Microstructure Evolution and Modelling During Tempering Heat Treatment at 670 °C in 9–12 wt.% Cr Ferritic/Martensitic Heat-Resistant Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Procedures
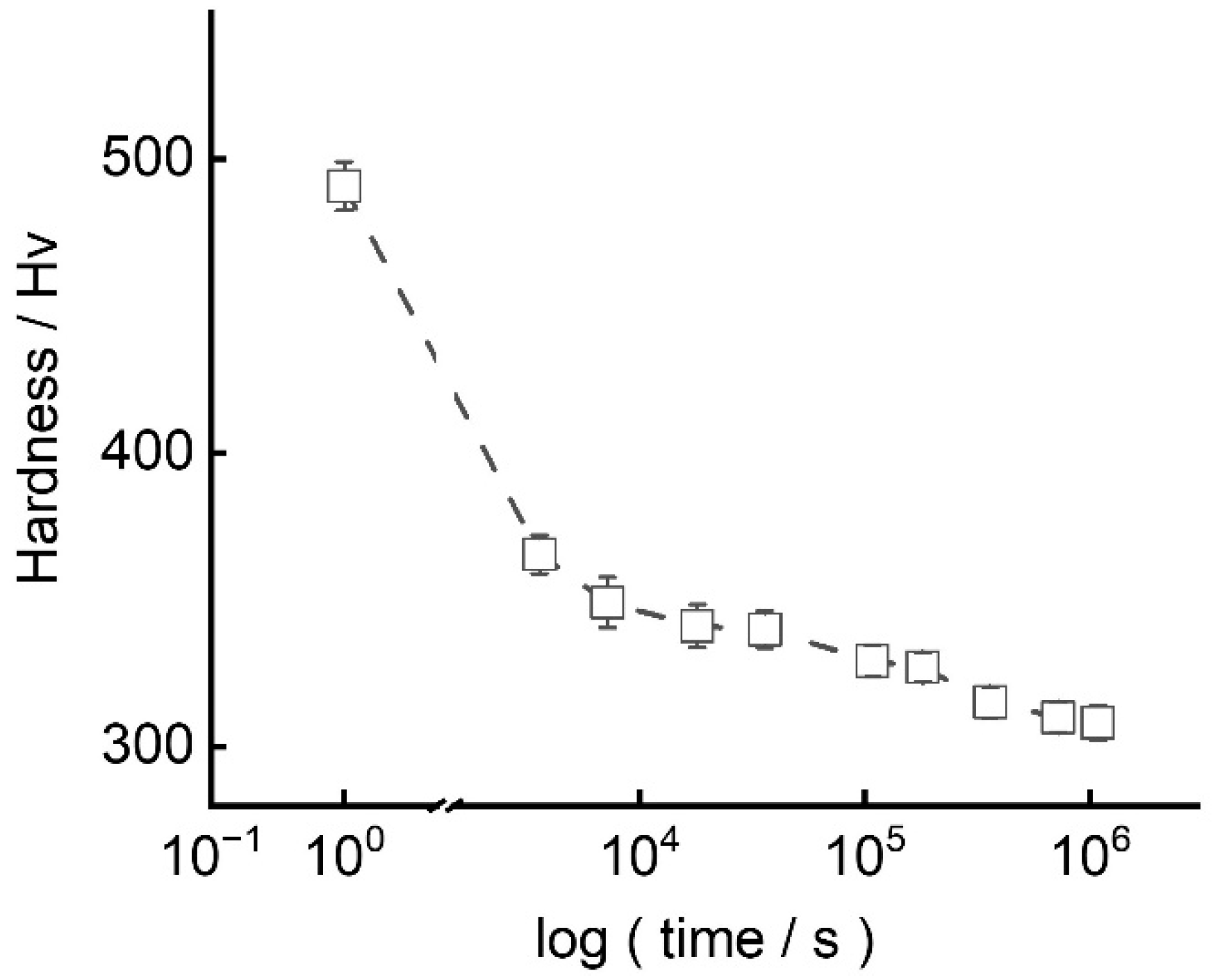
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rojas, D.; Garcia, J.; Prat, O.; Sauthoff, G.; Kaysser-Pyzalla, A.R. 9% Cr heat resistant steels: Alloy design, microstructure evolution and creep response at 650 °C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 5164–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudova, N. 9–12% Cr heat-resistant martensitic steels with increased boron and decreased nitrogen contents. Metals 2022, 12, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Yan, W.; Sha, W.; Wang, W.; Shan, Y.; Yang, K. Microstructure evolution of a 10Cr heat-resistant steel during high temperature creep. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuyama, F. History of power plants and progress in heat resistant steels. ISIJ Int. 2001, 41, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachadel, U.A.; Morris, P.F.; Clarke, P.D. Design of 10 Cr martensitic steels for improved creep resistance in power plant applications. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.K.; Behera, S.; Pandey, C.; Guguloth, K. Creep deformation behaviour of Grade 91 steel and its weld joints: A comparative study. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2025, 219, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Qu, F.; Han, J.; Ma, Y. Precipitates and particles coarsening of 9Cr–1.7W–0.4Mo–Co ferritic heat-resistant steel after isothermal aging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, F. Analysis of creep rates of tempered martensitic 9% Cr steel based on microstructure evolution. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 510, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipelova, A.; Kaibyshev, R.; Belyakov, A.; Molodov, D. Microstructure evolution in a 3% Co modified P911 heat resistant steel under tempering and creep conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, W.; van Zwaag, S.; Shi, Q.; Wang, W.; Yang, K.; Shan, Y. On the 650 °C thermostability of 9–12Cr heat resistant steels containing different precipitates. Acta Mater. 2017, 134, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.C.; Kim, S.D.; Park, I.; Shin, J.H.; Jang, J.H.; Kang, N. Effect of Nb on austenite grain growth in 10Cr–3Co–2W martensitic heat-resistant steel. Metall. Mater. Int. 2024, 30, 3311–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, O.; Garcia, J.; Rojas, D.; Sauthoff, G.; Inden, G. The role of Laves phase on microstructure evolution and creep strength of novel 9% Cr heat resistant steels. Intermetallics 2013, 32, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, V.; Sauthoff, G.; Vilk, J.; Inden, G.; Schneider, A.; Agamennone, R.; Singheiser, L. Martensitic/ferritic super heat-resistant 650 °C steels—Design and testing of model alloys. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, F. Effect of boron on microstructure and creep strength of advanced ferritic power plant steels. Procedia Eng. 2011, 10, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.D.; Wang, L.; Zhu, B.Y.; Jin, X.; Li, C.F.; Busso, E.P.; Li, D.F. Experimental and micromechanical investigation of precipitate size effects on the creep behaviour of a high chromium martensitic steel. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 2025, 111, 105591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Tang, L. Microstructural evolution of P92 steel with different creep life consumptions after long-term service. Metals 2024, 14, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, F. Development of creep-resistant steels and alloys for use in power plants. In Structural Alloys for Power Plants; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 250–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, J.; Fischer, F.D.; Fratzl, P.; Kozeschnik, E. Modelling of kinetics in multi-component multi-phase systems with spherical precipitates: I: Theory. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 385, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozeschnik, E.; Svoboda, J.; Fischer, F.D. Modified evolution equations for the precipitation kinetics of complex phases in multi-component systems. Calphad 2004, 28, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.Q.; Zhang, D.T.; Liu, Y.C.; Ning, B.Q.; Qiao, Z.X.; Yan, Z.S.; Li, H.J. Precipitation behavior and martensite lath coarsening during tempering of T/P92 ferritic heat-resistant steel. Int. J. Min. Metall. Mater. 2014, 21, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yan, Z. Investigation on the precipitation behavior of M3C phase in T91 ferritic steels. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2011, 241, 2411–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudova, N.; Kaibyshev, R. On the precipitation sequence in a 10% Cr steel under tempering. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Ex situ and in situ TEM investigations of carbide precipitation in a 10Cr martensitic steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 7845–7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Igarashi, M.; Muneki, S.; Abe, F. Effect of heat treatment on precipitation kinetics in high-Cr ferritic steels. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajek, H. Computer Simulation of Precipitation Kinetics in Solid Metals and Application to the Complex Power Plant Steel CB8. 2005. Available online: https://graz.pure.elsevier.com/en/projects/computer-simulation-of-precipitation-kinetics-in-solid-metals-and (accessed on 28 November 2025).
- Holzer, I.; Sommitsch, C.; Reichmann, K.; Hofer, F. Modelling and Simulation of Strengthening in Complex Martensitic 9–12% Cr Steel and a Binary Fe–Cu Alloy; Verlag der Technischen Universität Graz: Graz, Austria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gururaj, K.; Pal, S. Influence of dislocation density and grain size on precipitation kinetics on P92 grade steel. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 1364–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Matrix Phase | Grain Size/m | Sub-Grain Size | Dislocation Density/m−2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCC_A2 | 30 × 10−6 | 10 × 10−6 | 1.0 × 1015 |
| Precipitates Phase | Nucleation Site | γ/(J/m2) |
|---|---|---|
| M23C6 | Grain boundary | 0.190 |
| Laves phase | Sub-grain boundary | 0.105 |
| Nb-rich MX | Grain boundary | 0.575 |
| V-rich MX | Sub-grain boundary Dislocation | 0.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, B.C.; Kim, S.-D.; Park, I.; Jang, J.H.; Kang, N. Microstructure Evolution and Modelling During Tempering Heat Treatment at 670 °C in 9–12 wt.% Cr Ferritic/Martensitic Heat-Resistant Steel. Metals 2025, 15, 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121350
Park BC, Kim S-D, Park I, Jang JH, Kang N. Microstructure Evolution and Modelling During Tempering Heat Treatment at 670 °C in 9–12 wt.% Cr Ferritic/Martensitic Heat-Resistant Steel. Metals. 2025; 15(12):1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121350
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Bong Cheon, Sung-Dae Kim, Ihho Park, Jae Hoon Jang, and Namhyun Kang. 2025. "Microstructure Evolution and Modelling During Tempering Heat Treatment at 670 °C in 9–12 wt.% Cr Ferritic/Martensitic Heat-Resistant Steel" Metals 15, no. 12: 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121350
APA StylePark, B. C., Kim, S.-D., Park, I., Jang, J. H., & Kang, N. (2025). Microstructure Evolution and Modelling During Tempering Heat Treatment at 670 °C in 9–12 wt.% Cr Ferritic/Martensitic Heat-Resistant Steel. Metals, 15(12), 1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121350







