Selective Recovery of Cobalt and Nickel from Spent Lithium-Ion Battery NMC Cathodes Using a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent
2.3. Leaching Experiments
2.4. Analysis of Metal Content
2.5. Physicochemical Characterization of HDES
3. Results and Discussion
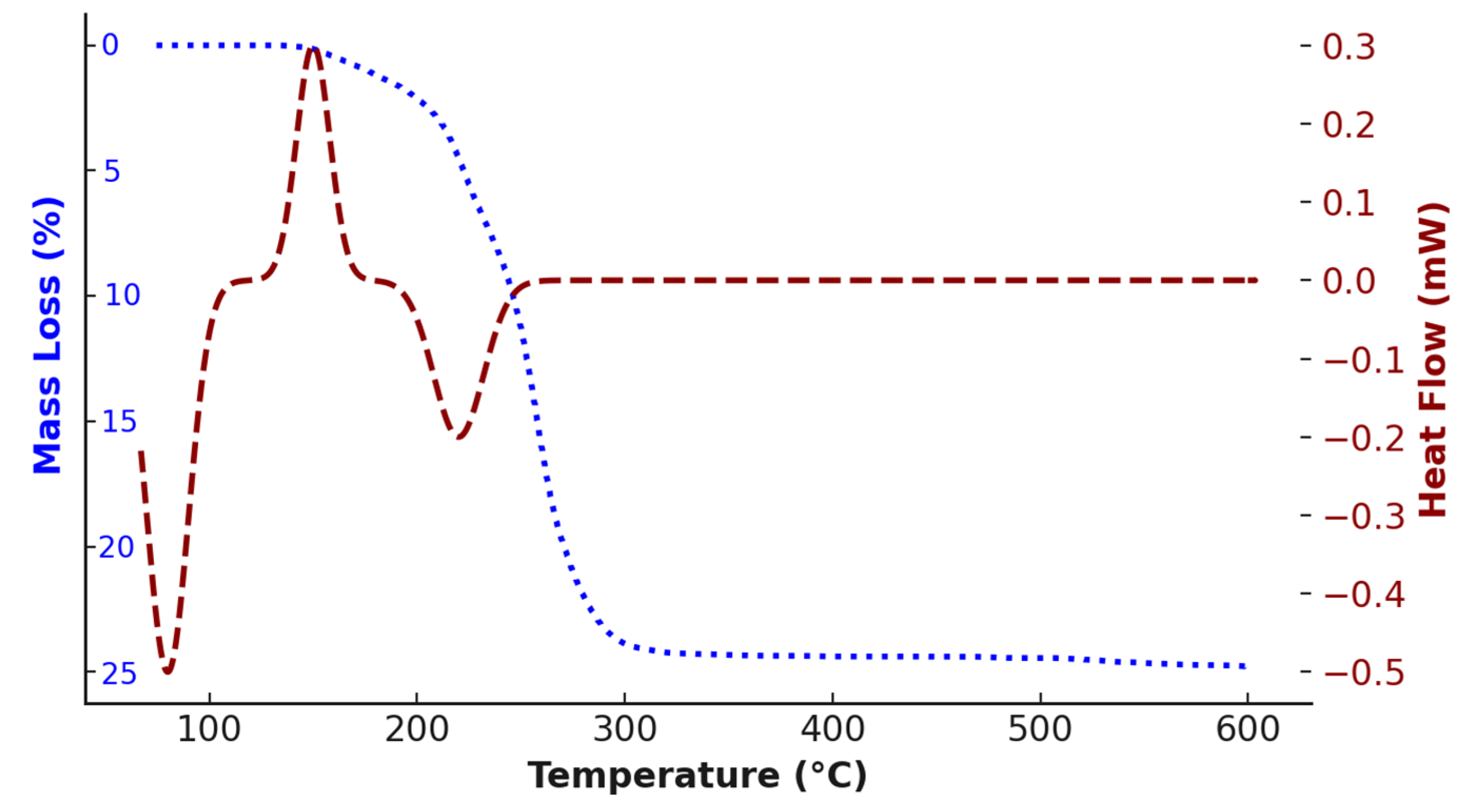
3.1. Characterization of NMC Powder Sample
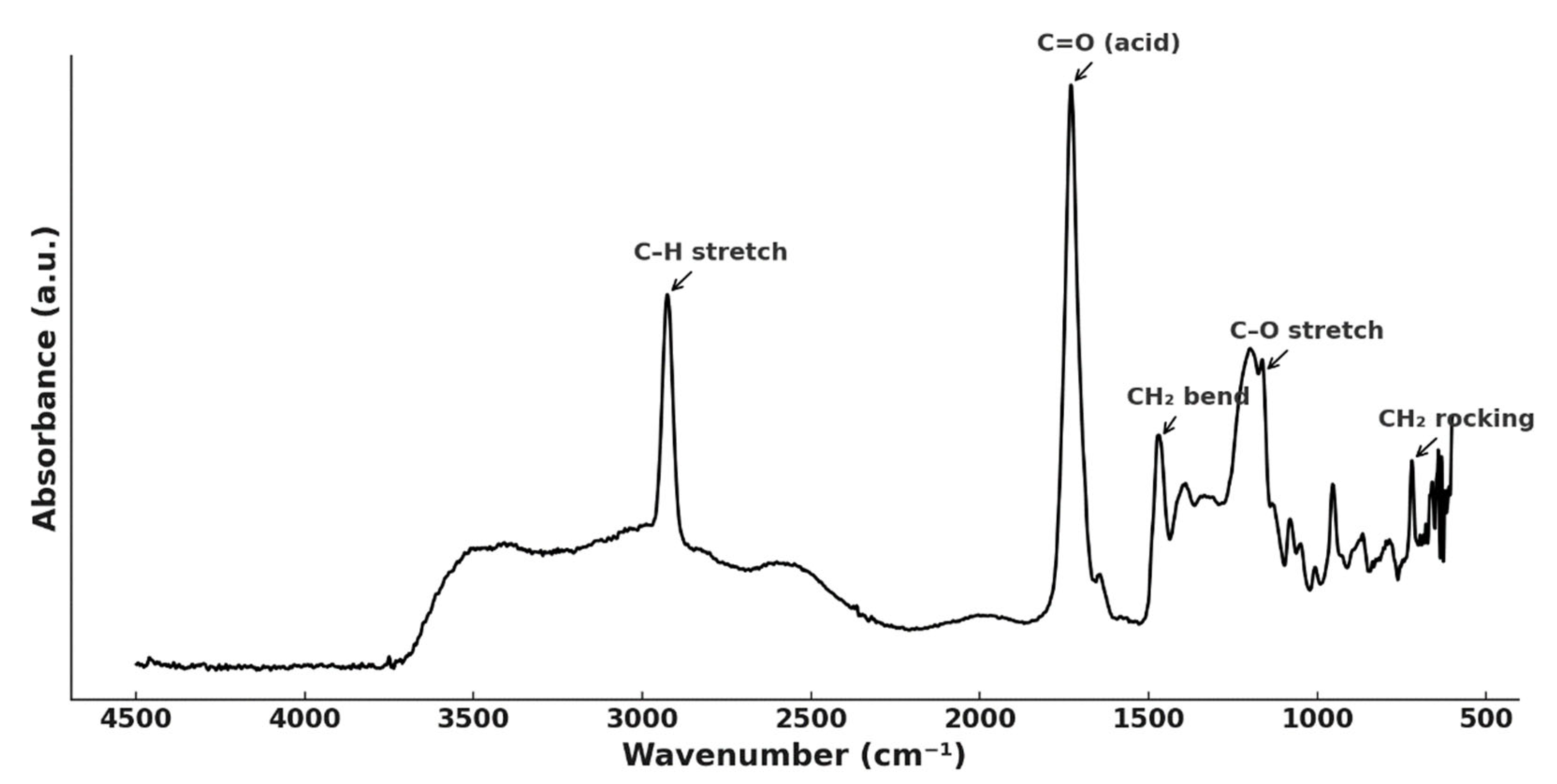
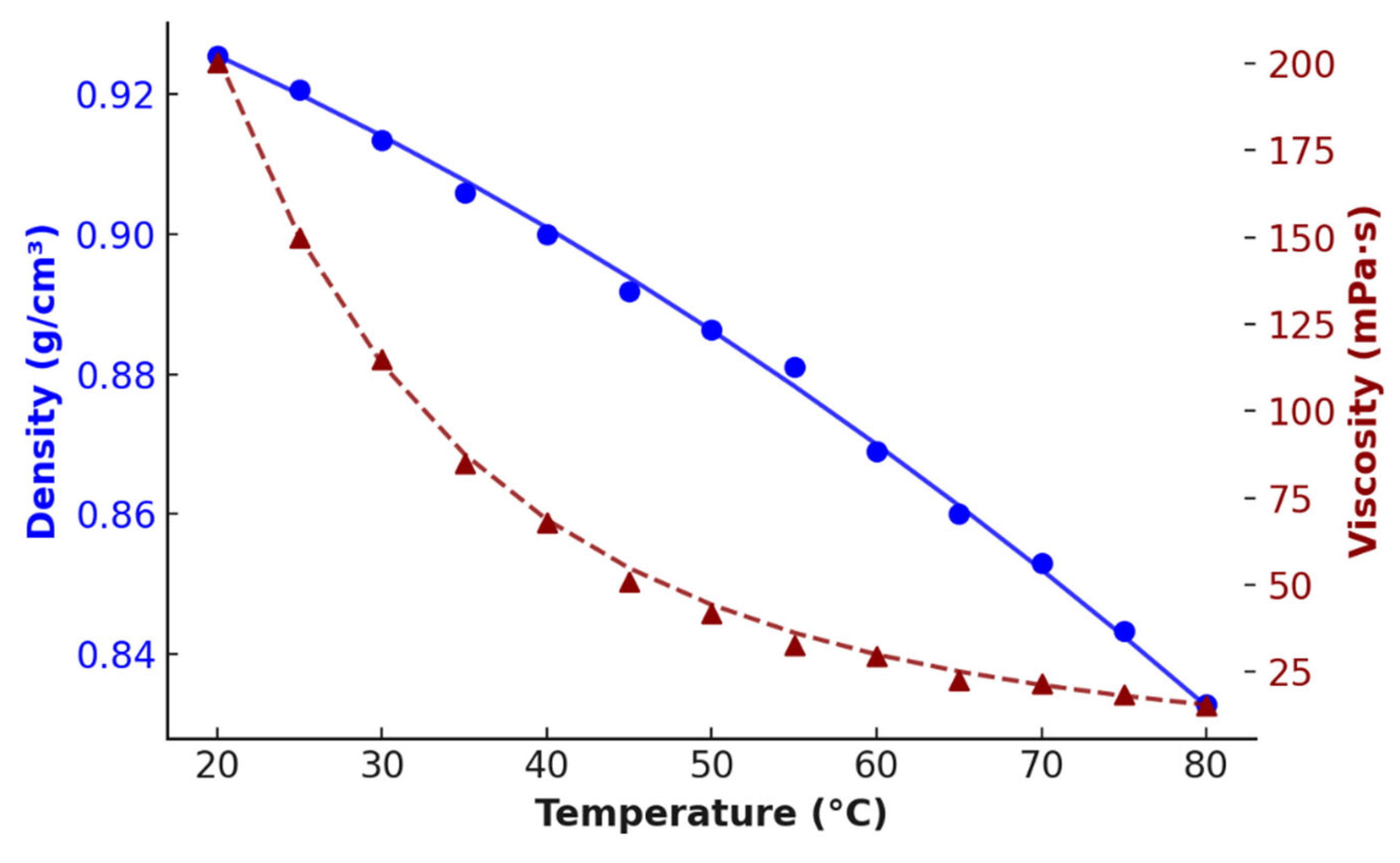
3.2. HDES Characterization
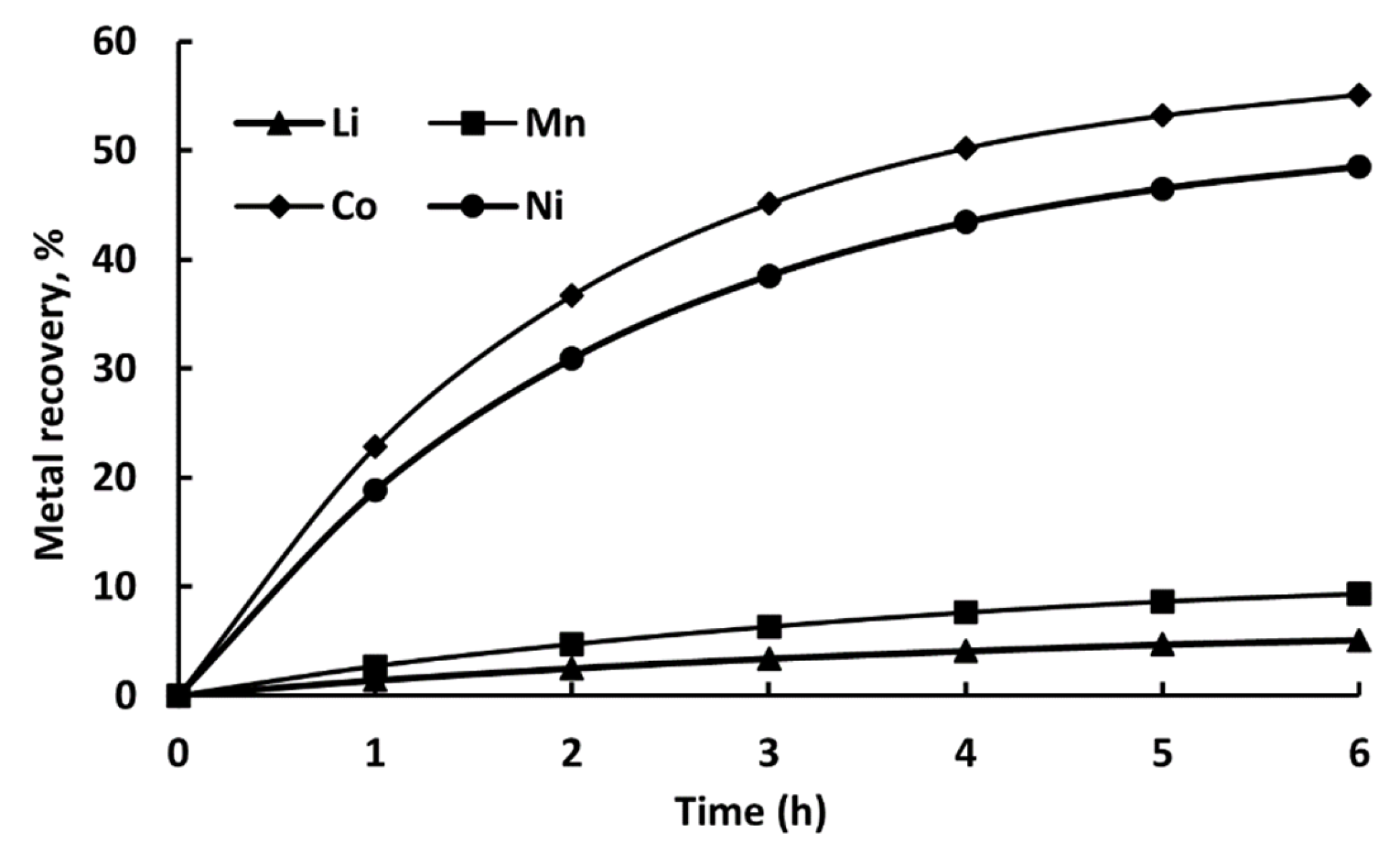
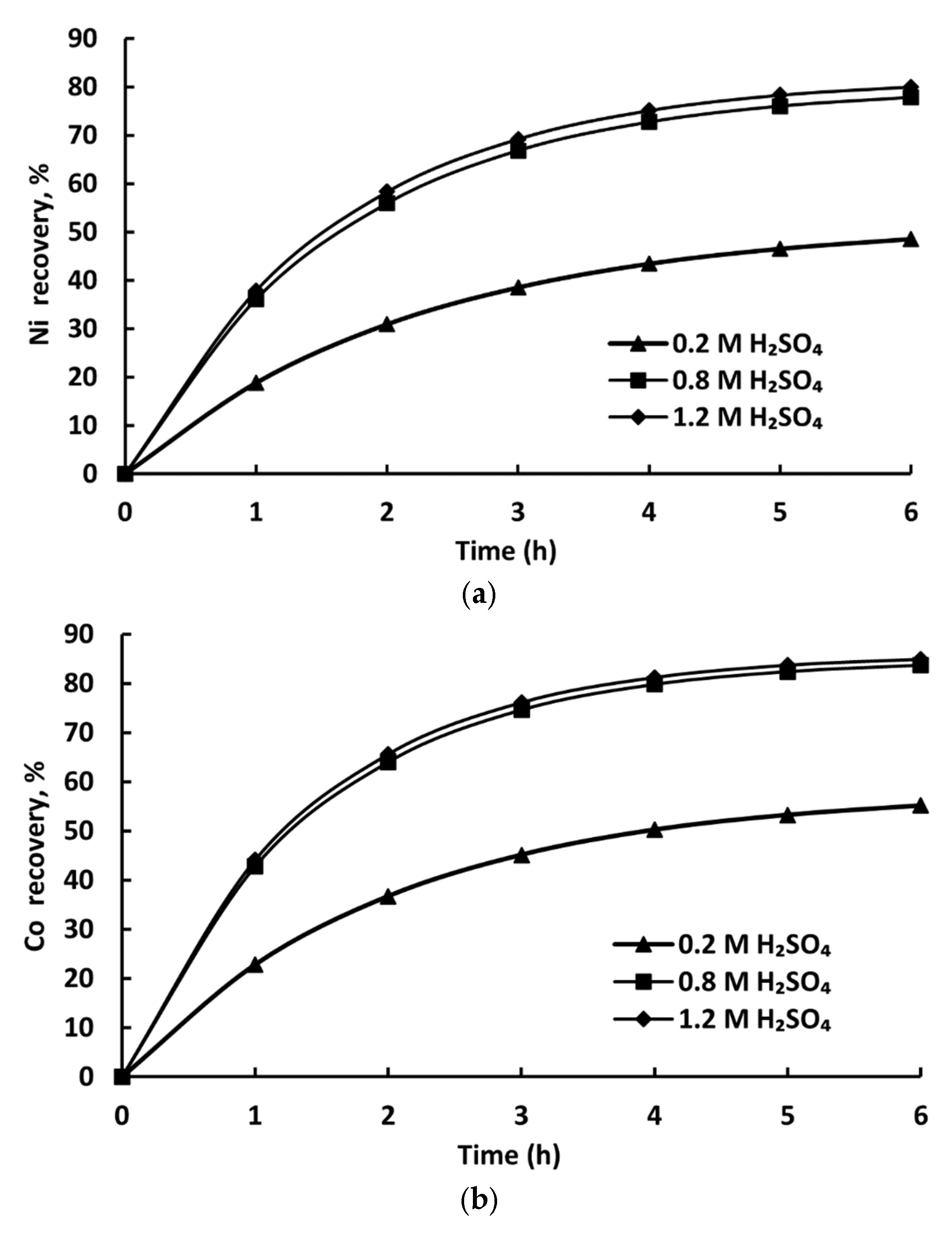
3.3. Leaching Results
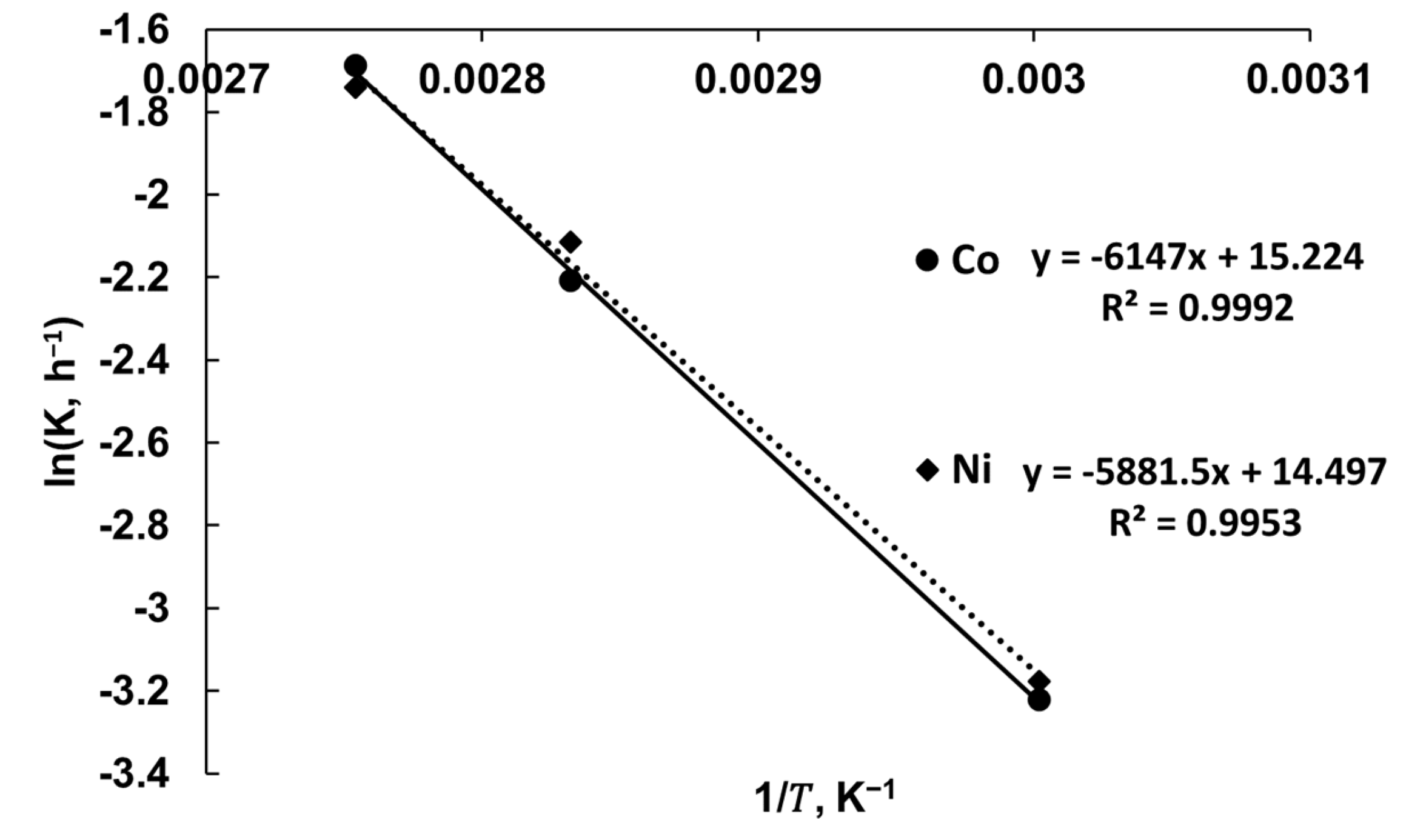
3.4. Leaching Kinetic Analysis
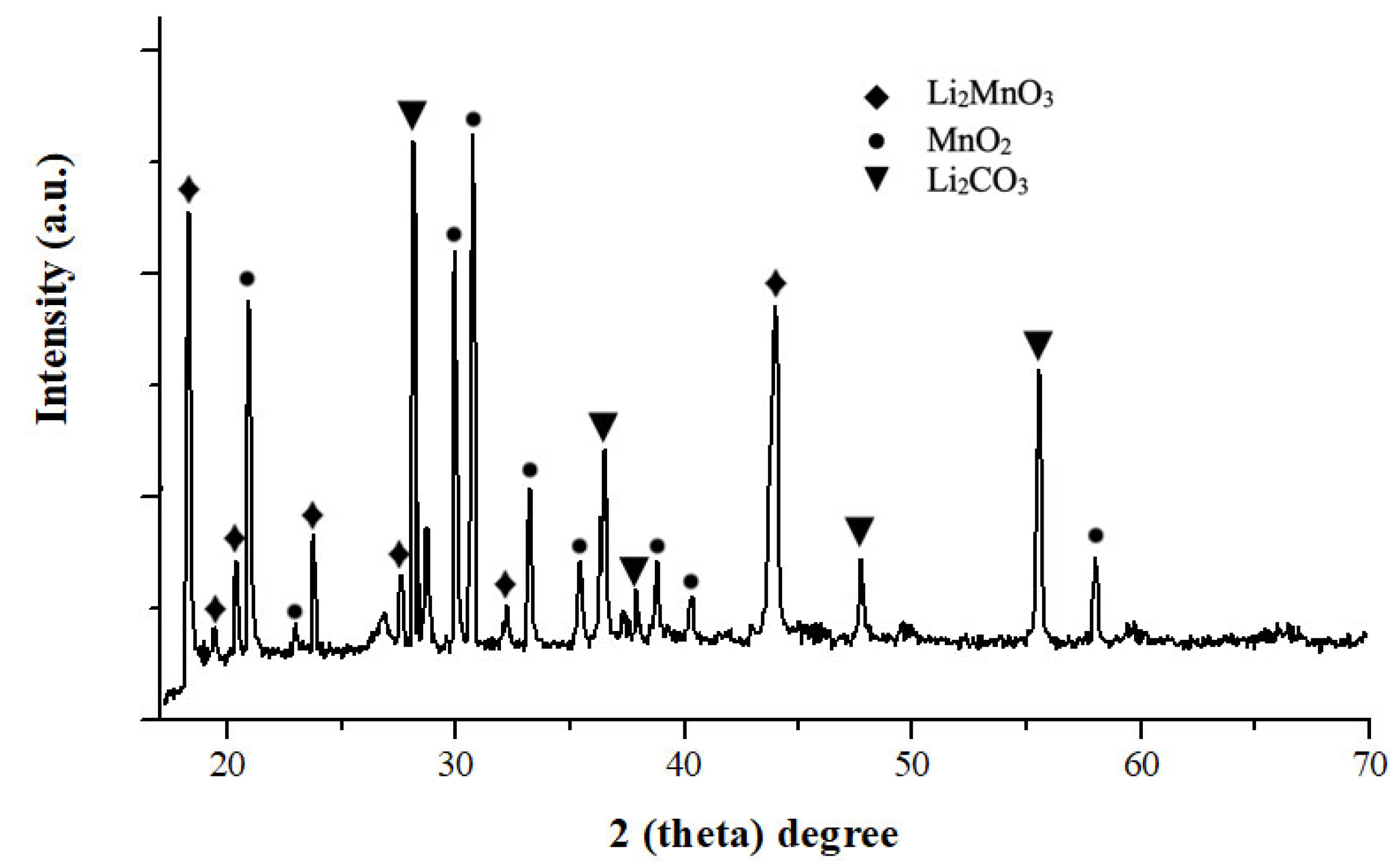
3.5. Leaching Residue Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, B.; Pan, Z.; Su, X.; An, L. Recycling of lithium-ion batteries: Recent advances and perspectives. J. Power Sources 2018, 399, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Luo, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xu, C.; Guo, J.; Cheali, P.; Xia, X. Progress, challenges, and prospects of spent lithium-ion batteries recycling: A review. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 89, 144–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.; Kim, Y. Technologies of lithium recycling from waste lithium ion batteries: A review. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 3234–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Shen, Y. Pyrometallurgical recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries from conventional roasting to synergistic pyrolysis with organic wastes. J. Energy Chem. 2023, 85, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückner, L.; Frank, J.; Elwert, T. Industrial recycling of lithium-ion batteries—A critical review of metallurgical process routes. Metals 2020, 10, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. Pyrometallurgical technology in the recycling of a spent lithium ion battery: Evolution and the challenge. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 1, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, L.; Vrucak, D.; Woeste, R.; Lucas, H.; Rombach, E.; Friedrich, B.; Letmathe, P. Pyrometallurgical recycling of different lithium-ion battery cell systems: Economic and technical analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 416, 137834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ge, J.; Chen, R.; Wu, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X. Environmental friendly leaching reagent for cobalt and lithium recovery from spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2615–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaltonen, M.; Peng, C.; Wilson, B.P.; Lundström, M. Leaching of metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. Recycling 2017, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dunn, J.B.; Zhang, X.X.; Gaines, L.; Chen, R.J.; Wu, F.; Amine, K. Recovery of metals from spent lithium-ion batteries with organic acids as leaching reagents and environmental assessment. J. Power Sources 2013, 233, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liu, C.; Cao, H.; Zheng, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Comprehensive evaluation on effective leaching of critical metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guan, Y.; Fan, E.; Wu, F.; Chen, R. Process for recycling mixed-cathode materials from spent lithium-ion batteries and kinetics of leaching. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, M.; Shafaie, S.Z.; Abdollahi, H.; Entezari-Zarandi, A. Green recycling of spent Li-ion batteries by deep eutectic solvents (DESs): Leaching mechanism and effect of ternary DES. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 109014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Reyes, I.G.; Mendoza-Pérez, J.A.; Ruiz-Guerrero, R.; Medina-Velázquez, D.Y.; Zepeda-Vallejo, L.G.; Morales-Ramírez, Á.d.J. Kinetics of Zn–C battery leaching with choline chloride/urea natural deep eutectic solvents. Recycling 2022, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yan, X.; Shi, M.; Wu, C. Deep eutectic solvent for spent lithium-ion battery recycling: Comparison with inorganic acid leaching. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 19029–19051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, M.; Cao, Y.; Yu, K.; Fan, Z.; Cao, Y. Designing Low Toxic Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Green Recycle of Lithium--Ion Batteries Cathodes. ChemSusChem 2024, 17, e202301953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.K.J.; Rana, M.; Khan, I.H.; Jo, Y.T.; Park, J.-H. Choline chloride-lactic acid-ascorbic acid (ChCl-LA-AA) based green deep eutectic solvent for leaching LiMn2O4 cathode material of spent Li-ion batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2025, 236, 106529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lyu, Y.; Zeng, R.; Zhang, S.; Davey, K.; Mao, J.; Guo, Z. Green recycling of spent Li-ion battery cathodes via deep-eutectic solvents. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 867–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, E.; Kordloo, M.; Khodadadmahmoudi, G.; Rezaei, A.; Ganjali, M.; Azimi, G. Solvometallurgical recycling of spent LiNixCoyMnzO2 (NCM) cathode material using ternary choline chloride-ethylene glycol-p-toluenesulfonic acid deep eutectic solvent. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 222, 106184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Sahadevan, S.A.; Ramani, V.; Sankarasubramanian, S. Recommended Practices for the Electrochemical Recovery of Cobalt from Lithium Cobalt Oxide: A Case Study of the Choline Chloride:Ethylene Glycol Deep Eutectic Solvent. ChemSusChem 2025, 18, e202401205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhashim, S.H.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Tromer, R.; Kabbani, A.; Babu, G.; Oliveira, E.F.; Galvao, D.S.; Ajayan, P.M. Mechanistic study of lithium-ion battery cathode recycling using deep eutectic solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 6914–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, H.; Schaeffer, N.; Pringle, J.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Pozo-Gonzalo, C. Enhanced Dissolution of Metal Oxides in Hydroxylated Solvents—Towards Application in Lithium-Ion Battery Leaching. ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202300455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Wang, K.; Li, X. Recovery of cobalt from spent lithium-ion battery cathode materials by using choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent. Green Process. Synth. 2022, 11, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shao, H.; Zhao, Q.; Liang, Z. Use of microwave-assisted deep eutectic solvents to recycle lithium manganese oxide from li-ion batteries. JOM 2021, 73, 2104–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyo, E.; Muryanta, W.A.; Anggraini, A.G.; Sudibyo, S.; Amin, M.; Al Muttaqii, M. Tannic acid as a novel and green leaching reagent for cobalt and lithium recycling from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2022, 24, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Chao, Y.; Sun, J.; Ji, H.; Zhu, W. Sustainable and convenient recovery of valuable metals from spent li-ion batteries by a one-pot extraction process. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 13851–13861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liang, Z. An efficient and precipitant-free approach to selectively recover lithium cobalt oxide made for cathode materials using a microwave-assisted deep eutectic solvent. Energy Fuels 2022, 37, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, N.; Liu, W.; Feng, H.; Su, J.; Fu, D.; Liu, X.; Qiu, M.; Wang, L. A reusable deep eutectic solvent for the regeneration of Li and Co metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloy. Compd. 2023, 966, 171517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.L.; Pateli, I.M.; Lei, C.; Jarvis, A.; Abbott, A.P.; Hartley, J.M. Separation of nickel from cobalt and manganese in lithium ion batteries using deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 4877–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Fan, M.; Gu, C.F.; He, W.H.; Meng, Q.; Wan, L.J.; Guo, Y.G. Selective extraction of transition metals from spent LiNixCoyMn1−x−yO2 cathode via regulation of coordination environment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jin, J.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wu, L.; Wang, C. A Review on Leaching of Spent Lithium Battery Cathode Materials Adopting Deep Eutectic Solvents. ChemistryOpen 2024, 14, e202400258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.K.; Rodrigues, M.-T.F.F.; Kato, K.; Babu, G.; Ajayan, P.M. Deep eutectic solvents for cathode recycling of Li-ion batteries. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, F.; Lyu, M.; Yang, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L. Ni-rich cathode materials for stable high-energy lithium-ion batteries. Nano Energy 2024, 126, 109620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Sun, D.; Tang, J.; Shen, X.; Pishva, P.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, K.; Peng, Z. Ecofriendly, Highly Selective Lithium Extraction by Redox-Mediated Electrodialysis. ACS Central Sci. 2024, 10, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Zhou, G.; Lu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Chao, Y.; Zhu, W. Tailoring hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for selective lithium recovery from the mother liquor of Li2CO3. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Hanada, T.; Sato, H.; Kamisono, M.; Goto, M. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for the direct leaching of nickel laterite ores: Selectivity and reusability investigations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 331, 125619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, F.; Sun, Z.; Chi, Q.; Li, Y. Efficient selective leaching of ytterbium and lutetium oxides by new hy-drophobic deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 343, 127097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisono, M.; Hanada, T.; Goto, M. Platinum group metal recycling from spent automotive catalysts using reusable hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. ACS Sustain. Resour. Manag. 2024, 1, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Kamisono, M.; Goto, M. High-Purity Nickel Recovery from Low-Grade Nickel Laterite Ore Using Hydro-phobic Diluted Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Resour. Manag. 2025, 2, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, H.; Sharma, V.K.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Mitra, S. Solvation and transport of lithium ions in deep eutectic solvents. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 104505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyanarayanan, S.; Babu, M.P.; Murugan, R.; Muthuraj, D.; Ramanujam, K.; Nicholls, I.A. Highly efficient recovery and recycling of cobalt from spent lithium-ion batteries using an N-Methylurea–Acetamide nonionic deep eutectic solvent. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 6959–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amphlett, J.T.M.; Choi, S. The effect of increasing water content on transition metal speciation in deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadirov, R.; Karamyrzayev, G. Selective ozone-assisted acid leaching of copper from copper smelter slag by using isopropanol as a solvent. Minerals 2022, 12, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbor, P.K.; Jia, C.Q. Critical evaluation of coupling particle size distribution with the shrinking core model. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadirov, R.; Karamyrzayev, G. Enhancing Synthetic Zinc Ferrite Hydrochloric Acid Leaching by Using Isopropanol as a Solvent. Min. Metall. Explor. 2022, 39, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, V.; Arzpeyma, G.; Rashchi, F.; Mostoufi, N. A shrinking particle—Shrinking core model for leaching of a zinc ore containing silica. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2009, 93, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| No. | DES Composition | T (°C) | Time (h) | Extracted Metals | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ChCl:Oxalic Acid:H2O | 100 | 0.17 | Li: 99.05%, Co: 99.21% | [24] |
| 2 | ChCl:Oxalic Acid + microwave | 100 | 0.17 | Li: 99.05%, Co: 99.21% | [24] |
| 3 | ChCl:Formic Acid + H2O | 70 | 0.17 | Co, Li ≈ 100% | [25] |
| 4 | ChCl:Lactic Acid | 70 | 24 | Li, Ni, Co, Mn ≈ 100% | [26] |
| 5 | ChCl:p-toluenesulfonic acid:H2O | 90 | 0.25 | Co, Li ≈ 100% | [27] |
| 6 | ChCl:Benzenesulfonic Acid: Ethanolamine | 90 | 2 | Co: 98%, Li: 99% | [28] |
| 7 | ChCl:Malonic Acid:PTSA | 100 | 24 | Co: 98.6%, Li: 98.8% | [29] |
| 8 | ChCl:Oxalic Acid | 120 | 2 | Li, Mn > 96% | [30] |
| 9 | ChCl:Citric Acid + 35% H2O | 40 | 1 | Co > 98% | [31] |
| 10 | ChCl:Ethylene Glycol | 180 | 240 | Li: 91.6%, Co: 92.5%, Ni: 94.9%, Mn: 95.5% | [32] |
| Li (wt%) | Co (wt%) | Ni (wt%) | Mn (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6.79 | 19.21 | 19.13 | 17.65 |
| Time (h) | Li (%) | Mn (%) | Co (%) | Ni (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.2 | 2.5 | 15.4 | 17.8 |
| 2 | 2.5 | 4.1 | 26.7 | 29.3 |
| 3 | 3.6 | 5.6 | 33.5 | 37.2 |
| 4 | 4.5 | 6.8 | 38.2 | 42.7 |
| Time (h) | L:S = 10:1 | L:S = 20:1 | L:S = 40:1 | L:S = 10:1 | L:S = 20:1 | L:S = 40:1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | Co | Co | Ni | Ni | Ni | |
| 1 | 33.2 | 39.4 | 39.8 | 30.2 | 35.1 | 35.9 |
| 2 | 50.4 | 59 | 60.2 | 45.5 | 53.1 | 54.3 |
| 3 | 61.6 | 71.1 | 72.4 | 55.6 | 65.3 | 66.7 |
| 4 | 68.3 | 78.1 | 79.4 | 61.7 | 72.9 | 74.3 |
| 5 | 72.4 | 81.7 | 82.9 | 65.4 | 77.1 | 78.5 |
| 6 | 75.0 | 83.9 | 85.1 | 70.3 | 79.6 | 80.8 |
| Equation | Temperature, °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 80 | 90 | |
| 1 | R2 = 0.7095 | R2 = 0.6371 | R2 = 0.6849 |
| 2 | R2 = 0.9641 | R2 = 0.9263 | R2 = 0.9572 |
| 3 | R2 = 0.6460 | R2 = 0.7516 | R2 = 0.6993 |
| Equation | Temperature, °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 80 | 90 | |
| 1 | R2 = 0.6835 | R2 = 0.7219 | R2 = 0.7105 |
| 2 | R2 = 0.9547 | R2 = 0.9063 | R2 = 0.9342 |
| 3 | R2 = 0.5952 | R2 = 0.6834 | R2 = 0.6711 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nadirov, R.; Kamunur, K.; Mussapyrova, L.; Batkal, A.; Tyumentseva, O. Selective Recovery of Cobalt and Nickel from Spent Lithium-Ion Battery NMC Cathodes Using a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent. Metals 2025, 15, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101113
Nadirov R, Kamunur K, Mussapyrova L, Batkal A, Tyumentseva O. Selective Recovery of Cobalt and Nickel from Spent Lithium-Ion Battery NMC Cathodes Using a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101113
Chicago/Turabian StyleNadirov, Rashid, Kaster Kamunur, Lyazzat Mussapyrova, Aisulu Batkal, and Olesya Tyumentseva. 2025. "Selective Recovery of Cobalt and Nickel from Spent Lithium-Ion Battery NMC Cathodes Using a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent" Metals 15, no. 10: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101113
APA StyleNadirov, R., Kamunur, K., Mussapyrova, L., Batkal, A., & Tyumentseva, O. (2025). Selective Recovery of Cobalt and Nickel from Spent Lithium-Ion Battery NMC Cathodes Using a Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent. Metals, 15(10), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101113






