Microstructural Influences Caused by Different Aging Strategies on the Strain-Dependent Damping of the High-Strength Aluminum Alloy AA7075
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
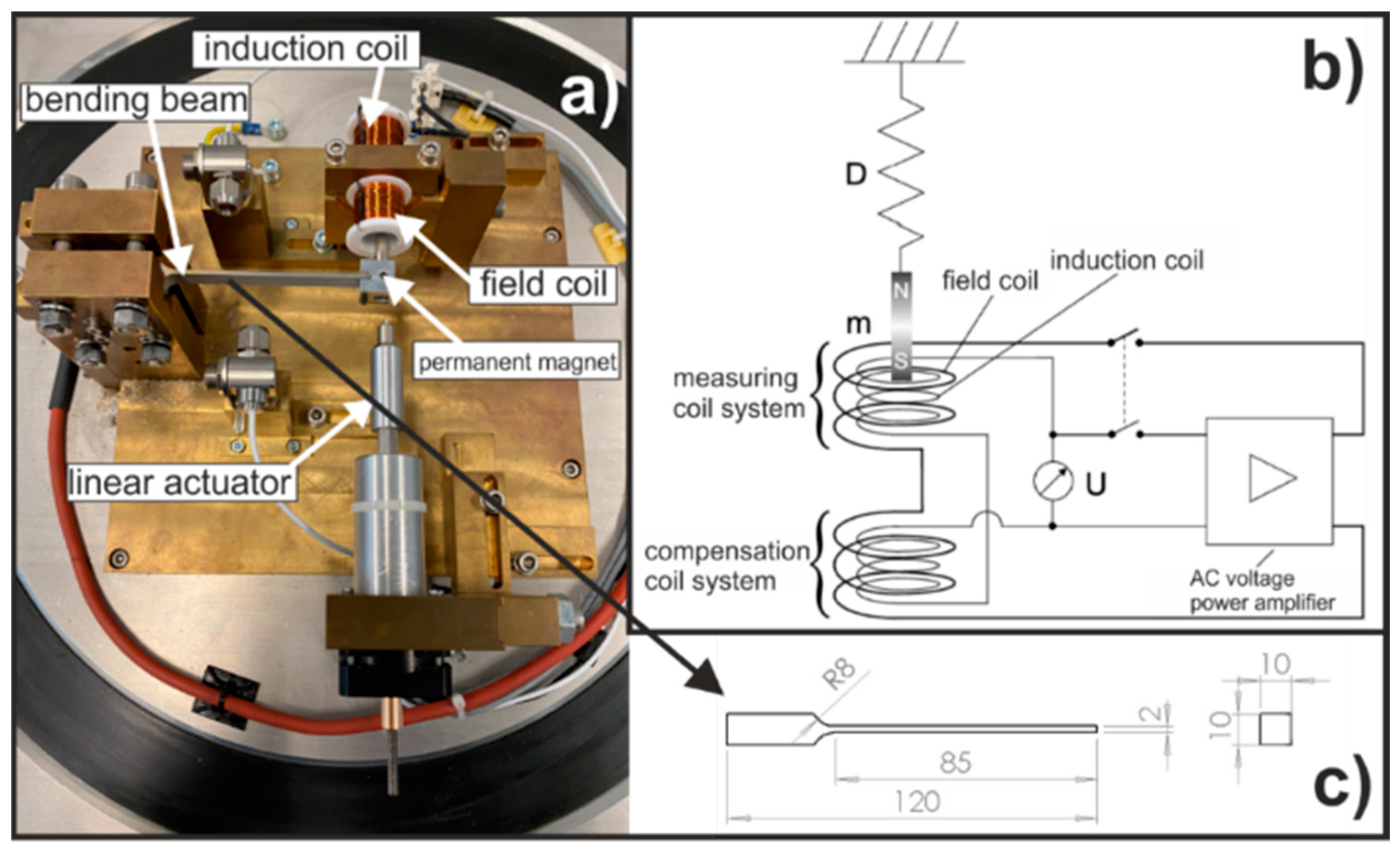
2.2. Experimental Setup and Program
2.3. Microstructural Characterization
3. Results
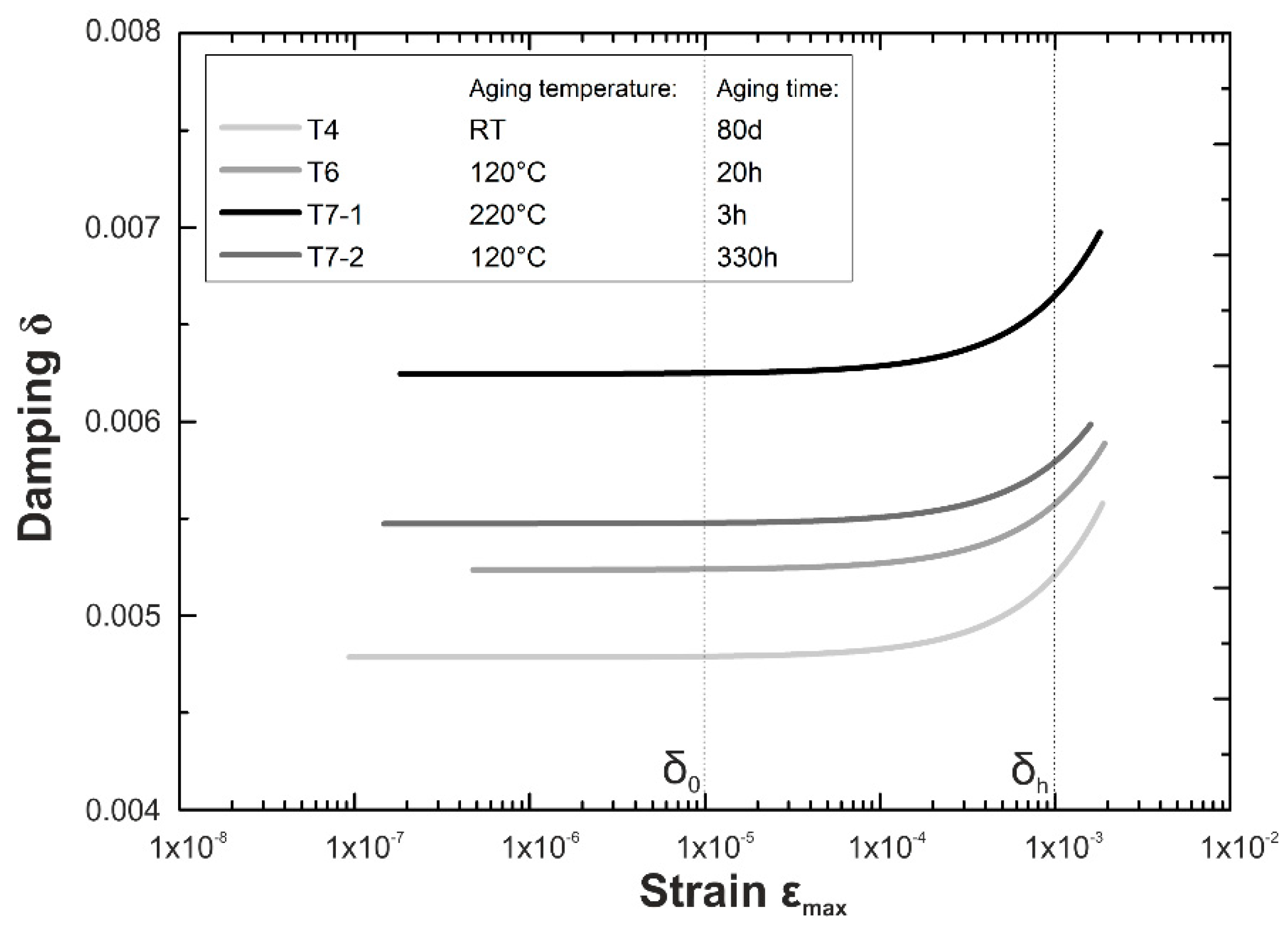
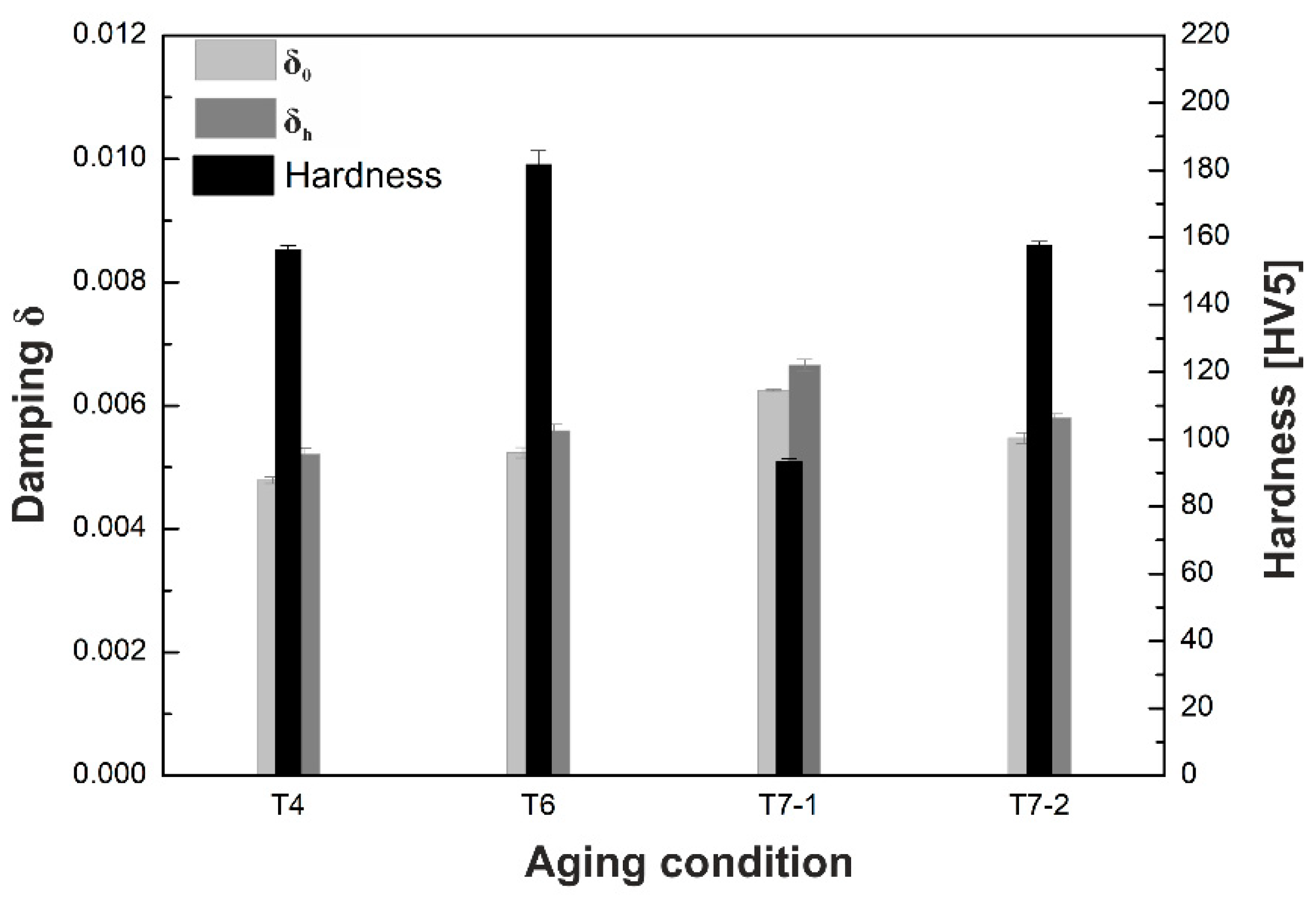
3.1. Damping and Hardness
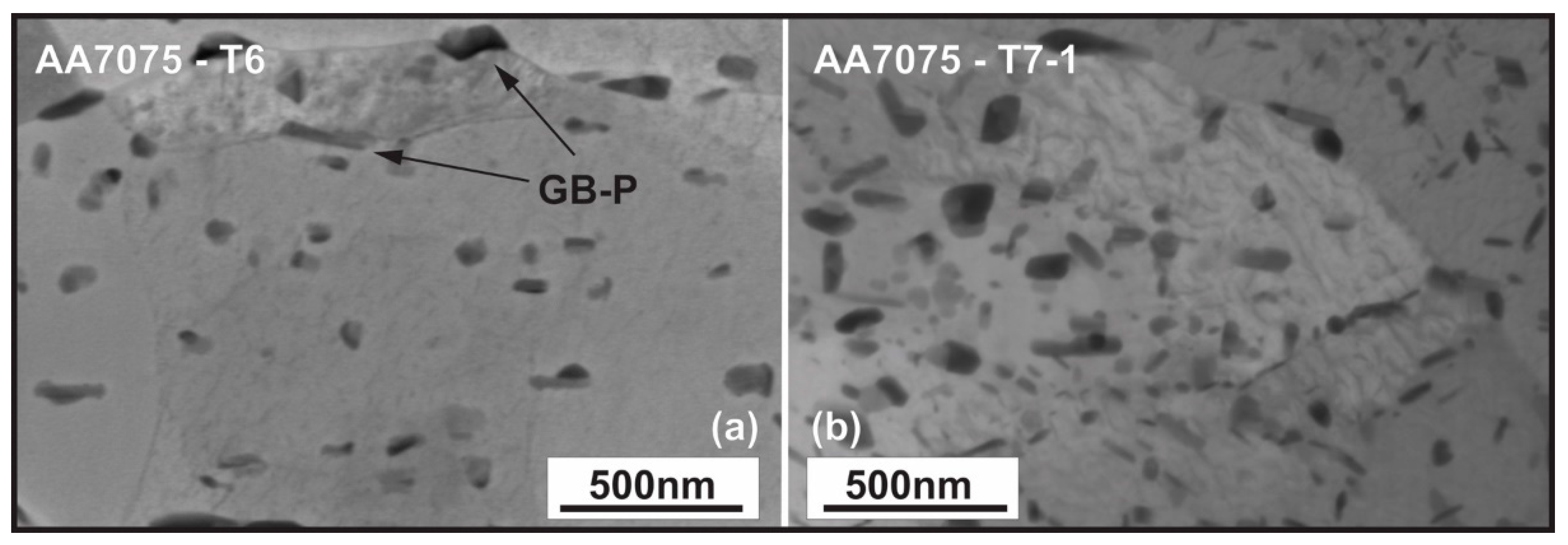
3.2. Microstructural Investigation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hornbogen, E.; Starke, E.A. Overview no. 102 Theory assisted design of high strength low alloy aluminum. Acta Metall. Mater. 1993, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starke, E.A.; Staley, J.T. Application of modern aluminum alloys to aircraft. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 1996, 32, 131–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Updike, C.A.; Bhagat, R.B.; Pechersky, M.J.; Amateau, M.F. The damping performance of aluminum-based composites. JOM 1990, 42, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.Y.; Schaller, R.; Jaquerod, C. High damping capacity after precipitation in some commercial aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 252, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavernia, E.J.; Perez, R.J.; Zhang, J. Damping behavior of discontinuously reinforced ai alloy metal-matrix composites. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1995, 26, 2803–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göken, J. Dämpfungspotential der Magnesiumlegierung AZ91 bei Raumtemperatur. Ph.D. Thesis, GKSS-Forschungszentrum, Geesthacht, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Göken, J.; Riehemann, W. Dehnungsabhängige Dämpfungsmessungen an abklingenden Biegeschwingungen von Werkstoffen. Technol. Mess. 2001, 68, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martínez, R.; Göken, J.; Letzig, D.; Steinhoff, K.; Kainer, K.U. Influence of aging on damping of the magnesium-aluminium-zinc series. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 437, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharifi, E.; Savaci, U.; Kavaklioglu, Z.B.; Weidig, U.; Turan, S.; Steinhoff, K. Effect of thermo-mechanical processing on quench-induced precipitates morphology and mechanical properties in high strength AA7075 aluminum alloy. Mater. Charact. 2021, 174, 111026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, A.; Lücke, K. Theory of Mechanical Damping Due to Dislocations. J. Appl. Phys. 1956, 27, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göken, J.; Riehemann, W. Dependence of internal friction of fibre-reinforced and unreinforced AZ91 on heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 324, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajadifar, S.V.; Scharifi, E.; Weidig, U.; Steinhoff, K.; Niendorf, T. Performance of thermo-mechanically processed AA7075 alloy at elevated temperatures—From microstructure to mechanical properties. Metals 2020, 10, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajadifar, S.V.; Scharifi, E.; Weidig, U.; Steinhoff, K.; Niendorf, T. Effect of tool temperature on mechanical properties and microstructure of thermo-mechanically processed AA6082 and AA7075 aluminum alloys. HTM J. Heat Treat. Mater. 2020, 75, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharifi, E.; Roscher, M.; Lotz, S.; Weidig, U.; Steinhoff, K. Functional Gradation in Precipitation Hardenable AA7075 alloy by Differential Cooling Strategies. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zürich, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
| Chemical Elements (wt.%) | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Zn | Ti | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA7075—as received (AR) | 0.08 | 0.12 | 1.6 | 0.04 | 2.7 | 0.19 | 5.9 | 0.05 | Balance |
| Condition | T4 | T6 | T7-1 | T7-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solution Heat Treatment [°C] | 480 | 480 | 480 | 480 |
| Aging Temperature [°C] | 24 | 120 | 220 | 120 |
| Aging Time | 80 d | 20 h | 3 h | 330 h |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lotz, S.; Zhang, J.; Scharifi, E.; Morak, R.; Weidig, U.; Göken, J.; Broeckmann, C.; Steinhoff, K. Microstructural Influences Caused by Different Aging Strategies on the Strain-Dependent Damping of the High-Strength Aluminum Alloy AA7075. Metals 2022, 12, 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122172
Lotz S, Zhang J, Scharifi E, Morak R, Weidig U, Göken J, Broeckmann C, Steinhoff K. Microstructural Influences Caused by Different Aging Strategies on the Strain-Dependent Damping of the High-Strength Aluminum Alloy AA7075. Metals. 2022; 12(12):2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122172
Chicago/Turabian StyleLotz, Steffen, Jiali Zhang, Emad Scharifi, Roland Morak, Ursula Weidig, Jürgen Göken, Christoph Broeckmann, and Kurt Steinhoff. 2022. "Microstructural Influences Caused by Different Aging Strategies on the Strain-Dependent Damping of the High-Strength Aluminum Alloy AA7075" Metals 12, no. 12: 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122172
APA StyleLotz, S., Zhang, J., Scharifi, E., Morak, R., Weidig, U., Göken, J., Broeckmann, C., & Steinhoff, K. (2022). Microstructural Influences Caused by Different Aging Strategies on the Strain-Dependent Damping of the High-Strength Aluminum Alloy AA7075. Metals, 12(12), 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122172






