Experimental Study on Backwater-Assisted Picosecond Laser Trepanning of 304 Stainless Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Laser Drilling Experiment
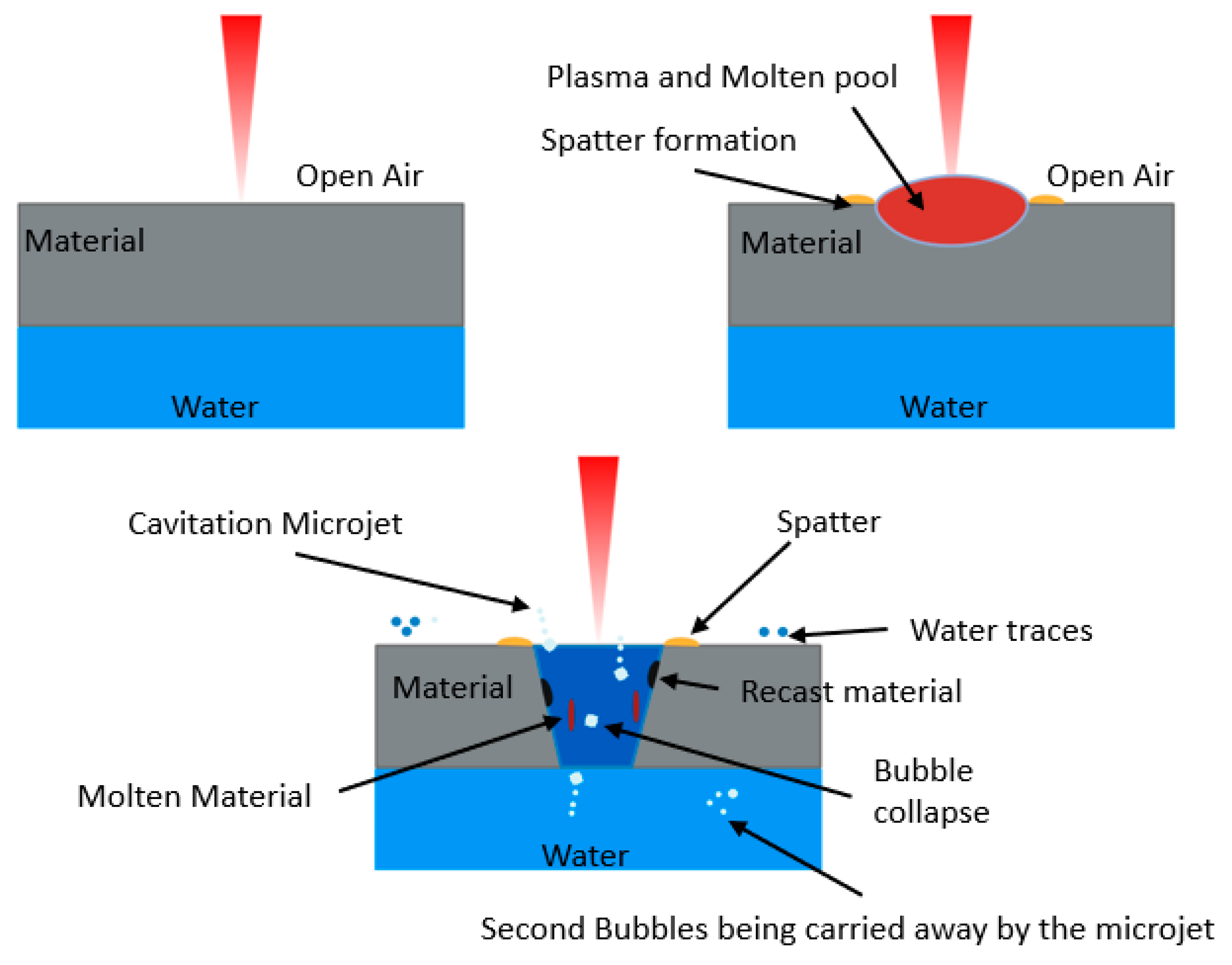
2.1. Principle of Backwater-Assisted Laser Drilling
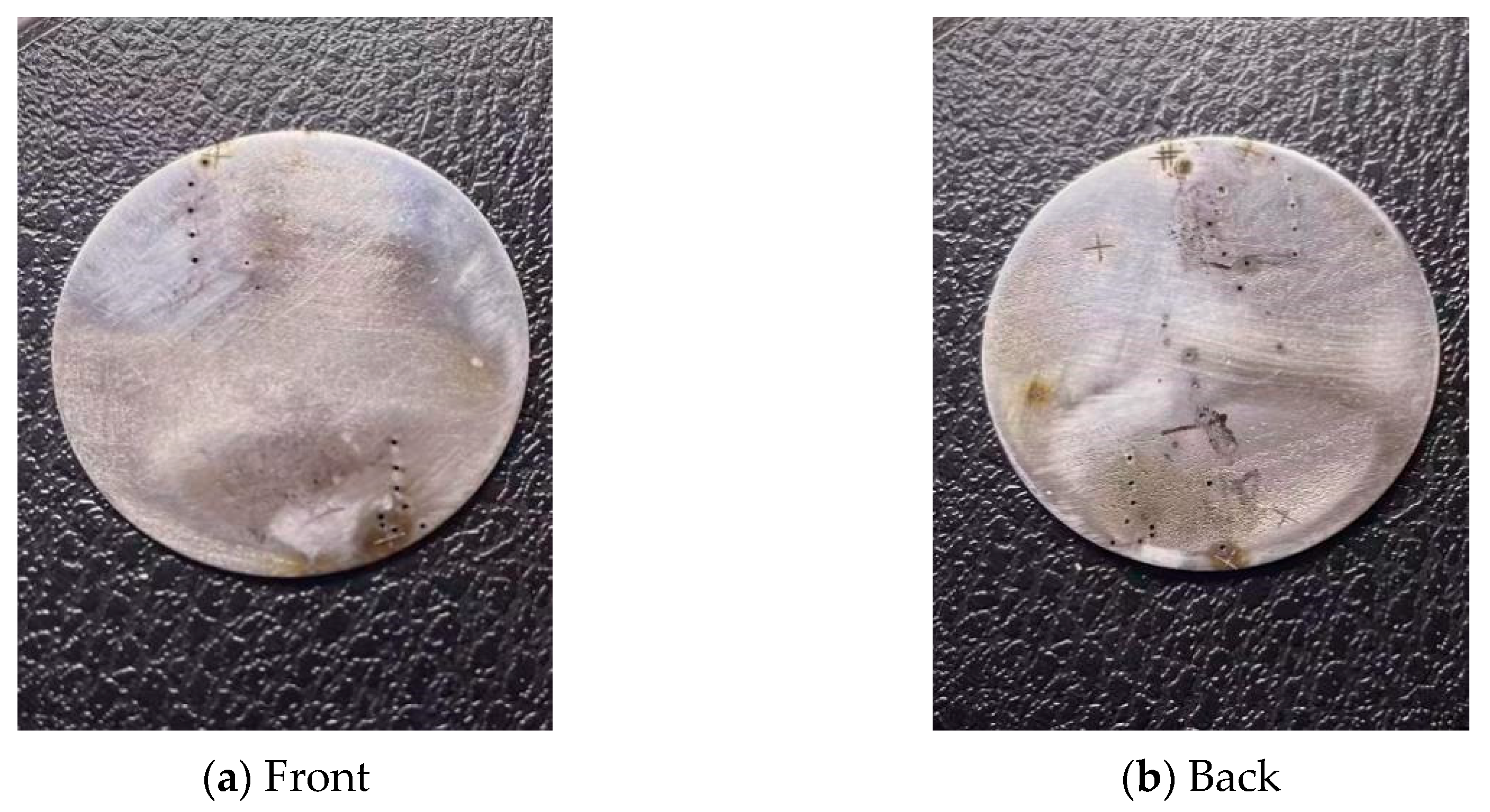
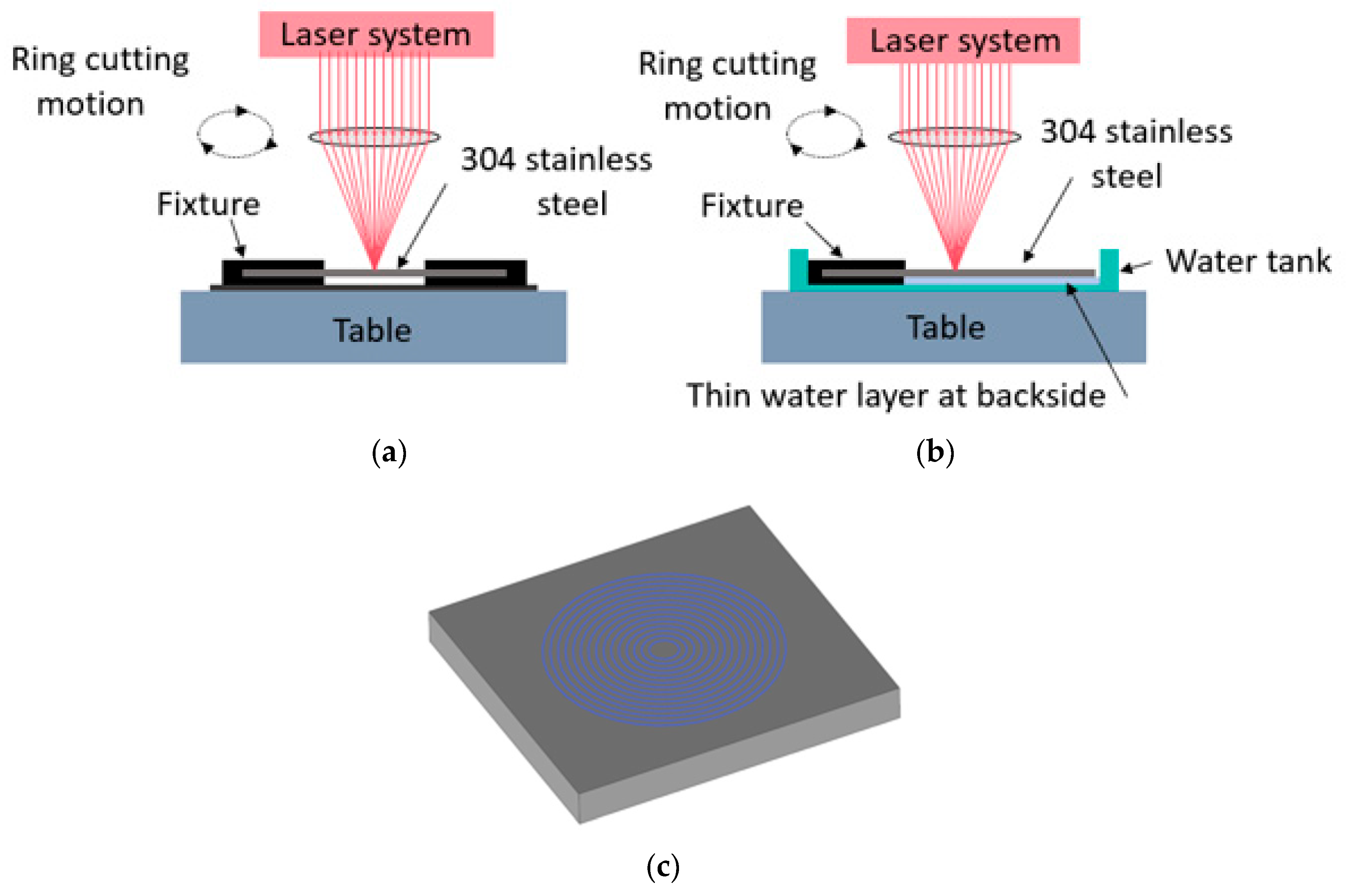
2.2. Experimental Materials and Setup
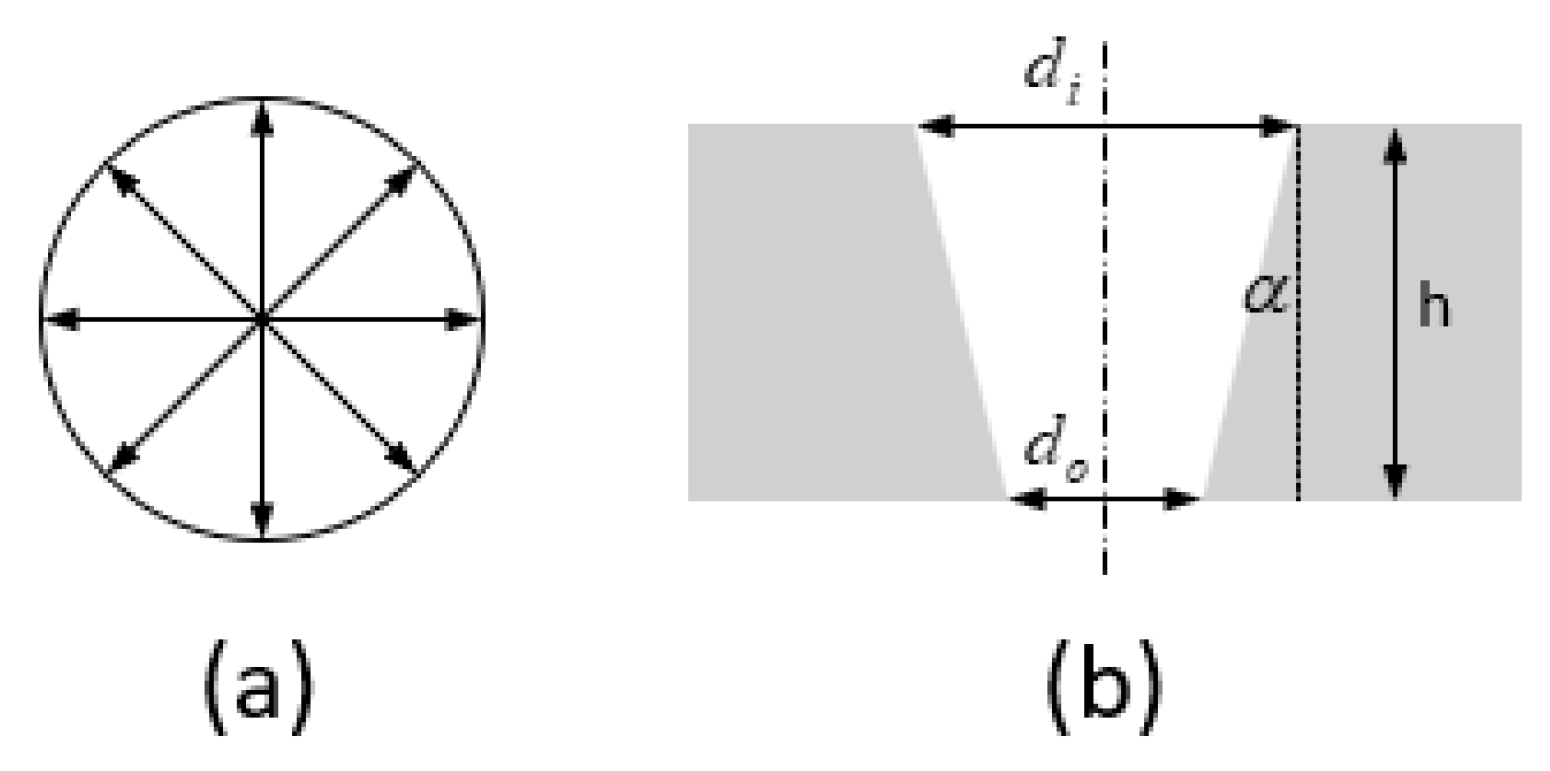
2.3. Experimental Results
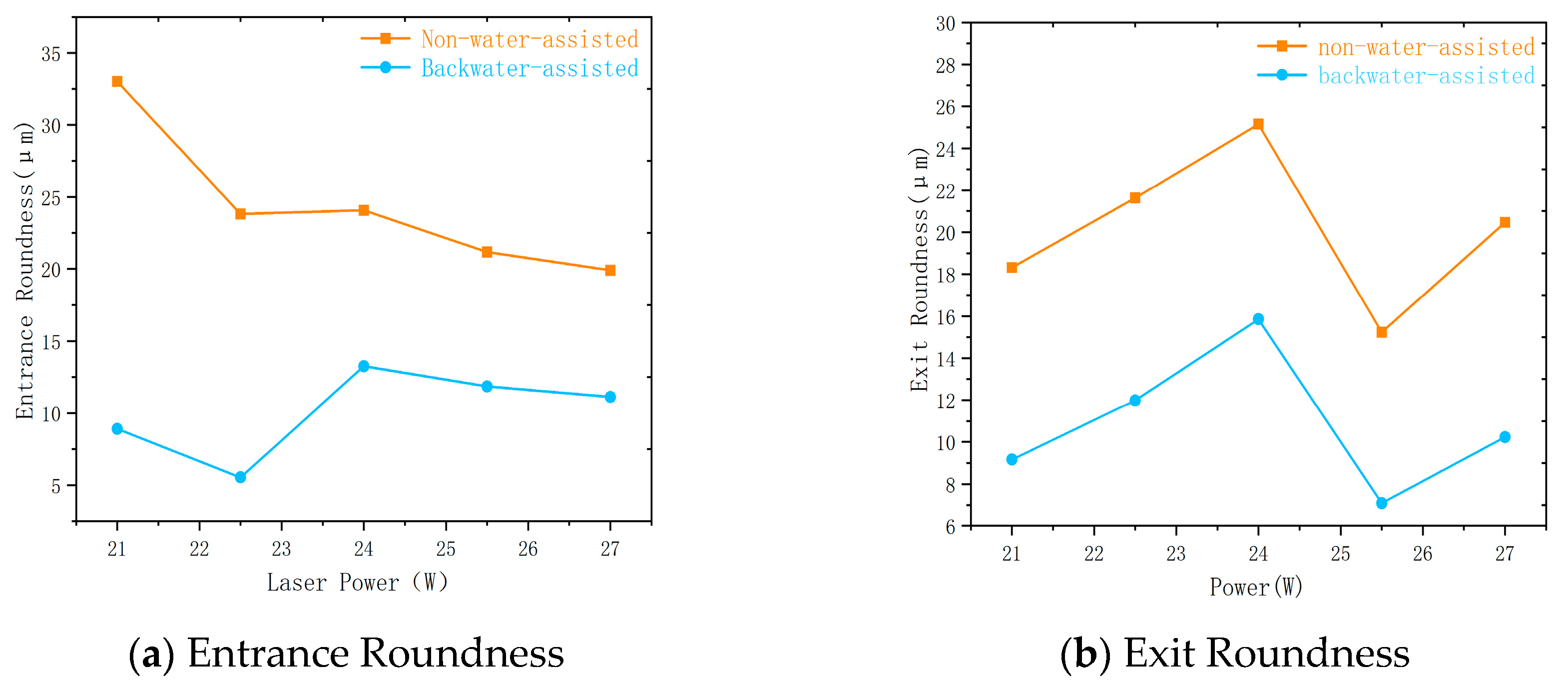
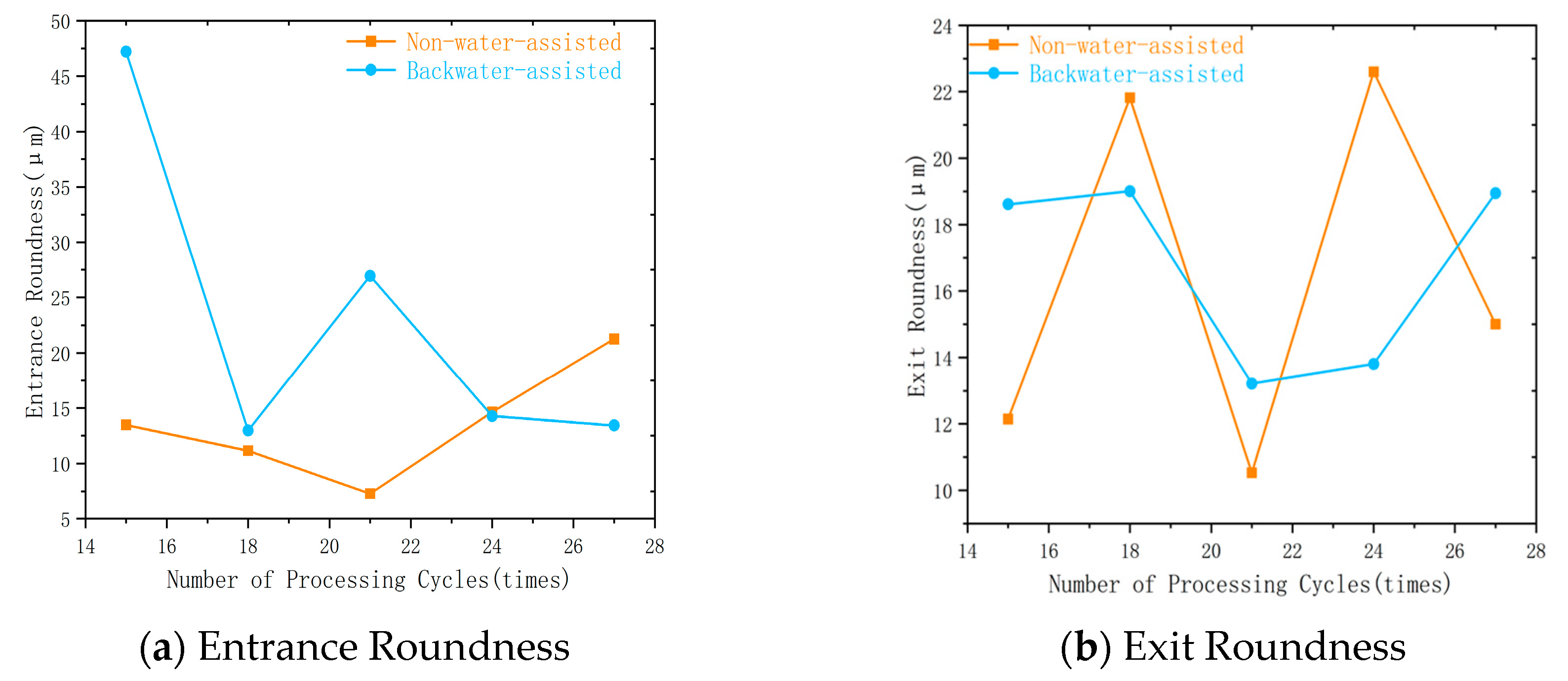
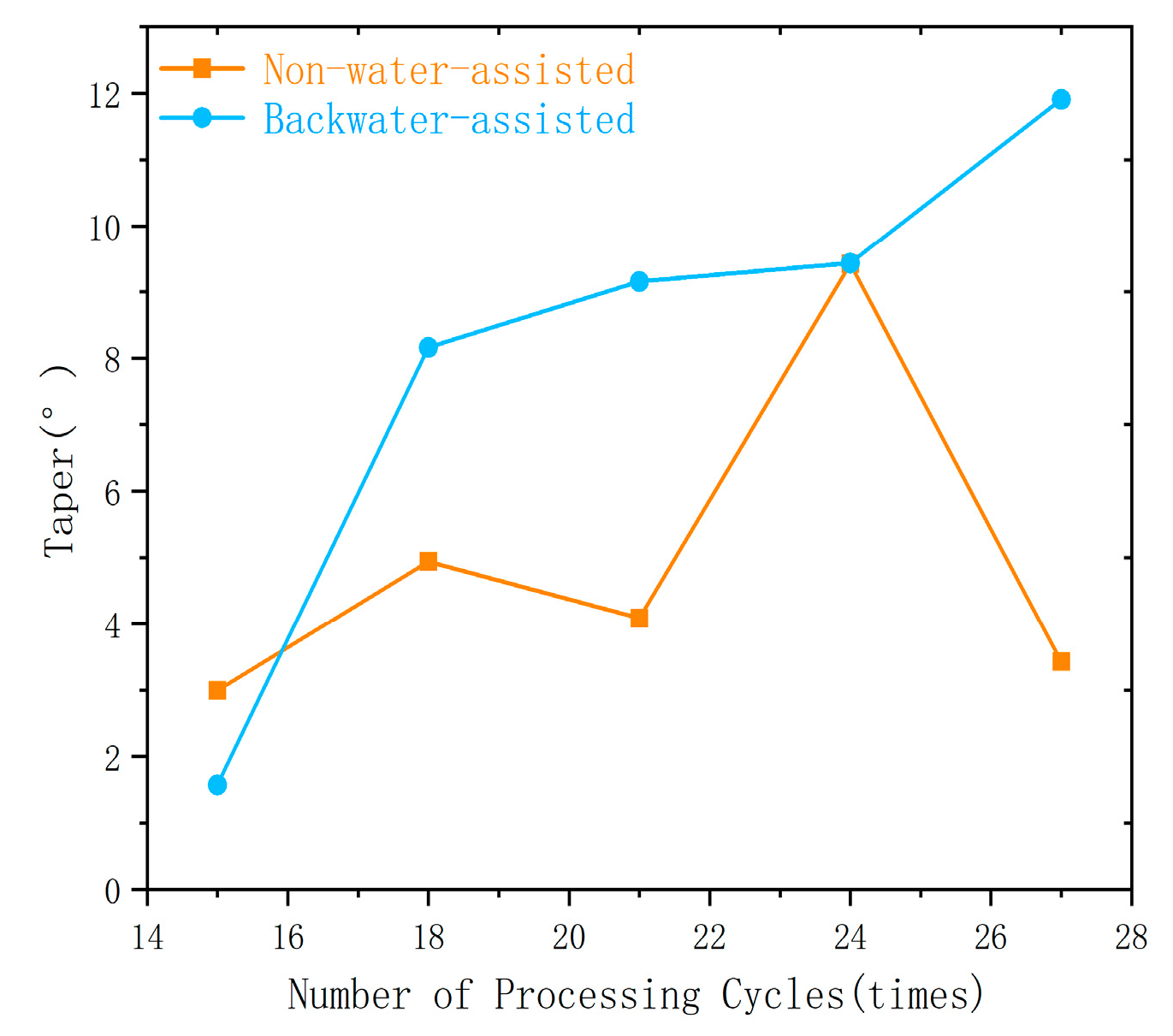
3. Comparison and Analysis of Laser Drilling Results in Two Processing Environments
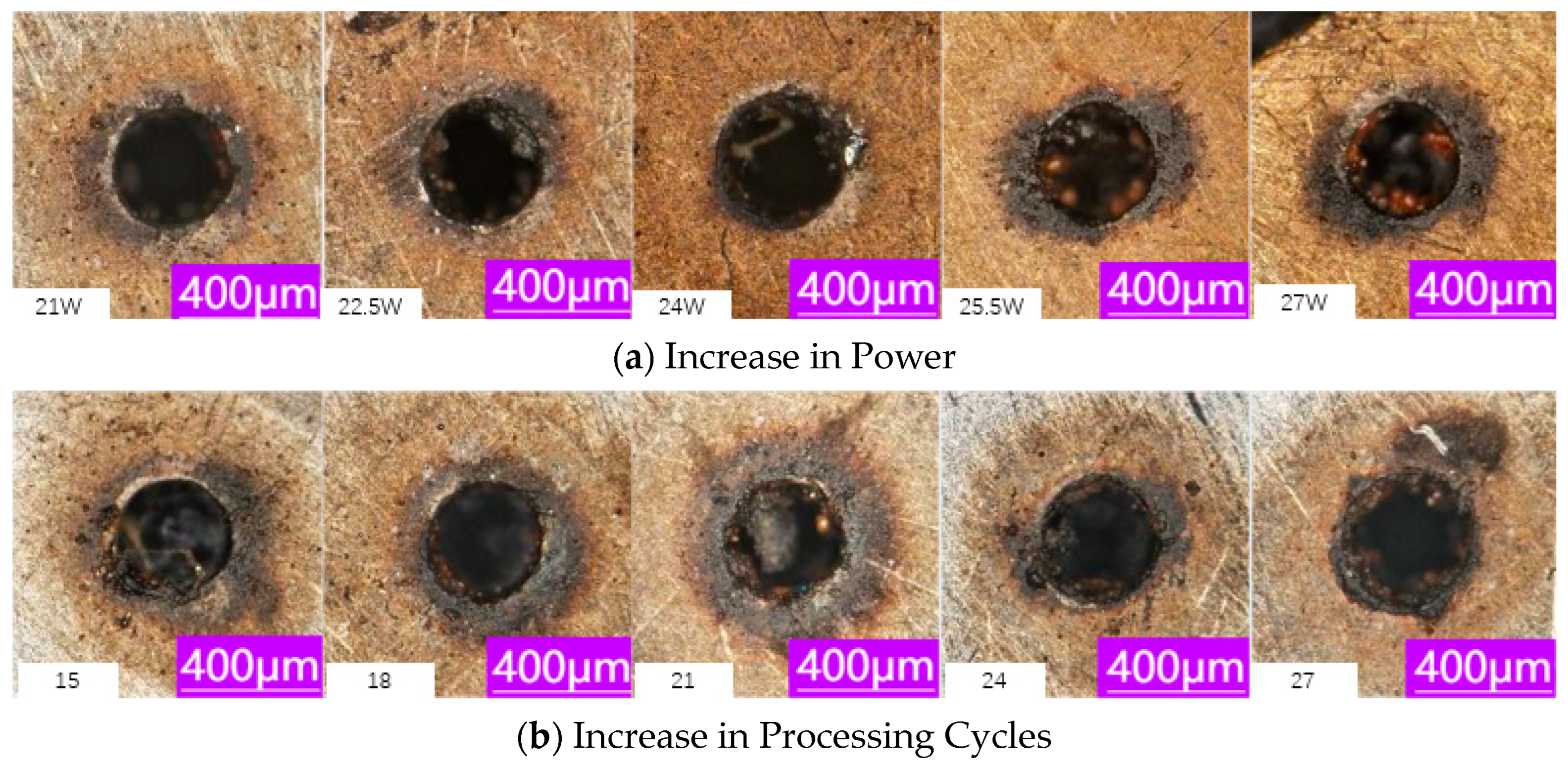
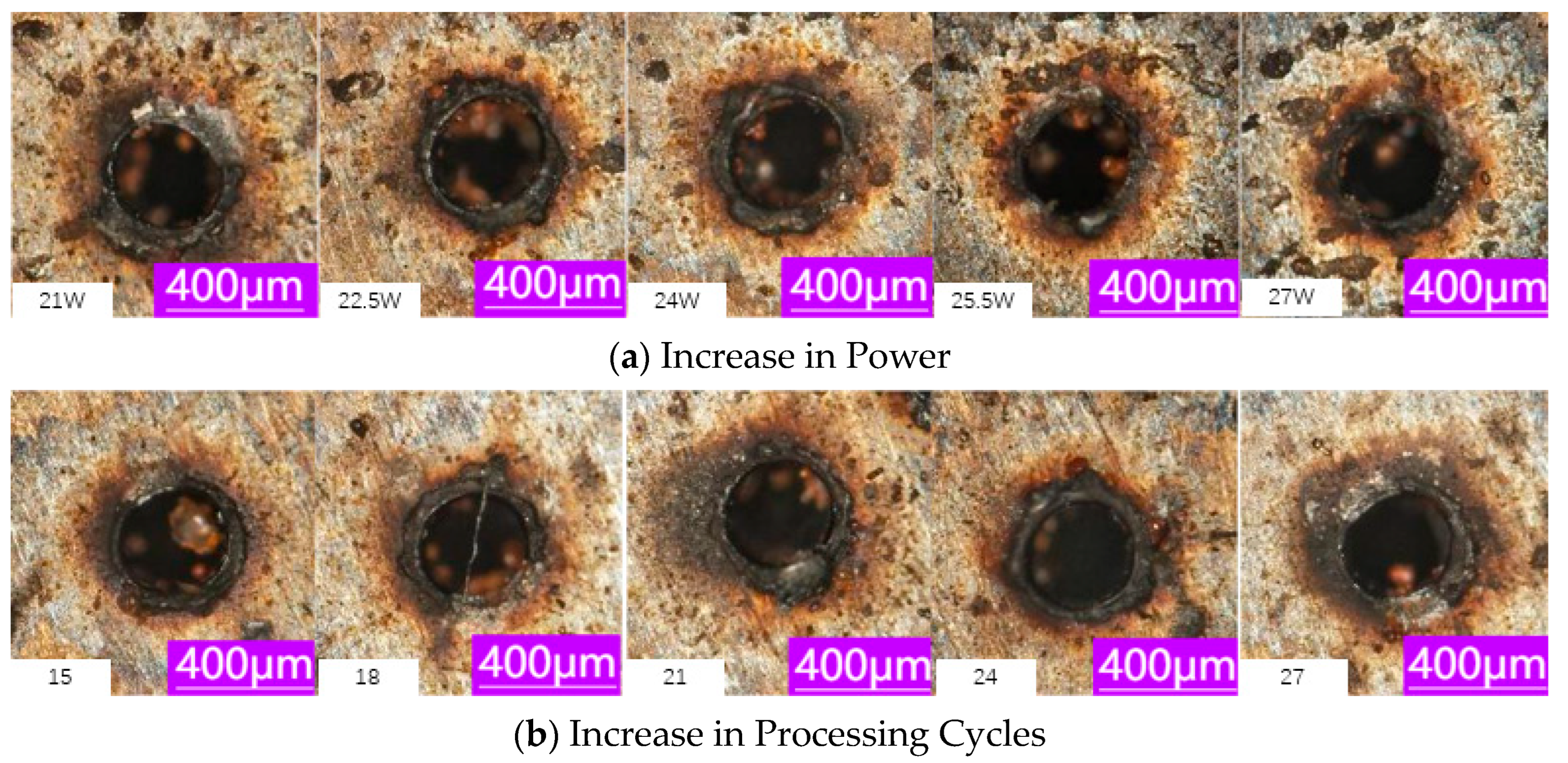
3.1. Laser Power
3.2. Number of Processing Cycles
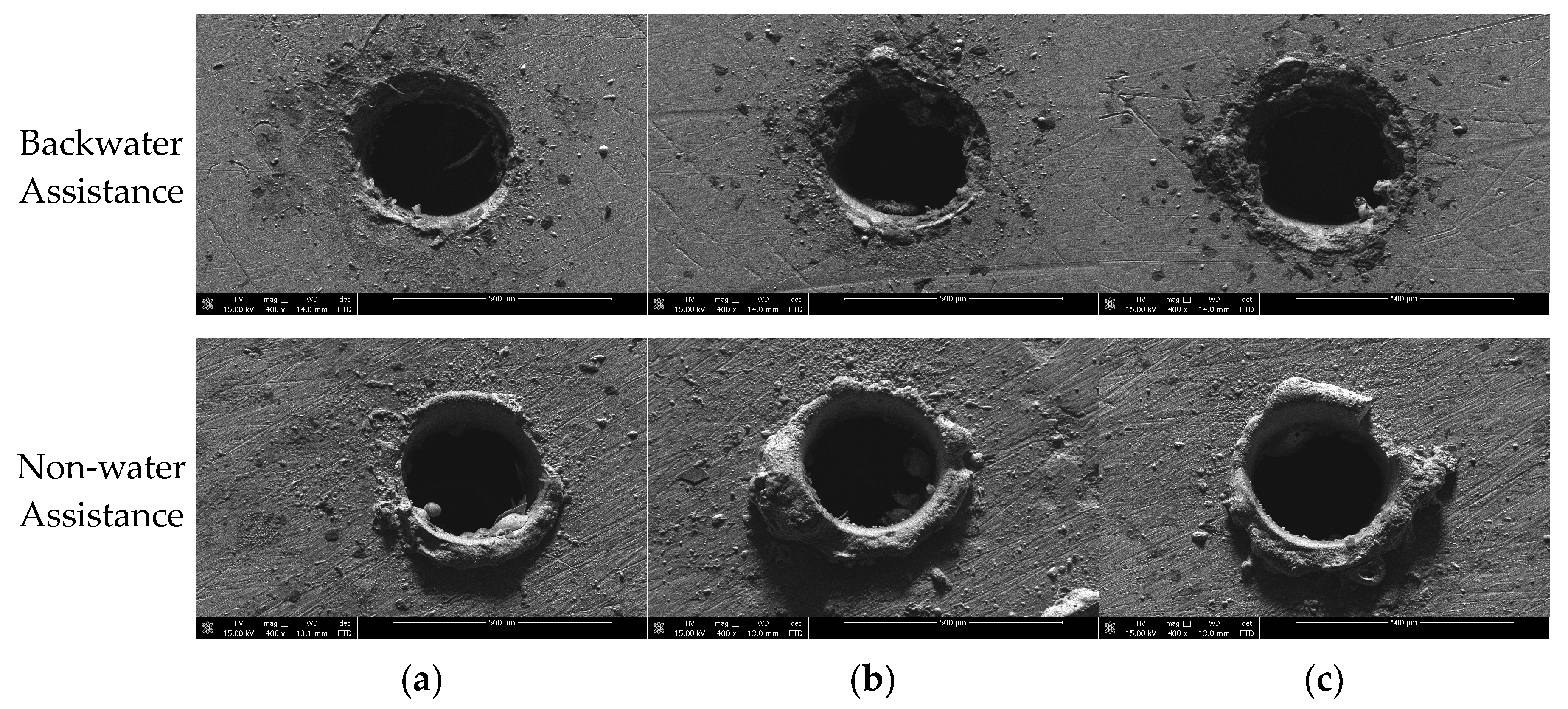
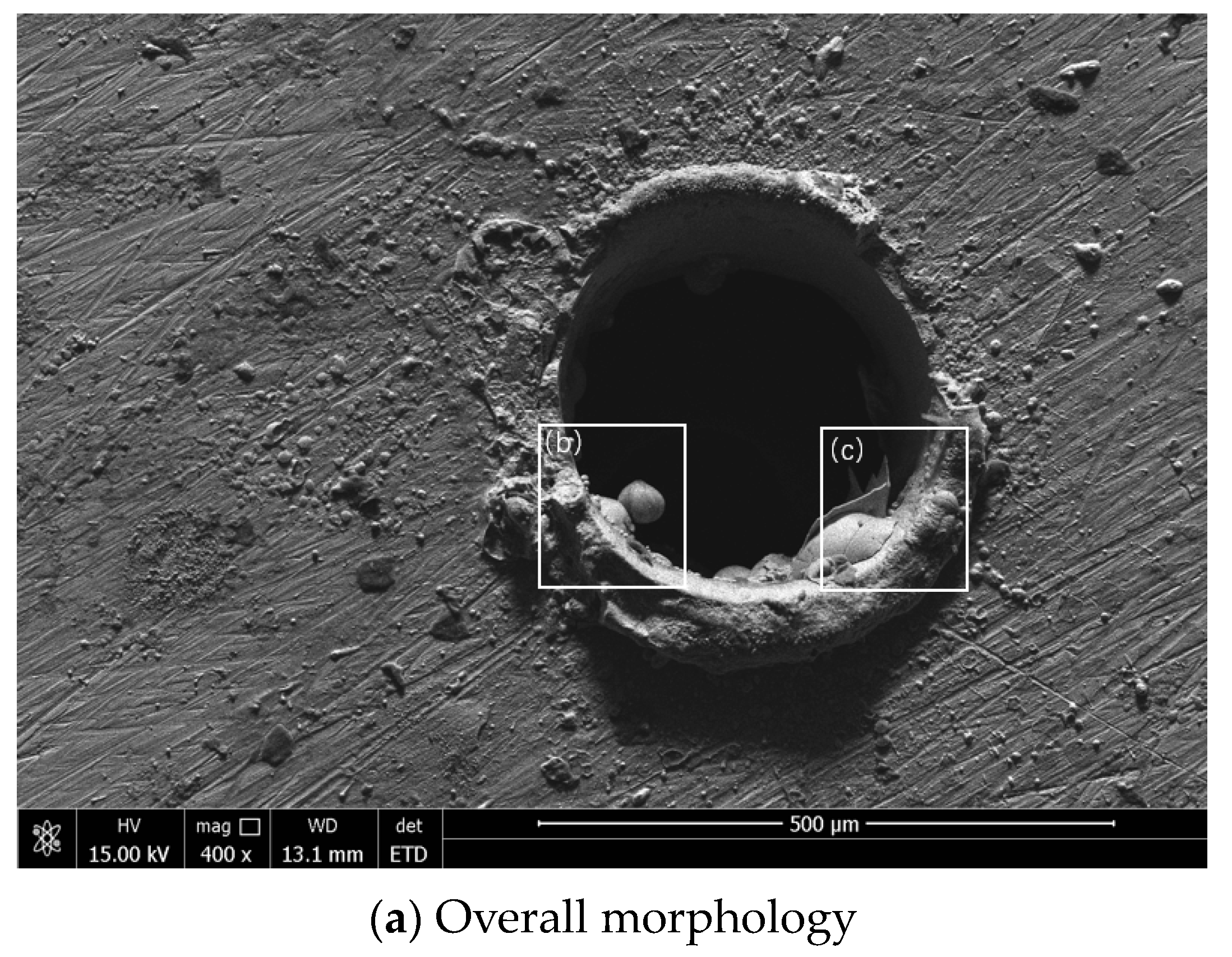
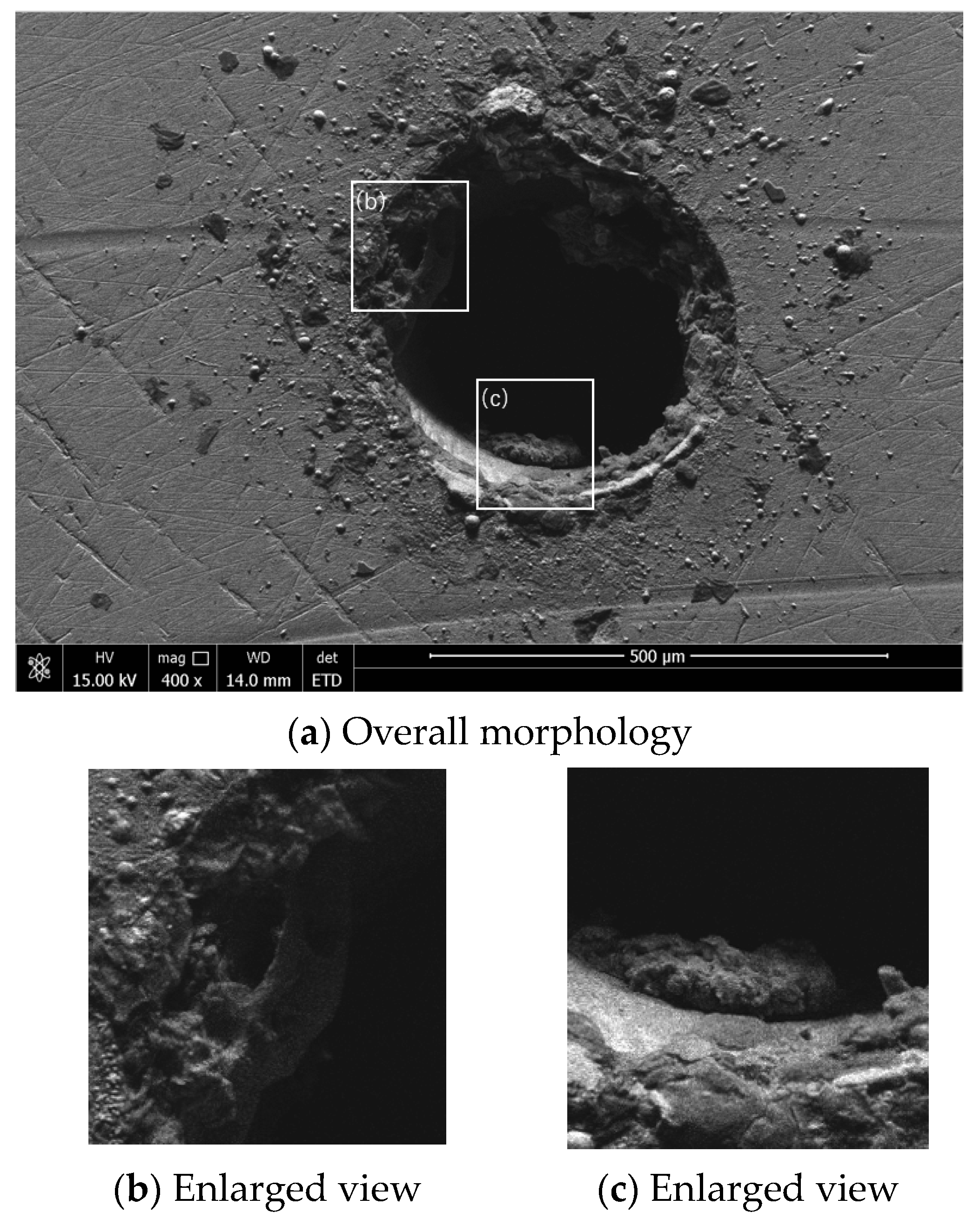
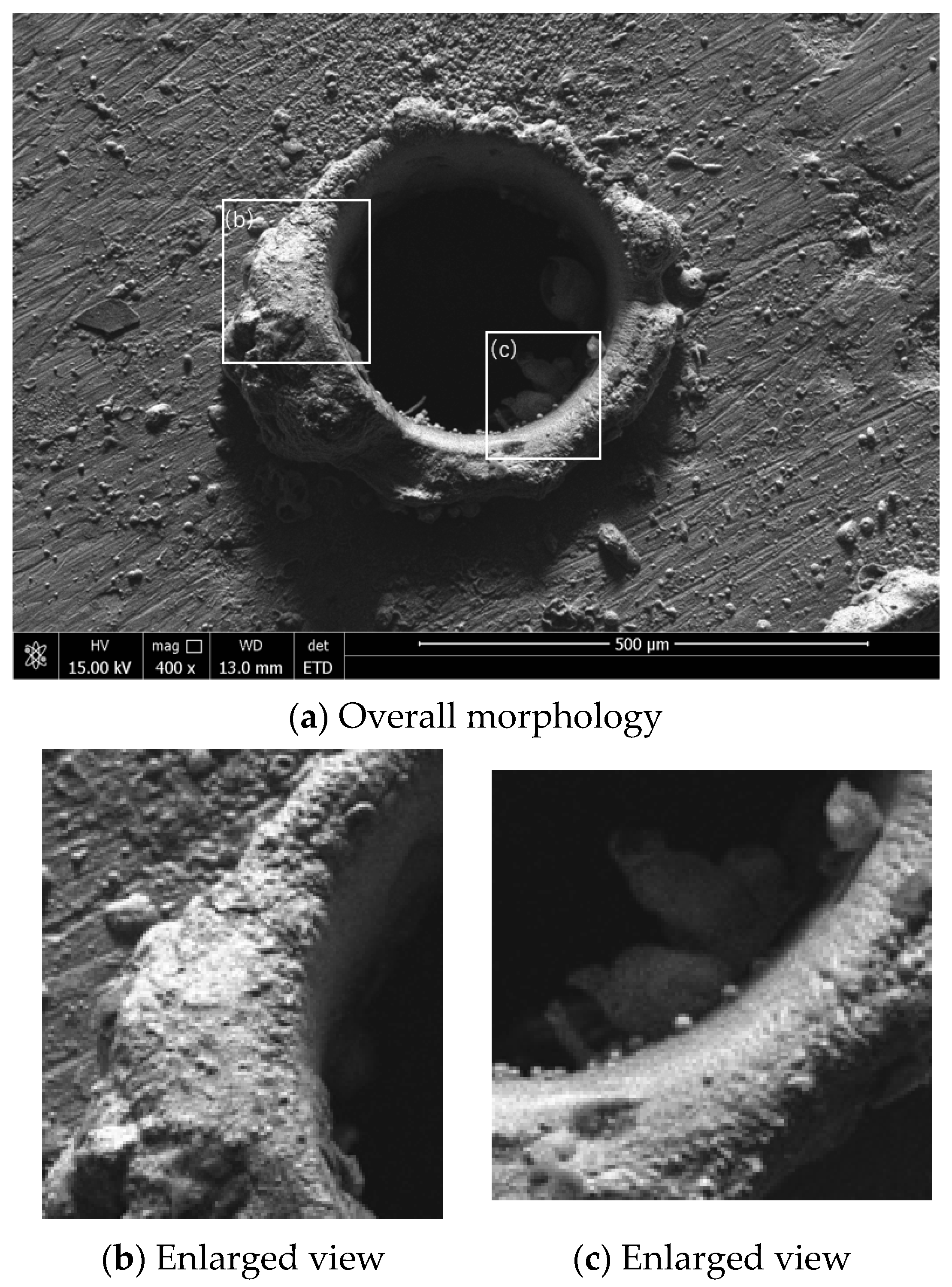
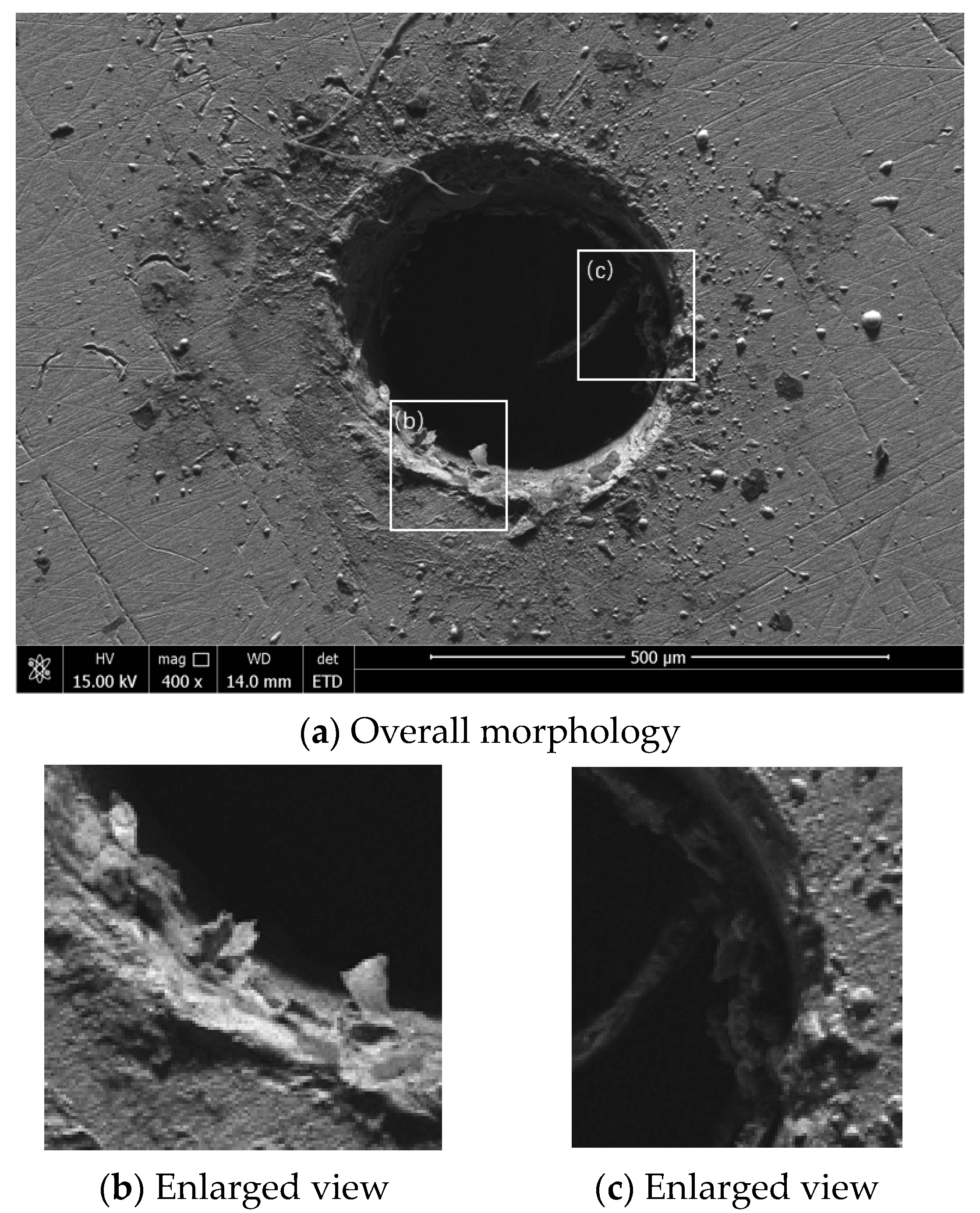
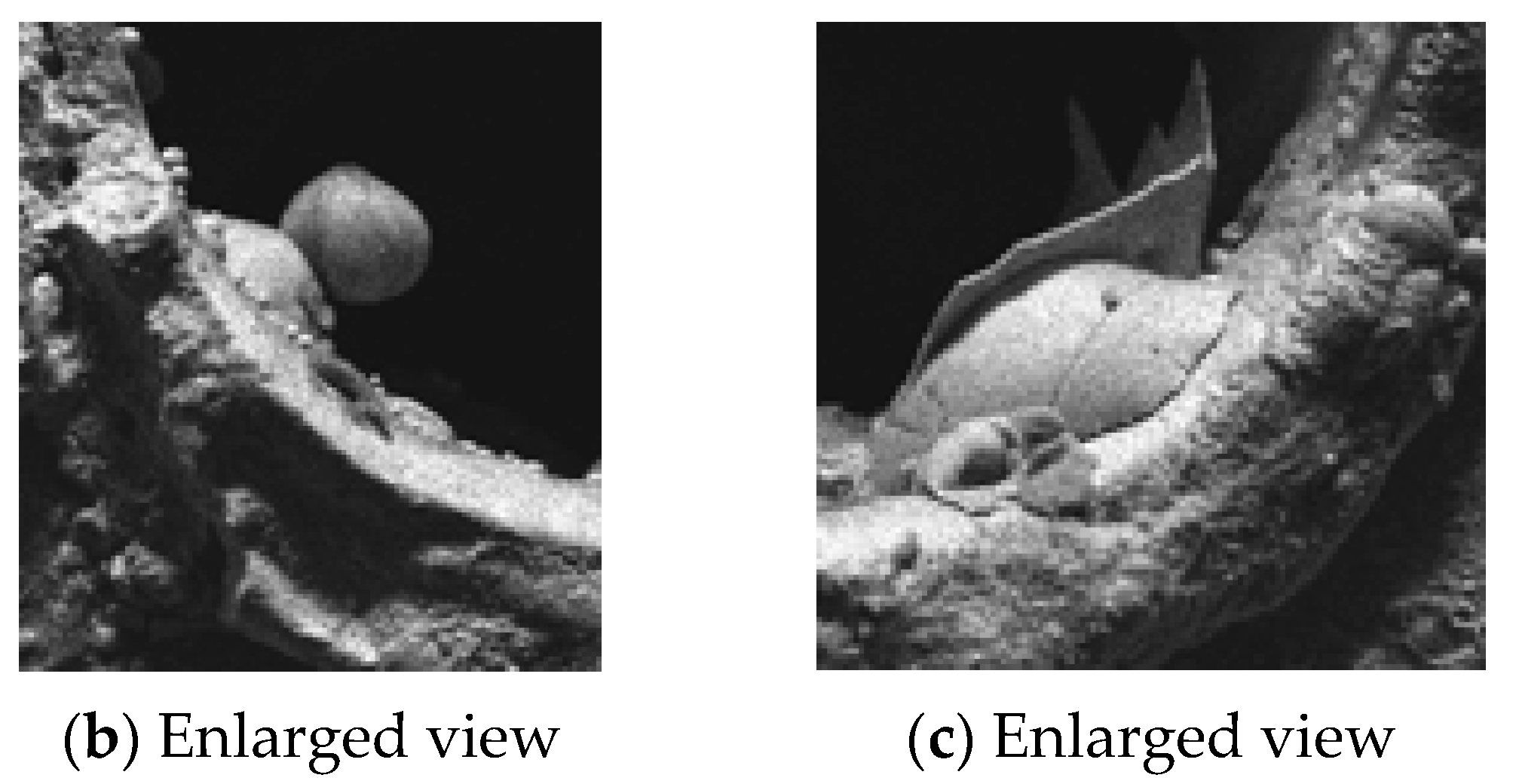
3.3. SEM Analysis of Microhole Morphology Under Different Environments
4. Study on Heat-Affected Zone Under Backwater-Assisted and Non-Water-Assisted Conditions
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Backwater assistance outperforms the non-water environment in terms of hole roundness and hole wall surface quality. However, the taper angle shows greater deviation compared to the non-water condition.
- (2)
- Backwater can effectively remove molten material and dissipate heat, reducing the recast layer and the heat-affected zone.
- (3)
- Backwater assistance provides an effective means to improve microhole machining quality and has practical value for high-precision manufacturing.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, S.; Zhang, C.; Sun, W.; Ma, Y.; Yao, Y. Application of laser microfabrication technology in the medical device field. Optoelectron. Eng. 2023, 50, 220306. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H. Research on Femtosecond Laser Processing Method for Aviation Blade Shaped Film Holes. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T. Study on the Mechanisms of Molten Splashing, Recast Layer, and Micro-Crack Formation During Millisecond Laser Drilling. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T. Preparation and Sensing Research of Microhole Structure Optical Fiber Devices. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an Petroleum University, Xi’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, N.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Qi, D.; Zhang, H.; Xia, K. The Effects of Static- and Flowing-Water-Assisted Methods on the Quality of Femtosecond Laser Drilling of Thermal-Barrier-Coated Superalloys. Metals 2025, 15, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, W.; Du, Y. Injection nozzle hole processing technology. Mod. Automot. Power 2010, 1, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhanwen, A.; Zou, G.; Yu, H.; Feng, B.; Du, C.; Liu, L. Polarization-dependent, beam reflection-regulated hole shaping dynamics visualized by in-situ imaging of ultrafast laser drilling process. Precis. Eng. 2024, 86, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Chichkov, B.N.; Momma, C.; Nolte, S.; Von Alvensleben, F.; Tünnermann, A. Femtosecond, picosecond, and nanosecond laser ablation of solids. Appl. Phys. A 1996, 63, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ready, J.F. Effects of High-Power Laser Radiation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder, J.; Steen, W.M. Heat transfer model for CW laser material interaction. J. Appl. Phys. 1980, 51, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiratta, M.; Prakash, S. Investigation and process optimization of backside thin water layer assisted laser micro-drilling of titanium. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 12, 318–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Song, H.; Liao, K.; Mei, X. Water-assisted femtosecond laser drilling of 4H-SiC to eliminate cracks and surface material shedding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 112, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Rong, Y.; Xu, L.; Wu, C.; Xia, K. Experimental Study and Defect Control in Picosecond Laser Trepanning Drilling of Superalloy. Metals 2025, 15, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q. Fundamental Study on Laser Machining Assisted by Jet Electrolyte. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J. Study on Micropore Machining of Metal Materials by Picosecond Laser. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]







| C | Mn | Ni | Si | P | S | Cr | N | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤0.08 | ≤2 | 8~11 | ≤1 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.030 | 17~20 | ≤0.1 | Balance |
| Processing Environment | Power | Number of Processing Cycles or Number of Passes |
|---|---|---|
| Backwater-assisted processing | 27 | 15 |
| 25.5 | 15 | |
| 24 | 15 | |
| 22.5 | 15 | |
| 21 | 15 | |
| 22.5 | 15 | |
| 22.5 | 18 | |
| 22.5 | 21 | |
| 22.5 | 24 | |
| 22.5 | 27 | |
| Non-water-assisted processing | 21 | 15 |
| 22.5 | 15 | |
| 24 | 15 | |
| 25.5 | 15 | |
| 27 | 15 | |
| 22.5 | 15 | |
| 22.5 | 18 | |
| 22.5 | 21 | |
| 22.5 | 24 | |
| 22.5 | 27 |
| Power/W | Number of Processing Cycles | Entrance Diameter/μm | Exit Diameter/μm | Entrance Roundness/μm | Exit Roundness/μm | Taper/° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | 15 | 335.696 | 288.337 | 33.023 | 18.322 | 4.513 |
| 22.5 | 15 | 340.638 | 282.368 | 23.821 | 21.632 | 5.546 |
| 24 | 15 | 368.541 | 287.728 | 24.078 | 25.153 | 7.670 |
| 25.5 | 15 | 342.989 | 297.214 | 21.166 | 15.229 | 4.362 |
| 27 | 15 | 343.172 | 296.471 | 19.904 | 20.468 | 4.450 |
| 22.5 | 15 | 323.667 | 292.268 | 13.479 | 12.145 | 2.995 |
| 22.5 | 18 | 323.774 | 271.875 | 11.169 | 21.820 | 4.943 |
| 22.5 | 21 | 328.792 | 285.909 | 7.297 | 10.529 | 4.088 |
| 22.5 | 24 | 325.438 | 225.858 | 14.656 | 22.598 | 9.423 |
| 22.5 | 27 | 342.991 | 307.038 | 21.266 | 15.001 | 3.429 |
| Power/W | Number of Processing Cycles | Entrance Diameter/μm | Exit Diameter/μm | Entrance Roundness/μm | Exit Roundness/μm | Taper/° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | 18 | 356.431 | 294.245 | 8.909 | 9.162 | 5.917 |
| 22.5 | 18 | 373.335 | 290.972 | 5.528 | 11.985 | 7.816 |
| 24 | 18 | 391.143 | 293.188 | 13.250 | 15.848 | 9.272 |
| 25.5 | 18 | 382.745 | 301.427 | 11.841 | 7.092 | 7.718 |
| 27 | 18 | 373.301 | 292.802 | 11.102 | 10.232 | 7.641 |
| 22.5 | 15 | 308.323 | 291.853 | 47.206 | 18.610 | 1.572 |
| 22.5 | 18 | 381.586 | 295.537 | 12.976 | 19.006 | 8.161 |
| 22.5 | 21 | 379.884 | 283.163 | 26.934 | 13.215 | 9.157 |
| 22.5 | 24 | 396.306 | 296.589 | 14.278 | 13.800 | 9.436 |
| 22.5 | 27 | 427.989 | 301.449 | 13.425 | 18.944 | 11.909 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Xia, R.; Zhou, J.; Rong, Y.; Wu, C.; Xu, L.; Han, X.; Xia, K. Experimental Study on Backwater-Assisted Picosecond Laser Trepanning of 304 Stainless Steel. Metals 2025, 15, 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101138
Wang L, Xia R, Zhou J, Rong Y, Wu C, Xu L, Han X, Xia K. Experimental Study on Backwater-Assisted Picosecond Laser Trepanning of 304 Stainless Steel. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101138
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liang, Rui Xia, Jie Zhou, Yefei Rong, Changjian Wu, Long Xu, Xiaoxu Han, and Kaibo Xia. 2025. "Experimental Study on Backwater-Assisted Picosecond Laser Trepanning of 304 Stainless Steel" Metals 15, no. 10: 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101138
APA StyleWang, L., Xia, R., Zhou, J., Rong, Y., Wu, C., Xu, L., Han, X., & Xia, K. (2025). Experimental Study on Backwater-Assisted Picosecond Laser Trepanning of 304 Stainless Steel. Metals, 15(10), 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101138






