High-Entropy Alloys: Innovative Materials with Unique Properties for Hydrogen Storage and Technologies for Their Production
Abstract
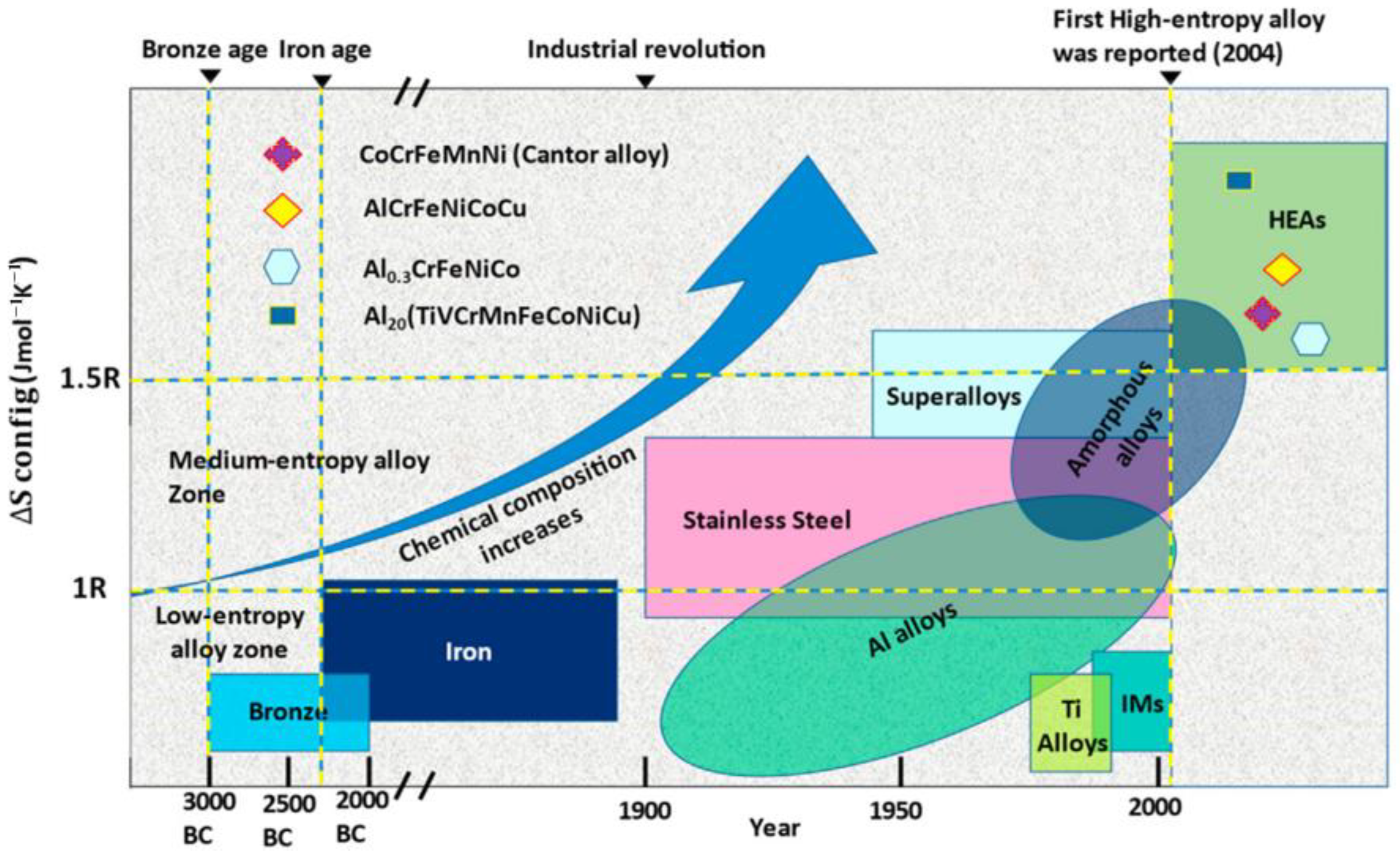
1. Introduction
2. Relevance of Research on the Properties of HEAs for Hydrogen Storage
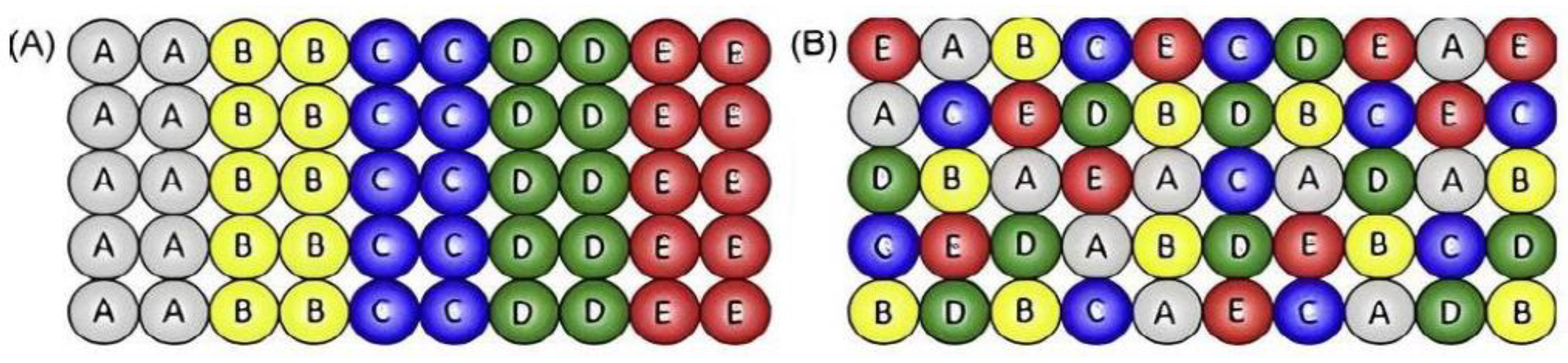
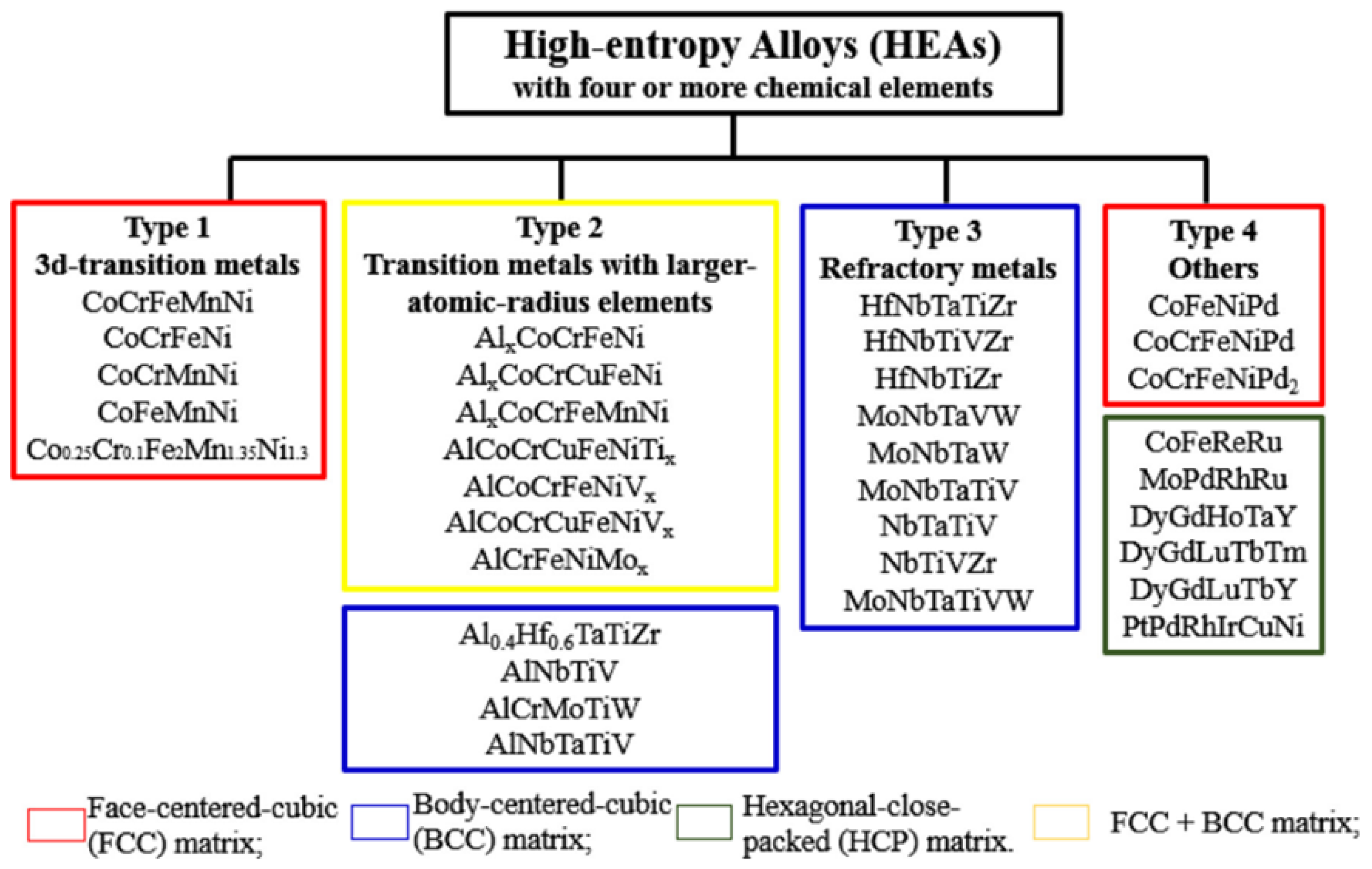
3. Structural Features and Properties of HEAs
- -
- Enthalpy of mixing [36]:where ci and cj are the content (at. %) of the i-th and j-th elements in the alloy, respectively, and is a concentration-dependent parameter characterizing the interaction between the elements in solid solution.
- -
- The average difference in atomic radii:where ci is the content (at.%) of the i-th element in the alloy, ri is the atomic radius of the i-th element in the alloy, and is the average atomic radius of the alloy.
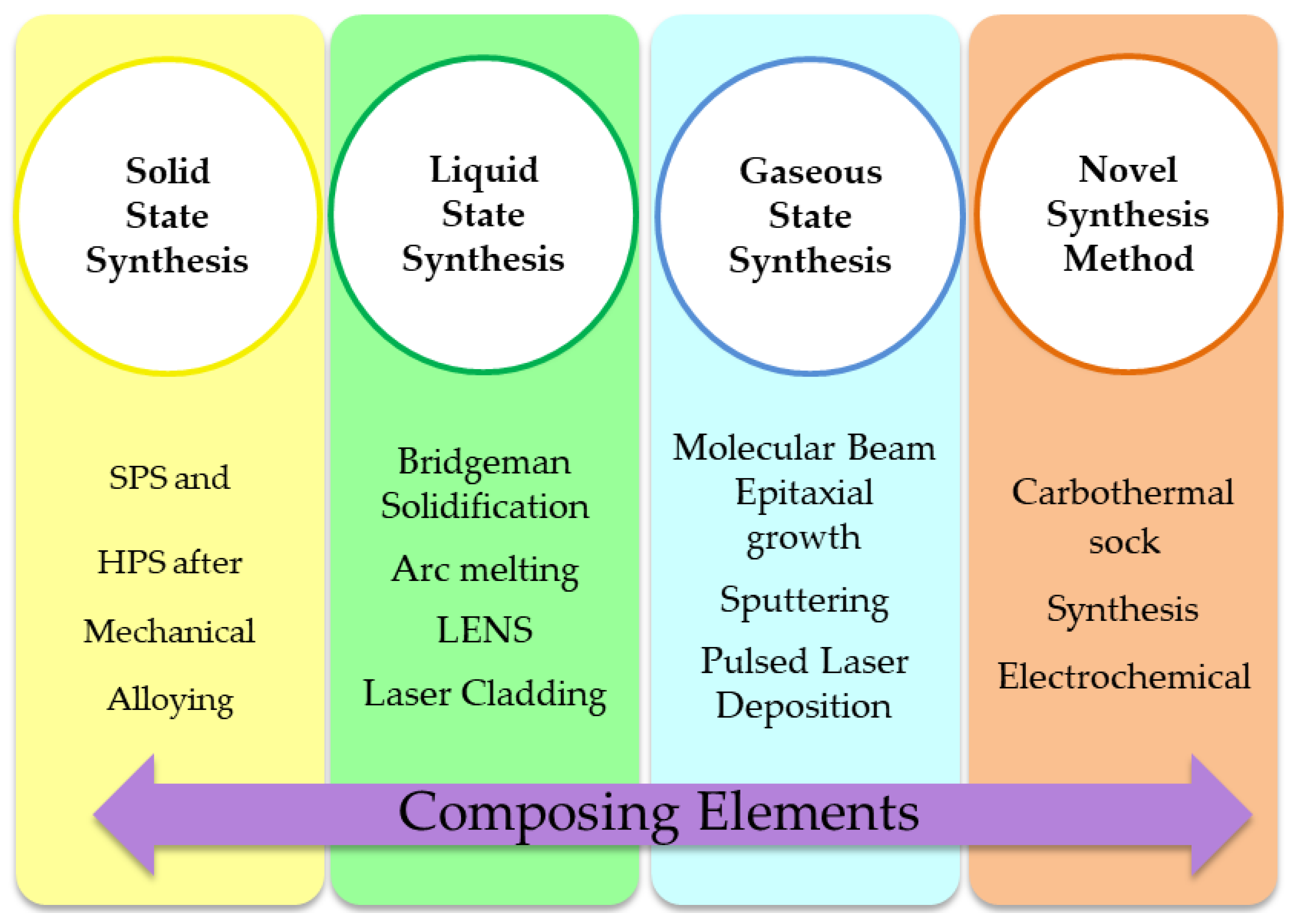
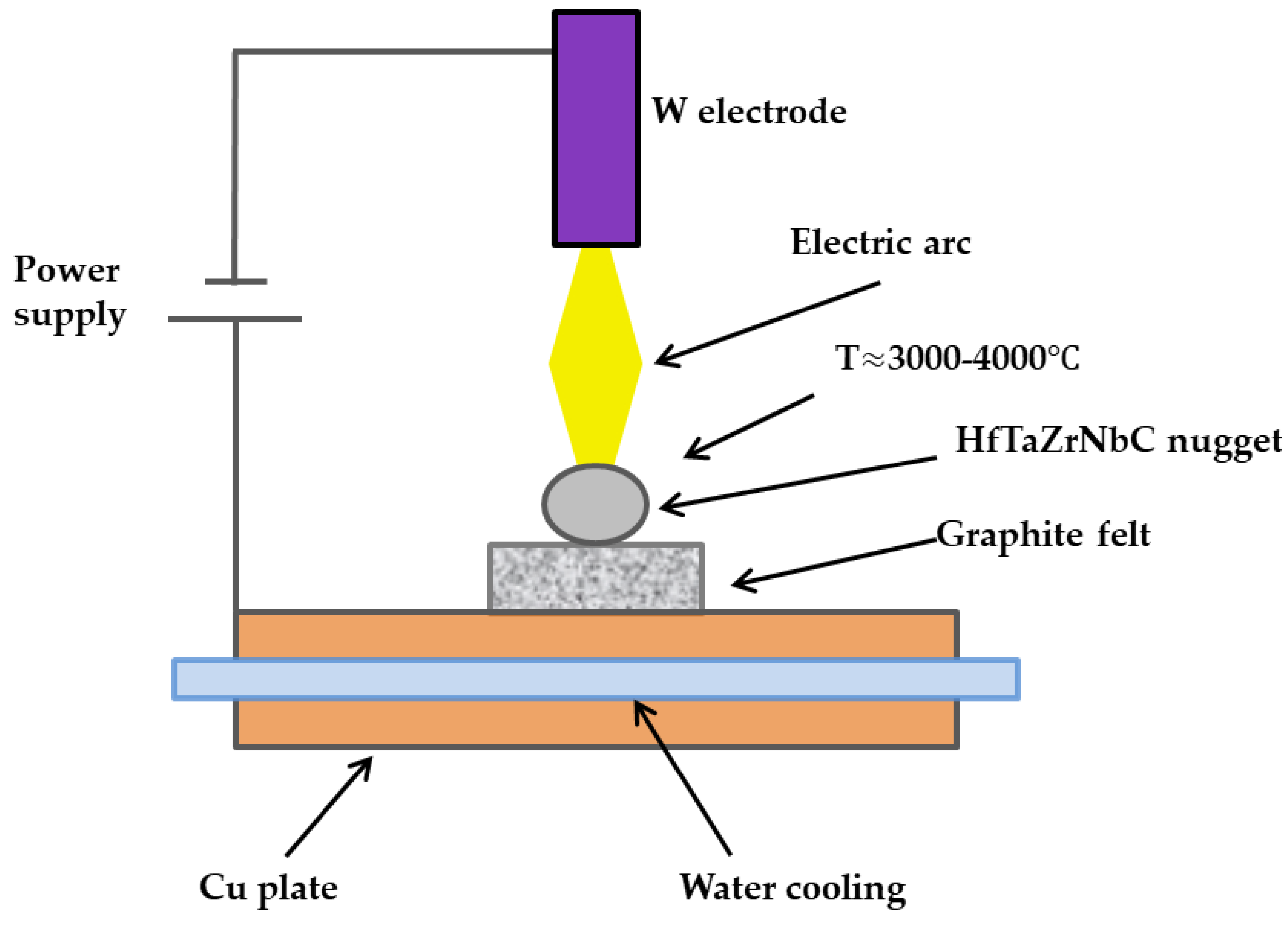
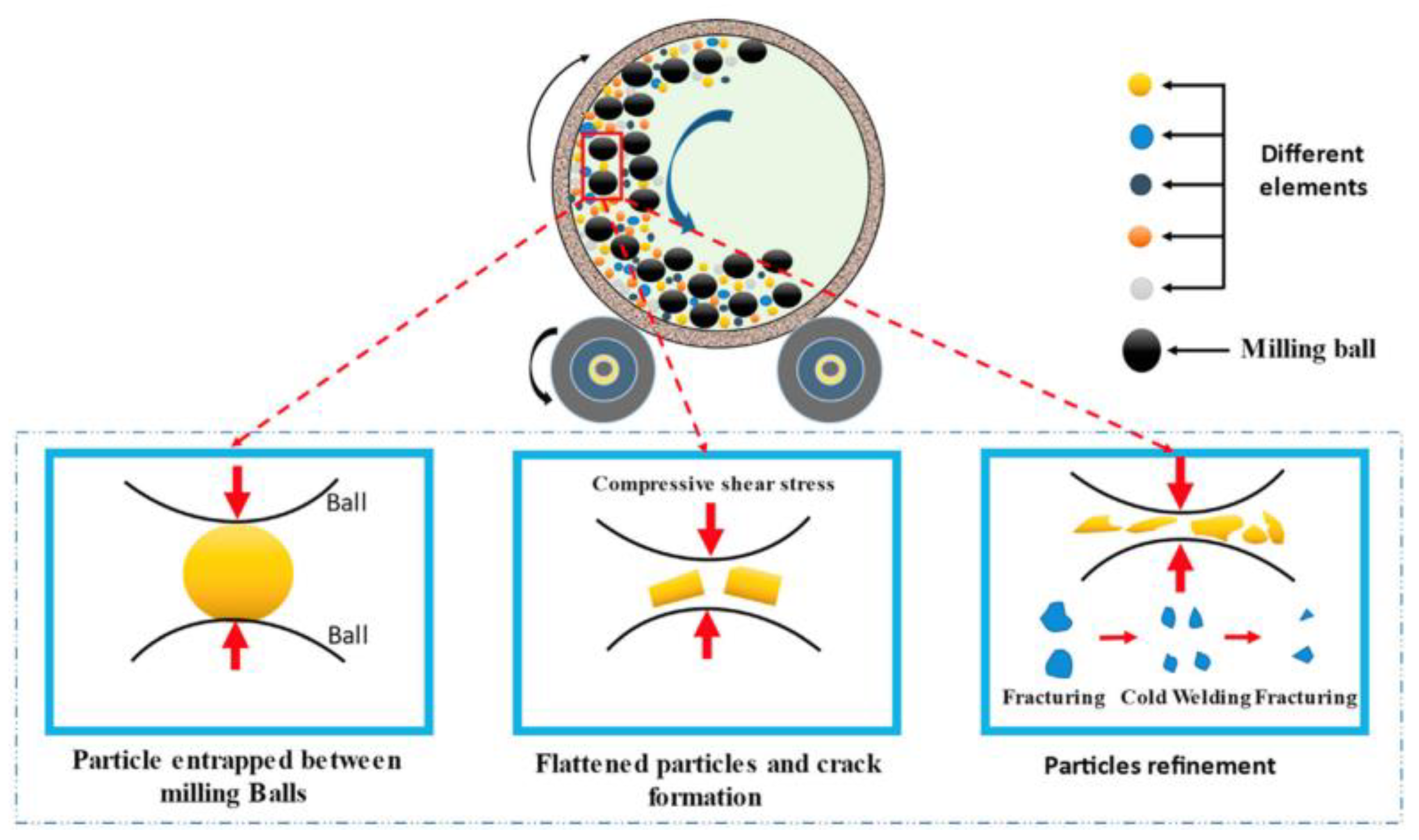
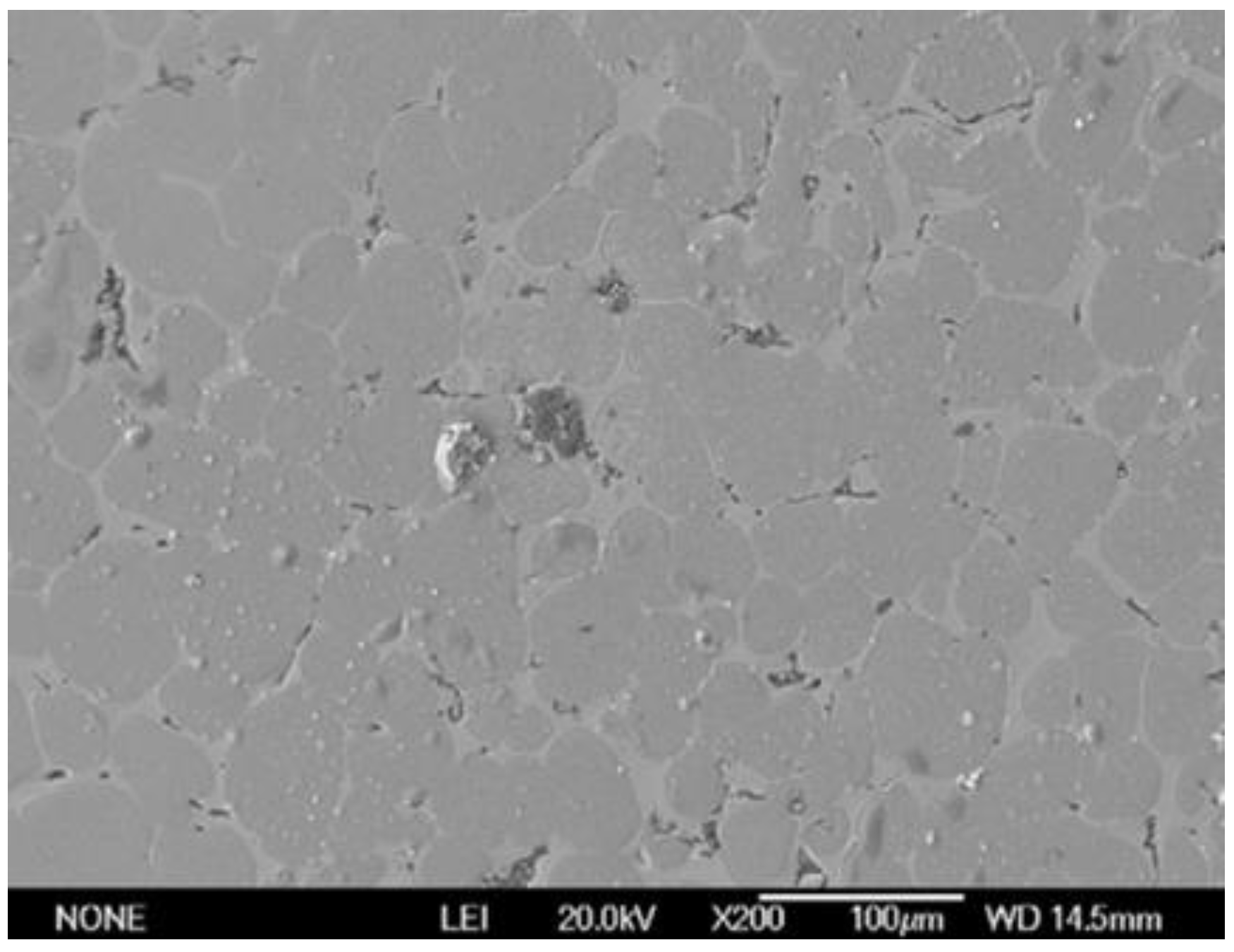
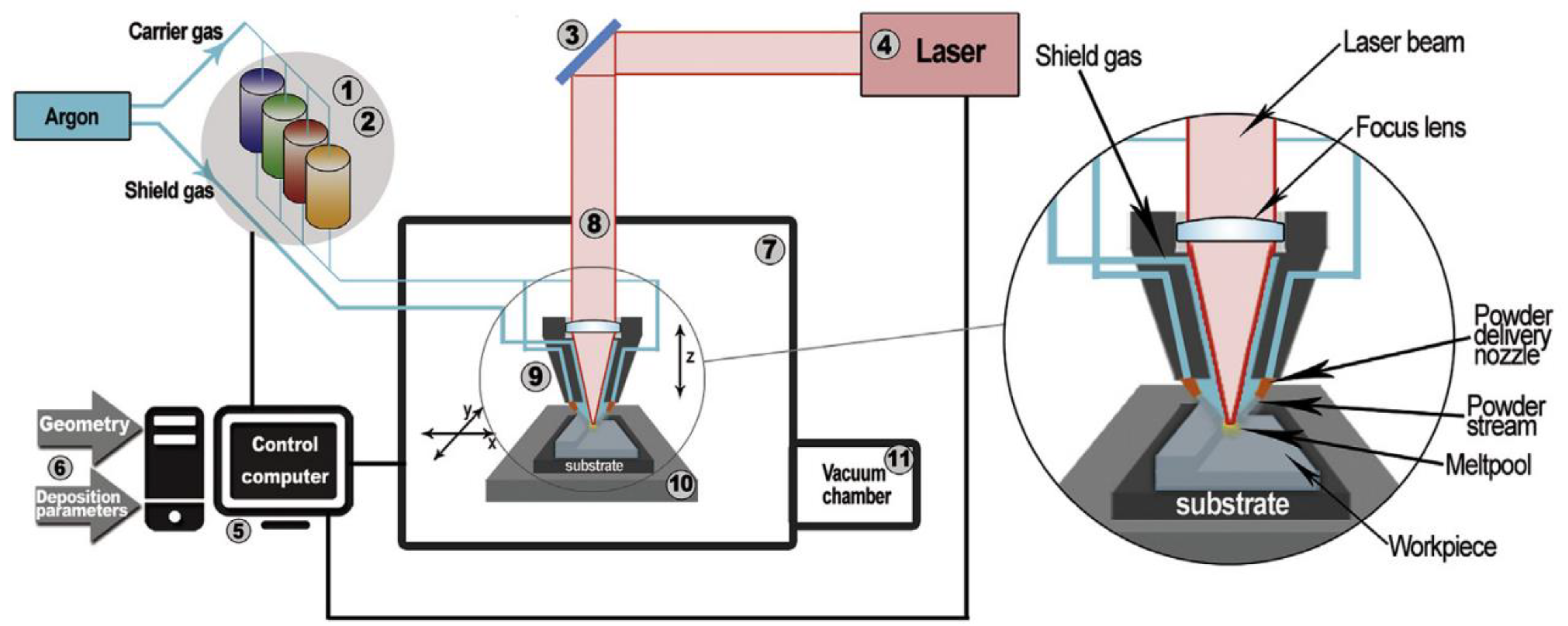
4. Methods of HEA Synthesis
5. Hydrogen Sorption Properties of HEAs and Prospects of Their Application in Hydrogen Power Engineering
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, M.Y.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhao, X.L.; Fang, F.; Jia, N. Ultrahigh Strength Induced by Multiple Heterostructures in a FeMnCoCrN High-Entropy Alloy Fabricated by Powder Metallurgy Technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 846, 143304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, A.M.; Hossain, S.; Nisfindy, O.B.; Azad, A.T.; Dawood, M.; Azad, A.K. Hydrogen Production, Storage, Transportation and Key Challenges with Applications: A Review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 165, 602–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, J.O.; Popoola, A.P.I.; Ajenifuja, E.; Popoola, O.M. Hydrogen Energy, Economy and Storage: Review and Recommendation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 15072–15086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency. Global Hydrogen Review 2023; International Energy Agency Reports: Paris, France, 2023; Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-hydrogen-review-2023 (accessed on 22 September 2023).
- Sreedhar, I.; Kamani, K.M.; Kamani, B.M.; Reddy, B.M.; Venugopal, A. A Bird’s Eye View on Process and Engineering Aspects of Hydrogen Storage. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 91, 838–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Musyoka, N.M.; Langmi, H.W.; Mathe, M.; Liao, S. Current Research Trends and Perspectives on Materials-Based Hydrogen Storage Solutions: A Critical Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.F.; Ding, Z.Y.; Ye, Y.F.; Yang, Y.C. Design of High-Entropy Alloy: A Perspective from Nonideal Mixing. JOM 2017, 69, 2092–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural Development in Equiatomic Multicomponent Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys With Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts And Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.T.; Liu, C.T.; Yang, Y.C. Design of High Entropy Alloys: A Single-Parameter Thermodynamic Rule. Scr. Mater. 2015, 104, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, G.; Gao, W.; Chen, C.; Huang, X.; Feng, M. Review on Hard Particle Reinforced Laser Cladding High-Entropy Alloy Coatings. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 1366–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Chen, H.; Niu, M.; Cheng, J. Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNi-X (X = Ti, Sn) High Entropy Alloy And Tribological Properties in Simulated Seawater Environment. Tribol. Int. 2025, 202, 110306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Gong, P.; Hu, Z.; Li, B. Effect of Cr Content on the High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of FeCoNiMnCrx_xx Porous High-Entropy Alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 3324–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floriano, R.; Zepon, G.; Edalati, K.; Fontana, G.L.; Mohammadi, A.; Ma, Z.; Contieri, R.J. Hydrogen Storage in TiZrNbFeNi High Entropy Alloys, Designed by Thermodynamic Calculations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 33759–33770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.; You, L.; Cao, X.; Lu, Z.; Song, X. Investigation on the Activation Mechanism of Hydrogen Absorption in TiZrNbTa High Entropy Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Y. High-Entropy Alloys for Solid Hydrogen Storage: A Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 406–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewangan, S.K.; Sharma, V.K.; Sahu, P.; Kumar, V. Synthesis and Characterization of Hydrogenated Novel AlCrFeMnNiW High Entropy Alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 16984–16991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygård, M.M.; Ek, G.; Karlsson, D.; Sørby, M.H.; Sahlberg, M.; Hauback, B.C. Counting Electrons—A New Approach to Tailor the Hydrogen Sorption Properties of High-Entropy Alloys. Acta Mater. 2019, 175, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yadav, T.P.; Mukhopadhyay, N.K. Notable Hydrogen Storage in Ti–Zr–V–Cr–Ni High Entropy Alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 22893–22900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornheim, M. Thermodynamics–Interaction Studies–Solids. Liq. Gases 2011, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.P.; Raabe, D.; Ritchie, R.O. High-entropy alloys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, T.; Khan, M.M.; Pali, H.S. The Future of Hydrogen Economy: Role of High-Entropy Alloys in Hydrogen Storage. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1004, 175668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.; Ek, G.; Sahlberg, M.; Zlotea, C. Improving the Hydrogen Cycling Properties by Mg Addition in Ti-V-Zr-Nb Refractory High Entropy Alloy. Scr. Mater. 2021, 194, 113699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichii, K.; Koyama, M.; Tasan, C.C.; Tsuzaki, K. Comparative Study of Hydrogen Embrittlement in Stable and Metastable High-Entropy Alloys. Scr. Mater. 2018, 150, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareipour, F.; Shahmir, H.; Huang, Y.; Patel, A.K.; Dematteis, E.M.; Baricco, M. Hydrogen Storage in TiVCr(Fe, Co)(Zr, Ta) Multi-Phase High-Entropy Alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 94, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygård, M.M.; Fjellvåg, Ø.S.; Sørby, M.H.; Sakaki, K.; Ikeda, K.; Armstrong, J.; Vajeeston, P.; Sławiński, W.A.; Kim, H.; Machida, A.; et al. The Average and Local Structure of TiVCrNbDx (x = 0, 2.2, 8) from Total Scattering and Neutron Spectroscopy. Acta Mater. 2020, 205, 116496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Modi, P.; Cazorla, C.; Demirci, U.B.; Ares Fernandez, J.R.; Leardini, F.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.F. How to Design Hydrogen Storage Materials? Fundamentals, Synthesis, and Storage Tanks. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2019, 3, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felderhoff, M.; Weidenthaler, C.; von Helmolt, R.; Eberle, U. Hydrogen Storage: The Remaining Scientific and Technological Challenges. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 2643–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidenthaler, C.; Felderhoff, M. Solid-State Hydrogen Storage for Mobile Applications: Quo Vadis? Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uenishi, K.; Kobayashi, K.F.; Ishihara, K.N.; Shingu, P.H. Formation of a Super-Saturated Solid Solution in the Ag Cu System by Mechanical Alloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 134, 1342–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendrachari, S. An Overview of High-Entropy Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying Followed by the Characterization of Their Microstructure and Various Properties. Alloys 2022, 1, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, N. High-Entropy Alloys: An Interview with Jien-Wei Yeh. MRS Bull. 2016, 41, 905–906. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1557/mrs.2016.257 (accessed on 27 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Murty, B.S.; Yeh, J.W.; Ranganathan, S.; Bhattacharjee, P.P. High-Entropy Alloys; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K. Introduction to Statistical Physics, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA; New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Xiao, X.; Xia, L.; Li, W.; Dong, Y. Relationship between the Widths of Supercooled Liquid Region and Bond Parameters of Mg-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 321, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Quantitative Evaluation on Critical Cooling Rate for Metallic Glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 304–306, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, M.; Pradeep, K.G.; Murty, B.S.; Wilde, G.; Divinski, S.V. Bulk Tracer Diffusion in CoCrFeNi and CoCrFeMnNi High Entropy Alloys. Acta Mater. 2018, 146, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Liu, W.H.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. Effects of Al Addition on Structural Evolution and Tensile Properties of the FeCoNiCrMn High-Entropy Alloy System. Acta Mater. 2014, 62, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Diao, H.; Yang, T.; Liu, J.; Zuo, T.; Egami, T. Aluminum Alloying Effects on Lattice Types, Microstructures, and Mechanical Behavior of High-Entropy Alloy Systems. JOM 2013, 65, 1848–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pradeep, K.G.; Deng, Y.; Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C. Metastable High-Entropy Dual-Phase Alloys Overcome the Strength–Ductility Trade-Off. Nature 2016, 534, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasan, C.C.; Deng, Y.; Pradeep, K.G.; Yao, M.J.; Springer, H.; Raabe, D. Composition Dependence of Phase Stability, Deformation Mechanisms, and Mechanical Properties of the CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloy System. JOM 2014, 66, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yao, M.; Pradeep, K.G.; Tasan, C.C.; Springer, H.; Raabe, D. Phase Stability of Non-Equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi High Entropy Alloys. Acta Mater. 2015, 98, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwalani, B.; Soni, V.; Choudhuri, D.; Lee, M.; Hwang, J.Y.; Nam, S.J.; Banerjee, R. Stability of Ordered L12 and B2 Precipitates in Face-Centered Cubic Based High Entropy Alloys-Al0.3CoFeCrNi and Al0.3CuFeCrNi2. Scr. Mater. 2016, 123, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A Critical Review of High Entropy Alloys and Related Concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, H.Y.; Feng, R.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K. Fundamental Deformation Behavior in High-Entropy Alloys: An Overview. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 21, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami, S.; Edalati, P.; Fuji, M.; Edalati, K. High-Entropy Ceramics: Review of Principles, Production and Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2021, 146, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oses, C.; Toher, C.; Curtarolo, S. High-Entropy Ceramics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalati, P.; Wang, Q.; Razavi-Khosroshahi, H.; Fuji, M.; Ishihara, T.; Edalati, K. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution on a High-Entropy Oxide. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 3814–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, A.; Xiang, H.-Z.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Kuramoto, K.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Y. A New Class of Spinel High-Entropy Oxides with Controllable Magnetic Properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 497, 165884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, R.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Ji, J.; Wei, T.; Ouyang, T. Microstructure and Dielectric Properties of High-Entropy Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.2Sn0.2Hf0.2Me0.2)O3 Perovskite Oxides. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 7430–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.X.; Patra, J.; Chang, J.-K.; Ting, J.-M. High-Entropy Spinel Oxide Nanoparticles for Superior Lithiation–Delithiation Performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 18963–18973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.L.; Rost, C.M.; Lim, M.; Giri, A.; Olson, D.H.; Kotsonis, G.N.; Stan, G.; Brenner, D.W.; Maria, J.; Hopkins, P.E. Charge-Induced Disorder Controls the Thermal Conductivity of Entropy-Stabilized Oxides. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1805004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalati, P.; Shen, X.-F.; Watanabe, M.; Ishihara, T.; Arita, M.; Fuji, M.; Edalati, K. High-Entropy Oxynitride as a Low-Bandgap and Stable Photocatalyst for Hydrogen Production. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 15076–15086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami, S.; Edalati, P.; Shundo, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Ishihara, T.; Fuji, M.; Edalati, K. Significant CO2 Photoreduction on a High-Entropy Oxynitride. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 449, 137800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, S.; Radhika, N.; Saleh, B. Advances in Vacuum Arc Melting for High-Entropy Alloys: A Review. Vacuum 2024, 226, 113314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, W.; Fu, Y. High-Entropy Alloys: Emerging Materials for Advanced Functional Applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2021, 9, 663–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesuz, M.; Saunders, T.G.; Veverka, J.; Bortolotti, M.; Vontorová, J.; Vilémová, M.; Reece, M.J. Solidification Microstructures of Multielement Carbides in the High Entropy Zr-Nb-Hf-Ta-Cx System Produced by Arc Melting. Scr. Mater. 2021, 203, 114091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, T.P.; Kumar, A.; Verma, S.K.; Mukhopadhyay, N.K. High-Entropy Alloys for Solid Hydrogen Storage: Potentials and Prospects. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2022, 7, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strozi, R.B.; Leiva, D.R.; Zepon, G.; Botta, W.J.; Huot, J. Effects of the Chromium Content in (TiVNb)100−xCrx Body-Centered Cubic High Entropy Alloys Designed for Hydrogen Storage Applications. Energies 2021, 14, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, Q. Microstructure and the Properties of FeCoCuNiSnx High Entropy Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 548, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C. Mechanical Properties of Low-Density, Refractory Multi-Principal Element Alloys of the Cr–Nb–Ti–V–Zr System. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 565, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.X.; Yang, F.S.; Feng, P.H.; Wang, Y.Q. Hydrogen Storage Properties and Mechanisms of Magnesium-Based Alloys with Mesoporous Surface. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 2771–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, F.S.; Bao, Z.W.; Nyamsi, S.N.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.X. Microstructure and Improved Hydrogen Storage Properties of Mg-Based Alloy Powders Prepared by Modified Milling Method. Powder Metall. 2014, 57, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Lu, Y.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, H. Thermodynamic Tuning of Mg-Based Hydrogen Storage Alloys: A Review. Materials 2013, 6, 4654–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.L.; Zhang, Y.H. Research Progress in Mg-Based Hydrogen Storage Alloys. Rare Met. 2014, 33, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepon, G.; Leiva, D.R.; Strozi, R.B.; Bedoch, A.; Figueroa, S.J.A.; Ishikawa, T.T.; Botta, W.J. Hydrogen-Induced Phase Transition of MgZrTiFe₀.₅Co₀.₅Ni₀.₅ High Entropy Alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Marco, M.O.; Li, Y.; Li, H.W.; Edalati, K.; Floriano, R. Mechanical Synthesis and Hydrogen Storage Characterization of MgVCr and MgVTiCrFe High-Entropy Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 1901079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, K.R.; Roche, V.; Jorge, A.M., Jr.; Antiqueira, F.J.; Zepon, G.; Champion, Y. Hydrogen Storage in MgAlTiFeNi High Entropy Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 858, 158357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, H.; Qiu, J.; Pan, F. The Integral Role of High-Entropy Alloys in Advancing Solid-State Hydrogen Storage. Interdiscip. Mater. 2024, 7, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, A.O.; Shaburova, N.A.; Samodurova, M.N.; Abdollahzadeh, A.; Trofimov, E.A. Additive Manufacturing of High Entropy Alloys: A Practical Review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 77, 131–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.W.; Zhang, Y.P.; He, L.; Liu, C.G. Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of AlCrFeCuCo High Entropy Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 549, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunce, I.; Polanski, M.; Bystrzycki, J. Microstructure and Hydrogen Storage Properties of a TiZrNbMoV High Entropy Alloy Synthesized Using Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 9904–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunce, I.; Polanski, M.; Bystrzycki, J. Structure and Hydrogen Storage Properties of a High Entropy ZrTiVCrFeNi Alloy Synthesized Using Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 12180–12189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunce, I.; Polański, M.; Czujko, T. Microstructures and Hydrogen Storage Properties of LaNiFeVMn Alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27154–27164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Novaković, N. Recent Progress on the Development of High Entropy Alloys (HEAs) for Solid Hydrogen Storage: A Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 11236–11249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.; Zlotea, C.; Ek, G.; Crivello, J.C.; Laversenne, L.; Sahlberg, M. TiVZrNb Multi-Principal-Element Alloy: Synthesis Optimization, Structural, and Hydrogen Sorption Properties. Molecules 2019, 24, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Cheng, X.W.; Wang, F.C.; Zhang, Y.F.; Li, S.L. A Review of Multi-Physical Fields Induced Phenomena and Effects in Spark Plasma Sintering: Fundamentals and Applications. Mater. Des. 2020, 191, 108662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, A.; Zhou, S.; Shi, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, M. Effects of Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of IN718 Reinforced by Reduced Graphene Oxide through Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 767, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravcik, I.; Cizek, J.; Zapletal, J.; Kovacova, Z.; Vesely, J.; Minarik, P.; Dlouhy, I. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ni1,5Co1,5CrFeTi0,5 High Entropy Alloy Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering. Mater. Des. 2017, 119, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.B.; Park, J.Y.; Do Kim, Y.; Na, T.W.; Mo, C.B.; Choi, J.I.; Park, H.K. Spark Plasma Sintering Behavior of TaNbHfZrTi High-Entropy Alloy Powder Synthesized by Hydrogenation-Dehydrogenation Reaction. Intermetallics 2021, 130, 107077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhakhmetov, Y.; Skakov, M.; Mukhamedova, N.; Kurbanbekov, S.; Ramankulov, S.; Wieleba, W. Changes in the Microstructural State of Ti-Al-Nb-Based Alloys Depending on the Temperature Cycle During Spark Plasma Sintering. Mater. Test. 2021, 63, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhakhmetov, Y.; Skakov, M.; Wieleba, W.; Kurbanbekov, S.; Mukhamedova, N. Evolution of Intermetallic Compounds in the Ti-Al-Nb System by the Action of Mechanoactivation and Spark Plasma Sintering. J. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2020, 7, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhakhmetov, Y.A.; Skakov, M.K.; Kurbanbekov, S.R.; Mukhamedov, N.M.; Mukhamedov, N.Y. Powder Composition Structurization of the Ti-25Al-25Nb (At.%) System upon Mechanical Activation and Subsequent Spark Plasma Sintering. Eurasian Chem.-Technol. J. 2021, 23, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Jin, Q.; Su, G.; Lu, W. A Review of Hydrogen Storage and Transportation: Progresses and Challenges. Energies 2024, 17, 4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free, Z.; Hernandez, M.; Mashal, M.; Mondal, K. A Review on Advanced Manufacturing for Hydrogen Storage Applications. Energies 2021, 14, 8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Q.; Algburi, S.; Sameen, A.Z.; Jaszczur, M.; Salman, H.M. Hydrogen as an Energy Carrier: Properties, Storage Methods, Challenges, and Future Implications. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2024, 44, 327–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangwal, S.; Edalati, K. High-Entropy Alloy TiV2ZrCrMnFeNi for Hydrogen Storage at Room Temperature with Full Reversibility and Good Activation. Scr. Mater. 2024, 238, 115774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Schweidler, S.; Botros, M.; Fu, T.; Breitung, B. High-Entropy Energy Materials: Challenges and New Opportunities. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 2883–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Z.; Zhang, X.X.; Li, S.S.; Yi, L.C.; Chen, Q.J. A Review of Body-Centered Cubic-Structured Alloys for Hydrogen Storage: Composition, Structure, and Properties. Rare Met. 2024, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Cheng, B.; Wan, D.; Xue, Y. A Review on BCC-Structured High-Entropy Alloys for Hydrogen Storage. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1135864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somo, T.R.; Lototskyy, M.V.; Yartys, V.A.; Davids, M.W.; Nyamsi, S.N. Hydrogen Storage Behaviours of High-Entropy Alloys: A Review. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 108969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, W. High Entropy Alloys: Emerging Materials for Advanced Hydrogen Storage. Energy Technol. 2024, 12, 2401061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, F.; Martínez, C.; Martin, P.; Aguilar, C. High-Entropy Alloys: A Review of Their Performance as Promising Materials for Hydrogen and Molten Salt Storage. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2023, 62, 20230150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryltsev, R.; Gaviko, V.; Estemirova, S.; Sterkhov, E.; Cherepanova, L.; Yagodin, D.; Uporov, S. Laves Phase Formation in High Entropy Alloys. Metals 2021, 11, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xaba, M.S. Additively Manufactured High-Entropy Alloys for Hydrogen Storage: Predictions. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, F.; Balcerzak, M.; Winkelmann, F.; Zepon, G.; Felderhoff, M. Review and Outlook on High-Entropy Alloys for Hydrogen Storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 5191–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, R.R.; Gupta, A.K.; Kumari, P. Perspectives of High Entropy Alloys as Hydrogen Storage Materials. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 21412–21428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.F.; Chen, S.K.; Sheu, J.H.; Lin, J.T.; Lin, W.E.; Yeh, J.W.; Wang, C.W. Hydrogen Storage Properties of Multi-Principal-Component CoFeMnTixVyZrz Alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 9046–9059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalati, P.; Floriano, R.; Mohammadi, A.; Li, Y.; Zepon, G.; Li, H.W.; Edalati, K. Reversible Room Temperature Hydrogen Storage in High-Entropy Alloy TiZrCrMnFeNi. Scr. Mater. 2020, 178, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukagawa, T.; Saito, Y.; Matsuyama, A. Effect of Varying Ni Content on Hydrogen Absorption–Desorption and Electrochemical Properties of Zr-Ti-Ni-Cr-Mn High-Entropy Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 896, 163118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.M.; Wilson, J.A.; Rushton, M.J.D.; Lee, W.E.; Astbury, J.O.; Middleburgh, S.C. Hydrogen Accommodation in the TiZrNbHfTa High Entropy Alloy. Acta Mater. 2022, 229, 117832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, G.; Nygård, M.M.; Pavan, A.F.; Montero, J.; Henry, P.F.; Sørby, M.H.; Sahlberg, M. Elucidating the Effects of the Composition on Hydrogen Sorption in TiVZrNbHf-Based High-Entropy Alloys. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 60, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygård, M.; Ek, G.; Karlsson, D.; Sahlberg, M.; Sørby, M.H.; Hauback, B.C. Hydrogen Storage in High-Entropy Alloys with Varying Degree of Local Lattice Strain. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 29140–29149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Mao, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, X.; Zu, X. A Novel TiZrHfMoNb High-Entropy Alloy for Solar Thermal Energy Storage. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strozi, R.B.; Leiva, D.R.; Huot, J.; Botta, W.J.; Zepon, G. Synthesis and Hydrogen Storage Behavior of Mg–V–Al–Cr–Ni High Entropy Alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 2351–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.; Ek, G.; Laversenne, L.; Nassif, V.; Zepon, G.; Sahlberg, M.; Zlotea, C. Hydrogen Storage Properties of the Refractory Ti–V–Zr–Nb–Ta Multi-Principal Element Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 835, 155376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhamedova, N.; Kozhakhmetov, Y.; Skakov, M.; Kurbanbekov, S.; Mukhamedov, N. Microstructural Stability of a Two-Phase (O+B2) Alloy of the Ti-25Al-25Nb System (At.%) During Thermal Cycling in a Hydrogen Atmosphere. J. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2022, 9, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
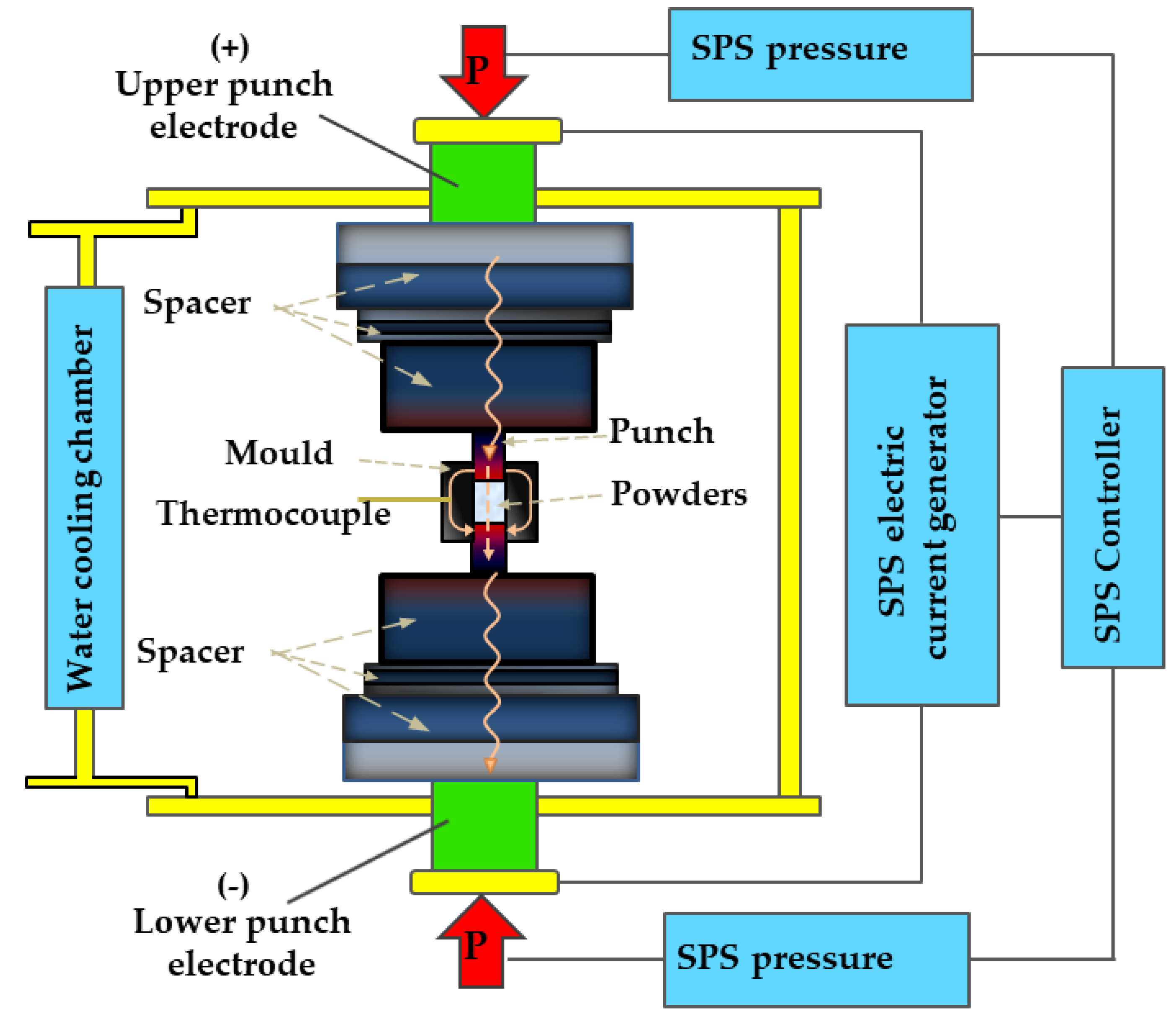
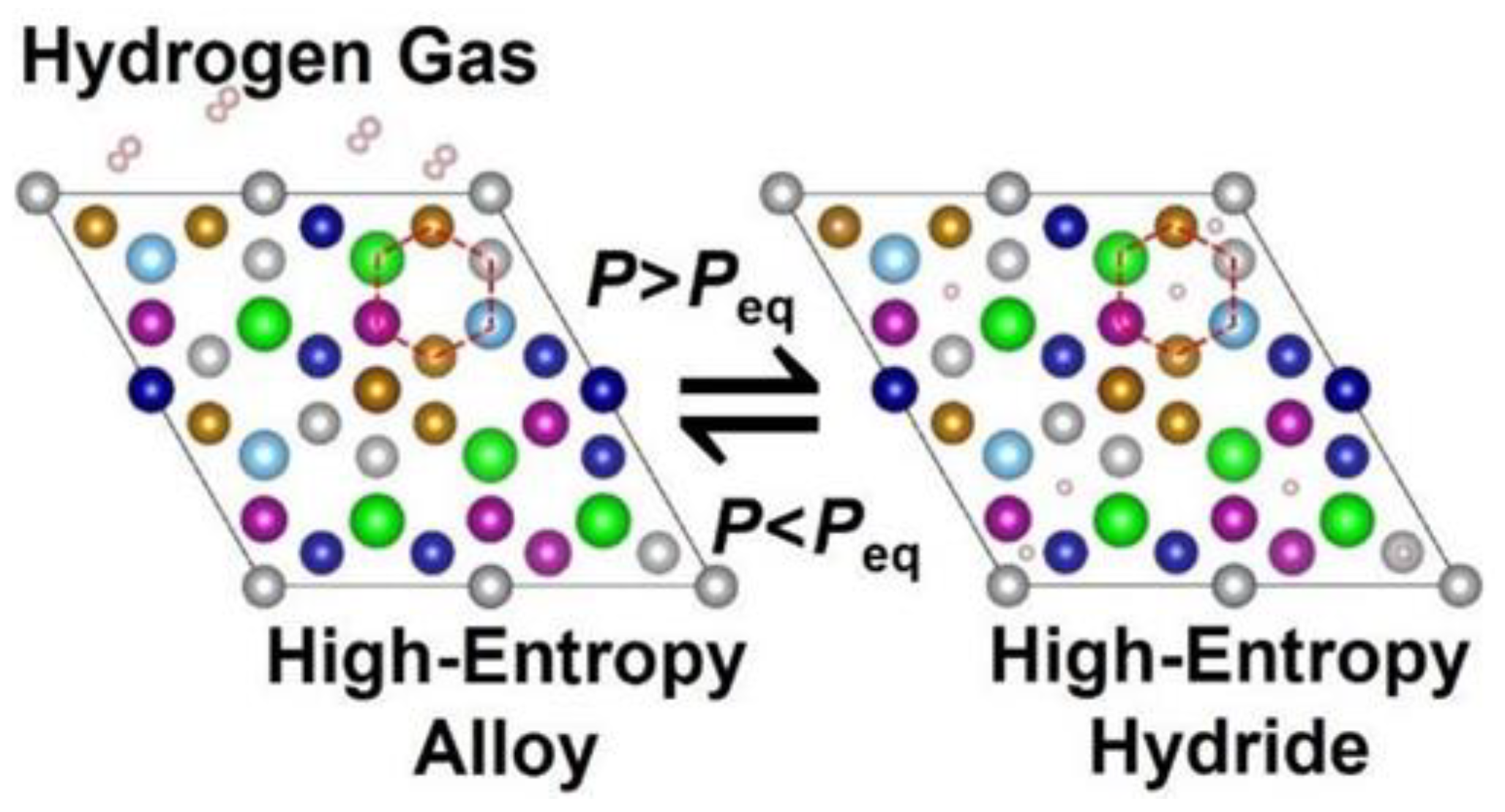
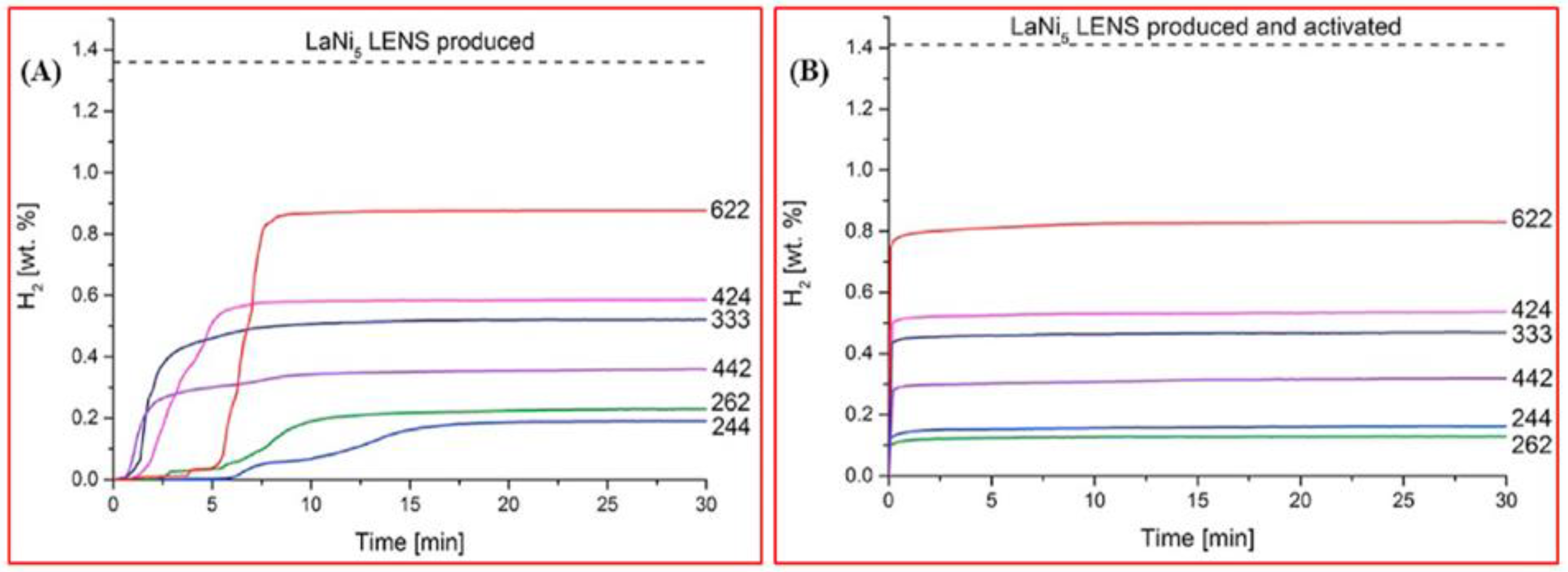
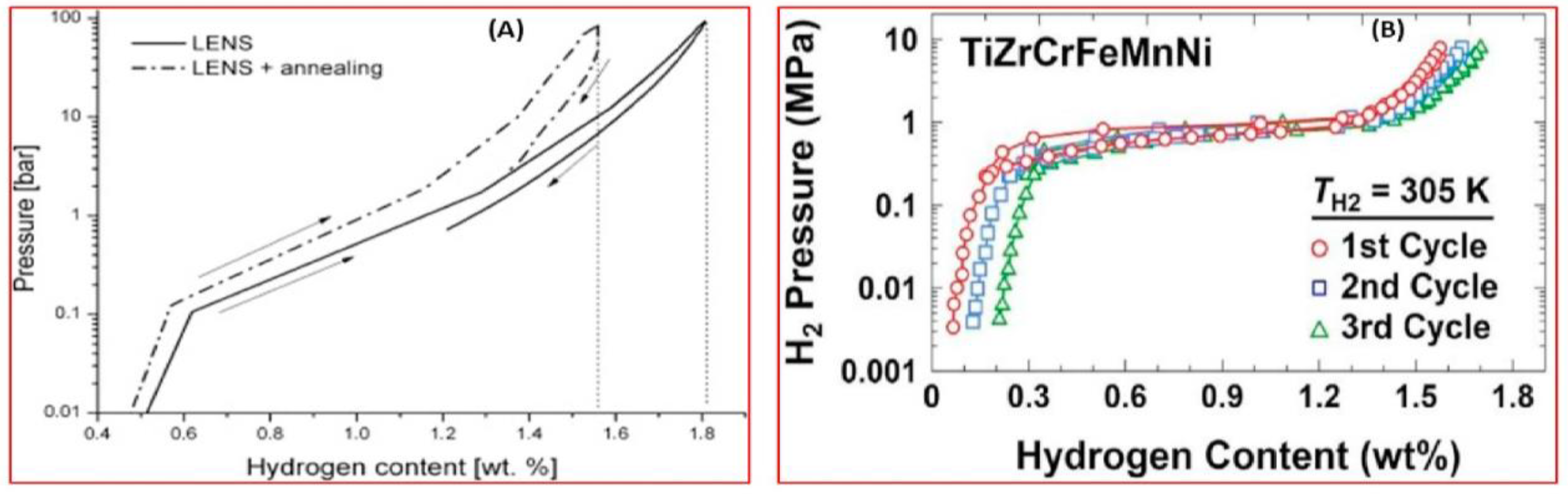
| Normalized Chemical Com- Position Ordered by Atomic Number | Nominal Composition | Synthesis and Processing | VEC | Alloy Phase | Hydride Phase | H2 Absorp. Capacity (wt%) | H/M | Rev. H2 Capacity (wt%/H/M) | H2 Absorp. Kinetics | Hydride Decompos. Onset/Peak Temperatures (K) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti0.2V0.2Zr0.2Nb0.2Mo0.2 | TiZrNbMoV | LENS (300 W) | 4.8 a | BCC (major) NbNi4 (minor) | FCCTiHx | 2.3 (323 K)–1.78 (after activation 673 K) | - | - | 2.3 wt% in 1380 s (303 K, 8.5 MPa H2) | - | [72] |
| Ti0.2V0.2Zr0.2Nb0.2Mo0.2 | TiZrNbMoV | LENS (1000 W three times) | 4.8 a | BCC (major) Zr-rich (Ppt) | BCC (major) Zr-rich (Ppt) | 0.59 (323 K) 0.61 (after activation 673 K) | - | - | 0.59 wt% in 1380 s (303 K, 8.5 MPa H2) | [72] | |
| Ti0.22V0.22Zr0.22Nb0.11Hf0.22 | TiVZrHfNb0.5 | Arc melting | 4.33 | BCC | BCT | - | 1.82 (293 K) | - | - | ~573/- | [102] |
| Ti0.22V0.22Zr0.11Nb0.22Hf0.22 | TiVZr0.5HfNb | Arc melting | 4.44 | BCC | FCC | - | 1.99 (293 K) | - | - | ~593/- | [102] |
| Ti0.22V0.22Zr0.22Nb0.22Hf0.11 | TiVZrHf0.5Nb | Arc melting | 4.44 | BCC | FCC | - | 2.00 (293 K) | - | - | ~593/- | [102] |
| Ti0.22V0.11Zr0.22Nb0.22Hf0.22 | TiV0.5ZrHfNb | Arc melting | 4.33 | BCC | FCC | - | 1.96 (293 K) | - | - | ~573/- | [102] |
| Ti0.11V0.22Zr0.22Nb0.22Hf0.22 | Ti0.5VZrHfNb | Arc melting | 4.44 | BCC | FCC | - | 1.97 (273 K) | - | - | ~573/- | [102] |
| Ti0.25V0.25Zr0.04Nb0.25Ta0.21 | TiVZr0.15NbTa0.85 | Arc melting | 4.71 a | BCC | FCC (major) BCT (minor) | - | - | - | - | [103] | |
| Ti0.25V0.25Zr0.125Nb0.25Ta0.125 | TiVZr0.50NbTa0.50 | Arc melting | 4.63 a | BCC | FCC (major) BCC (minor) | - | ~1.9 | - | - | - | [103] |
| Ti0.25V0.25Zr0.19Nb0.25Ta0.06 | TiVZr0.74NbTa0.26 | Arc melting | 4.57 a | BCC | FCC (major) BCC (minor) | - | ~1.9 | - | - | - | [103] |
| Ti0.2Zr0.2Nb0.2Mo0.2Hf0.2 | TiZrHfMoNb | Arc melting | 4.6 | BCC | FCC | 1.18 | - | - | - | ~540/575 | [104] |
| Ti0.2Zr0.2Nb0.2Hf0.2Ta0.2 | TiZrNbHfTa | Arc melting (homogenized by induction heating) | 4.4 | BCC | FCC | - | ~2.0 (573 K) | - | - | 648 | [105] |
| Ti0.25V0.25Zr0.04Nb0.25Ta0.21 | TiVZr0.15NbTa0.85 | Arc melting | 4.71 a | BCC | FCC (major) BCT (minor) | - | - | - | - | [103] | |
| Ti0.25V0.25Zr0.125Nb0.25Ta0.125 | TiVZr0.50NbTa0.50 | Arc melting | 4.63 a | BCC | FCC (major) BCC (minor) | - | ~1.9 | - | - | - | [103] |
| Ti0.25V0.25Zr0.19Nb0.25Ta0.06 | TiVZr0.74NbTa0.26 | Arc melting | 4.57 a | BCC | FCC (major) BCC (minor) | - | ~1.9 | - | - | - | [103] |
| Ti0.2Zr0.2Nb0.2Mo0.2Hf0.2 | TiZrHfMoNb | Arc melting | 4.6 | BCC | FCC | 1.18 | - | - | - | 540/575 | [104] |
| Ti0.2Zr0.2Nb0.2Hf0.2Ta0.2 | TiZrNbHfTa | Arc melting (homogenized by induction heating) | 4.4 | BCC | FCC | - | ~2.0 (573 K) | - | - | 648 | [105] |
| Ti0.25V0.25Zr0.04Nb0.25Ta0.21 | TiVZr0.15NbTa0.85 | Arc melting | 4.71 a | BCC | FCC (major) BCT (minor) | - | - | - | - | [105] | |
| Ti0.25V0.25Zr0.125Nb0.25Ta0.125 | TiVZr0.50NbTa0.50 | Arc melting | 4.63 a | BCC | FCC (major) BCC (minor) | - | ~1.9 | - | - | - | [103] |
| Ti0.25V0.25Zr0.19Nb0.25Ta0.06 | TiVZr0.74NbTa0.26 | Arc melting | 4.57 a | BCC | FCC (major) BCC (minor) | - | ~1.9 | - | - | - | [103] |
| Ti0.25V0.25Nb0.25Hf0.25 | TiVHfNb | Arc melting | 4.50 | BCC | FCC | - | 1.99 (293 K) | - | - | [103] | |
| MgVAlCrNi | MgVAlCrNi | High-energy ball milling | - | BCC | BCC | - | ~0.15 | - | - | [105] | |
| Mg28V28Al19Cr19Ni6 | Mg28V28Al19Cr19Ni6 | High-energy ball milling | - | BCC | BCC | - | ~0.15 | - | - | [105] | |
| Mg26V31Al31Cr6Ni6 | Mg26V31Al31Cr6Ni6 | High-energy ball milling | - | BCC | BCC | - | - | - | - | - | [105] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozhakhmetov, Y.; Skakov, M.; Kurbanbekov, S.; Uazyrkhanova, G.; Kurmantayev, A.; Kizatov, A.; Mussakhan, N. High-Entropy Alloys: Innovative Materials with Unique Properties for Hydrogen Storage and Technologies for Their Production. Metals 2025, 15, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020100
Kozhakhmetov Y, Skakov M, Kurbanbekov S, Uazyrkhanova G, Kurmantayev A, Kizatov A, Mussakhan N. High-Entropy Alloys: Innovative Materials with Unique Properties for Hydrogen Storage and Technologies for Their Production. Metals. 2025; 15(2):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020100
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozhakhmetov, Yernat, Mazhyn Skakov, Sherzod Kurbanbekov, Gulzhaz Uazyrkhanova, Abil Kurmantayev, Aibar Kizatov, and Nurken Mussakhan. 2025. "High-Entropy Alloys: Innovative Materials with Unique Properties for Hydrogen Storage and Technologies for Their Production" Metals 15, no. 2: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020100
APA StyleKozhakhmetov, Y., Skakov, M., Kurbanbekov, S., Uazyrkhanova, G., Kurmantayev, A., Kizatov, A., & Mussakhan, N. (2025). High-Entropy Alloys: Innovative Materials with Unique Properties for Hydrogen Storage and Technologies for Their Production. Metals, 15(2), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15020100







