Study of Assimilation of Cored Wire into Liquid Steel Baths
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
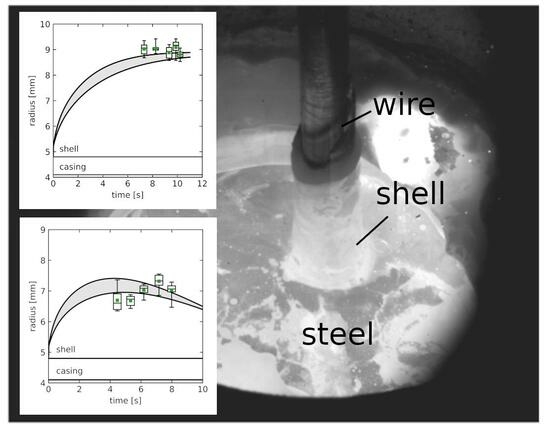
3.1. Estimations of Wire Residence Time in the Bath and Diameter of the Wire + Solidified Metal Shell Ensemble, Post Immersion
3.2. Comparison of Experimental Results and Numerical Simulations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holappa, L. Secondary Steelmaking. In Treatise on Process Metallurgy, 1st ed.; Seetharaman, S., McLean, A., Guthrie, R., Seetharaman, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; Volume 3A, pp. 301–346. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L. Modification of Non-Metallic Inclusions in Steel by Calcium Treatment: A Review. ISIJ Int. 2023, 63, 1927–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Ren, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, F. Formation and Prevention of Nozle Clogging during the Continuous Casting of Steels: A Review. ISIJ Int. 2024, 64, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ototani, T. Calcium Clean Steel, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1986; pp. 20–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kor, G.J.W.; Glaws, P.C. Ladle Refining and Vacuum Degassing. In The Making, Shaping and Treating of Steel, 11th ed.; Fruehan, R.J., Ed.; AISE Steel Foundation: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1998; Steelmaking and Refining Volume; pp. 661–713. [Google Scholar]
- Argyropoulos, S.A.; Li, S. Kinetics of Assimilation of Additions in Liquid Metals. In Treatise on Process Metallurgy, 1st ed.; Seetharaman, S., McLean, A., Guthrie, R., Seetharaman, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 359–426. [Google Scholar]
- Brabie, L.C.; Kawakami, M. Kinetics of Steel Scrap Melting in Molten Fe-C Bath. High. Temp. Mater. Process 2000, 19, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penz, F.M.; Schenk, J. A Review of Steel Scrap Melting in Molten Iron-Carbon Melts. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1900124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekely, J.; Chuang, Y.K.; Hlinka, J.W. The Melting and Dissolution of Low-Carbon Steels in Iron-Carbon Melts. Metall. Trans. 1972, 3, 2825–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.U.; Pehlke, R.D. Mass Transfer During Dissolution of a Solid into Liquid in the Iron-Carbon System. Metall. Trans. 1974, 5, 2527–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.U.; Pehlke, R.D. Transient Heat Transfer During Initial Stages of Steel Scrap Melting. Metall. Trans. B 1975, 6, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.K. Steel Dissolution in Quiescent and Gas Stirred Fe/C Melts. Metall. Trans. B 1989, 20, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, K.; Maede, H.; Ozawa, K.; Umezawa, K.; Saito, C. Analysis of the Scrap Melting in High Carbon Molten Iron. Tetsu-To-Hagane 1990, 76, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kawakami, M.; Takatani, K.; Brabie, L.C. Heat and Mass Transfer Analysis of Scrap Melting in Steel Bath. Tetsu-To-Hagane 1999, 85, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, H.; Mizukami, Y.; Ueshima, Y.; Miyazawa, K. Effect of Molten Steel Flow on Nonuniformity of Initially Solidified Shell. High. Temp. Mater. Process 2000, 19, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Zhu, R.; Tang, T.; Dong, K. Study on the Melting Characteristics of Steel Scrap in Molten Steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2019, 46, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Li, S.; Yang, S.; Zhao, M.; Li, J. Melting Characteristics of Steel Scrap with Different Carbon Contents in Liquid Steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2020, 47, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Gao, J.T.; Zhang, Y.L. Evaluation of Mass Transfer Coefficient during Scrap Melting. Metals 2021, 11, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Provatas, N. Kinetics of Scrap Melting in Liquid Steel: Multipiece Scrap Melting. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2008, 39, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Chen, S.; Yang, S.; Ye, M.; Li, J. Melting Characteristics of Multipiece Steel Scrap in Liquid Steel. ISIJ Int. 2021, 61, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzpeyma, N.; Windlund, O.; Ersson, M.; Jönsson, P. Mathematical Modeling of Scrap Melting in an EAF Using Electromagnetic Stirring. ISIJ Int. 2013, 53, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskopf, A. A Model for Scrap Melting in Steel Converter. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Xu, A.; Yang, G.; Wang, H. Analyses and Calculation of Steel Scrap Melting in a Multifunctional Hot Metal Ladle. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1800435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ryan, S.; Silaen, A.K.; Zhou, C.Q. Simulation of Scrap Melting Process in an AC Electric Arc Furnace: CFD Model Development and Experimental Validation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2022, 53, 2675–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ryan, S.; Silaen, A.K.; Zhou, C.Q. An Investigation into EAF Burner Preheating and Melting Characteristics: CFD Model Development and Experimental Validation. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2023, 54, 1068–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, P. Scrap Dissolution effect in BOF Converter Process. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2023, 50, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Oeters, F. Melting and Mixing of Alloying Agents in Steel Melts: Methods of Mathematical Modeling, 2nd ed.; Verlag Stahleisen GmbH: Dusseldorf, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Karasev, A.; Park, J.H.; Jönsson, P.G. Non-metallic Inclusions in Different Ferroalloys and Their Effect on the Steel Quality: A Review. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 2892–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Karasev, A.; Jönsson, P.G. Characterization of Nonmetallic Inclusions in Different Ferroalloys used in the Steelmaking Processes. Steel Res. Int. 2021, 92, 2100269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannenberg, K.; Harste, K.; Bode, O. Aufschmelzverhalten von Fülldrähten Während des Einspulens. Stahl. Eisen 1992, 12, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Du Terrail, Y.; Fautrelle, Y.; Rebiere, M.; Quemener, O. Predictions of Melting or Dissolution Times with a 1D Heat Transfer Simulation Package. Trans. Eng. Sci. 1994, 5, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal, S.; Chandra, S.; Kumar, S.; Roy, G.G. An Improved Model of Cored Wire Injection in Steel Melts. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, S.; Chandra, S.; Kumar, S.; Roy, G.G. Dissolution Kinetics of Cored Wire in Molten Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2006, 77, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Cedeno, E.I.; Jardy, A.; Carré, A.; Gerardin, S.; Bellot, J.P. A Thermal Model of Cored Wire Injection. In Proceedings of the Liquid Metal Processing and Casting Conference LMPC 2017, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 10–13 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Cedeno, E.I.; Jardy, A.; Carré, A.; Gerardin, S.; Bellot, J.P. Thermal Modeling of the Injection of Standard and Thermally Insulated Cored Wire. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2017, 48, 3316–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Cedeno, E.I.; Carré, A.; Lujan, J. Advances in Cored Wire Injection and Calcium Treatment in Steelmaking. In Proceedings of the Iron & Steel Technology Conference, AISTech 2022, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 18 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.G.; Yan, M.; Sun, J.N.; Du, F.S. Heat transfer of Calcium Cored Wire and CFD Simulation on Flow and Mixing Efficiency in the Argon-Stirred Ladle. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2017, 45, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingang, L.; Shuomeng, S.; Weihua, W.; Zhanjun, L.; Rensheng, C.; Ning, H. Study on Heat Transfer Mechanisms of Pure Calcium Cored Wire in Molten Steel by Feeding Rate. Metal. Ital. 2019, 111, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Chen, M.; Xu, L. Heat Transfer and Melting Characteristics of Calcium-Cored Wire in Molten Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2023, 95, 2300249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Su, J. An Improved Simulation Modelling on the Heat Transfer Process of Wire-Feeding Spheroidization in Iron Melt. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2023, 50, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucciardi, F.A. Heat Flow to Cylinders Submerged in Liquid Metal Baths. Master’s Thesis, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Argyropoulos, S.A. The Kinetics of Ferro-Alloy Solution in Liquid Steel. Master’s Thesis, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Argyropoulos, S.A. Dissolution of High Melting Point Additions in Liquid Steel. Ph.D. Thesis, McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, R.; Li, J.; Shi, C. Evolution of Inclusions with Ce Addition and Ca Treatment in Al-killed Steel during RH Refining Process. ISIJ Int. 2021, 61, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Kacar, Y.; Webler, B.; Pistorius, P.C. Chemical Composition Modification of Inclusions in Steels by Controlled Ca Treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 2837–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, J. Evolution Behaviour and Modification Mechanism of Inclusions in NM500 Wear-Resistant Steel with Calcium Treatment. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2022, 49, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Cedeno, E.I.; Carré, A.; Bustos-Canairca, A.A. Calcium addition cleanliness and its potential effects on steel quality. In Proceedings of the 52 Seminário de Acieria, Fundicao e Metalurgia de Nao-Ferrosos, ABM Week 2023, Sao Paolo, Brasil, 3 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Cheng, G.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Pan, J.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, S. Evolution Mechanism of Ca-Containing Inclusions in 20Mn23AlV High-Manganese Non-Magnetic Steel During the Refining Process. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2023, 50, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Meng, X.; Deng, X.; Li, S. Evolution of Sulphide Inclusion in Mg-Ca Treating Gear Steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2023, 50, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wu, W.; Zhi, J.; Su, C.; Zhang, J. Study on the Formation Mechanism of Clogging Layer of Rare Earth Microalloyed Q355 Steel’s Submerged Entry Nozzle and Process Optimization. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2023, 50, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Pu, G.; Cai, B.; He, S.; Du, W.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y. Evolution mechanism of inclusions during refining and continuous casting process of 321 H stainless steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2023, 50, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, N.; Chen, M.; Du, Z. Effect of Molten Steel Composition on Inclusion Modification by Calcium Treatment in Al-Killed Tinplate Steel. ISIJ Int. 2023, 63, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Jian, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhen, X.; Zhan, H.; Li, T.; Wang, X. Formation and Evolution of Inclusions in AH36 Steel During LF-RH-CC Process: The Influences of Ca-Treatment, Reoxidation, and Solidification. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2023, 54, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Ba, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L. Evolution of Non-Metallic Inclusions in a 303-ton Calcium-Treated Heavy Ingot. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2023, 54, 1565–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiraj, A.R.; Haidar, S.K.; Pande, M.M.; Hazra, S.S. Optimizing Ferrotitanium Wire Injection Parameters for Improving Titanium Recovery in Ladle Furnace Steelmaking. Steel Res. Int. 2024, in press. [CrossRef]
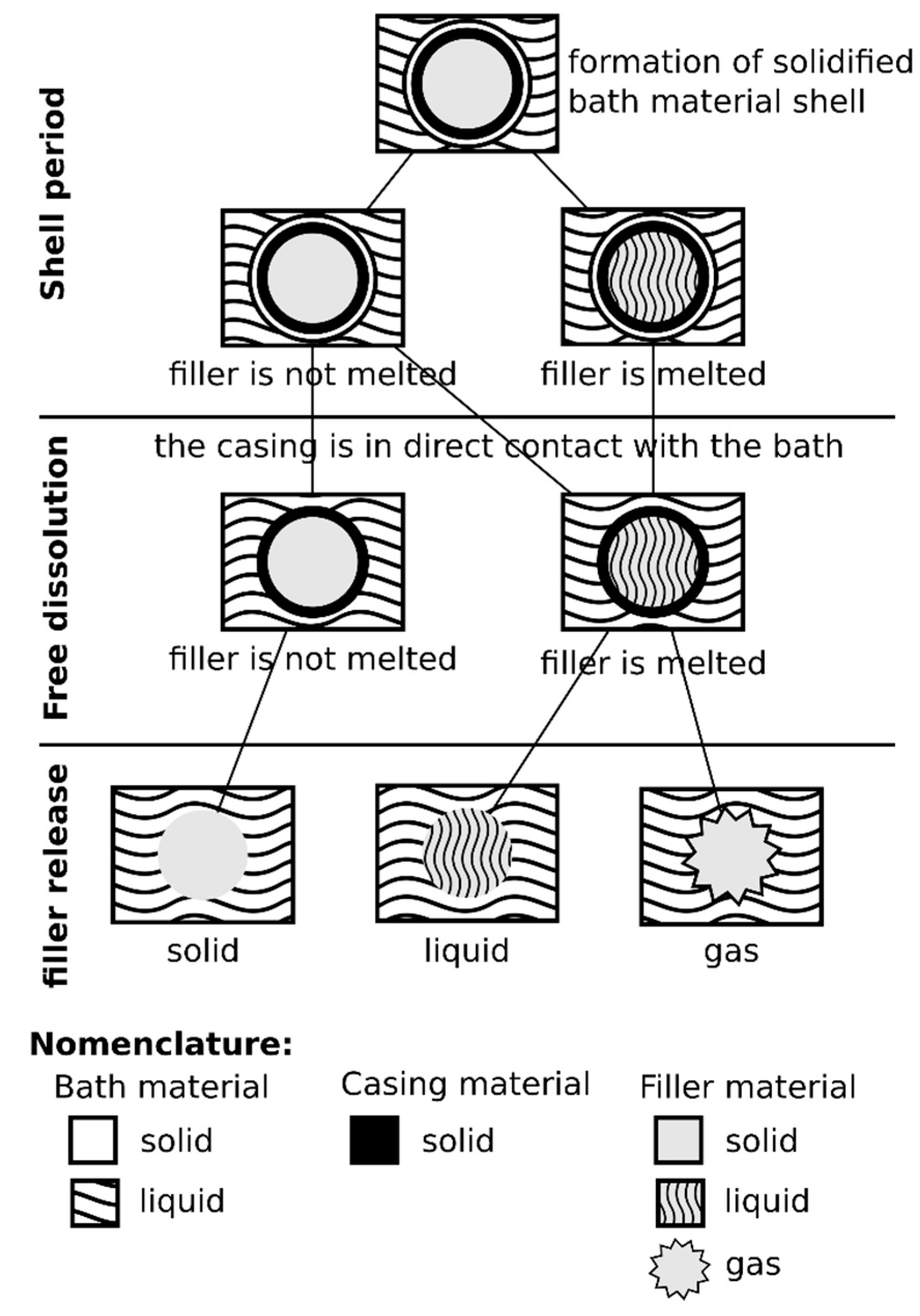
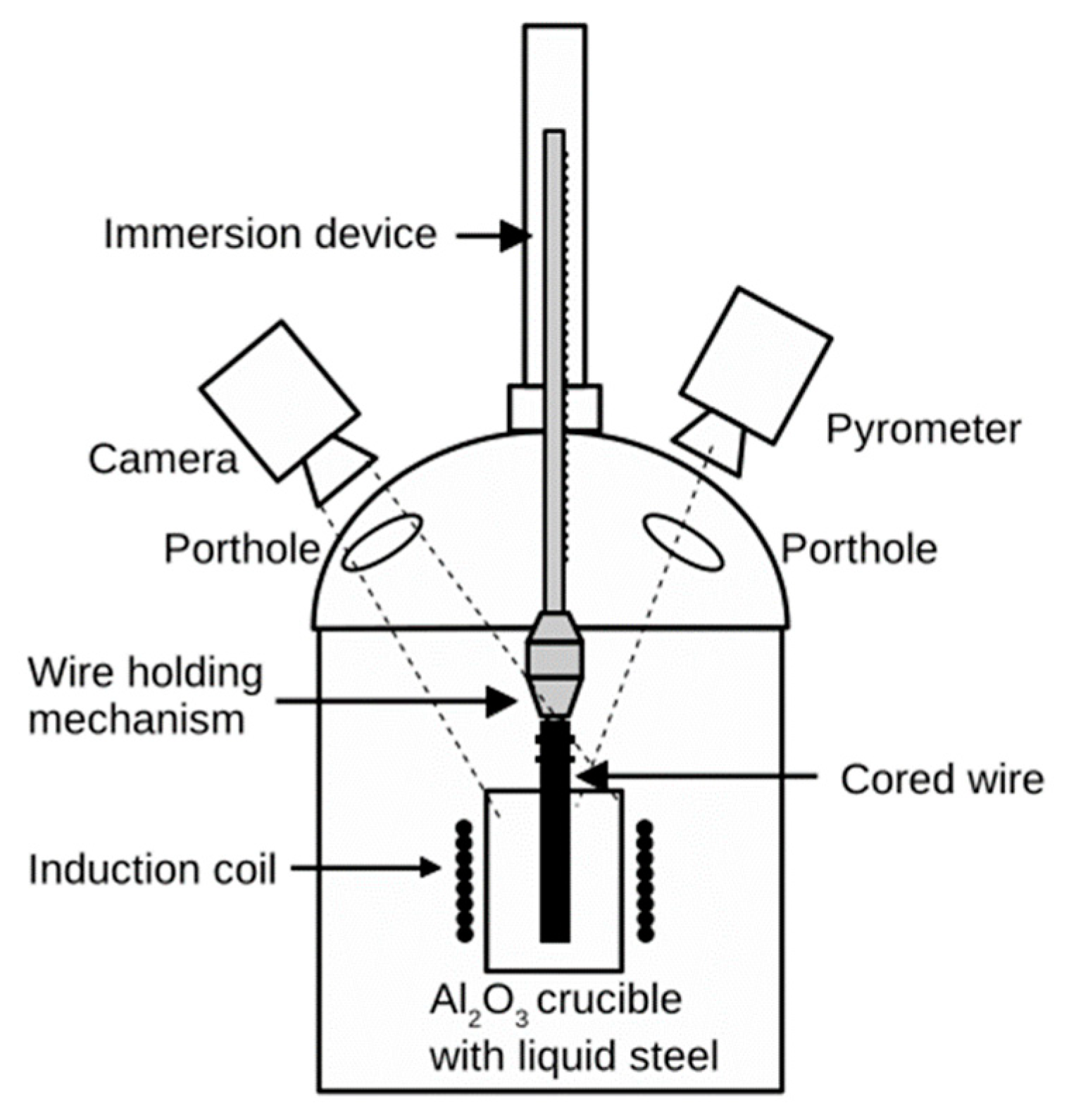
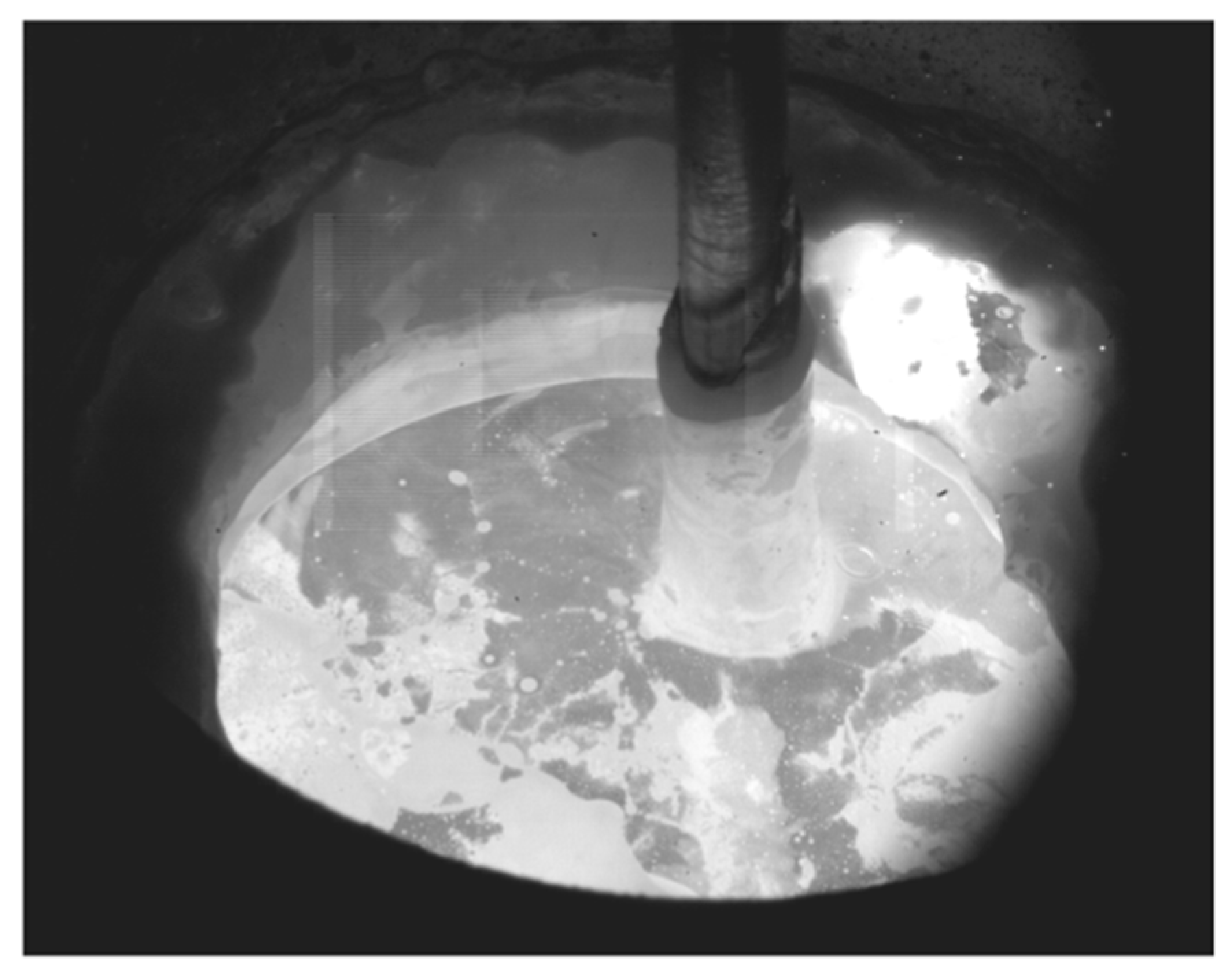

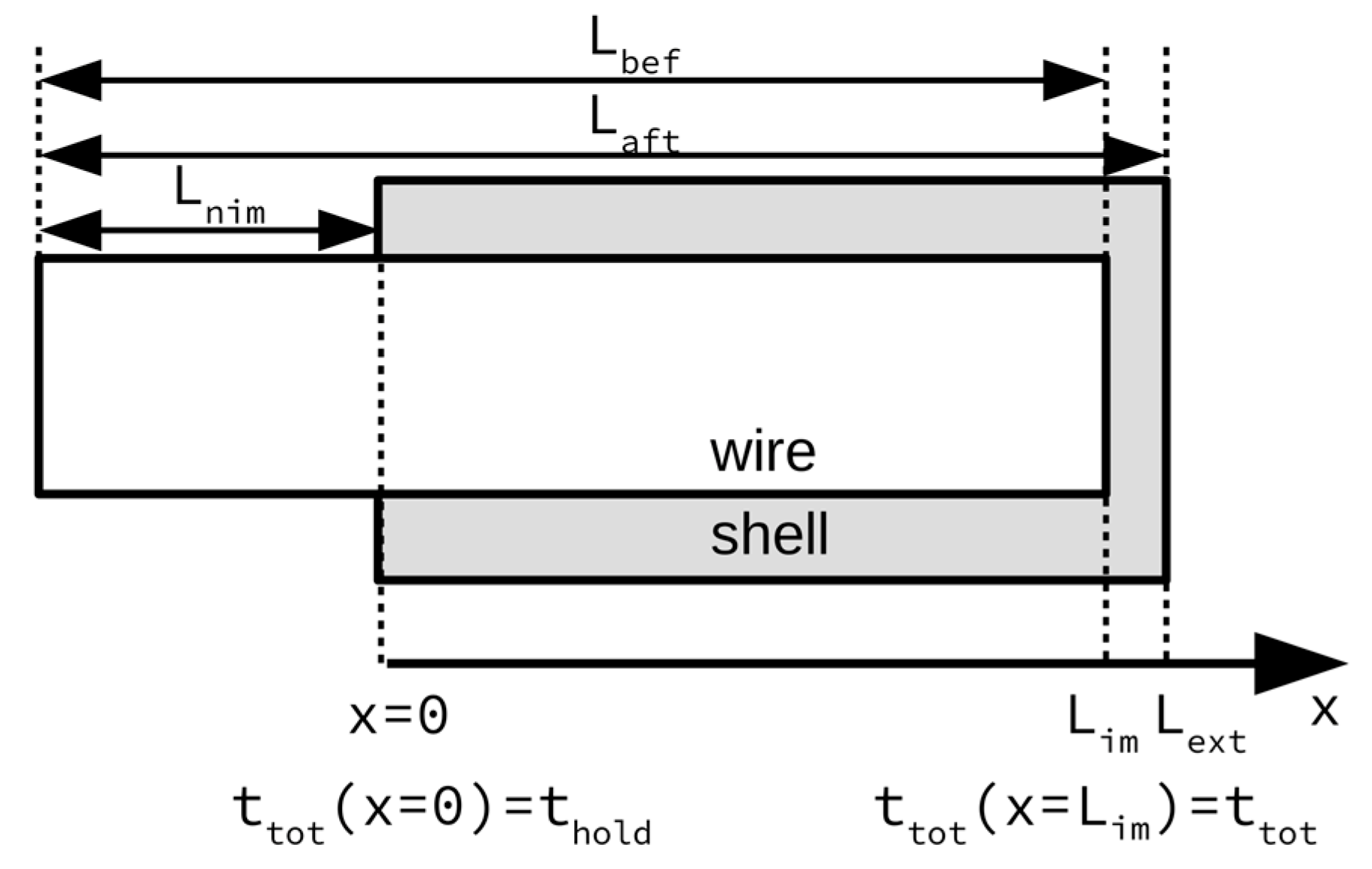
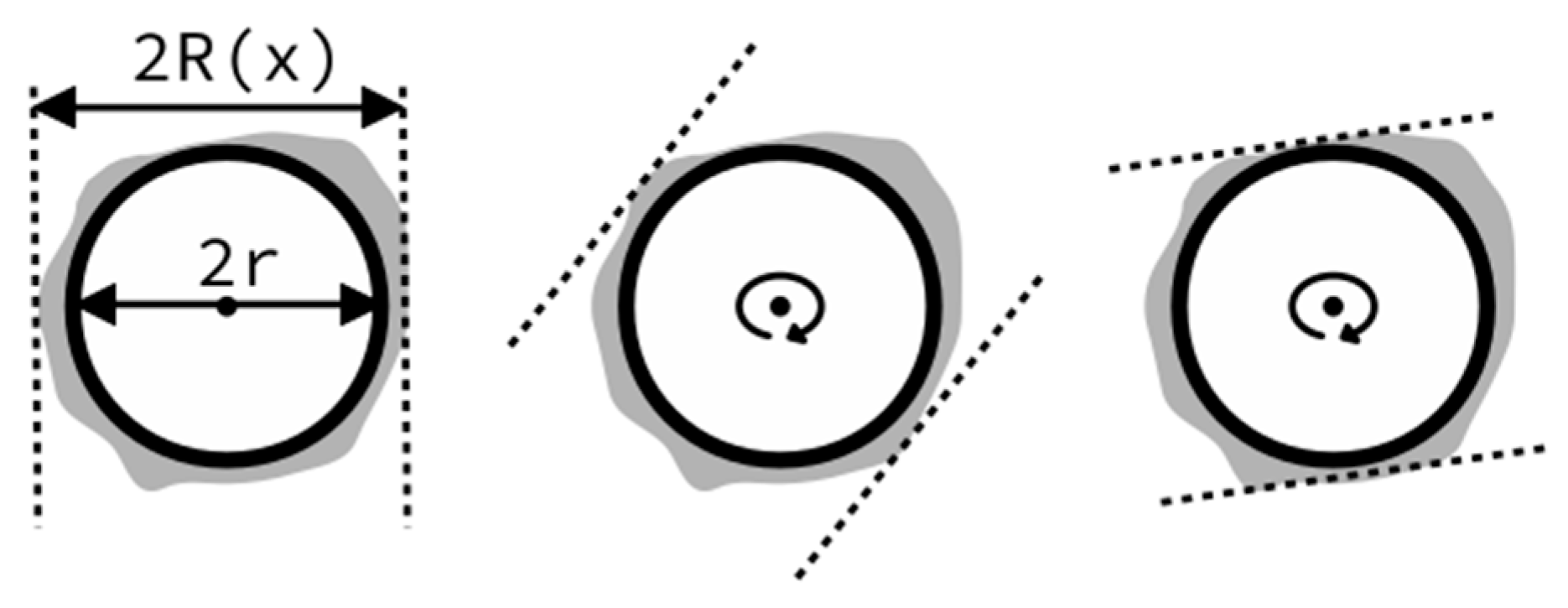

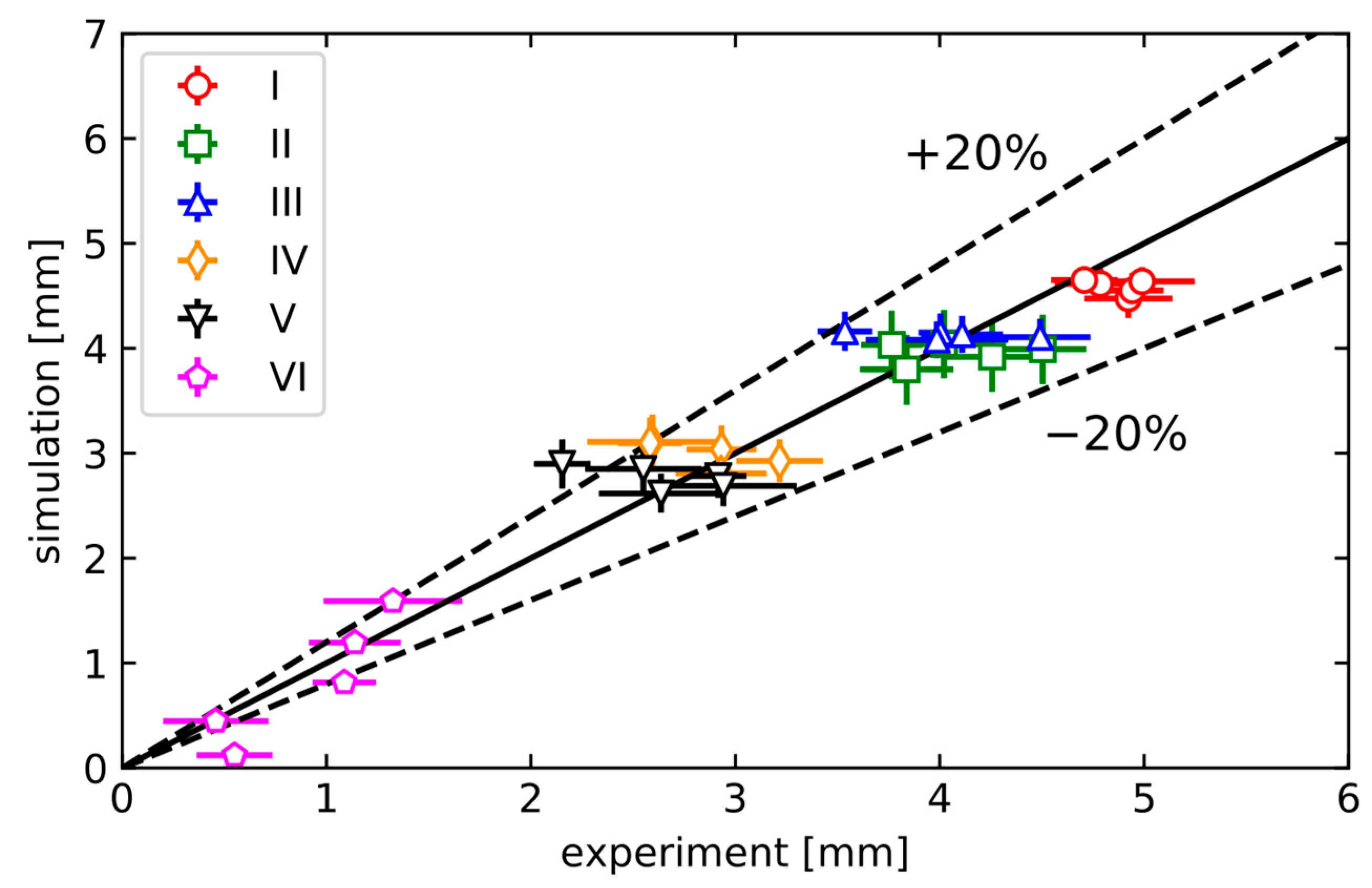
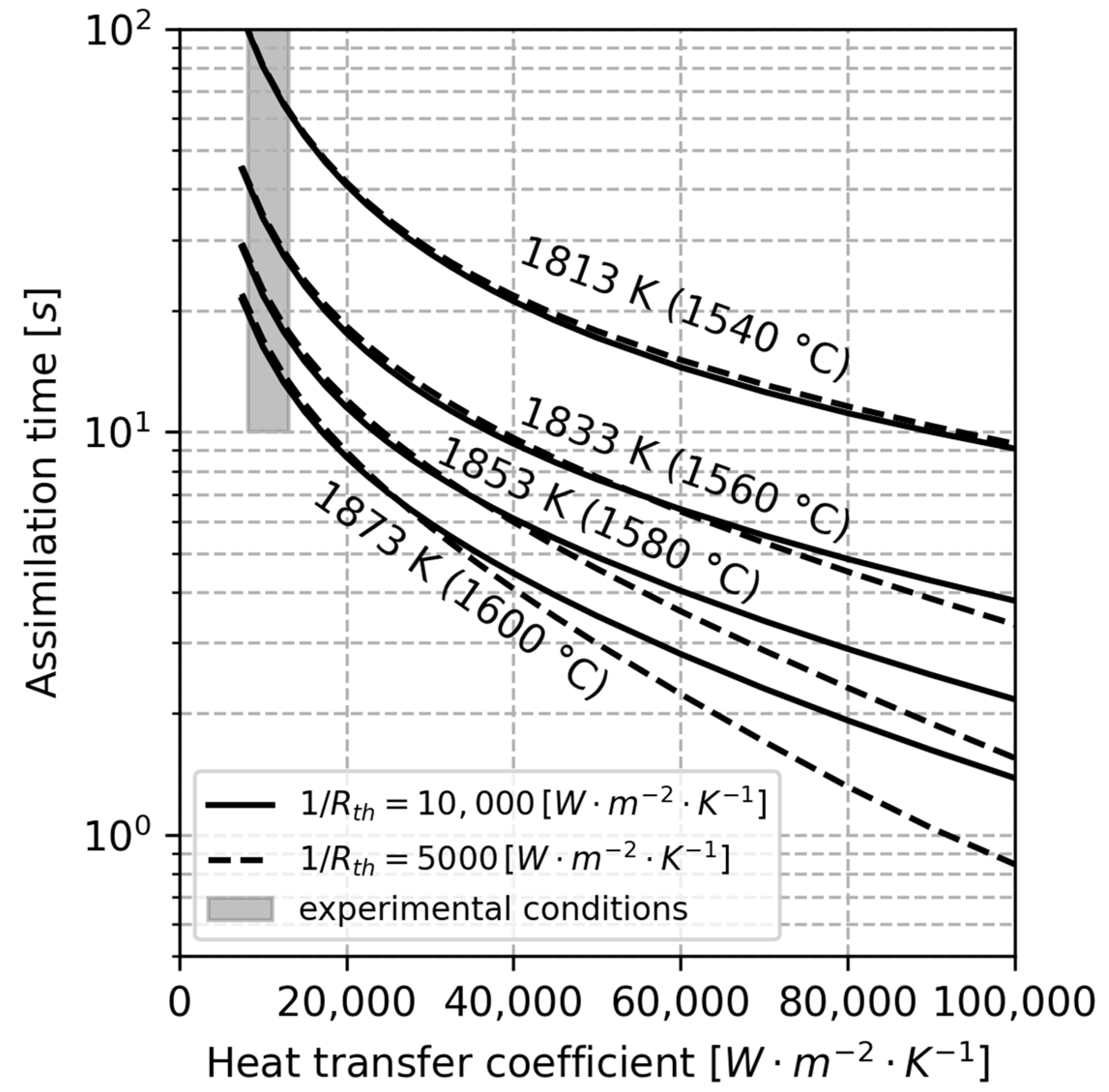
| Material | C | Mn | Si | P | S | O | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wire filler | 0.003 | 0.114 | Bal | ||||
| Wire casing | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.015 | 0.01 | 0.009 | Bal | |
| Steel bath | <0.002 | 0.03 | <0.001 | <0.005 | <0.01 | Bal |
| Wire | Tbath,ini | ΔTini |
|---|---|---|
| I | 1818 K (1545 °C) | 11 K |
| II | 1823 K (1550 °C) | 16 K |
| III | 1823 K (1550 °C) | 16 K |
| IV | 1853 K (1580 °C) | 46 K |
| V | 1858 K (1585 °C) | 51 K |
| VI | 1873 K (1600 °C) | 66 K |
| Wire | ttot(x) | x | Rmean | Rstdev | Rmin | RQ1 | RQ2 | RQ3 | Rmax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (1818 K) | 7.32 | 38.5 | 9.02 | 0.23 | 8.68 | 8.83 | 9.06 | 9.18 | 9.35 |
| 8.26 | 48 | 9.04 | 0.16 | 8.85 | 8.98 | 9.02 | 9.08 | 9.42 | |
| 9.34 | 59 | 8.89 | 0.24 | 8.58 | 8.67 | 8.93 | 9.08 | 9.20 | |
| 9.88 | 64.5 | 9.09 | 0.27 | 8.58 | 8.97 | 9.17 | 9.29 | 9.42 | |
| 10.22 | 68 | 8.81 | 0.17 | 8.54 | 8.71 | 8.82 | 8.90 | 9.06 | |
| II (1823 K) | 4.8 | 33 | 7.94 | 0.24 | 7.44 | 7.84 | 7.95 | 8.01 | 8.29 |
| 5.8 | 43.5 | 8.36 | 0.23 | 7.98 | 8.24 | 8.33 | 8.48 | 8.79 | |
| 6.8 | 54 | 8.6 | 0.22 | 8.42 | 8.46 | 8.50 | 8.79 | 8.97 | |
| 7.94 | 66 | 7.87 | 0.16 | 7.62 | 7.74 | 7.92 | 7.98 | 8.07 | |
| 8.89 | 76 | 8.12 | 0.23 | 7.85 | 7.95 | 8.10 | 8.24 | 8.52 | |
| III (1823 K) | 10.69 | 16.5 | 7.64 | 0.14 | 7.51 | 7.51 | 7.57 | 7.77 | 7.83 |
| 11.45 | 26 | 8.1 | 0.11 | 7.94 | 8.01 | 8.12 | 8.17 | 8.28 | |
| 12.37 | 37.5 | 8.21 | 0.21 | 7.84 | 8.09 | 8.17 | 8.35 | 8.62 | |
| 13.52 | 52 | 8.59 | 0.26 | 8.22 | 8.37 | 8.57 | 8.83 | 8.92 | |
| 14.64 | 66 | 8.09 | 0.37 | 7.57 | 7.73 | 8.16 | 8.44 | 8.49 | |
| IV (1853 K) | 4.46 | 23 | 6.7 | 0.34 | 6.35 | 6.40 | 6.60 | 6.91 | 7.36 |
| 5.32 | 33 | 6.68 | 0.17 | 6.43 | 6.53 | 6.73 | 6.82 | 6.88 | |
| 6.18 | 44 | 7.03 | 0.18 | 6.70 | 6.95 | 7.09 | 7.16 | 7.23 | |
| 7.16 | 54 | 7.32 | 0.22 | 6.86 | 7.19 | 7.33 | 7.51 | 7.55 | |
| 7.98 | 69 | 7.03 | 0.24 | 6.47 | 6.97 | 7.07 | 7.17 | 7.29 | |
| V (1858 K) | 5.81 | 15 | 6.25 | 0.15 | 5.98 | 6.22 | 6.26 | 6.36 | 6.45 |
| 6.22 | 25.5 | 6.65 | 0.3 | 6.32 | 6.42 | 6.58 | 6.79 | 7.22 | |
| 6.71 | 38 | 7.02 | 0.15 | 6.79 | 6.92 | 6.98 | 7.23 | 7.23 | |
| 7.31 | 53.5 | 7 | 0.38 | 6.38 | 6.73 | 7.05 | 7.23 | 7.53 | |
| 7.71 | 63.5 | 6.75 | 0.33 | 6.34 | 6.45 | 6.78 | 6.95 | 7.38 | |
| VI (1873 K) | 8.08 | 13.5 | 5.42 | 0.36 | 5.02 | 5.13 | 5.33 | 5.75 | 5.90 |
| 9.24 | 23 | 5.24 | 0.24 | 4.90 | 5.02 | 5.30 | 5.41 | 5.57 | |
| 10.27 | 31.5 | 5.19 | 0.16 | 4.81 | 5.14 | 5.17 | 5.32 | 5.38 | |
| 11.37 | 40.5 | 4.56 | 0.27 | 4.13 | 4.36 | 4.58 | 4.82 | 4.84 | |
| 12.22 | 47.5 | 4.65 | 0.2 | 4.28 | 4.60 | 4.70 | 4.78 | 4.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castro-Cedeno, E.-I.; Jourdan, J.; Martens, J.; Bellot, J.-P.; Jardy, A. Study of Assimilation of Cored Wire into Liquid Steel Baths. Metals 2024, 14, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14040462
Castro-Cedeno E-I, Jourdan J, Martens J, Bellot J-P, Jardy A. Study of Assimilation of Cored Wire into Liquid Steel Baths. Metals. 2024; 14(4):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14040462
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastro-Cedeno, Edgar-Ivan, Julien Jourdan, Jonathan Martens, Jean-Pierre Bellot, and Alain Jardy. 2024. "Study of Assimilation of Cored Wire into Liquid Steel Baths" Metals 14, no. 4: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14040462
APA StyleCastro-Cedeno, E.-I., Jourdan, J., Martens, J., Bellot, J.-P., & Jardy, A. (2024). Study of Assimilation of Cored Wire into Liquid Steel Baths. Metals, 14(4), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14040462