Mechanisms of the Reverse Martensite-to-Austenite Transformation in a Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. As-Received and As-Processed Condition
2.2. Continuous Heating and Phase Reversion Annealing of the As-Processed Program Steel
2.3. Structure and Hardness Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
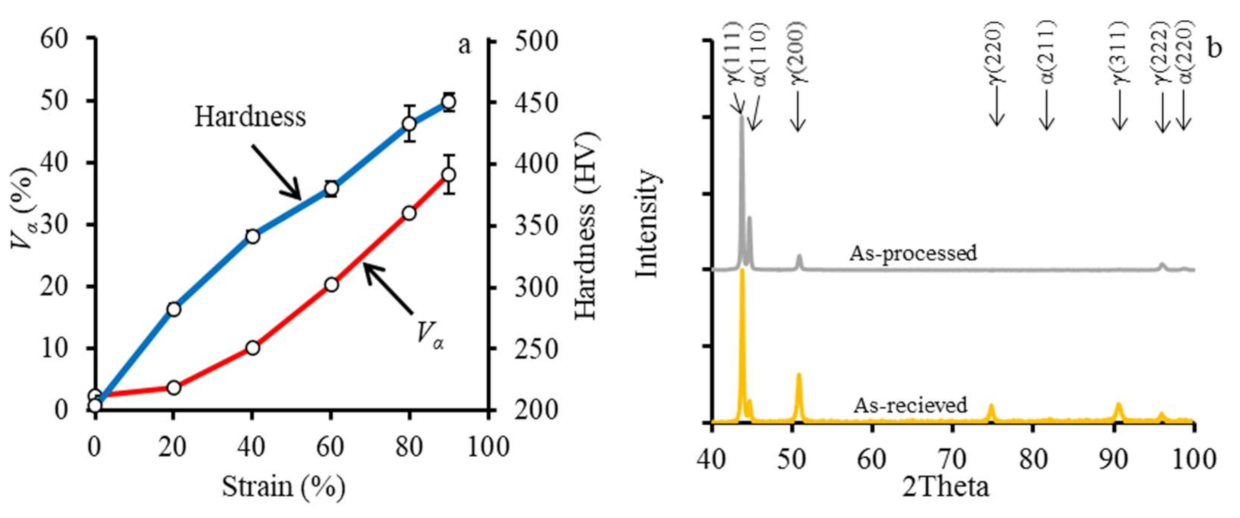
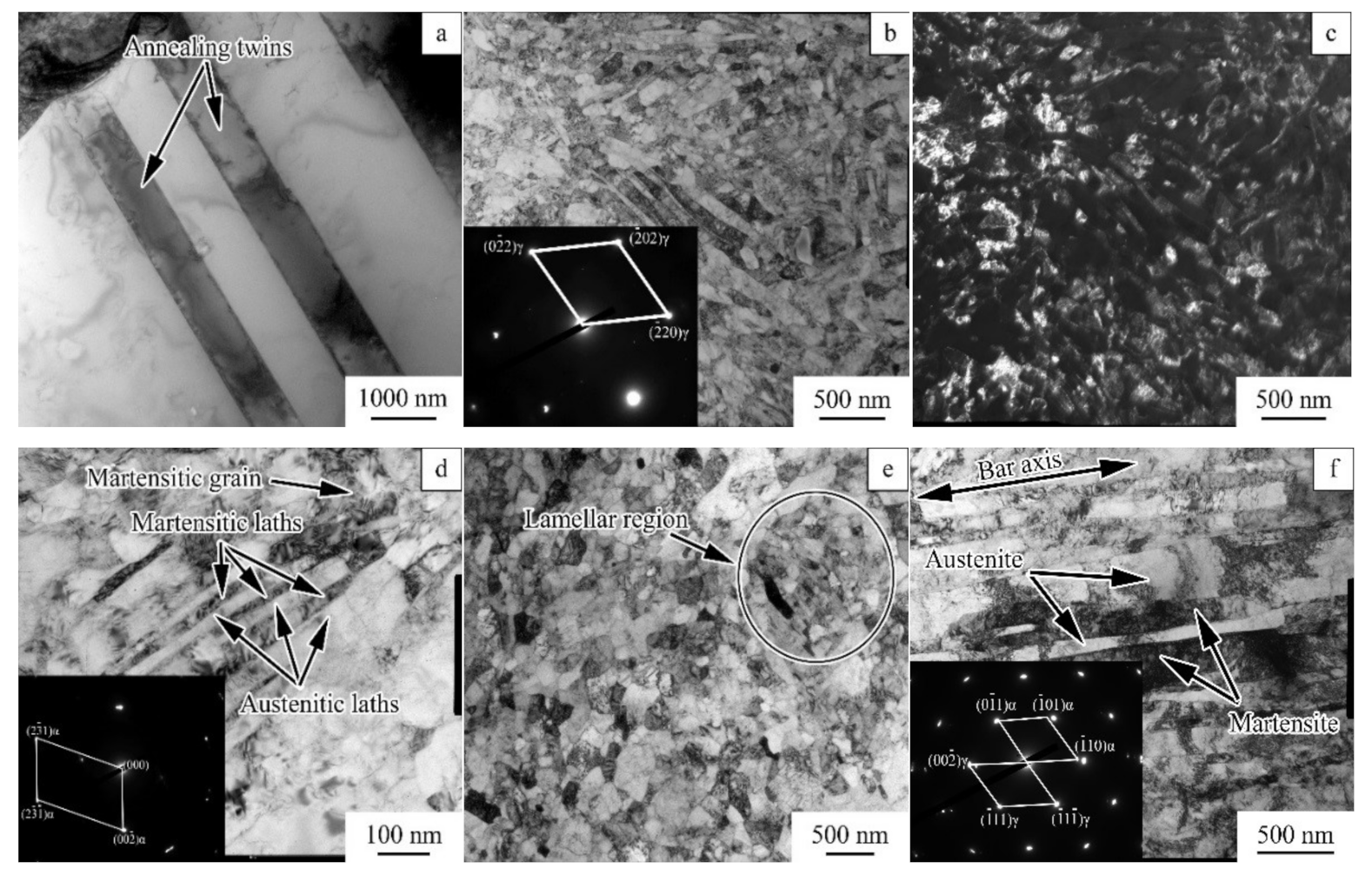
3.1. As-Received and As-Processed Microstructure
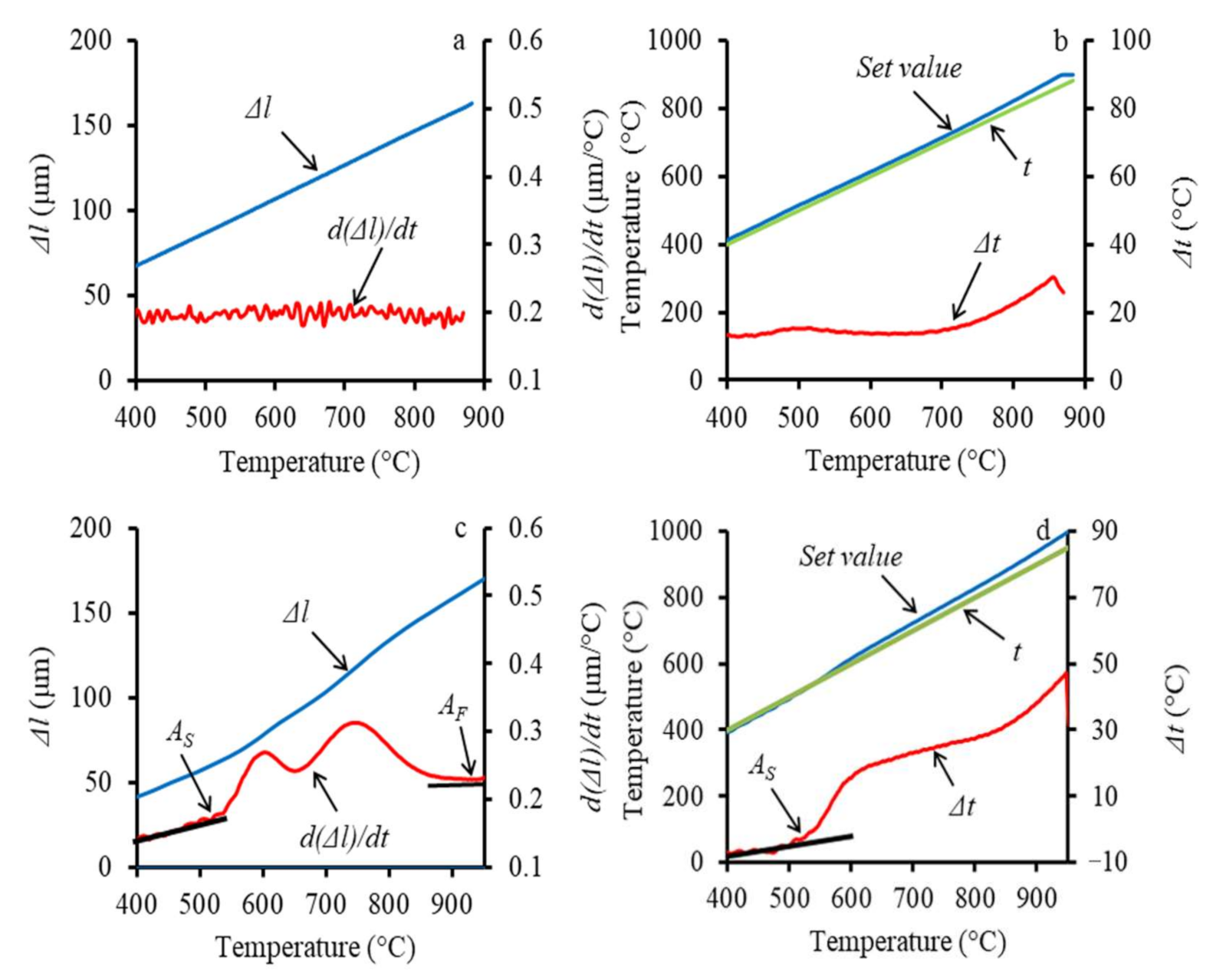
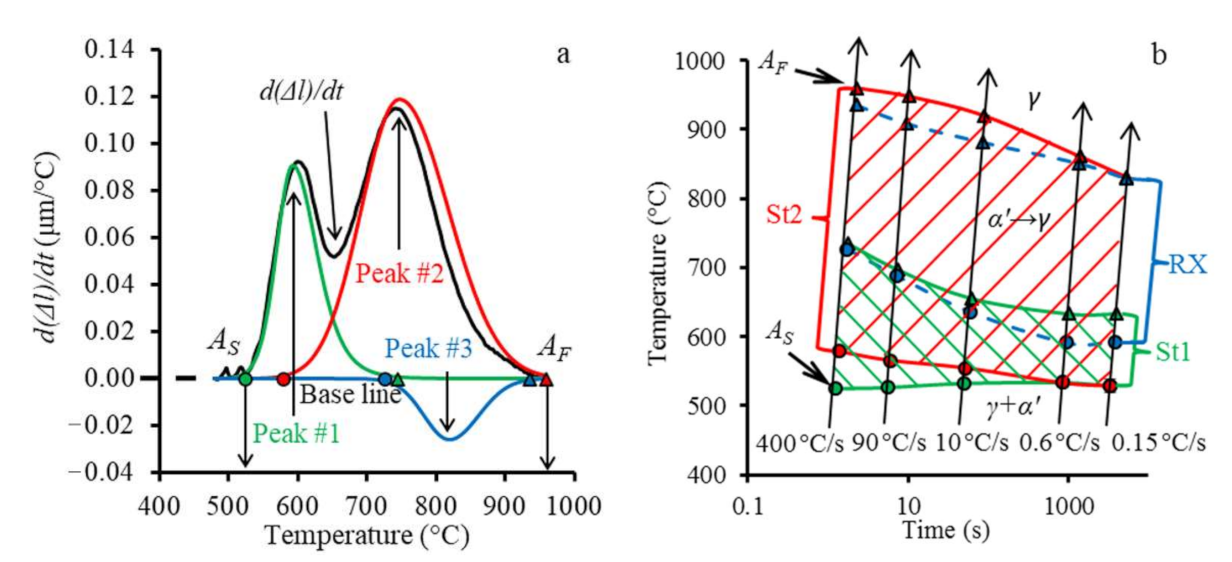
3.2. High-Resolution Dilatometry during Continuous Heating
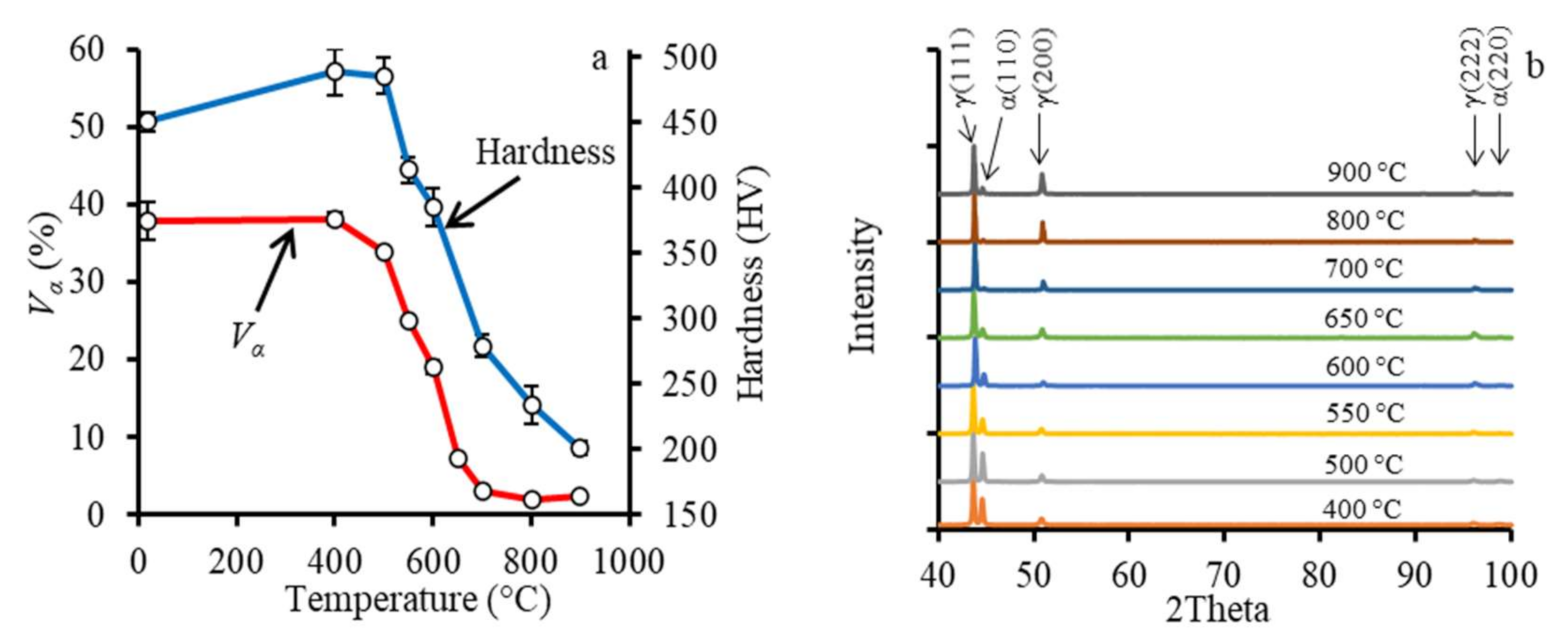
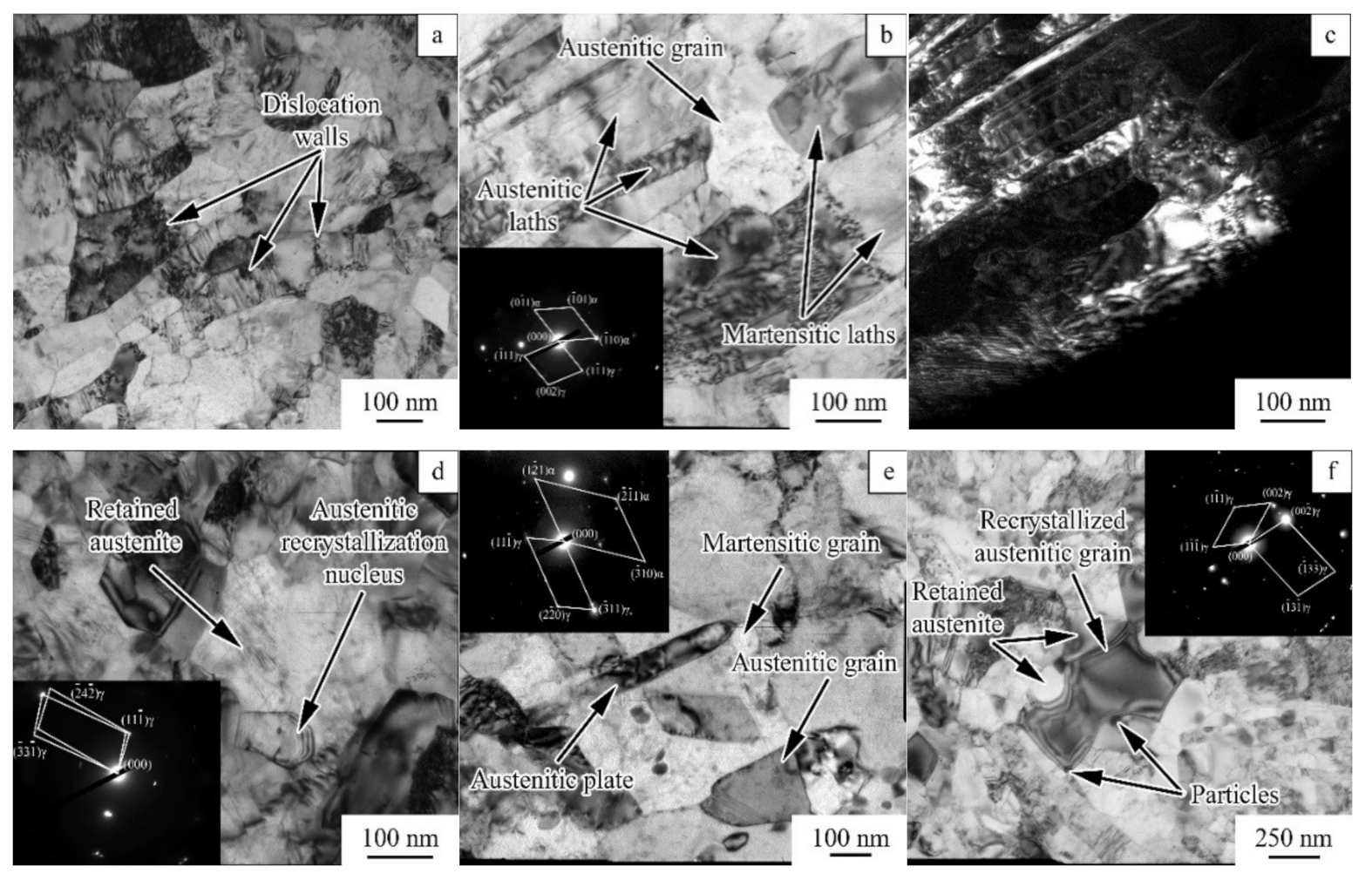
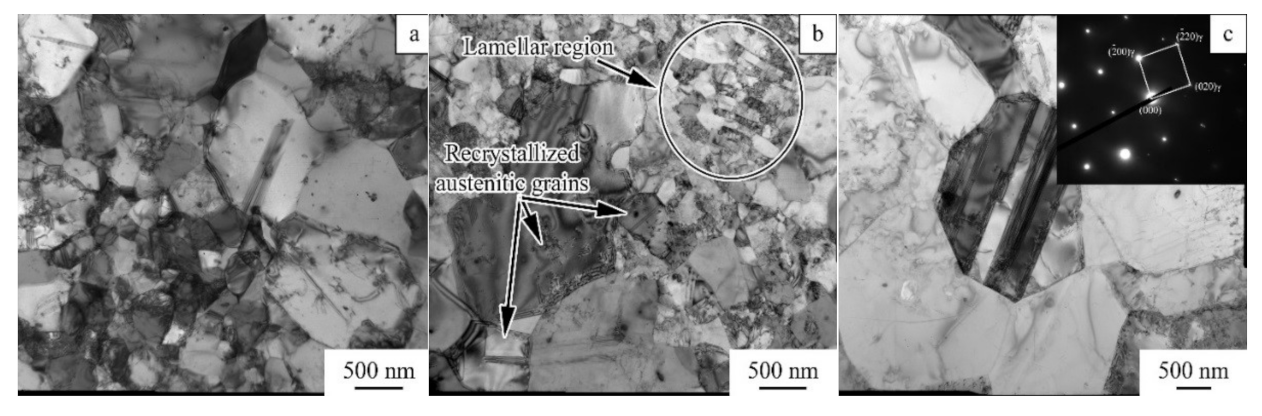
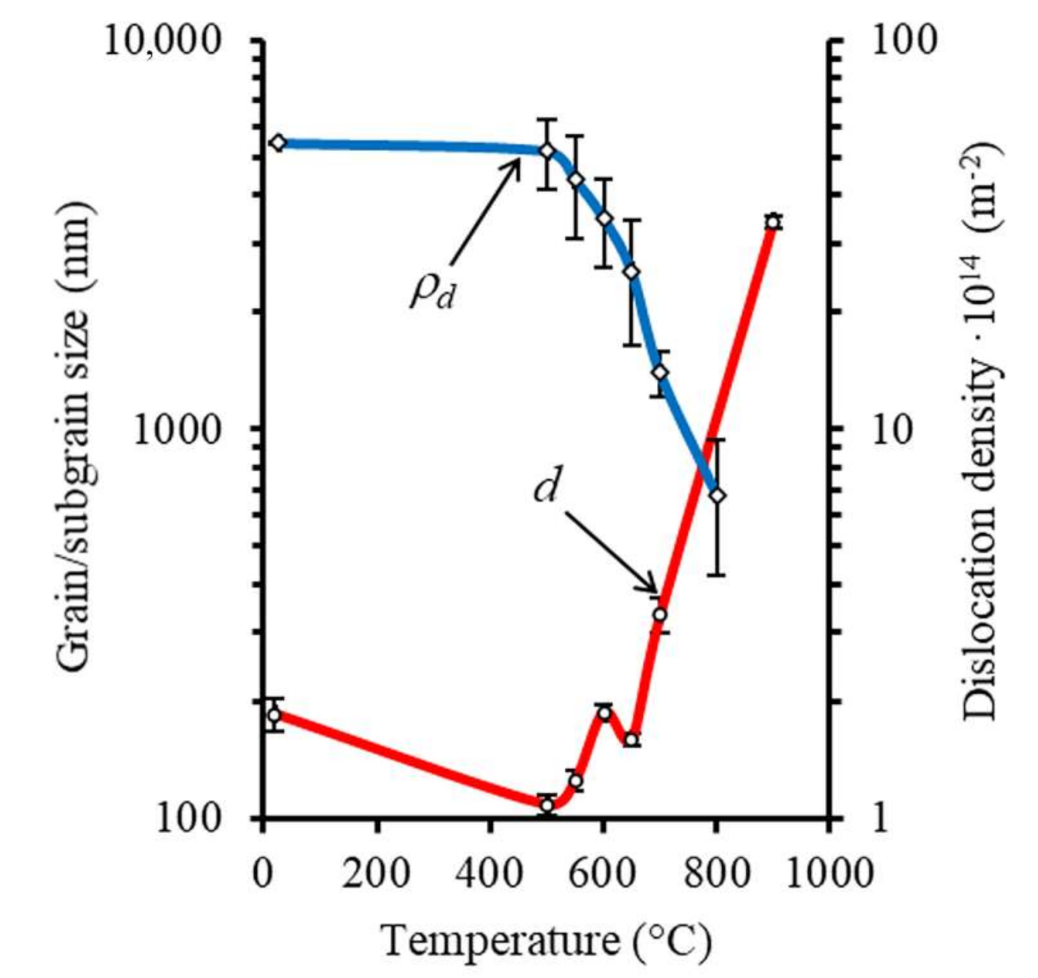
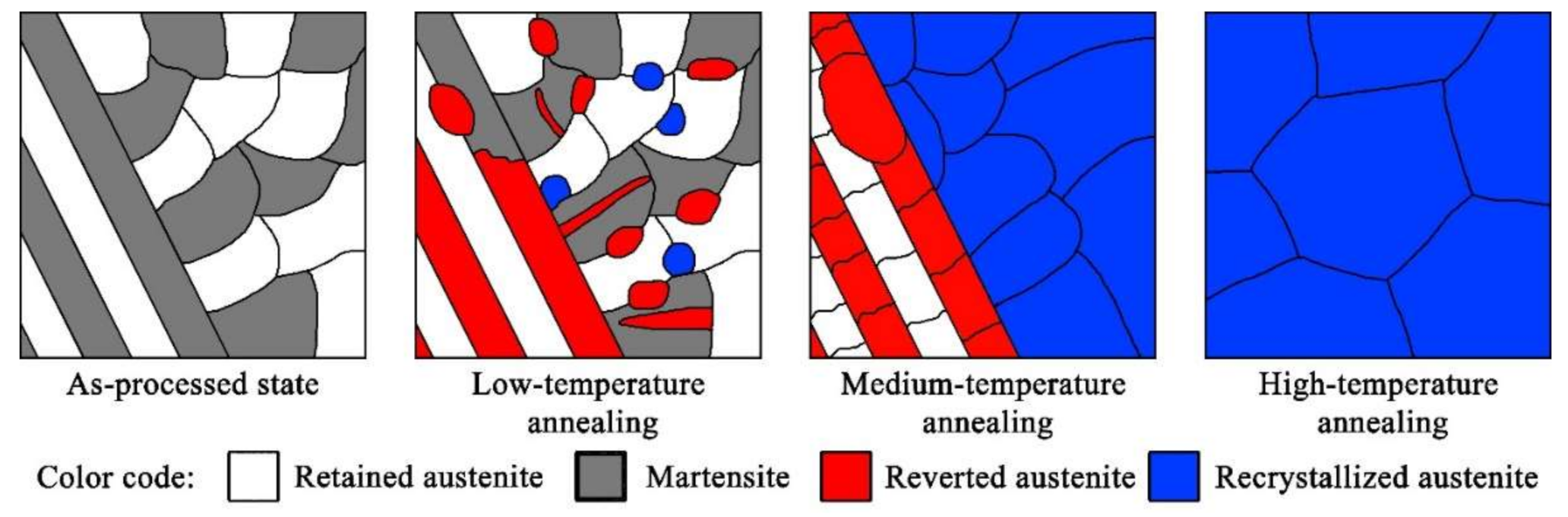
3.3. Microstructural Evolution during Annealing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beddoes, J.; Parr, J.G. Introduction to Stainless Steels, 3rd ed.; ASM International, Materials Park: Russell, OH, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, K.H.; Shek, C.H.; Lai, J.K.L. Recent developments in stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2009, 65, 39–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.O. The deformation and aging of mild steel: III. Discussion of results. Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. 1951, 64, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petch, N.J. The ductile-brittle transition in the fracture of α-iron: I. Philos. Mag. 1958, 3, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, H.A.; Ghazani, M.S.; Eghbali, B. Effect of post deformation annealing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of cold rolled AISI 321 austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 736, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobatkin, S.V.; Skrotzki, W.; Rybalchenko, O.V.; Terent’ev, V.F.; Belyakov, A.N.; Prosvirnin, D.V.; Raab, G.I.; Zolotarev, E.V. Structural changes in metastable austenitic steel during equal channel angular pressing and subsequent cyclic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 723, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobatkin, S.V.; Rybal’chenko, O.V.; Raab, G.I. Structure formation, phase transformations and properties in Cr-Ni austenitic steel after equal-channel angular pressing and heating. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 463, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Guo, K.; Wang, T.S. Effect of carbide precipitation on strain-hardening behavior and deformation mechanism of metastable austenitic stainless steel after repetitive cold rolling and reversion annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 708, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salishchev, G.A.; Zaripova, R.G.; Zakirova, A.A. Structure and properties of stainless steels subjected to severe plastic deformation. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2006, 48, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, D.; Pertsev, A.; Smirnov, A.; Khotinov, V.; Simonov, Y. Metastable austenitic steel structure and mechanical properties evolution in the process of cold radial forging. Materials 2019, 12, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.K.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K.; Murdock, D.C.; Mataya, M.C.; Comstock, R.J. Deformation-induced phase transformation and strain hardening in type 304 austenitic stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2006, 37, 1875–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhova, I.; Dudko, V.; Belyakov, A.; Tsuzaki, K.; Kaibyshev, R. Effect of large strain cold rolling and subsequent annealing on microstructure and mechanical properties of an austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 545, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.W.; Loretto, M.H.; Smallman, R.E. Direct observations of martensite nuclei in stainless steel. Acta Metall. 1979, 27, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.F.; Li, X.X.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.D.; Zuo, L. Twinning and martensite in a 304 austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 552, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wu, X.; Raabe, D.; Li, Z. Deformation-driven bidirectional transformation promotes bulk nanostructure formation in a metastable interstitial high entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2019, 167, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wan, X.; Yu, J.; Xu, G.; Li, G. Effect of cold deformation on microstructures and mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steel. Metals 2018, 8, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Zhang, L.; Ni, S.; Song, M. Effects of grain size on the microstructures and mechanical properties of 304 austenitic steel processed by torsional deformation. Micron 2018, 105, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakhova, I.; Belyakov, A.; Kaibyshev, R.; Kimura, Y.; Tsuzaki, K. Submicrocrystalline structures and tensile behaviour of stainless steels subjected to large strain deformation and subsequent annealing. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 409, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Deng, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Simultaneous enhancement of strength and ductility through coordination deformation and multi-stage transformation induced plasticity (TRIP) effect in heterogeneous metastable austenitic steel. Scr. Mater. 2019, 162, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomimura, K.; Takaki, S.; Tokunaga, Y. Reversion Mechanism from Deformation Induced Martensite to Austenite in Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steels. ISIJ Int. 1991, 31, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, R.D.K.; Zhang, Z.; Venkatasurya, P.K.C.; Somani, M.C.; Karjalainen, L.P. Martensite shear phase reversion-induced nanograined/ultrafine-grained Fe-16Cr-10Ni alloy: The effect of interstitial alloying elements and degree of austenite stability on phase reversion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 7779–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, H.; Miyamoto, G.; Hossein Nedjad, S.; Chiba, T.; Nili Ahmadabadi, M.; Furuhara, T. Microstructure evolution during austenite reversion in Fe-Ni martensitic alloys. Acta Mater. 2018, 144, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, D.L.; Kyrolainen, A.; Ferreira, P.J. Influence of annealing treatment on the formation of nano/submicron grain size AISI 301 Austenitic stainless steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 2325–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, D.S.; Lee, Y.D.; Jun, J.H.; Choi, C.S. Amount of retained austenite at room temperature after reverse transformation of martensite to austenite in an Fe-13%Cr-7%Ni-3%Si martensitic stainless steel. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletdinov, A.; Mironov, S.; Korznikova, G.F.; Konkova, T.; Zaripova, R.G.; Myshlyaev, M.M.; Semiatin, S.L. Martensite-to-Austenite Reversion and Recrystallization in Cryogenically-Rolled Type 321 Metastable Austenitic Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2019, 50, 1346–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiamiyu, A.A.; Odeshi, A.G.; Szpunar, J.A. Austenitic Reversion of Cryo-rolled Ti-Stabilized Austenitic Stainless Steel: High-Resolution EBSD Investigation. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagaradze, V.V.; Danilchenko, V.E.; L’Heritier, P.; Shabashov, V.A. The structure and properties of Fe-Ni alloys with a nanocrystalline austenite formed under different conditions of γ-α-γ transformations. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 337, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, N.; Tsuchiyama, T.; Takaki, S.; Hashizume, S. Variant selection of reversed austenite in lath martensite. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Miyamoto, G.; Toji, Y.; Nambu, S.; Koseki, T.; Furuhara, T. Orientation of austenite reverted from martensite in Fe-2Mn-1.5Si-0.3C alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 144, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisko, A.; Hamada, A.S.; Talonen, J.; Porter, D.; Karjalainen, L.P. Effects of reversion and recrystallization on microstructure and mechanical properties of Nb-alloyed low-Ni high-Mn austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 657, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, Y.K. Reverse transformation mechanism of martensite to austenite in a metastable austenitic alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 515, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.I.; Lee, Y.K.; Park, K.T. Reverse transformation of ferrite and pearlite to austenite in an ultrafine-grained low-carbon steel fabricated by severe plastic deformation. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2006, 37, 3161–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłowski, B. Determination of critical points of hypoeutectoid steels. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2012, 57, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Panov, D.O.; Smirnov, A.I. Features of austenite formation in low-carbon steel upon heating in the intercritical temperature range. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2017, 118, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.S.; Du, L.X.; Hu, J.; Misra, R.D.K. Microstructural evolution and recrystallization behavior of cold rolled austenitic stainless steel with dual phase microstructure during isothermal annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 709, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdyr, M. Fityk: A general-purpose peak fitting program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2010, 43, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, D.O.; Smirnov, A.I.; Pertsev, A.S. Formation of Structure in Metastable Austenitic Steel during Cold Plastic Deformation by the Radial Forging Method. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2019, 120, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiamiyu, A.A.; Odeshi, A.G.; Szpunar, J.A. Multiple strengthening sources and adiabatic shear banding during high strain-rate deformation of AISI 321 austenitic stainless steel: Effects of grain size and strain rate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 711, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Li, X.; Deng, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G. Deformation mechanism and ductile fracture behavior in high strength high ductility nano/ultrafine grained Fe-17Cr-6Ni austenitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 709, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherepin, V.T. Eksperimental’naia Tekhnika v Fizicheskom Metallovedenii; Tekhnika: Kiev, Ukraine, 1968. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T. The expansion behavior caused by deformation-induced martensite to austenite transformation in heavily cold-rolled metastable austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 739, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Meng, Q. Dilatometric study on the recrystallization and austenization behavior of cold-rolled steel with different heating rates. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 666, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Du, L.X. The significant role of heating rate on reverse transformation and coordinated straining behavior in a cold-rolled austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 732, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, A.; Hangen, U.D.; Biermann, H. Nanoindentation measurements on deformation-induced α-martensite in a metastable austenitic high-alloy CrMnNi steel. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2014, 94, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apple, C.A.; Krauss, G. The Effect of heating rate on the martensite to austenite transformation in Fe-Ni-C Alloys. Acta Met. 1972, 20, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhara, S.; Karjalainen, L.P.; Kyröläinen, A.; Ferreira, P.J. Microstructure evolution in nano/submicron grained AISI 301LN stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 1986–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Schino, A.; Barteri, M.; Kenny, J.M. Development of ultra fine grain structure by martensitic reversion in stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2002, 21, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Du, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Misra, R.D.K. On the influence of deformation mechanism during cold and warm rolling on annealing behavior of a 304 stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 746, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Chemical Elements | C | Cr | Ni | Mn | Si | Ti | P | S | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (% wt.) | 0.07 | 18.75 | 9.20 | 1.12 | 0.39 | 0.59 | 0.019 | 0.005 | basis |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panov, D.; Kudryavtsev, E.; Chernichenko, R.; Smirnov, A.; Stepanov, N.; Simonov, Y.; Zherebtsov, S.; Salishchev, G. Mechanisms of the Reverse Martensite-to-Austenite Transformation in a Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steel. Metals 2021, 11, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11040599
Panov D, Kudryavtsev E, Chernichenko R, Smirnov A, Stepanov N, Simonov Y, Zherebtsov S, Salishchev G. Mechanisms of the Reverse Martensite-to-Austenite Transformation in a Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steel. Metals. 2021; 11(4):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11040599
Chicago/Turabian StylePanov, Dmitrii, Egor Kudryavtsev, Ruslan Chernichenko, Aleksandr Smirnov, Nikita Stepanov, Yuri Simonov, Sergey Zherebtsov, and Gennady Salishchev. 2021. "Mechanisms of the Reverse Martensite-to-Austenite Transformation in a Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steel" Metals 11, no. 4: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11040599
APA StylePanov, D., Kudryavtsev, E., Chernichenko, R., Smirnov, A., Stepanov, N., Simonov, Y., Zherebtsov, S., & Salishchev, G. (2021). Mechanisms of the Reverse Martensite-to-Austenite Transformation in a Metastable Austenitic Stainless Steel. Metals, 11(4), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11040599








