Research Progress on Injection Technology in Converter Steelmaking Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Top Blowing Element Types and Applications
2.1. Conventional Supersonic Oxygen Lance
2.2. Coherent Jet Oxygen Lance
2.3. Nozzle-Twisted Oxygen Lance
2.4. Secondary Combustion Oxygen Lance
2.5. Double-Parameter Oxygen Lance
3. Combined Blowing Process and Bottom Blowing Element Types
3.1. Combined Blowing Process
3.2. Bottom Blowing Element Types
3.2.1. Nozzle Type Element
3.2.2. Brick Type Element
4. Injection Medium Types and Applications
4.1. Oxygen Injection
4.2. Inert Gas Injection
4.3. Carbon Dioxide Injection
4.4. Powder Injection
5. Development Direction of Injecting Technology
5.1. High Efficiency
5.2. Reduce Environmental Burden
5.3. Long Life
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, L.; Yu, Z.X.; Xiao, Z.M. Development and prospects of converter steelmaking technology. China Metall. 2001, 1, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Nilles, P. Present Status and Developments of Oxygen Steelmaking in Western Europe. Radex Rundsch. 1987, 75, 426–437. [Google Scholar]
- Schlautmann, M.; Kleimt, B.; Teiter, T.; Schnabel, S.; Ponten, H.J. Model-based dynamic monitoring and end-point control of converter process. In Proceedings of the 6th European Oxygen Steelmaking Conference (EOSC), Stockholm, Sweden, 7–9 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Berthet, A.; Cesselin, P. Present State of Development of Oxygen Steelmaking Plant: Review of the International Congress on Oxygen Steelmaking (Strasbourg, June 1984). In Proceedings of the Journees Siderurgiques (Steelmaking Meeting) ATS 1984, Strasbourg, Germany, June 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.J. Research on Dynamic Conditions of Full Campaign Life and Furnace Lining Evolution during the 300 t Converter Steelmaking Process. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, E.; Pirklbauer, W.; Antlinger, K. The economics of modern LD-steelmaking. In Proceedings of the EOSC’97: 2nd European Oxygen Steelmaking Congress, Taranto, Italy, 13–15 October 1997; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Primas, K.; Hubner, F.; Krieger, W.; Poferl, G. Development and Application of Advanced BOF-Steelmaking Technology at Voest-Alpine’s Linz Works, Austria. Steelmak. Proc. 1986, 69, 563–571. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, J.Q.; Yang, L.B.; Wang, C.Y. Fine control technology and its co-optimization of converter steelmaking. Iron Steel 2022, 57, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Hu, Z.Y.; Chen, X.H. Production practice of high-quality tire cord steel with BOF steelmaking process in NISCO. China Metall. 2018, 28, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, D.H. Interpretation of the development of converter steelmaking production technology. China Steel Focus 2019, 21, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, Y.H. Development and application of intelligent steelmaking model in converter. Tianjin Metall. 2019, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.B.; Zeng, J.Q.; Deng, Y.; Xu, X.W.; Wu, L.P. Highly efficiency and long-life combined blowing technology of big converter. Iron Steel 2020, 55, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.Y. Review of progress of steelmaking technology in the first decade of the new century and outlook in the “12th five-year development” period. Steelmaking 2012, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. Key production-technology for high-quality special steels. Iron Steel 2018, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.F.; Pan, Y.F. Oxygen Lance Technology for Steelmaking; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Chen, W. Trends and development of steel demand in China: A bottom-up analysis. Resour. Policy 2013, 38, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Feng, L.H.; Han, R.Z. Experimental study on oxygen lance flow field of convergent jet. Metal. Int. 2012, 17, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Matti, J.L.; Timo, M.; Juhani, F.; Esa, O.V. Splashing and spitting behaviour in the combined blown steel-making converter. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2002, 42, 944–949. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.Q.; Pan, Y.F.; Wang, L.P.; Liang, Z.; Li, S.Q. Further understanding of theories and practice for low-cost and high-efficient clean steel production by combined blowing converter. Iron Steel 2014, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.H.; He, Y.; Shi, G.M. Mathematical modeling of fluid flow in bath during combined side and top blowing AOD refining process of stainless steel: Mathematical model of the fluid flow. Steel Res. Int. 2011, 82, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhu, L.G.; Zhou, Q.L. Numerical simulation of high Mach number oxygen lance under high oxygen pressure. Iron Steel 2019, 54, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.Y.; Feng, C.; Wang, M.L.; Lv, Y.H.; Hu, Y.B.; Peng, X.Y. Water model experiment of high supplying oxygen blowing in large converter. J. Iron Steel Res. 2017, 29, 807–815. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.Y.; Zhu, R.; Dong, K. Numerical simulation research on flow fields in combined blown converter at steelmaking temperature. Chin. J. Eng. 2018, 40, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, R.; Gu, Y.L.; Wang, C.J. Behaviours of supersonic oxygen jet injected from four-hole lance during top-blown converter steelmaking process. Can. Metall. Q. 2014, 53, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambasivam, R.; Lenka, S.N.; Durst, F.; Ajmani, S.K. A new lance design for BOF steelmaking. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2007, 38, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Li, Q.; Kuang, S.B.; Zou, Z.S. Coalescence characteristics of supersonic jets from multi-nozzle oxygen lance in steelmaking BOF. Steel Res. Int. 2015, 86, 1517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Chen, W. Numerical simulation of three-phase flow in a top-blown converter with a 4-hole oxygen lance. Iron Steel Vanadium Titan. 2016, 37, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lou, W.T.; Zhu, M.Y. Numerical simulation of gas and liquid flow in steelmaking converter with top and bottom combined blowing. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2013, 40, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.L. Modeling of Gas-Slag-Metal Multiphase Fluid during Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Process. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Balkos, T.; Batham, J.; Russo, T.; Fash, R.; Howanski, B. Cold shroud-boosting converter performance. In Proceedings of the 6th European Oxygen Steelmaking Conference, Aachen, Germany, 26–28 June 2006; pp. 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.F. Numerical simulation of multiphase flow in converter top blowing process. China Metall. 2018, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, K.; Zhu, R.; He, C.L.; Wei, X.Y.; Liu, F.H. Numerical simulation of three-phase flow in an oxygen top-blown converter. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2011, 11, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.H.; Hu, Z.Y.; Zhu, R.; Liu, F.H.; Yao, L.J.; Feng, Q. Simulation and application research about the flow field characteristic for top-blowing lance in 110t converter steelmaking process. Henan Metall. 2019, 27, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhou, Q.L. Numerical simulation and optimization practice of high Mach oxygen lance. Steelmaking 2018, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, M.; Chen, S.P.; Li, H.; Guo, H.M.; Li, J.K.; Li, T. Effect of the wear of supersonic oxygen lance on the stirring characteristics and metallurgical effects in the converter steelmaking process. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Sun, D.; Zhu, R.; Zhao, F.; Ke, J. Effect of nozzle twisted oxygen lance on flow field and dephosphorisation rate in converter steelmaking process. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2017, 44, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokako, J.I.; Ishii, R.; Fujimoto, H.; Hatta, N.; Umeda, Y. Numerical study on supersonic flows of gas-liquid particle mixtures in a De laval nozzle. ISIJ Int. 1989, 29, 911–918. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.C.; Han, T. Gas-particle flow in a De laval nozzle with curved convergent configuration. ISIJ Int. 1996, 36, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.S.; Zhu, R.; Chen, S.J.; Liu, F.H.; Dong, K.; Yao, L.J. Flow field characteristics of a coherent jet using various lance tip structures. Chin. J. Eng. 2020, 42, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.S. Simulation study of converter coherent jet oxygen lance. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 1335, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.B.; Liang, H.K.; Feng, L.H.; Liu, G.L. Simulation study on the jet characteristics of coherent jet oxygen lance used in basic oxygen furnace (BOF). Metalurgija 2018, 57, 223–225. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, R. Effect of shrouding oxygen temperature on characteristics of supersonic oxygen jet. China Metall. 2016, 26, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.H.; Zhu, R.; Jiao, Y.L. Numerical simulation on high temperature oxygen stream field of coherent jet oxygen lance. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2009, 9, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Liang, H.K.; Feng, L.H.; Liu, G.L. Comparative study between traditional and coherent jet oxygen lance interaction with molten pool. Metalurgija 2018, 57, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, M.; Zhu, R. Research on coherent jet oxygen lance in BOF steelmaking process. Metall. Res. Technol. 2019, 116, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.F.; Xu, A.J.; Li, J.S.; Bao, Y.P.; Gu, K.J.; Gu, Y.Z.; Xu, H.R.; Yang, H.P.; Wang, C.H.; Wang, A.J.; et al. Characteristics of swirl-flow oxygen lance and analysis of its application slag splashing technology. Iron Steel 1998, 33, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, Y.; Tago, Y. Effect of nozzle twisted lance on jet behavior and spitting rate in top blown process. ISIJ Int. 2003, 43, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.J.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, D.S.; Yuan, Z.F. Application of φ168 cyclone-lance nozzle in BOF steelmaking. Res. Iron Steel 1998, 2, 8–9 + 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kadrolkar, A.; Dogan, N. Model development for refining rates in oxygen steelmaking: Impact and slag-metal bulk zones. Metals 2019, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z. Application and practice of new swirl oxygen lance nozzle in 120 t converter. Steelmaking 2019, 35, 6–11; discussion 59. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.X.; Li, C.L.; Wang, X.J.; Li, G.J. 6t converter rotary flow oxygen lance flow unit dynamic pressure and velocity decay law. Henan Metall. 1996, 2, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.M.; Li, Q.; Zou, Z.S.; An, X.Z. Computational investigation of swirling supersonic jets generated through a nozzle-twisted lance. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2017, 48, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, M.M.; Shao, L.; Li, Q.; Zou, Z.S. Physical and mathematical modeling of swirling gas jets impinging onto a liquid bath using a novel nozzles-twisted lance. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 91, 1900684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, M.M.; Li, Q.; Zou, Z.S. Melt splashing behavior of steelmaking converter with nozzle-twisted lance. Iron Steel 2020, 55, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Lu, J.; Li, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, R.; Fan, X.; Lin, H.; Huang, Y.; Tan, D. Optimized scheme for accelerating the slagging reaction and slag-metal-gas emulsification in a basic oxygen furnace. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Li, H.; Lin, T.C.; Xie, K.; Xue, K. Behavior of gas–slag–metal emulsion with nozzle–twisted lance in converter steelmaking process. Steel Res. Int. 2021, 92, 2100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Research on the Technology of Secondary Combustion Oxygen Gun of 180 t Converter. Master’s Thesis, Northeastern University, Shenyang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Du, F. Secondary combustion oxygen gun to prevent the converter from sticking to cold steel. Shanghai Met. 2003, 4, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.G.; Zhu, M.Y. Research progress of oxygen lance technology for secondary combustion in converter. Angang Technol. 2021, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.C.; Li, R.Z. Development of single circuit and dual-flow oxygen lance nozzle for 150 t BOF at anshan iron and steel co. Iron Steel 1989, 24, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.Y.; Zhang, D.M.; Liu, Z.C.; Chen, E. Development and application of converter oxygen lance with post-combustion. Iron Steel 1994, 29, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.Y.; Liu, J.J. Application of national and international technology of lance for converter secondary burning. Steelmaking 1998, 2, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Tu, H.; Cai, Z.P. Development of secondary combustion technology for top and bottom combined blowing converter. Steelmaking 1987, 2, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.Q.; Li, J.N.; Guo, L.X.; Pang, H.X.; Liu, K. Industrial experiment of six-hole dual-structure oxygen lance for large and medium-sized converters. J. Dezhou Univ. 2021, 37, 35–38; discussion 46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.X.; Liu, G.Q.; Liu, K.; Li, H.X. Water model experiment on interaction between innovated double-structure oxygen lance and converter molten pool. Special Steel 2020, 41, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.F.; Yang, X.; Lu, Z.X.; Huang, J.N.; Pan, Y.F.; Ma, E.X. Jet behavior and metallurgical performance of innovated double-parameter oxygen lance in BOF. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2007, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Zeng, Y.N.; Wang, J.Q.; Han, Z.J. Simulation of flow field of oxygen lance gas jet utilized for 50 t converter. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2011, 18, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.L.; Li, J.G.; Feng, S. Numerical simulation of death zones in bath under impact of variable angle oxygen lances. Iron Steel Vanadium Titan. 2014, 35, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.Q.; Liu, K.; Han, P. Metallurgical performance of innovative double-parameter oxygen lance in BOF steelmaking. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2021, 48, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.Z.; Feng, S.; Zeng, Y.N.; Li, J.G. Effect of orifice spacing on the impact area of molten bath under gas jet sprayed from oxygen lance. Iron Steel Vanadium Titan. 2016, 37, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.Q.; Zhu, G.Q.; Zhang, G.X.; Liu, K.; Li, H.X. Industrial experiment of new type double-structure oxygen lance for 260 t converter. Spec. Steel 2020, 41, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.F.; Yang, W.Y.; Wu, Y.M.; Wang, M.L.; Li, H.T.; Hu, Y.B. High oxygen supply intensity steelmaking with dual-angle oxygen lance nozzle in large converter. Iron Steel 2021, 56, 62–73. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Zhu, R.; Han, B.C.; Yao, L.J.; Wu, W.H.; Wei, G.S.; Dong, J.F.; Jiang, J.J.; Hu, S.Y. Effect of nozzle exit wear on the fluid flow characteristics of supersonic oxygen lance. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2020, 51, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odentha, H.J.; Falkenreck, U.; Kempken, J.; Schlüter, J.; Uebber, N. CFD simulation of melt flow mixing phenomena in combined blowing converters. In Proceedings of the 6th European Oxygen Steelmaking Conference, Aachen, Germany, 26–28 June 2006; pp. 454–466. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.F.; Li, J.S.; Tian, D.F.; Ding, X.M. Study on the bottom tuyere configuration of a 150 t vanadium extraction converter using cold model. Ind. Heat. 2011, 40, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Hu, J.X. Status of research and application of plug for combined blown converter in China and its trend of development. China Metall. 2012, 22, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.M.; Lv, S.H.; Ma, C.X.; Zhao, G.; Qi, C.J.; Qiao, C.G.; Lv, T.F.; Wei, S.Y.; Xu, G.F. GOR Converter Top and Bottom Combined Blowing Stainless Steel Smelting Technology; Shandong Taishan Iron and Steel Group Co., Ltd.: Laiwu, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, H.; Liu, J.L. Transformation of bottom blowing gas supply system in 180t converter of hot sheet rolling company. Tianjin Metall. 2020, 1, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Wu, W.; Yang, L.B.; Zhao, K.; Luo, Q.L.; Jiang, Z.H. Control model of gas supply system of bottom blowing for 120 t converter and application effect. Spec. Steel 2020, 41, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.L.; Zhang, W.Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Yang, J.W.; Chen, W.; Ma, J.W.; Wen, Y.B. Optimization and practice on top and bottom combined blowing process of 120 t converter with high strength and long life time. Yunnan Metall. 2021, 50, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, W.; Wu, L.; You, X.M.; He, C.L. Study on MHP selection in converter bottom blowing. Steelmaking 2018, 34, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.Z. The Study on the Technology of BOF Oxygen Supply and Model Development. Master’s Thesis, Anhui University of Technology, Maanshan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Tong, F.Q.; Wei, Z.Q.; Han, Z.K. The BOF smelting process of the whole process bottom blowing N2 [A]. In Proceedings of the 8th (2011) China Steel Annual Conference, Beijing, China, 26–28 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, X.D.; Qiao, W. Influence of nitrogen and argon switching on nitrogen mass fraction in converter bottom blowing. China Metall. 2019, 29, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Han, B.C.; Dong, K.; Wei, G.S. A review of carbon dioxide disposal technology in the converter steelmaking process. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, E.P.; Ikäheimonen, T.; Mattila, O.; Fabritius, T.; Visuri, V.V. Behaviour of silicon, carbon and chromium in the ferrochrome converter-a comparison between CTD and process samples. In Proceedings of the EOSC 2011 6th European Oxygen Steelmaking Conference, Stockholm, Sweden, 7–9 September 2011; pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Keskinkilic, E. New trends in basic oxygen furnace dephosphorization. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2020, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhu, R.; Dong, K.; Wei, G.S.; Han, B.C.; Li, W.F.; Wu, W.H. Effects of nozzle layout and parameters on the jet characteristics of a CO2 + O2 mixed oxygen Lance. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wei, G.; Zhu, R.; Wu, W.; Jiang, J.J.; Feng, C.; Dong, J.F.; Hu, S.Y.; Liu, R.Z. Utilization of carbon dioxide injection in BOF-RH steelmaking process. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 34, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Zhu, R.; Yang, L.Z. High efficiency dephosphorization by mixed injection during steelmaking process. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1800454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.S.; Zhu, R.; Yang, S.F.; Hu, S.Y.; Yang, L.Z.; Chen, F.W. Carbon Powder Mixed Injection with a Shrouding Supersonic Oxygen Jet in Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking. Metall. Mater. Trans. B-Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2020, 51, 2298–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.F. Development history and future prospects of steelmaking(1)—Development history. Iron Steel. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.P. 40 years of LD converter steelmaking—Development, achievements and prospects. Shanxi Metall. 1994, 1, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Q.Z.; Su, T.N.; Liu, K.W. Experiment on technique of dephosphorization with powder injection in LD converter. Iron Steel 1983, 3, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, H.; Qi, S.K.; Deng, K.W. Blowing pre-treated hot metal containing 3% P in oxygen bottom-blowing converter with lime powder injection. Iron Steel 1982, 8, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Wang, X.M.; Zou, Z.S.; Sun, G.Q. Physical simulation of BOF limestone particles blowing via top lance. J. Northeast. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2014, 35, 695–699. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; He, Y.B.; Zou, Z.S.; Yu, A.B. Physical simulation of bottom powder injection in combined blown converter. J. Northeast. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2014, 35, 236–240. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Q.; Cai, J. Water modeling experiment on bottom lime injection base fluxes with oxygen into combined blown converter. Iron Steel 2020, 55, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, R.; Wei, G.S. Application of submerged gas-powder injection technology to steelmaking and ladle refining processes. Powder Technol. 2021, 389, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, R.; Hu, S.Y.; Li, W.F. Study on metallurgical characteristics of the bottom-blown O2-CaO converter. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2021, 48, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.G.; Lv, M.; Zhu, R.; Bao, X.; Zhang, X.L.; Gao, H. Water simulation on vanadium extraction by powder injection in 150 t converter. Iron Steel 2012, 47, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.J.; Wang, Z.G.; Ning, W. Research and application of high efficiency smelting technology with single slag retaining in converter. Ind. Heat. 2021, 50, 12–14; discussion 22. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.P.; Yu, F. Study on high efficiency smelting process of 120 t converter. Hebei Metall. 2021, 07, 46–49; discussion 74. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.C.; Li, H.; Guo, J.X.; Gu, B.H.; Zeng, Y. Energy-saving and emission-reduction technology selection and CO2 emission reduction potential of China’s iron and steel industry under energy substitution policy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.L.; Kong, Y.L.; Niu, C. Influence of Different oxygen lance nozzle structures on oxygen lance life. Auto Time 2022, 16, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.Z. Improved service life of converter bottom-blowing elements. China New Telecommun. 2019, 21, 236. [Google Scholar]

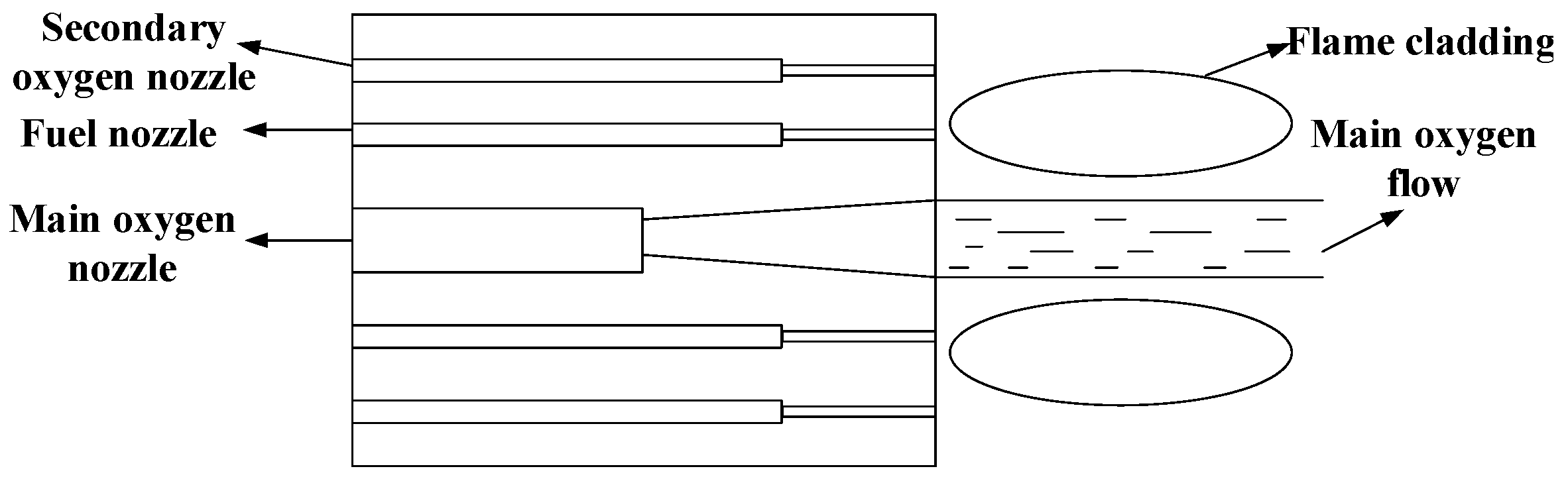




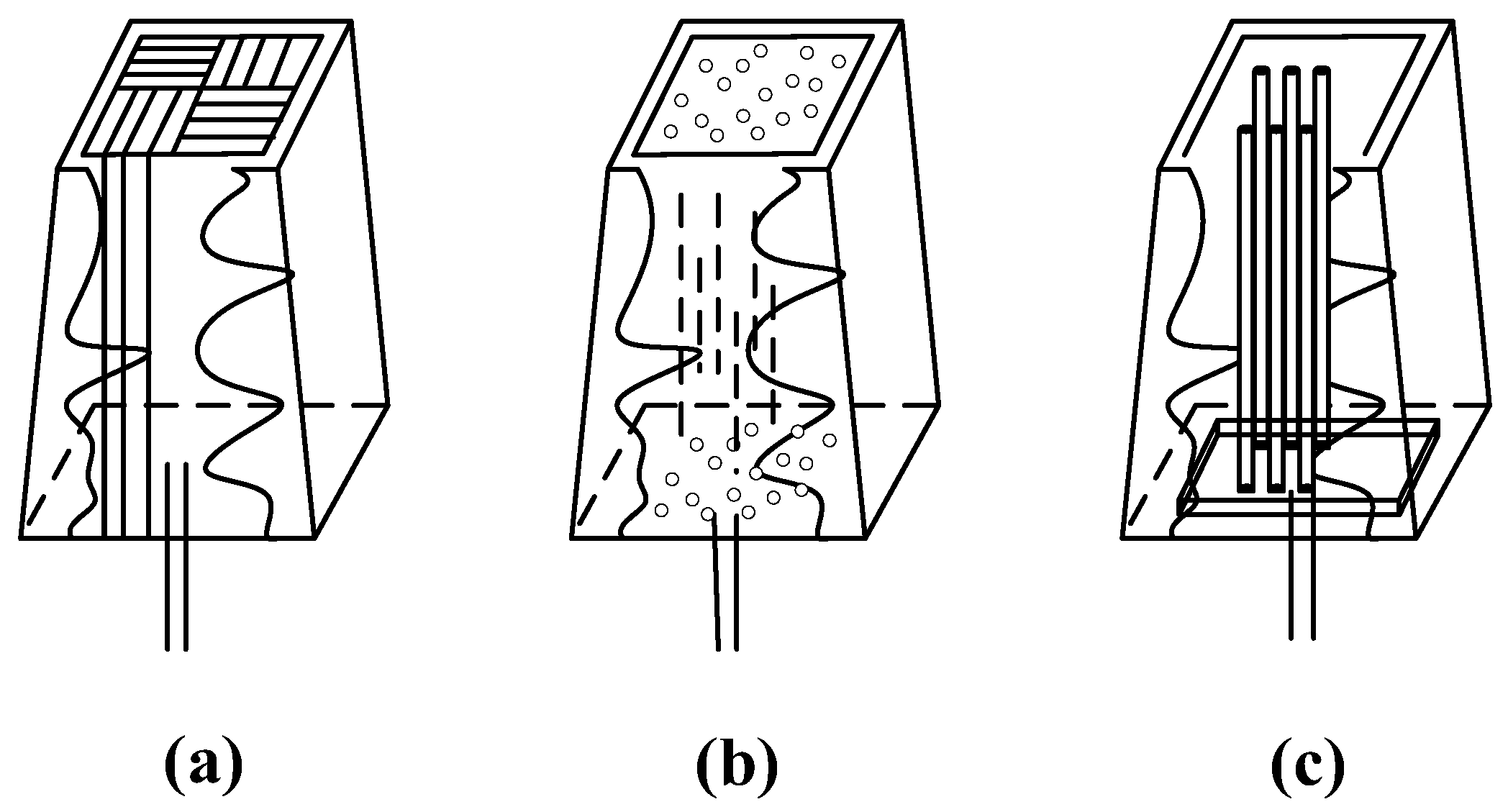
| Production Method | Casting Method | Forging Method | Assembling Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advantages | The oxygen lance has long life, good performance and high production efficiency | Simple processing method and good thermal conductivity | Reasonable nozzle structure, good water-cooling effect, long life |
| Disadvantages | Easy to produce casting defects such as porosity and cracks | Short life of oxygen lance nozzles | High precision is required and the manufacturing process is complex |
| Research Methodology | Research Aspects | Specific Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Numerical simulation | Jet dynamics parameters | Study the attenuation law of kinetic parameters, such as jet velocity, dynamic pressure, and Mach number. |
| Jet impact characteristics | Study the impact effect of jets on the molten bath through parameters such as impact depth and impact radius. | |
| Molten bath stirring effect | Analysis of the molten bath velocity distribution pattern. | |
| Furnace lining erosion pattern | Study of furnace lining erosion patterns by shear stress distribution and turbulent kinetic energy. | |
| Water Simulation | Oxygen lance operating parameters | Study the effects of oxygen lance flow rate, lance height, and inlet pressure on jet behavior. |
| Impact dent size | Study on the morphology of impact dents and molten bath splashes. | |
| Mixing effect | Study on the mixing effect of the molten bath by mixing time. |
| Testers | Test Contents | Test Results |
|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. [33] | Optimized oxygen lance; increased nozzle hole angle and oxygen flow rate | The average smelting time and the end-point [%C]· [%O] decreased by 1.5 min and 0.0003, respectively; the dephosphorization rate increased by 4.1% and T.Fe content decreased by 1.7%. |
| Zhang et al. [34] | Increased nozzle hole angle and Mach number | Reduced the splashing rate, end-point [%C]· [%O], and T.Fe content by 5%, 0.0005 and 3.2%, respectively. |
| Lv et al. [35] | The effect of oxygen lance nozzle outlet wear angle on metallurgical effects was studied | The phosphorus content, end-point [%C]· [%O], and T.Fe content increased from 0.029%, 0.0023, and 12.92% to 0.032%, 0.0028, and 14.58%, respectively. |
| Liu et al. [36] | Studied the stirring ability and flow field characteristics of a conventional and nozzle-twisted oxygen lance | It showed that the 8° oxygen lance could stir molten better during the steelmaking process for the 120 t dephosphorization converter. These findings agree well with the experimental results of water experiments and numerical simulations. |
| Classification | Top Blowing Oxygen, Bottom Blowing Inert Gas Process | Combined Oxygen Blowing Process | Top-Bottom Oxygen Blowing, Fuel Injection Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Features | The bottom blowing gas is N2, Ar and CO2, and other weak oxidizing gases, and bottom-blowing intensity is roughly 0.3 m3/(t·min) or less. The purpose of which is to strengthen molten bath stirring. | This process refers to the simultaneous blowing of oxygen at the top and bottom, which is an intensive refining type of combined blowing process. | This technology refers to top blowing oxygen and bottom blowing or side-blowing oxygen, while bottom blowing into the fuel, which is used to increase scrap types in the combined blowing process. |
| Representative processes | LBE, LD-KG, LD-OTB, NK-CB, LD-AB | BSC-BAP, LD-OB, LD-HC, STB, STB-P, K-BOP | OBM-S, KMS, KS |
| Name | Dispersion-Type Breathable Brick | Single Tube Type | Sleeve Type | Circular Seam Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Features | Multiple metal capillary tubes buried in refractories | A large diameter metal tube buried in refractories | Hollow straight circular tube and outer ring seam tube buried in refractories | Center tube filled with refractories, outer ring seam tube buried in refractories |
| Blockage condition | Easily blocked | Extremely easy to block | The central tube is easily clogged | Not easy to block |
| Element life/heat | 2000–2500 | 100–200 | 2000 | More than 10,000 |
| Flow rate adjustment range | 2–3 times | 2–3 times | 10 times | More than 10 times |
| Mushroom head cooling capacity | Weak | Weaker | Stronger | Strong |
| Gas Type | N2 | Ar | CO2 | CO | O2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advantages | N2 is the cheapest of the inert gases | It not only ensures the stirring effect of the molten bath, but also has no adverse effect on the quality of the molten steel | Reacts with C in the molten bath and produces CO gas equal to twice the volume of CO2, which facilitates the stirring of the molten bath | CO has good physical cooling properties and its metallurgical effect is comparable to that of Ar | When O2 is used as the bottom blowing gas source, its dosage should preferably not exceed 10% of the total oxygen supply |
| Disadvantages | Bottom-blowing N2 throughout the blowing process increases the nitrogen content of molten steel | Limited Ar resources and expensive Ar production equipment | Damage to the carbon gas supply elements | CO is highly toxic and has an explosion risk | Some erosion of the gas supply elements |
| Steel Mills | Converter Capacity/t | Oxygen Supply Intensity/Nm3·(t−1·min−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Weiyuan steel mill | 55 | 4.3 |
| Taiyuan Second Steelmaking | 80 | 4.1 |
| LY Steel | 90 | 4.2 |
| Long Steel Company | 120 | 4.5 |
| Baosteel Second Steelmaking | 250 | 3.33 |
| Baosteel One Steelmaking | 300 | 3.78 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, M.; Chen, S.; Yang, L.; Wei, G. Research Progress on Injection Technology in Converter Steelmaking Process. Metals 2022, 12, 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111918
Lv M, Chen S, Yang L, Wei G. Research Progress on Injection Technology in Converter Steelmaking Process. Metals. 2022; 12(11):1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111918
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Ming, Shuangping Chen, Lingzhi Yang, and Guangsheng Wei. 2022. "Research Progress on Injection Technology in Converter Steelmaking Process" Metals 12, no. 11: 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111918
APA StyleLv, M., Chen, S., Yang, L., & Wei, G. (2022). Research Progress on Injection Technology in Converter Steelmaking Process. Metals, 12(11), 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111918









