Experimental Investigation Concerning the Influence of Face Sheet Thickness on the Blast Resistance of Aluminum Foam Sandwich Structures Subjected to Localized Impulsive Loading
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material Properties
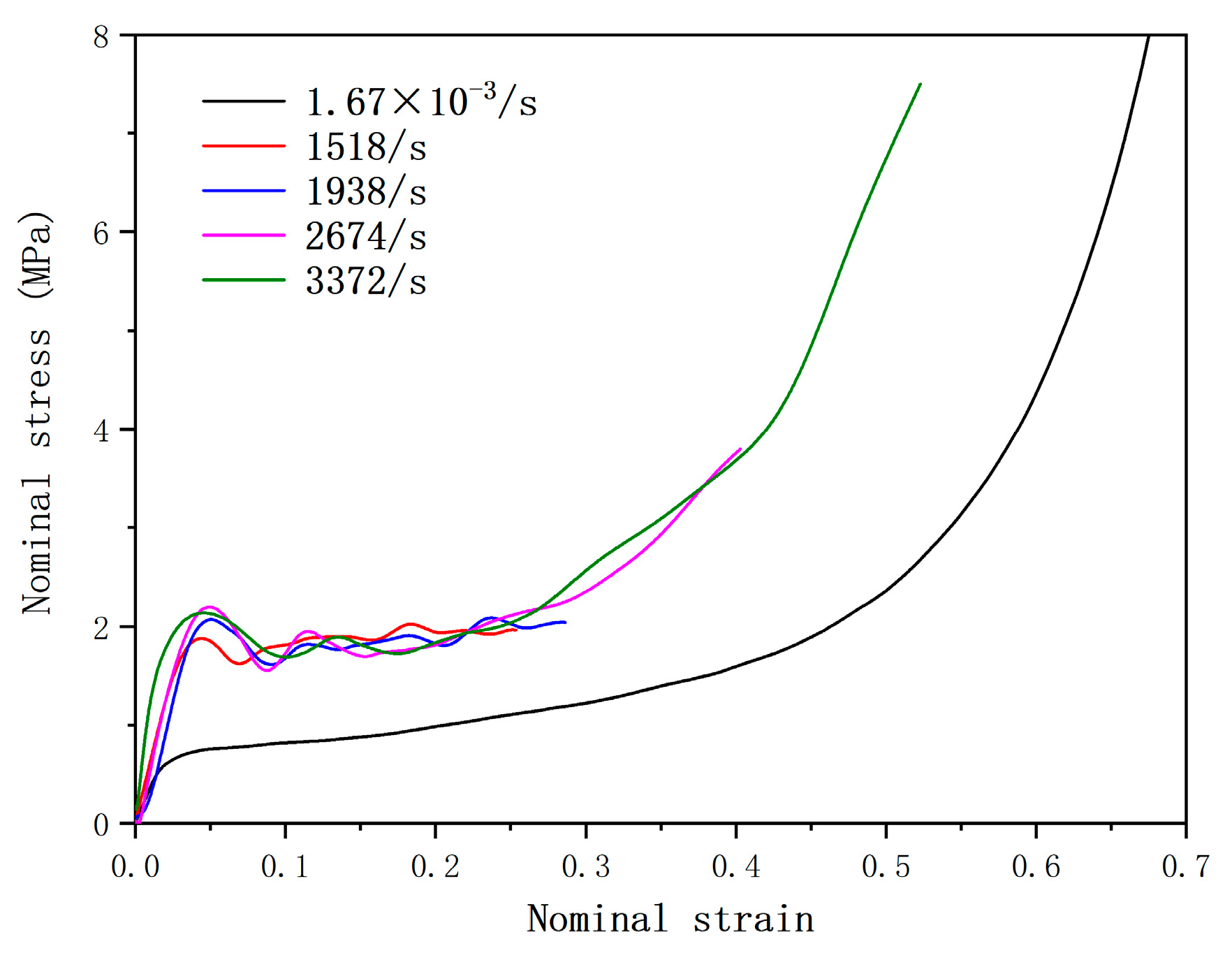
2.1. Aluminum Foam
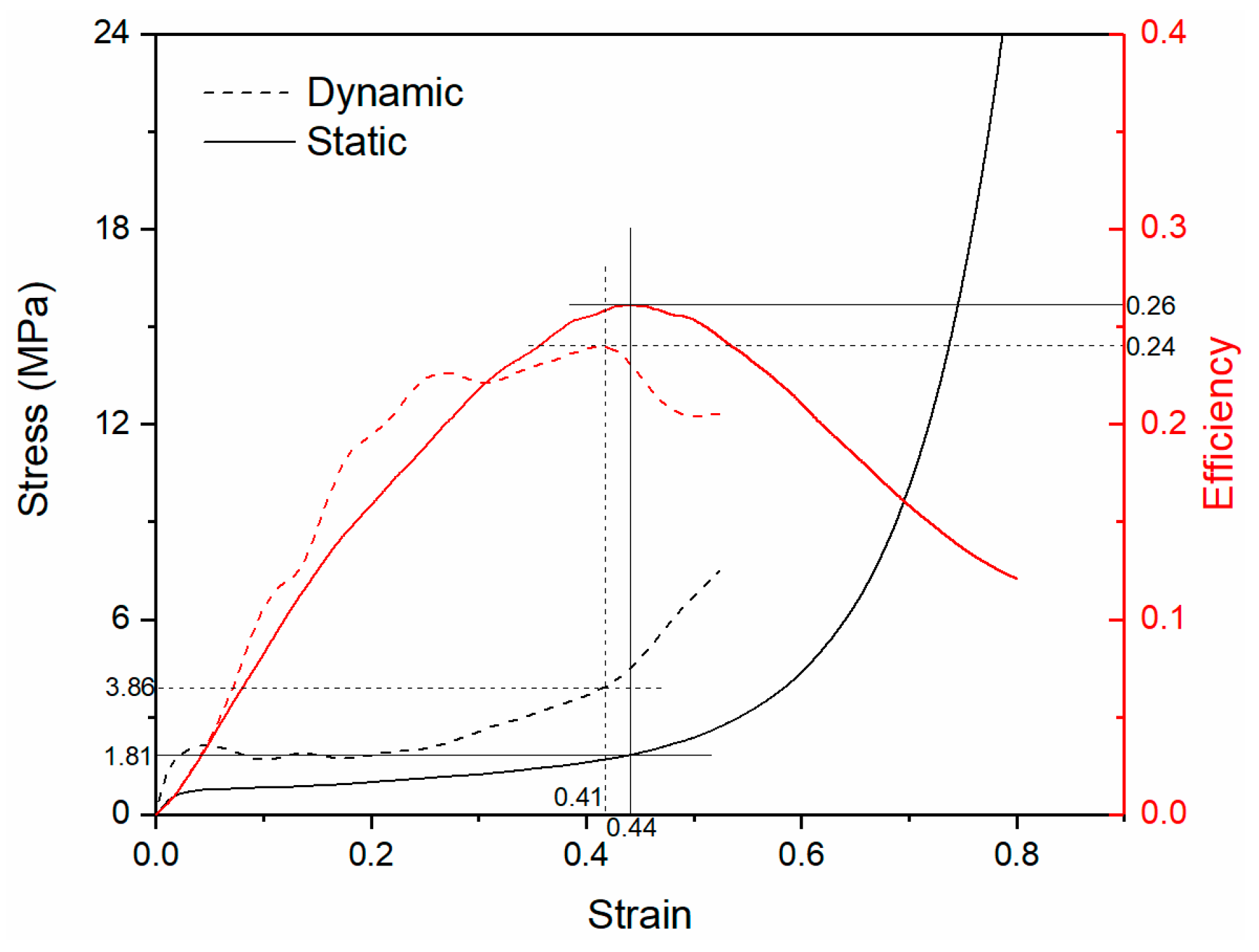
2.2. 5A06 Aluminum Alloy
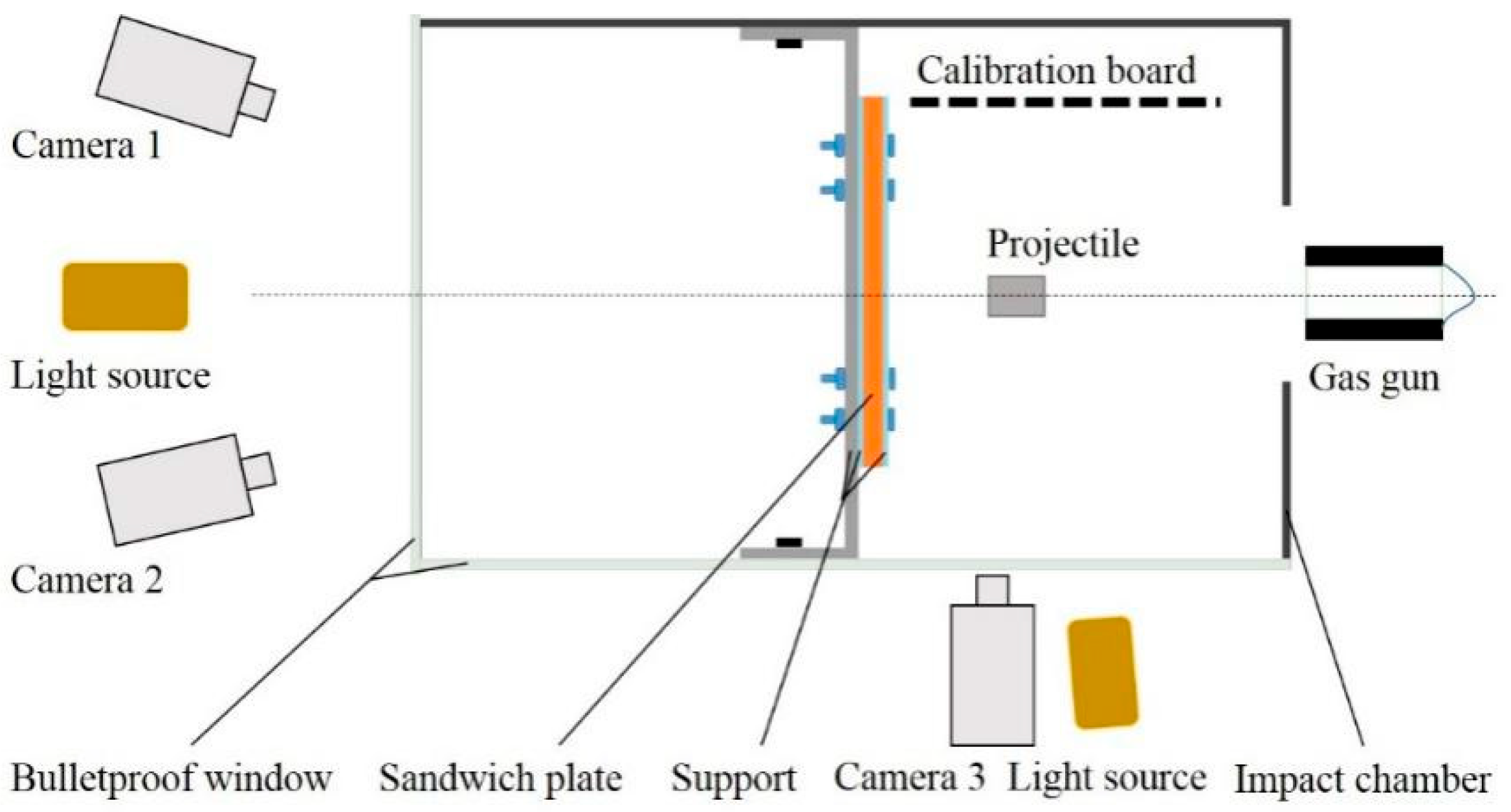
3. Experimental Setup
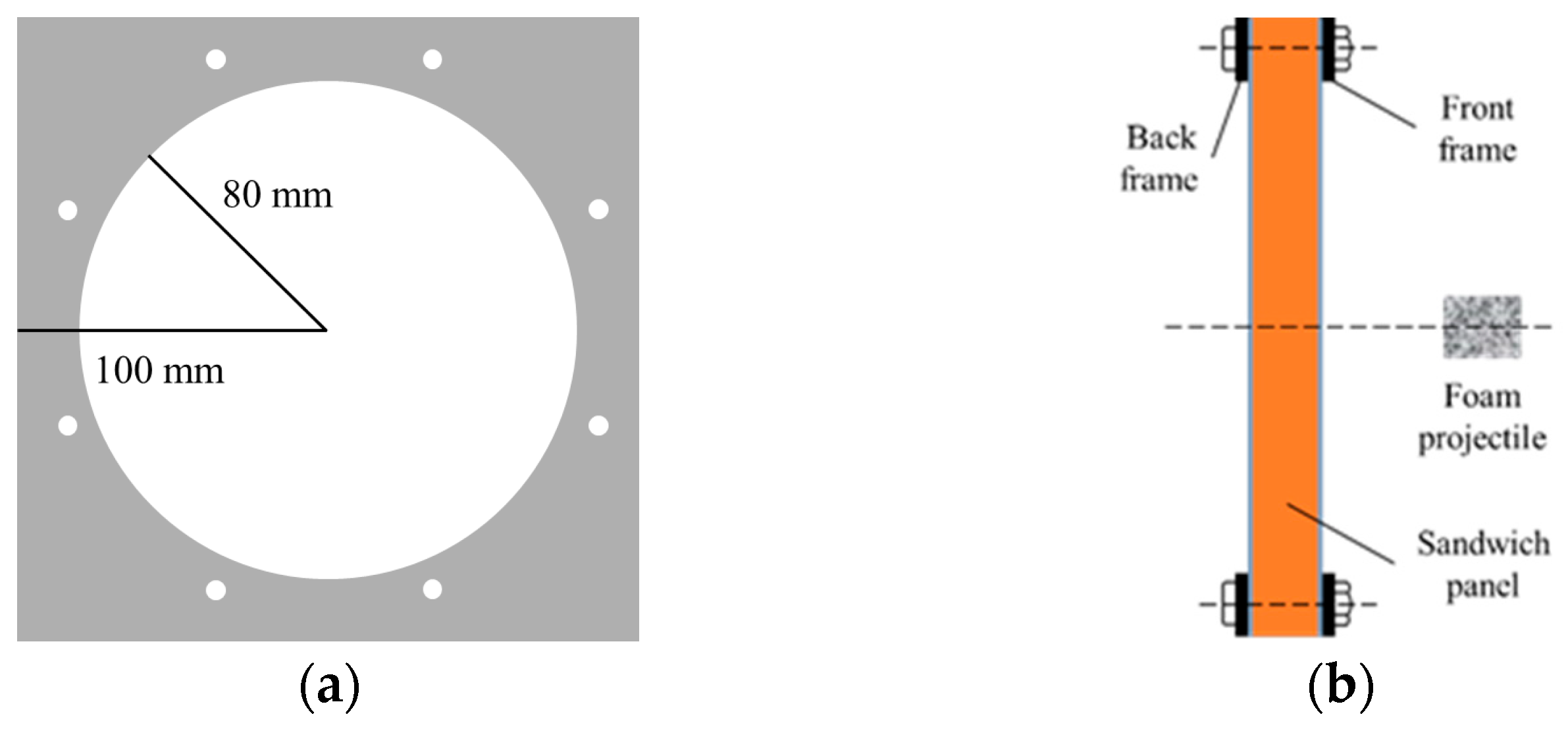
3.1. Sandwich Configurations
3.2. Test Configurations
4. Results and Discussion
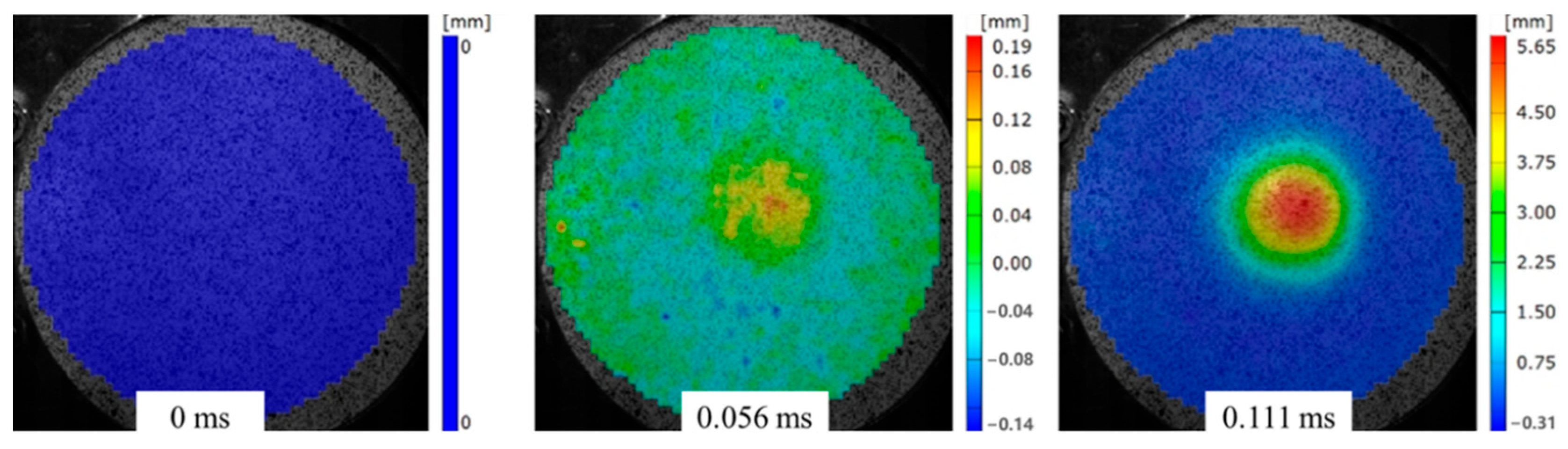
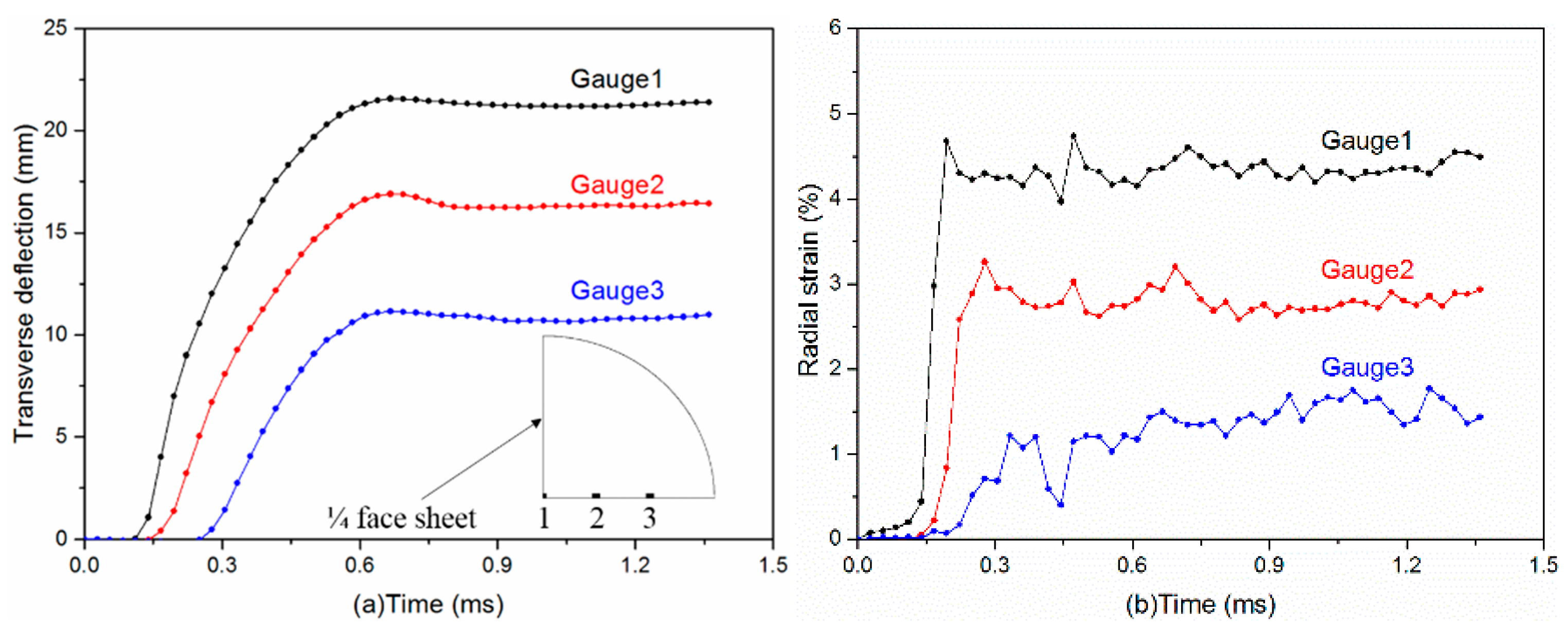
4.1. Dynamic Response of Sandwich Panels
4.2. Failure Modes and Associated Mechanisms of Sandwich Panels
4.2.1. Failure Modes of Front and Back Face Sheets
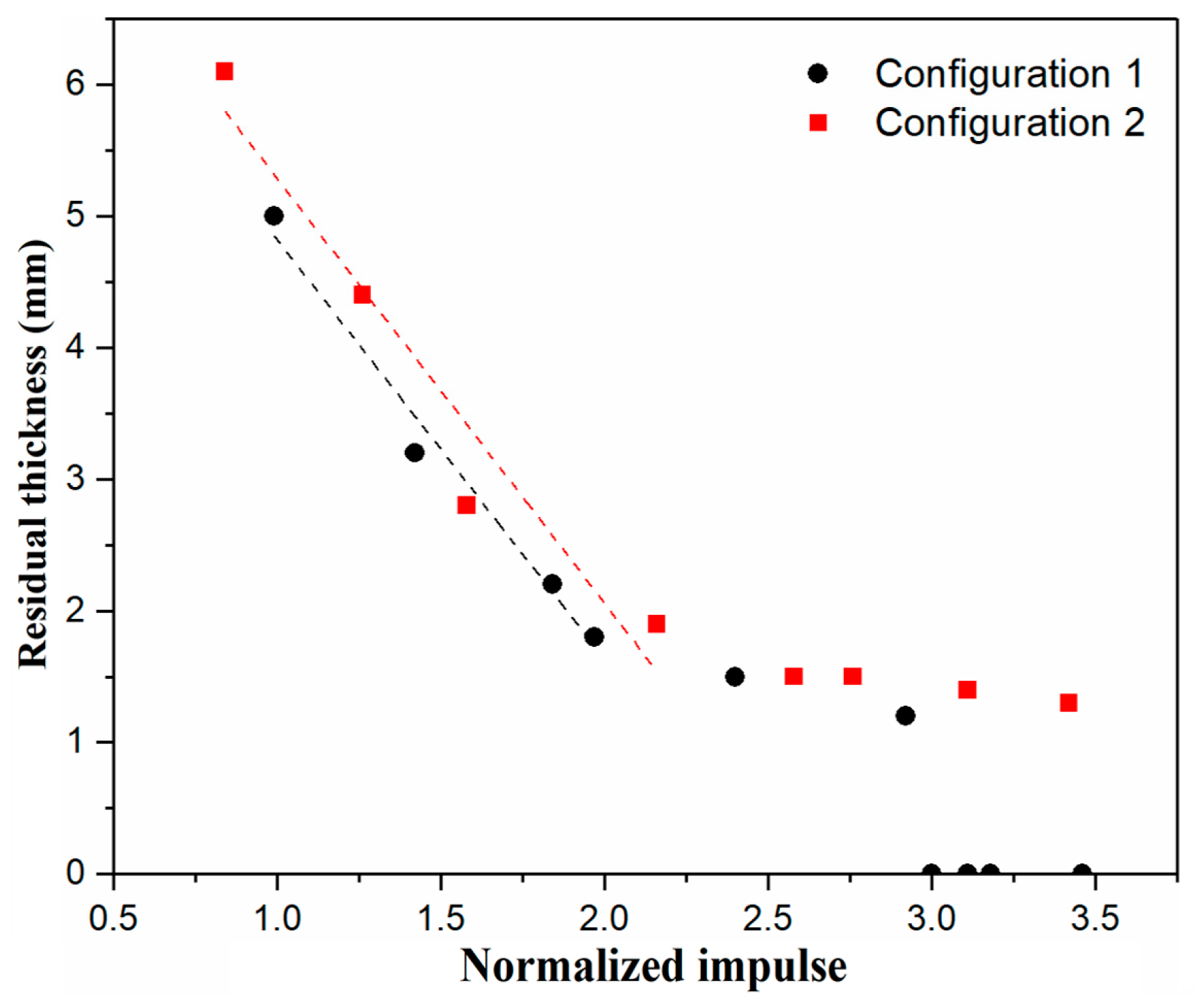
4.2.2. Failure Modes and Residual Thicknesses of the Core Layer
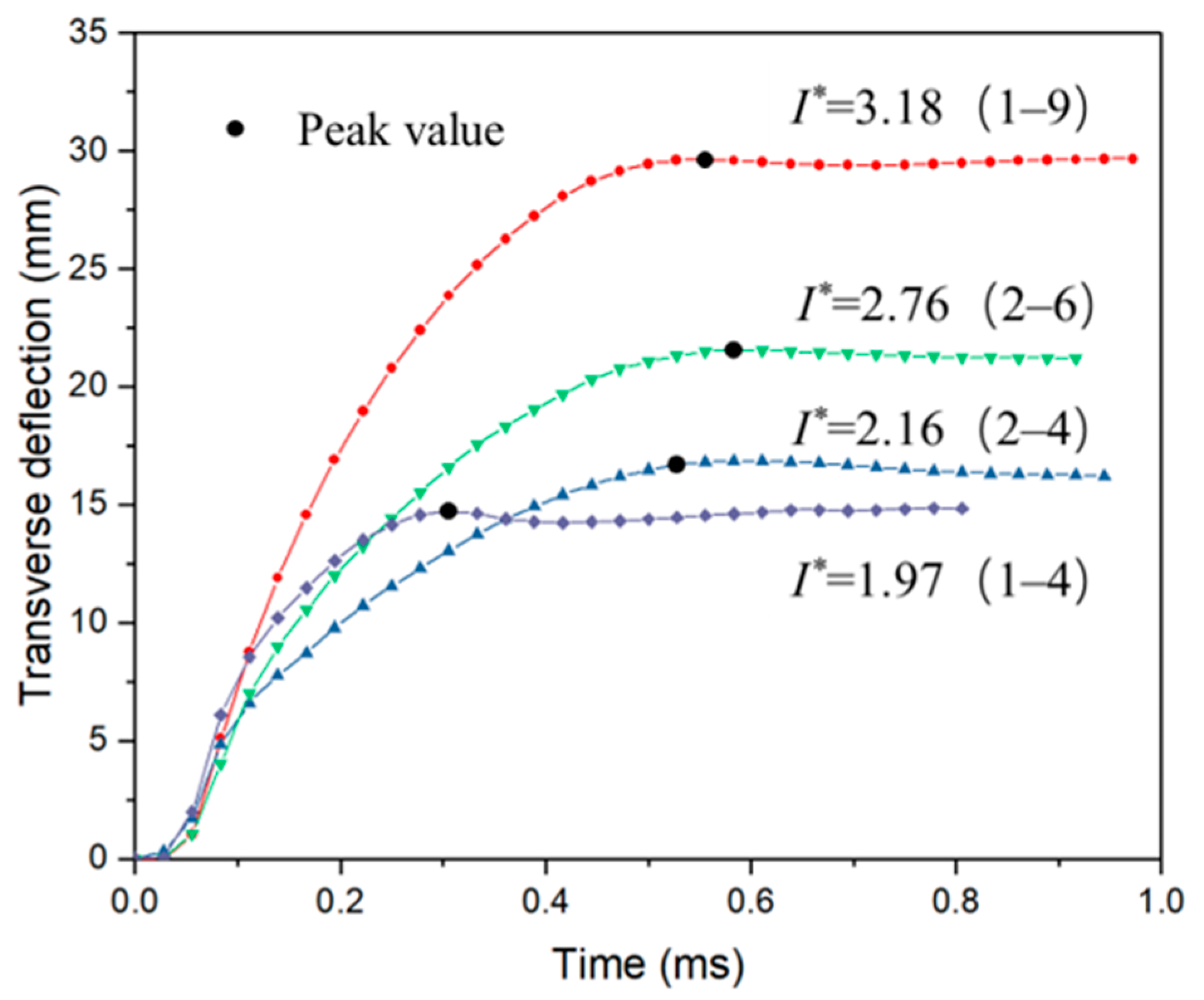
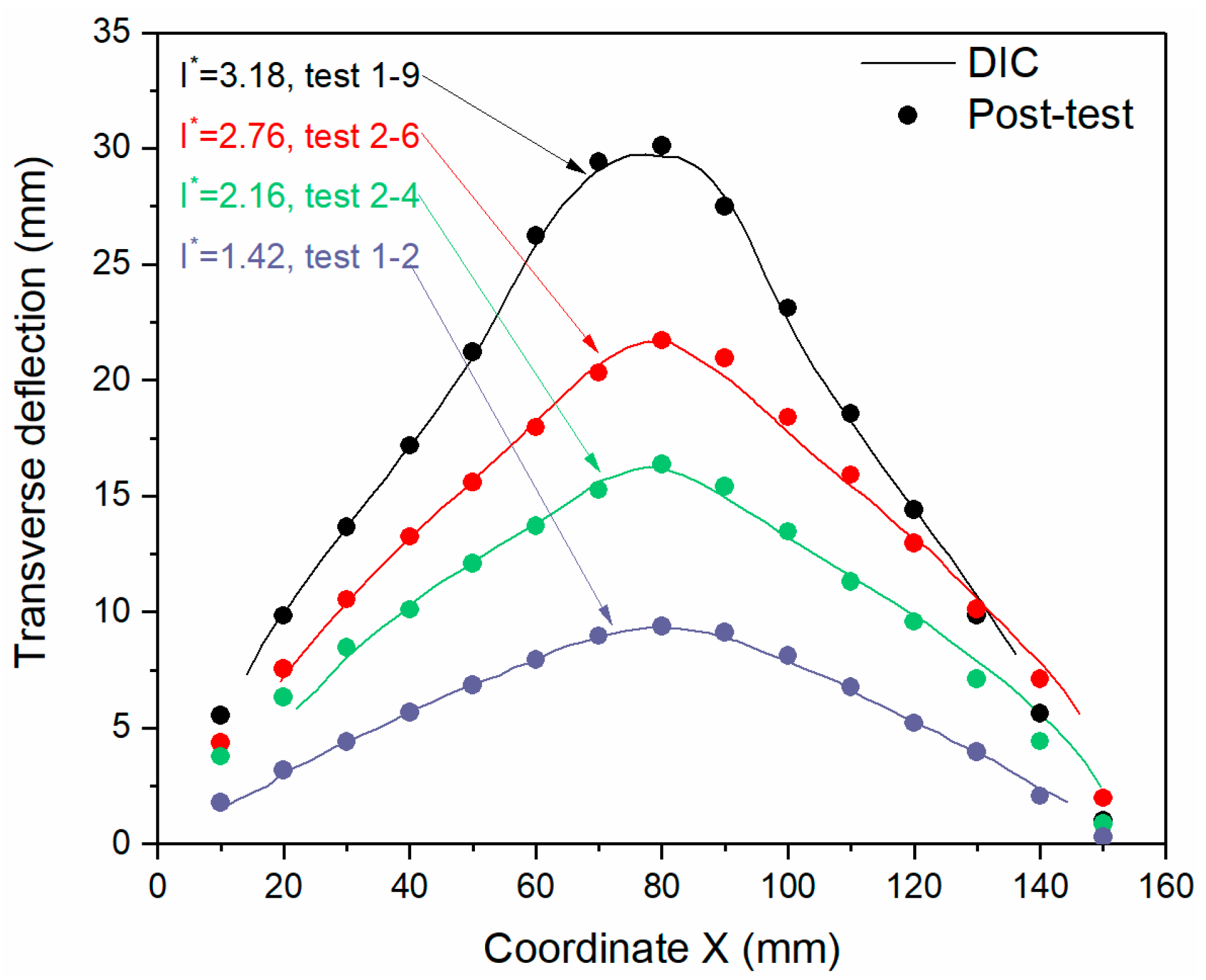
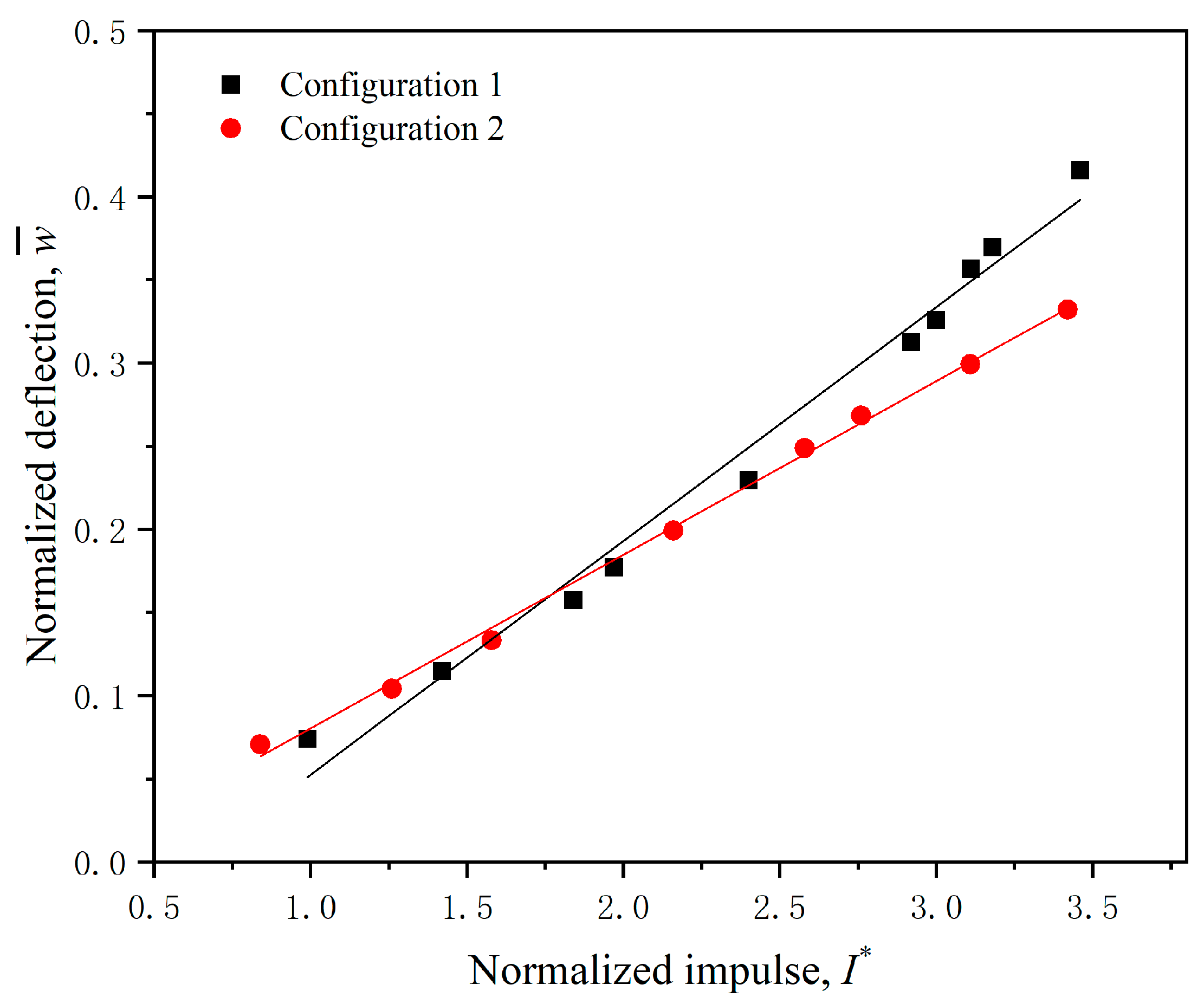
4.3. Permanent Deformation of Sandwich Panels
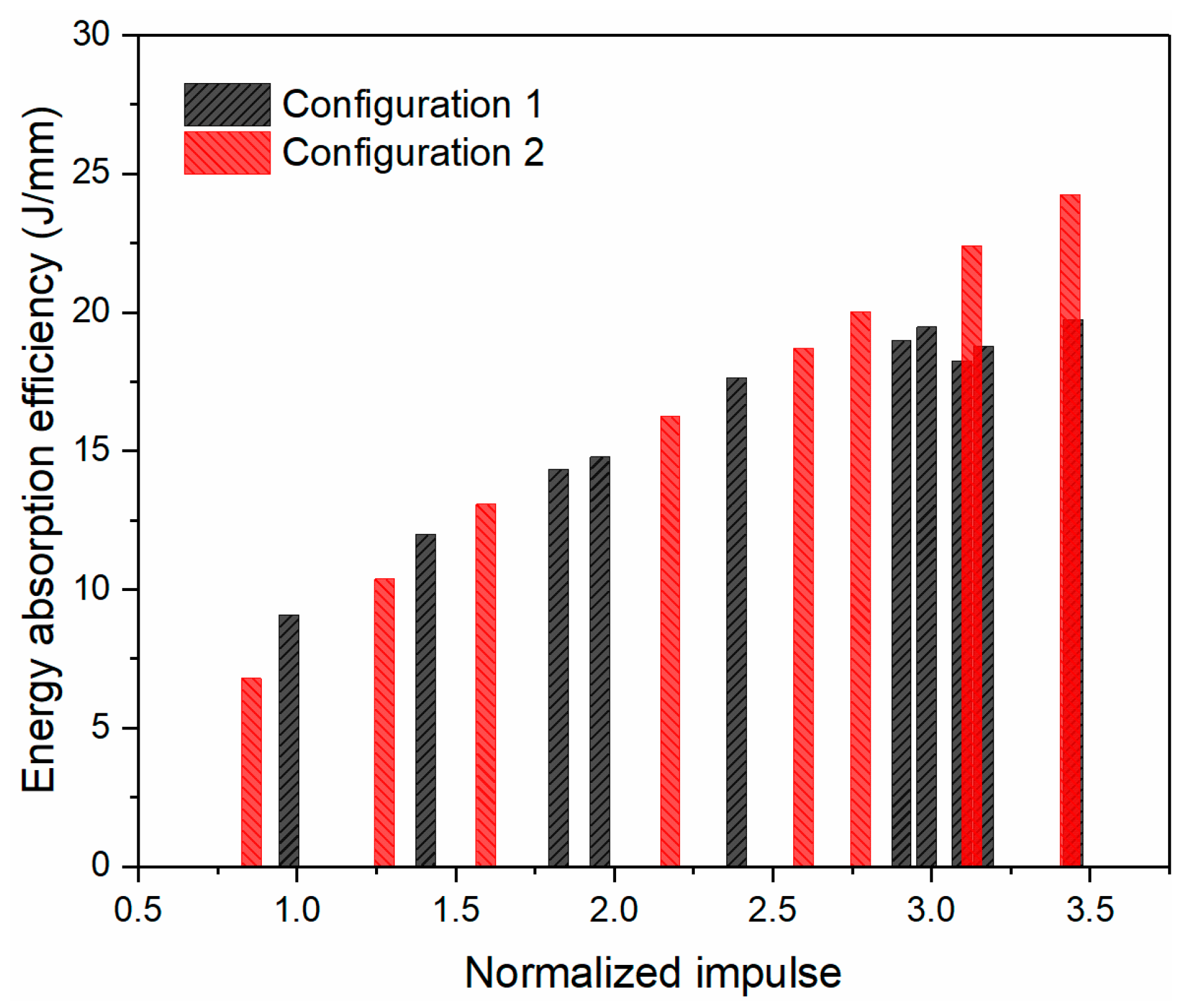
4.4. Energy Absorption Evaluation of the Sandwich Panels
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajapakse, Y.D.S.; Hui, D. Marine Composites and Sandwich Structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurick, G.N.; Shave, G.C. The deformation and tearing of thin square plates subjected to impulsive loads—An experimental study. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1996, 18, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Tang, H.; Li, Y.; Fu, H.; Zheng, X.X. Simplified mode solutions for final plastic deformation of circular plates under localized impulsive loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2025, 204, 105397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagesh, C.; Gupta, N.K. Large deformations and failure of clamped circular steel plates under uniform impulsive loads using various phenomenological damage models. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2022, 166, 104255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Shu, X. Uniaxial and biaxial failure behaviors of aluminum alloy foams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 61, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, D.D.; McShane, G.J.; Deshpande, V.S.; Fleck, N.A. The response of clamped sandwich plates with metallic foam cores to simulated blast loading. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 2243–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y. Study on quasi-static compressive properties of aluminum foam-epoxy resin composite structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 79, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, S.; Wang, Q.; Tanaka, Y.; Kagawa, Y. Compressive mechanical properties of closed-cell aluminum foam-polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 64, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, J. Bi-surface induction in biomimetic multi-gradient foam-filled tubes with enhanced energy absorption: Theory, experiment, and simulation. J. Appl. Mech. 2025, 92, 051010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Russell, B.P.; Fleck, N.A.; Wadley, H.N.G.; Deshpande, V.S. The effect of shear strength on the ballistic response of laminated composite plates. Eur. J. Mech.-A/Solids 2013, 42, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleck, N.A.; Deshpande, V.S. The Resistance of clamped sandwich beams to shock loading. J. Appl. Mech. 2004, 71, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Deshpande, V.S.; Fleck, N.A. Dynamic response of a clamped circular sandwich plate subject to shock loading. J. Appl. Mech. 2004, 71, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, Z.; Lu, G.; Nurick, G. Some theoretical considerations on the dynamic response of sandwich structures under impulsive loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2010, 37, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Tao, Q.; Yin, L.; Ma, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, W.; Mu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, Z. High-velocity impact response of metallic sandwich structures with PVC foam core. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2020, 144, 103657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Ye, N.; Xie, W.; Ren, P. Dynamic failure of honeycomb-core sandwich structures subjected to underwater impulsive loads. Eur. J. Mech.-A/Solids 2016, 60, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Vodenitcharova, T.; Kabir, K.; Flores-Johnson, E.A.; Hoffman, M. Finite element analysis of indentation of aluminium foam and sandwich panels with aluminium foam core. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 599, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Lu, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L. Large deflection behavior of circular sandwich plates with metal foam-core. Eur. J. Mech.-A/Solids 2016, 55, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, D.; Kaviarasu, K.; Alagappan, P. Experimental study on the dynamic response of steel structure subjected to blast load. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2025, 205, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, D.D.; Deshpande, V.S.; Fleck, N.A. The use of metal foam projectiles to simulate shock loading on a structure. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2005, 31, 1152–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Huang, W.; Xie, W.; Huang, X. Dynamic response and failure of sandwich plates with PVC foam core subjected to impulsive loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 109, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Tian, R.; Hu, A.; Wu, H.; Zhou, N.; Wei, G. Experimental investigation into the response of GFRP S-shaped foldcore sandwich panels to impulsive loading. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 52, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Huang, W. Experimental and theoretical study on the response of the X-frame CFRP sandwich beam under the local impulsive loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2024, 186, 104885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhang, Q.C.; Wei, Z.H.; Li, L.; Yue, Z.S.; Wang, X.; Lu, T.J. Dynamic response of fully-clamped steel plate under laboratory-simulated sequential fragment impact and blast loading. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 182, 110144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Gao, S.; Wu, W.; Li, Y. Dynamic response of sandwich beam with star-shaped reentrant honeycomb core subjected to local impulsive loading. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 161, 107420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Rong, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, F.; Wang, S.; Zhu, P.; Zhao, R. Dynamic response of hemispherical-shell sandwich structures subjected to underwater impulsive loading. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 205, 112550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, Q.; Zheng, J.; Wang, T.J. Uniaxial crushing of sandwich plates with continuously density-graded cellular cores subjected to impulsive loading. Eur. J. Mech.-A/solid 2021, 90, 104361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirfatah, S.M.; Tayebikhorami, S.; Shahmohammadi, M.A.; Salehipour, H.; Civalek, Ö. Geometrically nonlinear analysis of sandwich panels with auxetic honeycomb core and nanocomposite enriched face-sheets under periodic and impulsive loads. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 135, 108195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, X.; He, X.; Liu, J.; Yu, S.; Huang, W. The dynamic response of composite auxetic re-entrant honeycomb structure subjected to underwater impulsive loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2024, 191, 104999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, A.; Guan, Z.W.; Cantwell, W.J.; Zhang, X.F.; Langdon, G.S.; Wang, Q.Y. Blast response of aluminium/thermoplastic polyurethane sandwich panels—Experimental work and numerical analysis. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2019, 127, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Sadighi, M. Experimental investigation on the energy absorption characteristics of honeycomb sandwich panels under quasi-static punch loading. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Elnasri, I.; Abdennadher, S. An experimental study on the behaviour under impact loading of metallic cellular materials. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2005, 47, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalle, M.; Belingardi, G.; Montanini, R. Characterization of polymeric structural foams under compressive impact loading by means of energy-absorption diagram. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2001, 25, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Birch, R.S.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, X.; Vergara, E.F.; Geng, B.; Li, S.; Zeng, H. Experimental investigation of energy dissipation of aluminum matrix syntactic foam under impulsive loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2025, 203, 105373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohotti, D.; Ngo, T.; Raman, S.N.; Ali, M.; Mendis, P. Plastic deformation of polyurea coated composite aluminium plates subjected to low velocity impact. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 696–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | Density (Kg/m3) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5A06 aluminum alloy | 2780 | 74,000 | 0.32 |
| aluminum foam | 300 | 80 | 0.10 |
| Material | A (MPa) | B (MPa) | N | C | m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5A06 aluminum alloy | 167.0 | 443.7 | 0.44 | 0.02 | 2.3 |
| Configuration | Thickness of Front Sheet | Thickness of Back Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| 2 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| Label | Impact Velocity (m/s) | Normalized Impulse | Failure Mode of Front Face Sheet | Residual Thickness of the Core (mm) | Deformation (mm) | Energy Absorption (J/mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1 | 85.8 | 0.99 | I | 5.0 | 5.92 | 9.09 |
| 1-2 | 122.3 | 1.42 | I | 3.2 | 9.18 | 11.98 |
| 1-3 | 155.5 | 1.84 | I | 2.2 | 12.58 | 14.33 |
| 1-4 | 168.2 | 1.97 | I | 1.8 | 14.17 | 14.78 |
| 1-5 | 213.5 | 2.40 | I | 1.5 | 18.38 | 17.61 |
| 1-6 | 257.5 | 2.92 | III | 1.2 | 25.00 | 18.96 |
| 1-7 | 268.2 | 3.00 | III | Shear | 26.06 | 19.46 |
| 1-8 | 263.8 | 3.11 | III | Shear | 28.54 | 18.25 |
| 1-9 | 276.7 | 3.18 | III | Shear | 29.58 | 18.77 |
| 1-10 | 300.9 | 3.46 | III | Shear | 33.27 | 19.73 |
| 2-1 | 72.8 | 0.84 | I | 6.1 | 5.66 | 6.79 |
| 2-2 | 109.2 | 1.26 | I | 4.4 | 8.33 | 10.38 |
| 2-3 | 139.5 | 1.58 | I | 2.8 | 10.65 | 13.07 |
| 2-4 | 190.3 | 2.16 | I | 1.9 | 15.94 | 16.24 |
| 2-5 | 228.9 | 2.58 | I | 1.5 | 19.90 | 18.69 |
| 2-6 | 246.9 | 2.76 | I | 1.5 | 21.48 | 20.01 |
| 2-7 | 272.9 | 3.11 | I | 1.4 | 23.95 | 22.39 |
| 2-8 | 298.0 | 3.42 | I | 1.3 | 26.57 | 24.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, N.; Sun, Z.; Guo, Q.; Ma, C.; Shi, Z. Experimental Investigation Concerning the Influence of Face Sheet Thickness on the Blast Resistance of Aluminum Foam Sandwich Structures Subjected to Localized Impulsive Loading. Metals 2025, 15, 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101122
Ye N, Sun Z, Guo Q, Ma C, Shi Z. Experimental Investigation Concerning the Influence of Face Sheet Thickness on the Blast Resistance of Aluminum Foam Sandwich Structures Subjected to Localized Impulsive Loading. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101122
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Nan, Zhiwei Sun, Qiyu Guo, Chicheng Ma, and Zhenyu Shi. 2025. "Experimental Investigation Concerning the Influence of Face Sheet Thickness on the Blast Resistance of Aluminum Foam Sandwich Structures Subjected to Localized Impulsive Loading" Metals 15, no. 10: 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101122
APA StyleYe, N., Sun, Z., Guo, Q., Ma, C., & Shi, Z. (2025). Experimental Investigation Concerning the Influence of Face Sheet Thickness on the Blast Resistance of Aluminum Foam Sandwich Structures Subjected to Localized Impulsive Loading. Metals, 15(10), 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101122




