Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing Treatment on Refractory High-Entropy Alloy WTaMoNbV Produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process
Abstract
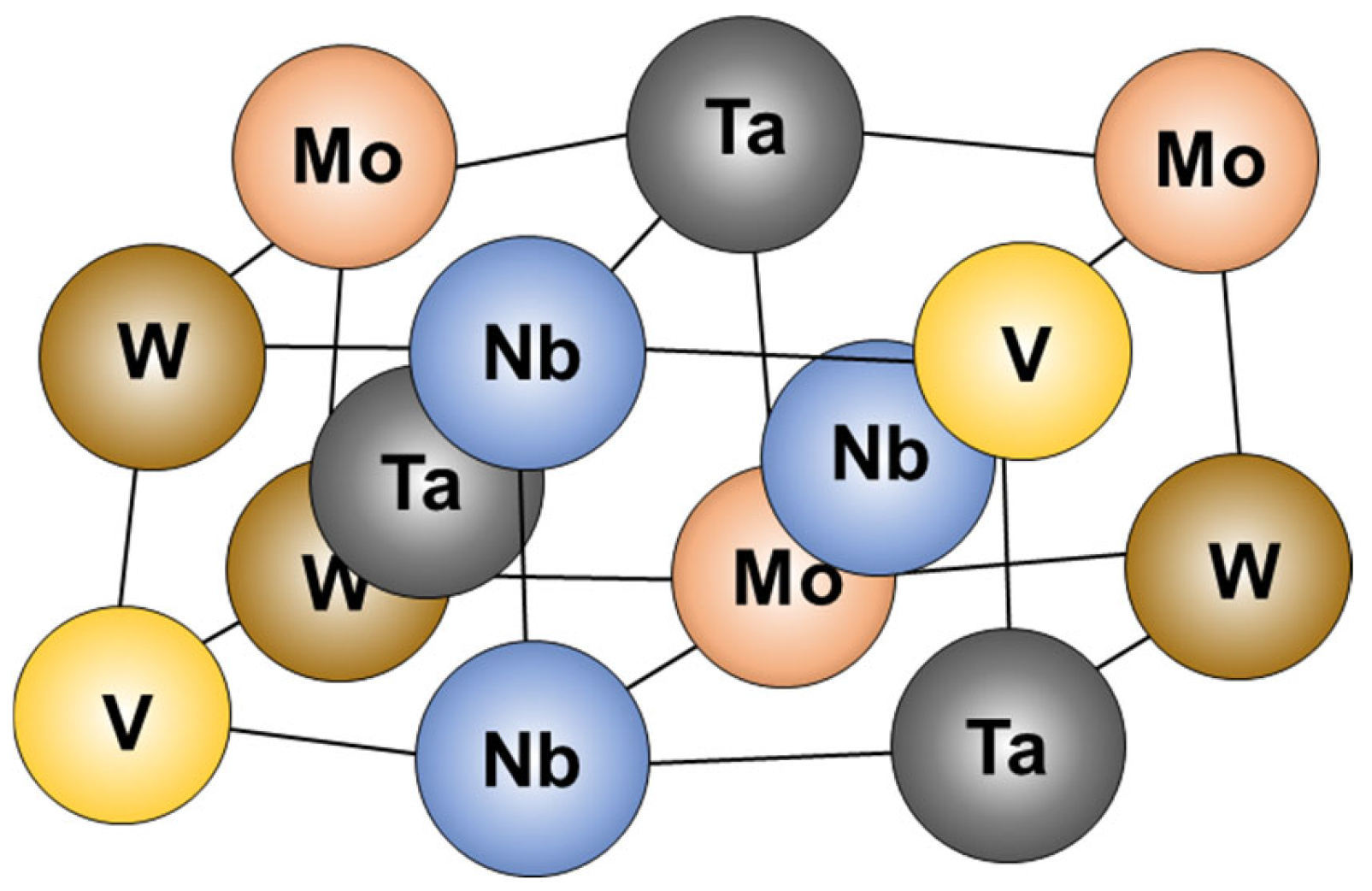
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production of HEA WTaMoNbVby LPBF and HIP Treatment
2.2. Density, Surface Roughness, and Microstructure Characterization
2.3. Mechanical Properties and Environmental Performance
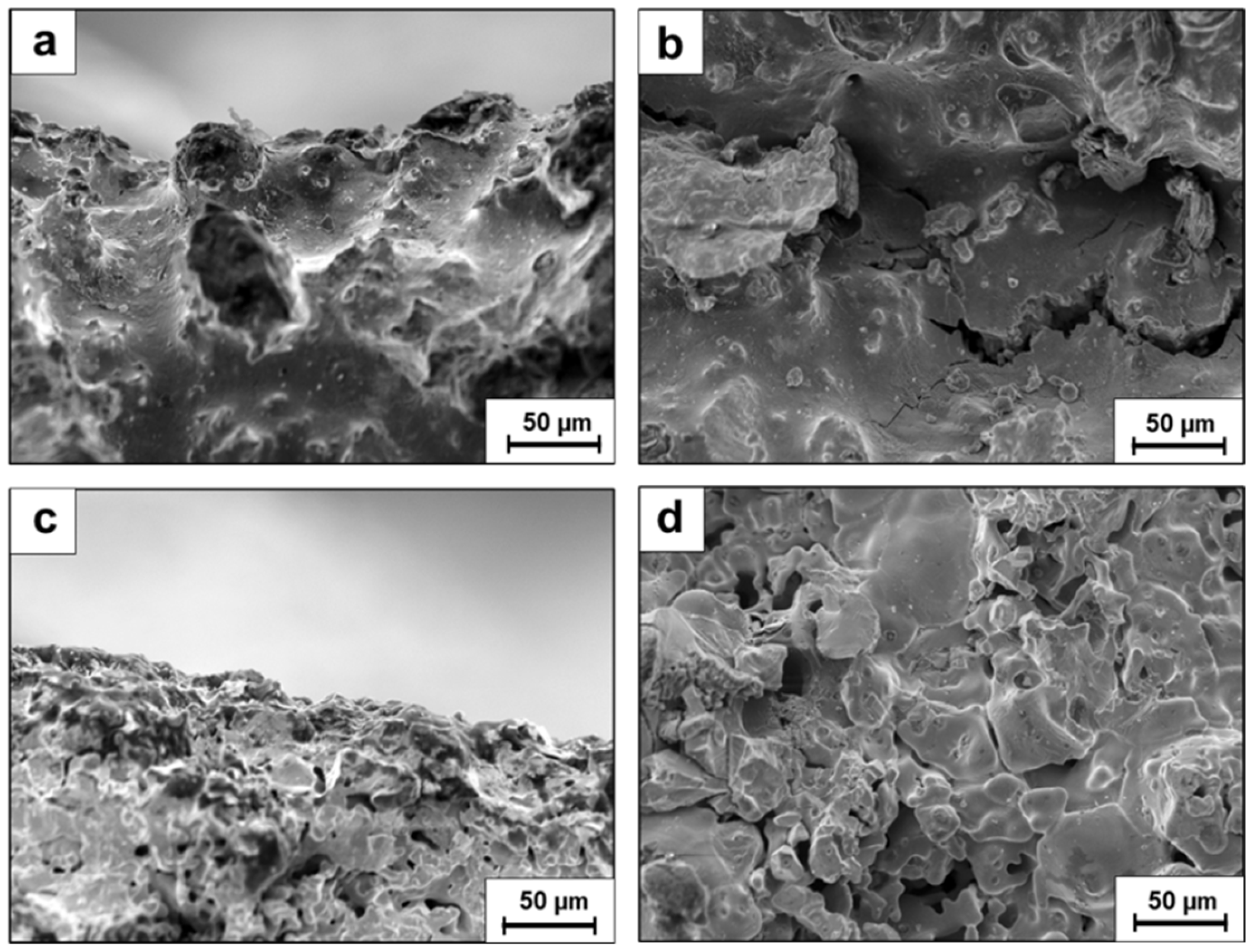
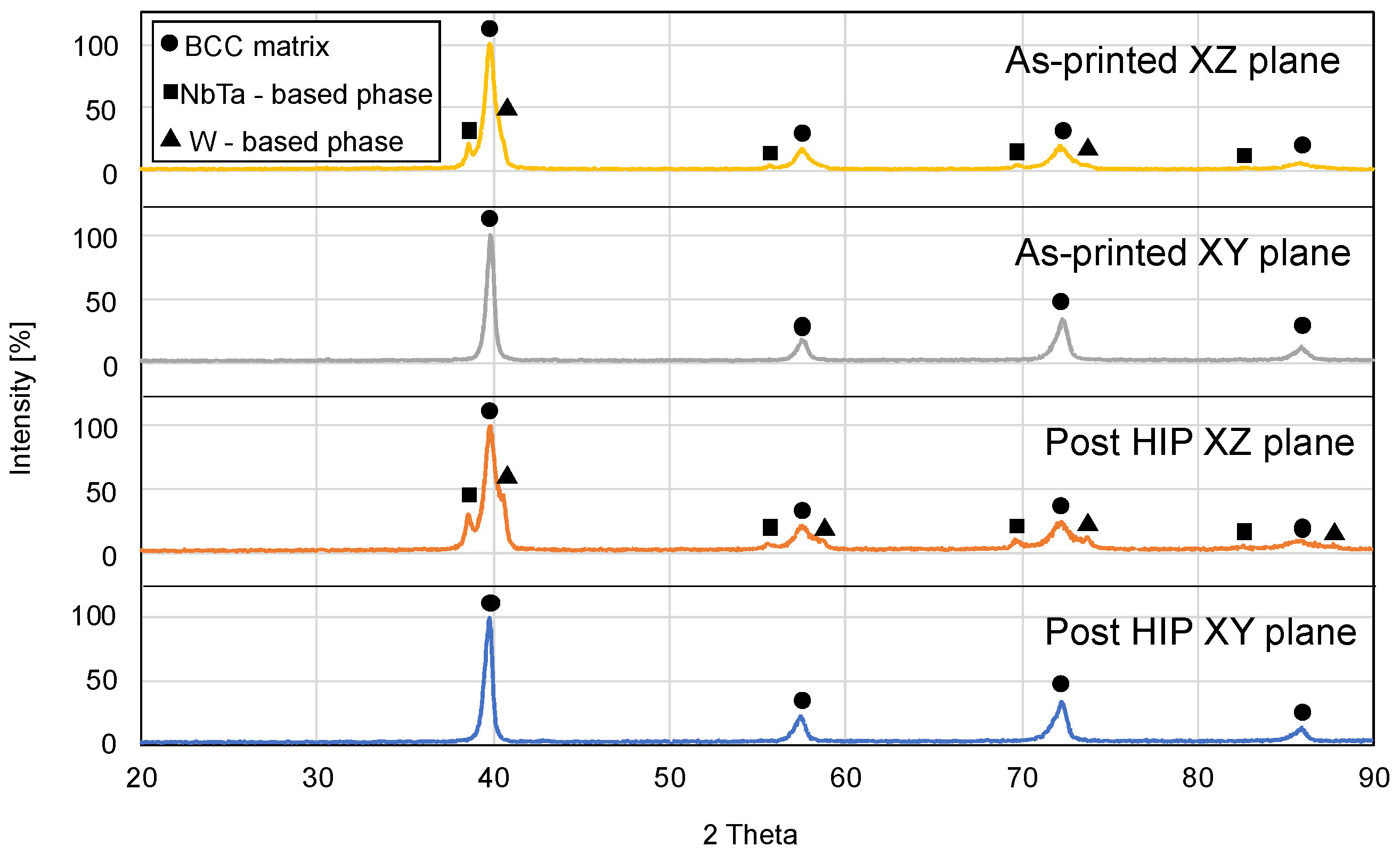
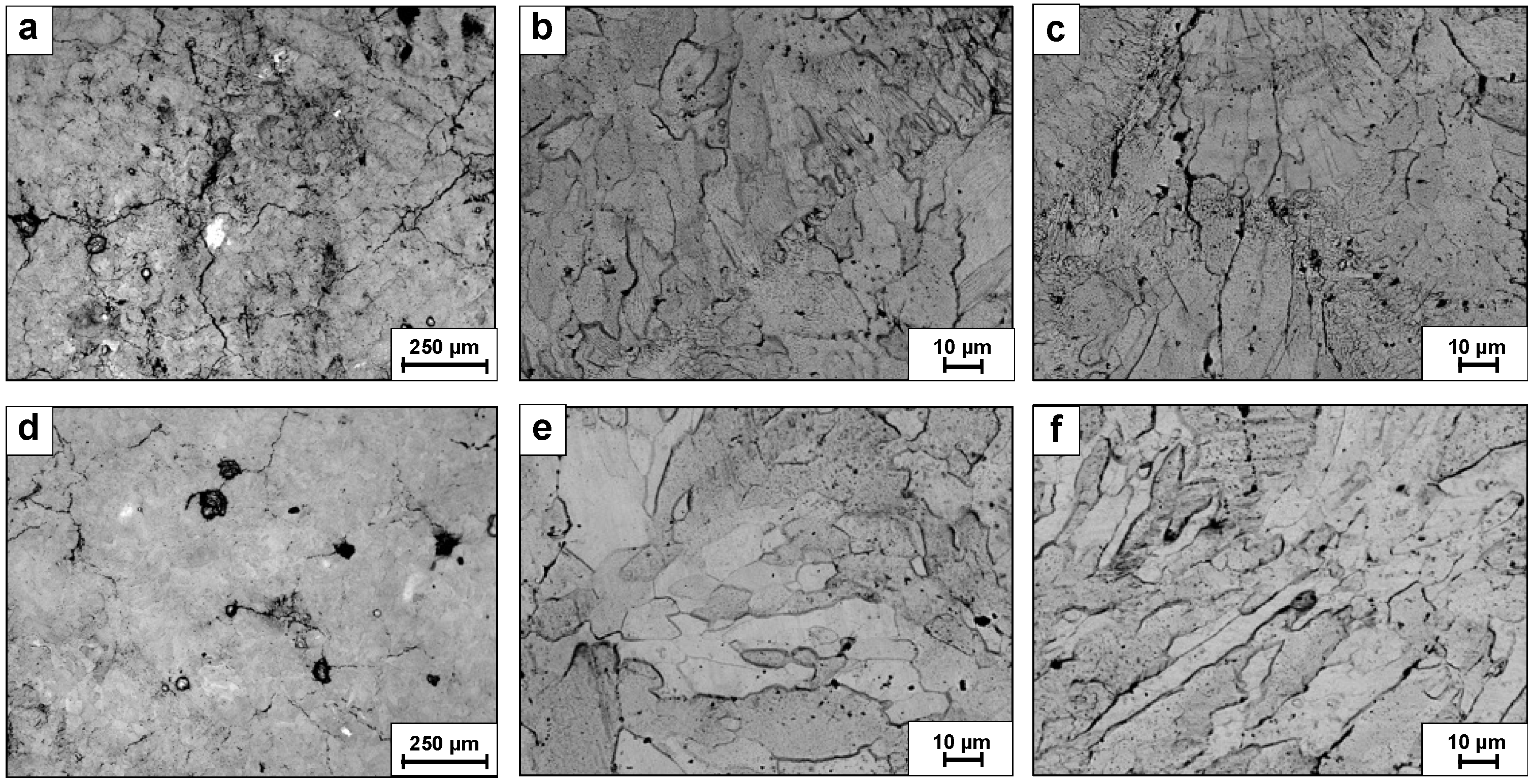
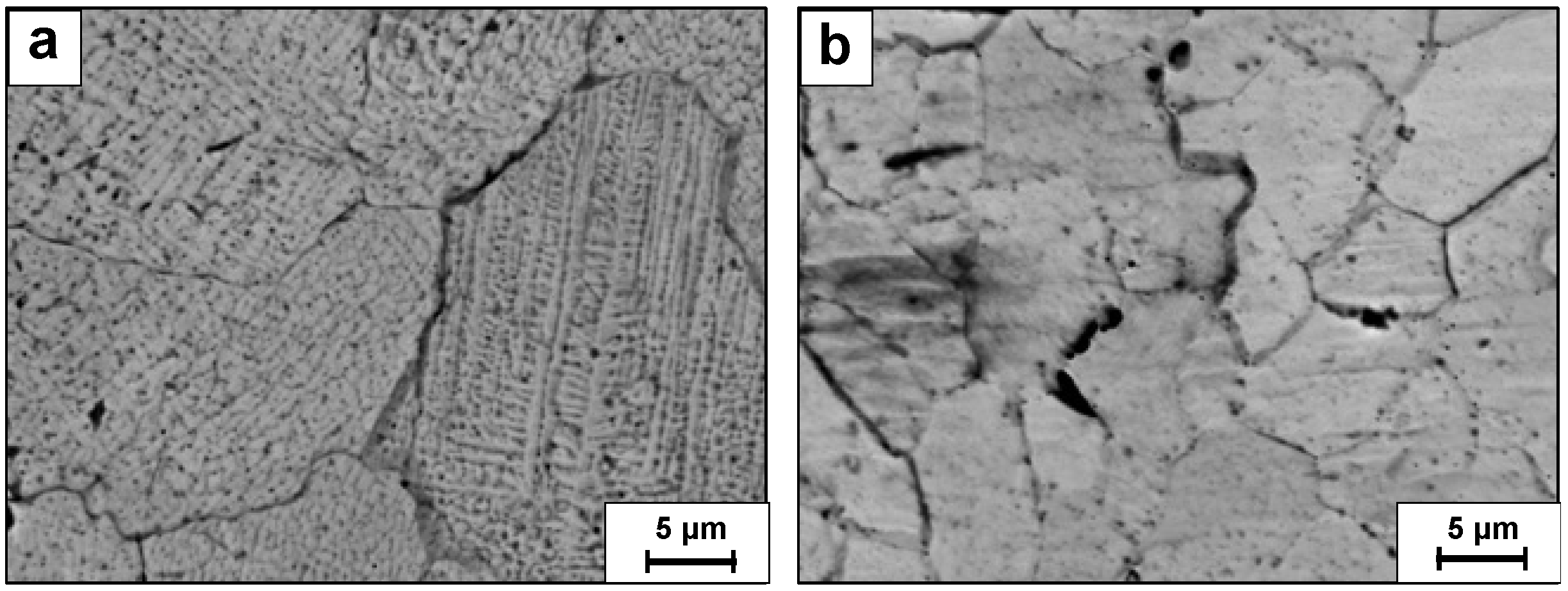
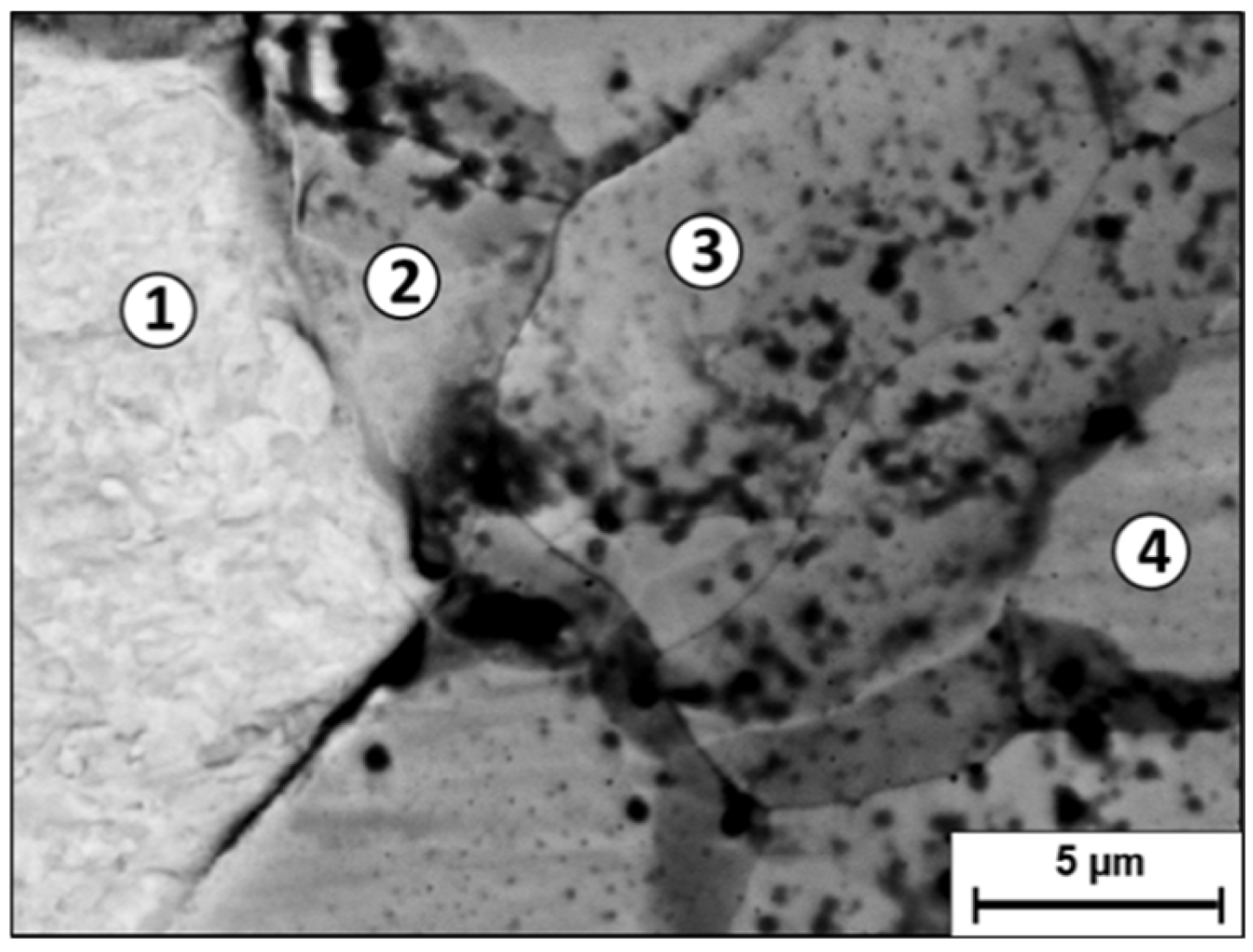
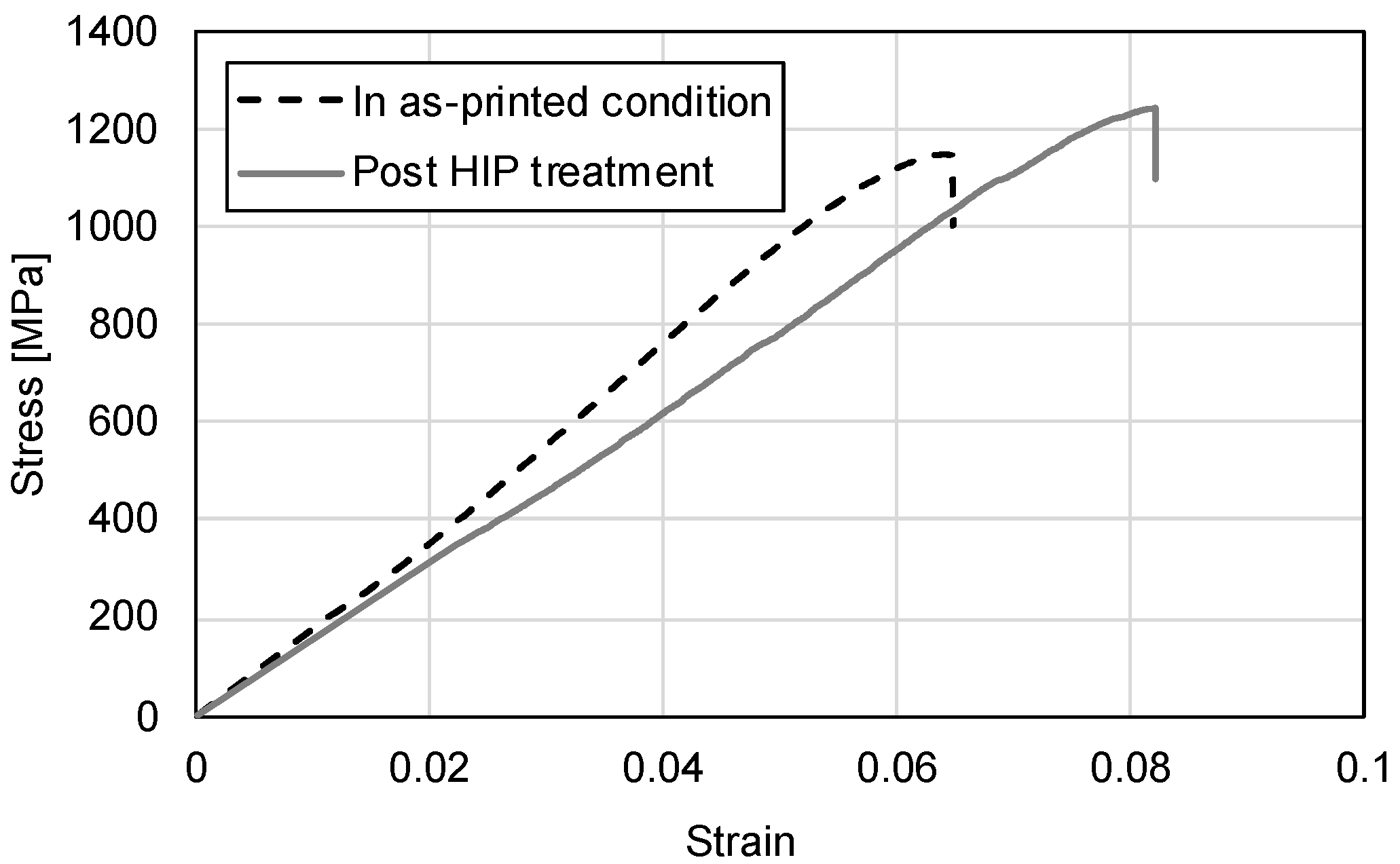
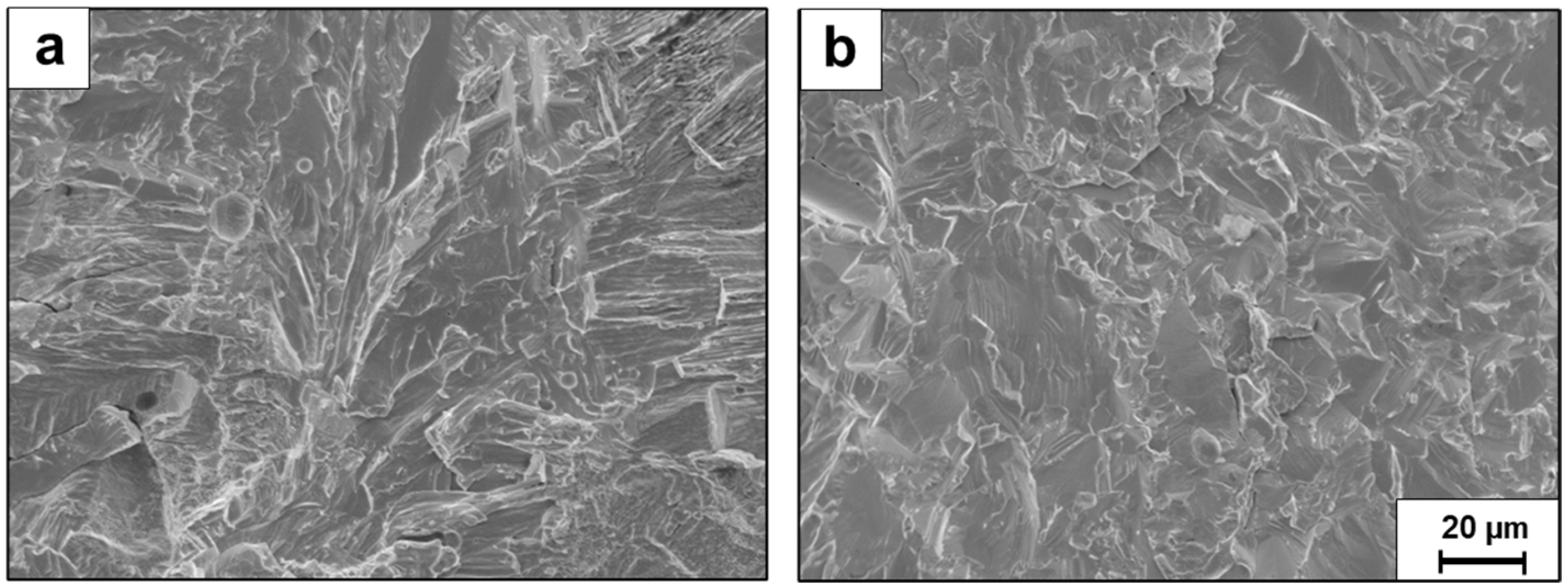
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (a)
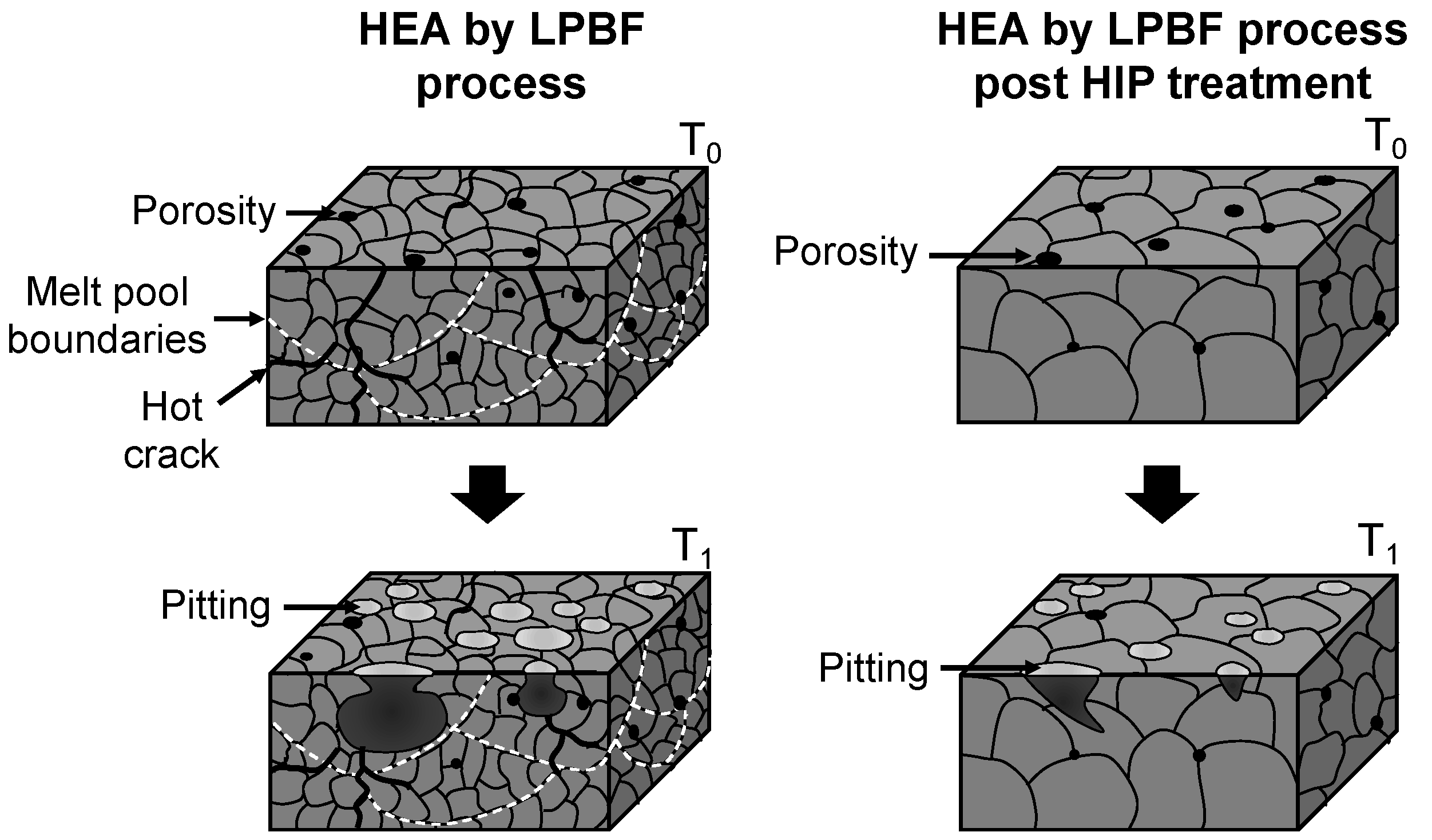
- The HIP treatment clearly improved the structural integrity of LPBF-produced WTaMoNbV HEA, increasing density from 11.27 to 11.38 g/cm3 and enhancing surface quality from grade N11 to N10. This treatment effectively eliminated sub-grain boundaries and significantly reduced internal cracking while maintaining the fundamental BCC structure.
- (b)
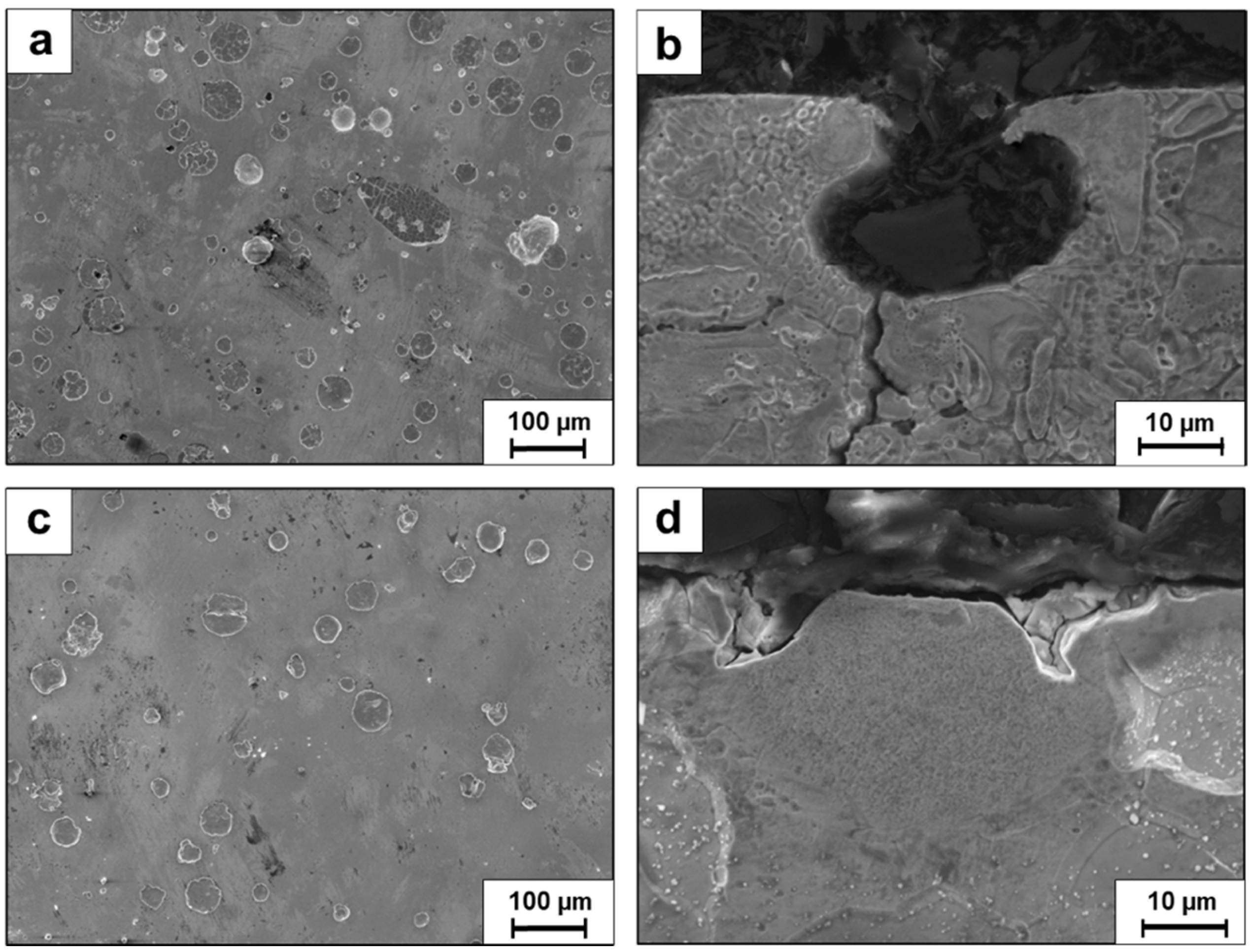
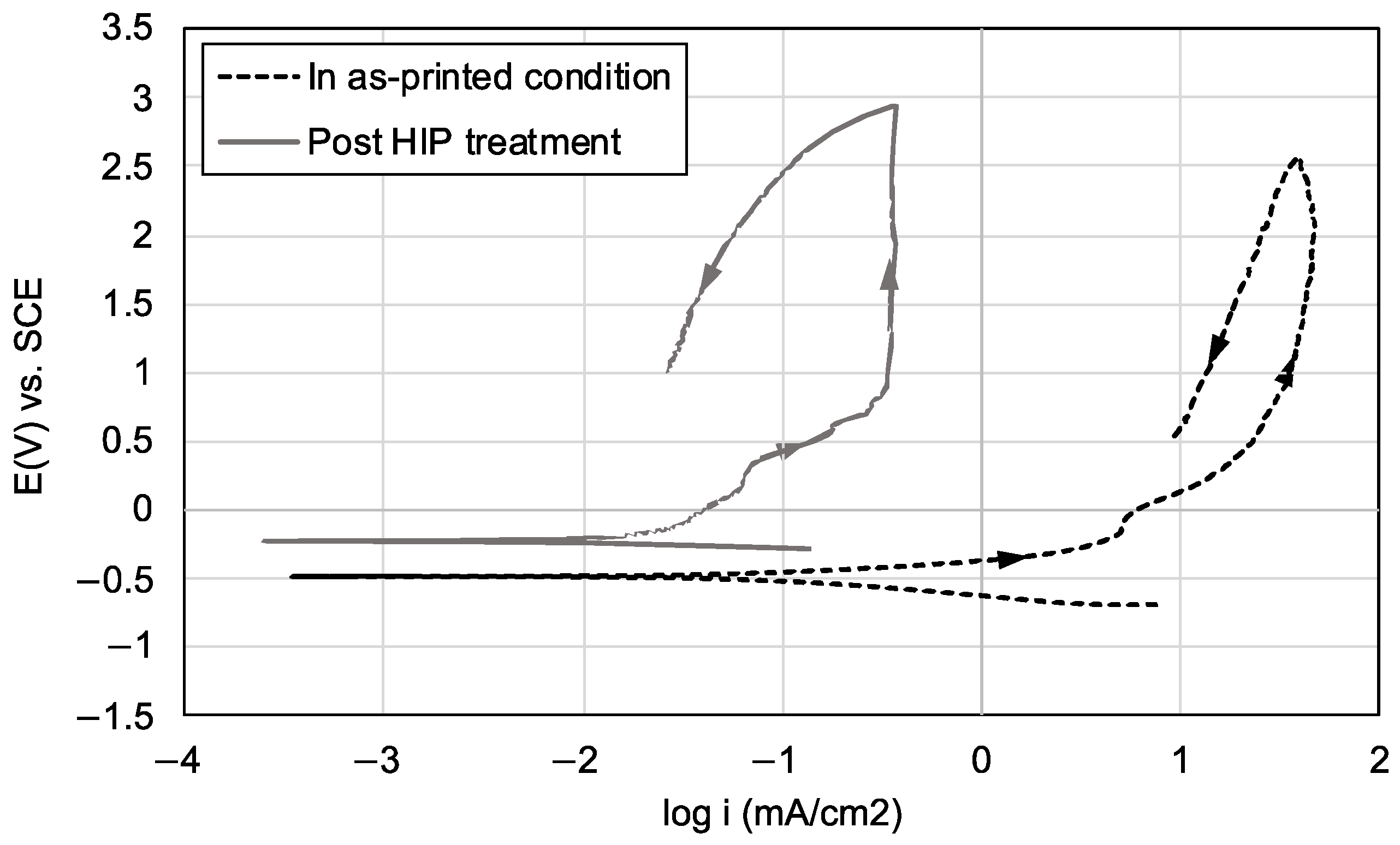
- Mechanical properties showed notable enhancement post-HIP treatment, with an 11.5% increase in ultimate compression strength (1220 vs. 1094 MPa) and 29% improvement in ductility (8.0% vs. 6.2% strain). Environmental performance also improved significantly, demonstrated by a 71.7% reduction in pitting density (from 34,155 to 9677 pits/cm2).
- (c)
- The above improvements can indicate that HIP treatment can be related as an effective post-processing method for refractory HEAs produced by LPBF process. Nevertheless, further optimization of both HIP and LPBF parameters is essential to obtain additional enhancements.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poulia, A.; Georgatis, E.; Lekatou, A.; Karantzalis, A.E. Microstructure and wear behavior of a refractory high entropy alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2016, 57, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Miracle, D.B.; Chuang, C.P.; Liaw, P.K. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralba, J.M.; Alvaredo, P.; García-Junceda, A. High-entropy alloys fabricated via powder metallurgy. A critical review. Powder Metall. 2019, 62, 84–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, T.; Chen, M.; Shiratori, H.; Kuwabara, K.; Yamanaka, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Chiba, A.; Watanabe, S. Mechanical and corrosion properties of CoCrFeNiTi-based high-entropy alloy additive manufactured using selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Goh, M.; Zhu, Z.; Lee, X.; Nai, M.L.S.; Wei, J. On the machining of selective laser melting CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2018, 153, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Gao, P.; Yu, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, X. Selective laser melting of an equiatomic AlCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy: Processability, non-equilibrium microstructure and mechanical behavior. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 771, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, T.; Shirizly, A.; Aghion, E. Additive Manufacturing Technologies of High Entropy Alloys (HEA): Review and Prospects. Materials 2023, 16, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.D.; Li, R.D.; Yuan, T.C.; Zhu, S.Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, M.B.; Huang, L. Microstructures and properties of an equimolar AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy printed by selective laser melting. Intermetallics 2019, 104, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrouzet, F.; Hachet, D.; Soulas, R.; Navone, C.; Godet, S.; Gorsse, S. Selective laser melting of Al0. 3CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy: Printability, microstructure, and mechanical properties. JOM 2019, 71, 3443–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Q.; Guo, T.; Jarvis, T.; Wu, X.; Hodgson, P.; Fabijanic, D. Direct laser deposition cladding of AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys on a high-temperature stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 332, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, L.; Karnati, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liou, F. Fabrication and characterization of Al x CoFeNiCu1− x high entropy alloys by laser metal deposition. Coatings 2017, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzief, D.; Evirgen, A.; Pedersen, M.; Hecht, U. Laser powder bed fusion of an Al-Cr-Fe-Ni high-entropy alloy produced by blending of prealloyed and elemental powder: Process parameters, microstructures and mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 918, 165658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; Qu, N.; Liao, M.; Lai, Z.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, J. Effect of annealing on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCrFe2Ni2 medium entropy alloy fabricated by laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 839, 142868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.F. AlCoCuFeNi high-entropy alloy with tailored microstructure and outstanding compressive properties fabricated via selective laser melting with heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 743, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xu, L.; Jing, H.; Han, Y.; Zhao, L.; Minami, F. Effects of annealing on the structure and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNi high-entropy alloy fabricated via selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 32, 101058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Dai, T.; Lu, T.; Ni, X.; Dai, J.; Li, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and Ti8Nb23Mo23Ta23W23 high entropy alloys prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 738, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.D.; Luan, H.W.; Liu, X.; Chen, N.; Li, X.Y.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K.F. Microstructures and mechanical properties of TixNbMoTaW refractory high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunce, I.; Polanski, M.; Bystrzycki, J. Microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of a TiZrNbMoV high entropy alloy synthesized using Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 9904–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbelstein, H.; Thiele, M.; Gurevich, E.L.; George, E.P.; Ostendorf, A. Direct Metal Deposition of Refractory High Entropy Alloy MoNbTaW. Phys. Procedia 2016, 83, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorehead, M.; Bertsch, K.; Niezgoda, M.; Parkin, C.; Elbakhshwan, M.; Sridharan, K.; Zhang, C.; Thoma, D.; Couet, A. High-throughput synthesis of Mo-Nb-Ta-W high-entropy alloys via additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 2020, 187, 108358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melia, M.A.; Whetten, S.R.; Puckett, R.; Jones, M.; Heiden, M.J.; Argibay, N.; Kustas, A.B. High-throughput additive manufacturing and characterization of refractory high entropy alloys. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 19, 100560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Liu, H.; Jia, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L. Cracking suppression in selective electron beam melted WMoTaNbC refractory high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 948, 169787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Bartels, D.; Schmidt, M. In-situ alloy formation of a WMoTaNbV refractory metal high entropy alloy by laser powder bed fusion (PBF-LB/M). Materials 2021, 14, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, D. Manufacturing and analysis of high-performance refractory high-entropy alloy via selective laser melting (SLM). Materials 2019, 12, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron, T.; Leon, A.; Popov, V.; Strokin, E.; Eliezer, D.; Shirizly, A.; Aghion, E. Synthesis of Refractory High-Entropy Alloy WTaMoNbV by Powder Bed Fusion Process Using Mixed Elemental Alloying Powder. Materials 2022, 15, 4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, J.; Kollo, L.; Rahmani, R.; Ma, P.; Jia, Y.D.; Prashanth, K.G. Selective laser melting of in-situ CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy: Effect of remelting. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 84, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Jing, H.; Qin, G.; Pang, H.; Minami, F. A Si-containing FeCoCrNi high-entropy alloy with high strength and ductility synthesized in situ via selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, C.; Tang, F.; Wilms, M.B.; Weisheit, A.; Hallstedt, B. Combining thermodynamic modeling and 3D printing of elemental powder blends for high-throughput investigation of high-entropy alloys—Towards rapid alloy screening and design. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 688, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, B.Y.; Xu, H.H.; Chen, H.L.; Pan, Z. Thermodynamic assessment of the Mo–Nb–Ta system. Calphad 2004, 28, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, C.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Valsakumar, M.C.; van de Walle, A. First-principles calculation of phase equilibrium of V-Nb, V-Ta, and Nb-Ta alloys. Phys. Rev. B—Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2012, 85, 054202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, A.; Levy, G.K.; Ron, T.; Shirizly, A.; Aghion, E. The effect of hot isostatic pressure on the corrosion performance of Ti-6Al-4 V produced by an electron-beam melting additive manufacturing process. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 33, 101039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolev, O.; Ron, T.; Aghion, E.; Shirizly, A. Effect of HIP Defects on the Mechanical Properties of Additive Manufactured Ti6Al4V Alloy. Metals 2022, 12, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Xing, L.; Yu, C.; Liu, H.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Shen, Z. The effect of hot isostatic pressing on thermal conductivity of additively manufactured pure tungsten. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2020, 87, 105135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Senkov, O.N.; Parish, C.M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Santodonato, L.J.; Wang, G.; Zhao, G.; Yang, F.; Liaw, P.K. Tensile ductility of an AlCoCrFeNi multi-phase high-entropy alloy through hot isostatic pressing (HIP) and homogenization. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 647, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Hodgson, P.; Jarvis, T.; Wu, X.; Stanford, N.; Fabijanic, D.M. Effect of hot isostatic pressing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of additive manufactured AlxCoCrFeNi high entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 733, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, G.; Yang, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, B.; Gou, G. Tuning the mechanical properties of powder bed fusion printed CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloys by annealing and hot isostatic pressing. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 946, 169376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Ai, Z.; He, J.; Yang, B.; Gou, G.; Han, L. Effect of Annealing and Hot Isostatic Pressing on the Structure and Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance of Powder-Bed Fusion-Printed CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2023, 13, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vock, S.; Klöden, B.; Kirchner, A.; Weißgärber, T.; Kieback, B. Powders for powder bed fusion: A review. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 4, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, A.T.; Kriewall, C.S.; Leu, M.C.; Newkirk, J.W. Powder characterisation techniques and effects of powder characteristics on part properties in powder-bed fusion processes. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2017, 12, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, M.; Lee, K. 1.45 GPa ultrastrong cryogenic strength with superior impact toughness in the in-situ nano oxide reinforced CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy matrix nanocomposite manufactured by laser powder bed fusion. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 97, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laleh, M.; Sadeghi, E.; Revilla, R.I.; Chao, Q.; Haghdadi, N.; Hughes, A.E.; Xu, W.; De Graeve, I.; Qian, M.; Gibson, I.; et al. Heat treatment for metal additive manufacturing. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 133, 101051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 21920-2:2021; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile. Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Kaya, A.A.; Uzan, P.; Eliezer, D.; Aghion, E. Electron microscopical investigation of as cast AZ91D alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2000, 16, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Xu, J.; Buchanan, R.C. Surface roughness: A review of its measurement at micro-/nano-scale. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2018, 3, 20170057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itzhak, D.; Aghion, E. An anodic behaviour study of an analogical sintered system of austenitic stainless steel in H2SO4 solution. Corros. Sci. 1984, 24, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, M.; Garciandia, F.; Sainz, S.; Jorge-Badiola, D.; Guraya, T.; Sebastian, M.S. The limit of hot isostatic pressing for healing cracks present in an additively manufactured nickel superalloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 300, 117398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocchi, J.; Biffi, C.A.; Elnemr, M.; Shipley, J.; Tuissi, A.; Casati, R. Hot isostatic pressing and heat treatments of LPBFed CoCuFeMnNiTi0. 13 high-entropy alloy: Microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 9127–9138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ji, H.; Li, S.; Jin, W.; Lei, J. Effect of hot isostatic pressing on the mechanical and corrosive properties of Ti–Ni alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 4595–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
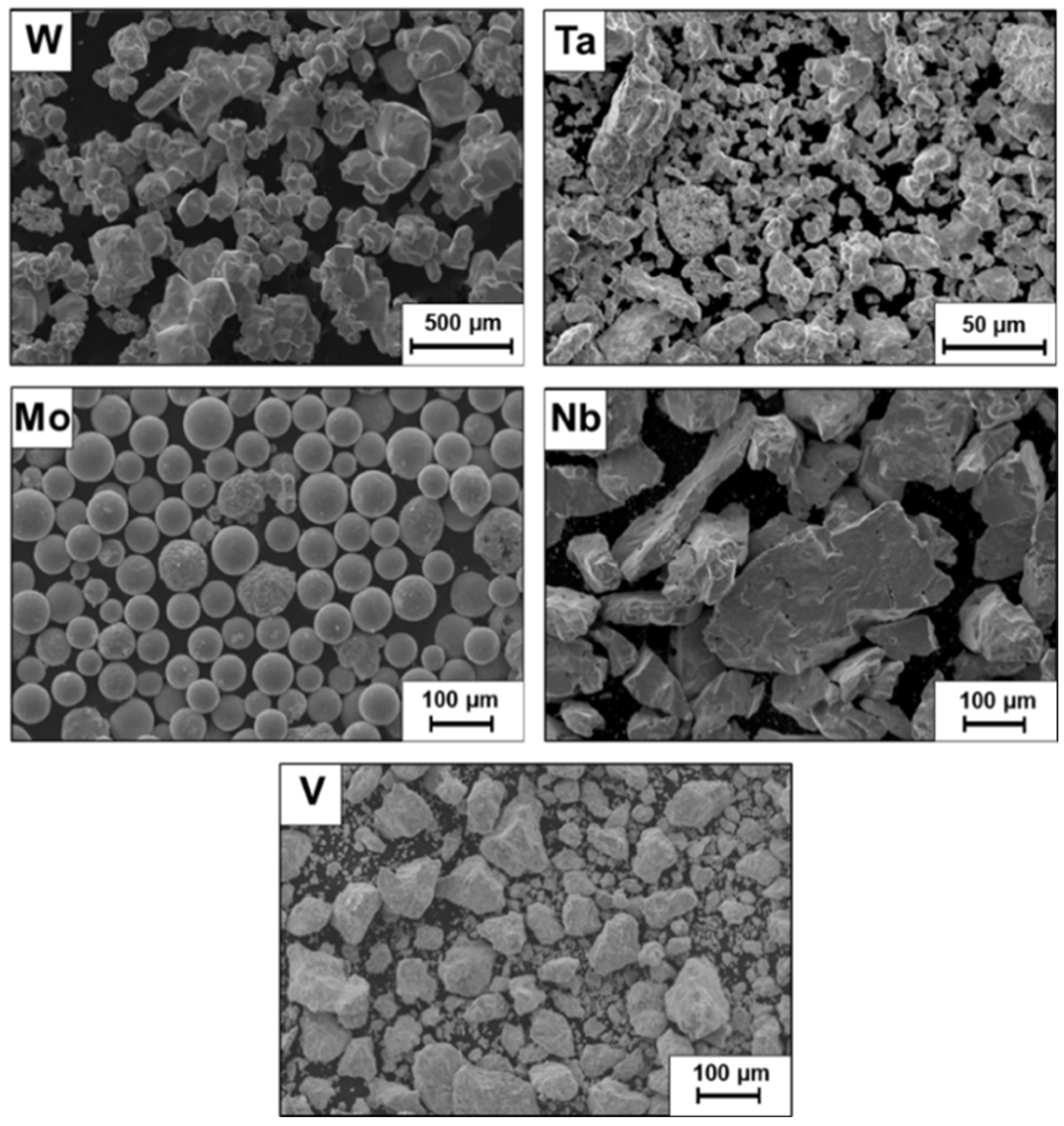



| Alloy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTaMoNbV | 3.15 | −4.642 | 13.38 | 2833 | 8.54 |
| C | N | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | Ti | V | Cr | Fe | Ni | Cu | Nb | Mo | Ta | W | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tungsten | 30 | - | 200 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 7 | - | - | 5 | 28 | - | 1 | - | 10 | - | Bal. |
| Tantalum | 30 | - | - | - | - | 17 | 10 | - | - | 14 | 18 | - | - | - | Bal. | 12 | |
| Molybdenum | 35 | - | 500 | - | 2 | 3 | 9 | - | - | 3 | 38 | 16 | 3 | - | Bal. | - | 80 |
| Niobium | 127 | 185 | 1147 | - | - | 5 | 20 | 3 | - | 6 | 40 | 6 | 2 | Bal. | 2 | 17 | 12 |
| Vanadium | 50 | 20 | 180 | - | - | 100 | 40 | - | Bal. | 120 | 260 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Experimental Parameters | Units |
|---|---|
| Laser power | 244 w |
| Scanning speed | 300 [mm/s] |
| Hatch spacing | 0.1 [mm] |
| Layer thickness | 0.03 [mm] |
| Energy density | 162.7 [J/mm3] |
| Density | ||
|---|---|---|
| In as-printed condition | 15.8 ± 1.7 | 11.27 ± 0.18 |
| Post HIP treatment | 11.7 ± 0.8 | 11.38 ± 0.20 |
| W | Ta | Mo | Nb | V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In as-printed condition | 14.6 ± 3.9 | 24.1 ± 0.7 | 23.1 ± 0.7 | 22.9 ± 2.5 | 15.3 ± 1.2 |
| Post HIP treatment | 14.3 ± 7.5 | 21.6 ± 3.7 | 21.6 ± 3.5 | 25.7 ± 1.5 | 16.8 ± 1.1 |
| W | Ta | Mo | Nb | V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | 99.15 ± 0.72 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0.85 ± 0.13 | 0 ± 0 |
| Point 2 | 54.93 ± 0.92 | 10.05 ± 1.74 | 7.13 ± 0.43 | 15.29 ± 0.45 | 12.6 ± 0.24 |
| Point 3 | 24.23 ± 0.39 | 16.67 ± 3.89 | 16.67 ± 0.55 | 26.05 ± 0.56 | 16.38 ± 0.29 |
| Point 4 | 23.65 ± 0.38 | 17.94 ± 3.80 | 18.11 ± 0.54 | 25.72 ± 0.54 | 14.59 ± 0.28 |
| UCS [MPa] | E [GPa] | Strain to Failure [%] | Plastic Strain [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In as-printed condition | 1094 ± 52 | 21.1 ± 1.7 | 6.2 ± 0.8 | 0.97 ± 0.7 |
| Post HIP treatment | 1220 ± 140 | 17.2 ± 2.1 | 8.0 ± 0.9 | 0.74 ± 0.5 |
| Ecorr [V] | icorr [µA] | Corrosion Rate [mm/yr] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| In as-printed condition | −0.48 ± 0.01 | 104 ± 27 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Post HIP treatment | −0.35 ± 0.1 | 18.2 ± 16 | 0.004 ± 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ron, T.; Leon, A.; Bassis, M.; Chen, Z.; Shirizly, A.; Aghion, E. Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing Treatment on Refractory High-Entropy Alloy WTaMoNbV Produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process. Metals 2025, 15, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030243
Ron T, Leon A, Bassis M, Chen Z, Shirizly A, Aghion E. Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing Treatment on Refractory High-Entropy Alloy WTaMoNbV Produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process. Metals. 2025; 15(3):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030243
Chicago/Turabian StyleRon, Tomer, Avi Leon, Maxim Bassis, Zhan Chen, Amnon Shirizly, and Eli Aghion. 2025. "Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing Treatment on Refractory High-Entropy Alloy WTaMoNbV Produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process" Metals 15, no. 3: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030243
APA StyleRon, T., Leon, A., Bassis, M., Chen, Z., Shirizly, A., & Aghion, E. (2025). Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing Treatment on Refractory High-Entropy Alloy WTaMoNbV Produced by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process. Metals, 15(3), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15030243








