Effective Extraction of Vanadium from Bauxite-Type Vanadium Ore Using Roasting and Leaching
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Experimental
2.3. Analysis and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
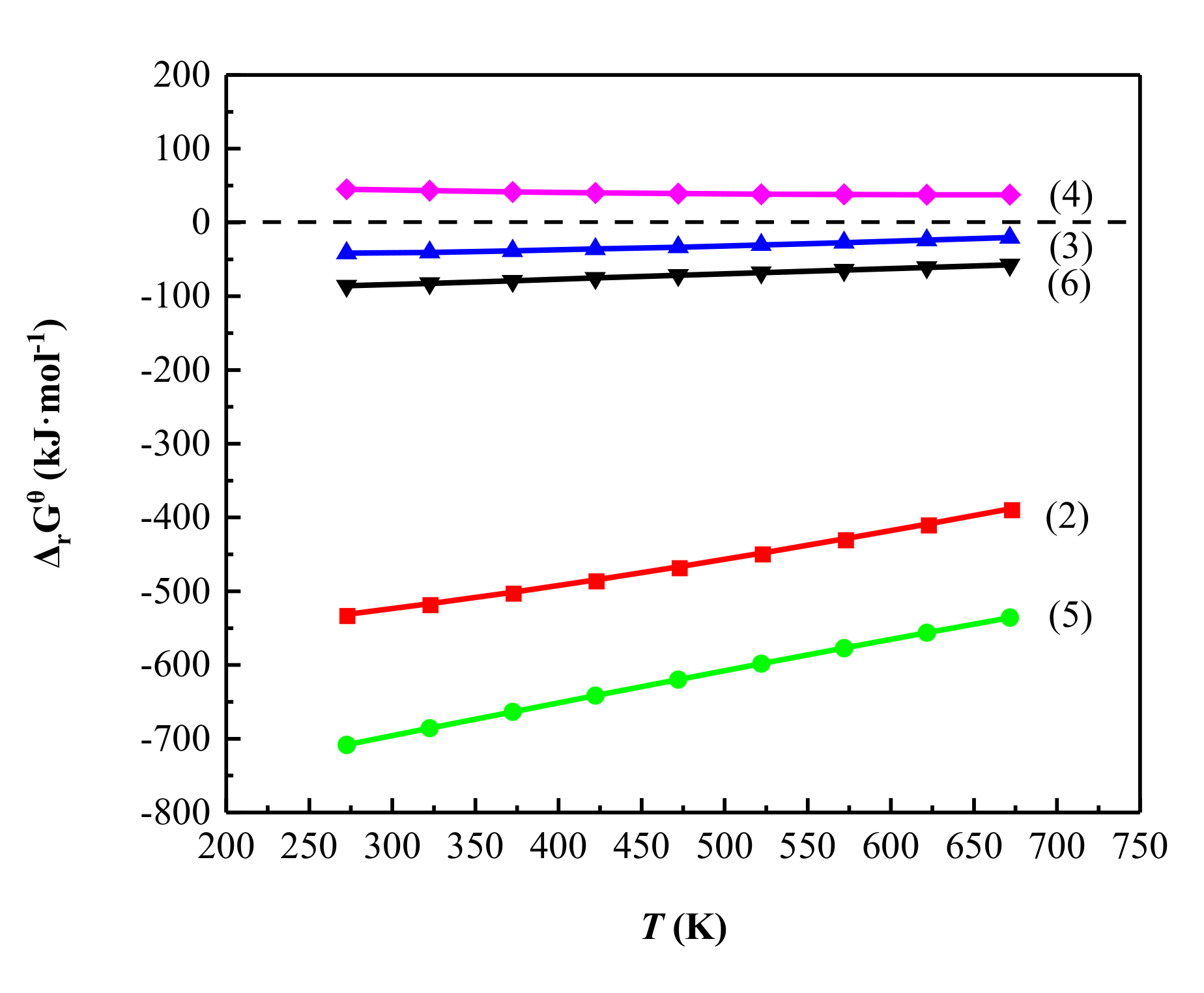
3.1. Thermodynamic Analysis
3.2. Effects of Roasting Parameters on Vanadium Extraction
3.2.1. Roasting Temperature
3.2.2. Roasting Time
3.2.3. Particle Size of Vanadium Ore
3.2.4. H2SO4 Dosage
3.3. Repeated Tests
3.4. Mechanism Analysis of the Roasting Process
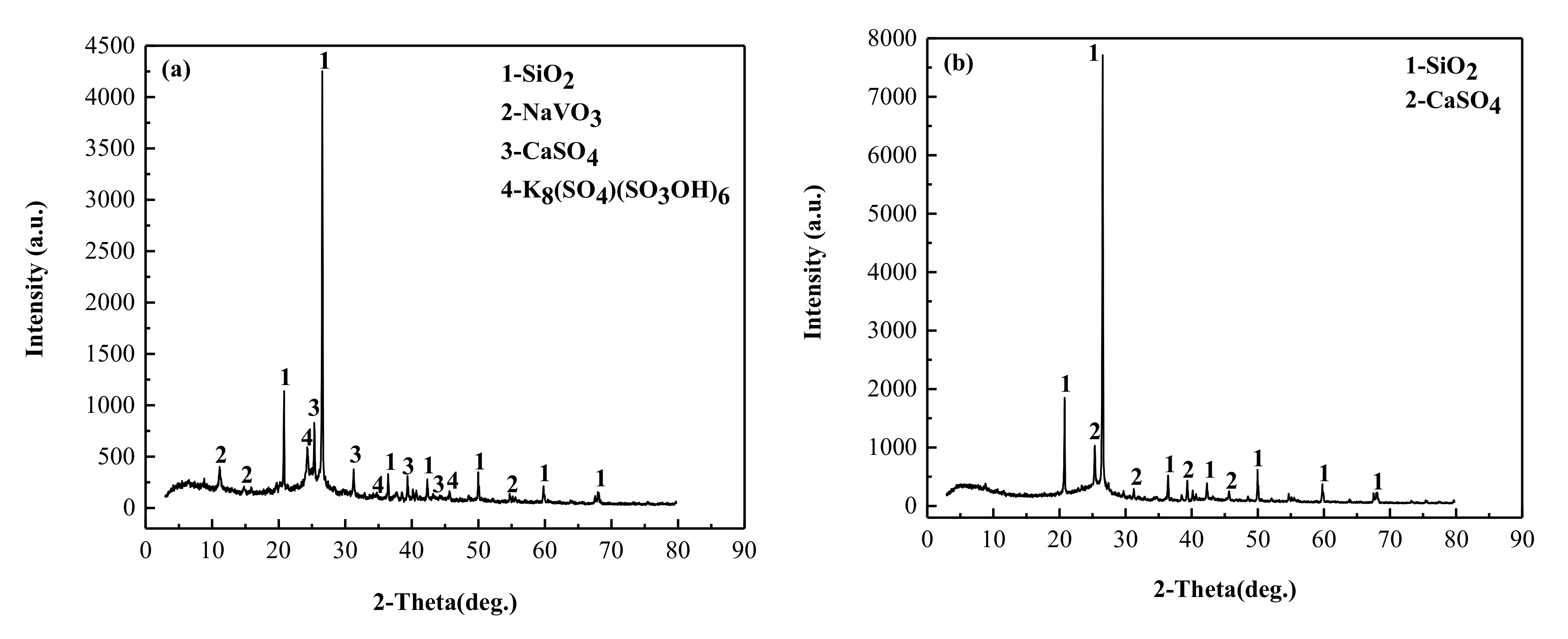
3.4.1. Mineral Phase Transformation Analysis
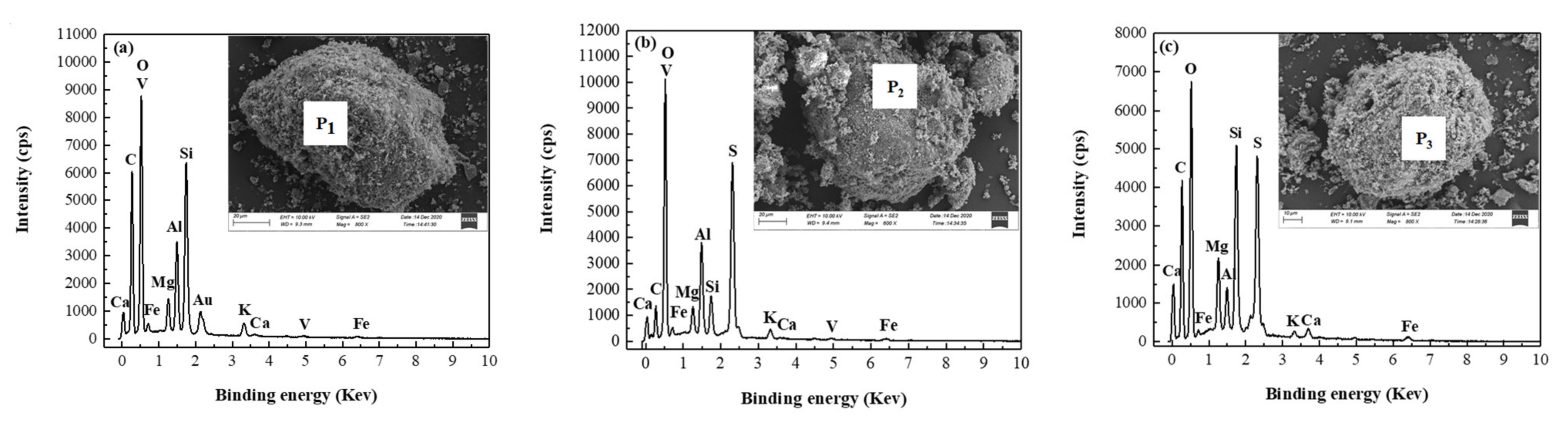
3.4.2. Analysis of Morphology and Microstructure
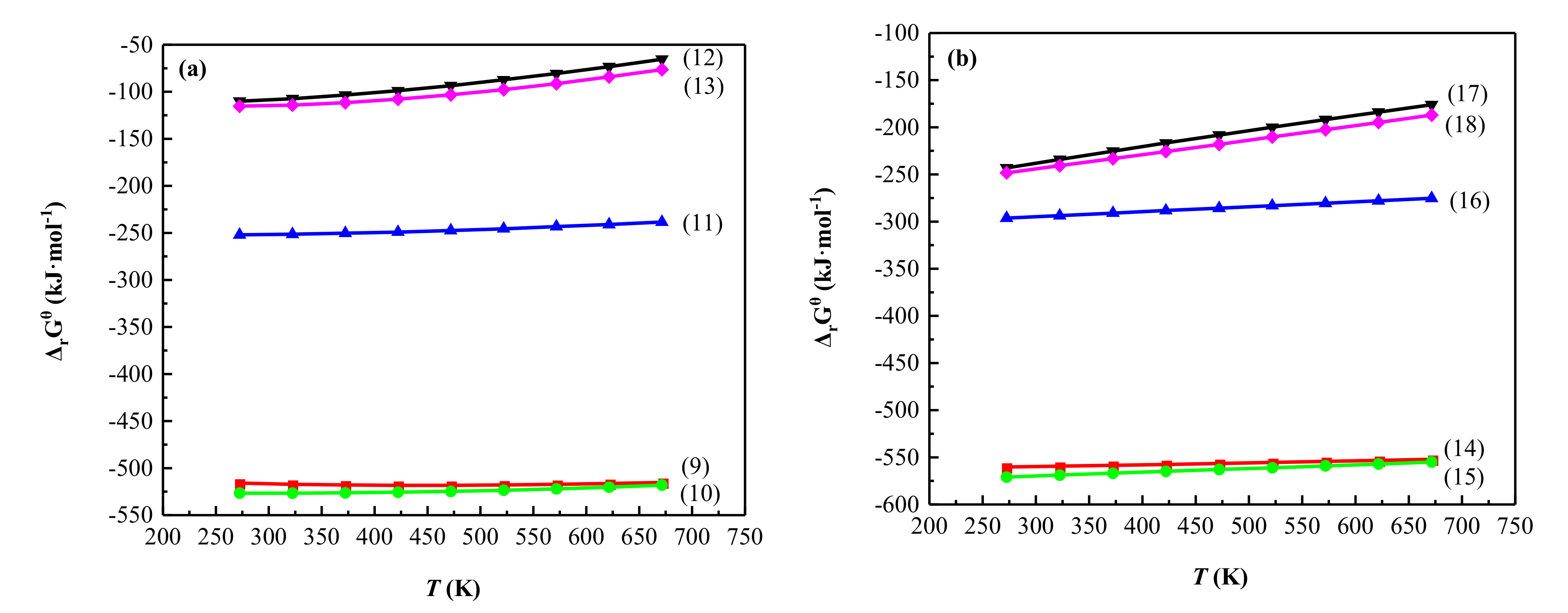
3.4.3. Thermodynamic Analysis of the Main Chemical Reactions
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The bauxite-type vanadium ore with a lower V2O5 content of 0.96%, is comprised of mica, illite, and calcite. Vanadium occurs in illite aluminosilicate crystals by isomorphism, instead of Al3+, and extracting this vanadium is difficult.
- (2)
- A promising low-temperature sulfating roasting–water leaching process was used to recover vanadium from the vanadium ore. Sulfuric acid was added to promote the release of vanadium-bearing minerals during sulfating roasting and ammonium molybdate was added to enhance vanadium extraction during water leaching. The results of the effects of different roasting process parameters on vanadium extraction showed that an optimal vanadium extraction index with leaching efficiency of 90.33% was obtained under the following conditions: particle size of <0.096 mm, sulfating roasting temperature of 523 K, sulfating roasting time of 120 min, H2SO4 dosage of 40 wt.%, water leaching liquid/solid ratio of 3:1, water leaching temperature of 333 K, water leaching time of 120 min, and ammonium molybdate dosage of 6 wt.%.
- (3)
- The analysis of phase transformation mechanism of sulfating roasting shows that when illite, as the main vanadium-bearing mineral, reacts with H2SO4, the aluminosilicate crystal lattice is destroyed, and Na and V are released with H2SO4 to form NaVO3 and K8(SO4)(SO3OH)6, which are easily leached using water leaching. The thermodynamic calculation theory was in good agreement with the experimental results.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, F.; Olayiwola, A.U.; Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Du, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Y. Review of Vanadium Production Part I: Primary Resources. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. Rev. 2021, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Luo, D.; Deng, C.; Lv, L.; Liang, B.; Li, C. Simultaneous extraction of vanadium and titanium from vanadium slag using ammonium sulfate roasting-leaching process. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 742, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. 2010. Mineral Commodity Summaries. Available online: http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/mcs/ (accessed on 20 April 2011).
- Peng, H. A literature review on leaching and recovery of vanadium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ou, L.; Lu, Y. An environmentally-friendly technology of vanadium extraction from stone coal. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 1184–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, M.; Dreisinger, D. Separation of vanadium from iron by solvent extraction using acidic and neutral organophosporus extractants. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 141, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vuuren, C.; Stander, P. The oxidation of FeV2O4 by oxygen in a sodium carbonate mixture. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-M.; Bao, S.-X.; Liu, T.; Chen, T.-J.; Huang, J. The technology of extracting vanadium from stone coal in China: History, current status and future prospects. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 109, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Y.; Wang, K.; Hua, W.-H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Xie, B. Selective leaching of vanadium in calcification-roasted vanadium slag by ammonium carbonate. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 160, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Y.; Fang, H.-X.; Wang, K.; Zhou, W.; Yang, Z.; Yan, X.-M.; Ge, W.-S.; Li, Q.-W.; Xie, B. Asynchronous extraction of vanadium and chromium from vanadium slag by stepwise sodium roasting–water leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 156, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Song, S.; Bao, S. In-situ investigation on mineral phase transition during roasting of vanadium-bearing stone coal. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Gu, S. Mechanism of vanadium slag roasting with calcium oxide. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 138, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Huang, Q.; Lv, X.; Bai, C. Extraction of vanadium from converter slag by two-step sulfuric acid leaching process. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.T.; Zhu, P.W.; Shi, Z.L.; Jiang, X.; Zeng, W.Q. Additive-free roasting technique for extracting vanadium from resi-due of mica-type vanadium-bearing stone coal. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2014, 38, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zheng, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Dreisinger, D.; Zhang, Y.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y. A clean and efficient method for recovery of vanadium from vanadium slag: Non-salt roasting and ammonium carbonate leaching processes. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. Rev. 2017, 38, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-G.; Zhang, G.-F.; Feng, Q.-M.; Lu, Y.-P.; Ou, L.-M.; Huang, S.-J. Acid leaching of vanadium from roasted residue of stone coal. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, s107–s111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, L. Effect of vanadium occurrence state on the choice of extracting vanadium technology from stone coal. Rare Met. 2008, 27, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, D.G.; Khanchi, A.R.; Taghizadeh, M. Recovery of Vanadium from Magnetite Ore Using Direct Acid Leaching: Optimization of Parameters by Plackett–Burman and Response Surface Methodologies. JOM 2018, 70, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.-G.; Wei, C.; Fan, G.; Li, M.-T.; Li, C.-X.; Li, X.-B. Extracting vanadium from stone-coal by oxygen pressure acid leaching and solvent extraction. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, s118–s122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.L.; Wang, X.W.; Wang, M.Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.P. Mineral decomposition process of vanadium recovery from stone coal by low temperature sulphating roasting. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2009, 19, 943–948. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cheng, Q.; Qi, J.Y.; Li, J.; Ning, X.X.; Jin, J.P. Process of vanadium extraction from stone coal vanadium ore by sulfuric acid low temperature curing and column leaching. Min. Metall. 2020, 29, 62–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Huang, J. Vanadium Extraction from Shale via Sulfuric Acid Baking and Leaching. JOM 2018, 70, 1972–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Luo, W.; Ou, L. Study on leaching vanadium from roasted residue of stone coal. Min. Met. Explor. 2008, 25, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Xiong, W.; Zou, K.; Chen, T.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. Extraction of Nickel from Magnesia–Nickel Silicate Ore. J. Sustain. Met. 2021, 7, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zou, K.; Chen, T.; Peng, Y.; Ding, W.; Chen, J.; Deng, B.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. Extraction of Sc from Sc-Bearing V–Ti Magnetite Tailings. JOM 2021, 73, 1836–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zou, K.; Chen, T.; Xiong, W.; Deng, B. Extraction of Manganese and Iron from a Refractory Coarse Manganese Concentrate. Metals 2021, 11, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.F.; Zhang, G.F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.H. Aid-leaching reagent of leaching scandium from scandium concentrate in complex silicate. Chin. J. Rare Met. 2012, 2, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| V2O5 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | CaO | Al2O3 | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.96 | 51.86 | 9.26 | 8.66 | 18.42 | 5.13 |
| Na2O | MgO | TiO2 | CuO | NiO | Cr2O3 |
| 2.41 | 1.37 | 1.15 | 0.2 | 0.22 | 0.29 |
| Repeat | Leaching Efficiency of Vanadium (%) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 90.23 |
| 2 | 89.88 |
| 3 | 90.88 |
| Average | 90.33 |
| Rang () | 1.00 |
| Arithmetic mean error () | 0.367 |
| Sum square variation | 0.515 |
| Average deviation | 0.172 |
| Standard deviation | 0.415 |
| Products | SiO2 | V2O5 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | CaO | K2O | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roasted ore | 53.72 | 1.03 | 8.32 | 15.23 | 9.63 | 2.68 | 2.53 |
| Leaching residue | 60.80 | 0.11 | 4.10 | 7.79 | 8.28 | 2.45 | 1.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, K.; Xiao, J.; Liang, G.; Huang, W.; Xiong, W. Effective Extraction of Vanadium from Bauxite-Type Vanadium Ore Using Roasting and Leaching. Metals 2021, 11, 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091342
Zou K, Xiao J, Liang G, Huang W, Xiong W. Effective Extraction of Vanadium from Bauxite-Type Vanadium Ore Using Roasting and Leaching. Metals. 2021; 11(9):1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091342
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Kai, Junhui Xiao, Guanjie Liang, Wenxiao Huang, and Wenliang Xiong. 2021. "Effective Extraction of Vanadium from Bauxite-Type Vanadium Ore Using Roasting and Leaching" Metals 11, no. 9: 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091342
APA StyleZou, K., Xiao, J., Liang, G., Huang, W., & Xiong, W. (2021). Effective Extraction of Vanadium from Bauxite-Type Vanadium Ore Using Roasting and Leaching. Metals, 11(9), 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11091342







