Microstructural and Electrochemical Analysis of the Physically Simulated Heat-Affected Zone of Super-Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S32750
Abstract
1. Introduction
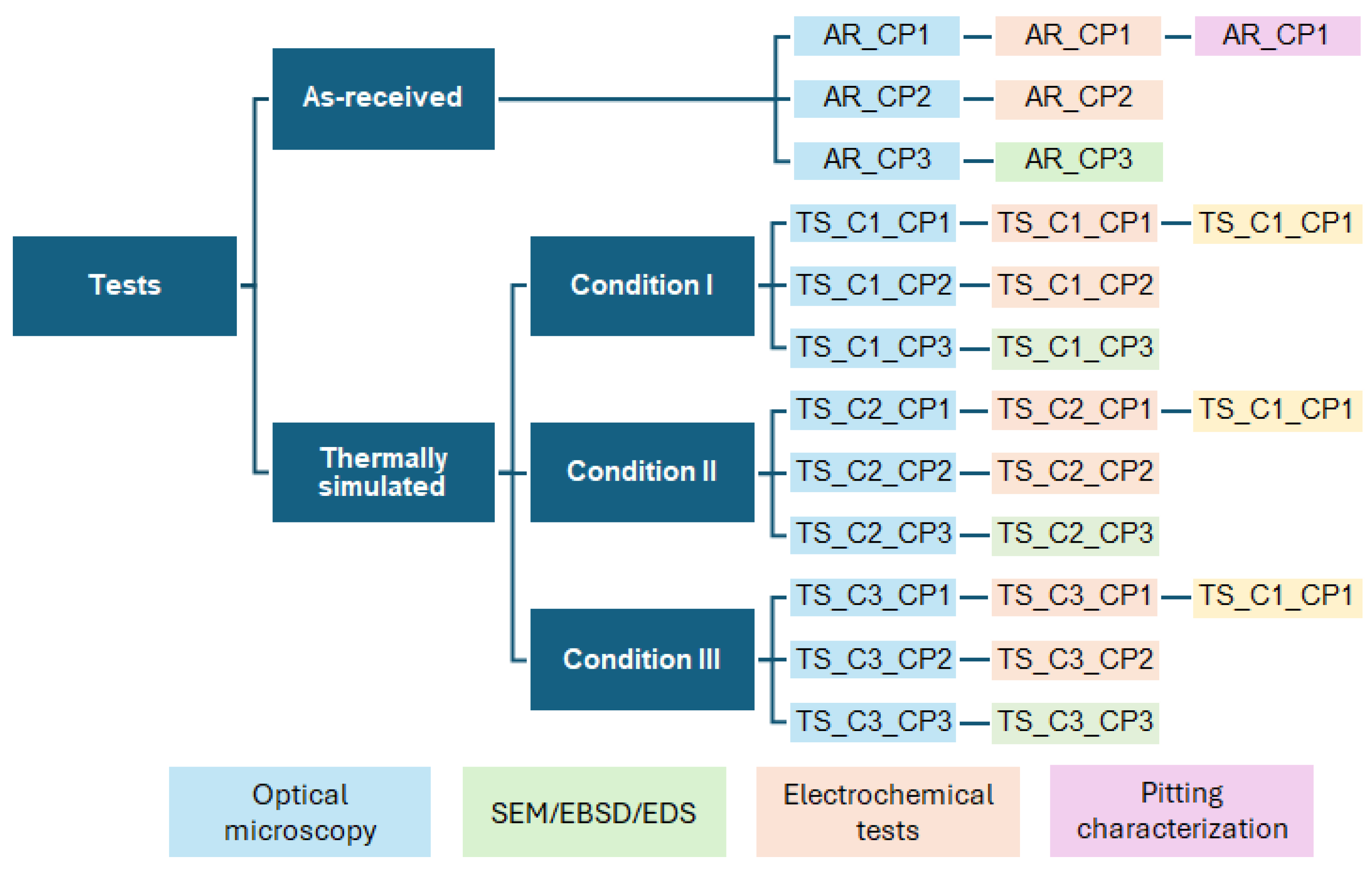
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Physical Simulation
2.3. Microstructural Characterization
2.4. Electrochemical Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Simulation
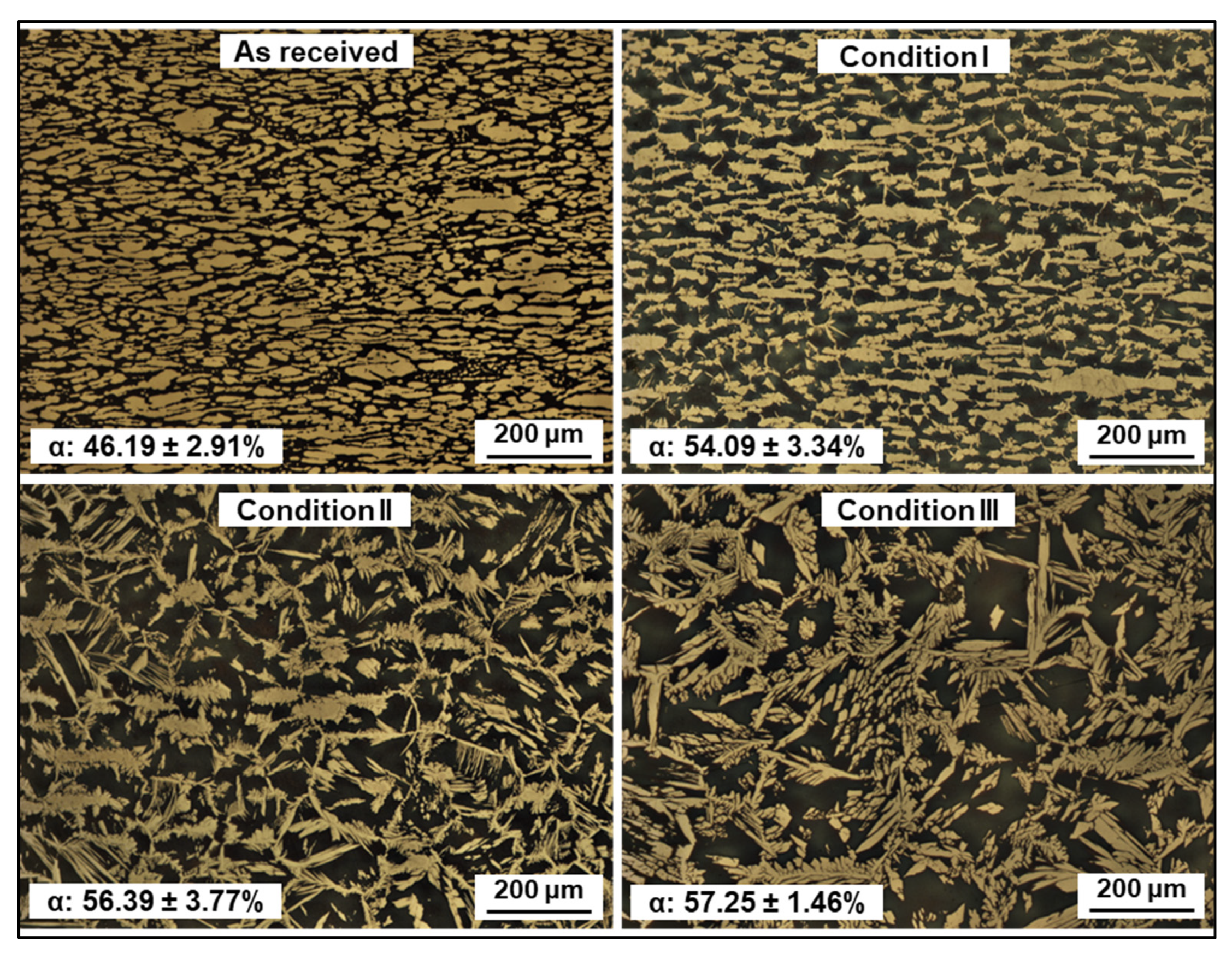
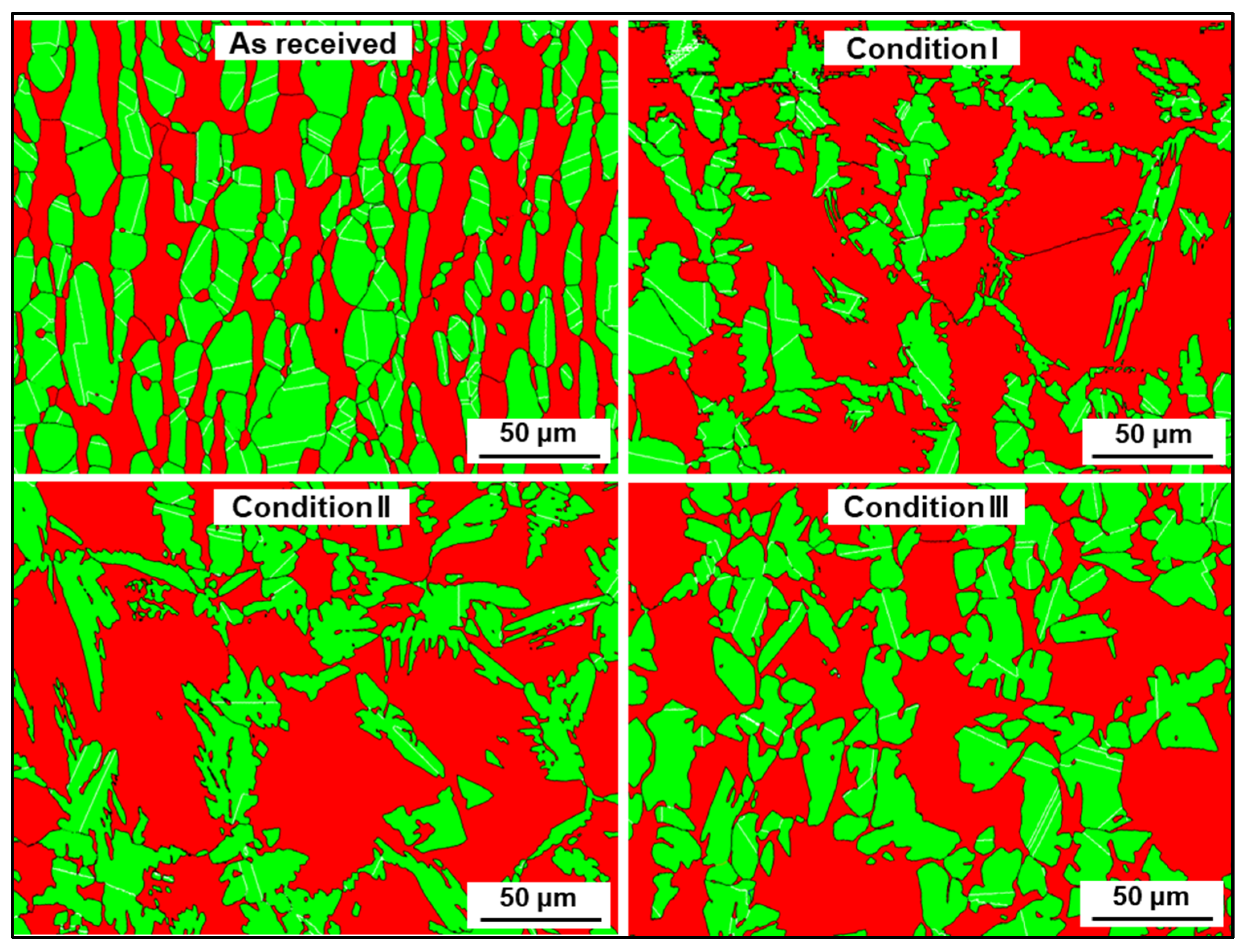
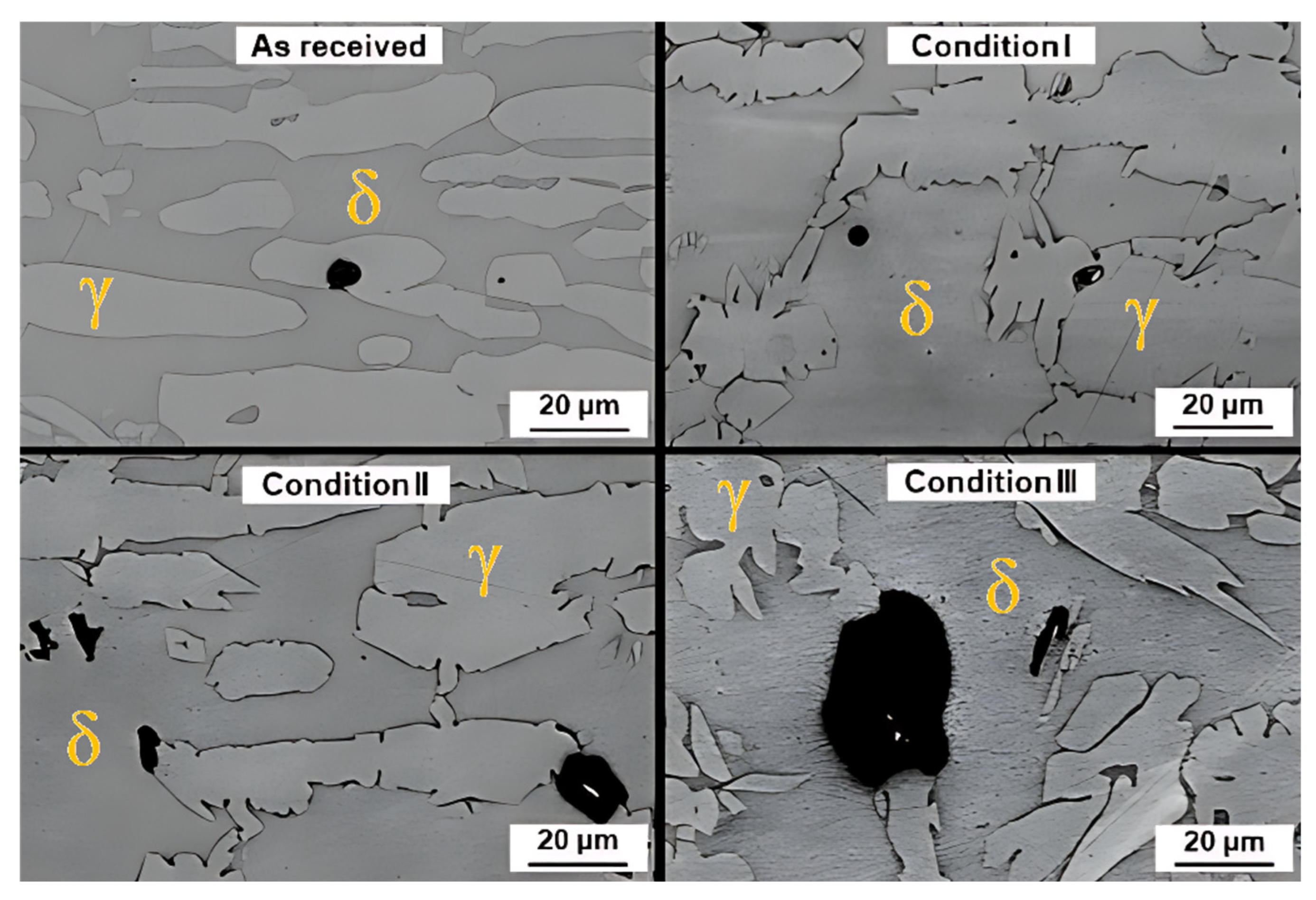
3.2. Microstructure
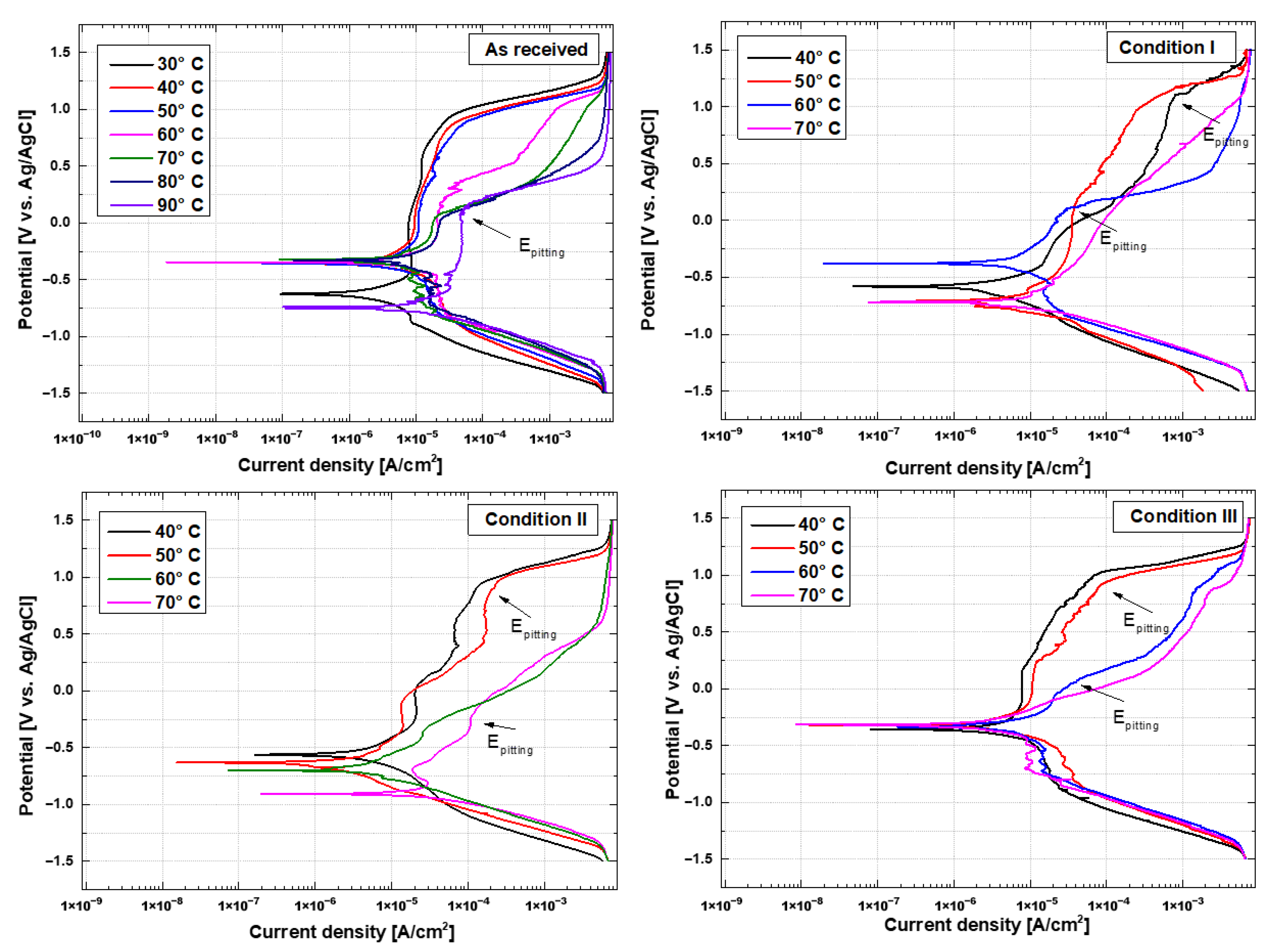
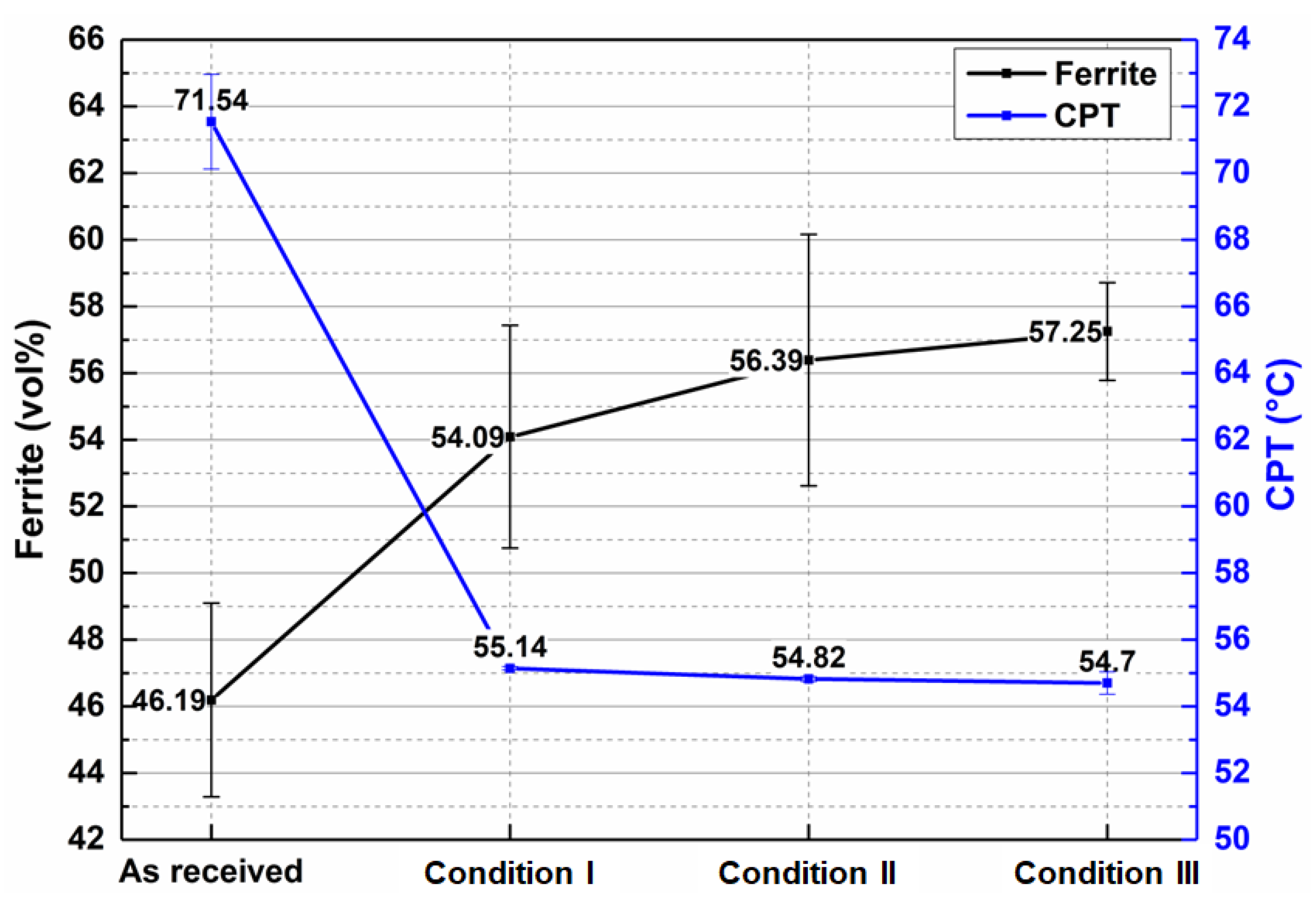
3.3. Potentiodynamic Polarization and Critical Pitting Temperature (CPT)
4. Conclusions
- All conditions experienced an increase in ferrite amount with respect to the as-received material, which is an expected consequence of the thermal input. Differences in phase morphologies through all conditions were noticeable, with the presence of Widmanstätten austenite and small portions of secondary austenite. Deleterious phases, such as sigma or chi, were not detected either by conventional OM, SEM, or EBSD characterization.
- Super-duplex steel, in the “as-received” condition, exhibits excellent pitting corrosion resistance, with an average pitting potential (Ep) of approximately 1 V vs. Ag/AgCl at temperatures up to 50 °C, indicating stable passive film formation. However, as the temperature increases to 90 °C, resistance drops sharply, with the pitting potential falling to 0.17741 V, highlighting greater susceptibility to corrosion due to the breakdown of the passive layer. In the thermally treated samples, pitting corrosion resistance was significantly reduced. This behavior was evidenced by the polarization curves, which did not show a uniform passive region and exhibited multiple passivation, indicating a complex electrochemical behavior in response to variations in the applied potential.
- The critical pitting temperature (CPT) of the treated samples was lower than that of the “as-received” condition (71.54 °C), with values of 55.14 °C, 54.82 °C, and 54.7 °C for conditions I, II, and III, respectively. This result suggests that the increase in ferrite fraction observed in the simulated samples is the main factor responsible for the reduction in corrosion resistance. It was possible to correlate chemical composition with the preferential location of pits at temperatures close to CPT: in the as-received material, corrosion occurred preferentially in austenitic grains and grain boundaries due to the difference in chemical composition of ferrite and austenite phases. After thermal cycling, however, pitting occurred preferentially in ferritic regions.
- To prevent the loss of corrosion resistance and unbalanced microstructure, it is important to control welding parameters such as current, voltage, and heat input. Using filler materials with austenitizing elements helps to prevent an increase in ferrite. Additionally, using appropriate shielding and purge gases is crucial to avoid contamination of the material. Mechanizing the welding process can help prevent significant variations in welding parameters. Proper control of welding time and temperature is essential to avoid the formation of deleterious phases and ensure a balanced microstructure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, Y.; Chi, R.; Chen, Q.; Wang, B.; Liu, W.; He, Y. Microstructural Evolution and Coarsening Behavior of the Precipitates in 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Aged at 850 °C. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 2560–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, D.; Devendranath Ramkumar, K.; Vimala, R. Multi-Pass Arc Welding Techniques of 12 mm Thick Super-Duplex Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2019, 271, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, M.; Kadoi, K.; Inoue, H. Age-Hardening Behaviors of the Weld Metals of 22% Cr and 25% Cr Duplex Stainless Steels at 400 °C. J. Nucl. Mater. 2023, 581, 154438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jing, H.; Xu, L.; Han, Y.; Zhao, L. Investigation on Microstructure Evolution and Properties of Duplex Stainless Steel Joint Multi-Pass Welded by Using Different Methods. Mater. Des. 2016, 109, 670–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuna, A.; Ramirez, A.J. Sigma Phase Formation Kinetics in Hyper Duplex Stainless Steel Welding Filler Metal. Mater. Charact. 2023, 200, 112832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorca-Isern, N.; López-Luque, H.; López-Jiménez, I.; Biezma, M.V. Identification of Sigma and Chi Phases in Duplex Stainless Steels. Mater. Charact. 2016, 112, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelas, P.H.; Payão Filho, J.D.; Moraes e Oliveira, V.H.; Farias, F.W. Influence of Interpass Temperature on the Simulated Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of a Circumferentially Welded 2.25Cr-1Mo Steel Pipe Joint. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, C.M.; Serna, C.A.; Brandi, S.D.; Ramirez, A.J. The Relationship between Atomic Partitioning and Corrosion Resistance in the Weld-Heat Affected Zone Microstructures of UNS S32304 Duplex Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 9021–9029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jing, H.; Xu, L.; Han, Y.; Zhao, L.; Lv, X. Effect of Post-Weld Heat Treatment on Microstructure Evolution and Pitting Corrosion Resistance of Electron Beam-Welded Duplex Stainless Steel. Corros. Sci. 2018, 141, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfallah, A.; Moradi, M.; Beygi, R. Welding and Joining of Metallic Materials: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Crystals 2024, 14, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tan, H.; Wang, Z.; Hong, J.; Jiang, L.; Li, J. Influence of Creq/Nieq on Pitting Corrosion Resistance and Mechanical Properties of UNS S32304 Duplex Stainless Steel Welded Joints. Corros. Sci. 2013, 70, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y. The Microstructure and Pitting Resistance of 2002 Lean Duplex Stainless Steel after the Simulated Welding Thermal Cycle Process. Materials 2019, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Hosseini, V.; Karlsson, L. Physical and Kinetic Simulation of Nitrogen Loss in High Temperature Heat Affected Zone of Duplex Stainless Steels. Materialia 2019, 6, 100325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuna, A.; Riffel, K.C.; Ramirez, A. A Comparison of Sigma Phase Formation in Solubilized Hyper Duplex Stainless Steel and Super Duplex Stainless Steel Filler Metals. Met. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Met. Mater. Sci. 2024, 55, 2881–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Deng, B.; Song, H.; Li, J. Influence of Welding Thermal Cycles on Microstructure and Pitting Corrosion Resistance of 2304 Duplex Stainless Steels. Corros. Sci. 2012, 55, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.O.P.; Lima, T.N.; Júnior, F.M.d.S.; Callegari, B.; Folle, L.F.; Coelho, R.S. Heat-Affected Zone Microstructural Study via Coupled Numerical/Physical Simulation in Welded Superduplex Stainless Steels. Crystals 2024, 14, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, T.; Hu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, J. Microstructure Evolution and Pitting Corrosion Resistance of the Gleeble-Simulated Heat-Affected Zone of a Newly Developed Lean Duplex Stainless Steel 2002. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 658, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, E.M.; Raducanu, D.; Nocivin, A.; Cojocaru, V.D. Influence of Ageing Treatment Temperature and Duration on σ-Phase Precipitation and Mechanical Properties of UNS S32750 SDSS Alloy. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 30, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Vargas, G.; Ruiz, A.; López-Morelos, V.H.; Kim, J.Y.; González-Sánchez, J.; Medina-Flores, A. Evaluation of 475 °C Embrittlement in UNS S32750 Super Duplex Stainless Steel Using Four-Point Electric Conductivity Measurements. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2021, 53, 2982–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, R.; Maurya, R.; Katiyar, P.K. Examining Sigma Phase in Super Duplex Stainless Steels (UNS S32750) after Isothermal Aging, Focusing on Its Influence on Etching and Pitting Corrosion with Optical Microscopy. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2024, 13, 741–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajay, E.; Prasad, A.D.V.; Rao, A.G.; Raja, V.S. Role of Microstructure on the Varying Corrosion Behavior across the UNS S32750 Super Duplex Stainless Steel Friction Stir Weld. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, F.M.R.; Borges, W.F.A.; Santos, R.L.P.; Leal, V.S.; dos Santos Júnior, J.R.; Lobo, A.O.; de Sousa, R.R.M. Corrosion Resistance and Microstructural Evaluation of a Plasma Nitrided Weld Joint of UNS S32750 Super Duplex Stainless Steel. Mater. Res. 2021, 24, e20210087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devendranath Ramkumar, K.; Thiruvengatam, G.; Sudharsan, S.P.; Mishra, D.; Arivazhagan, N.; Sridhar, R. Characterization of Weld Strength and Impact Toughness in the Multi-Pass Welding of Super-Duplex Stainless Steel UNS 32750. Mater. Des. 2014, 60, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Qi, X.; Bian, Y.; Shen, A.; Xu, P.; Zhao, Y. Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Briefly Heat-Treated SAF 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel Welds. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 168, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias Azevedo, C.R.; Boschetti Pereira, H.; Wolynec, S.; Padilha, A.F. An Overview of the Recurrent Failures of Duplex Stainless Steels. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 97, 161–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, S.S.M.; Pardal, J.M.; Almeida, B.B.; Mendes, M.T.; Freire, J.L.F.; Vidal, A.C. Failure of Superduplex Stainless Steel Flange Due to Inadequate Microstructure and Fabrication Process. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 84, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, H.-Y.; Hsieh, R.-I.; Tsai, W.-T. Microstructure and Stress Corrosion Cracking in Simulated Heat-Affected Zones of Duplex Stainless Steels. Corros. Sci. 2002, 44, 2841–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reccagni, P.; Guilherme, L.H.; Lu, Q.; Gittos, M.F.; Engelberg, D.L. Reduction of Austenite-Ferrite Galvanic Activity in the Heat-Affected Zone of a Gleeble-Simulated Grade 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Weld. Corros. Sci. 2019, 161, 108198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, B.; Li, J.; Wang, J. The Effect of Large Heat Input on the Microstructure and Corrosion Behaviour of Simulated Heat Affected Zone in 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3756–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jing, H.; Xu, L.; Han, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J. Microstructural Characterization and Electron Backscatter Diffraction Analysis across the Welded Interface of Duplex Stainless Steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 413, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cláudia, T.; Farias, C.; Tadeu, Y.; Henrique, D.; Zanini, S.; Coelho, R.; Simas Filho, E.; Silva, I. Influence of Deleterious Phases in Super-Duplex Steel SAF 2507 in the Ultrasonic Lamb Waves Propagation. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Non-Destructive Testing (ECNDT 2014), Prague, Czech Republic, 6–11 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Putz, A.; Althuber, M.; Zelić, A.; Westin, E.; Willidal, T.; Enzinger, N. Methods for the Measurement of Ferrite Content in Multipass Duplex Stainless Steel Welds. Weld. World 2019, 63, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.A.; Hsu, C. The Electrochemical Polishing Behavior of Duplex Stainless Steel (SAF 2205) in Phosphoric-Sulfuric Mixed Acids. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 34, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM G5—Standard Reference Test Method for Making Potentiodynamic Anodic Polarization Measurements. In Book 03.02, Standards Volume; Astm International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, J.P.B.d; Arias, A.d.G.; Pardal, J.M.; Mainier, F.B.; Ferreira, M.L.R.; Tavares, S.S.M. Análise Da Resistência à Corrosão Por Pite Em Soldas de Reparo Pelo Processo TIG Em Aço Inoxidável Superduplex UNS S32750. Soldag. Inspeção 2011, 16, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.L.R.; Silva, C.A.F.d.; Pardal, J.M.; Tavares, S.S.M. Influência Dos Gases de Proteção Na Soldagem Do Aço UNS S31803 Com Arame E2209-T1/4 Pelo Processo FCAW. Soldag. Inspeção 2018, 23, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawczen, T. Electrochemical Characterization and Proposed Methodology for the Determination of Critical Pitting Temperature of UNS S32760 Super Duplex Stainless Steel; USP: North Bethesda, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Higelin, A.; Le Manchet, S.; Passot, G.; Cissé, S.; Grocki, J. Heat-Affected Zone Ferrite Content Control of a Duplex Stainless Steel Grade to Enhance Weldability. Weld. World 2022, 66, 1503–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.S.; Lins, V.d.F.C.; Silveira, D.M.d.; Costa, C.G.F.; Cardoso Junior, R.; Campos, F.R.; Bracarense, A.Q. Avaliação Da Soldagem Multipasse de Chapas Espessas de Aços Inoxidáveis Lean Duplex UNS S32304 Soldadas Pelos Processos SMAW, GMAW e FCAW -: Resistência à Corrosão. Soldag. Inspeção 2013, 18, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.; Taiwade, R.V. Effect of Welding Processes and Conditions on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Duplex Stainless Steel Weldments—A Review. J. Manuf. Process 2017, 25, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Wen, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 2205 DSS Metal Inert-Gaswelding Joints. Cailiao Yanjiu Xuebao/Chin. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 30, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.; Ahonen, M.; Virkkunen, I.; Nevasmaa, P.; Rautala, P.; Reinvall, H. Study of Cracking and Microstructure in Co-Free Valve Seat Hardfacing. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2022, 31, 101202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, M.; Hoseinpoor, M.; Moayed, M.H. A Statistical Study on the Effect of Annealing Temperature on Pitting Corrosion Resistance of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel. Corros. Sci. 2015, 94, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, G.; Tu, W.; Dong, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, K.; Sun, Y. Comparative Statistical Analysis of Pitting in Two 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Variants. npj Mater. Degrad. 2024, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. Precipitation of Sigma Phase in Duplex Stainless Steel and Recent Development on Its Detection by Electrochemical Potentiokinetic Reactivation:A Review. Corros. Commun. 2021, 2, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wiame, F.; Maurice, V.; Marcus, P. Origin of Nanoscale Heterogeneity in the Surface Oxide Film Protecting Stainless Steel against Corrosion. npj Mater. Degrad. 2019, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tong, A.; Li, J.; Sun, Y. Roles of Different Components of Complex Inclusion in Pitting of 321 Stainless Steel: Induction Effect of CaS and Inhibition Effect of TiN. Corros. Sci. 2022, 209, 110692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecly, P.H.R.; Almeida, B.B.; Perez, G.; Pimenta, A.R.; Tavares, S.S.M. Microstructure, Corrosion Resistance, and Hardness of Simulated Heat-Affected Zone of Duplex UNS S32205 and Superduplex UNS S32750 Stainless Steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 9019–9028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithin Raj, P.; Sivan, A.P.; Sekar, K.; Joseph, M.A. Effect of Austenite Reformation on Localized Corrosion Resistance of Hyper-Duplex Stainless Steel in Hot Chloride Solution. Int. J. Met. 2020, 14, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, B.; Sun, T.; Xu, J.; Li, J. Effect of Annealing Temperature on the Pitting Corrosion Resistance of Super Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S32750. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.Q.; Li, M.; Shi, X.L.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Qiao, L.J. Effect of Annealing Temperature on the Corrosion Behavior of Duplex Stainless Steel Studied by in Situ Techniques. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, B.; Sun, D.; Li, J. Influence of Annealing Treatment on the Corrosion Resistance of Lean Duplex Stainless Steel 2101. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 5387–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | N | PREN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.015 | 0.42 | 0.74 | 0.029 | 0.001 | 24.72 | 6.88 | 3.80 | 0.270 | 41.58 |
| Condition | CR12/8 (°C/s) | CR8/5 (°C/s) | ∆t12/8 (s) | ∆t8/5 (s) | Q (kJ/mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 84 | 21 | 5 | 14 | 1.0 |
| II | 34 | 9 | 12 | 35 | 1.5 |
| II | 8 | 2 | 48 | 140 | 3.0 |
| Condition | Temperature (°C) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As received | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 |
| Condition I | - | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | - | - |
| Condition II | - | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | - | - |
| Condition III | - | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | - | - |
| Condition | Phase | C * | Si | Mn | Ni | Cr | Mo | N * | PREN |
| As received | Austenite | 0.015 | 0.42 ± 0.02 | 1.02 ± 0.14 | 7.87 ± 0.16 | 24.34 ± 0.22 | 3.13 ± 0.10 | 0.27 | 38.99 ± 0.40 |
| Ferrite | 0.015 | 0.48 ± 0.05 | 0.99 ± 0.10 | 5.92 ± 1.26 | 25.95 ± 1.29 | 4.48 ± 0.81 | 0.27 | 45.05 ± 2.97 | |
| Condition I | Austenite | 0.015 | 0.46 ± 0.03 | 1.03 ± 0.07 | 8.06 ± 0.21 | 24.58 ± 0.16 | 2.63 ± 0.04 | 0.27 | 37.58 ± 0.21 |
| Ferrite | 0.015 | 0.46 ± 0.04 | 1.04 ± 0.15 | 6.51 ± 0.22 | 25.92 ± 0.22 | 3.63 ± 0.04 | 0.27 | 42.22 ± 0.26 | |
| Condition II | Austenite | 0.015 | 0.43 ± 0.04 | 1.12 ± 0.08 | 7.83 ± 0.09 | 24.65 ± 0.11 | 2.66 ± 0.06 | 0.27 | 37.75 ± 0.60 |
| Ferrite | 0.015 | 0.51 ± 0.02 | 1.14 ± 0.07 | 5.92 ± 0.30 | 26.40 ± 0.30 | 3.84 ± 0.11 | 0.27 | 43.39 ± 0.47 | |
| Condition III | Austenite | 0.015 | 0.47 ± 0.06 | 1.13 ± 0.19 | 7.77 ± 0.19 | 24.86 ± 0.42 | 2.76 ± 0.08 | 0.27 | 38.29 ± 0.50 |
| Ferrite | 0.015 | 0.57 ± 0.03 | 1.03 ± 0.08 | 5.79 ± 0.18 | 26.36 ± 0.23 | 3.97 ± 0.19 | 0.27 | 43.80 ± 0.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
dos Santos, F.M., Jr.; da Silva, L.O.P.; dos Santos, Y.T.B.; Callegari, B.; Lima, T.N.; Coelho, R.S. Microstructural and Electrochemical Analysis of the Physically Simulated Heat-Affected Zone of Super-Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S32750. Metals 2025, 15, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15010002
dos Santos FM Jr., da Silva LOP, dos Santos YTB, Callegari B, Lima TN, Coelho RS. Microstructural and Electrochemical Analysis of the Physically Simulated Heat-Affected Zone of Super-Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S32750. Metals. 2025; 15(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15010002
Chicago/Turabian Styledos Santos, Francisco Magalhães, Jr., Leonardo Oliveira Passos da Silva, Ygor Tadeu Bispo dos Santos, Bruna Callegari, Tiago Nunes Lima, and Rodrigo Santiago Coelho. 2025. "Microstructural and Electrochemical Analysis of the Physically Simulated Heat-Affected Zone of Super-Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S32750" Metals 15, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15010002
APA Styledos Santos, F. M., Jr., da Silva, L. O. P., dos Santos, Y. T. B., Callegari, B., Lima, T. N., & Coelho, R. S. (2025). Microstructural and Electrochemical Analysis of the Physically Simulated Heat-Affected Zone of Super-Duplex Stainless Steel UNS S32750. Metals, 15(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15010002






