Microstructural and Morphological Properties of AlNiCo and CoNi Alloys: An In-Depth Study Based on Low-Energy Mechanical Alloying
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
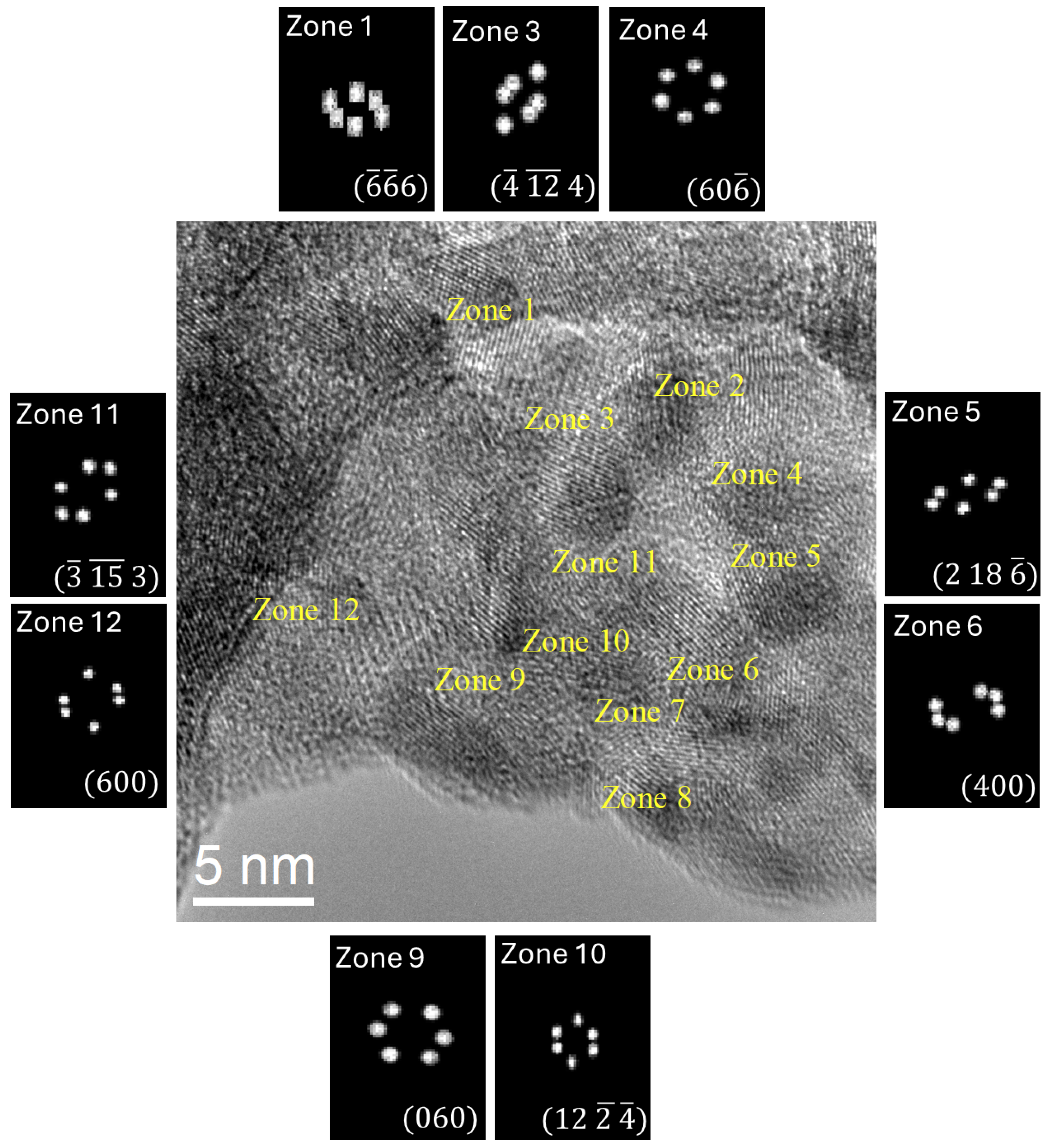
3.3. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pérez-Alcázar, G. Imanes permanentes: Características, aplicaciones y futuro. Rev. Acad. Colomb. Cienc. Exactas Físicas Nat. 2016, 40, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, I.E. Novel pre-alloyed powder processing of modified Alnico 8: Correlation of microstructure and magnetic properties. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 17D138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.S. Alnico permanent magnets: An overview. In Proceedings of the Electrical/Electronics Insulation Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 4–7 October 1993; pp. 373–383. [Google Scholar]
- Olvera, S.; Sánchez-Marcos, J.; Palomares, F.J.; Salas, E.; Arce, E.M.; Herrasti, P. Characterization and corrosion behaviour of CoNi alloys obtained by mechanical alloying. Mater. Charact. 2014, 93, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouar, N. Spark plasma sintering of Co80Ni20 nanopowders synthesized by polyol process and their magnetic and mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, S269–S275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera Olvera, J.N.; Hernández Maya, L.; Díaz Barriga Arceo, L.G. Novel morphology for NiWMo carbides obtained by mechanical alloying and quenching. C 2024, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera Olvera, J.N.; Paredes, G.J.G.; Serrano, A.R.; López, E.R.; Franco, E.M.; Meza, P.T. Synthesis and characterization of a MoWC-WC-NiC nanocomposite via mechanical alloying and sintering. Powder Technol. 2015, 271, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.M. Phase and elemental distributions in Alnico magnetic materials. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 3314–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, V. Al-Co-Ni. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2006, 27, 372–380. [Google Scholar]
- Lück, R. Phase diagram determination for modifications of the D phase in the Al-Ni-Co system. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1996, 553, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F. Enlightening from γ and β phase transformations in Al-Co-Ni alloy system: A review. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2019, 23, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D. Introduction to Magnetic Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical Alloying and Milling; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Esparza, C.D.; Campos-Venegas, K.; Solis-Canto, O.; Alvarado-Orozco, J.M.; Muñoz-Saldaña, J.; Herrera-Ramírez, J.M.; Martínez-Sánchez, R. Nanohardness and microstructure of NiCoAlFeCu and NiCoAlFeCuCr alloys produced by mechanical alloying. Microsc. Microanal. 2014, 20, 2106–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraga, K.; Yasuhara, A. The structure of an Al-Co-Ni decagonal quasicrystal in an Al72Co8Ni20 alloy studied by Cs-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X. Stress-induced FCC-HCP martensitic transformation in CoNi alloys under high pressure. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 904, 163119. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, B.; Qureshi, M.; Gupta, R.S.; Kaur, P. Alloys for catalytic production of syngas and bio-nanofilaments from biogas. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3501. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, P.; Marques, J.P.; Duarte, F.A.; Pires, A.; Pereira, L.G. Magnetic micromechanical structures based on CoNi and FeNi electrodeposited alloys. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2021, 31, 024001. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, R.; Castro, L.; García, R. Electrodeposition of Ni-Co alloys from cathode powder of Ni-MH spent batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 856, 157384. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L. Architecture and magnetism of AlNiCo. Acta Mater. 2014, 74, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainuma, R.; Maki, T. Phase equilibria and microstructural control in the Ni-Co-Al system. Intermetallics 1996, 4, S151–S158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arputhavalli, J.G.; Balasubramanian, S. Microstructure and phase transformation behavior of Co-Ni-Al alloy by spark plasma sintering. In Recent Trends in Materials Science and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 391–400. [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich, R.D.; Nesbitt, E. Physical structure and magnetic anisotropy of Alnico 5: Part 1. J. Appl. Phys. 1950, 23, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gille, P. Single crystal growth of Al-based intermetallic phases being approximants to quasicrystals. J. Cryst. Growth 2011, 318, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Wang, H. Phase equilibrium of ferromagnetic shape memory alloy Co39Ni33Al28. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, K.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K. Promising ferromagnetic Ni-Co-Al shape memory alloy system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 3290–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.P.; Nguyen, M. Phase equilibria in the Al-Co-Ni alloy system. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2017, 38, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.; Wells, A.F. The structure of Co2Al9. Acta Crystallogr. 1950, 3, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grushko, B.; Holland-Moritz, D. Decagonal quasicrystals in Al-Co and ternary alloys containing Cu and Ni. J. Alloys Compd. 1996, 236, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Tan, G.; Miyazaki, S.; Jiang, B.; Liu, Y. Stress-induced FCC-HCP martensitic transformation in CoNi. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 368, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Zhang, Z. Magneto-shape-memory effect in Co-Ni single crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 3660–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grushko, B.; Holland-Moritz, D. Quasicrystals and related structures in Al-Ni-Co. J. Alloys Compd. 1997, 262–263, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS). Powder Diffraction File; Card No. 00-045-1062; International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD): Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Buthainah, A.N.T. Alloys for catalytic production of syngas and carbon bio-nanofilaments via a biogas decomposition approach. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Schlesinger, M.; Mueller, E. Alloy Phase Diagrams Series: ASM Handbook; ASM International: Mumbai, India, 2016; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- SGTE. SGTE 2017 Alloy Phase Diagrams. Available online: https://www.crct.polymtl.ca/FACT/documentation/SGTE2017/SGTE2017_Figs.htm (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Smith, D.K.; Johnson, G.G. Quantitative X-ray powder diffraction analysis using the full pattern fitting method: I. The reference intensity ratio (RIR) approach. Adv. X-Ray Anal. 1987, 30, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD). Powder Diffraction File (PDF-4): Reference Intensity Ratio (RIR) Methodology. In ICDD Technical Manual; International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD): Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cullity, B.D.; Stock, S.R. Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- AMETEK. Digital Micrograph; Version 5.60; GATAN INC: Pleasanton, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Pérez, I.; Barriga-Arceo, L.D.; Febles, V.G.; Suárez-Parra, R.; Paz, R.L.; Santiago, P.; Rendon, L.; Jara, J.A.; Tapia, J.E.; González-Reyes, L. Self-organization of nickel nanoparticles dispersed in acetone: From separate nanoparticles to three-dimensional superstructures. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. Magnetic field-induced solvothermal synthesis of one-dimensional assemblies of NiCo alloy microstructures. Nano Res. 2008, 1, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. High-yield synthesis of bracelet-like hydrophilic Ni-Co magnetic alloy flux-closure nanorings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 11606–11607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoue, T.; Saito, M. Heat-assisted magnetic probe recording on a CoNi/Pt multilayered film. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 287, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Phase | Structural Details | Preparation Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| AlCoNi | Cubic | High-energy Mechanical Alloying | [22] |
| AlCoNi | BCC | Casting | [23] |
| (Co,Ni)4 | Martensitic | Casting | [24] |
| Orthogonal | Casting with Induction | [24] | |
| + , , tetragonal | Casting | [25] | |
| AlCoNi | + , FCC | Casting | [26] |
| NiAl | Casting | [26] | |
| (CoAl,NiAl) | Heat treatment | [27] | |
| (Co,Ni) | Heat treatment | [27] | |
| (Ni,Co)3Al | Heat treatment | [27] | |
| NiAl | ’ | Heat treatment | [27] |
| P2(1)/a | Casting | [28] | |
| P6(7)mmc | Casting | [29] | |
| AlCoNi | PmDm | Casting | [29] |
| CoNi | FCC | Casting | [30] |
| CoNi | FCC,HCP | Polyol reduction | [5] |
| CoNi | FCC, HCP | Casting | [31] |
| FCC, HCP | Casting | [4] |
| Phase | Lattice Parameters | Structure | Space Group | 2 | d (Å) | hkl | % Wt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlCo | a: 2.86 Å | Cubic | Pmm | 46.13 | 0.90 | (310) | 2.7 |
| a: 8.55 Å, b: 6.29 Å, c: 6.21 Å | Monoclinic | /a (14) | 15.42 | 2.63 | (121) | 44 | |
| 18.84 | 2.16 | (12) | |||||
| 28.74 | 1.43 | (323) | |||||
| 33.68 | 1.23 | (12) | |||||
| Ni | a: 12.06 Å, b: 7.55 Å, c: 15.35 Å | Orthorhombic | Immm (71) | 17.4 | 2.33 | (125) | 14.3 |
| a: 11.39 Å | Cubic BCC | Iad (230) | 17.82 | 2.32 | (422) | 27.9 | |
| 23.24 | 1.75 | (541) | |||||
| 33.1 | 1.24 | (842) | |||||
| 40.76 | 1.015 | (1051) | |||||
| a: 12.12 Å, b: 4.06 Å, c: 7.64 Å, : 105. | Monoclinic | C1 | 21.37 | 1.90 | (04) | 5.13 | |
| CoNi | a: 3.53 Å | FCC | Fmm (225) | 38.88 | 1.06 | (311) | 5.13 |
| Phase | Lattice Parameters | Structure | Space Group | 2 | d (Å) | h | k | l | % Wt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a: 2.5 Å, c: 4.06 Å | Hexagonal | /mmc (194) | 18.82 | 2.16 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 52.4 | |
| 20.09 | 2.03 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |||||
| 21.36 | 1.91 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||||
| 35.95 | 1.14 | 1 | 0 | 3 | |||||
| CoNi | a: 3.53 Å | Cubic FCC | Fmm (225) | 20.02 | 2.04 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 35.51 |
| 23.15 | 1.76 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| 32.97 | 1.24 | 2 | 2 | 0 | |||||
| 38.88 | 1.06 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 51.88 | 0.81 | 3 | 3 | 1 | |||||
| NiCo | a: 2.62 Å, c: 4.32 Å | Hexagonal | /mmc (194) | 17.97 | 2.27 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 8.35 |
| Co | a: 2.5 Å, c: 4.07 Å | Hexagonal | /mmc (194) | 27.64 | 1.48 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3.69 |
| 31.88 | 1.25 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |||||
| 40.80 | 1.01 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Zone | (nm) | (nm) | Phase | Structure | h | k | l |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.253 | 0.335 | Ni | Orthorhombic | −6 | −6 | 6 |
| 2 | 0.481 | 0.704 | Monoclinic | −3 | −3 | 0 | |
| 3 | 0.464 | 0.211 | Ni | Orthorhombic | −4 | −12 | 4 |
| 4 | 0.240 | 0.311 | Ni | Orthorhombic | 6 | 0 | −6 |
| 5 | 0.211 | 0.396 | Ni | Orthorhombic | 2 | 18 | −6 |
| 6 | 0.424 | 0.380 | Ni | Orthorhombic | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 0.453 | 0.735 | (Ni,Co)3 | Cubic | −1 | 3 | −1 |
| 8 | 0.819 | 0.576 | (Ni,Co)3 | Cubic | 0 | 16 | −16 |
| 9 | 0.311 | 0.408 | Ni | Orthorhombic | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| 10 | 0.916 | 0.479 | Ni | Orthorhombic | 12 | −2 | −4 |
| 11 | 0.606 | 0.580 | Ni | Orthorhombic | −3 | −15 | 3 |
| 12 | 0.535 | 0.296 | Ni | Orthorhombic | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Zone | (nm) | (nm) | Phase | Structure | h | k | l |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.8 | 1.275 | Ni | Cubic | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 2 | 1.248 | 1.7 | CoNi | Cubic | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 3 | 2.14 | 1.211 | Co | Hexagonal | 0 | −3 | 0 |
| 4 | 2.152 | 1.2025 | Co | Hexagonal | 0 | −3 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz Nieto, G.; Rivera Olvera, J.N.; Díaz de la Torre, S.; Garibay Febles, V.; Palacios Gómez, J.; Gonzalez Reyes, L.; Diaz Barriga Arceo, L.G. Microstructural and Morphological Properties of AlNiCo and CoNi Alloys: An In-Depth Study Based on Low-Energy Mechanical Alloying. Metals 2024, 14, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14111307
Cruz Nieto G, Rivera Olvera JN, Díaz de la Torre S, Garibay Febles V, Palacios Gómez J, Gonzalez Reyes L, Diaz Barriga Arceo LG. Microstructural and Morphological Properties of AlNiCo and CoNi Alloys: An In-Depth Study Based on Low-Energy Mechanical Alloying. Metals. 2024; 14(11):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14111307
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz Nieto, Gilberto, Jesús Noé Rivera Olvera, Sebastián Díaz de la Torre, Vicente Garibay Febles, Jesús Palacios Gómez, Leonardo Gonzalez Reyes, and Lucía Graciela Diaz Barriga Arceo. 2024. "Microstructural and Morphological Properties of AlNiCo and CoNi Alloys: An In-Depth Study Based on Low-Energy Mechanical Alloying" Metals 14, no. 11: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14111307
APA StyleCruz Nieto, G., Rivera Olvera, J. N., Díaz de la Torre, S., Garibay Febles, V., Palacios Gómez, J., Gonzalez Reyes, L., & Diaz Barriga Arceo, L. G. (2024). Microstructural and Morphological Properties of AlNiCo and CoNi Alloys: An In-Depth Study Based on Low-Energy Mechanical Alloying. Metals, 14(11), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14111307








