Phase Transformation Behaviors and Dislocation Evolutions of an Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy under Annealing Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties’ Evolutions
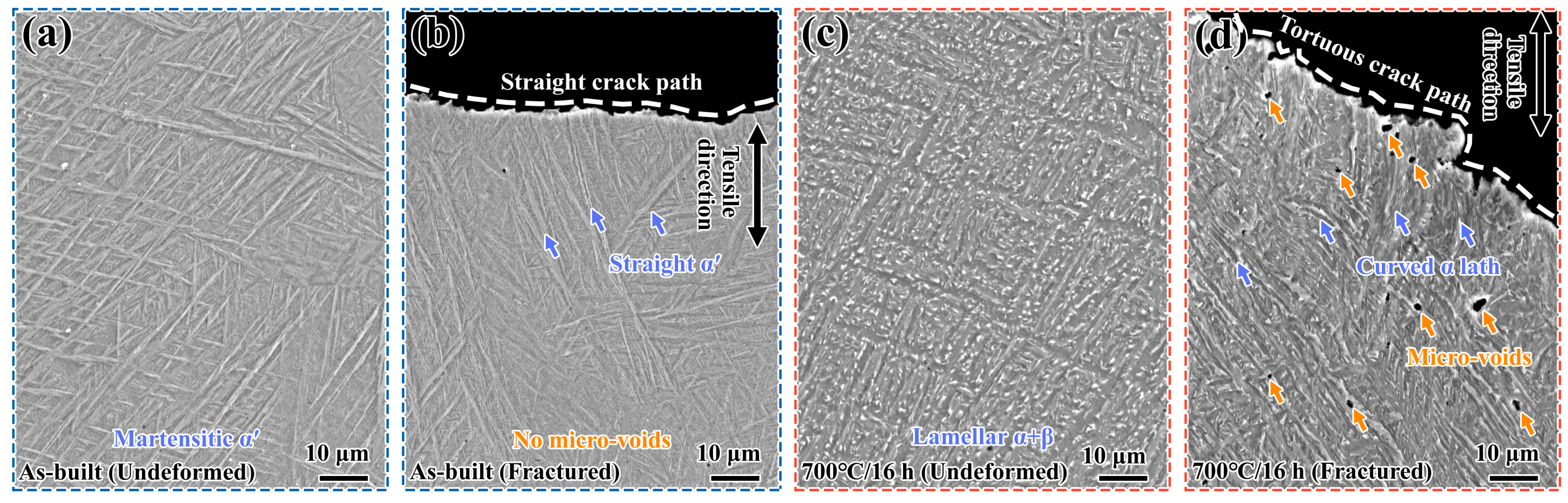
3.1.1. Microstructure
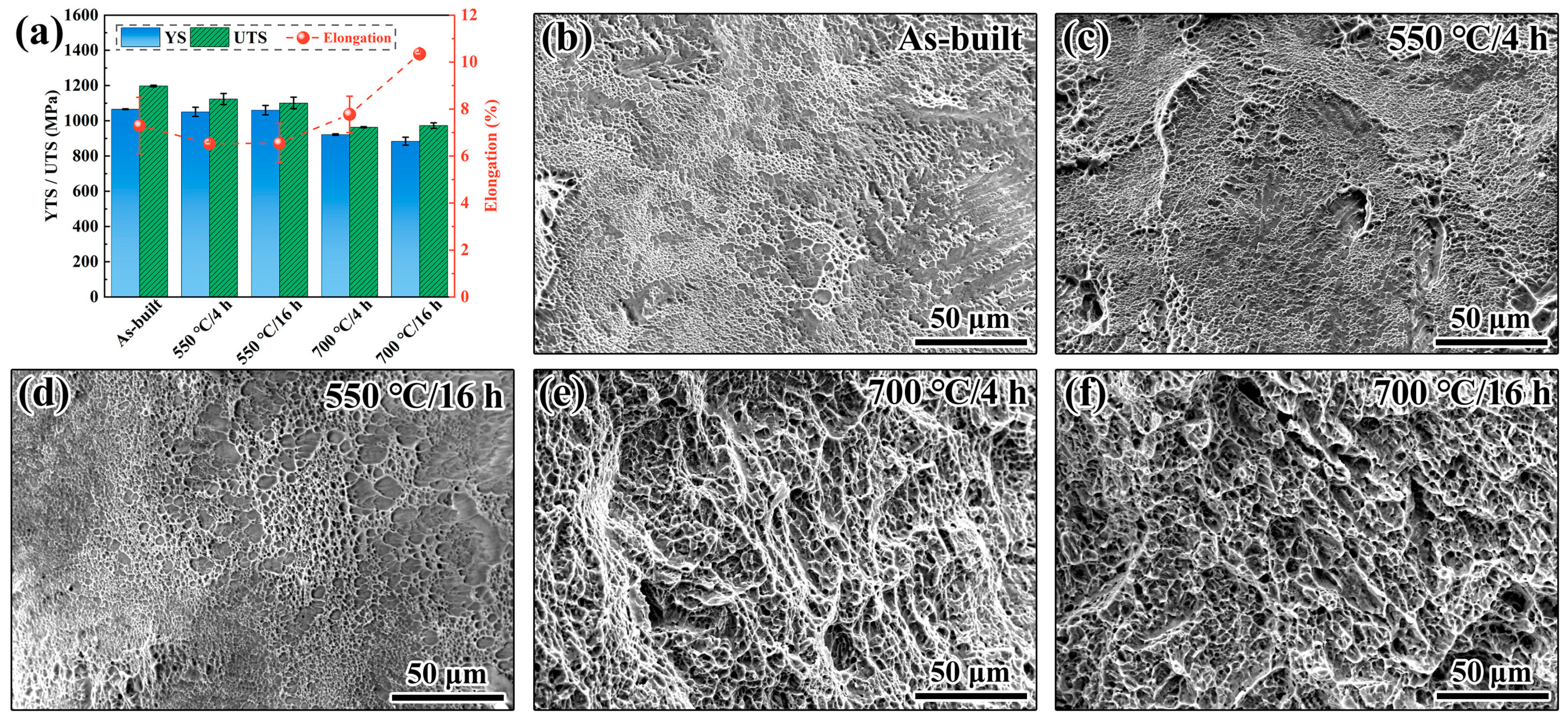
3.1.2. Mechanical Properties
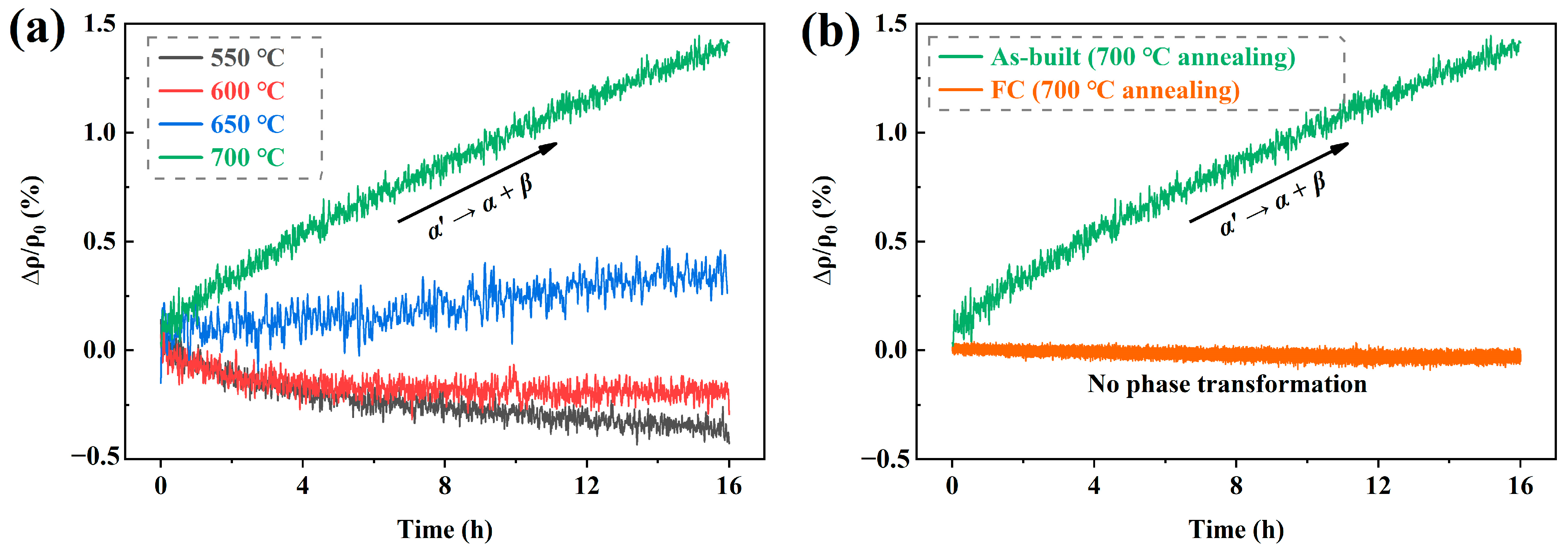
3.2. In Situ Electrical Resistivity Measurement
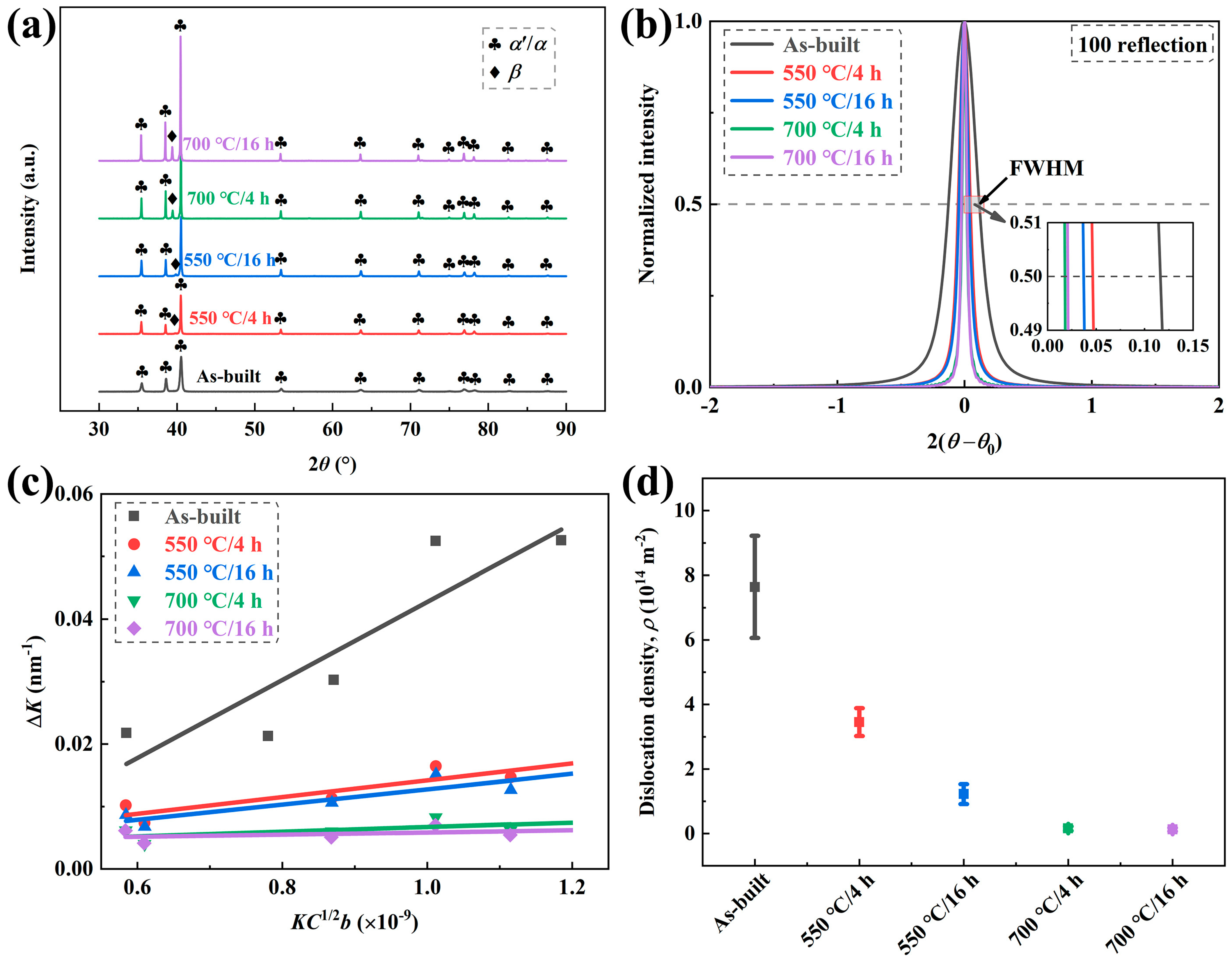
3.3. Line Profile Analysis of XRD
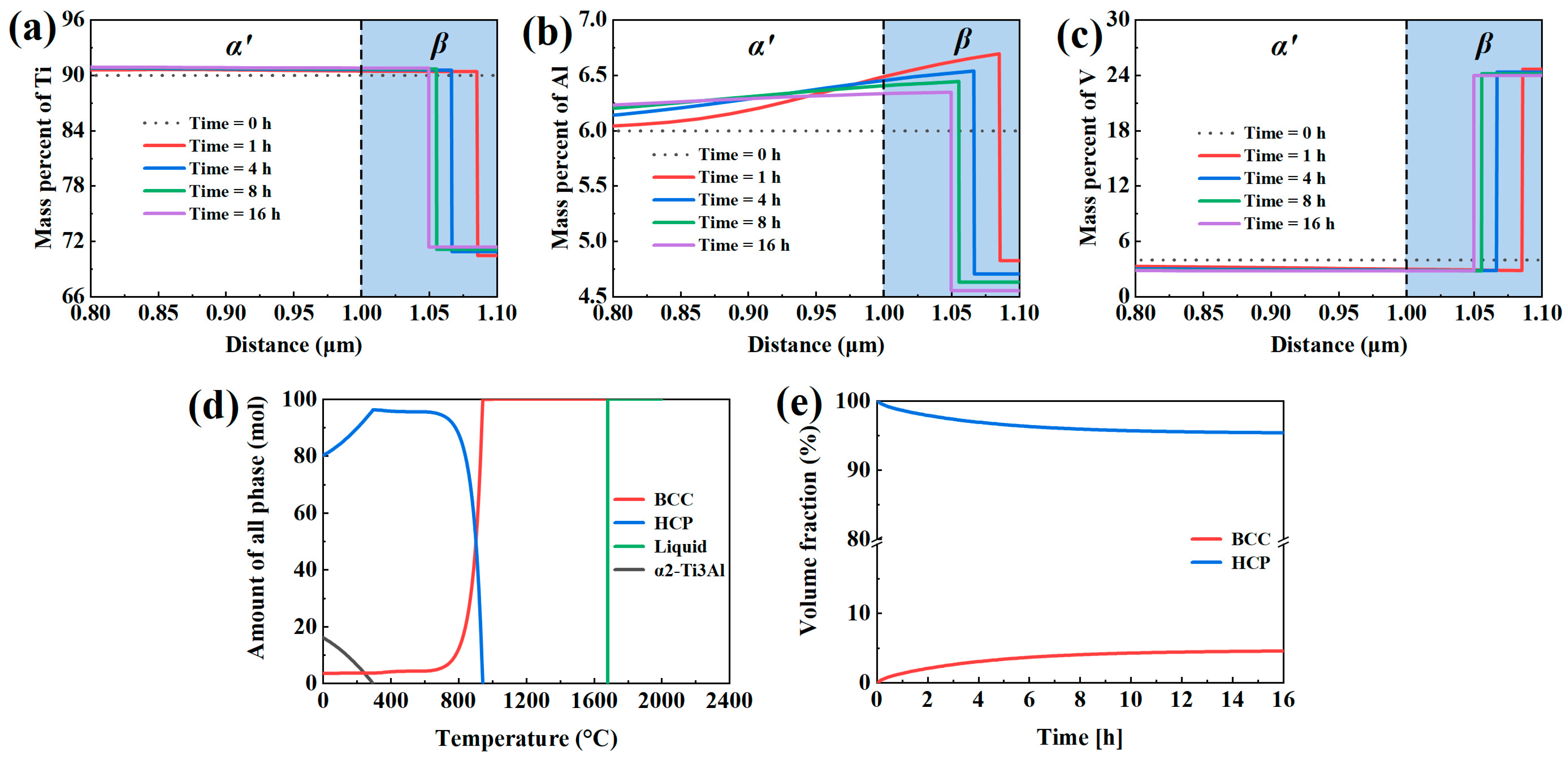
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The in situ electrical resistivity measurement was implemented to investigate the martensite decomposition behavior of the LPBF-built Ti-6Al-4V alloy under post annealing treatment. The relative increase of the electrical resistivity increased gradually with the increasing annealing temperature, representing that the martensite decomposition rate increases with the annealing temperature.
- (2)
- The dislocations in the as-built Ti-6Al-4V alloy were eliminated efficiently by the post annealing treatments. After annealing at 700 °C for 4 h, 98% of the dislocations were eliminated, and further prolonging the annealing time has only a marginal influence on the dislocation density. The reduced dislocations in the α lath provided space for storage of dislocations, which is beneficial for achieving high work-hardening capacity and superior ductility.
- (3)
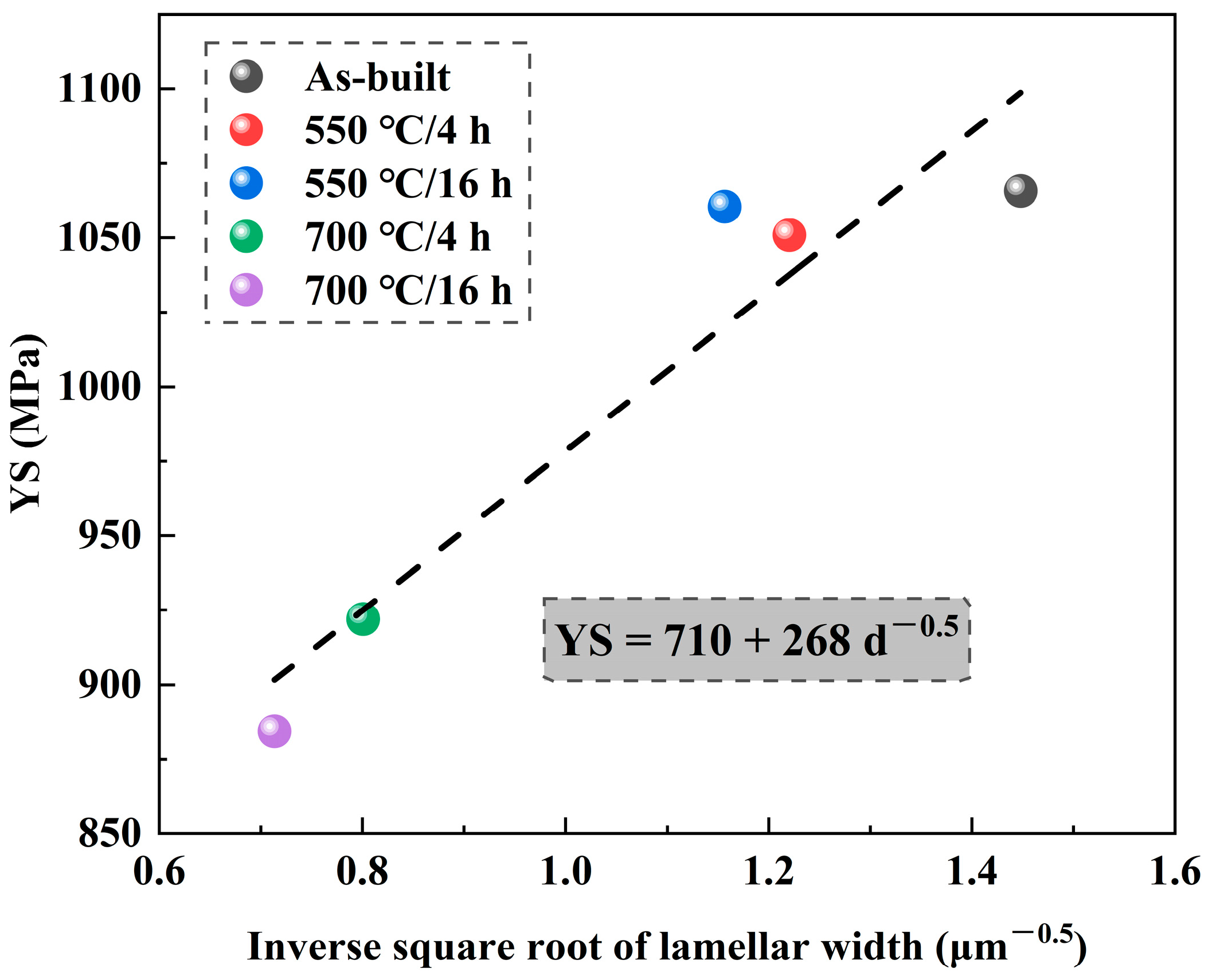
- A linear relationship exists between the yield strength and the inverse square root of the lamellar width of α′/α lath, indicating that the grain boundary strengthening plays a major role in controlling the yield strength of the alloy. After annealing at 700 °C for 4 h and 16 h, the ductility of the alloy was increased to 7.8% and 10.3%, respectively. The improvement in ductility can be attributed to the integrated effects of the reduced dislocations, formed β phase, and varied phase morphology.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, C.; Weng, F.; Sui, S.; Chew, Y.; Bi, G. Progress and Perspectives in Laser Additive Manufacturing of Key Aeroengine Materials. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2021, 170, 103804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, C.-T. Design of Titanium Alloys by Additive Manufacturing: A Critical Review. Adv. Powder Mater. 2021, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhuo, L. Additive Manufacturing of Titanium Alloys via Selective Laser Melting: Fabrication, Microstructure, Post-Processing, Performance and Prospect. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 111, 106110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zou, Y.; Lim, C.V.S.; Wu, X. Review of Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) Fabricated Ti-6Al-4V: Process, Post-Process Treatment, Microstructure, and Property. Light Adv. Manuf. 2021, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, S.; Moridi, A.; Liou, F.; Emdadi, A. The Trajectory of Additively Manufactured Titanium Alloys with Superior Mechanical Properties and Engineered Microstructures. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 60, 103245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, Ó.; Silva, F.J.G.; Ferreira, L.P.; Atzeni, E. A Review of Heat Treatments on Improving the Quality and Residual Stresses of the Ti-6Al-4V Parts Produced by Additive Manufacturing. Metals 2020, 10, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Narayan, R.L.; Tan, J.H.K.; Sing, S.L.; Yeong, W.Y. Resolving the Porosity-Unmelted Inclusion Dilemma during in-Situ Alloying of Ti34Nb via Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Acta Mater. 2021, 204, 116522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, S.; Chew, Y.; Weng, F.; Tan, C.; Du, Z.; Bi, G. Achieving Grain Refinement and Ultrahigh Yield Strength in Laser Aided Additive Manufacturing of Ti−6Al−4V Alloy by Trace Ni Addition. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2021, 16, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Jiang, F.; Li, J.; Tan, C.; Xu, Z.; Xie, H.; Liu, J.; Tang, J.; Fu, D.; Zhang, H.; et al. Phase Transformation Mechanisms, Microstructural Characteristics and Mechanical Performances of an Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy under Dual-Stage Heat Treatment. Mater. Des. 2022, 223, 111240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, S.; Chew, Y.; Hao, Z.; Weng, F.; Tan, C.; Du, Z.; Bi, G. Effect of Cyclic Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser Aided Additive Manufacturing Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo Alloy. Adv. Powder Mater. 2022, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beese, A.M.; Carroll, B.E. Review of Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Made by Laser-Based Additive Manufacturing Using Powder Feedstock. JOM 2016, 68, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarniya, A.; Colera, X.G.; Mirzaali, M.J.; Sovizi, S.; Bartolomeu, F.; St Weglowski, M.K.; Wits, W.W.; Yap, C.Y.; Ahn, J.; Miranda, G.; et al. Additive Manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V Parts through Laser Metal Deposition (LMD): Process, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 804, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Chu, R.; Zhou, X.; Yang, K.; Jia, Q.; Lim, C.V.S.; Huang, A.; Wu, X. Role of Martensite Decomposition in Tensile Properties of Selective Laser Melted Ti-6Al-4V. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 744, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Hu, Q.; Huang, A.; Chen, Z.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J.; Fu, C.; Jia, Q.; Lim, C.V.S.; Boyer, R.R.; et al. Static Coarsening Behaviour of Lamellar Microstructure in Selective Laser Melted Ti-6Al-4V. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chao, Q.; Chen, H.S.; Chen, Z.B.; Primig, S.; Xu, W.; Ringer, S.P.; Liao, X.Z. Formation of a Transition V-Rich Structure during the α’ to α + β Phase Transformation Process in Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Acta Mater. 2022, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Ramamurty, U. Microstructural Optimization through Heat Treatment for Enhancing the Fracture Toughness and Fatigue Crack Growth Resistance of Selective Laser Melted Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Acta Mater. 2019, 169, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinov, S.; Markovsky, P.; Sha, W.; Guo, Z. Resistivity Study and Computer Modelling of the Isothermal Transformation Kinetics of Ti-6Al-4V and Ti–6Al–2Sn–4Zr–2Mo–0.08Si Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 314, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinov, S.; Markovsky, P.; Sha, W. Resistivity Study and Computer Modelling of the Isothermal Transformation Kinetics of Ti–8Al–1Mo–1V Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 333, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Bo, G.; Jiang, F.; Xu, S.; Teng, J.; Fu, D.; Zhang, H. Unravelling the Precipitation Evolutions of AZ80 Magnesium Alloy during Non-Isothermal and Isothermal Processes. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 75, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.; Hall, W. X-Ray Line Broadening from Filed Aluminium and Wolfram. Acta Metall. 1953, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, B.E.; Averbach, B.L. The Effect of Cold-Work Distortion on X-ray Patterns. J. Appl. Phys. 1950, 21, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Jiang, F.; Tan, C.; Weng, F.; Ng, F.L.; Goh, M.H.; Xie, H.; Liu, J.; Chew, Y.; Teng, J. Additive Manufacturing of Fine-Grained High-Strength Titanium Alloy via Multi-Eutectoid Elements Alloying. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 249, 110399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Ji, X.; Liu, J.; Teng, J.; Jiang, F.; Fu, D.; Zhang, H. Revealing the Decomposition Mechanisms of Dislocations and Metastable α’ Phase and Their Effects on Mechanical Properties in a Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Sha, G.; Jin, S.; Hou, Z.; Bayat, M.; Yang, N.; Tan, Q.; Yin, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Designing against Phase and Property Heterogeneities in Additively Manufactured Titanium Alloys. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreon, H.; Ruiz, A.; Santoveña, B. Study of Aging Effects in a Ti-6AL-4V Alloy with Widmanstätten and Equiaxed Microstructures by Non-Destructive Means. AIP Conf. Proc. 2014, 1581, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Zurob, H.S.; Purdy, G.R.; Zhang, H. Characterizing Precipitate Evolution of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Based Commercial Alloy during Artificial Aging and Non-Isothermal Heat Treatments by in Situ Electrical Resistivity Monitoring. Mater. Charact. 2016, 117, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Xie, H.; Tan, C.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; Jiang, F.; Tang, J.; Fu, D.; Zhang, H.; Teng, J. Microstructural Characteristics and Tribological Behavior of an Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy under Direct Aging and Solution-Aging Treatments. Tribol. Int. 2022, 175, 107763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Kuroda, A.; Ito, M.; Mori, M.; Bian, H.; Shobu, T.; Sato, S.; Chiba, A. Quantifying the Dislocation Structures of Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloys Using X-Ray Diffraction Line Profile Analysis. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiatin, S.L.; Brown, T.M.; Goff, T.A.; Fagin, P.N.; Barker, D.R.; Turner, R.E.; Murry, J.M.; Miller, J.D.; Zhang, F. Diffusion Coefficients for Modeling the Heat Treatment of Ti-6Al-4V. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 3015–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, S.; Chew, Y.; Weng, F.; Tan, C.; Du, Z.; Bi, G. Study of the Intrinsic Mechanisms of Nickel Additive for Grain Refinement and Strength Enhancement of Laser Aided Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2022, 4, 035102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zheng, S.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, X.; Zhang, B.; Lei, J.; Yang, R.; et al. Twinning and Sequential Kinking in Lamellar Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Acta Mater. 2019, 181, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
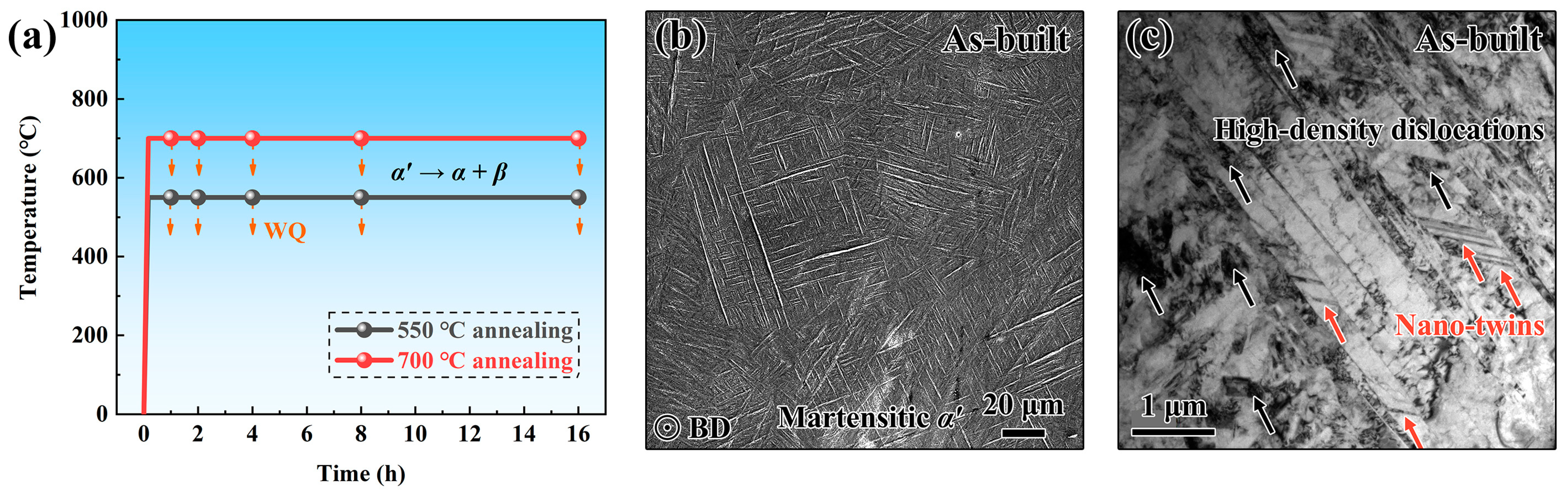
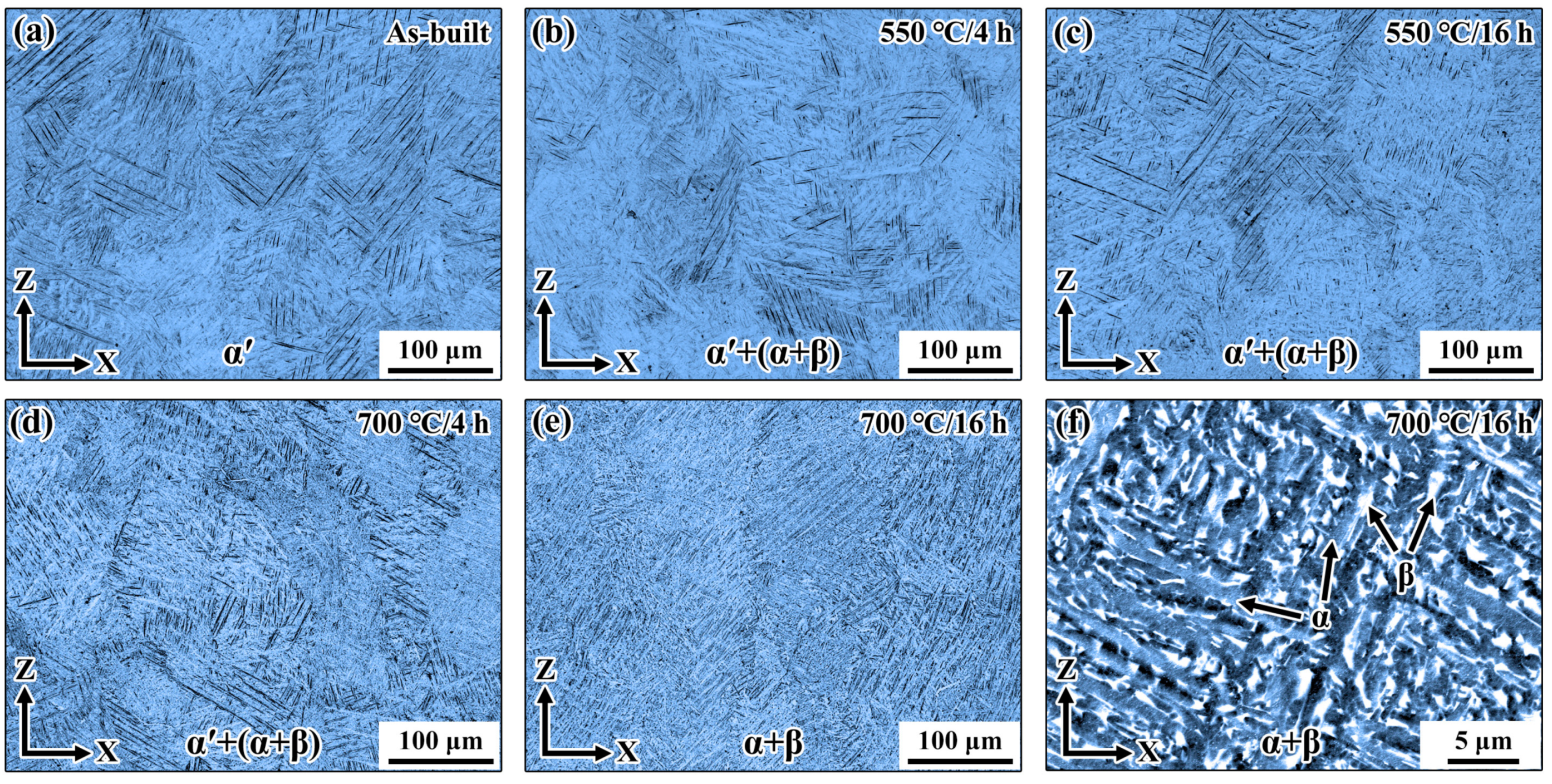
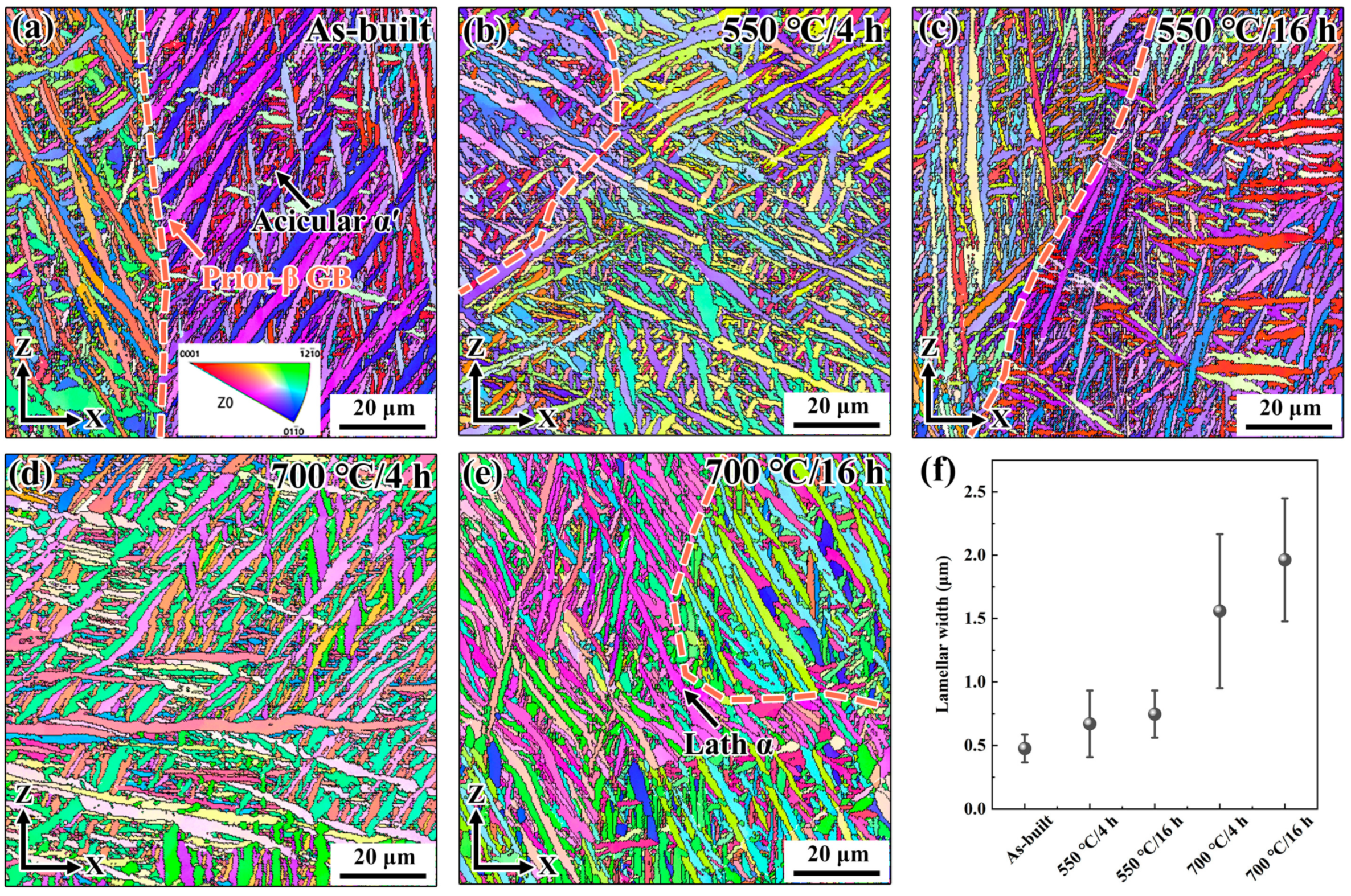
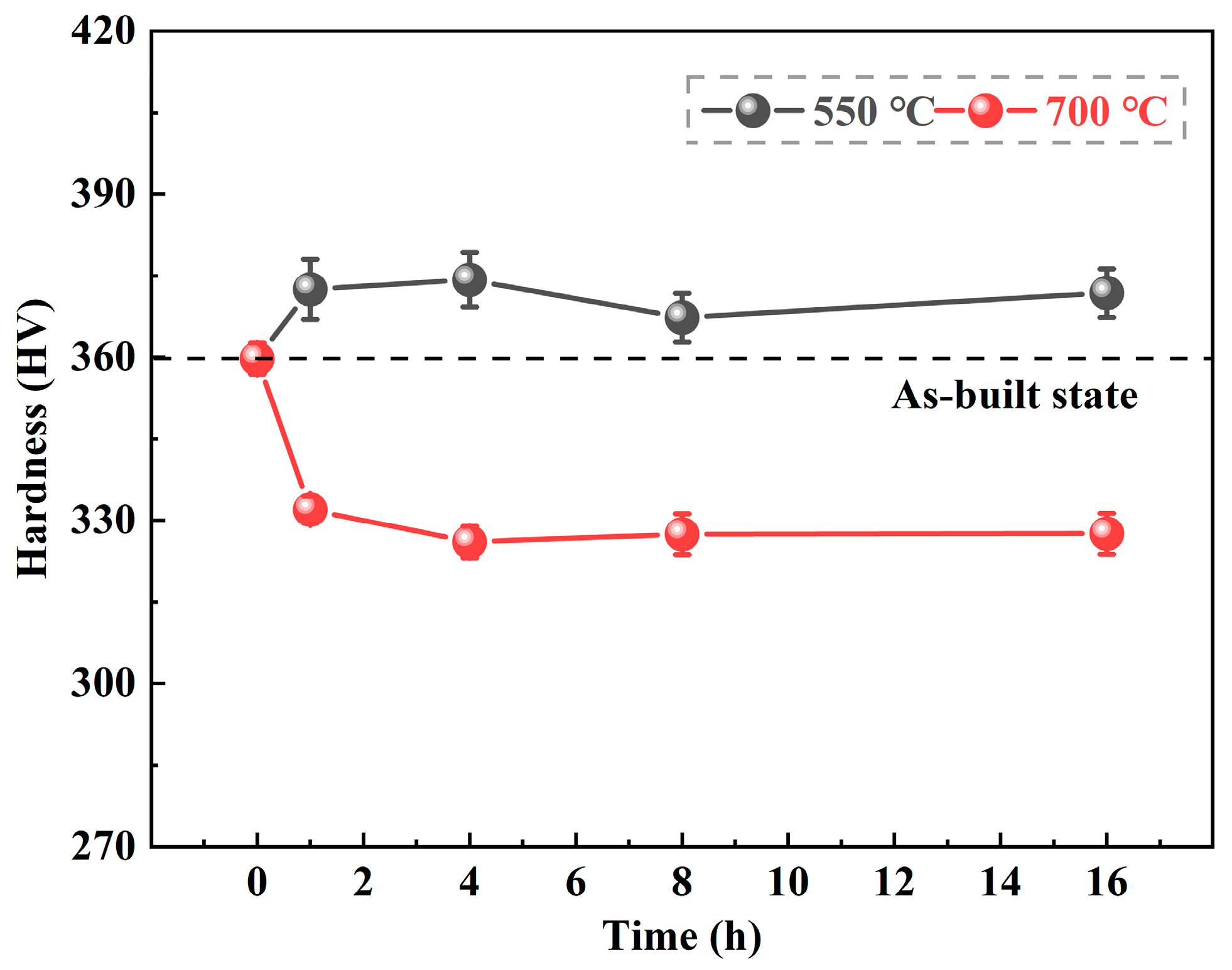
| Sample | As-Built | 550 °C/1 h | 550 °C/4 h | 550 °C/8 h | 550 °C/16 h | 700 °C/1 h | 700 °C/4 h | 700 °C/8 h | 700 °C/16 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV0.2) | 359.8 | 372.5 | 374.3 | 367.3 | 371.8 | 332.0 | 326.0 | 327.5 | 327.6 |
| Standard deviation | 2.9 | 5.6 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 3.8 | 3.8 |
| Sample | Yield Strength (MPa) | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-built | 1065.8 ± 2.2 | 1197.5 ± 4.5 | 7.3 ± 1.2 |
| 550 °C/4 h | 1050.9 ± 26.1 | 1123.3 ± 31.6 | 6.5 ± 0.1 |
| 550 °C/16 h | 1060.5 ± 26.9 | 1101.1 ± 33.1 | 6.6 ± 0.9 |
| 700 °C/4 h | 922.0 ± 4.0 | 963.4 ± 3.1 | 7.8 ± 0.8 |
| 700 °C/16 h | 884.3 ± 22.8 | 973.3 ± 15.4 | 10.4 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, X.; Xie, H.; Su, J.; Jiang, F.; Teng, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B. Phase Transformation Behaviors and Dislocation Evolutions of an Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy under Annealing Treatment. Metals 2023, 13, 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13061061
Ji X, Xie H, Su J, Jiang F, Teng J, Zhang H, Guo B. Phase Transformation Behaviors and Dislocation Evolutions of an Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy under Annealing Treatment. Metals. 2023; 13(6):1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13061061
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Xiankun, Haiming Xie, Jinlong Su, Fulin Jiang, Jie Teng, Hui Zhang, and Baoqi Guo. 2023. "Phase Transformation Behaviors and Dislocation Evolutions of an Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy under Annealing Treatment" Metals 13, no. 6: 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13061061
APA StyleJi, X., Xie, H., Su, J., Jiang, F., Teng, J., Zhang, H., & Guo, B. (2023). Phase Transformation Behaviors and Dislocation Evolutions of an Additively Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Alloy under Annealing Treatment. Metals, 13(6), 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13061061







