Integrity of 316/420 Stainless Steel Tribosystem Under Severe Marine Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Marine Environment Simulation
2.3. Tribological Tests
2.4. Lubricating Regime Estimation
2.5. Vickers Microhardness Tests
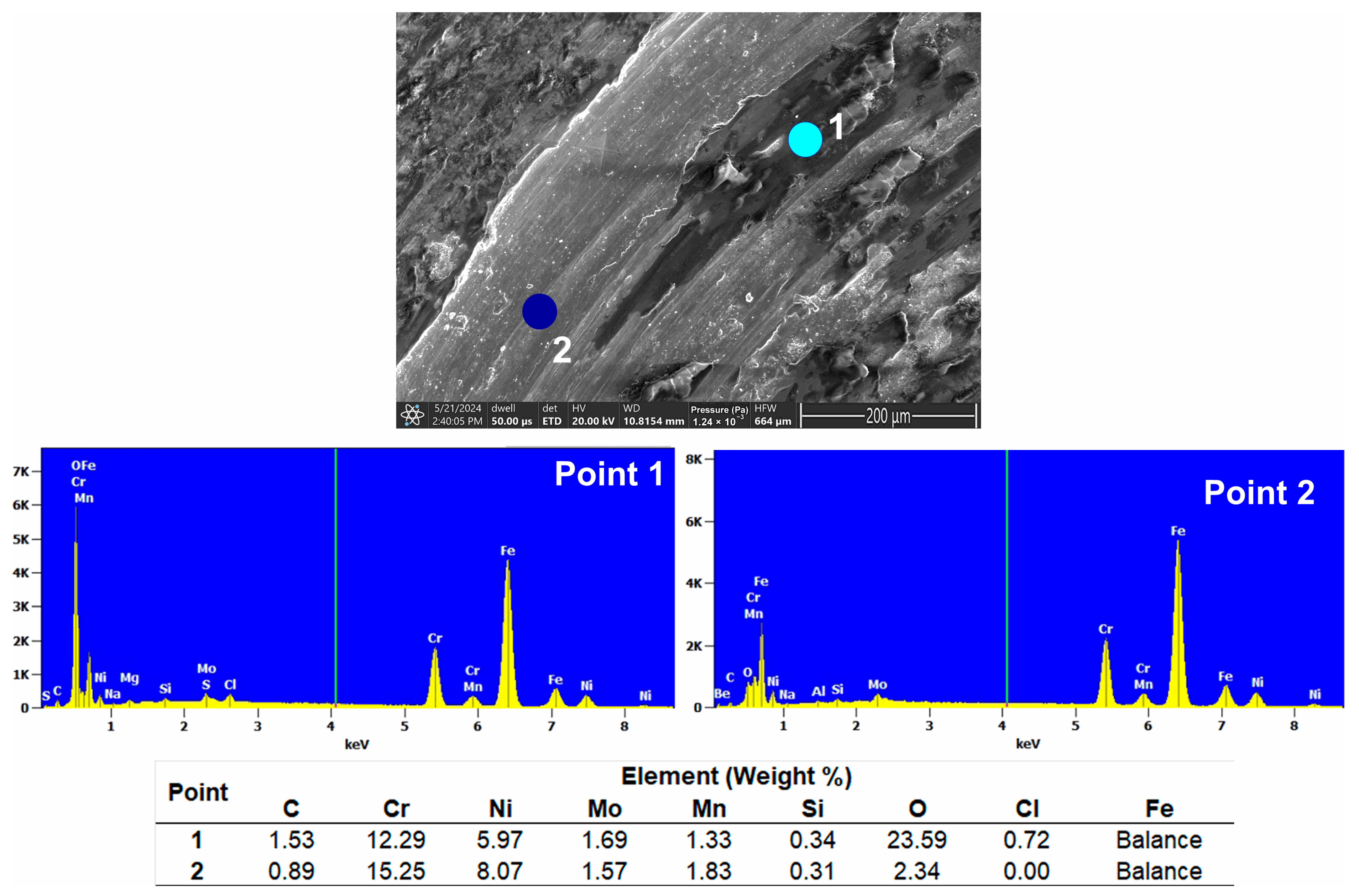
2.6. Microscopic and Spectroscopic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Friction Behavior
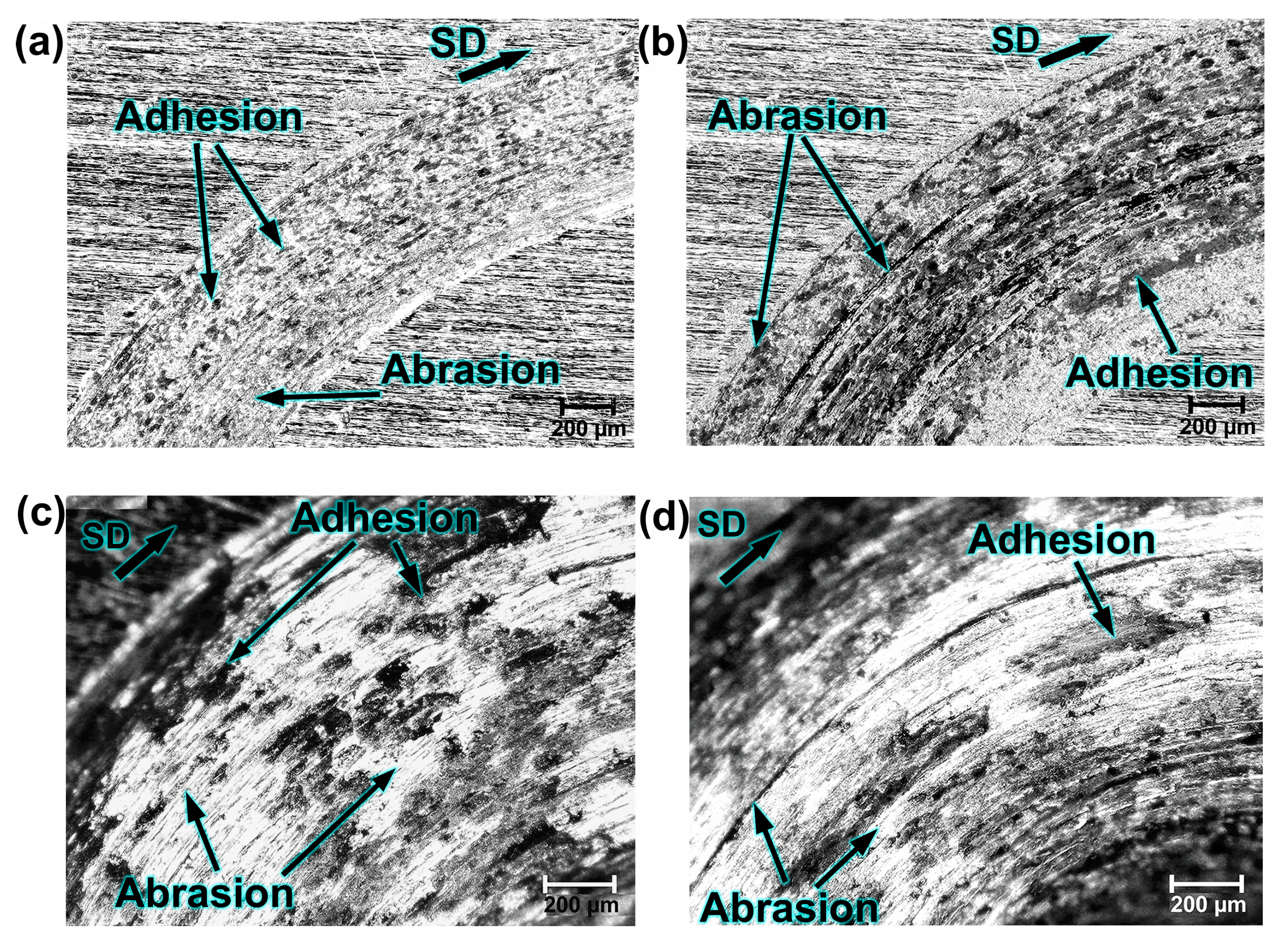
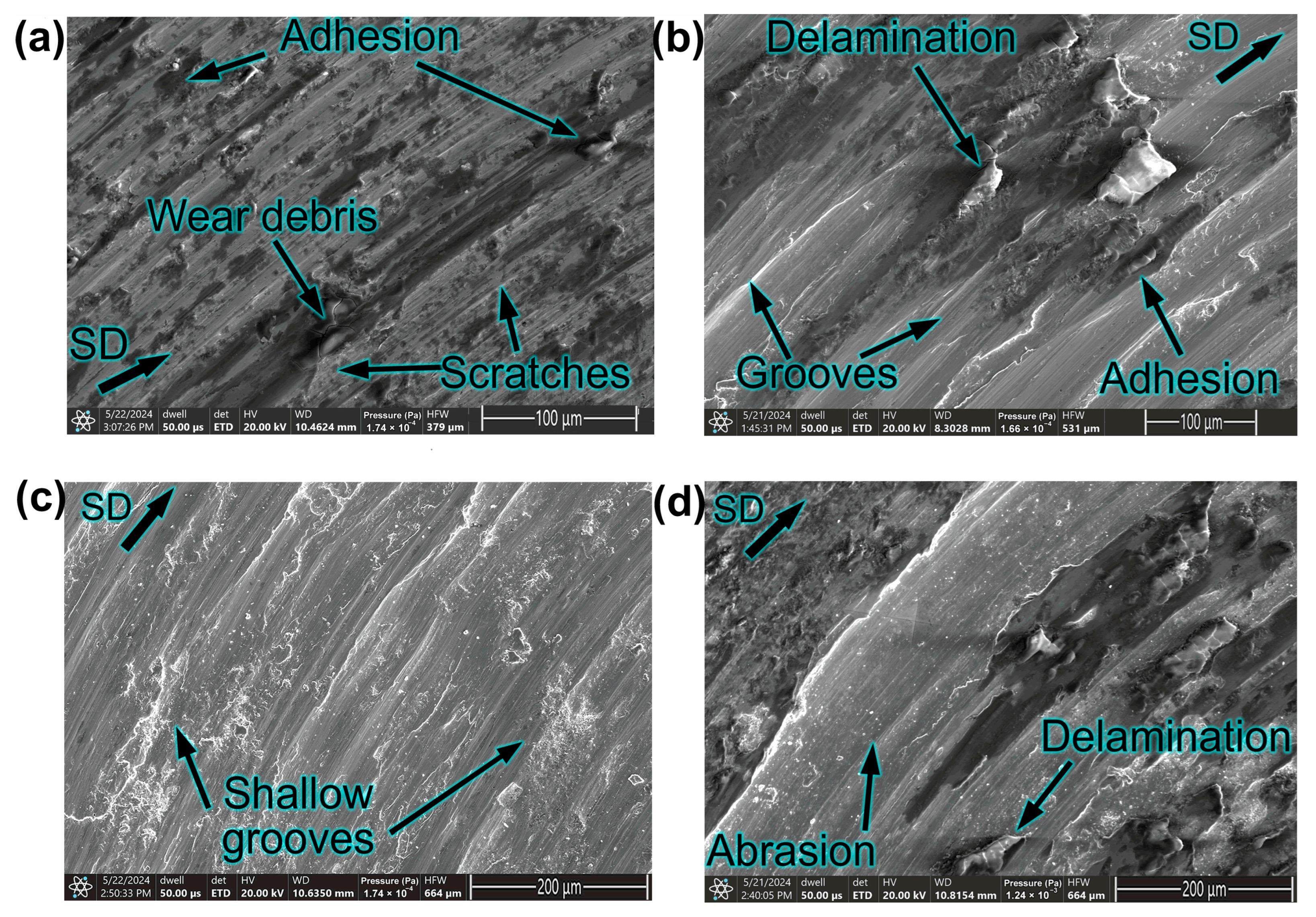
3.2. Wear Behavior
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
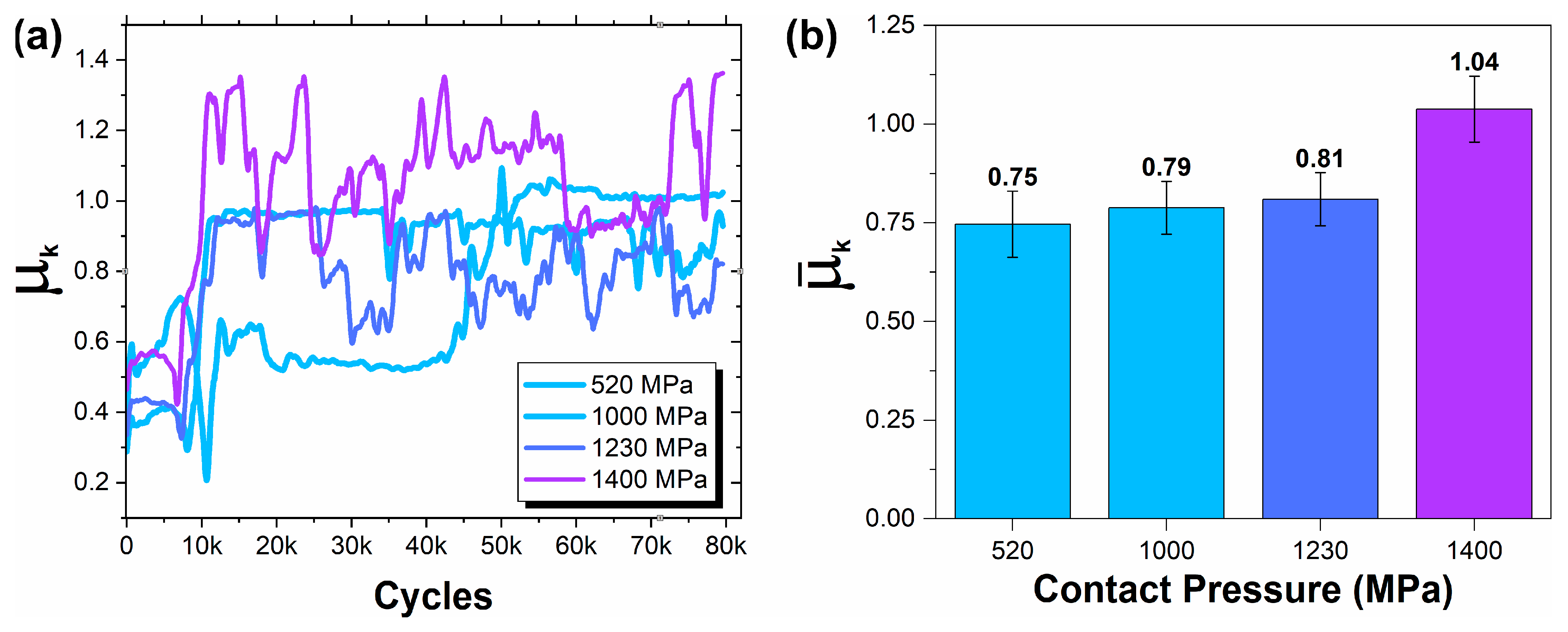
- The kinetic friction coefficient (μk) displayed dynamic behavior influenced by pressure and sliding cycles. Intermediate pressures, particularly at 1000 MPa, yielded the most stable friction response. However, a consistent increase in average values was evident with the progressive rise in contact pressure.
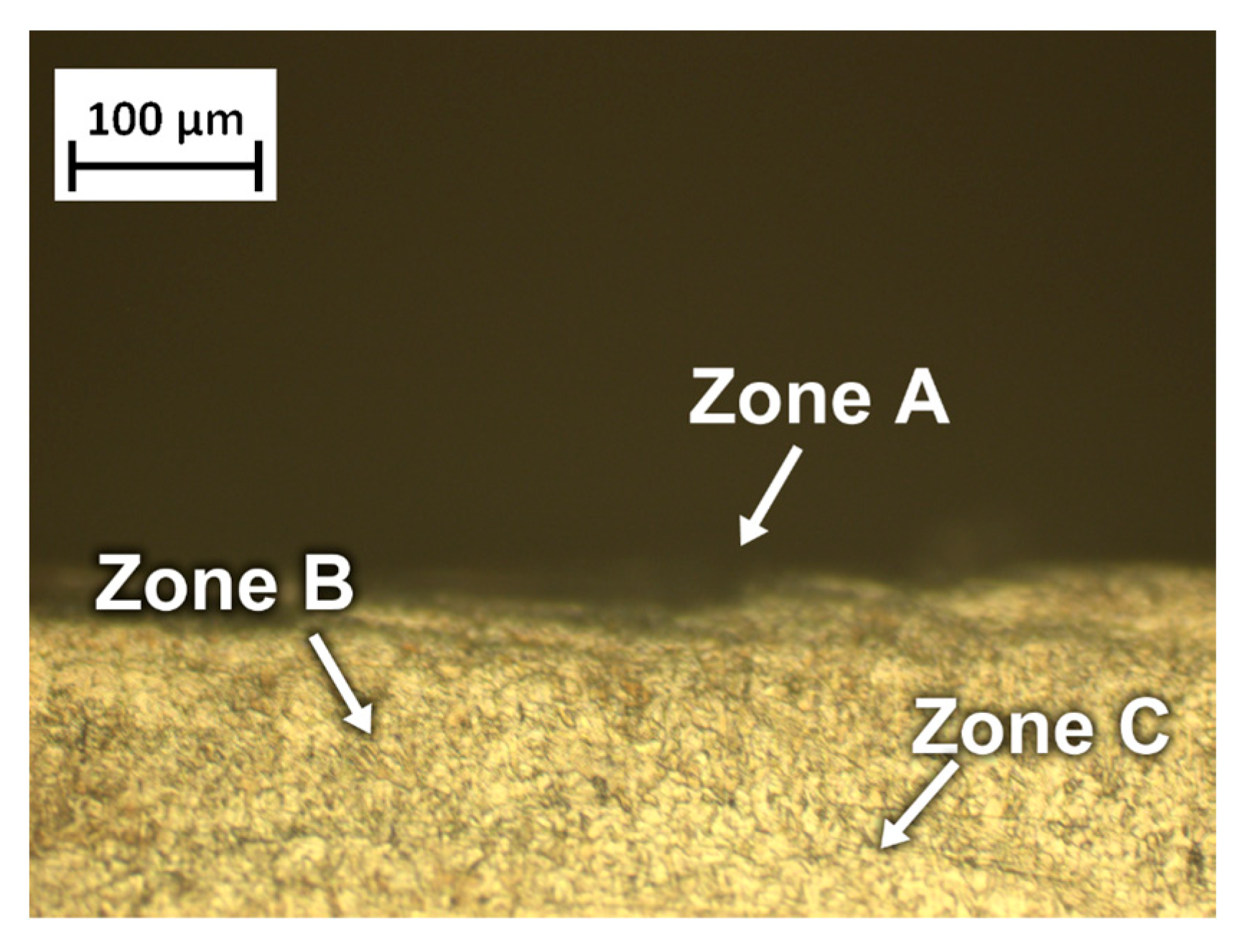
- Although wear volume increased with higher contact pressures, the wear rate decreased significantly. This inverse relationship is primarily attributed to the development of strain-hardened layers within the contact zone, which reduce the rate of further material loss.
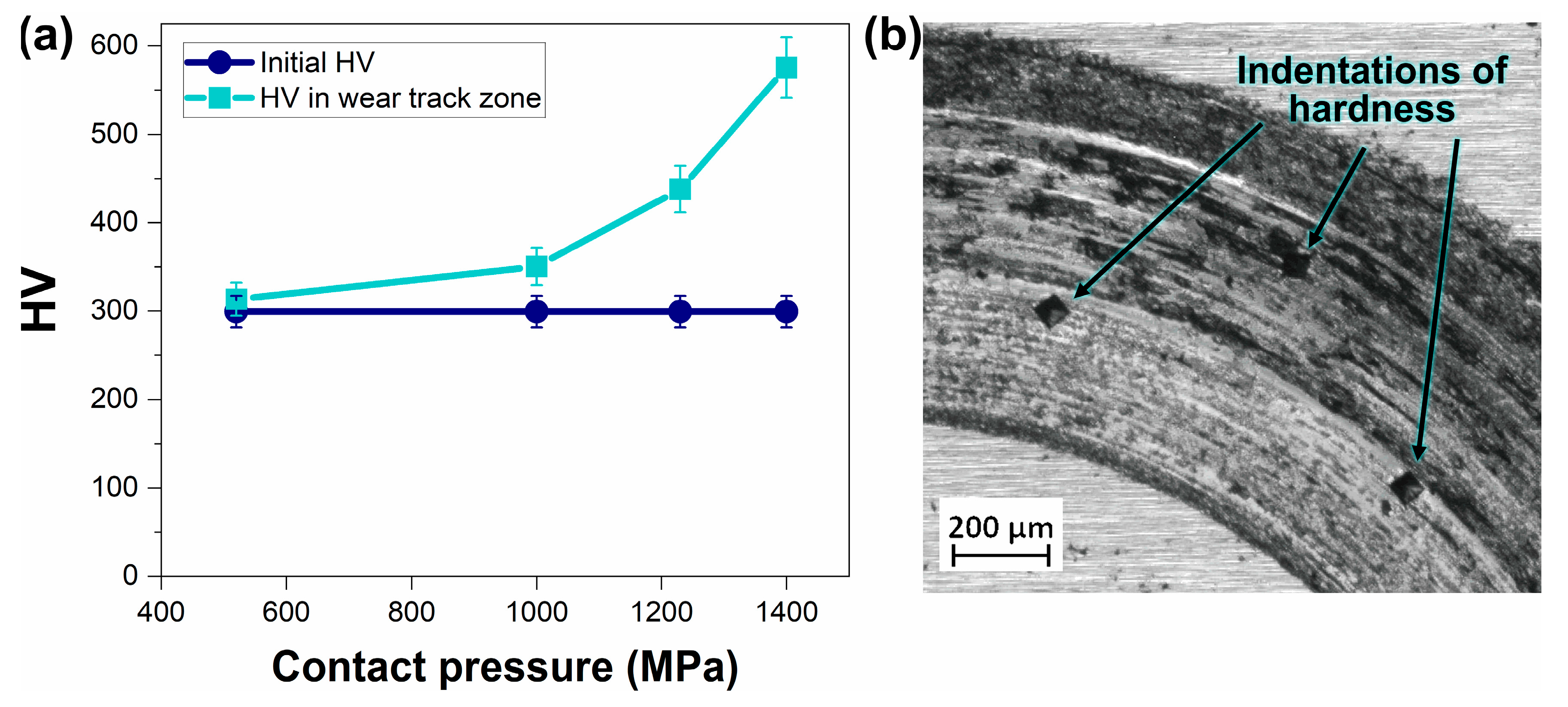
- Microhardness measurements revealed a progressive increase in hardness within the wear tracks, reaching up to 55.4% at 1400 MPa. This behavior supports the hypothesis that plastic deformation under cyclic loading contributed to localized work hardening and enhanced surface durability.
- Morphological analyses identified abrasion, adhesion, and delamination as the main wear mechanisms. The occurrence of oxidation on the worn surfaces, as confirmed by EDS analysis, indicated partial degradation of the passive chromium oxide layer due to salt attack.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
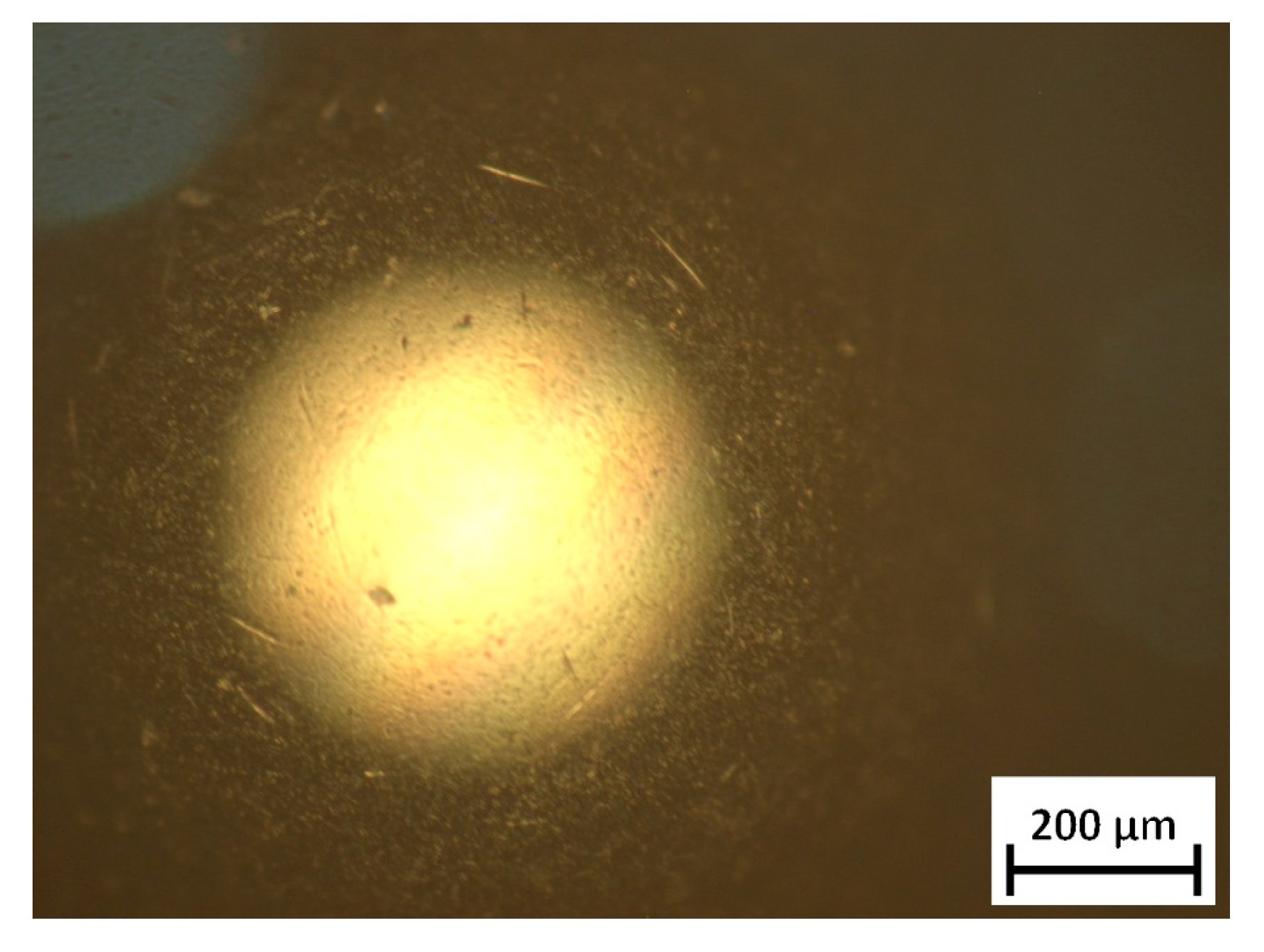
Appendix A. Wear of Ball Specimens
References
- López-Ortega, A.; Bayón, R.; Arana, J.L. Evaluation of protective coatings for offshore applications. Corrosion and tribocorrosion behavior in synthetic seawater. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Zhang, C.; Sui, X.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Hao, J.; Shi, Z. Microstructure, mechanical properties and tribo-corrosion mechanism of (CrNbTiAlVMo)xN1−x coated 316 L stainless steel in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. Tribol. Int. 2022, 173, 107638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, M.; Iraola-Arregui, I.; Youcef, H.B.; Rhouta, B.; Trabadelo, V. The synergistic effect of wear-corrosion in stainless steels: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 51, 1975–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifler, D.A. Understanding material interactions in marine environments to promote extended structural life. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 2335–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tieu, A.K.; Lu, S.; Jamali, S.; Hai, G.; Zhu, Q.; Nguyen, H.H.; Cui, S. Sliding wear behavior and electrochemical properties of binder jet additively manufactured 316SS/bronze composites in marine environment. Tribol. Int. 2021, 156, 106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y. Abrasion–Corrosion Behaviors of Steel–Steel Contact in Seawater Containing Abrasive Particles. Tribol. Trans. 2017, 61, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, S.; Gök, M.S. Effect of sliding wear and electrochemical potential on tribocorrosion behaviour of AISI 316 stainless steel in seawater. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Stainless Steel Forum. Stainless Steel Applications—Marine. Available online: https://worldstainless.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Marineapplications.pdf (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- Zhao, G.; Zhu, S. Al2O3/PTFE Composites for Marine Self-Lubricating Bearings: Modulation Mechanism of Alumina Particle Size on Material Mechanical Properties and Tribological Behavior. Lubricants 2025, 13, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.A.; Fu, S.L.; Wang, J.Z. Corrosion and tribocorrosion behaviors of AISI 316 stainless steel and Ti6Al4V alloys in artificial seawater. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C. The corrosion wear behaviors of Hastelloy C276 alloy in seawater. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Computer Science (ICAMCS), Phuket, Thailand, 21–22 April 2017; pp. 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, F.; Zhou, X.; Nie, S.; Ji, H.; Hu, Z. Tribocorrosion behavior of several corrosion-resistant alloys sliding against CF-PEEK: Application for hydraulic valve in seawater. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 4643–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Gao, D.; Zhao, J. Tribological properties of friction pair between 316L stainless steel and CF/PEEK with nonsmooth surface under seawater lubrication. Tribol. Trans. 2020, 63, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Gao, J.; Gao, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J. Effect of micro-textured surfaces and sliding speed on the lubrication mechanism and friction-wear characteristics of CF/PEEK rubbing against 316L stainless steel under seawater lubrication. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, M.; Ruggiero, A. Tribocorrosion of couplings in seawater environment: An investigation on the positive-negative role of synergy. Tribol. Int. 2024, 200, 110143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Demirsöz, R.; Korkmaz, M.E.; Ross, N.S. Wear and friction mechanism of stainless steel 420 under various lubrication conditions: A tribological assessment with ball on flat test. J. Tribol. 2023, 145, 041703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, K. Surface Hardness and Corrosion Behavior of AISI 420 Martensitic Stainless Steels Treated by Plasma Oxy-Nitriding Processing. Korean J. Mater. Res. 2023, 33, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadauria, A.; Reddy, K.V.; Khatirkar, R.K.; Bandhu, D.; Gangwar, P.K. Investigating the structural properties and wear resistance of martensitic stainless steels. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0312242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Tong, H.; Sui, Y.; Li, X.; Hou, J. Effect of Surface Roughness on the Corrosion Behavior of 304 Stainless Steel in Seawater. J. Mater. Eng Perform 2025, 34, 18287–18297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Sierra, M.T.; Bravo-Sánchez, M.G.; Báez, J.E.; Aguilera-Camacho, L.D.; García-Miranda, J.S.; Moreno, K.J. Improvement Effect of Green Lubricants on the Tribological and Mechanical Performance of 4140 Steel. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G99-17; Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin-on-Disk Apparatus. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Fischer-Cripps, A.C. The Hertzian contact surface. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciulli, E.; Betti, A.; Forte, P. The Applicability of the Hertzian Formulas to Point Contacts of Spheres and Spherical Caps. Lubricants 2022, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Song, C.; Lim, T.C.; Vijayakar, S. Geometry design and tooth contact analysis of crossedbeveloid gears for marine transmissions. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2012, 25, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slogén, M. Contact Mechanics in Gears. A Computer-Aided Approach for Analyzing Contacts in Spur and Helical Gears. Master’s Thesis, Department of Product and Production Development, Division of Product Development, Chalmers University of Technology Gothenburg, Chalmersgatan, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas-Osorio, S.; Moreno, K.J.; Aguilera-Camacho, L.D.; García-Miranda, J.S. Estudio de las Propiedades de Desgaste de Un Tribosistema de Acero Inoxidable para Aplicaciones en Ambientes Marinos (Study of the Wear Properties of A Stainless Steel Tribosystem for Marine Environment Applications). Pist. Educ. 2025, 46, 991–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe, W.H.; Titmuss, S.; Tiberg, F.; Thomas, R.K.; McGillivray, D.J.; Klein, J. Boundary lubrication under water. Nature 2006, 444, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, B.; Li, T.; Ma, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Lu, X.; Liu, Z. Lubrication analysis of the piston ring of a two-stroke marine diesel engine considering thermal effects. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 129, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Xing, S. Impact of oil-water emulsions on lubrication performance of ship stern bearings. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Srivastava, M.; Jain, P.K.; Rathee, S. Microstructure transformations and improving wear resistance of austenitic stainless steel additively fabricated by arc-based DED process. Def. Technol. 2024, 38, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.L. Contact Mechanics and Friction; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-3-662-53081-8. [Google Scholar]
- Blau, P.J. On the nature of running-in. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Larbi, A.; Dong, H.; Wang, D.; Li, S. A comparative investigation on wear behaviors of physical and chemical vapor deposited bronze coatings for hydraulic piston pump. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2024, 37, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, M.P.; Kodli, B.K.; Dey, S.R. Mechanical properties and Microstructural Characterization of friction stir welded AISI 316 Austenitic Stainless Steel. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 2376–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowski, T.; Kulikowski, K.; Adamczyk-Cieślak, B.; Rożniatowski, K.; Spychalski, M.; Tarnowski, M. Influence of nitrided and nitrocarburised layers on the functional properties of nitrogen-doped soft carbon-based coatings deposited on 316L steel under DC glow-discharge conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 392, 125705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ma, C.; Hai, X.; Song, K. 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Deformation Organization and Nitriding-Strengthened Layer Relationships. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachin, B.; Narendranath, S.; Chakradhar, D. Sustainable diamond burnishing of 17-4 PH stainless steel for enhanced surface integrity and product performance by using a novel modified tool. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 046501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, F.T.; Felho, C. Transforming Burnishing Techniques: A Novel Method to Enhance Efficiency and Surface Quality Through Tool Feed Variation. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| C | Cr | Ni | Mo | Mn | Si | P | S | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 316 | 0.08 | 17.4 | 13 | 2.21 | 1.76 | 0.35 | 0.045 | 0.029 | Balance |
| AISI 420 | 0.19 | 12.8 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.02 | Balance |
| Applied Load (N) | Mean Contact Pressure, pm (MPa) |
|---|---|
| 0.5 | 520 |
| 3.5 | 1000 |
| 6.5 | 1230 |
| 9.5 | 1400 |
| Contact Pressure (MPa) | αp (Pa−1) | hc (nm) | λc | Lubrication Regime |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 520 | 3.88 × 10−9 | 0.39 | 0.0093 | Boundary |
| 1000 | 0.35 | 0.0082 | ||
| 1230 | 0.33 | 0.0078 | ||
| 1400 | 0.32 | 0.0076 |
| Contact Pressure (MPa) | µinitial | Running-In Period a | Cycles to Reach Steady State | Steady State b | Full Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 520 | 0.34 | 0.60 | 10,588 and 45,162 | 0.6 and 1.0 | 0.75 |
| 1000 | 0.29 | 0.40 | 8043 | 0.92 | 0.79 |
| 1230 | 0.34 | 0.45 | 7219 | 0.82 | 0.81 |
| 1400 | 0.46 | 0.60 | 6470 | 1.10 | 1.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreno, K.J.; Hernández-Sierra, M.T.; García-Miranda, J.S.; Aguilera-Camacho, L.D. Integrity of 316/420 Stainless Steel Tribosystem Under Severe Marine Conditions. Metals 2025, 15, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101076
Moreno KJ, Hernández-Sierra MT, García-Miranda JS, Aguilera-Camacho LD. Integrity of 316/420 Stainless Steel Tribosystem Under Severe Marine Conditions. Metals. 2025; 15(10):1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101076
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreno, Karla J., María Teresa Hernández-Sierra, J. Santos García-Miranda, and Luis Daniel Aguilera-Camacho. 2025. "Integrity of 316/420 Stainless Steel Tribosystem Under Severe Marine Conditions" Metals 15, no. 10: 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101076
APA StyleMoreno, K. J., Hernández-Sierra, M. T., García-Miranda, J. S., & Aguilera-Camacho, L. D. (2025). Integrity of 316/420 Stainless Steel Tribosystem Under Severe Marine Conditions. Metals, 15(10), 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15101076








