Understanding the Influencing Mechanism of CNTs on the Microstructures and Wear Characterization of Semi-Solid Stir Casting Al-Cu-Mg-Si Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
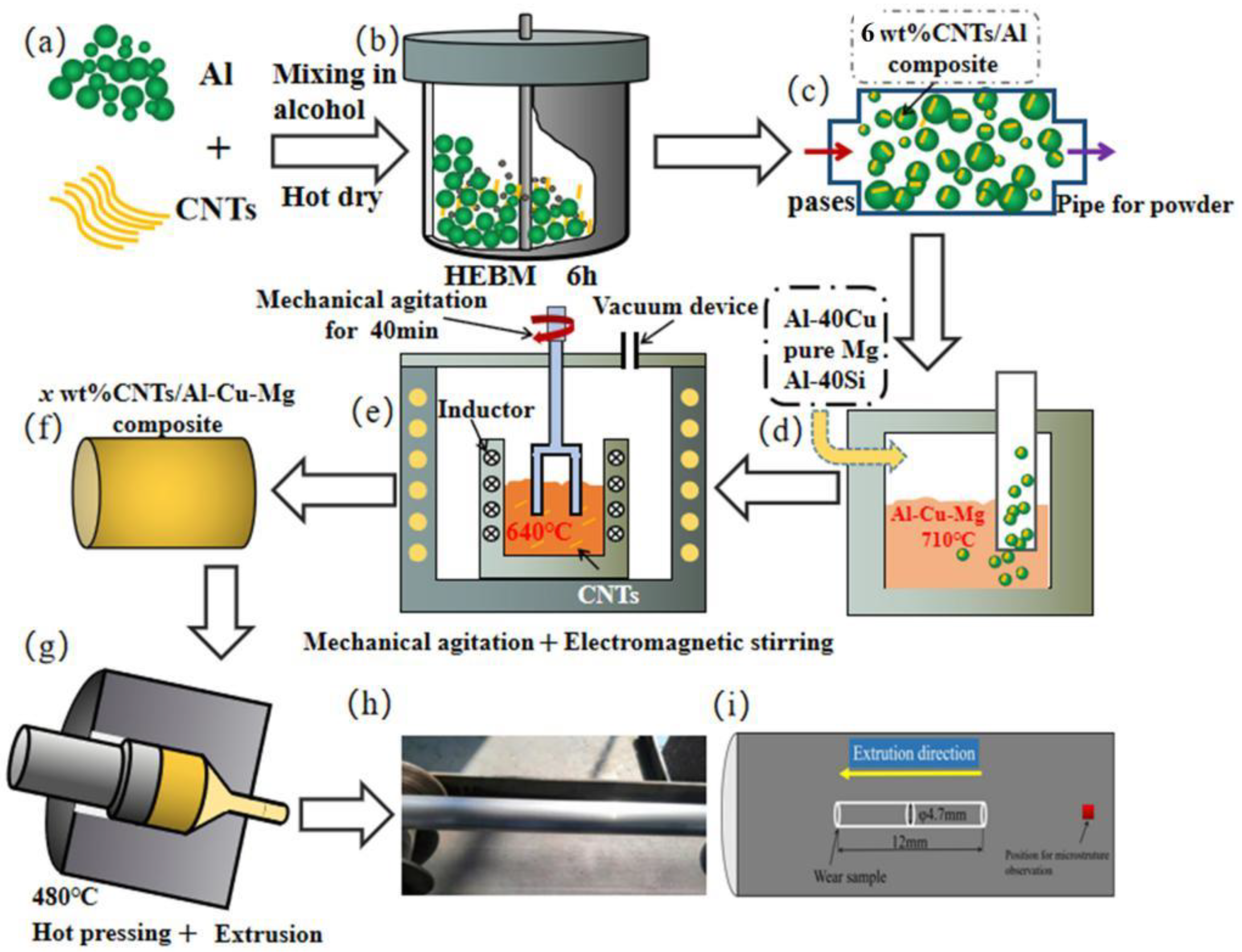
2.1. Preparation of the Materials
2.2. Microstructural Characterization
2.3. Wear Tests and Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
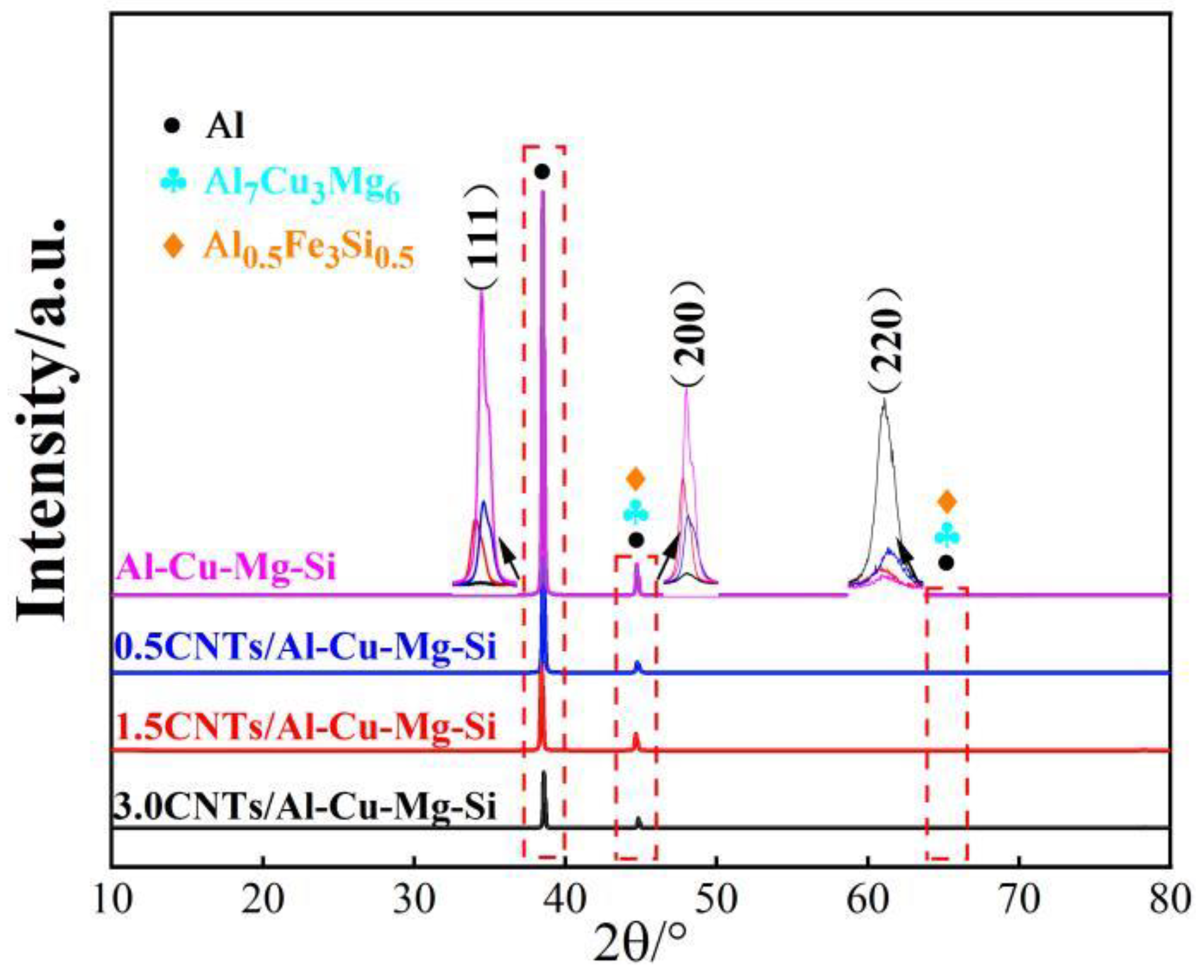
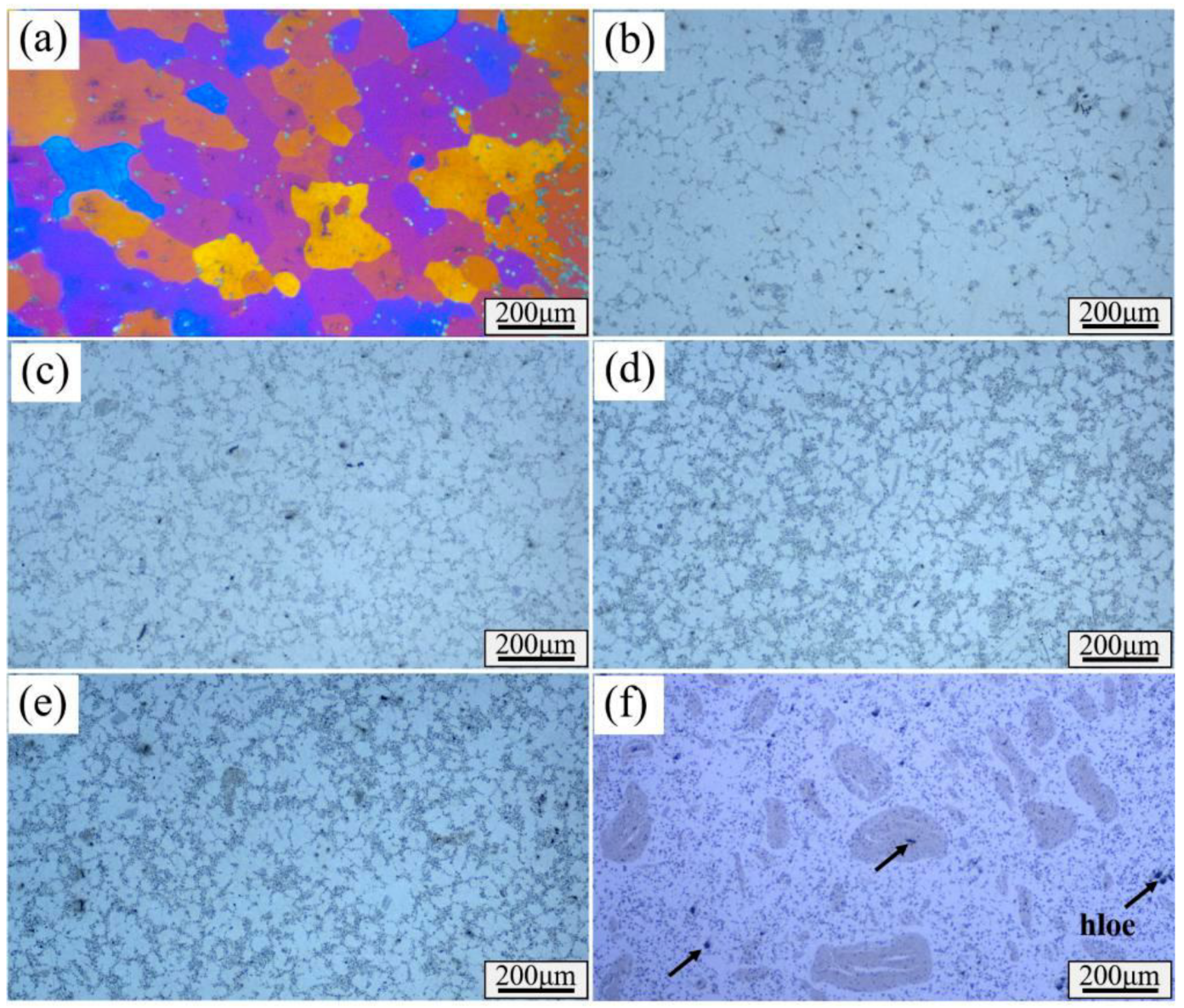
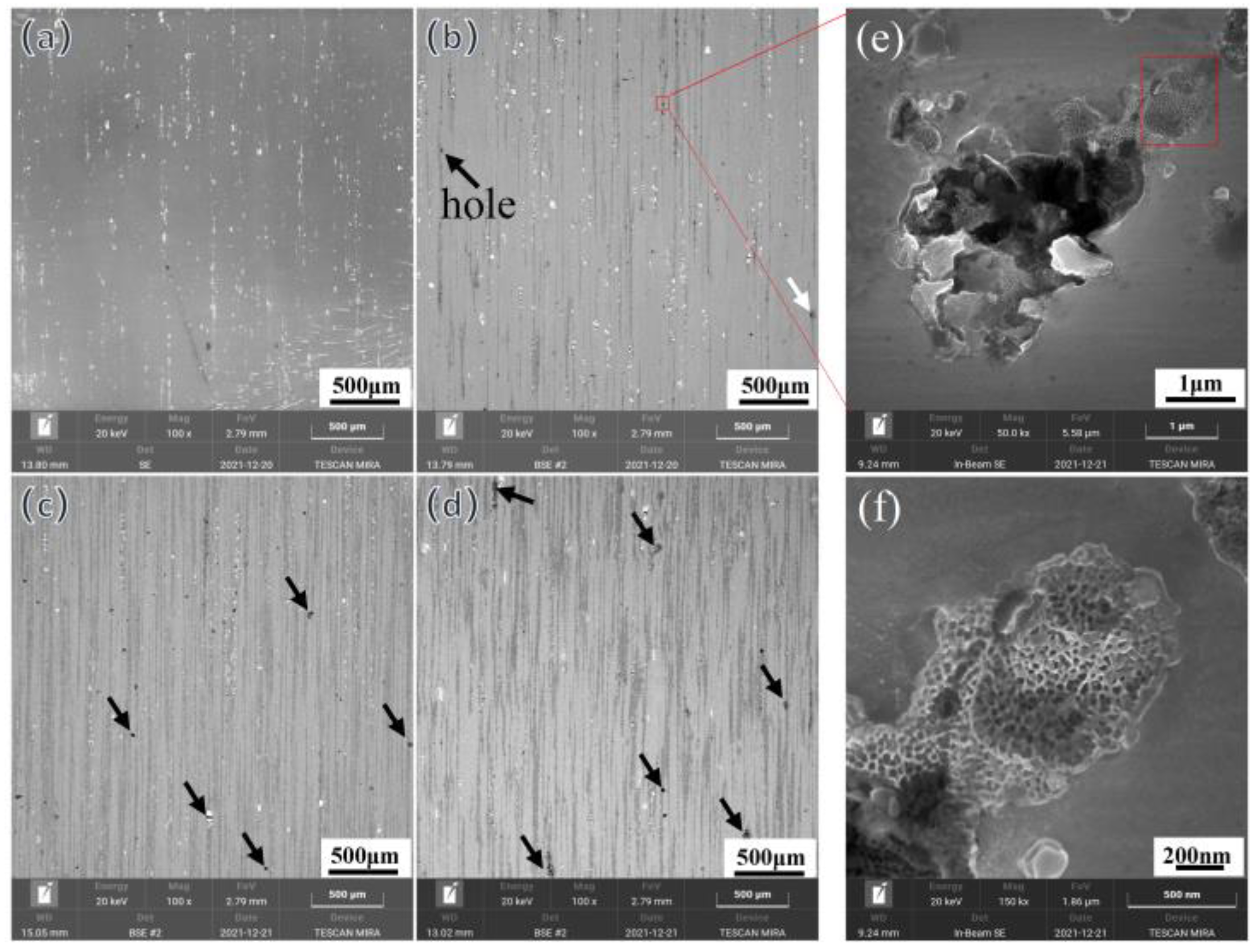
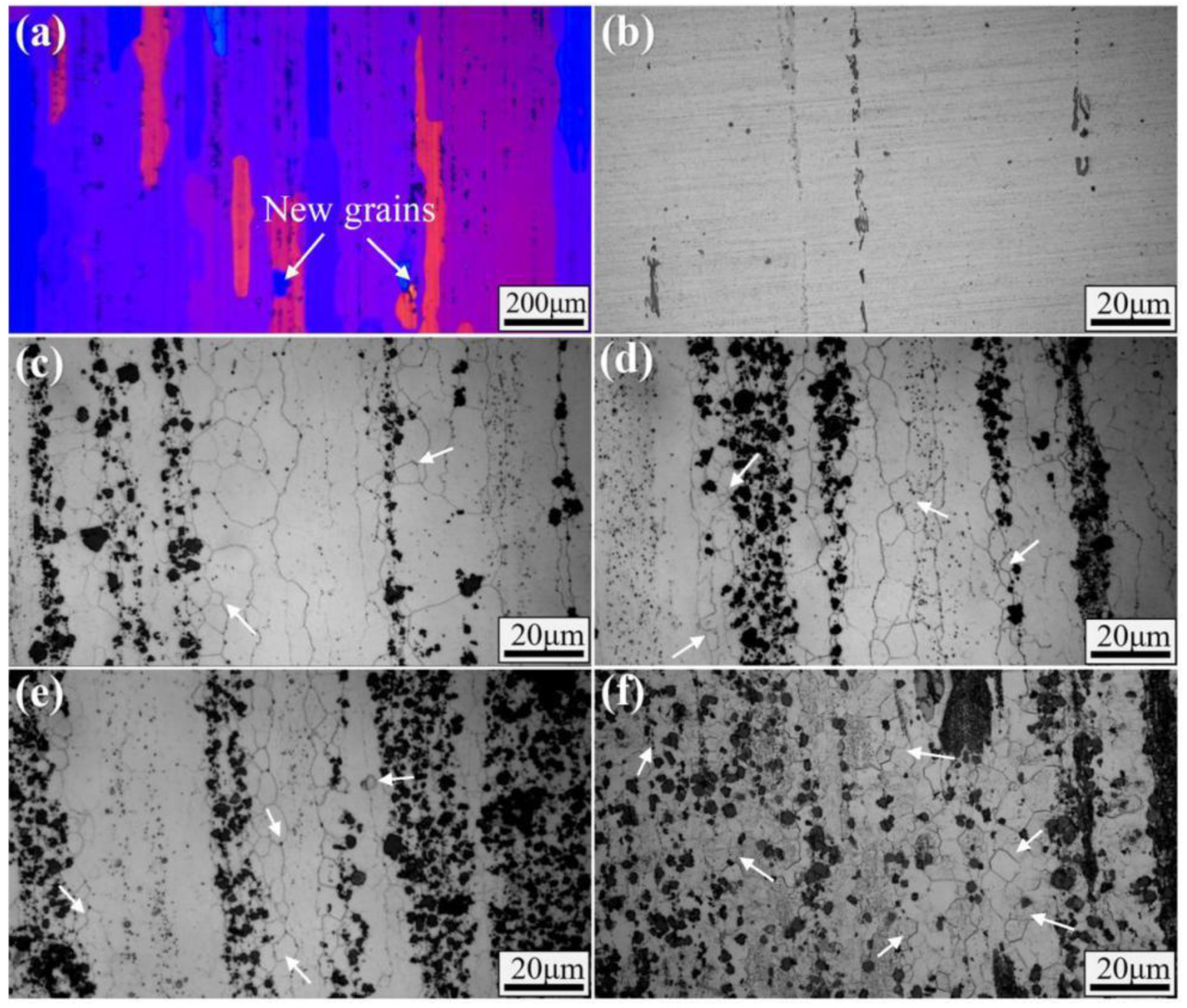
3.1. Microstructural Evolution upon Addition of CNTs
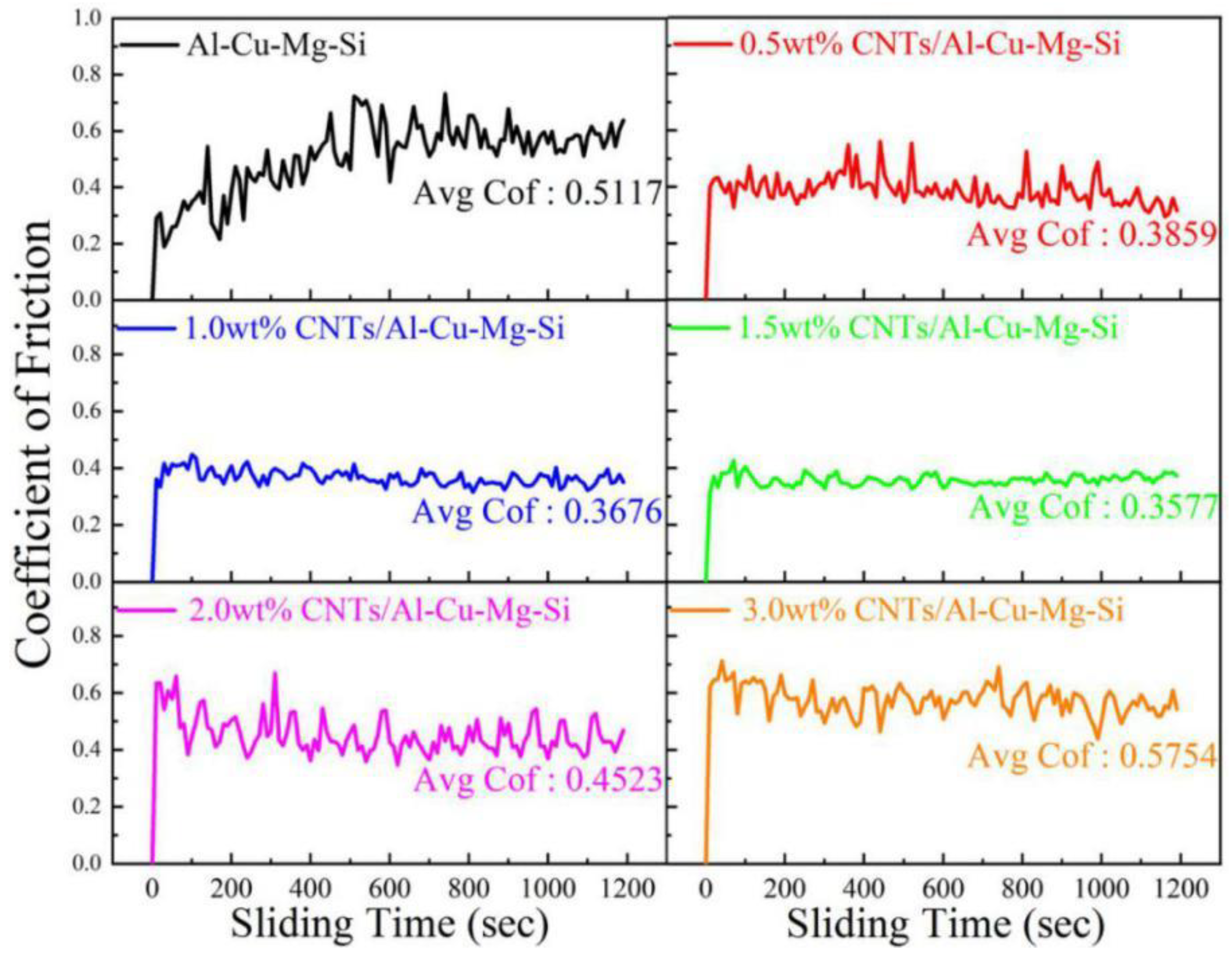
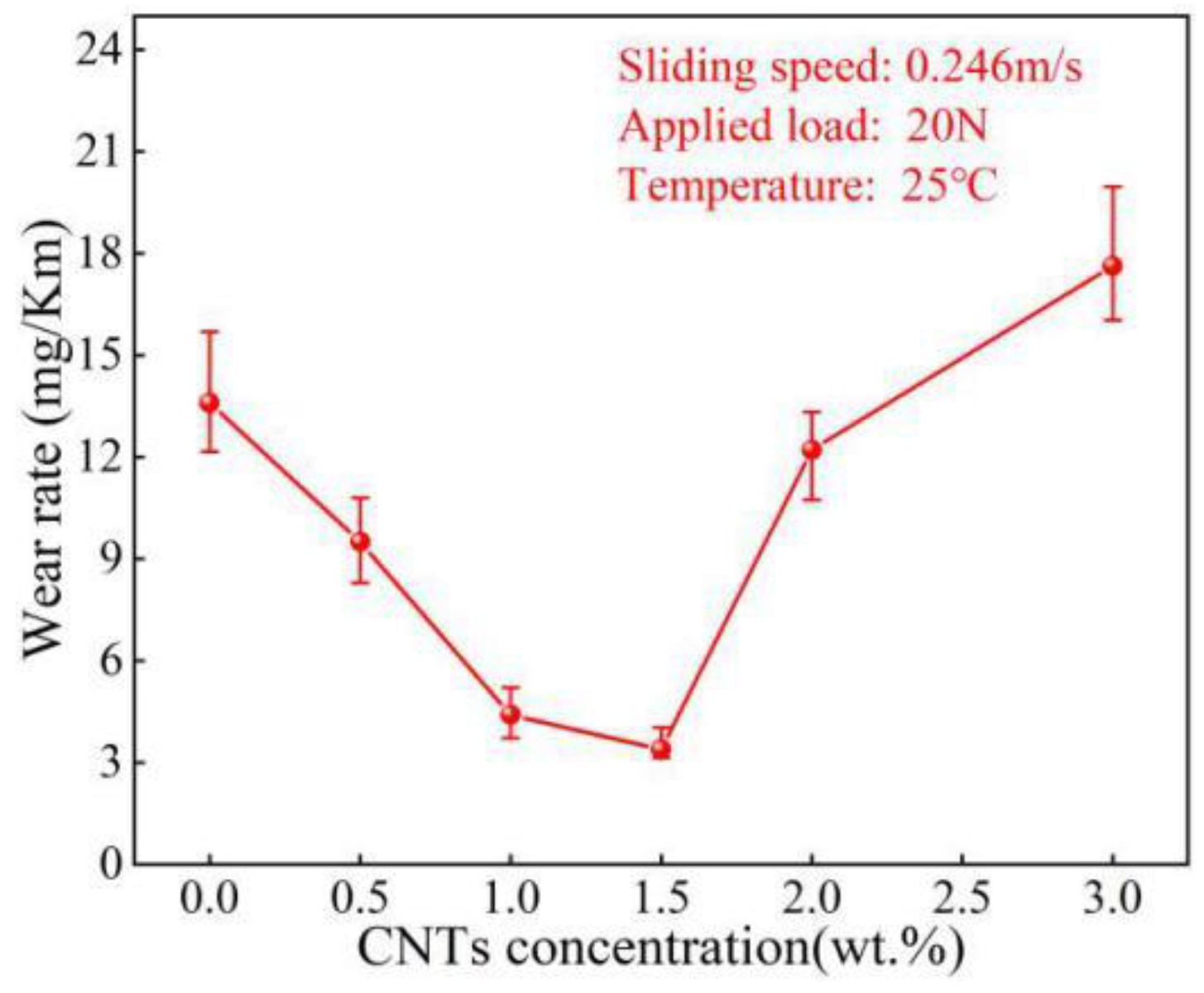
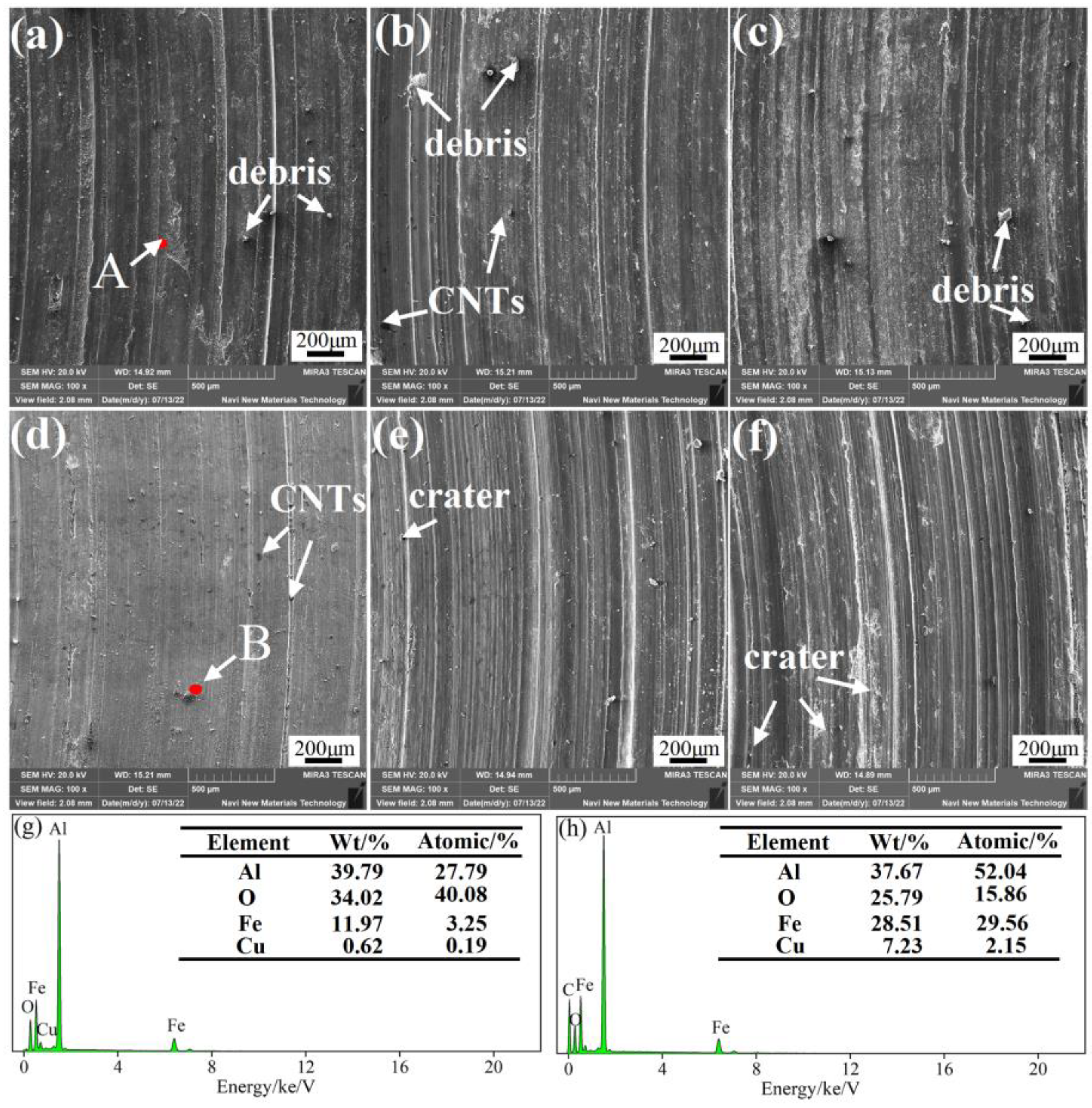
3.2. Tribological Behavior of CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si Nanocomposites
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- CNTs can pin the grain boundaries, hinder grain growth, and significantly refine the a-Al phase. As the content of CNTs increased from 0 to 3.0 wt%, the average grain diameter decreased from 150μm to 14μm. The addition of CNTs can considerably reduce the preferred orientation of the α-Al phase on the (111) lattice plane.
- (2)
- With the increase in the content of CNTs, the hardness of the hot-extruded CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si composite significantly increased. Moreover, the hardness increased by 62.2% compared with the Al-Cu-Mg-Si alloy when 3.0 wt% CNTs were added, reaching 157.7 HV.
- (3)
- With the increase in the content of CNTs, the degree of dynamic recrystallization of Al-Cu-Mg-Si alloy in hot extrusion gradually increased, the volume fraction of recrystallized grains increased from 1.3% to 68.3%, and the grain boundaries became clearer.
- (4)
- The friction and wear properties of x% CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si composites suggested that the friction coefficient and wear rate of the composites at 20 °C and 200 °C both decreased first and then increased with the increase in the content of CNTs. When the CNTs content was 1.5 wt%, the wear resistance of the composite was the best at 20 °C and 200 °C, and the COF was 30.09% and 73.03% lower than that of the Al-Cu-Mg-Si alloy. The main wear mechanism changed from adhesive wear to abrasive wear.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trojanowicz, M. Analytical applications of carbon nanotubes: A review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2006, 25, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Lin, Q.; Li, A. Preparation and characterization of carbon nanotubes/aluminum matrix composites. J. Shenyang Univ. 2013, 61, 1725–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cha, S.I.; Jung, S.I.; Lee, J.K.; Park, H.M.; Park, H.D.; Hong, S.H. Hardness and Wear Resistance of Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Aluminum-Copper Matrix Composites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 9134–9138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostovan, F.; Matori, K.A.; Toozandehjani, M.; Oskoueian, A.; Yusoff, H.M.; Yunus, R.; Mohamed Ariff, A.H. Nanomechanical Behavior of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Particulate Reinforced Aluminum Nanocomposites Prepared by Ball Milling. Materials 2016, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.T.; Li, Y.; He, J.L.; Zhang, Y.F. Influence of aging treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of CNTs/7075 Al composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 814, 152357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Tian, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y. Microstructure and wear characterization of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) reinforced aluminum matrix nanocomposites manufactured using selective laser melting—ScienceDirect. Wear 2020, 476, 203581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Wan, L.; Meng, X.; Xie, Y. Strengthening and toughening mechanisms of CNTs/Mg-6Zn composites via friction stir processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 732, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Bustamante, R.; Pérez-Bustamante, F.; Maldonado-Orozco, M.C.; Martínez-Sánchez, R. The effect of heat treatment on microstructure evolution in artificially aged carbon nanotube/Al2024 composites synthesized by mechanical alloying. Mater. Charact. 2017, 126, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y. Effect of CNTs content on the microstructures and properties of CNTs/Cu composite by microwave sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 771, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, N.; Bao, R.; Yi, J.; Tao, J.; Liu, Y.; Fang, D. Interface evolution and its influence on mechanical properties of CNTs/Cu-Ti composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 755, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Li, L.; Xi, S.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.; He, Y.; Zhou, R.; Jiang, Y. Enhanced combination of strength and ductility in the semi-solid rheocast hypereutectic Al Si alloy with the effect of in-situ TiB2 particles. Mater. Charact. 2021, 176, 111143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, J.; He, M.; Luo, Y.; Xiang, J. Understanding the Influencing Mechanism of Cnts on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Semi-Solid Stir Casting Al-Cu-Mg Alloys; Social Science Electronic Publishing: Rochester, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, D.H.; Cha, S.I.; Lim, B.K.; Park, H.M.; Han, D.S.; Hong, S.H. Synergistic strengthening by load transfer mechanism and grain refinement of CNT/Al–Cu composites. Carbon 2012, 50, 2417–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Han, Y.; Shi, Z.; Huang, G.; Zong, N.; Le, J.; Qiu, P.; Lu, W. Synergistic strengthening behavior and microstructural optimization of hybrid reinforced titanium matrix composites during thermomechanical processing—ScienceDirect. Mater. Charact. 2020, 168, 110527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, H.; Qi, L.; Tian, W.; Li, X.; Chao, X.; Wei, J. Fabrication and mechanical properties of CNTs/Mg composites prepared by combining friction stir processing and ultrasonic assisted extrusion. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 728, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.L.; Tan, M.J.; Guo, J.F.; Wei, J.; Chua, C.K. Dispersion of CNTs in Selective Laser Melting Printed AlSi10Mg Composites via Friction Stir Processing. Mater. Ence Forum 2016, 879, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.D.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, W.Q.; Shi, H.L.; Ding, C.; Hu, X.S.; Zheng, M.Y.; Wu, K. Effect of solidification on microstructures and mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes reinforced magnesium matrix composite. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Kondoh, K.; Li, J.S.; Qian, M.J.C.P.B.E. Extraordinary reinforcing effect of carbon nanotubes in aluminium matrix composites assisted by in-situ alumina nanoparticles. Composites 2020, 183, 107691.1–107691.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.D.; Wang, X.J.; Wu, K.; Liu, W.Q.; Xiang, S.L.; Ding, C.; Hu, X.S.; Zheng, M.Y. Distribution and integrity of carbon nanotubes in carbon nanotube/magnesium composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 612, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, G.S.; Baik, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, Y.Z. Friction and wear characteristics of the carbon nanotube-aluminum composites with different manufacturing conditions. Wear 2009, 267, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Kondoh, K.; Imai, H.; Umeda, J.; Takahashi, M. Simultaneously enhancing strength and ductility of carbon nanotube/aluminum composites by improving bonding conditions. Scr. Mater. 2016, 113, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basariya, M.R.; Srivastava, V.C.; Mukhopadhyay, N.K. Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum alloy composites produced by ball milling. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, A.; Hussain, M.A.; Khalid, F.A.; Bakhsh, N.; Hussain, A.; Kim, M.H. Mechanical characterization of copper coated carbon nanotubes reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Mater. Charact. 2013, 86, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Cha, S.I.; Hong, S.H. Effect of CNTs on precipitation hardening behavior of CNT/Al–Cu composites. Carbon 2012, 50, 4809–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yi, J.; Ni, S.; Du, Y.; Li, W.; Song, M. Enhancement of strength and ductility by interfacial nano-decoration in carbon nanotube/aluminum matrix composites. Carbon 2019, 159, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, B.; Ma, Z. Optimization and simulation of deformation parameters of SiC/2009Al composites. Acta Metall. Sin. 2019, 55, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, X.; Cen, X.; Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Song, M.; Ni, S.; Yi, J.; Shen, T.; Du, Y. Enhanced mechanical properties of aluminum based composites reinforced by chemically oxidized carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2018, 139, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Gao, Y.; Xu, F.; Yang, S.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, Q. An investigation on grain refinement mechanism of TiB2 particulate reinforced AZ91 composites and its effect on mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 780, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toozandehjani, M.; Matori, K.A.; Ostovan, F.; Jamaludin, K.R.; Amrin, A.; Shafiei, E. The Effect of the Addition of CNTs on the Microstructure, Densification and Mechanical Behavior in Al-CNT-Al2O3 Hybrid Nanocomposites. JOM J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2020, 72, 2283–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xi, S.; Ma, G.; Xiao, Y.; Li, L.; Yuan, Z.; He, Y.; Zhou, R.; Jiang, Y. Understanding the influencing mechanism of sub-micron sized TiB 2p on the microstructures and properties of rheological squeeze casting hypereutectic Al–Si alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.G.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, H.X.; Zhang, F.; Li, D.Q.; Midson, S.P. Microstructural evolution and thixoformability of semi-solid aluminum 319s alloy during re-melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 649, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qutub, A.M.; Khalil, A.; Saheb, N.; Hakeem, A.S. Wear and friction behavior of Al6061 alloy reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Wear 2013, 297, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, V.C.; Prewo, K.M. On the strength of discontinuous silicon carbide reinforced aluminum composites. Scr. Metall. 1986, 20, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Rao, X.; Dai, D.; Ma, C.; Xi, L.; Lin, K. Laser additive manufacturing of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) reinforced aluminum matrix nanocomposites: Processing optimization, microstructure evolution and mechanical properties. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 29, 100801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, E.; Li, J.; He, C.; Zhao, N. Investigation of the evolution and strengthening effect of aluminum carbide for in-situ preparation of carbon nanosheets/aluminum composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 764, 138139.1–138139.8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Feng, K.; Li, Z.; Kokawa, H. Effects of in-situ synthesized TiB2 on crystallographic orientation, grain size and nanohardness of AA6061 alloy by laser surface alloying. Mater. Lett. 2019, 253, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, S.; Ma, G.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, R.; Jiang, Y. Investigate on the phase interfaces and performance evaluation of TiB2p/Al-Si-Cu-Zn (T6) composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
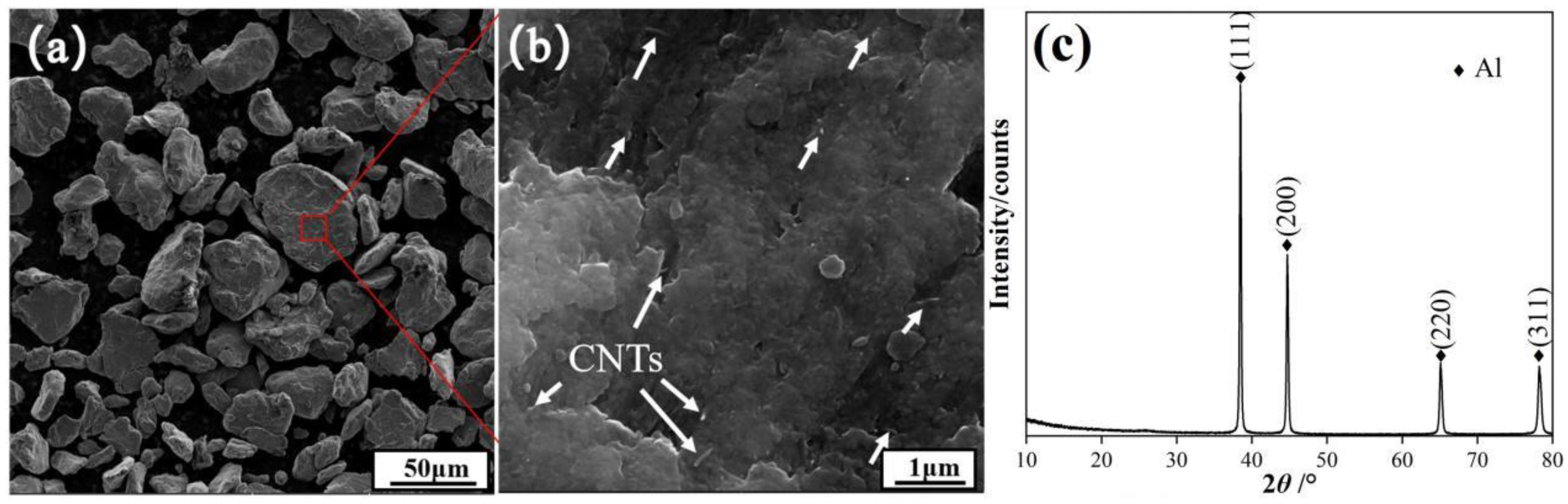







| Experimental Material | C | Cu | Mg | Si | Fe | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 wt%CNTs/Al composite | 6.231 | 0 | 0 | 0.037 | 0.598 | Balance |
| Al-Cu-Mg-Si alloy | 0.012 | 1.437 | 0.834 | 0.942 | 0.014 | Balance |
| 0.5 wt%CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si composite | 0.492 | 1.324 | 0.780 | 0.897 | 0.275 | Balance |
| 1.0 wt%CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si composite | 1.014 | 1.368 | 0.763 | 0.913 | 0.304 | Balance |
| 1.5 wt%CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si composite | 1.442 | 1.402 | 0.802 | 0.924 | 0.387 | Balance |
| 2.0 wt%CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si composite | 1.917 | 1.436 | 0.814 | 0.873 | 0.395 | Balance |
| 3.0 wt%CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si composite | 2.843 | 1.316 | 0.796 | 0.891 | 0.420 | Balance |
| XRD Parameters | Standard | Al-Cu-Mg-Si Alloy | 0.5CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si | 1.5CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si | 3.0CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2θ (deg.) (111) | 38.474 | 38.48615 | 38.51241 | 38.39424 | 38.49302 |
| Intensity (CPS) | 100 | 1,039,711 | 296,694 | 227,350 | 8282 |
| FWHM (deg.) | 0.141 | 0.167 | 0.169 | 0.224 | |
| 2θ (deg.) (200) | 44.722 | 44.7099 | 44.73616 | 44.65738 | 44.72303 |
| Intensity (CPS) | 45.5 | 80,285 | 28,001 | 43,753 | 4277 |
| FWHM(deg.) | 0.171 | 0.176 | 0.228 | 0.257 | |
| 2θ (deg.) (220) | 65.099 | 65.04871 | 65.16689 | 65.06184 | 65.11436 |
| Intensity (CPS) | 23.3 | 153 | 395 | 221 | 1727 |
| FWHM (deg.) | 0.460 | 0.448 | 0.429 | 0.346 |
| Material | Theoretical Density (g/cm3) | Relative Density (g/cm3) | Density (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Cu-Mg-Si alloy | 2.769 | 2.766 | 99.89 |
| 0.5CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si composite | 2.766 | 2.759 | 99.74 |
| 1.0CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si composite | 2.762 | 2.748 | 99.49 |
| 1.5CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si composite | 2.759 | 2.738 | 99.24 |
| 2.0CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si composite | 2.756 | 2.719 | 98.66 |
| 3.0CNTs/Al-Cu-Mg-Si composite | 2.749 | 2.670 | 97.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Tan, F.; Liu, K. Understanding the Influencing Mechanism of CNTs on the Microstructures and Wear Characterization of Semi-Solid Stir Casting Al-Cu-Mg-Si Alloys. Metals 2022, 12, 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122171
Wang L, Zhang Z, Luo Y, Xiao Y, Tan F, Liu K. Understanding the Influencing Mechanism of CNTs on the Microstructures and Wear Characterization of Semi-Solid Stir Casting Al-Cu-Mg-Si Alloys. Metals. 2022; 12(12):2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122171
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Li, Zhenlin Zhang, Yajun Luo, Ying Xiao, Fengliang Tan, and Kecai Liu. 2022. "Understanding the Influencing Mechanism of CNTs on the Microstructures and Wear Characterization of Semi-Solid Stir Casting Al-Cu-Mg-Si Alloys" Metals 12, no. 12: 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122171
APA StyleWang, L., Zhang, Z., Luo, Y., Xiao, Y., Tan, F., & Liu, K. (2022). Understanding the Influencing Mechanism of CNTs on the Microstructures and Wear Characterization of Semi-Solid Stir Casting Al-Cu-Mg-Si Alloys. Metals, 12(12), 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122171




