Effects of Quenching Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Strip-Cast Medium-Mn Steel Processed by Quenching and Partitioning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
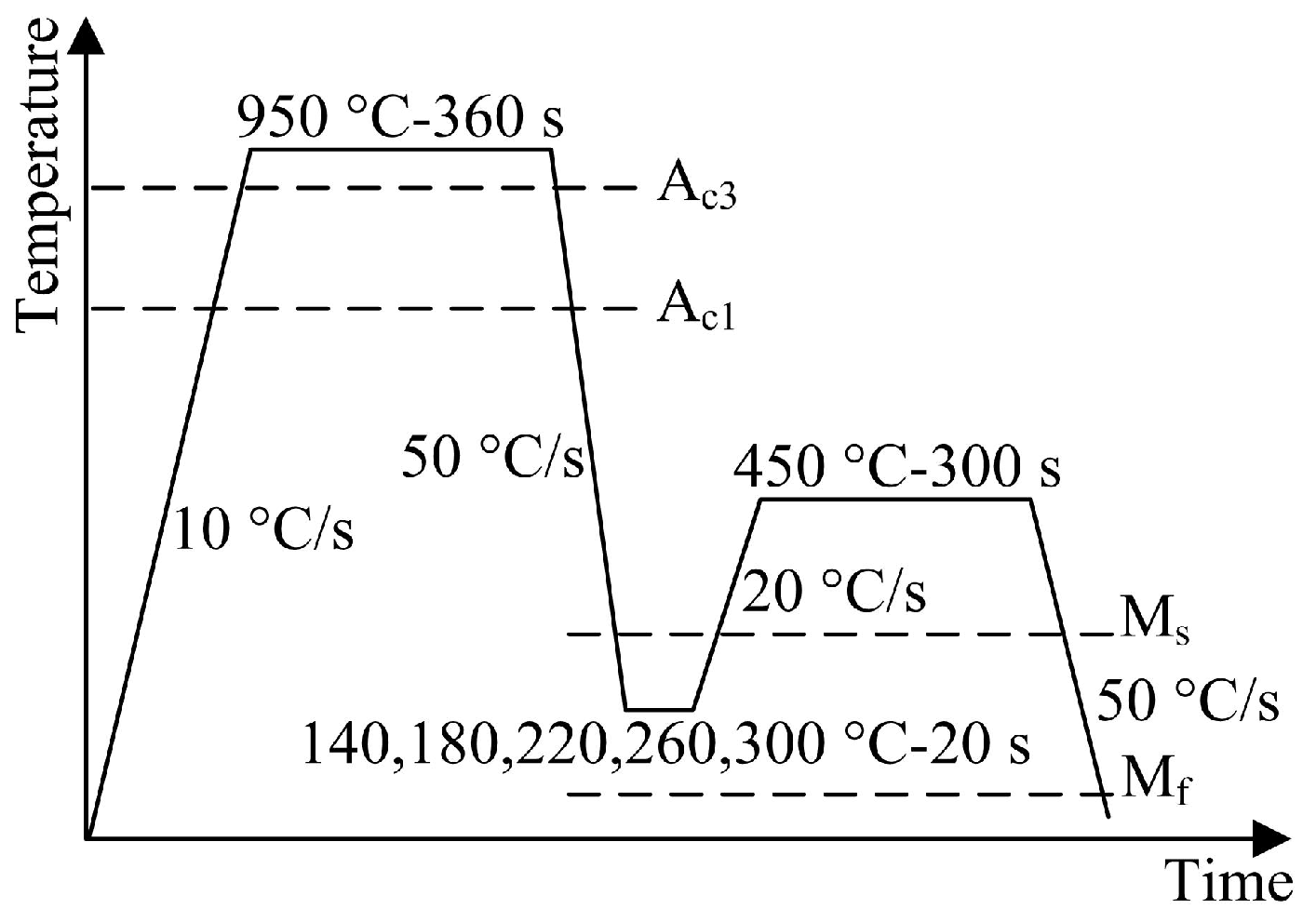
2.1. Materials Processing
2.2. Microstructure Characterization
2.3. Tensile Properties Examination
3. Results and Discussion
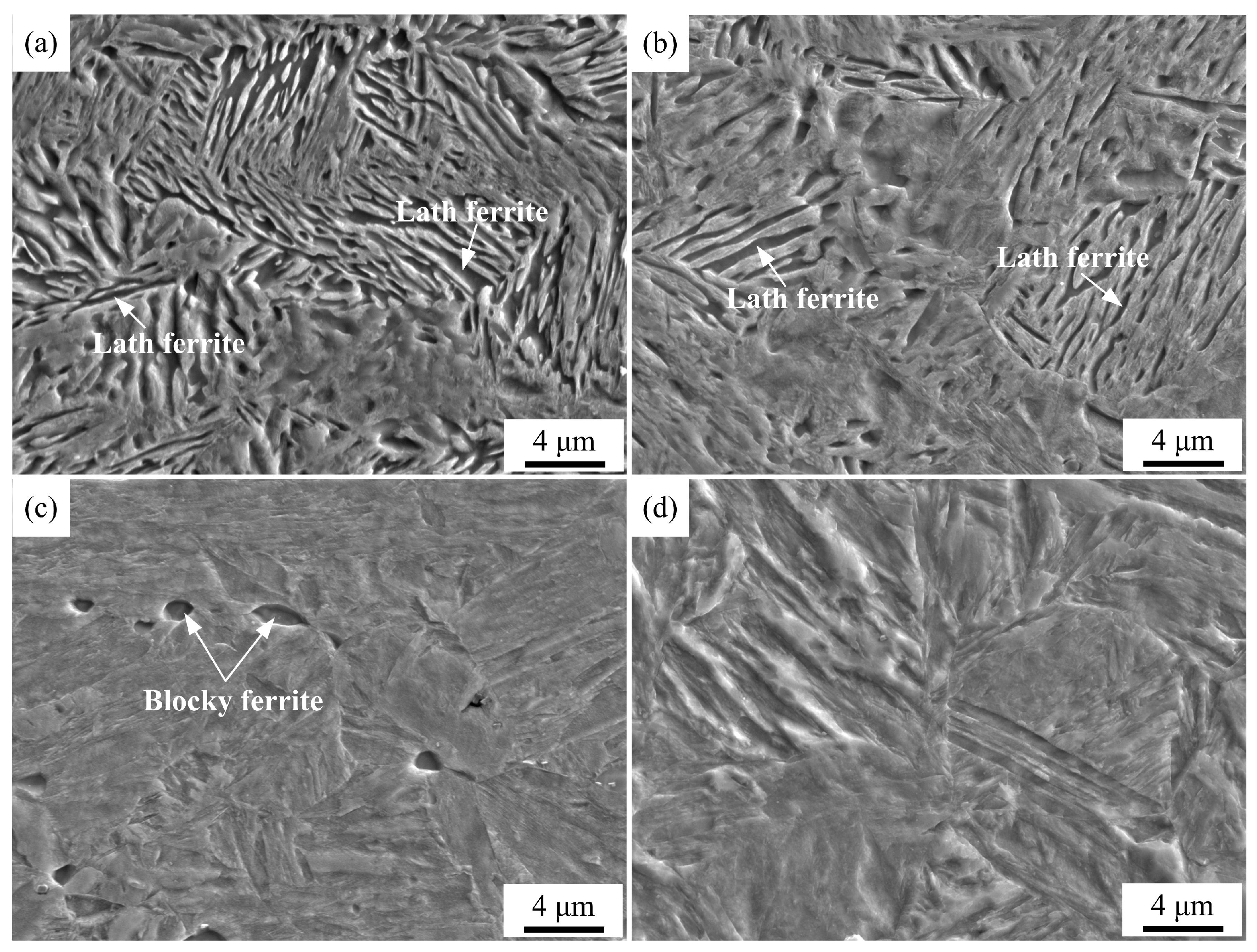
3.1. Microstructure of the Samples under Different Austenitizing Conditions
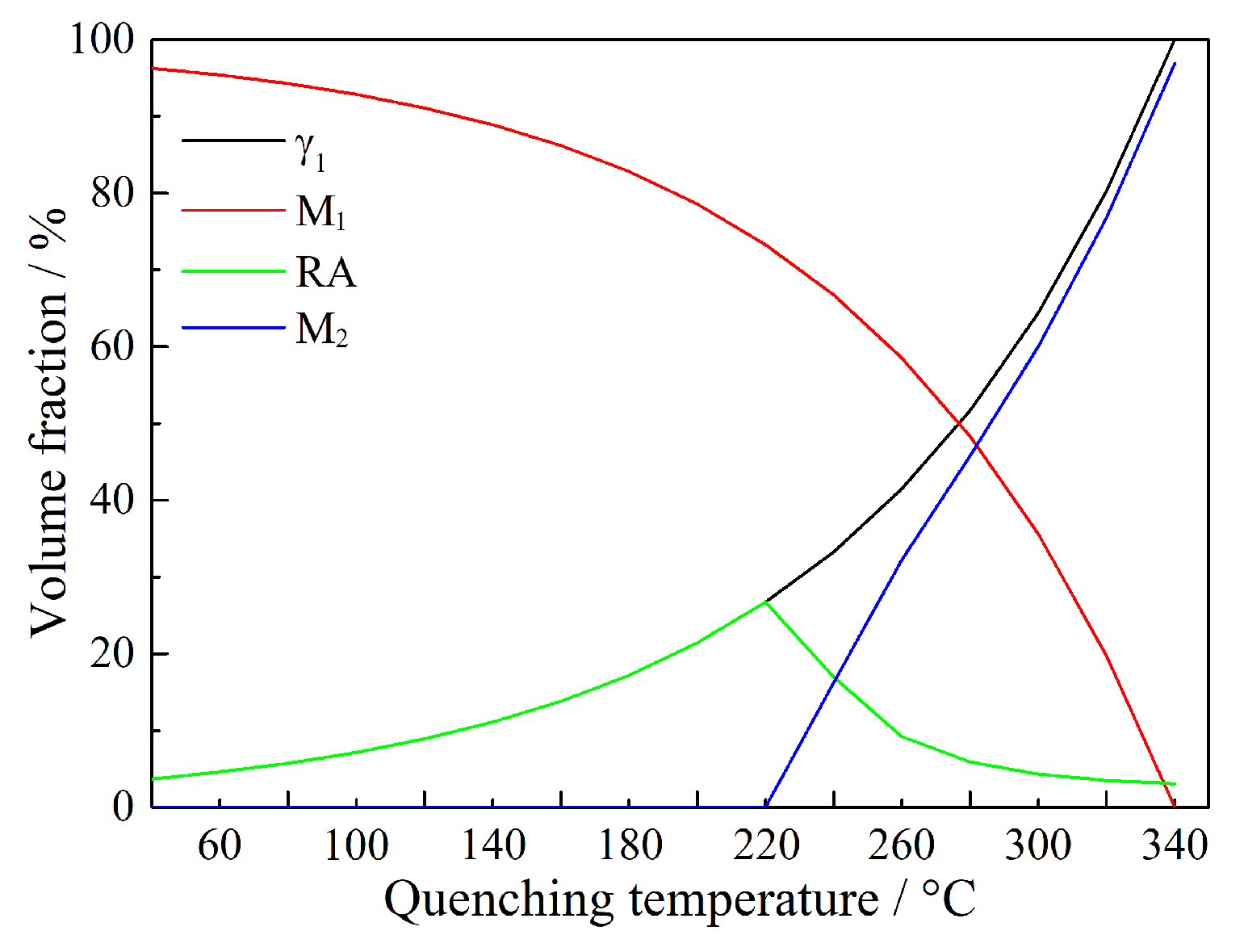
3.2. Predicted Phase Fraction Basing on CCE Model
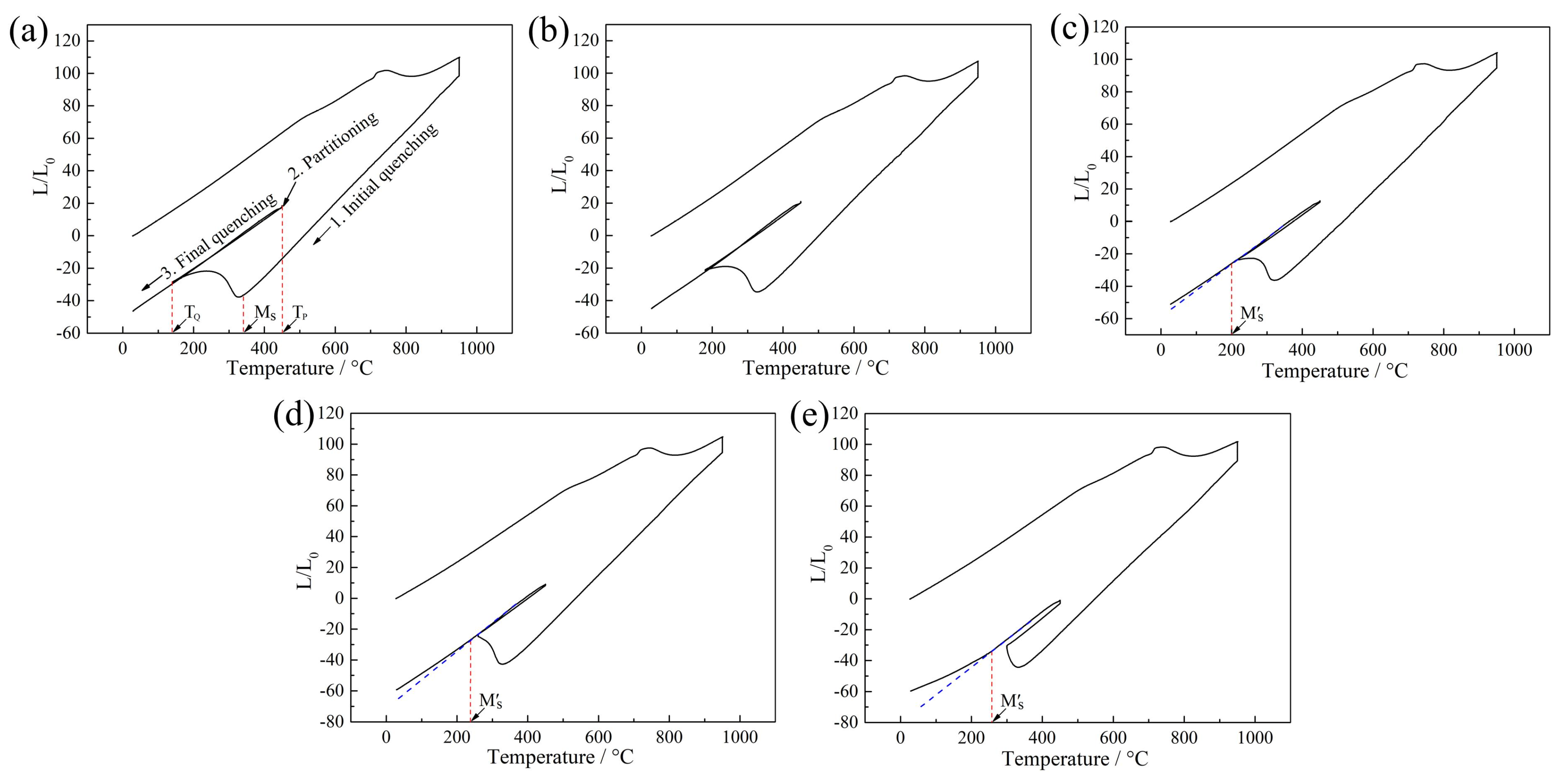
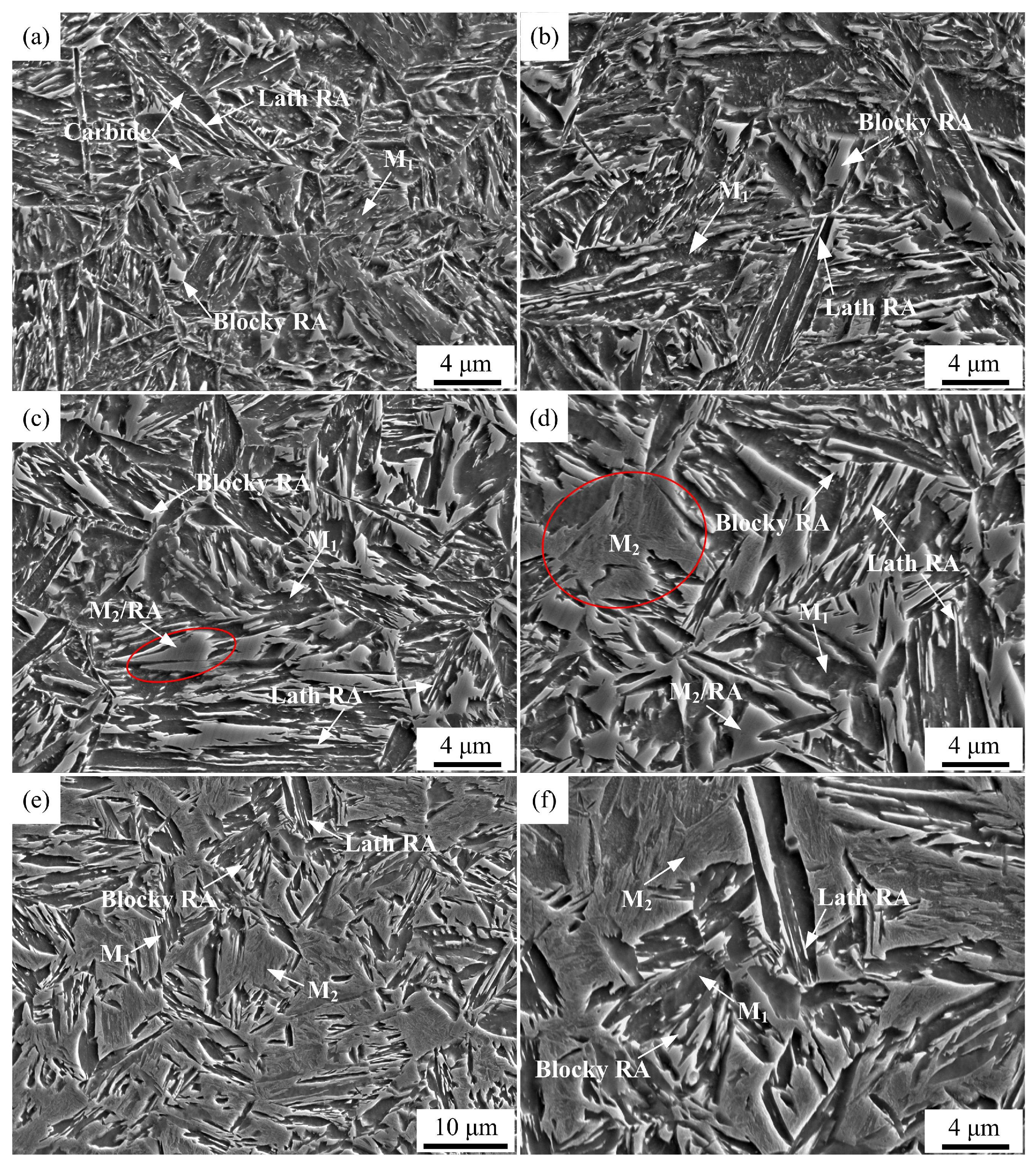
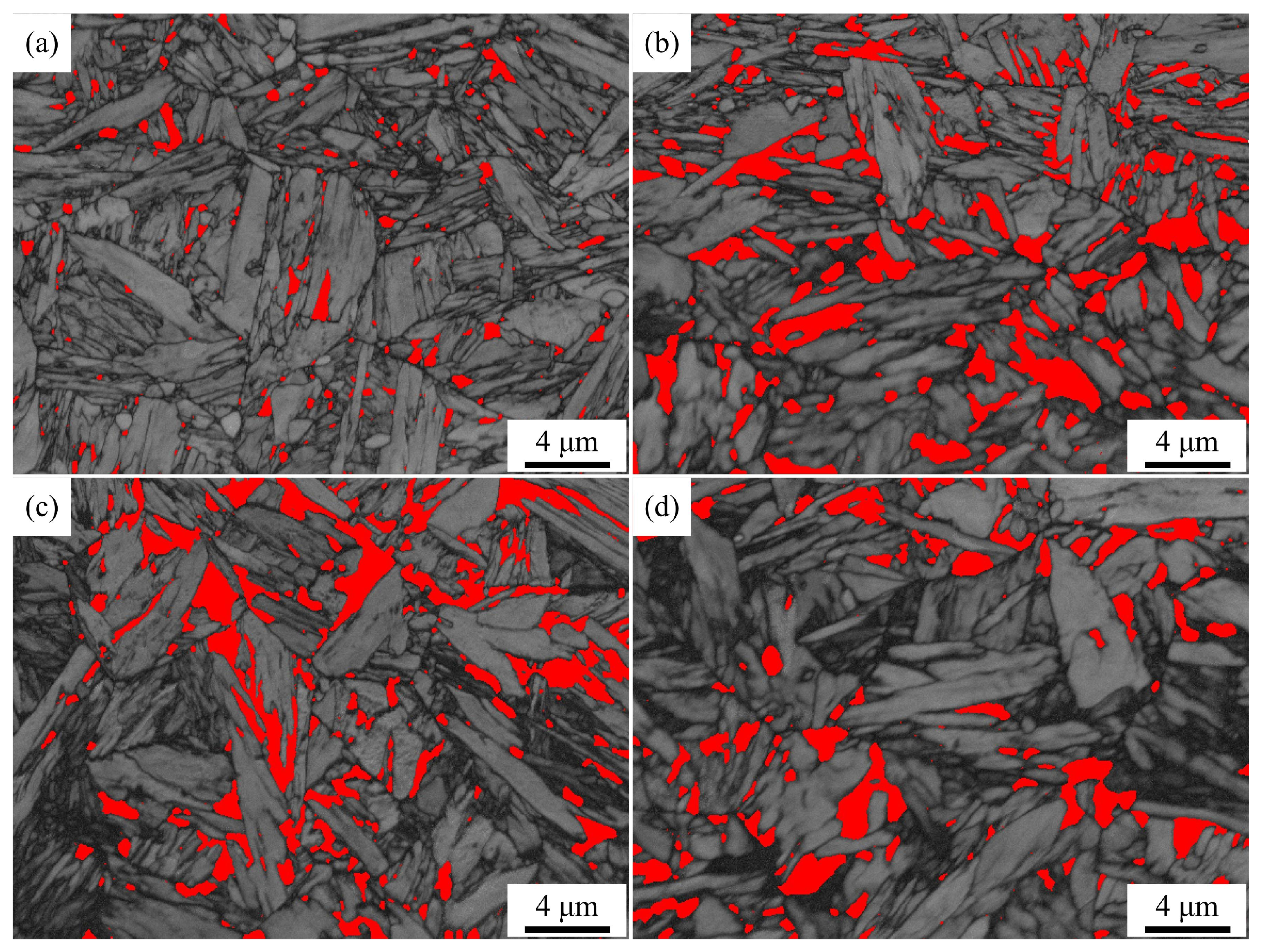
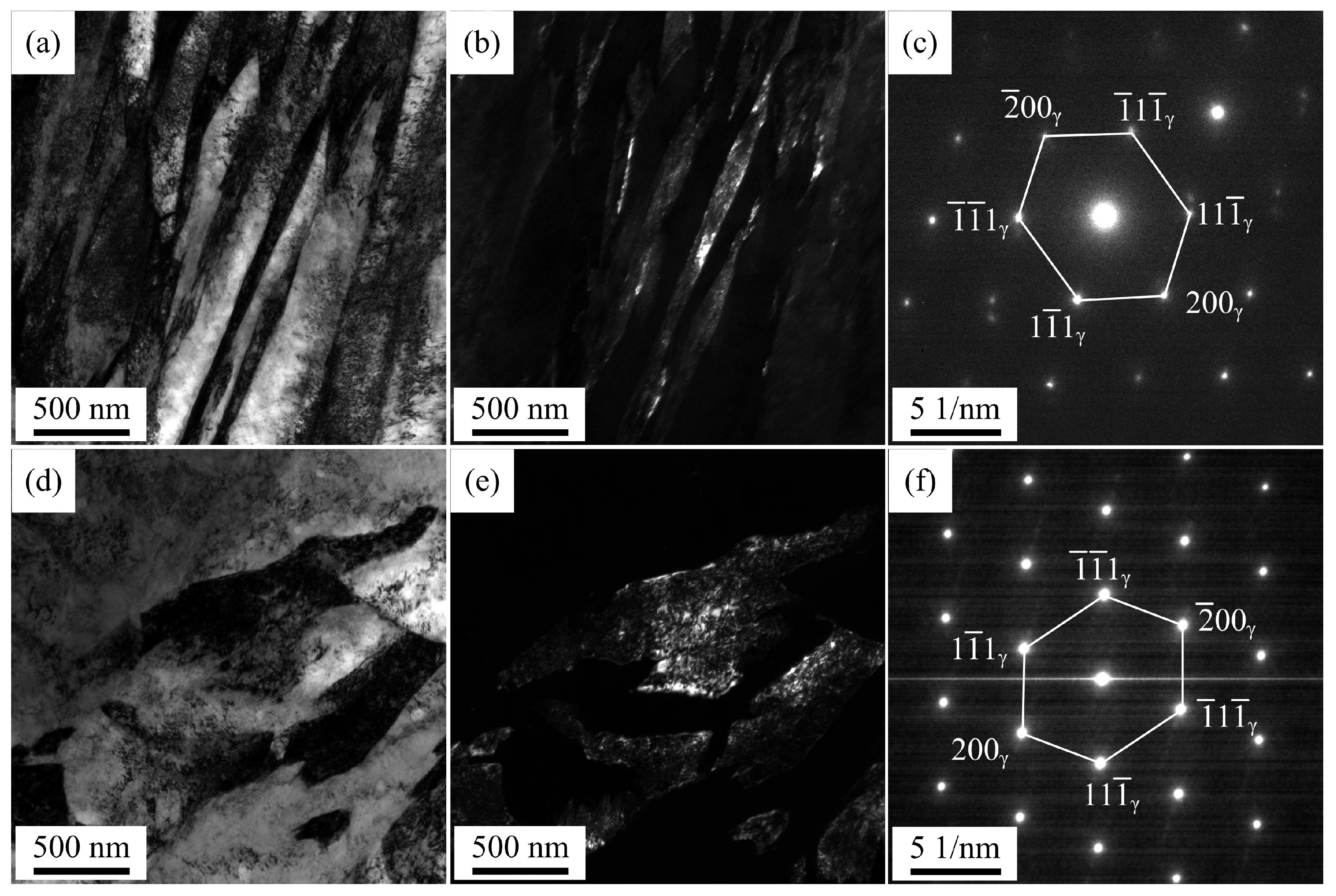
3.3. Dilatometric Curves and Microstructure of QP-Processed Samples
3.4. Mechanical Properties and Transformation of RA
3.5. Relationship between Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
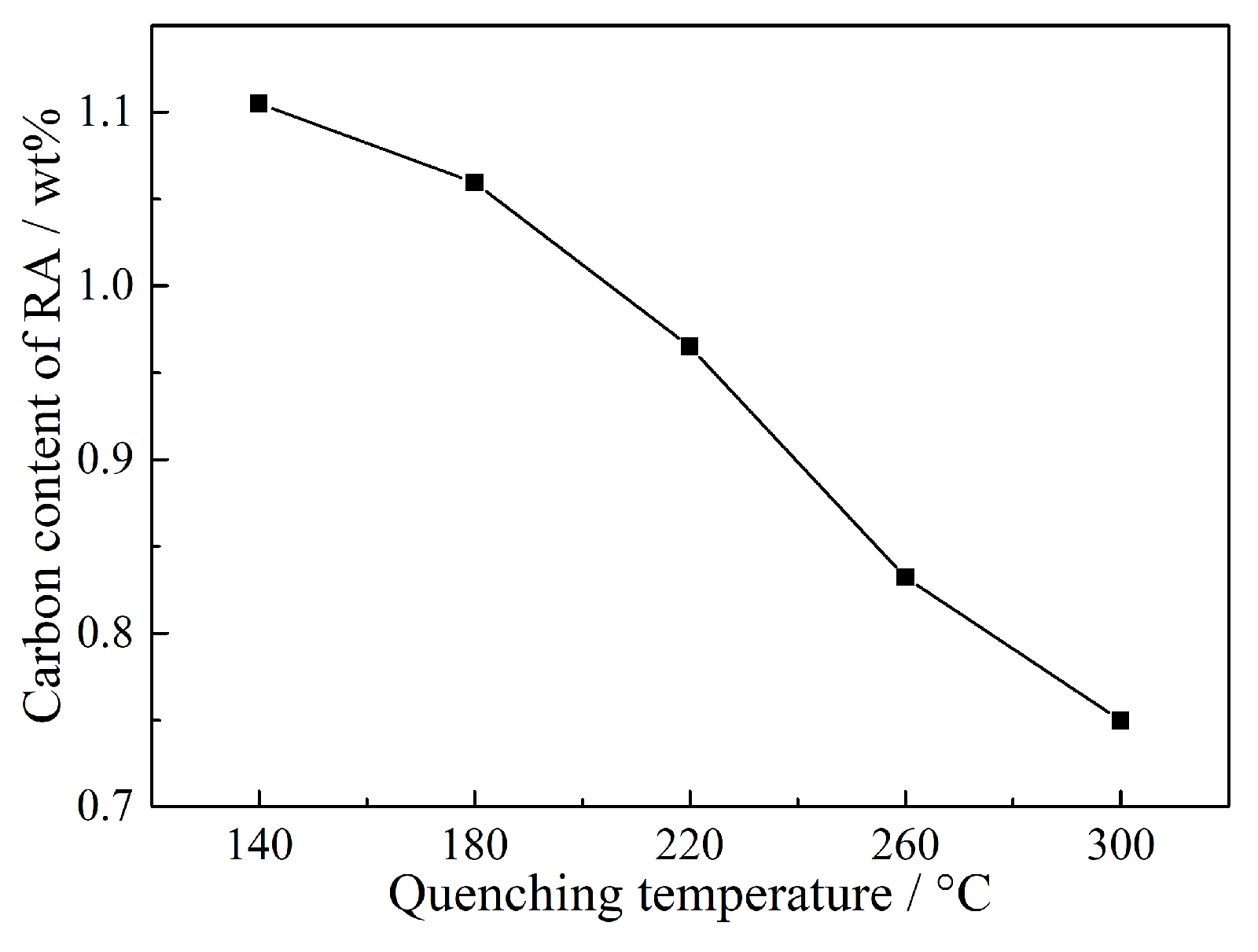
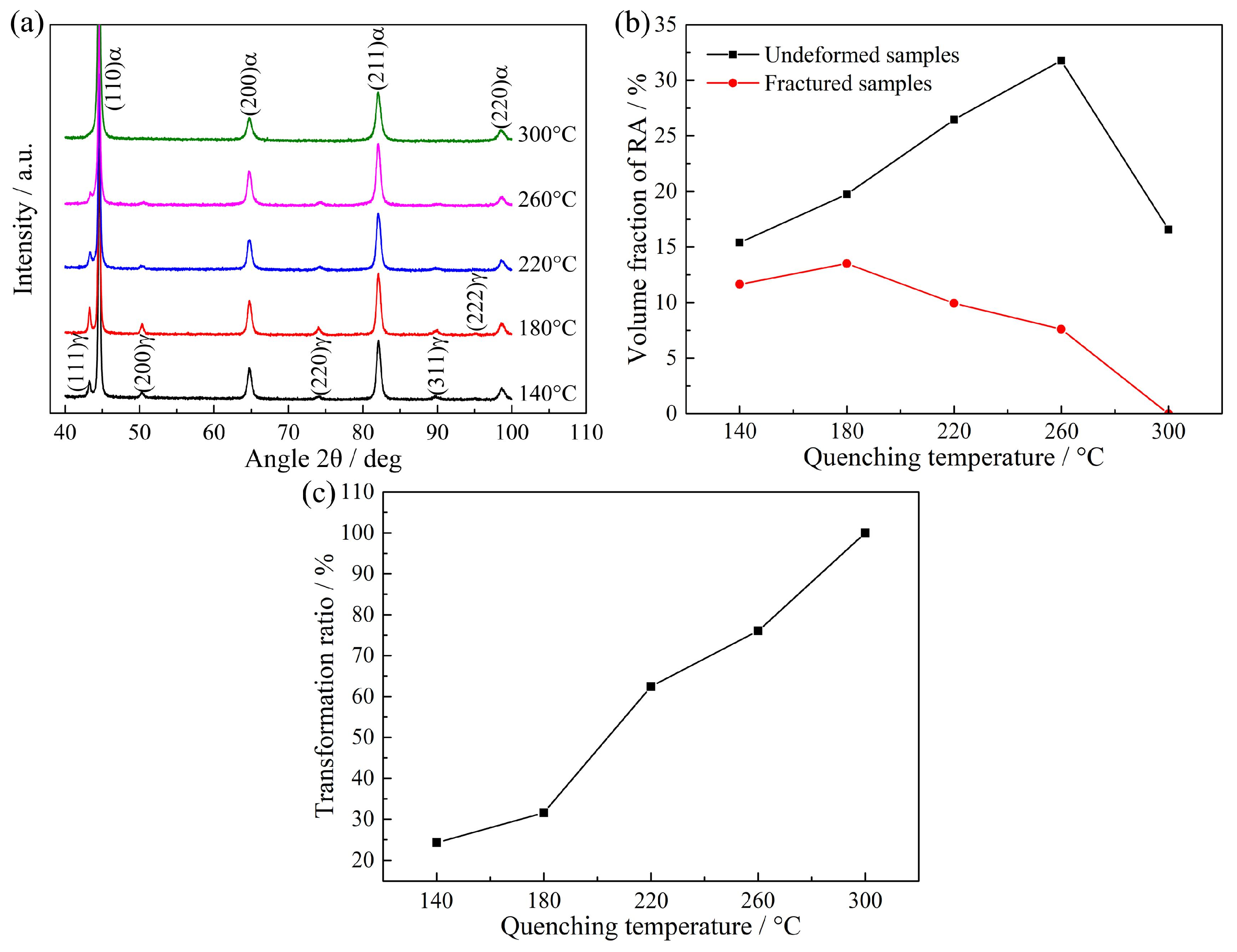
- When the quenching temperature was less than or equal to 180 °C, the microstructure of QP-processed samples consisted of primary martensite and RA. However, when the quenching temperature was in the range of 220 to 300 °C, secondary martensite was also obtained in the QP-processed samples besides primary martensite and RA. This is related to the lower carbon content of partitioned austenite at higher quenching temperatures, decreasing the thermal stability of partitioned austenite.
- (2)
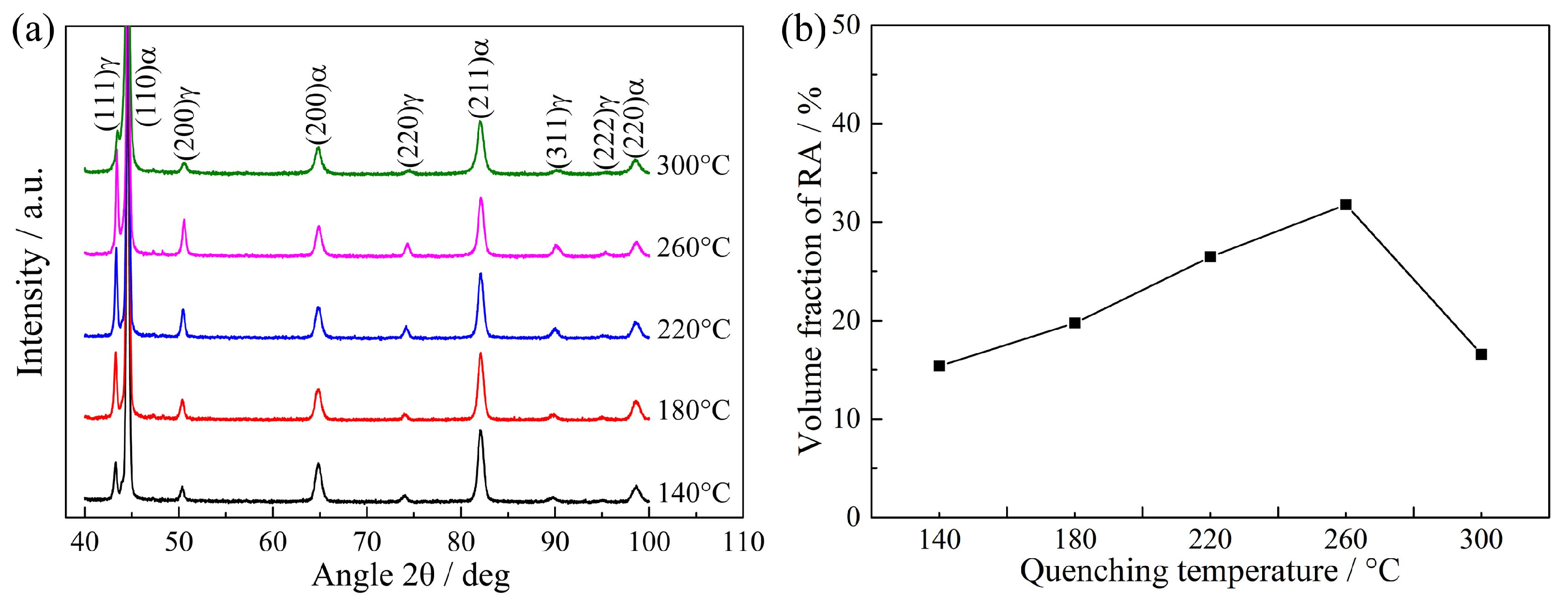
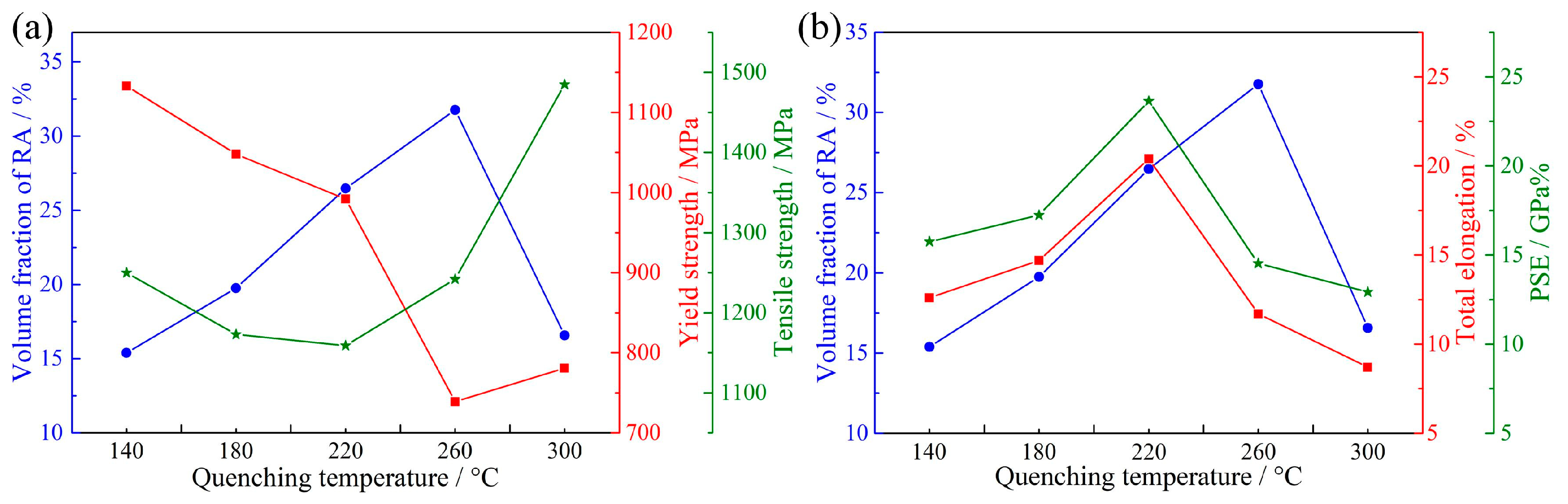
- Because of the carbon partitioning during the QP process, the RA with a volume fraction of ~ 15.4–31.8% was obtained in the QP-processed samples. The volume fraction of RA first increased from 15.4% to 31.8% when the quenching temperature increased from 140 to 260 °C, followed by a decrease to 16.6% on further increasing the quenching temperature to 300 °C.
- (3)
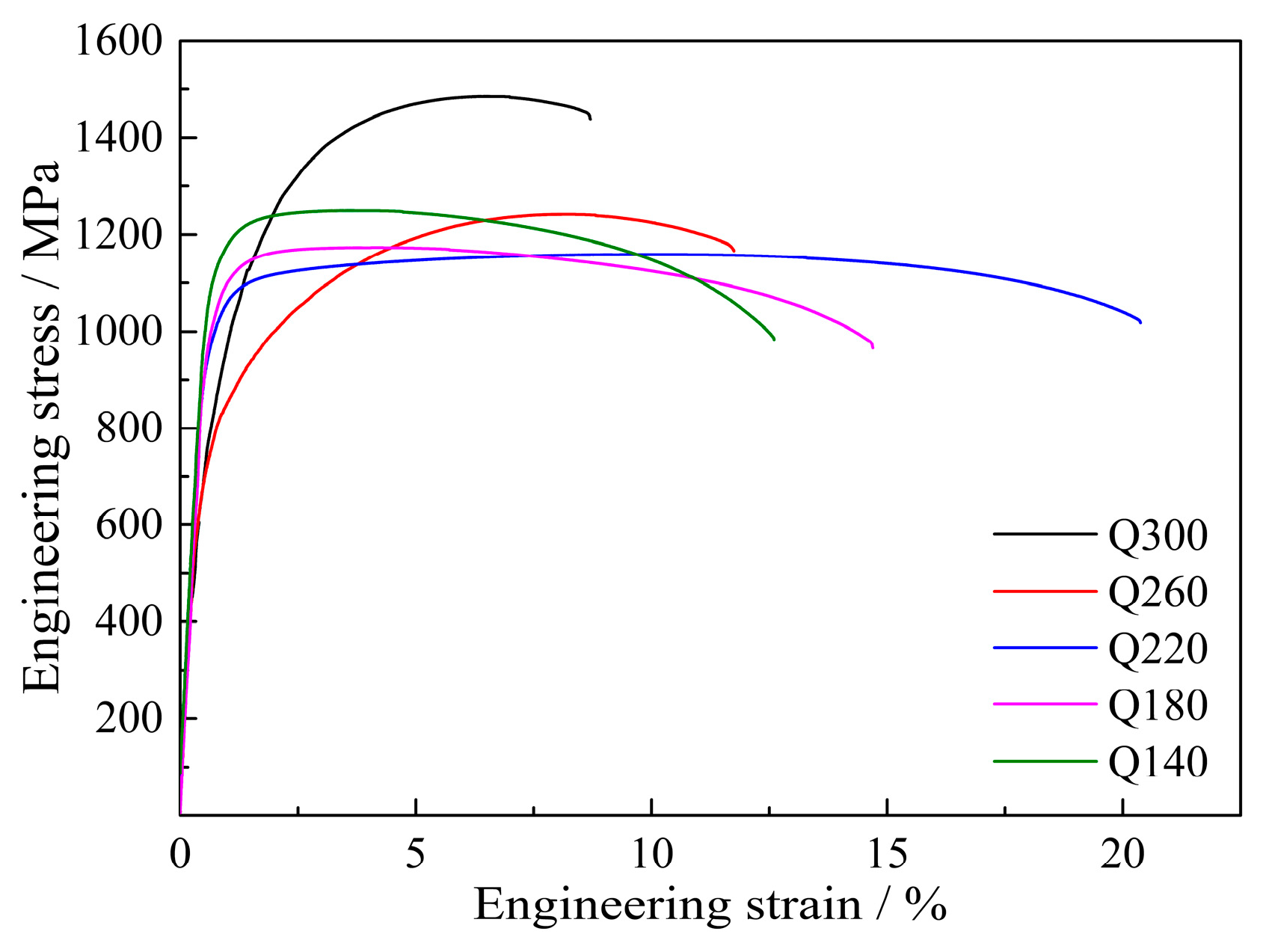
- The mechanical property with YS of 992 MPa, TS of 1159 MPa, TE of 20.4% and PSE of 23.64 GPa% was obtained in the QP-processed sample at a quenching temperature of 220 °C. Compared with the strip-cast medium-Mn steel processed by the IA process, the QP-processed sample had higher YS but lower TE than the IA-processed sample under the condition of similar TS.
- (4)
- The mechanical properties of QP-processed samples were related to the RA fraction, mechanical stability of RA and the presence of secondary martensite (or M2/RA island). The superior mechanical properties of Q220 steel were achieved by an optimum combination of high RA fraction (26.5 vol%), the appropriate mechanical stability of RA and a small number of M2/RA islands.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, Y.; Ding, H.; Tang, Z. Effect of carbon content on deformation behavior and partitioning of manganese in medium-Mn steels. Metals 2021, 11, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Tang, Z.; You, Z.; Guan, G.; Ding, H.; Misra, D. Microstructure, mechanical properties and deformation behavior of Fe-28.7Mn-10.2Al-1.06C high specific strength steel. Metals 2022, 12, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.L.; Sun, L.; Xiong, X.C. Challenges in the formability of the next generation of automotive steel sheets. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Shen, X.; Allam, T.; Richter, S.; Song, W.; Bleck, W. Tailoring the austenite fraction of a Cu and Ni containing medium-Mn steel via warm rolling. Metals 2021, 11, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, D.W.; Kim, S.J. Medium Mn transformation-induced plasticity steels: Recent progress and challenges. Scripta Mater. 2017, 126, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Han, J. Current opinion in medium manganese steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, R. Special issue on ‘Medium manganese steels’. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 2039–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Luo, H.; Yang, F.; Dong, H. Recent progress in medium-Mn steels made with new designing strategies, a review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.S.; Yuan, G.; Lan, M.F.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Cao, G.M.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, G.D. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a novel hot-rolled 4% Mn steel processed by intercritical annealing. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 12570–12582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, D.W.; Ryu, J.H.; Joo, M.S.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, K.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Medium-alloy manganese-rich transformation-induced plasticity steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.Q.; Wang, C.; Shi, J.; Wang, M.Q.; Hui, W.J.; Dong, H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe–0.2C–5Mn steel processed by ART-annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 6661–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlazarov, A.; Gouné, M.; Bouaziz, O.; Hazotte, A.; Petitgand, G.; Barges, P. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of medium Mn steels during double annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 542, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.P.; Xu, Y.B.; Tan, X.D.; Peng, F.; Gu, X.L.; Zou, Y.; Yu, S.C. Effect of rapid heating on a cold-rolled Mn–Al transformation-induced plasticity steel with coarse delta-ferrite. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2017, 9, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lee, Y.K. The effects of the heating rate on the reverse transformation mechanism and the phase stability of reverted austenite in medium Mn steels. Acta Mater. 2014, 67, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, T.; Huang, H.; Matsumura, O. Effects of carbon content on mechanical properties of 5%Mn steels exhibiting transformation induced plasticity. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1994, 10, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.J.; Cho, L.; De Cooman, B.C. Application of quenching and partitioning processing to medium Mn steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Z.; Liang, J.H.; Zhao, A.M.; Liang, J.T.; Tang, D.; Gao, Y.P. Effects of the austenitizing temperature on the mechanical properties of cold-rolled medium-Mn steel system. J. Alloy Compd. 2017, 691, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moor, E.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K.; Kwak, J.H.; Lee, S.B. Quenching and partitioning of CMnSi steels containing elevated manganese levels. Steel Res. Int. 2012, 83, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.H.; Huang, H.S.; Pan, H.J.; Sun, S.H.; Ding, H.; Hodgson, P. Microstructure and tensile properties of a Nb–Mo microalloyed 6.5Mn alloy processed by intercritical annealing and quenching and partitioning. Acta Metall. Sin. 2017, 30, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, R.; Wang, Y.; Kang, J.; Li, Y.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, G. A medium-Mn steel processed by novel twin-roll strip casting route. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.I.; Usui, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Hashimoto, S.I. Effects of volume fraction and stability of retained austenite on ductility of TRIP-aided dual-phase steels. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, N.H.; Butt, A.M.; Zhao, L.; Sietsma, J.; Offerman, S.E.; Wright, J.P.; van der Zwaag, S. Thermal stability of retained austenite in TRIP steels studied by synchrotron X-ray diffraction during cooling. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 5439–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, J.G.; Rizzo Assunção, F.C.; Matlock, D.K.; Edmonds, D.V. The “quenching and partitioning” process: Background and recent progress. Mater. Res. 2005, 8, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, D.V.; He, K.; Rizzo, F.C.; De Cooman, B.C.; Matlock, D.K.; Speer, J.G. Quenching and partitioning martensite—A novel steel heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438–440, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, J.; Matlock, D.K.; De Cooman, B.C.; Schroth, J.G. Carbon partitioning into austenite after martensite transformation. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koistinen, D.P.; Marburger, R.E. A general equation prescribing the extent of the austenite-martensite transformation in pure iron-carbon alloys and plain carbon steels. Acta Metall. 1959, 7, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.J.; Cho, L.; Estrin, Y.; De Cooman, B.C. Microstructure-mechanical properties relationships for quenching and partitioning (Q&P) processed steel. Acta Mater. 2016, 113, 124–139. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, S.S.; Lee, B.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, N.J.; Kwak, J.H. Effect of annealing temperature on microstructural modification and tensile properties in 0.35 C-3.5 Mn-5.8 Al lightweight steel. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 5050–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.S.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, Y.X.; Cao, G.M.; Li, C.G.; Kang, J.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, G.D. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of duplex TRIP steel produced by strip casting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 692, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Du, L.; Hu, J.; Misra, R.D.K. Effect of austenite stability on toughness, ductility, and work-hardening of medium-Mn steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 2134–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, R.; Zhou, N.; Li, J. An ultrahigh strength and enhanced ductility cold-rolled medium-Mn steel treated by intercritical annealing. Scripta Mater. 2018, 154, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.P.; Saleh, A.A.; Marceau, R.K.W.; Taylor, A.S.; Stanford, N.E.; Kostryzhev, A.G.; Pereloma, E.V. Site-specific atomic-scale characterisation of retained austenite in a strip cast TRIP steel. Acta Mater. 2017, 134, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.H.; Ding, H.; Misra, R.D.K.; Ying, Z.Y. Austenite stability and deformation behavior in a cold-rolled transformation-induced plasticity steel with medium manganese content. Acta Mater. 2015, 84, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, X.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, W. Tailoring retained austenite and mechanical property improvement in Al-Si-V containing medium Mn steel via direct intercritical rolling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 855, 143904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, H.S.; Yuan, G.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, G.D. Design of a low density Fe-Mn-Al-C steel with high strength-high ductility combination involving TRIP effect and dynamic carbon partitioning. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 742, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Du, L.X.; Dong, Y.; Meng, Q.W.; Misra, R.D.K. Effect of Ti variation on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of low carbon medium Mn heavy plate steel. Mater. Charact. 2019, 152, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Lu, B.; Yu, Y.; Jing, Y.; Sun, W. Improvement of strength-ductility combination in ultra-high-strength medium-Mn Q&P steel by tailoring the characteristics of martensite/retained austenite constituents. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 352–369. [Google Scholar]
- De Knijf, D.; Petrov, R.; Föjer, C.; Kestens, L.A.I. Effect of fresh martensite on the stability of retained austenite in quenching and partitioning steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 615, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Kang, J.; Chang, Z. Effects of Quenching Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Strip-Cast Medium-Mn Steel Processed by Quenching and Partitioning. Metals 2023, 13, 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13101772
Yu C, Wang H, Zhang Y, Li Y, Kang J, Chang Z. Effects of Quenching Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Strip-Cast Medium-Mn Steel Processed by Quenching and Partitioning. Metals. 2023; 13(10):1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13101772
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Cansheng, Hesong Wang, Yuanxiang Zhang, Yunjie Li, Jian Kang, and Zhiyuan Chang. 2023. "Effects of Quenching Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Strip-Cast Medium-Mn Steel Processed by Quenching and Partitioning" Metals 13, no. 10: 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13101772
APA StyleYu, C., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Kang, J., & Chang, Z. (2023). Effects of Quenching Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Strip-Cast Medium-Mn Steel Processed by Quenching and Partitioning. Metals, 13(10), 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13101772






