Influence of B on the Practical Properties of TiAl Alloys for Jet Engine Blades and a Comparison of TiAl4822 and XD Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Evaluation of Material Properties
2.2.1. Impact Resistance
2.2.2. Machinability
2.2.3. Castability
2.2.4. Other Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of B Addition on Practical Properties
3.1.1. Microstructure
3.1.2. Impact Resistance
3.1.3. Machinability
3.1.4. Castability
3.1.5. Creep Strength
3.1.6. High-Cycle Fatigue Properties
3.1.7. Summary of B Effects
3.2. Comparison of Practical Properties of TiAl4822 and XD Alloys as Jet Engine Blades
4. Conclusions
- In Ti-45Al-2Nb-2Mn alloys, which have an inherently large microstructures owing to their single fully lamellar structures, a reduction in the lamellar colony size was observed with up to 0.2 B addition; however, no further effect was observed at higher concentrations.
- The impact resistance at room temperature, 500 °C, and 700 °C, alongside the high-cycle fatigue properties at 700 °C, revealed occasional benefits due to the reduced microstructure size and increased tensile strength with the addition of 0.1–0.2 B.
- However, even low levels of B addition negatively impacted the machinability, castability, and creep strength.
- Adding 0.4 B or more significantly reduced most practical properties.
- Although B addition can benefit alloys with coarse microstructures, an addition of 0.1 to 0.2 B is generally adequate.
- Comparing the TiAl4822 and XD alloys, TiAl4822 provide a more balanced performance than XD alloys due to the adverse effect of high B contents (1.0 at.%) in XD alloys and the superior effectiveness of Cr over Mn in enhancing the high-temperature impact resistance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HIP | Hot Isostatic Pressing |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
References
- Hu, D. Role of boron in TiAl alloy development: A review. Rare Met. 2016, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, J.A.; Flower, H.M. The role of borides in near-γ titanium aluminides. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2000, 2, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.-H.; Liu, C.; Fang, Y.; Wei, X.; Jin, J.; Bei, H.; Ding, Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z. Effect of trace boron addition on the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties in Ti45Al8Nb2Cr-B alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1002, 175204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, D.E.; Christodoulou, L.; Kampe, S.L.; Sadler, R. Investment-cast processing of XD™ near-γ titanium aluminides. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 144, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, D.E. Status of investment cast gamma titanium aluminides in the USA. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 213, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Perez, M.; Blackwell, P. Integrating HIP and homogenisation heat treatment and its effect on the workability of a conventional peritectic TiAl alloy. Intermetallics 2023, 158, 107884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, A. Electrochemical dissolution behavior of Ti-45Al-2Mn-2Nb+0.8 vol% TiB2 XD alloy in NaCl and NaNO3 solutions. Corros. Sci. 2019, 157, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Wu, X.; Loretto, M.H. Advances in optimisation of mechanical properties in cast TiAl alloys. Intermetallics 2005, 13, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M.; Biermann, H. Thermo-mechanical fatigue behaviour of the gamma-titanium aluminide TNB-V5 with near-gamma microstructure. Mater. Sci. Forum 2007, 539–543, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, H.; Mayer, S. Design, processing, microstructure, properties, and applications of advanced intermetallic TiAl alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2013, 15, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couret, A.; Reyes, D.; Thomas, M.; Ratel-Ramond, N.; Deshayes, C.; Monchoux, J.-P. Effect of ageing on the properties of the W-containing IRIS-TiAl alloy. Acta Mater. 2020, 199, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolotta, P.; Barrett, J.; Kelly, T.; Smashey, R. The use of cast Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb in jet engines. JOM 1997, 49, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewlay, B.P.; Nag, S.; Suzuki, A.; Weimer, M.J. TiAl alloys in commercial aircraft engines. Mater. High Temp. 2016, 33, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewlay, B.P.; Weimer, M.; Kelly, T.; Suzuki, A.; Subramanian, P.R. The science, technology, and implementation of TiAl alloys in commercial aircraft engines. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2013, 1516, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voice, W. The future use of gamma titanium aluminides by Rolls-Royce. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 1999, 71, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-W.; Kim, S.-L. Advances in Gammalloy materials–processes–application technology: Successes, dilemmas, and future. JOM 2018, 70, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, H.; Mayer, S. Intermetallic titanium aluminides in aerospace applications—Processing, microstructure and properties. Mater. High Temp. 2016, 33, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habel, U.; Heutling, F.; Kunze, C.; Smarsly, W.; Das, G.; Clemens, H. Forged intermetallic γ-TiAl-based alloy low-pressure turbine blade in the geared turbofan. In Proceedings of the 13th World Conference on Titanium, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–20 August 2015; pp. 1223–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmerdinger, J. FlightGlobal.com, FAA Orders PW1100G Low-Pressure Turbine Blade Replacement. Available online: https://www.flightglobal.com/engines/faa-orders-pw1100g-low-pressure-turbine-blade-replacement/135575.article (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Brotzu, A.; Felli, F.; Mondal, A.; Pilone, D. Production issues in the manufacturing of TiAl turbine blades by investment casting. Procedia Struct. Integrity 2020, 25, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güther, V.; Allen, M.; Klose, J.; Clemens, H. Metallurgical processing of titanium aluminides on industrial scale. Intermetallics 2018, 103, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsui, T.; Mizuta, K. Detrimental effects of βo-phase on practical properties of TiAl Alloys. Metals 2024, 14, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaura, H.; Nishino, K.; Saito, T. Effects of alloying elements on foreign object damage resistance of cast-TiAl base alloys. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 2002, 66, 451–458. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsui, T. Effect of microstructure on impact resistance and machinability of TiAl alloys for jet engine turbine blade applications. Metals 2023, 13, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsui, T.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Vaubois, T.; Sallot, P. Effects of composition on melt fillability and impact resistance of TiAl alloys for thin-blade turbine wheels: Laboratory predictions and product verification. Metals 2024, 15, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Liu, R.; Yang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yang, R. Tensile behavior of cast γ-TiAl alloys with varied boride morphologies. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 888, 145807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, J.; Hojo, A. Development of pressureless sintered titanium boride ceramics. J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metall. 2001, 49, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Miyakawa, O.; Takada, Y.; Okuno, O.; Okabe, T. Casting behavior of titanium alloys in a centrifugal casting machine. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hénaff, G.; Gloanec, A.-L. Fatigue properties of TiAl alloys. Intermetallics 2005, 13, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrut, M.; Caron, P.; Thomas, M.; Couret, A. High temperature materials for aerospace applications: Ni-based superalloys and γ-TiAl alloys. Comptes Rendus. Phys. 2018, 19, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AeroEdge, AeroEdge was Invited to the Ceremony for Celebrating the Delivery of One Million TiAl Blades. 2023. Available online: https://aeroedge.co.jp/en/news/newsrelease/857/ (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Sallot, P.; Monchoux, J.P.; Joulie, S.; Couret, A.; Thomas, M. Impact of β-phase in TiAl alloys on mechanical properties after high temperature air exposure. Intermetallics 2020, 119, 106729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, R.; Laska, N.; Knittel, S.; Schulz, U. Effect of intermetallic coatings on the tensile properties of a γ-TiAl based TNM alloy. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 699, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galetz, M.C.; Ulrich, A.S.; Oskay, C.; Fähsing, D.; Laska, N.; Schulz, U.; Schütze, M. Oxidation-induced microstructural changes of the TiAl TNM-B1 alloy after exposure at 900 °C in air. Intermetallics 2020, 123, 106830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsui, T.; Fukuyo, T.; Mizuta, K. Comparison of the impact resistance of TiAl4822 and TNM alloy under expected service conditions of jet engine blade. Intermetallics 2025, 183, 108793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsui, T. Selection of additive elements focusing on impact resistance in practical TiAl cast alloy. Metals 2022, 12, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Composition (at.%) | Tensile Test Results at 700 °C | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | Al | Nb | Mn | B | 0.2% Yield Strength (MPa) | Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
| Bal. | 45.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 372 | 463 | 0.7 |
| Bal. | 45.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.2 | 408 | 553 | 1.3 |
| Bal. | 45.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 391 | 544 | 1.2 |
| Properties | Ti-45Al-2Nb-2Mn-1B | Ti-47Al-2Nb-2Mn-1B | Ti-47Al-2Nb-2Cr | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact resistance | Mean Charpy absorbed energy (J/cm2) | 25 °C | 3.7 | 3.3 | 4.8 |
| 500 °C | 5.0 | 4.3 | 19.0 | ||
| 700 °C | 4.0 | 4.2 | 14.6 | ||
| Machinability | Mean tool weight reduction (mg/cm3) | 2.9 | 1.9 | 0.3 | |
| Castability | Mean molten metal ratio flowing through ceramic mesh | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.75 | |
| Creep strength | Creep life at 750 °C and 200 MPa (h) | 153 | 413 | 751 | |
| High cycle fatigue properties | Cycles to failure at 700 °C, σa = 200 MPa, and R = 0.05 (N) | 6.5 × 105 | >1.0 × 107 | 4.1 × 106 | |
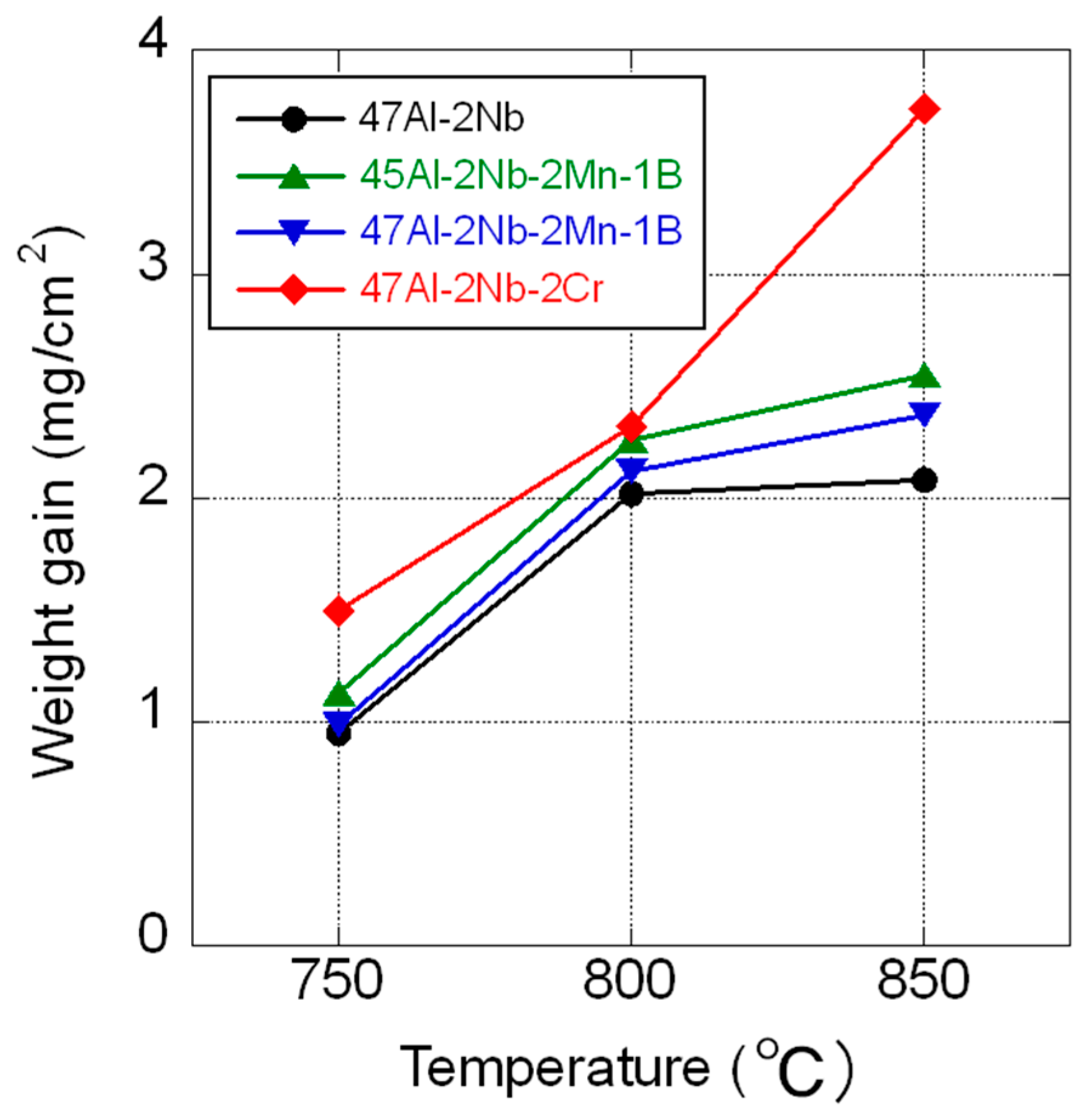
| Oxidation resistance | Weight gain at 1000 h (mg/cm2) | 750 °C | 1.13 | 0.99 | 1.50 |
| 800 °C | 2.26 | 2.12 | 2.32 | ||
| 850 °C | 2.55 | 2.37 | 3.74 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tetsui, T.; Mizuta, K. Influence of B on the Practical Properties of TiAl Alloys for Jet Engine Blades and a Comparison of TiAl4822 and XD Alloys. Metals 2025, 15, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101132
Tetsui T, Mizuta K. Influence of B on the Practical Properties of TiAl Alloys for Jet Engine Blades and a Comparison of TiAl4822 and XD Alloys. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101132
Chicago/Turabian StyleTetsui, Toshimitsu, and Kazuhiro Mizuta. 2025. "Influence of B on the Practical Properties of TiAl Alloys for Jet Engine Blades and a Comparison of TiAl4822 and XD Alloys" Metals 15, no. 10: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101132
APA StyleTetsui, T., & Mizuta, K. (2025). Influence of B on the Practical Properties of TiAl Alloys for Jet Engine Blades and a Comparison of TiAl4822 and XD Alloys. Metals, 15(10), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101132








