Reproducible Thermo-Fluid–Solid-Coupled Modeling of Wet Milling of Al6061: Parametric Influence and Surface Integrity Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
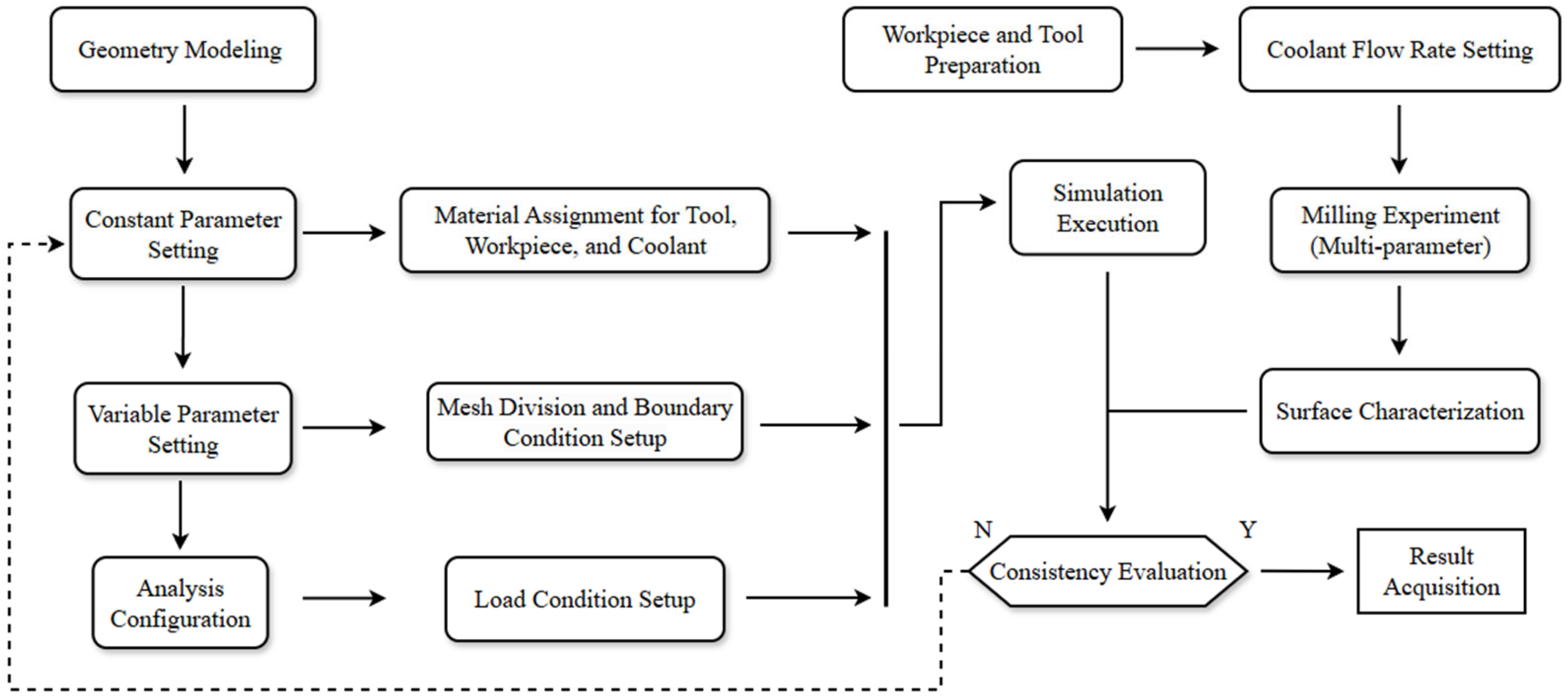
2. Methodology
2.1. CEL Method
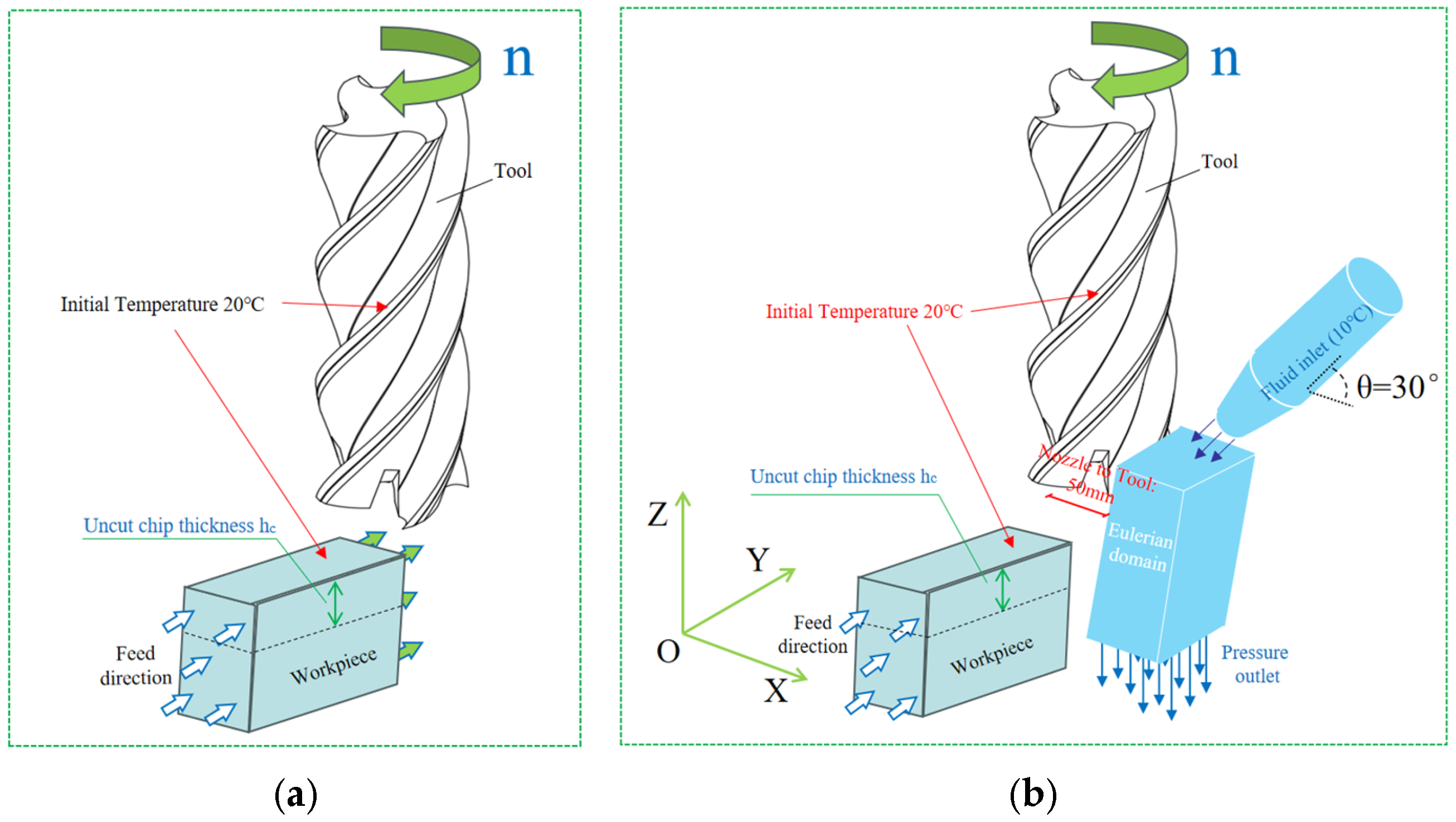
2.2. Modeling
2.3. Material Constitutive Model
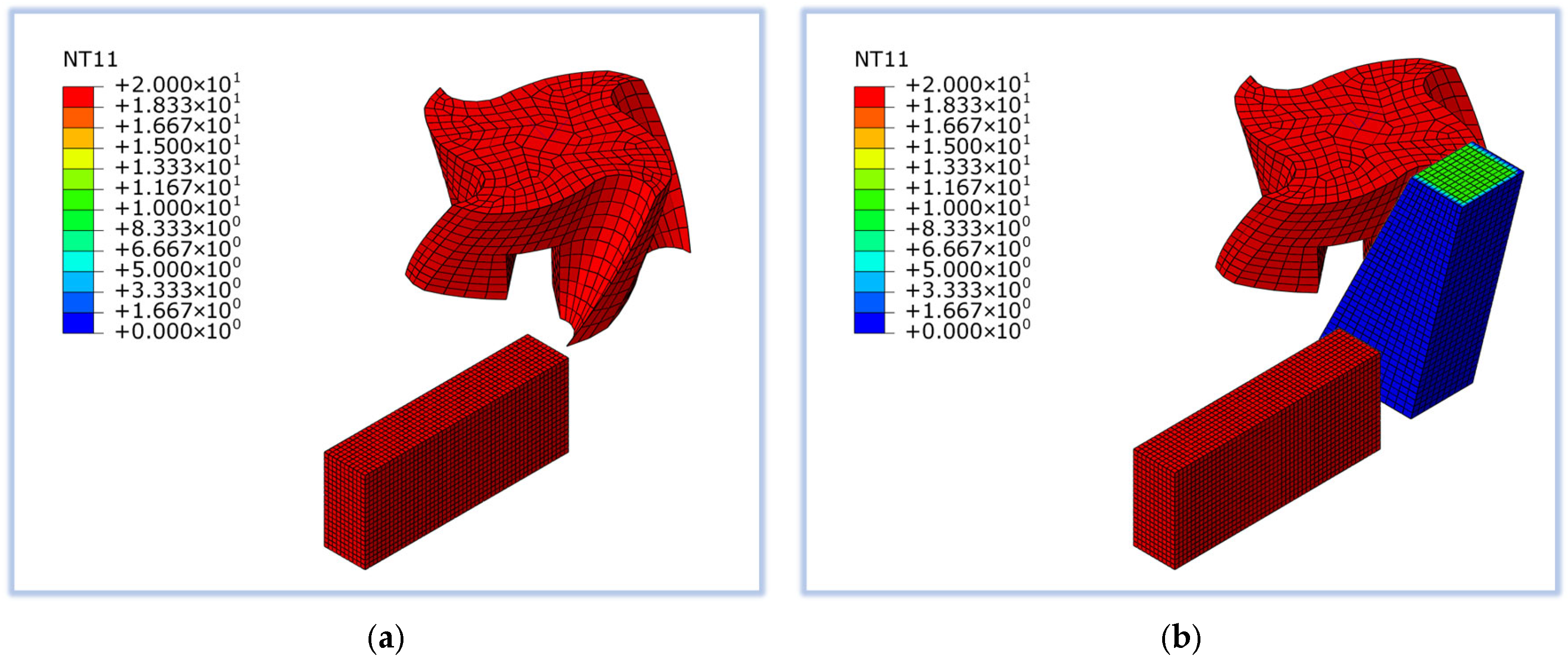
2.4. Mesh and Boundary Conditions
2.5. Operating Conditions Design
2.6. Output Results
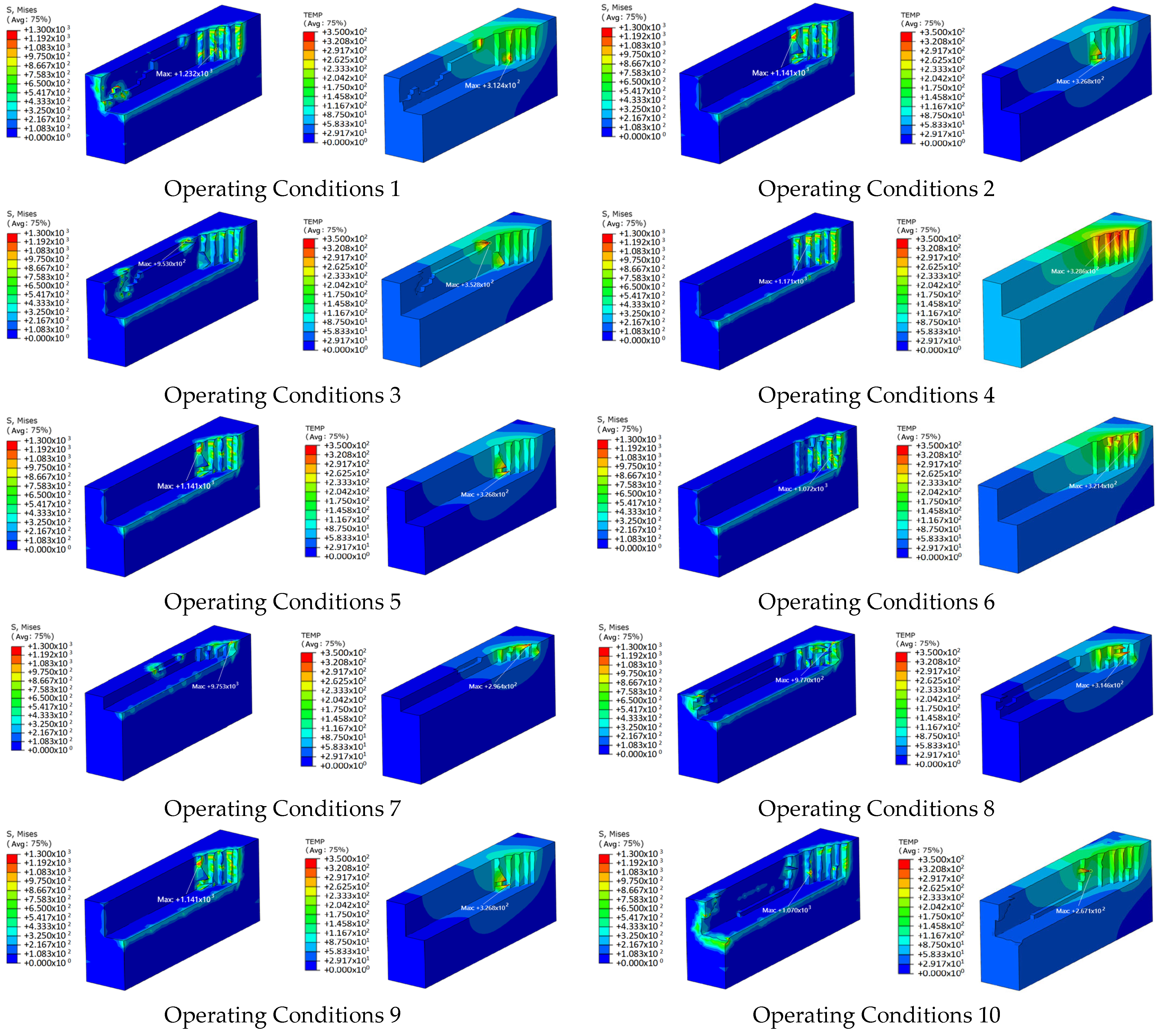
2.6.1. Influence of Cutting Parameters
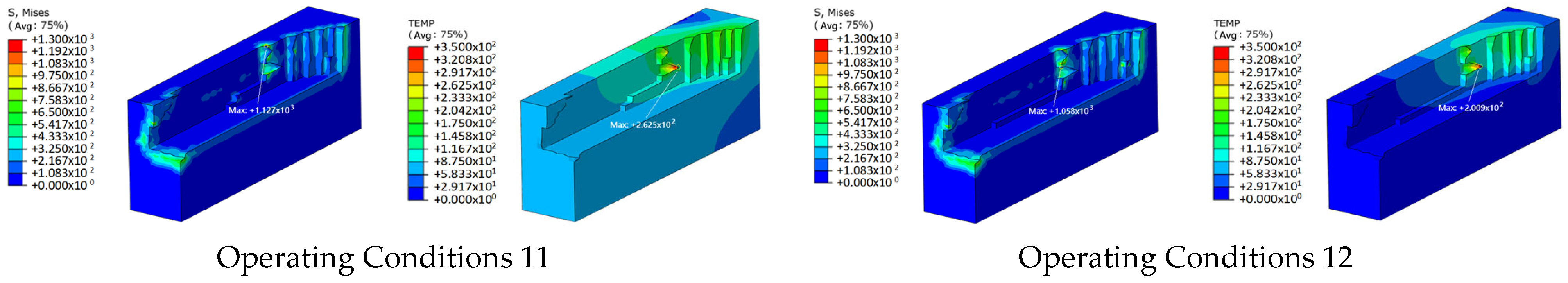
2.6.2. Effect of Coolant Flow Rate
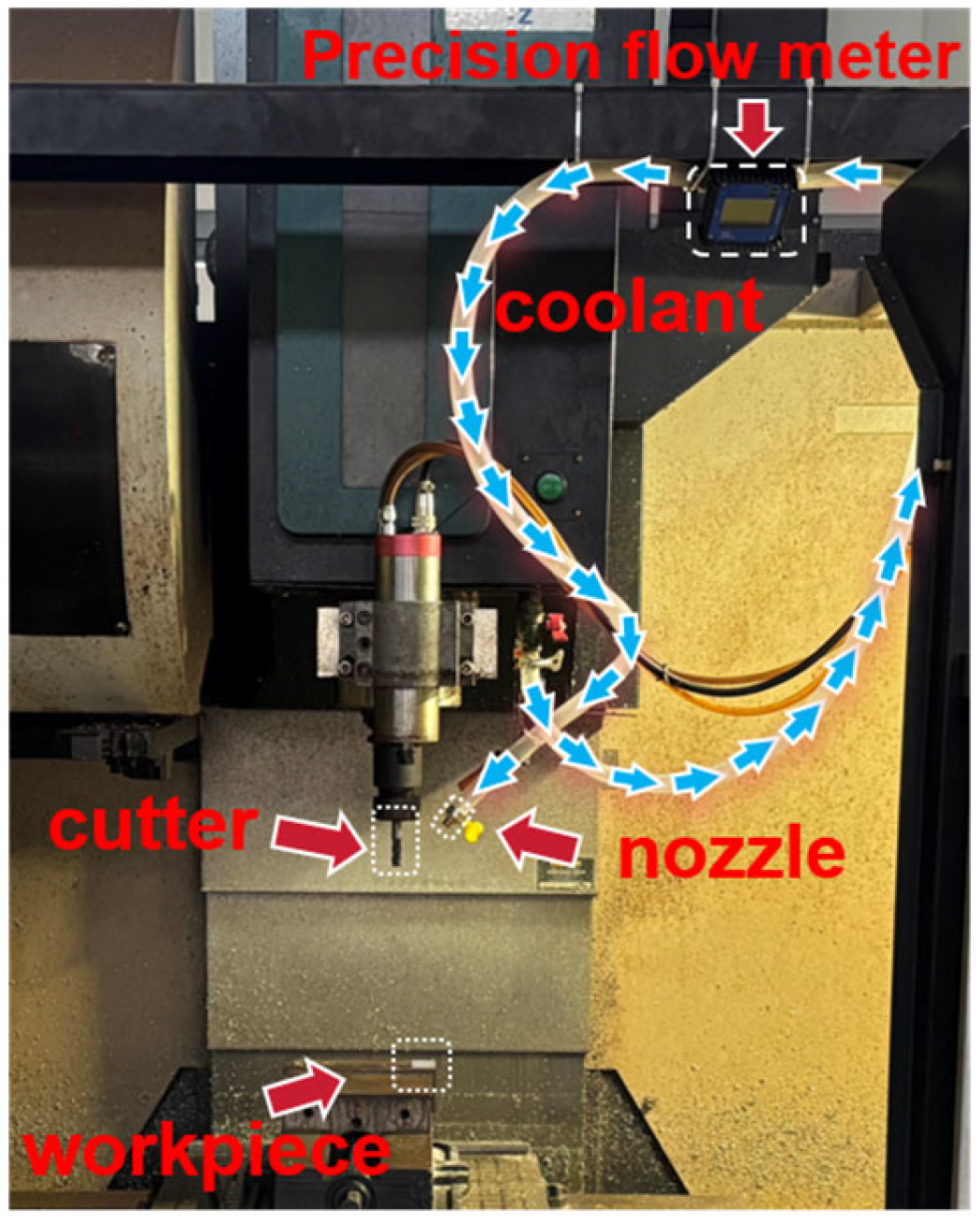
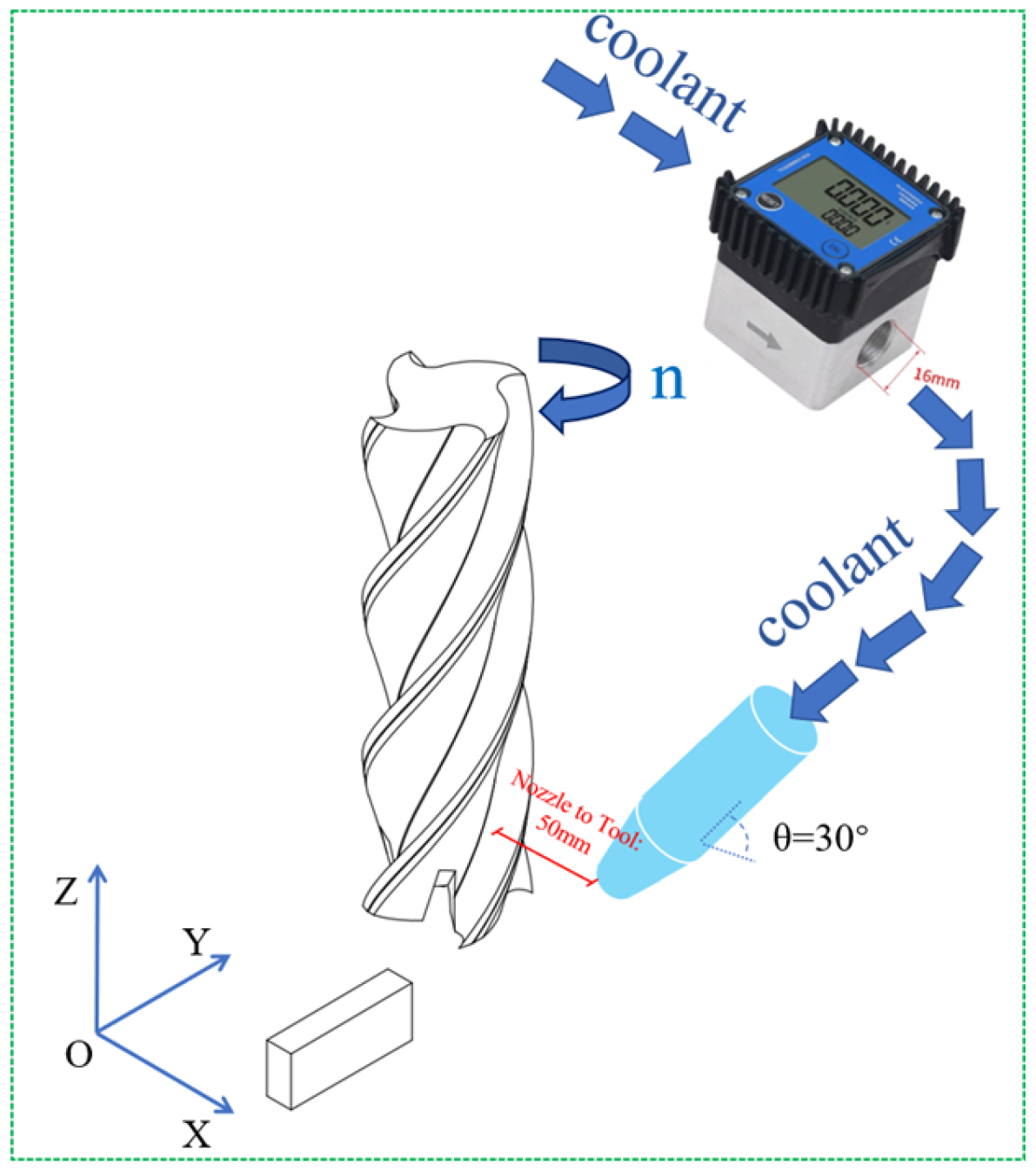
2.7. Experimental Protocol for Surface Based Trend Validation
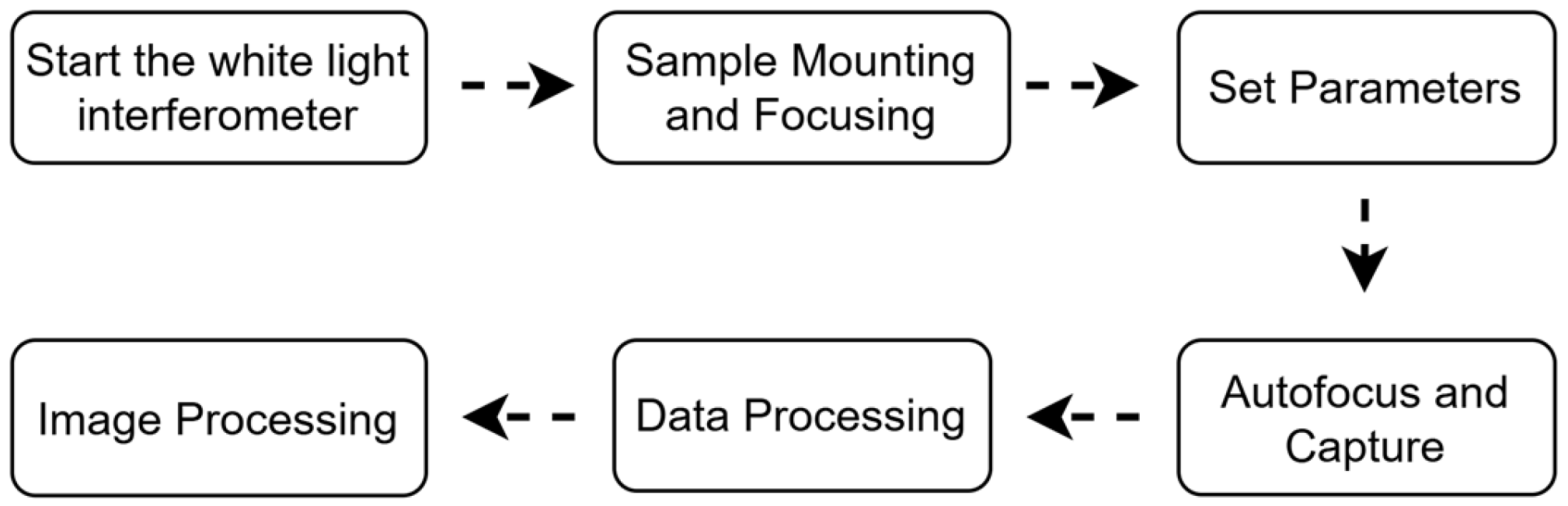
Optical Surface Observation
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
4.1. Principal Findings on Thermal and Mechanical Responses
4.2. Influence on Surface Integrity
4.3. Guidelines for Process Optimization
4.4. Scope and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trzepieciński, T.; Najm, S.M.; Oleksik, V.; Vasilca, D.; Paniti, I.; Szpunar, M. Recent developments and future challenges in incremental sheet forming of Aluminium and Aluminium alloy sheets. Metals 2022, 12, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibola, O.O.; Adebayo, A.O.; Borisade, S.G.; Adigun, O.D.; Babalola, B.A. Electrochemical Corrosion Behaviour of Heat-Treated AA6063 Aluminium Matrix Composites Reinforced with Alumina, Titania and Hybrid Powders in 1.0 M HCl Solution. FUOYE J. Pure Appl. Sci. (FJPAS) 2024, 9, 130–146. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, B.; Simões, S. Production and characterization of hybrid Al6061 nanocomposites. Metals 2024, 14, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttan, A.A.; Rajesh, R.; Anand, M.D. Enhancing Mechanical Properties of Al6061 Alloy with Zirconium and Titanium Carbide Reinforcements. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 25468–25482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Mol, J.M.C.; Hannour, F.; Zhuang, L.; Terryn, H.; De Wit, J.H.W. The influence of copper content on intergranular corrosion of model AlMgSi (Cu) alloys. Mater. Corros. 2008, 59, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairy, S.K.; Rometsch, P.A.; Diao, K.; Nie, J.F.; Davies, C.H.J.; Birbilis, N. Exploring the electrochemistry of 6xxx series aluminium alloys as a function of Si to Mg ratio, Cu content, ageing conditions and microstructure. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 190, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, A.P.; Mandal, A.B.; Das, D. Mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of artificially aged Al-Mg-Si alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 1005–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; To, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.D. An investigation on surface finishing in ultra-precision raster milling of aluminum alloy 6061. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 229, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, J.; Zheng, M.; Si, B.; Zhang, L. Based on the instantaneous milling thickness of unequal pitch end milling cutter milling force solution and simulation research. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 134, 1333–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.B.; Cho, D.W.; Lee, S.J.; Chu, C.N. A fluid dynamic analysis model of the ultra-precision cutting mechanism. CIRP Ann. 1999, 48, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.P.; Rolim, T.L.; Oliveira, C.A.; Moura, A.E.; Silva, J.C.A. Analysis of the surface roughness and cutting tool wear using a vapor compression assisted cooling system to cool the cutting fluid in turning operation. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 44, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xue, F.; Liu, G.; Chen, W.; Wang, C. Microstructure evolution of titanium alloy in cryogenic cooling cutting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2025, 341, 118914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Monaca, A.; Murray, J.W.; Liao, Z.; Speidel, A.; Robles-Linares, J.A.; Axinte, D.A.; Hardy, M.C.; Clare, A.T. Surface integrity in metal machining-Part II: Functional performance. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2021, 164, 103718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Cao, W.; Chen, Z.; Yan, J.; Wu, J.; Hu, Y.; Qu, J.; Zhang, M. Numerical simulation and experimental study of grinding temperature field of high-temperature alloy under different grinding parameters. Mach. Tool Hydraul. 2022, 50, 76–81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Ni, C.; Zhao, T.; He, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lan, J. Simulation study of orthogonal milling of 7150-T6 aluminum alloy based on ABAQUS. Tool Eng. 2023, 57, 80–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Morgan, M.N.; Chen, X.W.; Wang, Y.K. Study on the convection heat transfer coefficient of coolant and the maximum temperature in the grinding process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 42, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Meurer, M.; Schraknepper, D.; Bergs, T. Investigation of the cutting fluid’s flow and its thermomechanical effect on the cutting zone based on fluid–structure interaction (FSI) simulation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sofyani, S.; Marinescu, I.D. Analytical modeling of the thermal aspects of metalworking fluids in the milling process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 3953–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Jiao, F. Modeling of heat source in grinding zone and numerical simulation for grinding temperature field. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 3077–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Usuki, H.; Tanaka, R.; Morigo, C.; Yukinari, S. Research on effect of ultra-high pressure coolant supplied from flank face in end milling of Ti-6Al-4V supported by CFD simulations. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 118, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, C.; Tian, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S. Mechanical behaviors of pipeline inspection gauge (pig) in launching process based on Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian (CEL) method. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2022, 197, 104622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardt, M.; Bergs, T. Considering multiple process observables to determine material model parameters for FE-cutting simulations. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 113, 3419–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.R. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics, The Hague, The Netherlands, 19–21 April 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Huo, W. Finite element analysis of single-grit grinding of GH4169 superalloy based on ABAQUS. Tool Eng. 2023, 57, 86–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Akram, S.; Jaffery, S.H.I.; Khan, M.; Fahad, M.; Mubashar, A.; Ali, L. Numerical and experimental investigation of Johnson–Cook material models for aluminum (Al 6061-T6) alloy using orthogonal machining approach. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 1687814018797794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesuer, D.R.; Kay, G.J.; LeBlanc, M.M. Modeling Large-Strain, High-Rate Deformation in Metals; (No. UCRL-JC-134118); Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL): Livermore, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Zhao, M.; Mao, J.; Liang, S.Y. A Ti-6Al-4V milling force prediction model based on the Taylor factor model and microstructure evolution of the milling surface. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Deng, W.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, H. A study of diamond cutting mechanism for aluminum alloy 6061 with AlFeSi particle effect: Modeling and simulation. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 104, 384–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, N.S.; Hong, K.M.; Shin, Y.C. Comparative assessment of dendrite growth and microstructure predictions during laser welding of Al 6061 via 2D and 3D phase field models. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2020, 172, 109291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.H.; Ko, D.C.; Lim, H.J.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, B.M. FE-simulation coupled with CFD analysis for prediction of residual stresses relieved by cryogenic heat treatment of Al6061 tube. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 14, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, F.; Arnautovic, Z.; Heberle, F.; Brüggemann, D. Thermophysical Properties of Silicon Oxide Nanoparticles in Water and Ethylene Glycol–Water Dispersions. Fluids 2024, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandron, M.A.; Hurd, R.C.; Belden, J.L.; Bower, A.F.; Fennell, W.; Truscott, T.T. Modeling of hyperelastic water-skipping spheres using Abaqus/Explicit. In Proceedings of the SIMULIA Community Conference, Providence, RI, USA, 19–22 May 2014. [Google Scholar]

| Material | AL 6061 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (MPa) | B (MPa) | C | n | m |
| 324 | 114 | 0.002 | 0.42 | 1.34 |
| Initial failure strain, D1 | −0.77 | |||
| Exponential factor, D2 | 1.45 | |||
| Exponential factor, D3 | −0.47 | |||
| Exponential factor, D4 | 0.0 | |||
| Exponential factor, D5 | 1.6 | |||
| Troom | 20 °C | |||
| Tmelt | 652 °C | |||
| λ (W/m·K) | 180 | |||
| Material | ρ (kg/m3) | E (MPa) | ν | Expansion Coeff. (1/°C) | λ (W/m·K) | C (J/kg·K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YG6X | 14,600 | 640,000 | 0.22 | 4.7 × 10−6 | 79.6 | 176 |
| Density | Viscosity | Specific Heat Capacity | Thermal Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| ρ (kg/m) | ν (Pa·s) | (kJ/kg·K) | (W/m·K) |
| 1.000 × 103 | 8.9 × 10−4 | 4.181 | 0.607 |
| Linear Us-Up Model | |||
| C0 (m/s) | S | Γ0 | |
| 1.483 × 103 | 0 | 0 | |
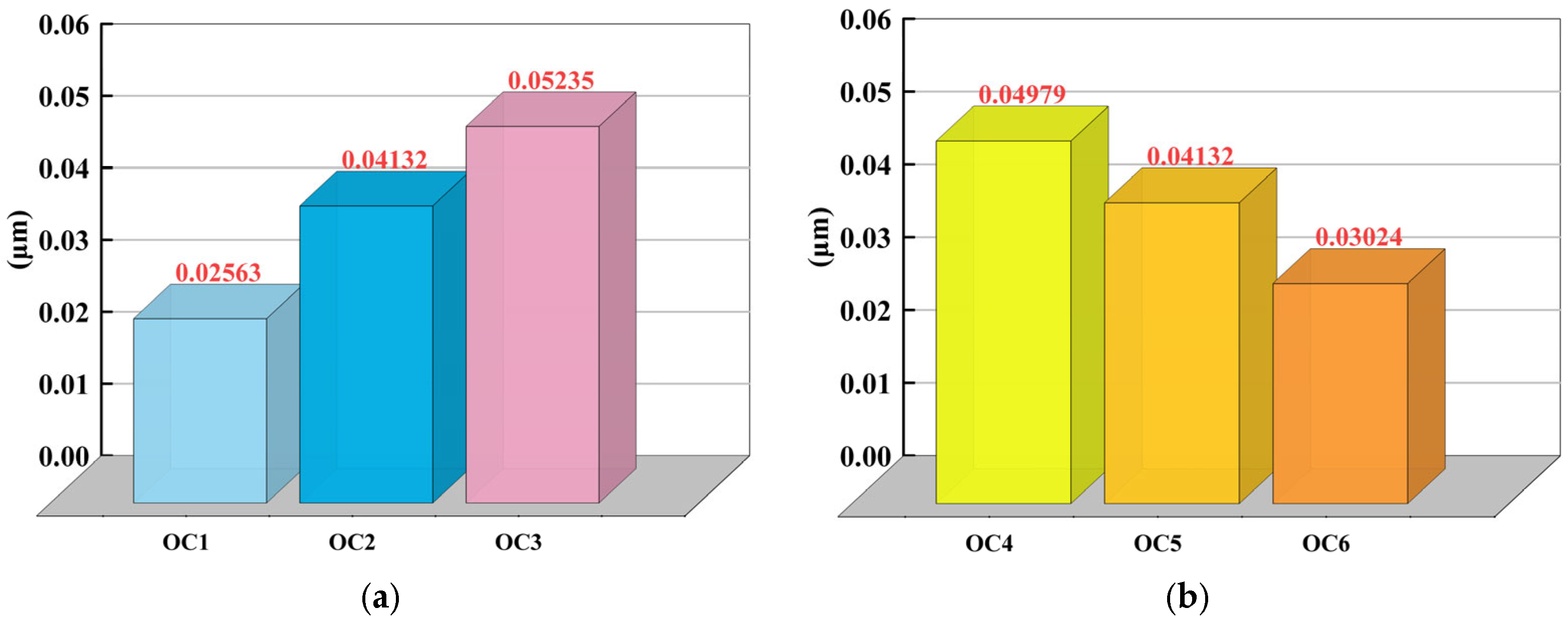
| Operating Conditions | Milling Depth (mm) | Feed Rate (mm/min) | Feed Per Tooth (mm/Tooth) | Spindle Speed (r/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.5 | 2100 | 0.088 | 6000 |
| 2 | 1.5 | 3000 | 0.125 | 6000 |
| 3 | 1.5 | 3900 | 0.163 | 6000 |
| 4 | 1.5 | 3000 | 0.188 | 4000 |
| 5 | 1.5 | 3000 | 0.125 | 6000 |
| 6 | 1.5 | 3000 | 0.094 | 8000 |
| 7 | 0.5 | 3000 | 0.125 | 6000 |
| 8 | 1 | 3000 | 0.125 | 6000 |
| 9 | 1.5 | 3000 | 0.125 | 6000 |
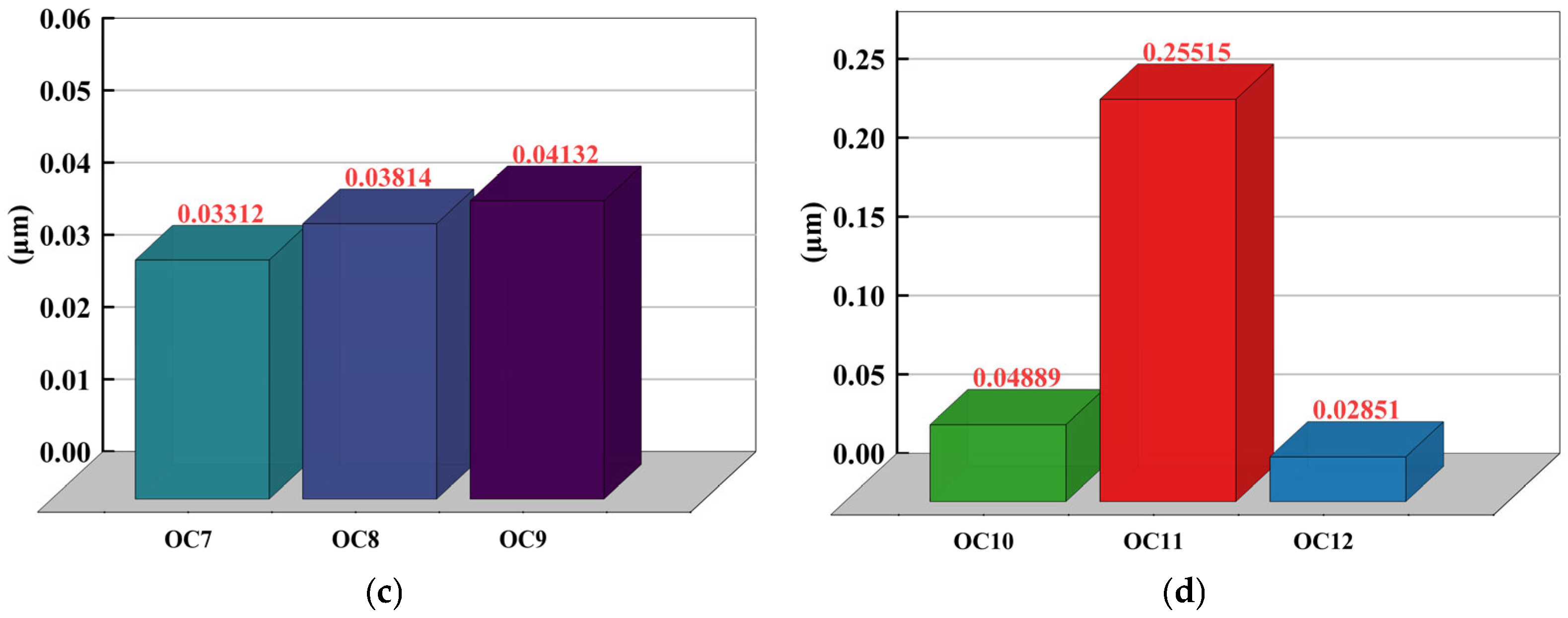
| Operating Conditions | Milling Depth (mm) | Feed Rate (mm/min) | Feed per Tooth (mm/Tooth) | Spindle Speed (r/min) | Coolant Flow Rate (mm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1.5 | 3000 | 0.125 | 6000 | 300 |
| 11 | 1.5 | 3000 | 0.125 | 6000 | 800 |
| 12 | 1.5 | 3000 | 0.125 | 6000 | 1300 |
| Operating Conditions | Average Line Roughness (μm) | Operating Conditions | Average Line Roughness (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.485 | 7 | 0.543 |
| 2 | 0.579 | 8 | 0.555 |
| 3 | 0.631 | 9 | 0.579 |
| 4 | 0.616 | 10 | 0.651 |
| 5 | 0.579 | 11 | 1.181 |
| 6 | 0.514 | 12 | 0.576 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Wu, X.; Tong, X.; Chen, E.; Zhang, C. Reproducible Thermo-Fluid–Solid-Coupled Modeling of Wet Milling of Al6061: Parametric Influence and Surface Integrity Assessment. Metals 2025, 15, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111256
Xiao Y, Wu X, Tong X, Chen E, Zhang C. Reproducible Thermo-Fluid–Solid-Coupled Modeling of Wet Milling of Al6061: Parametric Influence and Surface Integrity Assessment. Metals. 2025; 15(11):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111256
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yanping, Xuanzhong Wu, Xin Tong, Enqing Chen, and Cheng Zhang. 2025. "Reproducible Thermo-Fluid–Solid-Coupled Modeling of Wet Milling of Al6061: Parametric Influence and Surface Integrity Assessment" Metals 15, no. 11: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111256
APA StyleXiao, Y., Wu, X., Tong, X., Chen, E., & Zhang, C. (2025). Reproducible Thermo-Fluid–Solid-Coupled Modeling of Wet Milling of Al6061: Parametric Influence and Surface Integrity Assessment. Metals, 15(11), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15111256






