Effects of Pre-Peening on Fatigue Performance of Gas-Nitrided SCM 440 Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
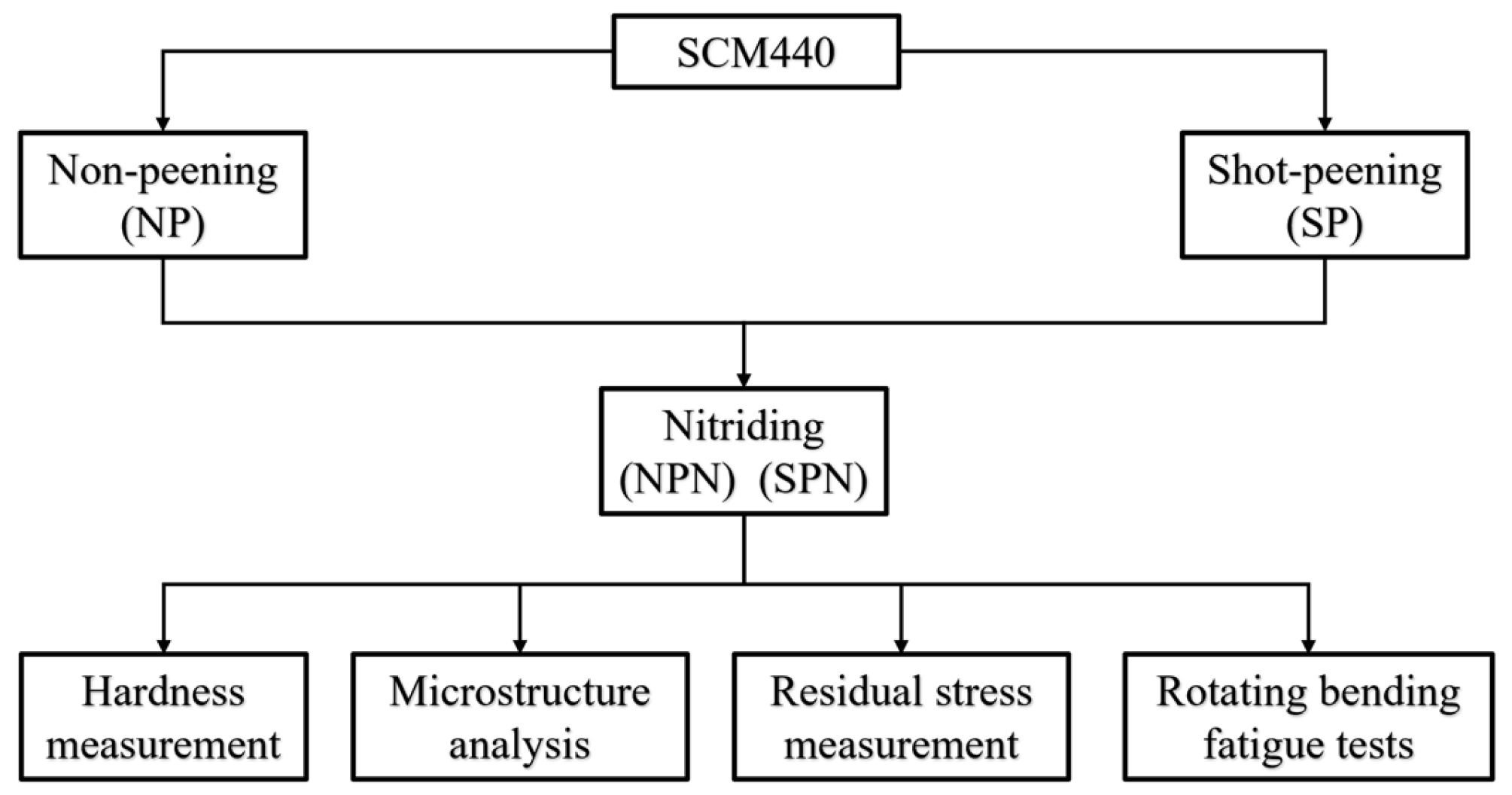
2. Materials and Experiments
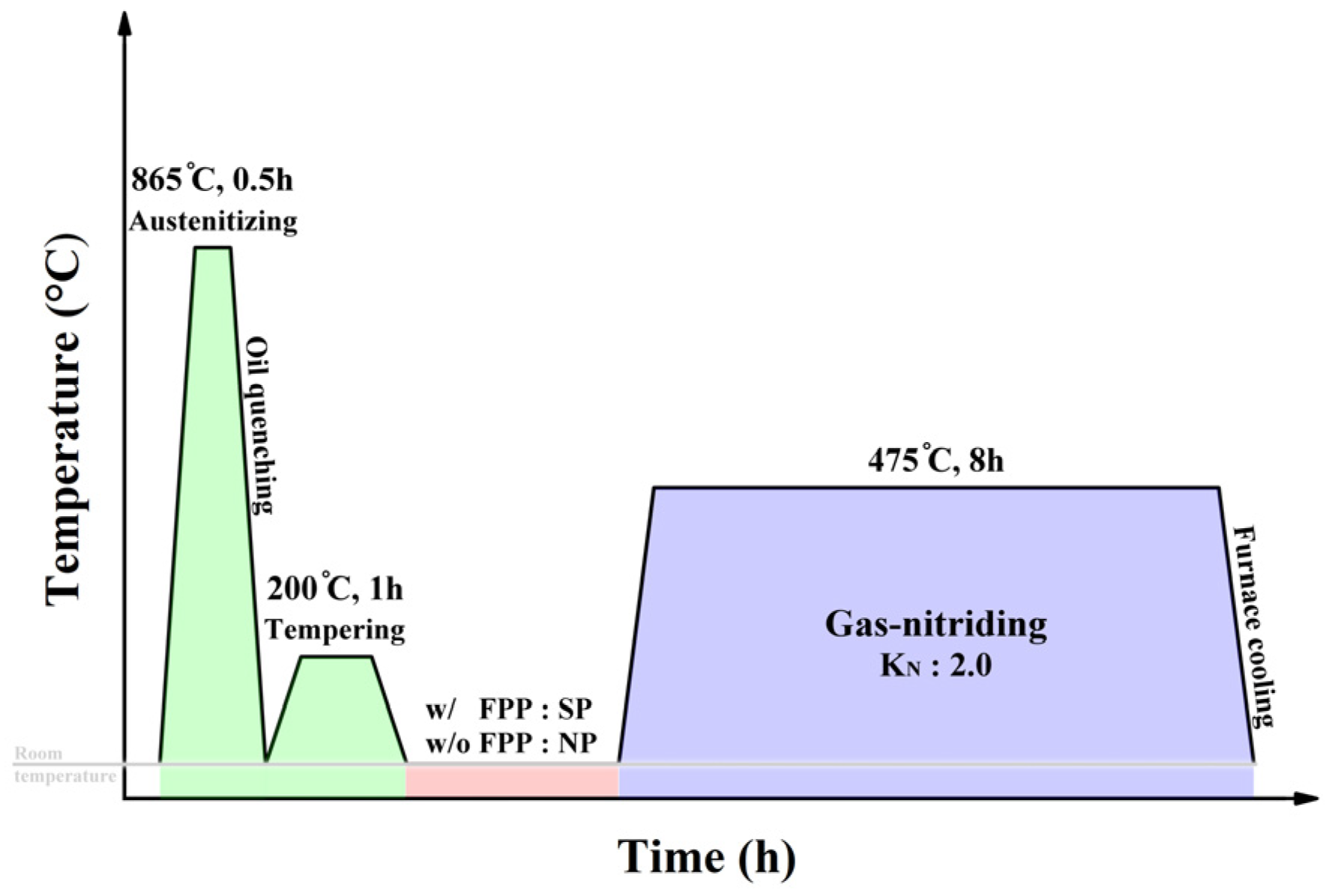
2.1. Preparation of Samples
2.2. Hardness Measurement and Fatigue Testing
2.3. Microstructural Observation
2.4. Measurement of Residual Stress
3. Results
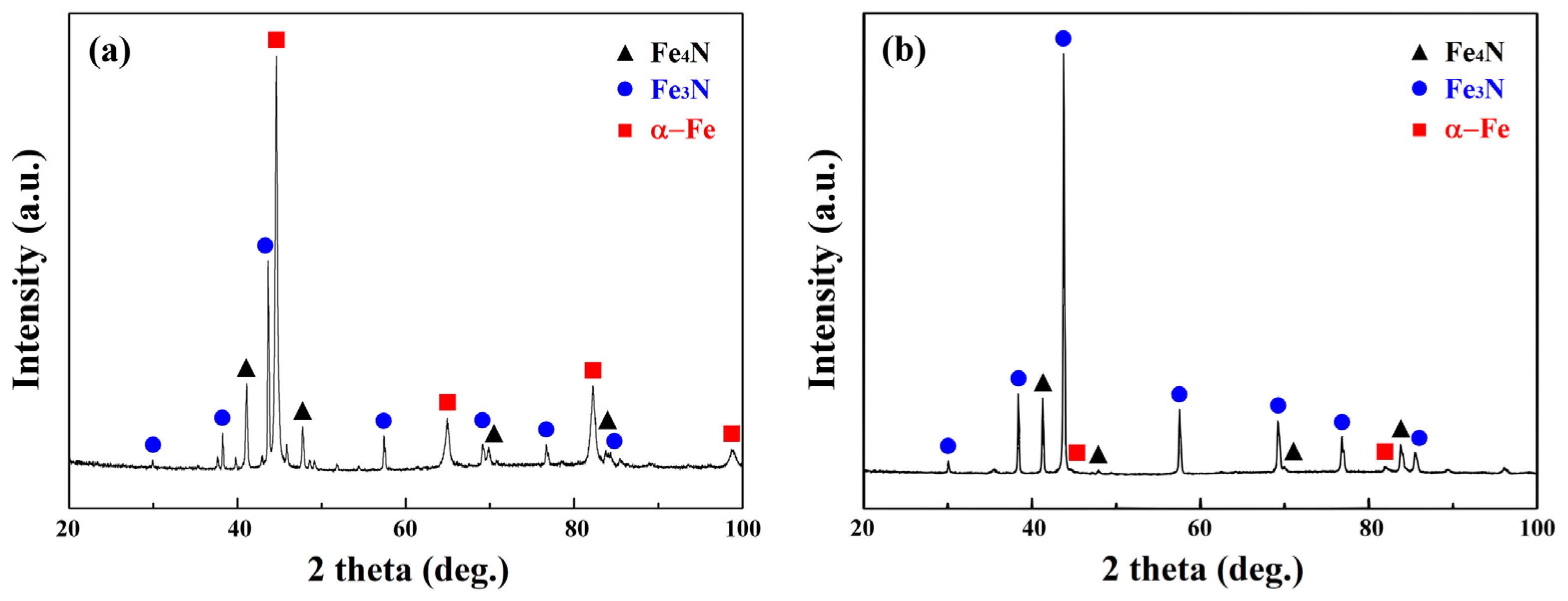
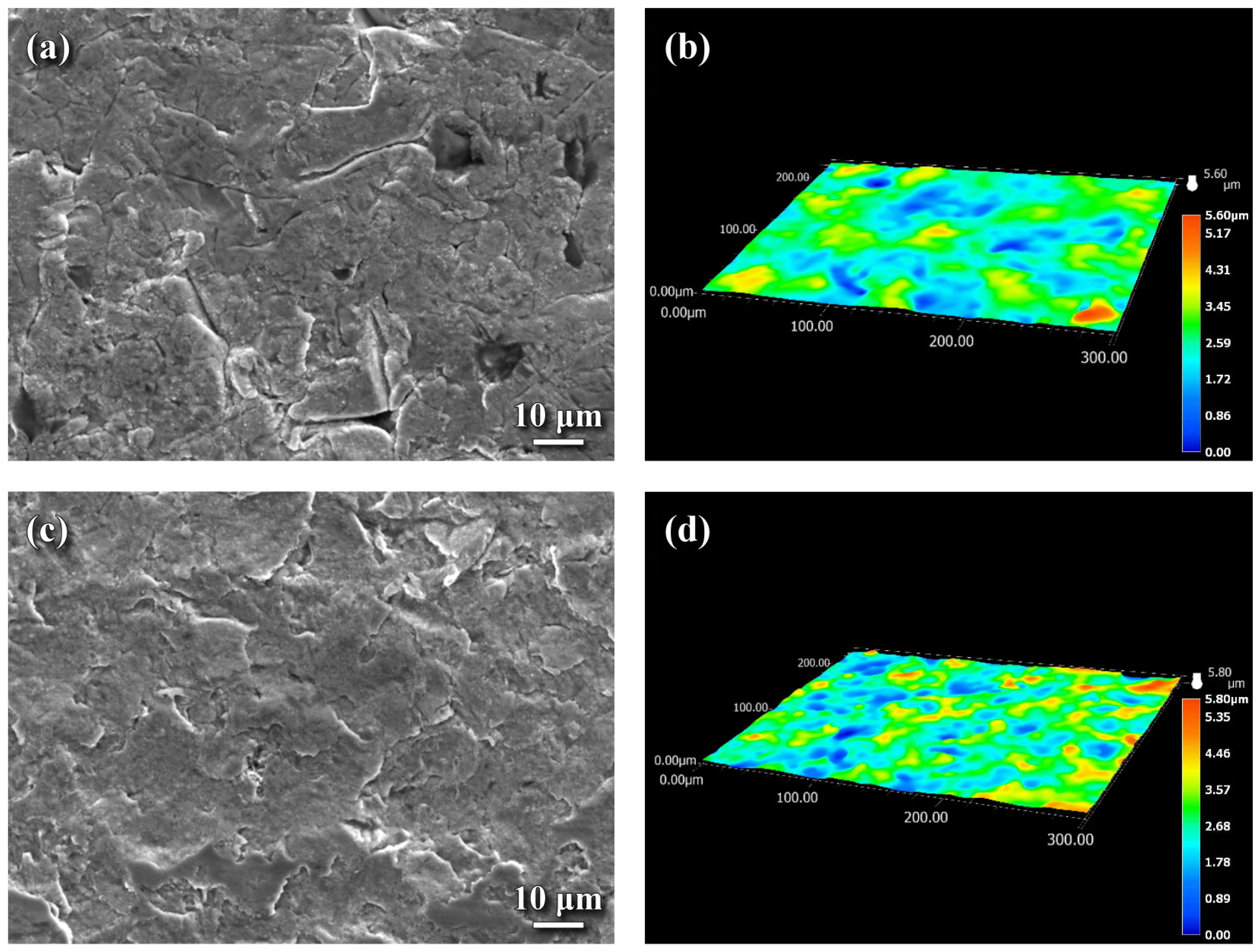
3.1. Phase and Surface Morphology of the Nitrided Sample
3.2. EPMA Analysis of the SPN Sample
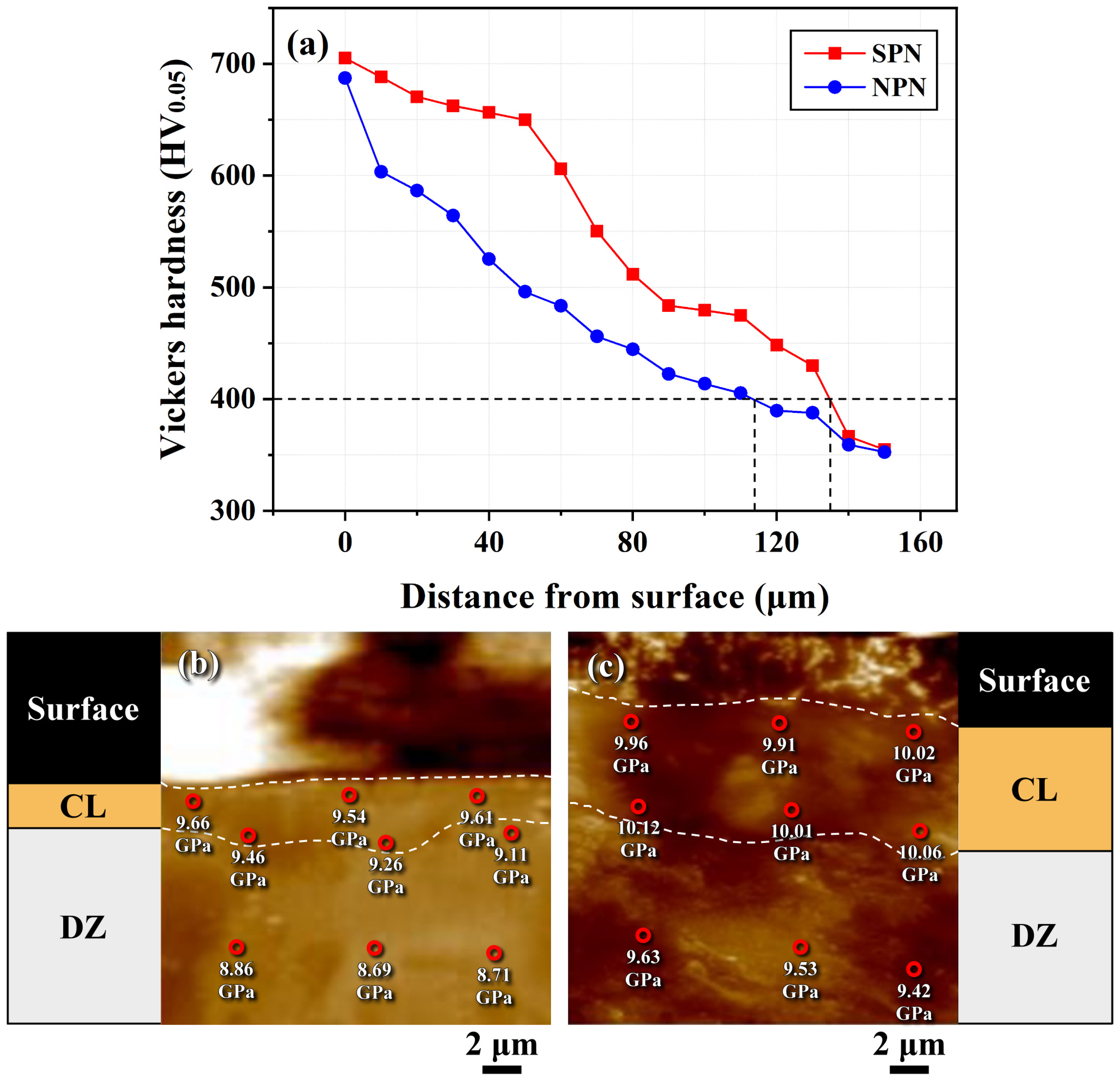
3.3. Hardness Profile of the Nitrided Specimens
3.4. EBSD Analysis
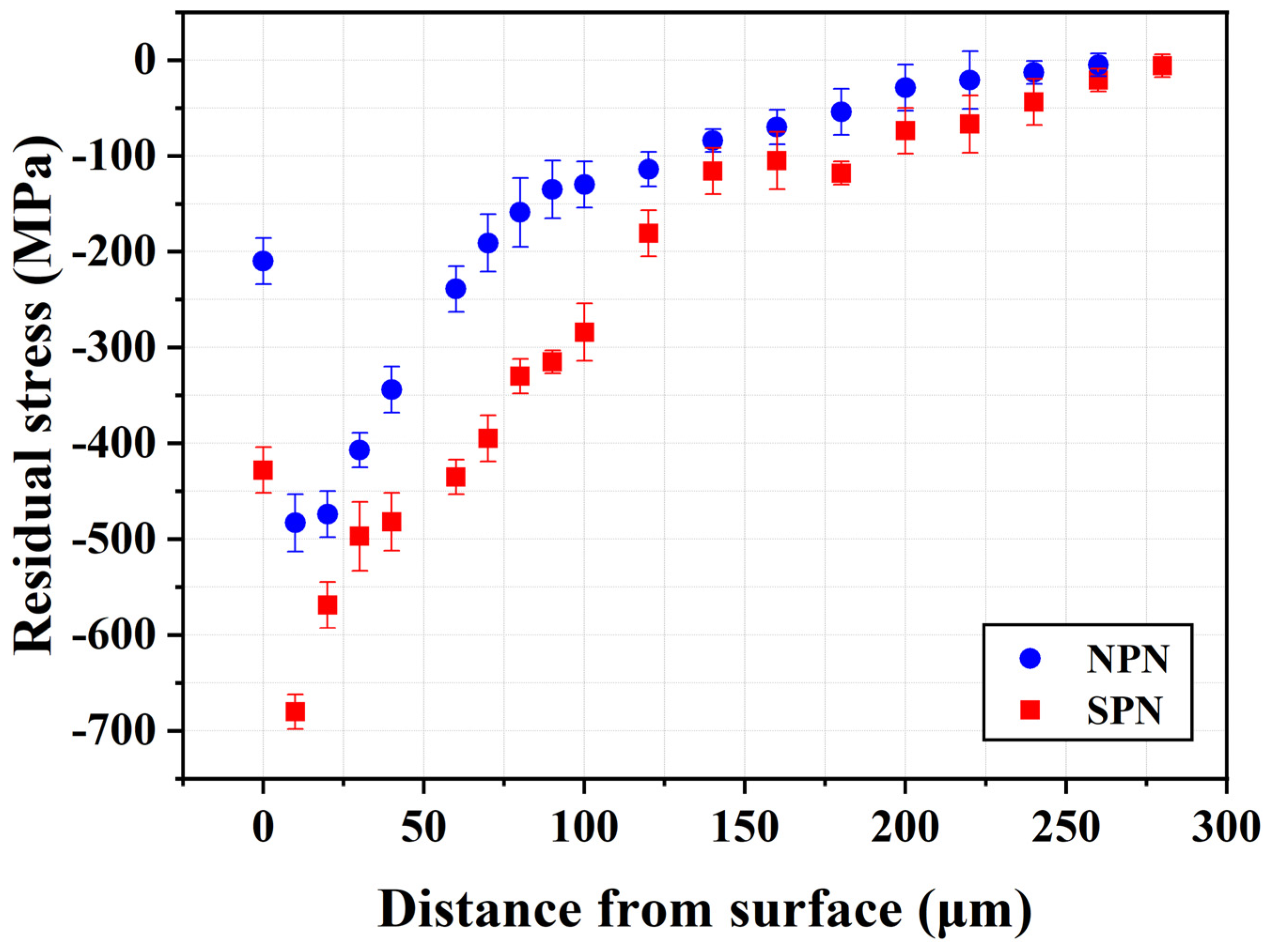
3.5. Residual Stress Measurements
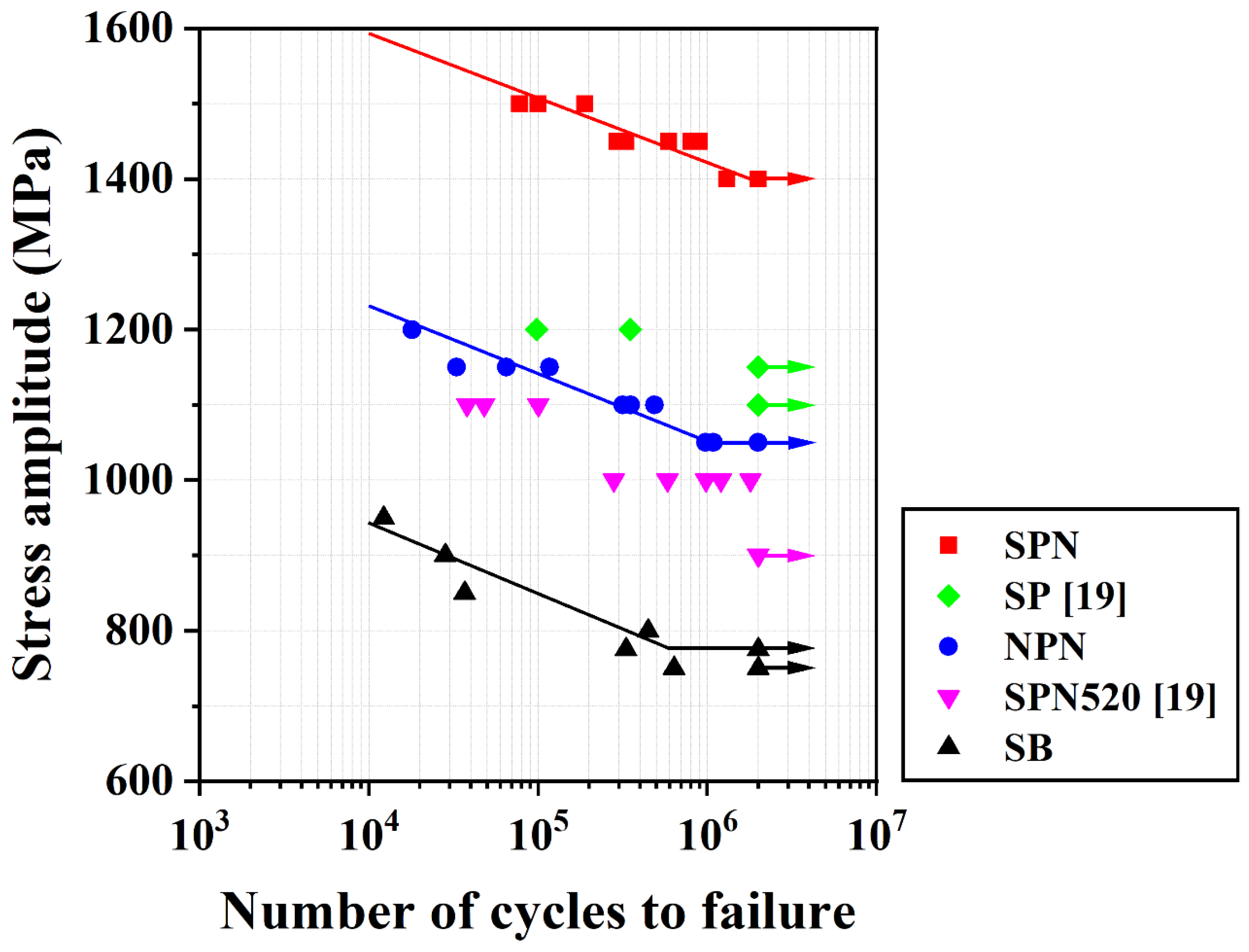
3.6. Fatigue Tests
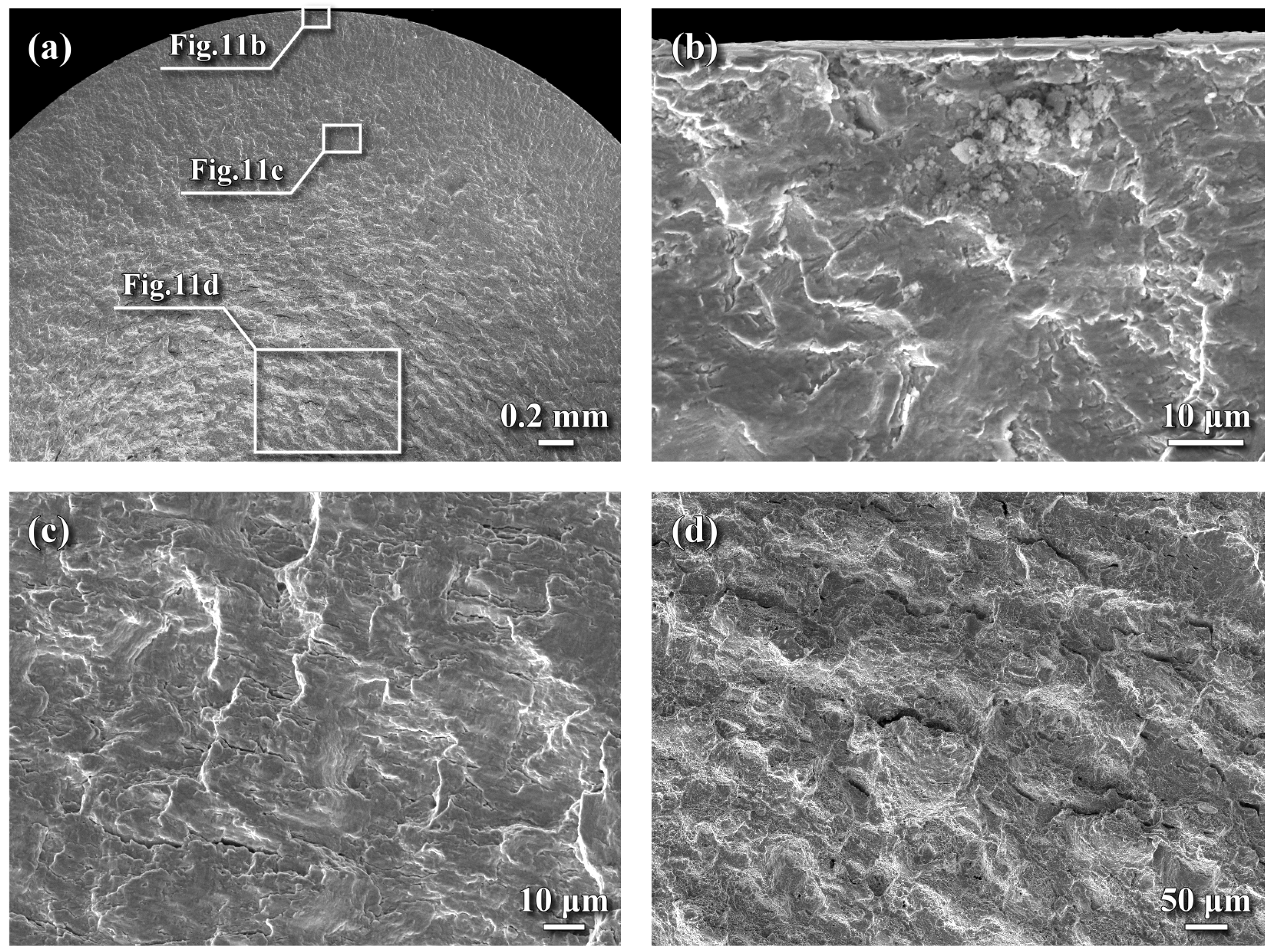
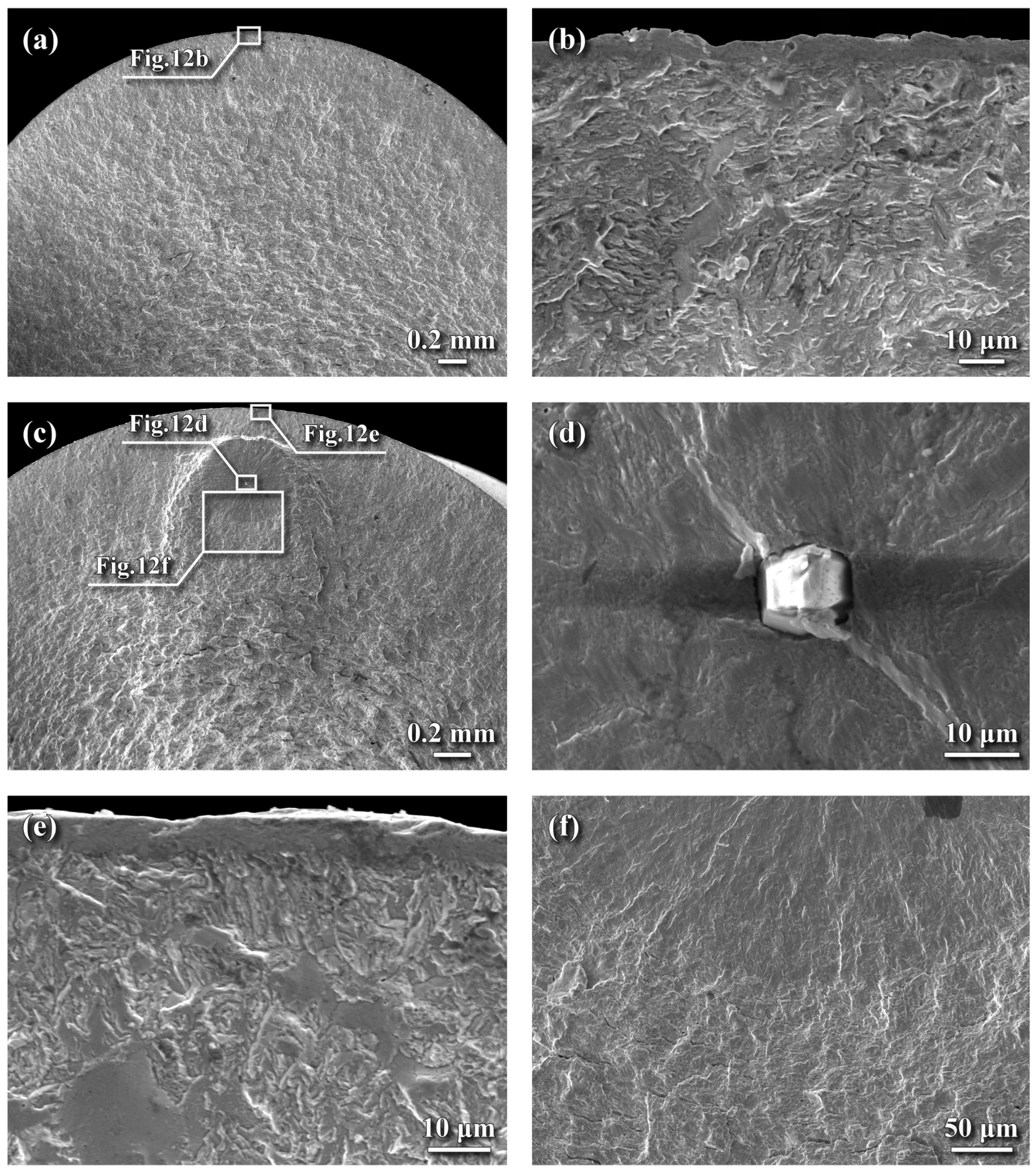
3.7. Fractured Surface Examinations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Pre-peening before nitriding could impose a refined structure and induce compressive residual stress (CRS) in the near-surface peened zone. The fine-grained structure provided numerous paths to enhance nitrogen diffusion inwards during nitriding. Therefore, the SPN specimen exhibited a higher fraction of iron nitrides in the compound layer, thicker compound layer and deeper case depth than the NPN one.
- The fatigue limits of the SB, NPN, and SPN specimens were approximately 750, 1050, and 1400 MPa, respectively. Comparing the fatigue limits of the SB and NPN samples, gas-nitriding significantly improved the fatigue properties of SCM 440 steel. Nitriding at 475 °C increased the fatigue limit of the peened + nitrided SCM440 steel to 1400 MPa. This significant improvement in fatigue performance of the peened + nitrided SCM440 steel can be attributed to the combined effects of a high CRS field and a hardened case, both of which retard surface crack initiation and growth.
- Fatigue cracks were prone to initiate at the external periphery of all tested specimens. In the SB specimen, quasi-cleavage at the crack initiation zone led to fatigue failure. In contrast, the NPN and SPN specimens exhibited a rubbed surface feature at the crack initiation site instead of quasi-cleavage. In both nitrided specimens, the compound layer remained firmly adhered to the surface, with no evidence of shattering or spalling, likely due to the presence of CRS.
- Surface morphology displayed a relatively flat surface interspersed with microcracks and fine pits in the NPN specimen. By contrast, numerous shallow dents without microcracks were obtained on the top surface of the SPN specimen. Surface microcracks and pits in the NPN specimen could be fatigue initiation sites and harmful to its fatigue resistance. Moreover, these surface dents were considered to be responsible for fatigue crack initiation in the SPN specimens. Therefore, polishing after nitriding to reduce surface roughness and or microcracks was expected to further increase the fatigue resistance and the reliability of nitrided SCM 440 steel.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vielma, A.T.; Llaneza, V.; Belzunce, F.J. Effect of coverage and double peening treatments on the fatigue life of a quenched and tempered structural steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 249, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, E.; Unal, O.; Amanov, A. Novel experimental methods for the determination of the boundaries between conventional, severe and over shot peening processes. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 13, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llaneza, V.; Belzunce, F.J. Optimal Shot Peening Treatments to Maximize the Fatigue Life of Quenched and Tempered Steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 2806–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, P.Q.; Khun, N.W.; Butler, D.L. Effect of Shot Peening Process on the Fatigue Life of Shot Peened Low Alloy Steel. ASME J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2018, 140, 011013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimbaev, R.; Pyun, Y.S.; Maleki, E.; Unal, O.; Amanov, A. An improvement in fatigue behavior of AISI 4340 steel by shot peening and ultrasonic nanocrystal surface modification. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 791, 139752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, F. Influence of plasma and gas nitriding on fatigue resistance of plain carbon (Ck45) steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 173–174, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirin, S.Y.; Sirin, K.; Kaluc, E. Effect of the ion nitriding surface hardening process on fatigue behavior of AISI 4340 steel. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirin, S.Y.; Sirin, K.; Kaluc, E. Influence of initial conditions on the mechanical behavior of ion nitrided AISI 4340 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 564, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, Y.; Ishida, A. Effect of Compound Layer Thickness Composed of γ’-Fe4N on Rotated-Bending Fatigue Strength in Gas-Nitrided JIS-SCM435 Steel. Mater. Trans. 2017, 58, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılan, F.; Kovacı, H. Investigation of the Combined Effects of Stress Concentrations and Plasma Nitriding Parameters on the Fatigue Performance of AISI 4140 Low Alloy Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 4402–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terčelj, M.; Kugler, G. An approach to increasing the service lifetimes of nitrided dies for aluminum hot extrusion: A case study. Wear 2017, 376–377, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-H.; Lee, S.-C.; Tang, T.-P. Effect of Shot Peening Treatment on Forging Die Life. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terčelj, M.; Smolej, A.; Fajfar, P.; Turk, R. Laboratory assessment of wear on nitrided surfaces of dies for hot extrusion of aluminium. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limodin, N.; Verreman, Y.; Tarfa, T. Axial fatigue of a gas nitrided quenched and tempered AISI 4140 steel: Effect of nitriding depth. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2003, 26, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, A.; Karadeniz, S. Improvement of the fatigue strength of AISI 4140 steel by an ion nitriding process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1995, 72, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genel, K.; Demirkol, M.; Çapa, M. Effect of ion nitriding on fatigue behaviour of AISI 4140 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 279, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani-Gangaraj, S.M.; Moridi, A.; Guagliano, M.; Ghidini, A.; Boniardi, M. The effect of nitriding, severe shot peening and their combination on the fatigue behavior and micro-structure of a low-alloy steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2014, 62, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limodin, N.; Verreman, Y. Fatigue strength improvement of a 4140 steel by gas nitriding: Influence of notch severity. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 435–436, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.W.; Chen, T.C.; Hsu, H.H.; Tsay, L.W. Synergetic effects of micro-shot peening and gas nitriding on the fatigue performance of AISI 4140 steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 485, 130856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terres, M.A.; Laalai, N.; Sidhom, H. Effect of nitriding and shot-peening on the fatigue behavior of 42CrMo4 steel: Experimental analysis and predictive approach. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, Y.; Komotori, J. Effect of micro ploughing during fine particle peening process on the microstructure of metallic materials. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 6146–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, S.; Komotori, J. Effect of Fine Particle Peening Treatment prior to Nitriding on Fatigue Properties of AISI 4135 Steel. J. Solid Mech. Mater. Eng. 2008, 2, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; Komotori, J. Effect of fine particle peening on fatigue properties of AISI 4135 steel with different hardness. In Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Fracture 2008: Multilevel Approach to Fracture of Materials, Components and Structures, Brno, Czech Republic, 2–5 September 2008; Volume 2, pp. 874–881. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, S.; Komotori, J. Evaluation of the Gas Nitriding of Fine Grained AISI 4135 Steel Treated with Fine Particle Peening and Its Effect on the Tribological Properties. Mater. Trans. 2015, 56, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Song, Q.; Lu, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z. A comparison of the effects of traditional shot peening and micro-shot peening on the scuffing resistance of carburized and quenched gear steel. Wear 2016, 368–369, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.H.; Chen, T.C.; Ding, Y.S.; Lu, G.X.; Tsay, L.W. Effects of Micro-Shot Peening on the Fatigue Strength of Anodized 7075-T6 Alloy. Materials 2023, 16, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, O.; Varol, R. Surface severe plastic deformation of AISI 304 via conventional shot peening, severe shot peening and repeening. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 351, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.H.; Chen, T.C.; Lee, H.B.; Tasy, L.W. Effect of Micro-Shot Peening on the Fatigue Performance of AISI 304 Stainless Steel. Metals 2021, 11, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanov, A.; Karimbaev, R.; Maleki, E.; Unal, O.; Pyun, Y.S.; Amanov, T. Effect of combined shot peening and ultrasonic nanocrystal surface modification processes on the fatigue performance of AISI 304. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 358, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Shen, L. The effect of surface nanocrystallization on plasma nitriding behaviour of AISI 4140 steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K. The cosα method for X-ray residual stress measurement using two-dimensional detector. Bull. JSME 2019, 6, 18-00378. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K. X-ray measurement of triaxial residual stress on machined surfaces by the cosα method using a two-dimensional detector. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2018, 51, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, T.C.; Hsu, H.H.; Tsay, L.W. Effect of microstructure and compressive residual stress on the fatigue performance of AISI 4140 steel with QPQ salt bath nitro-carburizing. Materials 2025, 18, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhan, Z.; Zhang, S. Influence of inclusion parameter and depth on the rotating bending fatigue behavior of bearing steel. Metals 2024, 14, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Lu, L.T.; Shiozawa, K.; Zhou, W.N.; Zhang, W.H. Effect of nitrocarburizing and post-oxidation on fatigue behavior of 35CrMo alloy steel in very high cycle fatigue regime. Int. J. Fatigue 2011, 33, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Shiozawa, K.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, W. Effects of nitrocarburizing on fatigue property of medium carbon steel in very high cycle regime. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 528A, 7060–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyo Kenmazai Kogyo Ltd. Shot Machine A One Polish. Available online: http://www.toyo-kenmazai-kogyo.jp/ (accessed on 21 June 2025).



| C | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Si | Ni | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.42 | 0.81 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 1.01 | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.01 | Bal. |
| Location | Distance from Surface (μm) | Chemical Composition in wt% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | O | Mn | Cr | Mo | Si | Fe | ||
| Compound layer | 2 | 0.36 | 4.27 | 0.15 | 0.50 | 0.77 | 0.12 | 0.23 | Bal. |
| 6 | 0.40 | 3.76 | 0.09 | 0.48 | 0.75 | 0.13 | 0.23 | Bal. | |
| Diffusion zone | 20 | 0.40 | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.82 | 1.01 | 0.12 | 0.23 | Bal. |
| 50 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.03 | 0.91 | 0.85 | 0.08 | 0.19 | Bal. | |
| 150 | 0.44 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.76 | 0.93 | 0.12 | 0.20 | Bal. | |
| Base | 250 | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.72 | 1.00 | 0.10 | 0.21 | Bal. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Chen, T.-C.; Chen, W.-H.; Hsu, H.-H.; Tsay, L.-W. Effects of Pre-Peening on Fatigue Performance of Gas-Nitrided SCM 440 Steel. Metals 2025, 15, 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101118
Chen H, Chen T-C, Chen W-H, Hsu H-H, Tsay L-W. Effects of Pre-Peening on Fatigue Performance of Gas-Nitrided SCM 440 Steel. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101118
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hao, Tai-Cheng Chen, Wen-Han Chen, Hsiao-Hung Hsu, and Leu-Wen Tsay. 2025. "Effects of Pre-Peening on Fatigue Performance of Gas-Nitrided SCM 440 Steel" Metals 15, no. 10: 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101118
APA StyleChen, H., Chen, T.-C., Chen, W.-H., Hsu, H.-H., & Tsay, L.-W. (2025). Effects of Pre-Peening on Fatigue Performance of Gas-Nitrided SCM 440 Steel. Metals, 15(10), 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101118








