Abstract
Additive manufacturing (AM) technology using the direct energy deposition (DED) process and wires as feedstock material is commonly used to produce large components at an affordable cost. The wire laser AM (WLAM) process is one type of DED technology that uses welding wire as the raw material and a laser beam as the energy source. The goal of this study was to understand and evaluate the effect of microstructure modifications on the stress corrosion endurance of 15-5 PH stainless steels produced through WLAM, compared to their counterpart wrought alloy AISI 15-5 PH. All the tested alloys were heat treated using a standard age hardening treatment (H-1150M) prior to their examination. The microstructure analysis was performed using optical and electron microscopy (SEM and TEM) and X-ray diffraction analysis. The environmental behavior was characterized through electrochemical examination using potentiodynamic polarization and impedance spectroscopy analysis, while stress corrosion behavior was evaluated by means of slow strain rate testing (SSRT). The corrosion experiments were conducted in a simulated corrosive environment in the form of a 3.5% NaCl solution. The results showed that the microstructure modifications in the WLAM alloy (mainly in terms of austenite content, passivation capability and inherent printing defects) have a significant detrimental effect on stress corrosion resistance.
1. Introduction
Additive manufacturing (AM) is considered a state-of-the-art technology that may substitute traditional techniques to produce both common and unique components [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. AM technology can make a variety of parts with complex structures and near-net-shape dimensions that require minimal post-processing and machining operations [9,10,11,12,13]. Various AM technologies have been developed in the last two decades; the most widespread process is powder bed fusion (PBF), such as selective laser melting (SLM) and electron beam melting (EBM). These methods use powders as their feedstock material, which are selectively melted to enable the production of 3D components layer-by-layer [14,15,16,17]. However, the inherent disadvantages of PBF processes, such as low production rate and part size constraints due to the limited space of the printing chamber, have highlighted the necessity to develop more affordable AM technologies. Hence, innovative AM methods based on the direct energy deposition (DED) process that uses wires as feedstock materials have been developed. The common energy sources used by those processes are mainly the electrical arc (wire arc additive manufacturing—WAAM) and the laser beam (wire laser additive manufacturing—WLAM). Both WAAM and WLAM enable a deposition rate of up to 3 kg/h, compared to 0.1 kg/h for PBF, as well as the production of large components with near-net-shape structures. In addition, it should be pointed out that WAAM and WLAM technologies allow the use of a wide range of metals and alloys to produce a variety of components for different industries [18,19,20]. The main disadvantage of those technologies compared to PBF is the relatively rough resultant surface that usually requires additional machining processes [21,22].
The primary challenge facing proper selection of the printing parameters for the WLAM process relates to the complex laser–wire interaction in terms of heat transfer. Heralic [23] has indicated that when the feedstock wire is being fed into the laser beam, it can create a shadow that obscures the laser beam, which can subsequently affect the process stability. The heat transfer should also consider energy dissipation to the surrounding atmosphere by radiation and evaporation. For example, this was addressed by Abadi et al. [24] in relation to the absorbed laser power, qlaser, by the solid substance as indicated by Equation (1):
where Plaser is the laser power, Ulaser is the travel speed of the laser beam, t is time, and rx and ry are the radius of the beam spot along the X and Y directions, respectively. Their simulations show that those process parameters can significantly affect the process physics, and subsequently, the microstructure of the solidified substance. Another interesting simulation that relates to the interaction between a laser beam and solid substance was presented by Chen et al. [25]. According to this simulation, the increased temperature of the solid substance is governed by the heat balance shown in Equation (2). This increased temperature can stimulate a phase transition of the solid prior to melting. The right-hand side of the equation incudes four terms: (i) absorbed energy by the solid substance; (ii) and (iii) convection and radiation segments with the environment, respectively; and (iv) possible phase transformation of the solid substance.
where mp is the mass of the solid substance, Cp is the specific heat, ηp is the laser absorptivity, hp is the coefficient of convective heat transfer, Ap is the surface area of the solid, ɛ is the equivalent emissivity, σ is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant, T∞ is the surrounding gas temperature and Lm is the latent heat of the solid.
So far, most of the research efforts using the WLAM process have been dedicated to particular alloys, including Ti-based alloys, Ni-based superalloys and carbon steels. There are also a few research studies that related to 17-4 PH stainless steel [26,27,28,29,30], but there is very limited research regarding 15-5 PH stainless steel. Guo et al. [31] investigated the microstructure and mechanical properties of AM 15-5 PH steel produced through WAAM. The quality for their printed alloy was adequate and the microstructure was mostly composed of a martensitic matrix with small amounts of retained austenite. In addition, no retained austenite was detected post-heat treatment. Nong et al. [32] also investigated AM 15-5 steel using DED technology, but in their case, the feedstock material was powder. Similar to the results of Guo et al. [31], they have also reported on the presence of retained austenite in the as-printed conditions mainly due to the use of N2 as a protective gas atmosphere. In general, 15-5 PH alloy is a ferrite-free martensitic stainless steel that can be modified in terms of its mechanical properties through heat treatment. The thermal hardening mechanism of this alloy is governed by Cu-based precipitates that are formed during the ageing heat treatment. The size and coherence of those precipitates dictate the final mechanical properties of the alloy, which mainly relate to the interaction between these precipitates and moving dislocations [33,34].
The main interest in 15-5 PH stainless steels derives from its outstanding combination of high strength, adequate corrosion resistance and superior transverse mechanical properties. Accordingly, this alloy is used in a variety of industries, including aerospace, chemical, food processing and other metalworking industries. Naturally, AM technologies, and the WLAM process in particular, are attractive options for producing components in these industries. However, one of the main challenges facing these components is to maintain their performance under the combined effect of mechanical loading and a corrosive environment. Hence, the present study aims to investigate and better understand the effect of microstructure modifications on the stress corrosion resistance of 15-5 PH stainless steels produced through WLAM, compared to its counterpart AISI wrought alloy. Both alloys are tested post-H-1150M heat treatment, which is considered to be a standard precipitation hardening practice.
2. Experimental Procedure
The general plan of the experimental work aims to understand the effect of microstructural modification on the mechanical and corrosion properties of the printed alloy. This was carried out by examining the inherent properties through tensile tests and the corrosion resistance through potentiodynamic polarization and impedance analysis. Further tests relating to the combined effect of corrosive environment and mechanical loading were evaluated through slow strain rate testing (SSRT) in comparison with a counterpart AISI alloy.
2.1. Preparation of Tested Samples
Test samples made of 15-5 PH stainless steel were produced through the WLAM process using a conventional wire of this alloy with a diameter of 1.2 mm under pure nitrogen gas (99%) as a protective atmosphere [35]. The printed samples of a rectangular shape were produced with the following dimensions, 70 mm length, 15 mm width and 2.5 mm thickness, using a CAD model to program the printing process. The optimal printing parameters were selected through a number of AM trials until adequate physical properties were obtained. This revealed that the optimal parameters were laser beam power of 1.5 kW, feeding speed of wire of 12 mm/s, traveling speed of the welding head of 7 mm/s, and the use of distilled water for continuous cooling of the printing tray. Altogether, these printing parameters created a deposition rate of about 200 gr/h and a sequence layer thickness of 0.7 mm. In parallel, a wrought alloy in the form of standard AISI 15-5 PH stainless steel was used for comparative examinations.
2.2. Age Hardening Heat Treatment
Age hardening treatment is a common practice applied to PH stainless steels to improve their mechanical properties and to obtain desirable strength and ductility values. This heat treatment is usually composed of two main stages: solution treatment of the principal alloying elements, such as copper, molybdenum and titanium, and precipitation hardening treatment at an intermediate temperature. The selected age hardening treatment for this study was H-1150M, which aims to decrease the inherent brittleness and susceptibility to stress corrosion cracking [36]. This heat treatment included 3 main stages: (i) primary solution treatment at 1038 °C for 0.5 h; (ii) secondary solution treatment at 760 °C for 2 h; and (iii) precipitation hardening treatment at 621 °C for 4 h. All the heat treatment stages were followed by air cooling. The H-1150M heat treatment was applied to all the tested alloys.
2.3. Microstructure Assessment
The general microstructure examination of the tested alloys was carried out using optical and scanning electron microscopy (SEM-JEOL 5600, Tokyo, Japan) [37]. For metallographic analysis, the tested samples were polished with a colloidal silica suspension to obtain a roughness level of 0.25 µm. Kaling’s No. 1 reagent (1.5 gr CuCl2, 33 mL HCl, 33 mL ethanol and 33 mL H2O) was then used for etching to reveal the martensitic structure of the tested alloys. X-ray diffraction analysis was utilized to identify phases, using a RIGAKU-2100H X-ray diffractometer (Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a CuKα radiation source. The diffraction analysis parameters were 40 kV/30 mA and the scanning rate was 2°/min. Phase quantities were revealed by calculating the integrated intensities of the peaks according to the ASTM E975-13 standard [38,39]. High-resolution analysis was carried out using transmission electron microscopy (JEOL JEM-2100F, Tokyo, Japan) operating at 200 kV. This analysis included bright-field imaging, selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) and EDS. The samples for TEM analysis were prepared using a focused ion-beam microscope (FEI, Thermo Fisher Verios-460 L, Hillsboro, OR, USA).
2.4. Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties were evaluated in terms of tensile strength using a Cormet C-76 set-up (Cormet Testing Systems, Vantaa, Finland). The tested samples had a gauge length of 25.4 mm and a rectangular cross-section of 7 mm2. The tensile specimens made of WLAM 15-5 PH alloy were cut off from the building orientation side (XZ plane), which represents the section with relatively inferior properties [3]. Hardness was measured using Wilson Rockwell hardness tester (Wilson Instrument, Bridgeport, CT, USA).
2.5. Electrochemical Analysis
Electrochemical examination of the tested alloys was carried out through potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis. The polarization tests were conducted using a standard three-electrode cell and a Bio-Logic SP-200 potentiostat (Bio-Logic Science Instruments, Seyssinet-Pariset, France) along with EC-Lab software v10.18. The scanning rate of the polarization analysis was 0.5 mV/s and a saturated calomel electrode was used as a reference electrode. Impedance spectroscopy evaluation was conducted between 10 kHz and 0.015 Hz, with a 10 mV amplitude signal. The simulated corrosive environment for the polarization and impedance spectroscopy analyses was 3.5% NaCl solution. Prior to the electrochemical tests, all the samples were polished with 1200-grit paper to ensure adequate and equal roughness.
2.6. Stress Corrosion Examination
The stress corrosion endurance of the tested alloys was evaluated by means of slow strain rate testing (SSRT) using a Cormet C-76 set-up (Cormet Testing Systems, Vantaa, Finland) in accordance with the ASTM G129-00 standard [40]. The test samples had a gauge length of 25.4 mm and a rectangular cross-section of 7 mm2. The SSRT tests were conducted using three different strain rates: (i) 2.5 × 10−7, (ii) 2.5 × 10−6 and (iii) 2.5 × 10−5 s−1. All the SSRT tests were carried out within a designated corrosive chamber and with a 3.5% NaCl solution at room temperature (25 °C).
3. Results
The chemical compositions of WLAM 15-5 PH stainless-steel alloy and its counterpart AISI 15-5 PH wrought alloy are shown in Table 1. It is revealed that both alloys had a very similar chemical composition with a negligible reduction in the content of the main alloying elements in the case of the WLAM alloy.

Table 1.
Chemical compositions of the tested alloys (in wt%).
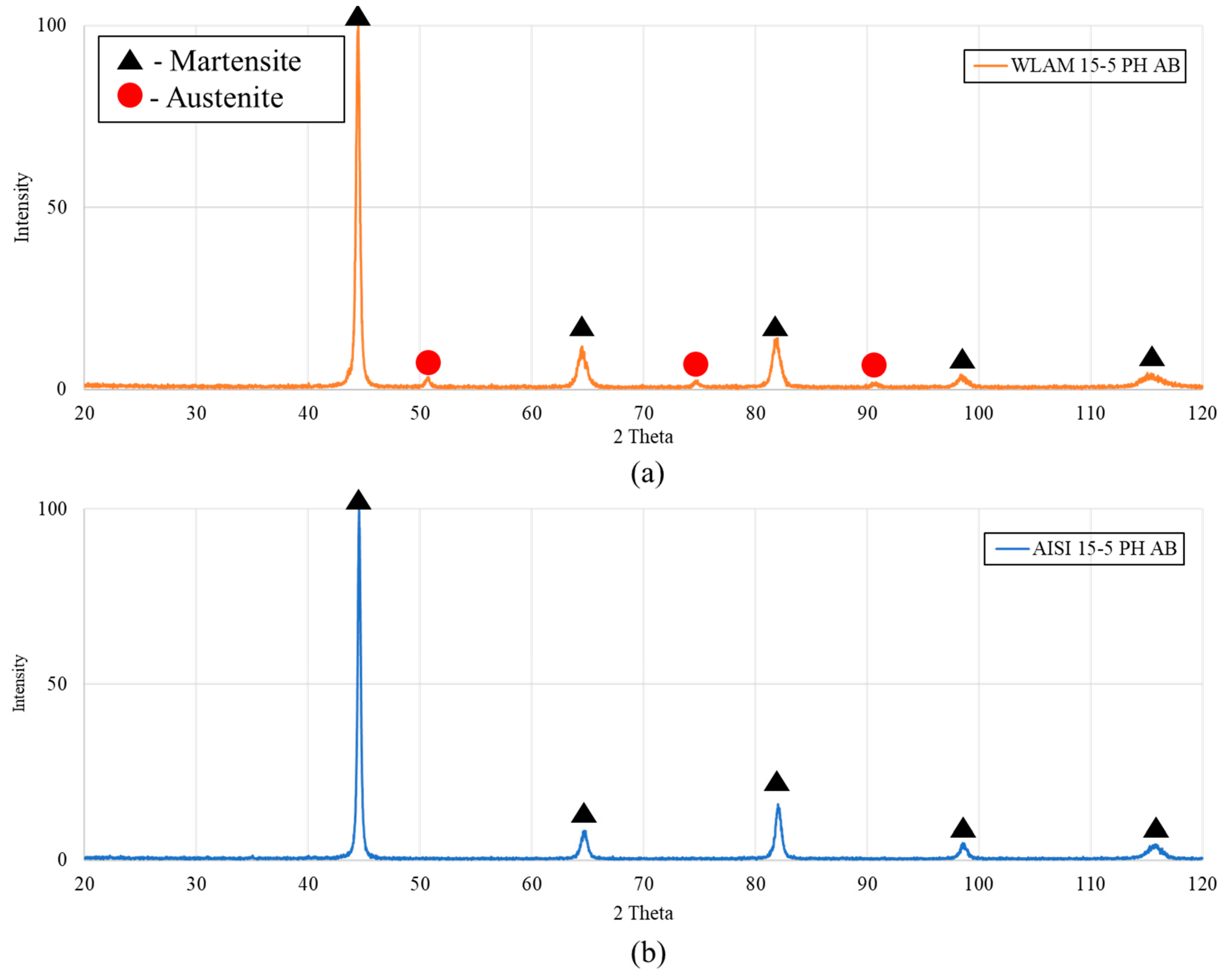
X-ray diffraction analysis prior to precipitation hardening heat treatment of the WLAM 15-5 PH alloy in as-built (AB) conditions and its counterpart AISI alloy is shown in Figure 1. It is revealed that the WLAM alloy (AB) contains a small amount of austenitic phase within a martensitic matrix, while its counterpart AISI alloy was solely composed of the martensitic phase, as anticipated. The presence of the austenitic phase in the WLAM alloy can be, in part, related to the effect of nitrogen as a protective gas atmosphere, which, according to Zai et al. [41], induces the formation of this phase during printing. The martensitic phase in both alloys was classified by ferritic phase peaks, due to their low carbon content that decreases the c/a parameters of the BCT structure to form a BCC-martensite [42].
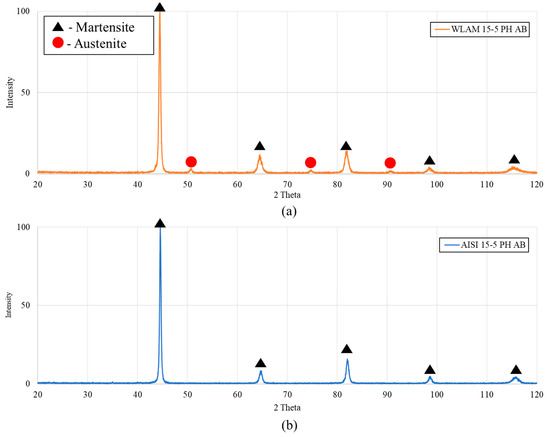
Figure 1.
XRD analysis prior to heat treatment: (a) WLAM 15-5 PH alloy in as-built (AB) conditions and (b) AISI 15-5 PH alloy as-received.
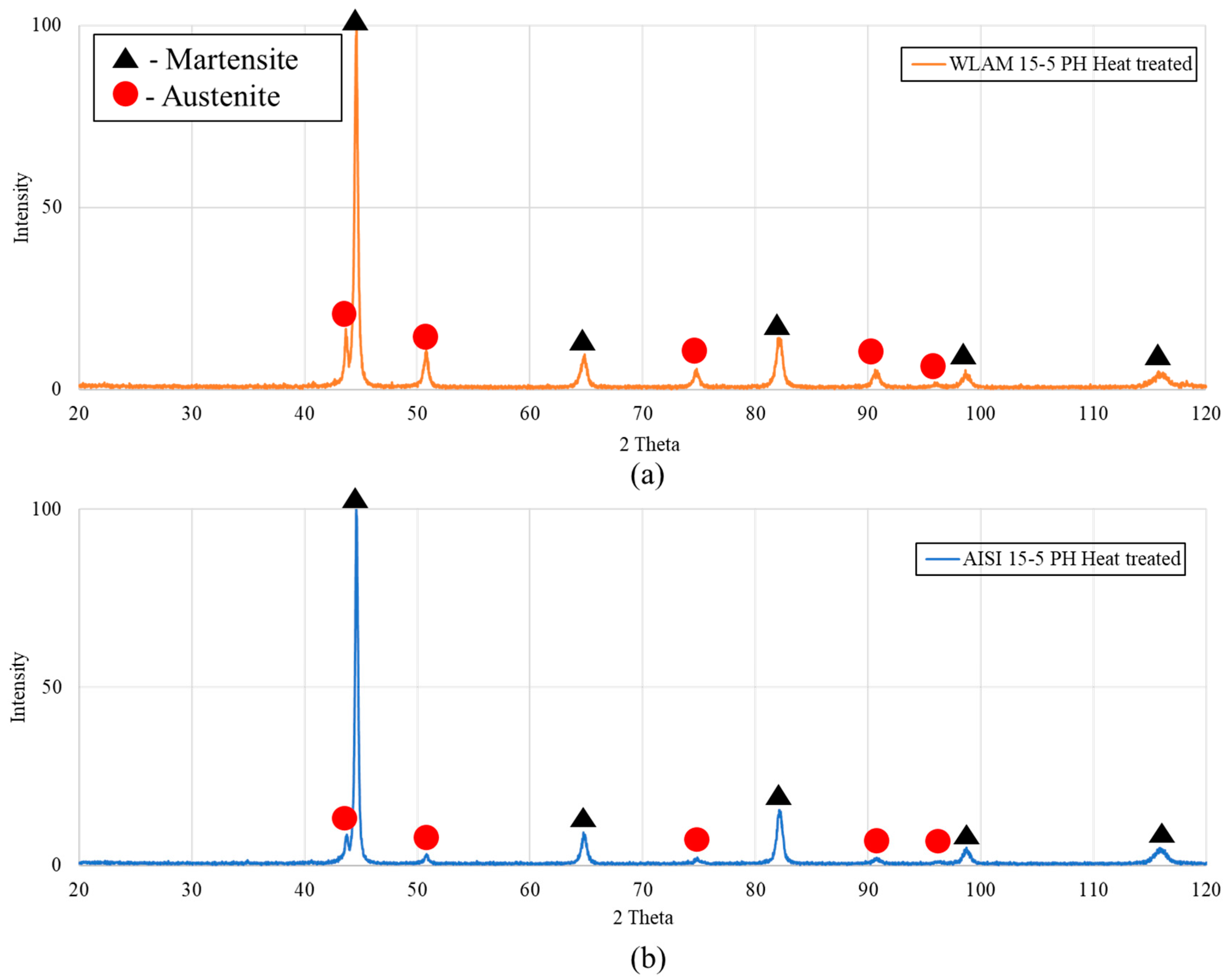
X-ray analysis of the tested alloys post-precipitation hardening heat treatment (H-1150M) is shown in Figure 2. It is revealed that both the WLAM and the AISI post-heat-treatment alloys contain retained austenite. Phase quantification derived from the XRD analysis, as shown in Table 2, clearly indicates that the amount of retained austenite in the WLAM post-heat-treatment alloy was 54%, compared to only 11% in the AISI alloy. It is claimed that the significant increase in retained austenite in the WLAM alloy is attributed to the use of nitrogen gas during the printing process. This assumption is supported by Wang et al. [43], who claims that the penetration of N2 gas during the printing process decreases the Ms temperature, and subsequently reduces the stability of martensite formation [43]. Comparing the XRD results shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, a slight shift in the peak mainly just above 80 degrees was evident in the WLAM alloy in as-printed conditions. In terms of calculating the lattice parameter using the Rietveld-like method assuming a constant zero shift, the following results were obtained: (i) WLAM alloy in as-printed conditions, a = 2.879 Å; (ii) WLAM alloy post-heat treatment, a = 2.873 Å; (iii) AISI alloy in as-received conditions, a = 2.875Å; and (iv) AISI alloy post-heat treatment, a = 2.872 Å. The increased lattice parameter of the WLAM alloy in as-printed conditions can be related to the presence of macro-strain generated due to the high cooling rate of the WLAM process.
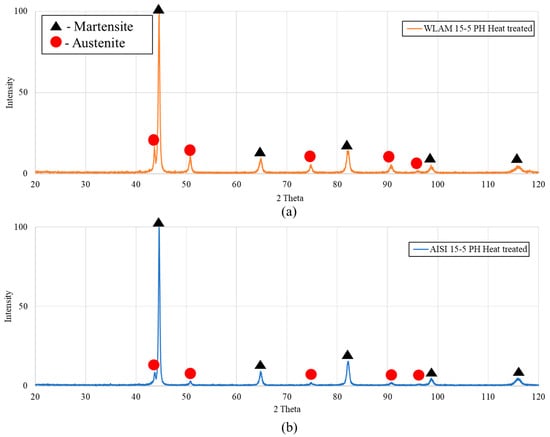
Figure 2.
XRD analysis post-heat treatment: (a) WLAM 15-5 PH alloy and (b) counterpart AISI alloy.

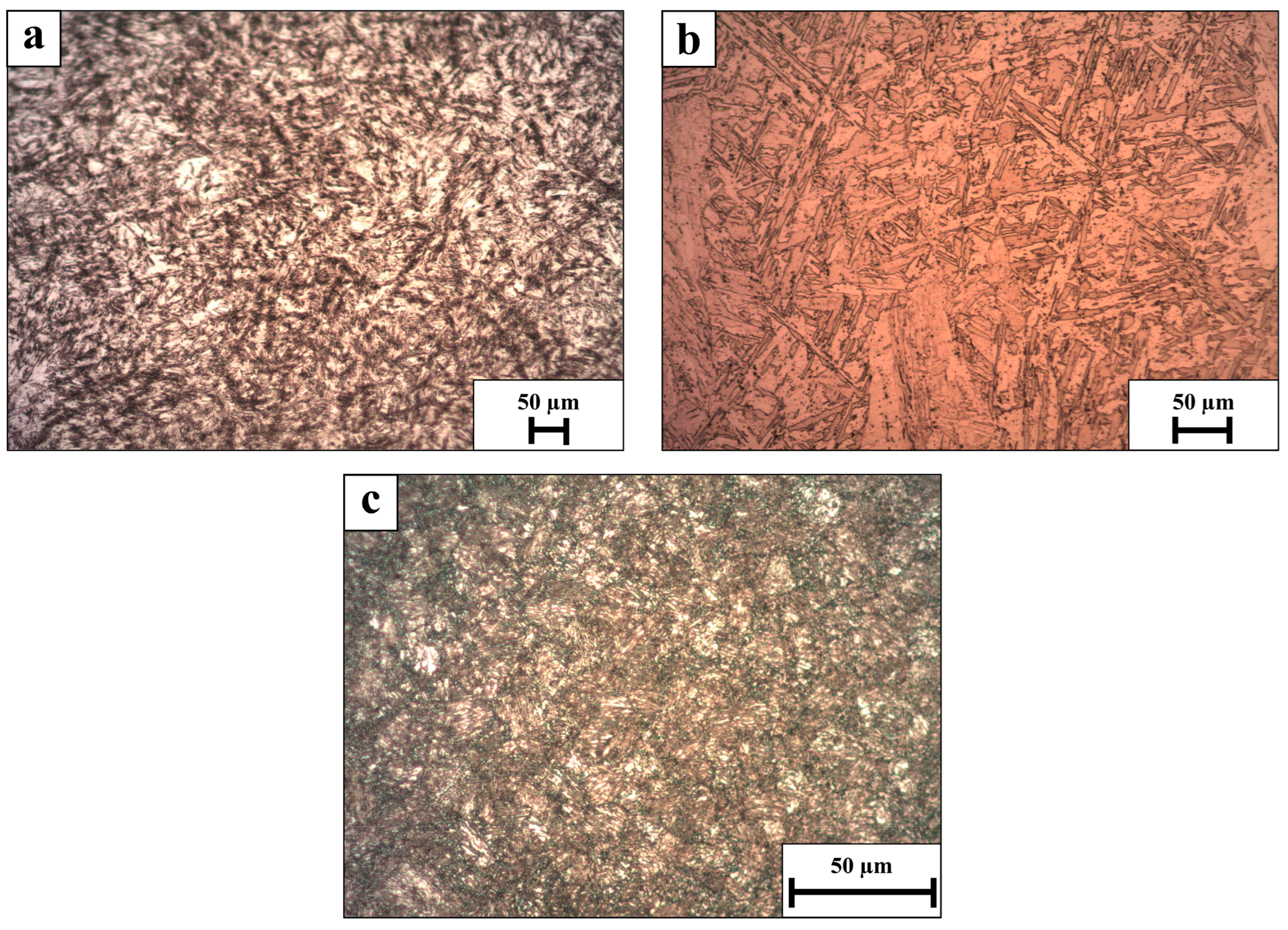
Optical microscopy analysis of WLAM 15-5 alloy and its counterpart AISI alloy, post-heat treatment, is shown in Figure 3. The microstructure of both alloys contains a martensitic matrix along with a secondary austenitic phase. However, the amount of austenitic phase in the WLAM alloy is significantly higher compared to its counterpart AISI alloy, as indicated by the XRD analysis. In addition, clear evidence of increased grain coarsening is seen in the WLAM alloy.
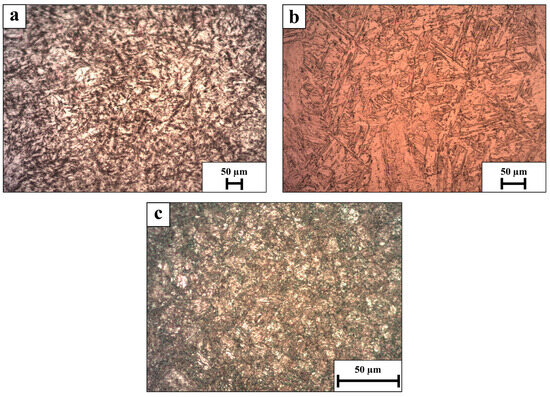
Figure 3.
Optical microscopy analysis (a) WLAM PH 15-5 XY plane, (b) WLAM PH 15-5 XZ plane, (c) AISI PH 15-5.
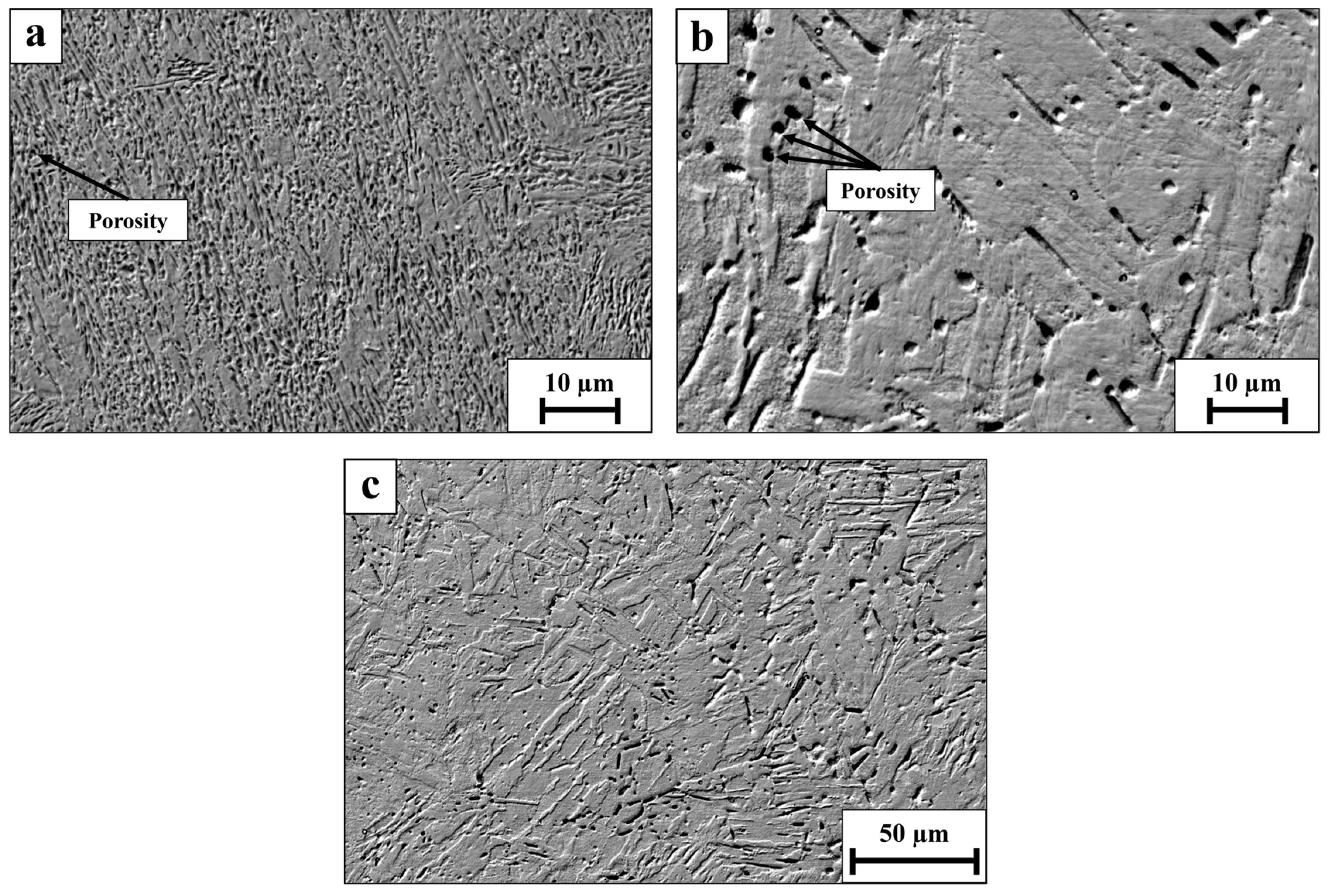
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the post-heat treatment WLAM 15-5 PH alloy and its counterpart AISI alloy are shown in Figure 4. The images reveal that while the counterpart AISI alloy was nearly free of porosity, the WLAM alloy contains cavities—known as “keyhole porosity” defects [44]. These defects are usually attributed to entrapment of the protective gas atmosphere during the printing and solidifying process. It should be noted that keyhole porosity is a major factor in the premature failure of AM components that are exposed to tensile or cyclic loading. In addition, the size of the porosity along the building orientation (XZ plane) was significantly higher compared to along the XY plane: 2–3 µm versus less than 1 µm, respectively. In quantitative measurements, the density of pores in the XY plane was around 0.002 pores/µm2 compared to 0.01 pores/µm in the XZ plane. The porosity size and density across the samples in the XY and XZ planes, respectively, were basically in accordance with the above measurements. Those differences can mainly be related to the higher cooling rate of the alloy in the building direction (XZ plane), which subsequently creates a relatively non-uniform microstructure that enhances the formation of keyhole porosity.
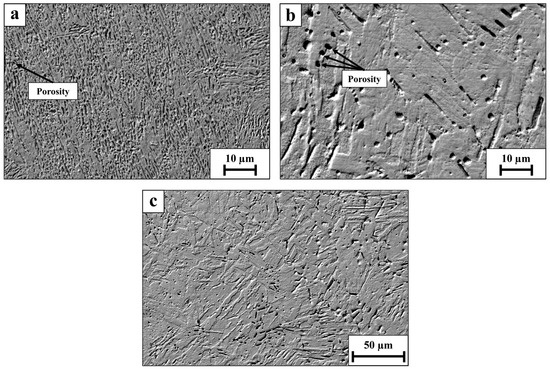
Figure 4.
Scanning electron microscopy images (a) WLAM 15-5 PH XY plane, (b) WLAM 15-5 PH XZ plane, (c) AISI 15-5 PH.
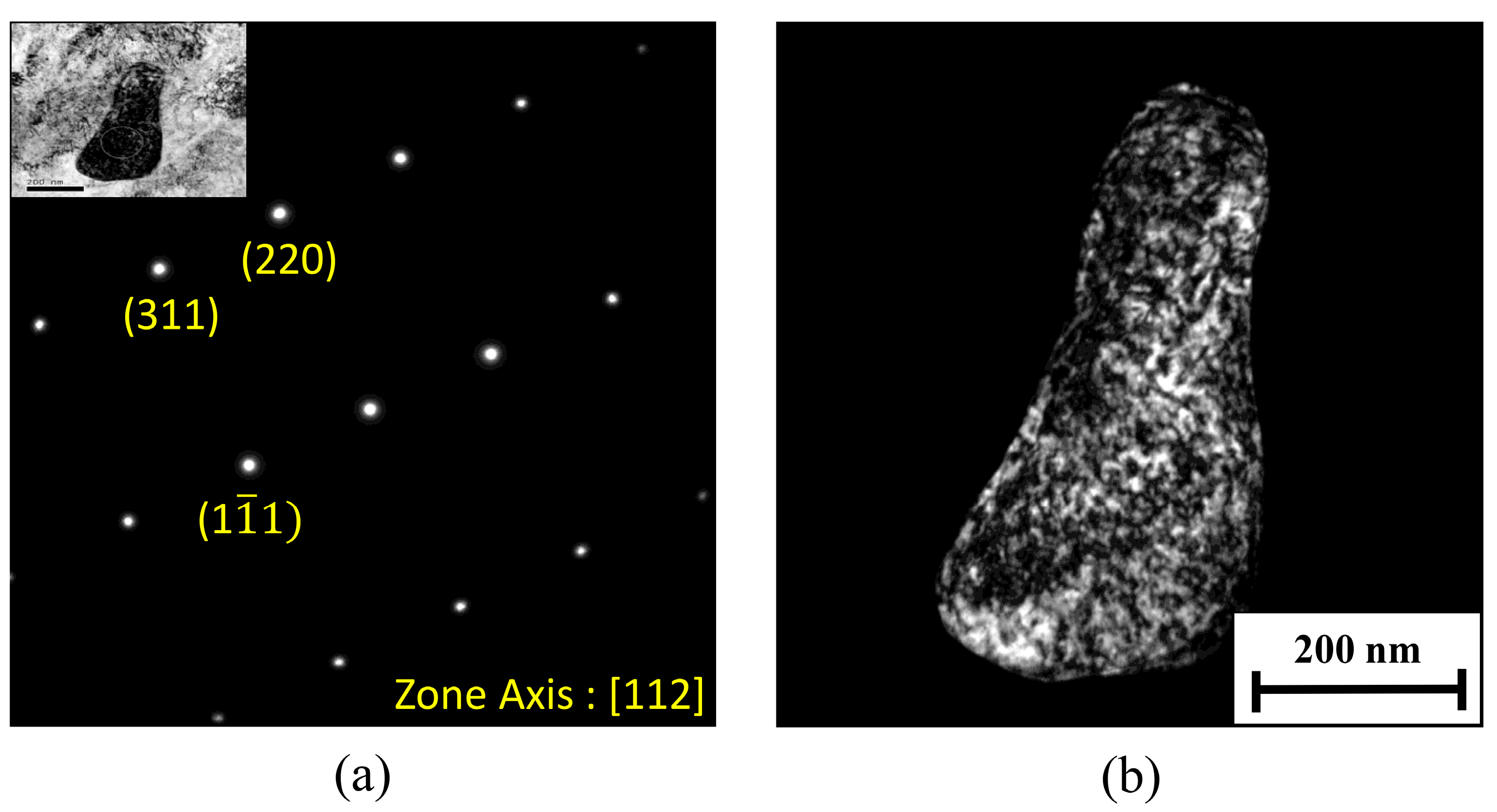
To characterize the main precipitation hardening phase in post-heat-treatment WLAM alloy, TEM analysis was carried out at the interface between this precipitate and the alloy matrix, as shown in Figure 5 and Table 3. This disclosed the presence of a semi-coherent precipitate in the form of a ε-Cu phase that was uniformly distributed throughout the martensitic matrix. The size of this phase was about 20 nm, which comes in line with the observations of Sarkar et al. [36] that explore the microstructure of 15-5 PH stainless steel produced using the SLM process.
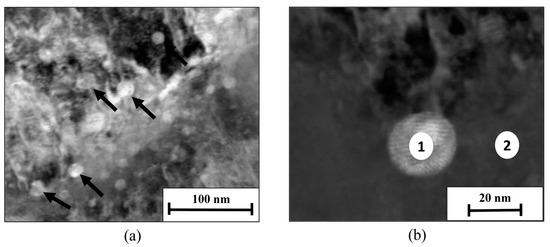
Figure 5.
TEM analysis of WLAM PH 15-5: (a) general view of the interface between the matrix and the main precipitate phase, and (b) close-up view showing locations of localized chemical analysis.
Figure 5.
TEM analysis of WLAM PH 15-5: (a) general view of the interface between the matrix and the main precipitate phase, and (b) close-up view showing locations of localized chemical analysis.


Table 3.
Spot chemical analysis at the interface between the WLAM alloy matrix and its main secondary phase according to Figure 4b.
Table 3.
Spot chemical analysis at the interface between the WLAM alloy matrix and its main secondary phase according to Figure 4b.
| Point of Measurement | Fe (wt%) | Cr (wt%) | Ni (wt%) | Cu (wt%) | Dominant Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 45.56 | 10.65 | 2.05 | 36.90 | Main precipitate ε-Cu phase |
| 2 | 78.44 | 17.23 | 2.78 | 0.55 | PH 15-5 matrix |
Another interesting precipitation phase that was discovered via the TEM analysis was a Nb-based phase, which had the composition of Nb0.3C0.3N0.7, as shown in Figure 6 along with chemical composition presented in Table 4. This phase has a NaCl structure, and it is believed that its formation was due to the reaction between a preliminary NbC carbide and nitrogen from the protective atmosphere. According to Brauer [45], Niobium Carbo-Nitrides (Nb(CN)) can be formed in various stoichiometries, depending on the ratio between the three composing elements. Ščetinec et al. [46] also confirm that the presence of Nb(CN) in 15-5 PH stainless steel produced through the DED process is of a similar size (about 20 nm) to that obtained in this study. Altogether, it is believed that the minor amount of Niobium Carbo-Nitride phase that was found in the WLAM alloy post-heat treatment has an insignificant effect on the properties.

Figure 6.
Diffraction analysis of the secondary phase Nb0.3C0.3N0.7. (a)—Electron diffraction image, (b)—Dark field image.

Table 4.
EDS analysis of Nb0.3C0.3N0.7 precipitate in Figure 5b.
Typical stress–strain curves of post-heat-treatment WLAM 15-5 PH and AISI 15-5 PH stainless steel are presented in Figure 7. The higher ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and yield point (Y.P.) of the counterpart AISI alloy can be related to its martensitic structure, as well as to the inherent defects (mainly in the form of porosity) that are present in the WLAM alloy. Statistical deviations in the mechanical properties, including hardness measurements, are shown in Table 5. A good correlation between the reduced ductility and increased hardness of the AISI alloy compared to the WLAM alloy is evident. In addition, it is also believed that the reduced amount of martensitic phase in the WLAM alloy (46% compared to 89% in the AISI alloy), as well as grain coarsening, influences its decreased hardness.
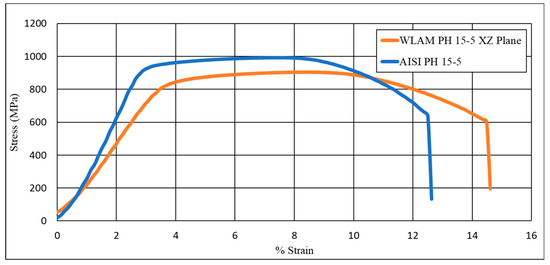
Figure 7.
Stress–strain curves of WLAM PH 15-5 alloy and AISI alloy in tension conditions.
Figure 7.
Stress–strain curves of WLAM PH 15-5 alloy and AISI alloy in tension conditions.

Table 5.
Mechanical properties of WLAM alloy and AISI PH 15-5 alloy as derived from the tensile tests displayed in Figure 6 along with hardness measurements.
Table 5.
Mechanical properties of WLAM alloy and AISI PH 15-5 alloy as derived from the tensile tests displayed in Figure 6 along with hardness measurements.
| UTS | Y. P | %Elongation | Hardness (HRC) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WLAM PH 15-5 | 939 ± 25 | 789 ± 5 | 16 ± 1.5 | 30.1 ± 0.5 |
| AISI PH 15-5 | 958 ± 30 | 847 ± 18 | 11 ± 0.8 | 35.6 ± 3.7 |
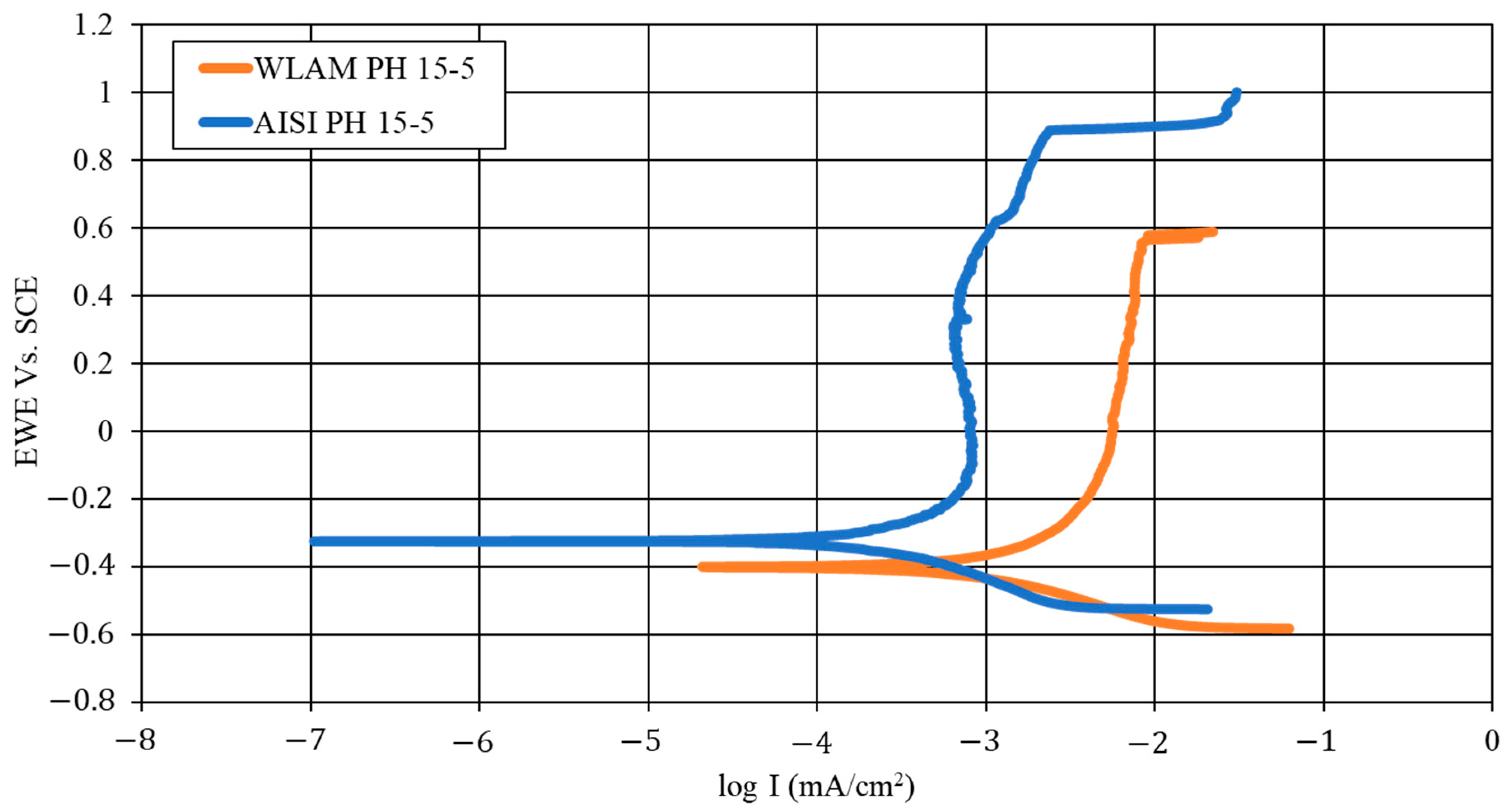
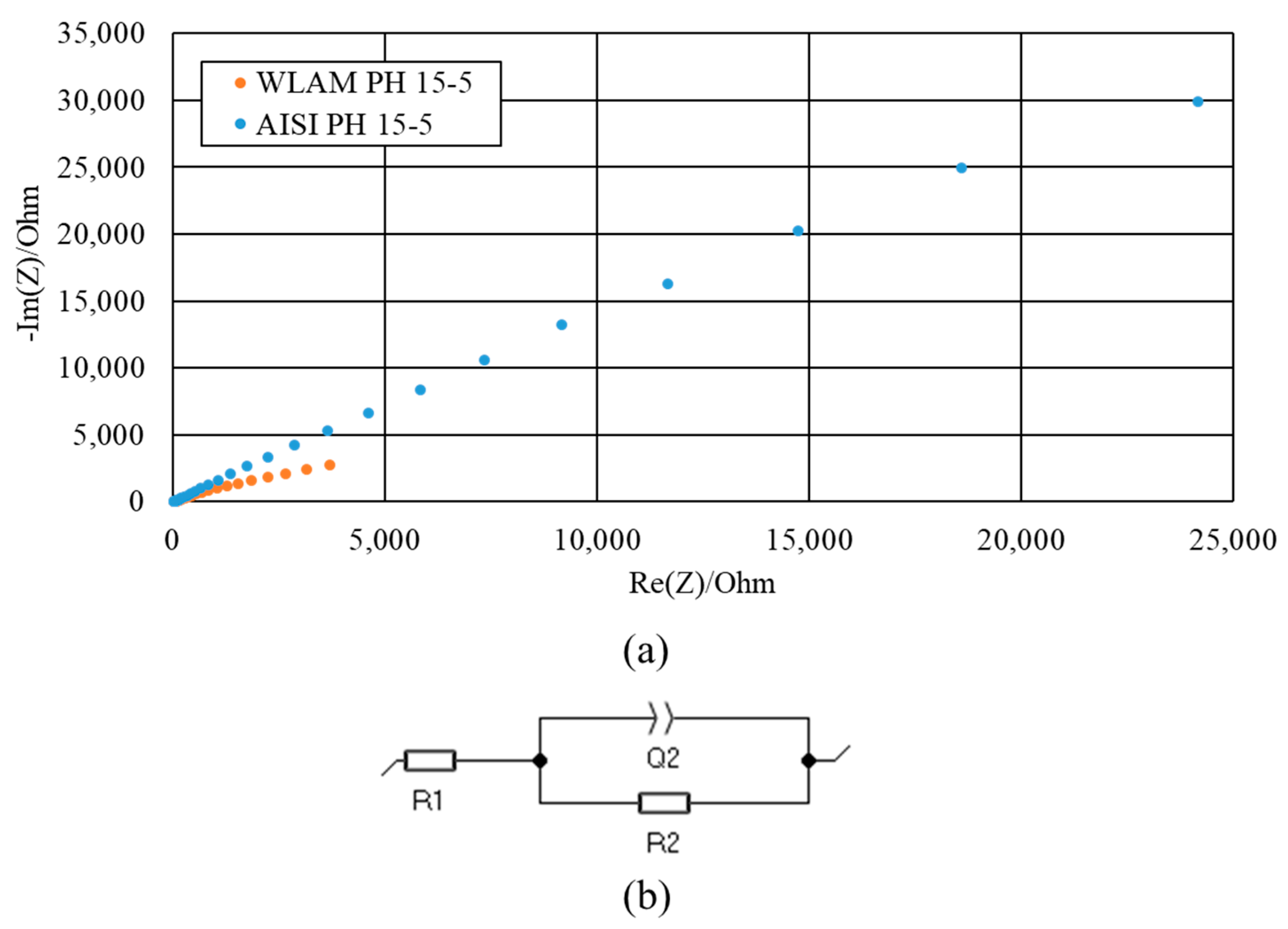
The corrosion performance of WLAM and AISI alloys, post-heat treatment, examined through potentiodynamic polarization analysis, is shown in Figure 8 along with the derived electrochemical parameters and corrosion rates in Table 6 Both alloys exhibit polarization curves with typical active–passive transitions, as expected from regular stainless steel [47,48]. However, the WLAM alloy shows higher corrosion currents, reduced corrosion potential and increased corrosion rate, compared to its counterpart AISI alloy. These are clear indications of the reduced corrosion resistance of the WLAM alloy. In addition, the reduced trans-passivation potential of the WLAM alloy also indicates relative difficulties in natural passivation capabilities. Nevertheless, although there are some differences in the corrosion rate between the two alloys, both alloys had a corrosion rate less than 0.02 mmpy, which is acceptable for most practical engineering applications [49]. The surface corrosion resistance of the two alloys evaluated through impedance spectroscopy analysis in terms of a Nyquist diagram is shown in Figure 9 along with equivalent circuit parameters shown in Table 7. This clearly indicates that the curve-radius of the WLAM alloy was significantly increased, compared to its counterpart AISI alloy. Practically, this means that the surface corrosion resistance of the AISI alloy was improved, which corroborates the potentiodynamic polarization results.
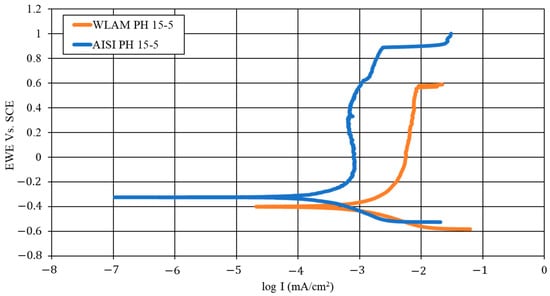
Figure 8.
Potentiodynamic polarization curves of WLAM PH 15-5 and AISI alloy.

Table 6.
Electrochemical parameters derived from Figure 7 along with corrosion rate measurements calculated using Tafel extrapolation.
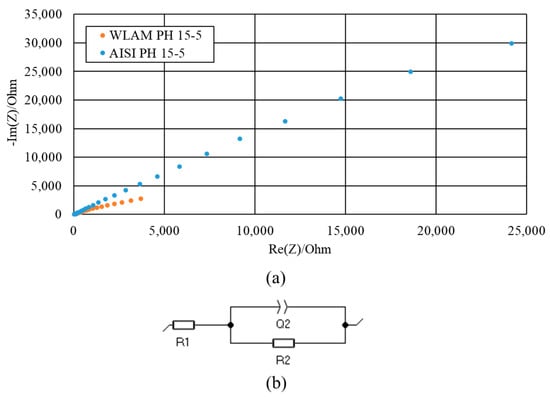
Figure 9.
Impedance spectroscopy analysis of WLAM and AISI alloys: (a) Nyquist diagrams; (b) fitted electrical equivalent circuit (R1—solution resistance, R2—charge transfer resistance and Q2—capacitance of the double layer).

Table 7.
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy circuit parameters as derived from the impedance test.
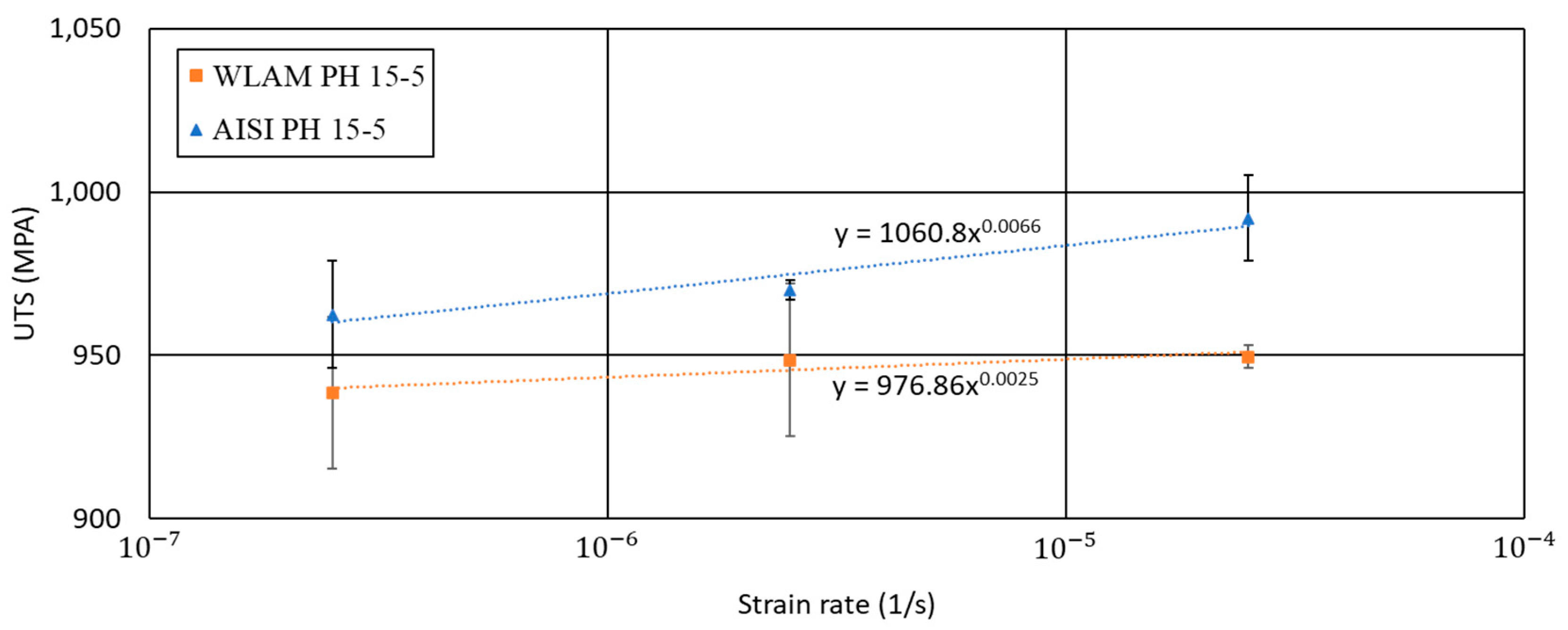
The stress corrosion behavior of the WLAM 15-5 PH alloy and its counterpart AISI alloy, post-heat treatment, in terms of SSRT in a corrosive solution is displayed in Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12 and Figure 13. The UTS vs. strain rate of the two alloys was similar and in accordance with their inherent mechanical properties. This was also supported by their strain rate sensitivity factor (m), which was of the same magnitude—00066 and 0.0025 for the WLAM and AISI alloys, respectively. m is derived from the line equation of UTS vs. strain rate, according to the following equation:
where C is a constant and ε* represents the strain rate.
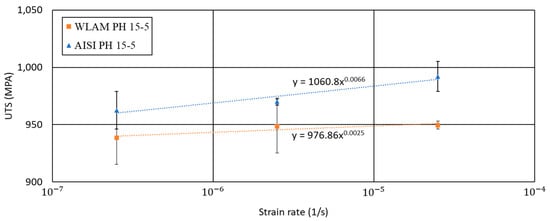
Figure 10.
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS) vs. strain rate of WLAM 15-5 PH and its counterpart AISI alloy.
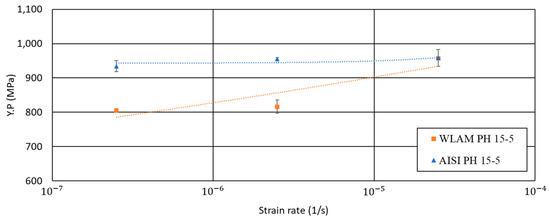
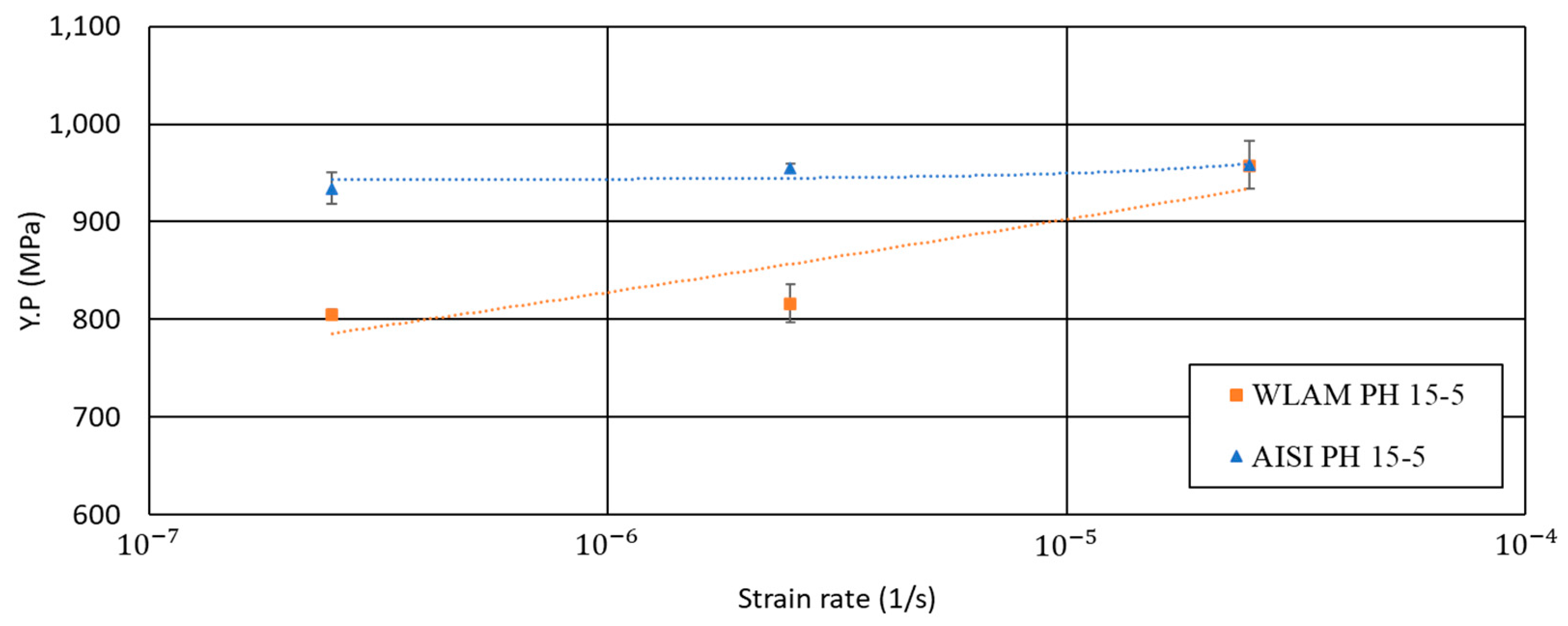
Figure 11.
Yield point (Y.P.) vs. strain rate of WLAM 15-5 PH and its counterpart AISI alloy.
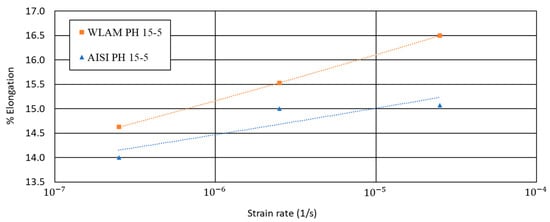
Figure 12.
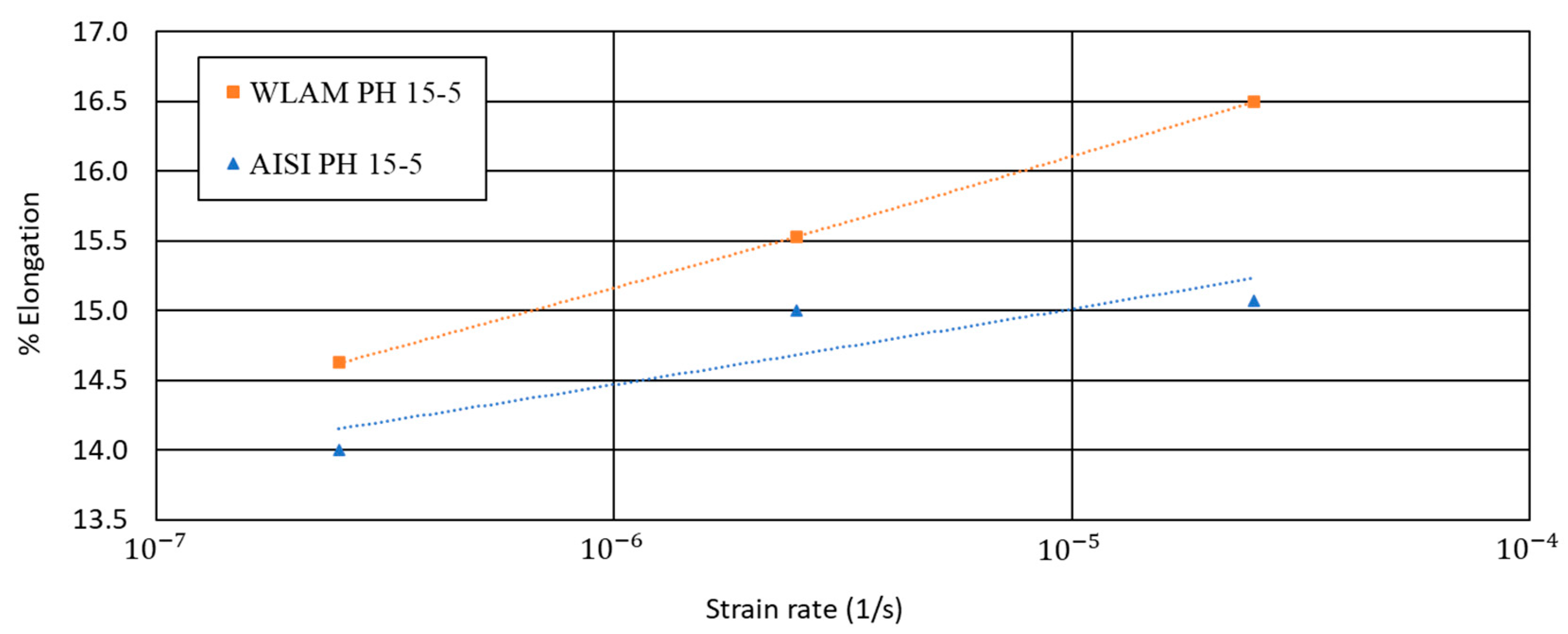
Elongation vs. strain rate of WLAM 15-5 PH and its counterpart AISI alloy.
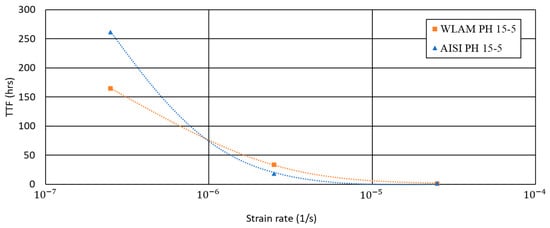
Figure 13.
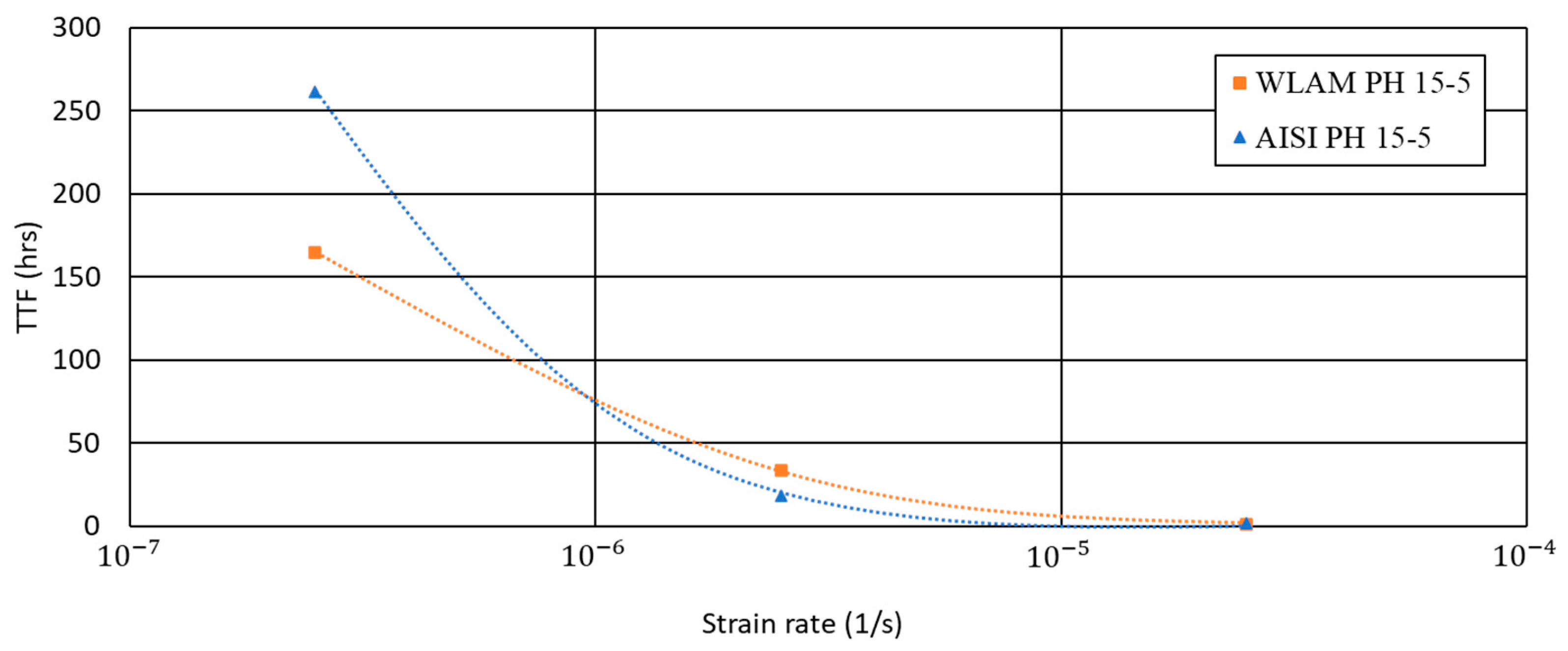
Time to failure (TTF) vs. strain rate of WLAM 15-5 PH and its counterpart AISI alloy.
In terms of Y.P. vs. strain rate, it was evident that while the AISI alloy was able to maintain its original strength at a low strain rate (2.5 × 10−7), the strength of the WLAM at this strain rate was notably reduced. This can be attributed to the decreased corrosion resistance of the WLAM alloy, which becomes dominant at low strain rates due to the prolonged exposure to the corrosive solution.
Regarding the elongation vs. strain rate, the behavior of the two alloys was quite similar and in accordance to their inherent properties. The most important and significant difference between the two alloys in terms of SSRT analysis relates to their time to failure (TTF) at the lowest strain rate (2.5 × 10−7). This was shown by the fact that the TTF of the WLAM alloy was 164 h compared to 261 h in the case of the AISI alloy. The considerable reduction in the TTF of the WLAM alloy versus its counterpart alloy is a clear indication that the stress corrosion resistance of the WLAM alloy was drastically decreased.
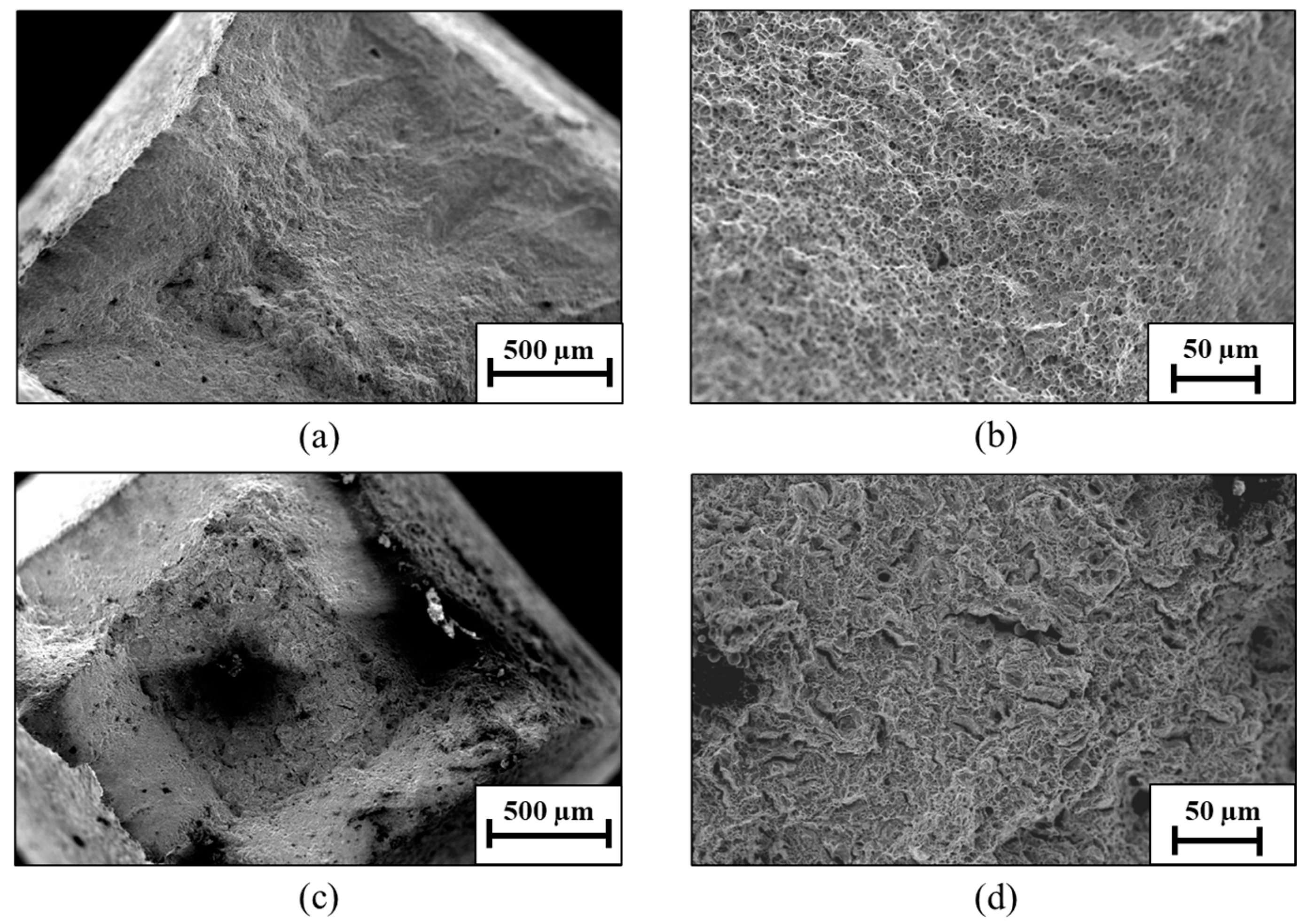
The fractography examination post-SSRT analysis at the low strain rate of 2.5 × 10−7 of the two alloys is shown in Figure 14. Although both alloys exhibit a relatively ductile fracture, the fact that the endurance of the WLAM alloy in the SSRT experiment was comparatively reduced is evident in terms of their fracture morphology. Accordingly, the fine dimples at the fracture surface of the WLAM alloy were diminished in the case of its counterpart AISI alloy that also showed microcracks and corrosion products on the fracture surface due to the extended exposure to the corrosive solution.
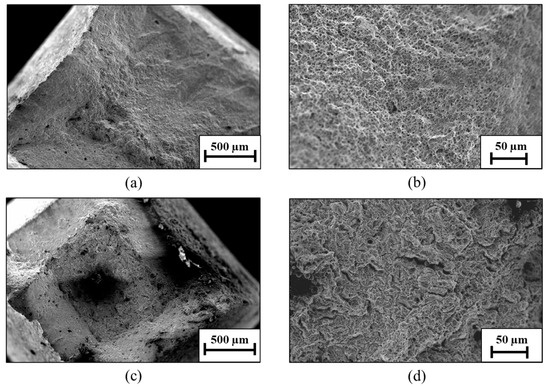
Figure 14.
Fractography images of the tested alloys post-SSRT analysis at a strain rate of 2.5 × 10−7: (a,c) WLAM 15-5 PH alloy and (b,d) counterpart AISI alloy.
4. Discussion
This study examined the effect of microstructure variations and inherent defects on the stress corrosion behavior of WLAM 15-5 PH stainless steel, compared to its counterpart AISI alloy. The microstructure of the WLAM alloy deviated from the conventional characteristics of the AISI alloy. Apart from the martensitic phase, the WLAM alloy, after H-1150M treatment, contains 54% austenitic phase compared to only 11% in the counterpart alloy. It is believed that the large amount of austenitic phase in the WLAM alloy can be partly attributed to the interaction between this alloy and the protective gas atmosphere (N2) during the printing process [50,51]. This assumption was mainly supported by the presence of a secondary Nb(CN) phase in the form of Nb0.3C0.3N0.7. The presence of Nb(CN) phases was also observed by Scetinec et al. [46] when evaluating the microstructure of the same alloy produced through a wire arc direct energy deposition process. Another factor that also induces the formation of the austenitic phase in the WLAM alloy, as well as in its counterpart AISI alloy, is the H-1150M heat treatment. This was clear from the obtained results, where the content of the austenitic phase in the WLAM alloy increased from 18% in as-printed conditions to 54% post-heat treatment, and similarly in the counterpart AISI alloy, from 1% to 11%. According to Chen et al. [5], who studied the formation of an austenitic phase in AM martensitic stainless steels, the creation of austenite around the martensitic laths is enhanced during the precipitation hardening stage (ageing). An explanation for this phenomenon was offered by Niu et al. [52] and Tapoglou et al. [53]. They claim that this phenomenon was governed by preferred segregation of C and Ni out of the martensite phase, which subsequently reduces the Ms temperature below room temperature and prevents the stabilization of a martensite phase. They support their claim by the fact that the Ni content in the austenite phase was higher than in the martensite phase by 1.5 wt%. Moreover, Niu et al. [52] indicated that the amount of reversed austenite was greatly increased at an ageing temperature around 620 °C, which is nearly the same ageing temperature used in the present study (621 °C).
Furthermore, the WLAM alloy contains spherical defects in the form of keyhole porosity that were probably produced due to gas entrapment [43]. These inherent defects, combined with the above phase transitions, had a damaging effect on strength (UTS and Y.P.) and on the corrosion resistance, as exhibited from the electrochemical analysis. The corrosion degradation may also be attributed to the relatively massive formation of an austenitic phase that creates micro-galvanic corrosion at the interface with the martensitic matrix. A similar electrochemical performance in terms of reduced potential corrosion and increased corrosion rate were obtained by Avula et al. [50] in a 15-5 PH alloy, post-H925 heat treatment, that was produced through direct metal laser sintering.
Altogether, the endurance of WLAM alloys under stress corrosion conditions reflected the combined detrimental effects generated by the microstructure modifications and inherent defects, compared to its counterpart AISI alloy. This was clearly demonstrated by the significant reduction in the TTF of nearly 100 h at a low strain rate (2.5 × 10−7) that simulates prolonged exposure to the joint effect of a corrosive environment and mechanical loading. The dominating factors that reduce the stress corrosion resistance of WLAM alloy were as follows: (i) excessive formation of austenitic phase during printing (due to the interaction with nitrogen) and during heat treatment (ageing); (ii) significant reduction in passivation capability, mainly due to micro-galvanic corrosion created at the interface between the austenitic phase and the martensitic matrix [26]; and (iii) inherent defects in the form of porosity that disrupted the material continuity of the alloy. To address the stress corrosion limitations of WLAM alloy (apart from replacing the protective atmosphere by another inert gas such as Ar), special attention should be devoted to the selection of printing parameters and conditions of the precipitation hardening heat treatment.
5. Conclusions
The detrimental effect of microstructure modifications on the properties of WLAM 15-5 PH stainless-steel alloy compared to its counterpart AISI alloy, post-H-1150M heat treatment, was quite noticeable. This was mainly attributed to the relatively high content of austenitic phase (54% vs. 11% in the AISI alloy) and the comparatively enlarged density and size of porosity. Consequently, this was demonstrated by the inferior strength (UTS: 939 vs. 958 MPa and YP: 789 vs. 847 MPa) and corrosion resistance (corrosion rate of 0.015 vs. 0.003 mmpy) of the WLAM alloy compared to the AISI alloy. The inherent differences between the two alloys were also reflected by their relative stress corrosion resistance in terms of SSRT analysis. This was clearly demonstrated by the reduced time to failure (TTF) at the lowest strain rate (2.5 × 10−7), which was 164 and 261 h for the WLAM and AISI alloy, respectively. The main factors that reduce the stress corrosion resistance of the WLAM alloy can be related to the disruption of the material continuity due to inherent porosity and to the reduced passivation capability that is mainly generated by the creation of micro-galvanic corrosion between the large amount of retained austenitic phase and martensitic matrix. Additional efforts should be devoted to upgrading the printing parameters of WLAM alloy to rectify its inherent microstructural defects in order to obtain similar properties as introduced by its counterpart AISI alloy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.A.; Methodology, E.A.; Formal analysis, M.B.; Investigation, M.B., T.R. and A.S.; Writing–original draft, M.B. and E.A.; Supervision, A.S. and E.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Experimental data from this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank A. Kotliar and R. Koltiar from A. Kotliar Ltd. Haifa, Israel for the preparation of the 3D-printed specimens using wire laser additive manufacturing (WLAM) technology.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ding, D.; Pan, Z.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H. Wire-feed additive manufacturing of metal components: Technologies, developments and future interests. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 81, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassis, M.; Kotliar, A.; Koltiar, R.; Ron, T.; Leon, A.; Shirizly, A.; Aghion, E. The effect of a slow strain rate on the stress corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steel produced by the wire laser additive manufacturing process. Metals 2021, 11, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabakhshi, F.; Farshidianfar, M.; Gerlich, A.; Nosko, M.; Trembošová, V.; Khajepour, A. Effects of laser additive manufacturing on microstructure and crystallographic texture of austenitic and martensitic stainless steels. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 31, 100915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lass, E.A.; Stoudt, M.R.; Williams, M.E. Additively Manufactured Nitrogen-Atomized 17-4 PH Stainless Steel with Mechanical Properties Comparable to Wrought. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Luan, J.; Xu, L.; Han, Y.; Zhao, L.; Kai, J.-J.; Xiao, B.; Jing, H. Reversed austenite in additively manufactured martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 834, 142597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Wang, M.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Ou, W. High-power wire arc additive manufacturing of stainless steel with active heat management. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2022, 27, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cheng, D.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, W.; Hu, B.; Xie, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Hu, D. Effect of laser power on the microstructure and properties of additive manufactured 17-4 PH stainless steel in different fabrication atmosphere. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 839, 142846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, C.; Merlin, M.; Fortini, A.; Fortunato, A. Direct energy depositions of a 17-4 PH stainless steel: Geometrical and microstructural characterizations. Coatings 2023, 13, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, A.; Shirizly, A.; Aghion, E. Corrosion behavior of AlSi10Mg alloy produced by additive manufacturing (AM) vs. Its counterpart gravity cast alloy. Metals 2016, 6, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, D.; Seyda, V.; Wycisk, E.; Emmelmann, C. Additive manufacturing of metals. Acta Mater. 2016, 117, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Piya, C.; Shin, Y.C.; Zhao, F.; Ramani, K. Remanufacturing of turbine blades by laser direct deposition with its energy and environmental impact analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 80, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Caspers, M. An overview of additive manufacturing (3D printing) for microfabrication. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, R.; Unotoro, I.; Kakinuma, Y.; Aoyama, T.; Oda, Y.; Kuriya, T.; Fujishima, M. Evaluation for mechanical characteristics of Inconel625–SUS316L joint produced with direct energy deposition. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 14, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ramanujan, D.; Ramani, K.; Chen, Y.; Williams, C.B.; Wang, C.C.L.; Shin, Y.C.; Zhang, S.; Zavattieri, P.D. The status, challenges, and future of additive manufacturing in engineering. Comput.-Aided Des. 2015, 69, 65–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, K.; Gao, X.; Lofaj, F.; Kvetková, L.; Shen, Z. Transformation of austenite to duplex austenite-ferrite assembly in annealed stainless steel 316L consolidated by laser melting. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 633, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulkhair, N.T.; Tuck, C.; Ashcroft, I.; Maskery, I.; Everitt, N.M. On the Precipitation Hardening of Selective Laser Melted AlSi10Mg. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 3337–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmetshin, R.G.; Fedorov, V.V.; Kostikov, K.S.; Martyushev, N.V.; Ovchinnikov, V.A.; Razin, A.V.; Yakovlev, A.N. SLS setup and its working procedure. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 685, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.-G. Directed Energy Deposition (DED) Process: State of the Art. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 8, 703–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Pan, Z.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H. A multi-bead overlapping model for robotic wire and arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2015, 31, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassis, M.; Ron, T.; Leon, A.; Kotliar, A.; Kotliar, R.; Shirizly, A.; Aghion, E. The Influence of Intralayer Porosity and Phase Transition on Corrosion Fatigue of Additively Manufactured 316L Stainless Steel Obtained by Direct Energy Deposition Process. Materials 2022, 15, 5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayed, A.; Bras, G.; Bernard, H.; Michaud, P.; Balcaen, Y.; Alexis, J. Additive Manufacturing of Ti6Al4V with Wire Laser Metal Deposition Process. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications, Ltd.: Bach, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1016, pp. 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Gisario, A.; Kazarian, M.; Martina, F.; Mehrpouya, M. Metal additive manufacturing in the commercial aviation industry: A review. J. Manuf. Syst. 2019, 53, 124–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heralic, A. Towards Full Automation of Robotized Laser Metal-Wire Deposition. Ph.D. Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, S.M.A.N.R.; Mi, Y.; Kisielewicz, A.; Sikström, F.; Choquet, I. Influence of laser-wire interaction on heat and metal transfer in directed energy deposition. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 205, 123894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gussev, M.; Balonis, M.; Bauchy, M.; Sant, G. Emergence of micro-galvanic corrosion in plastically deformed austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Des. 2021, 203, 109614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, A.; Lavecchia, F.; Guerra, M.G.; Galantucci, L.M. Influence of aging treatments on 17-4 PH stainless steel parts realized using material extrusion additive manufacturing technologies. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheruvathur, S.; Lass, E.A.; Campbell, C.E. Additive Manufacturing of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel: Post-processing Heat Treatment to Achieve Uniform Reproducible Microstructure. JOM 2016, 68, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giganto, S.; Martínez-Pellitero, S.; Barreiro, J.; Zapico, P. Influence of 17-4 PH stainless steel powder recycling on properties of SLM additive manufactured parts. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murr, L.E.; Martinez, E.; Hernandez, J.; Collins, S.; Amato, K.N.; Gaytan, S.M.; Shindo, P.W. Microstructures and properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2012, 1, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, P.; Nobile, R.; Barreiro, J.; Bagheri, S.; Mele, C. Precipitation hardening stainless steel samples processed by additive manufacturing: Process parameters and thermo mechanical treatments effects on microstructure and corrosion resistance. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 156, 108547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Hu, R.; Chen, F. Microstructure and performances for 15-5 PH stainless steel fabricated through the wire-arc additive manufacturing technology. Mater. Technol. 2020, 36, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Li, J. Effects of geometry, location, and direction on microstructure and mechanical properties of 15–5PH stainless steel fabricated by directed energy deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 821, 141587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, M.; Nemani, A.V.; Nasiri, A. Microstructural evolution and mechanical performance after precipitation hardening of PH 13-8Mo martensitic stainless steel fabricated by wire arc additive manufacturing. Materialia 2022, 24, 101507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, F.M.; Shakil, S.I.; Shaha, S.K.; Kacher, J.; Nasiri, A.; Haghshenas, M.; Hadadzadeh, A. Study of direct aging heat treatment of additively manufactured PH13–8Mo stainless steel: Role of the manufacturing process, phase transformation kinetics, and microstructure evolution. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 3772–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.; Newkirk, J.; Liou, F. Absorption of Nitrogen during Pulsed Wave L-PBF of 17-4 PH Steel. Materials 2021, 14, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Kumar, C.S.; Nath, A.K. Effects of heat treatment on microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of 15-5 PH stainless steel parts built by selective laser melting process. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 50, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.; Uzan, P.; Eliezer, D.; Aghion, E. Electron microscopical investigation of as cast AZ 91 D alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2000, 16, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, D.; Wilson-Heid, A.; Keist, J.; Beese, A.; Palmer, T. Impact of retained austenite on the aging response of additively manufactured 17-4 PH grade stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 817, 141363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, S.; Zuback, J.; Keist, J.; Palmer, T. Impact of composition on the heat treatment response of additively manufactured 17–4 PH grade stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 738, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G129-21; Standard Practice for Slow Strain Rate Testing to Evaluate the Susceptibility of Metallic Materials to Environmentally Assisted Cracking. Astm International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
- Zai, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Wellmann, D.; Tong, X.; Tian, Y. Laser powder bed fusion of precipitation-hardened martensitic stainless steels: A review. Metals 2020, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hebert, R.J.; Aindow, M. Effect of heat treatments on microstructural evolution of additively manufactured and wrought 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2018, 156, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chi, C.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, X.; Xie, Y. The effects of fabrication atmosphere condition on the microstructural and mechanical properties of laser direct manufactured stainless steel 17-4 PH. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.C.; Keist, J.S.; Palmer, T.A. Defects in metal additive manufacturing processes. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. JMEPEG 2021, 30, 4808–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, G. Journal of the less-commoii metals *3r nitrides, carronitrides and oxynitrides of niobium. J. Less-Common Met. 1960, 2, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ščetinec, A.; Klobčar, D.; Nagode, A.; Vuherer, T.; Bračun, D.; Trdan, U. Optimisation of precipitation hardening for 15-5 PH martensitic stainless steel produced by wire arc directed energy deposition. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2023, 28, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itzhak, D.; Aghion, E. An anodic behaviour study of an analogical sintered system of austenitic stainless steel in H2SO4 solution. Corros. Sci. 1984, 24, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itzhak, D.; Aghion, E. Corrosion behavior of hot-pressed austenitic stainless steel in H2SO4 solution at room temperature. Corros. Sci. 1983, 23, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabisi, O.; Khuraibut, Y.; Jarragh, A.; Mathew, A. Identifying key performance indicators for corrosion in oilfield water handling systems. In Proceedings of the Corrosion 2014, San Antonio, TA, USA, 9–13 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Avula, I.; Arohi, A.C.; Kumar, C.S.; Sen, I. Microstructure, Corrosion and Mechanical Behavior of 15-5 PH Stainless Steel Processed by Direct Metal Laser Sintering. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 6924–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vunnam, S.; Saboo, A.; Sudbrack, C.; Starr, T.L. Effect of powder chemical composition on the as-built microstructure of 17-4 PH stainless steel processed by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Cui, B.; Jin, H.; Yan, J.; Meng, W.; Min, C.; Xu, D. Effect of Post-Weld Aging Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Weld Metal of 15-5 PH Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 7026–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapoglou, N.; Clulow, J.; Curtis, D. Increased shielding of a Direct Energy Deposition process to enable Deposition of reactive materials; an investigation into Deposition of 15-5 PH Stainless Steel, Inconel 718 and Ti-6Al-4V. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).