of dissimilar steels via resistance element welding: A numerical simulation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 117, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abankar, M.; De Maddis, M.; Razza, V.; Spena, P.R. Resistance Element Welding (REW) of Steels with Non-Ferrous Materials: Potentials, Challenges, and Properties. Metals 2024, 14, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Dong, S.J.; Luo, P. Microstructural and mechanical characterization of steel-DP780/Al-5052 joints formed using resistance element welding with concealed rivet cover. Compos. Adv. Mater. 2022, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Park, M.; Kim, I.S. An Overview of Resistance Element Welding with Focus on Mechanical and Microstructure Joint and Optimization in Automotive Metal Joints. J. Weld. Join. 2023, 41, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bi, Y.B.; Zhang, Y.X.; Su, J.; Luo, Z. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Resistance Element Welded Joints for DP780 Steel and 6061 Aluminum Alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmal, C.; Meschut, G. Process characteristics and influences of production-related disturbances in resistance element welding of hybrid materials with steel cover sheets and polymer core. Weld. World 2020, 64, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meschut, G.; Hahn, O.; Janzen, V.; Olfermann, T. Innovative joining technologies for multi-material structures. Weld. World 2013, 58, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meschut, G.; Schmal, C.; Olfermann, T. Process characteristics and load-bearing capacities of joints welded with elements for the application in multi-material design. Weld. World 2017, 61, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Sun, H.; Shang, S.L.; Banu, M.; Wang, P.C.; Carlson, B.E.; Liu, Z.K.; Li, J.J. Understanding formation mechanisms of intermetallic compounds in dissimilar Al/steel joint processed by resistance spot welding. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 83, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.Q.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Gu, X.Y.; Li, H.M. Microstructures and mechanical properties of resistance spot welded joints of 16Mn steel and 6063-T6 aluminum alloy with different electrodes. Mater. Des. 2022, 109, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funabiki, Y.; Iyota, M.; Shobu, T.; Matsuda, T.; Yumoto, H.; Koyama, T.; Yamazaki, H.; Senba, Y.; Ohashi, H.; Inoue, I. Convection and joint characteristics in aluminum alloy melting zone during resistance spot welding of dissimilar Fe-Al material in external magnetic field. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 115, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Materials | C | Cr | Si | Mn | P | Fe | S | Mg | Al | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP780 | 0.10 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 2.10 | — | Bal. | — | — | 0.04 | — |
| 6061-T6 | — | 0.23 | 0.65 | 0.12 | — | 0.17 | — | 1.07 | Bal. | 0.27 |
| Q235 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.48 | 0.03 | Bal. | 0.02 | — | — | — |
| Materials | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DP780 | 826.71 | 838.32 | 23.88 |
| 6061-T6 | 280.00 | 311.00 | 12.50 |
| Q235 | 331.00 | 458.00 | 30.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, Q.; Luo, S.; Luo, Z. Microstructure and Properties of Resistance Element Welded Joints of DP780 Steel and 6061 Aluminum Alloy. Metals 2025, 15, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030283
Wu Q, Yang Y, Li Y, Guo Q, Luo S, Luo Z. Microstructure and Properties of Resistance Element Welded Joints of DP780 Steel and 6061 Aluminum Alloy. Metals. 2025; 15(3):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030283
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Qinglong, Yue Yang, Yingzhe Li, Qing Guo, Shuyue Luo, and Zhen Luo. 2025. "Microstructure and Properties of Resistance Element Welded Joints of DP780 Steel and 6061 Aluminum Alloy" Metals 15, no. 3: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030283
APA StyleWu, Q., Yang, Y., Li, Y., Guo, Q., Luo, S., & Luo, Z. (2025). Microstructure and Properties of Resistance Element Welded Joints of DP780 Steel and 6061 Aluminum Alloy. Metals, 15(3), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030283





