Toughness Property Control by Nb and Mo Additions in High-Strength Quenched and Tempered Boron Steels
Abstract
1. Introduction
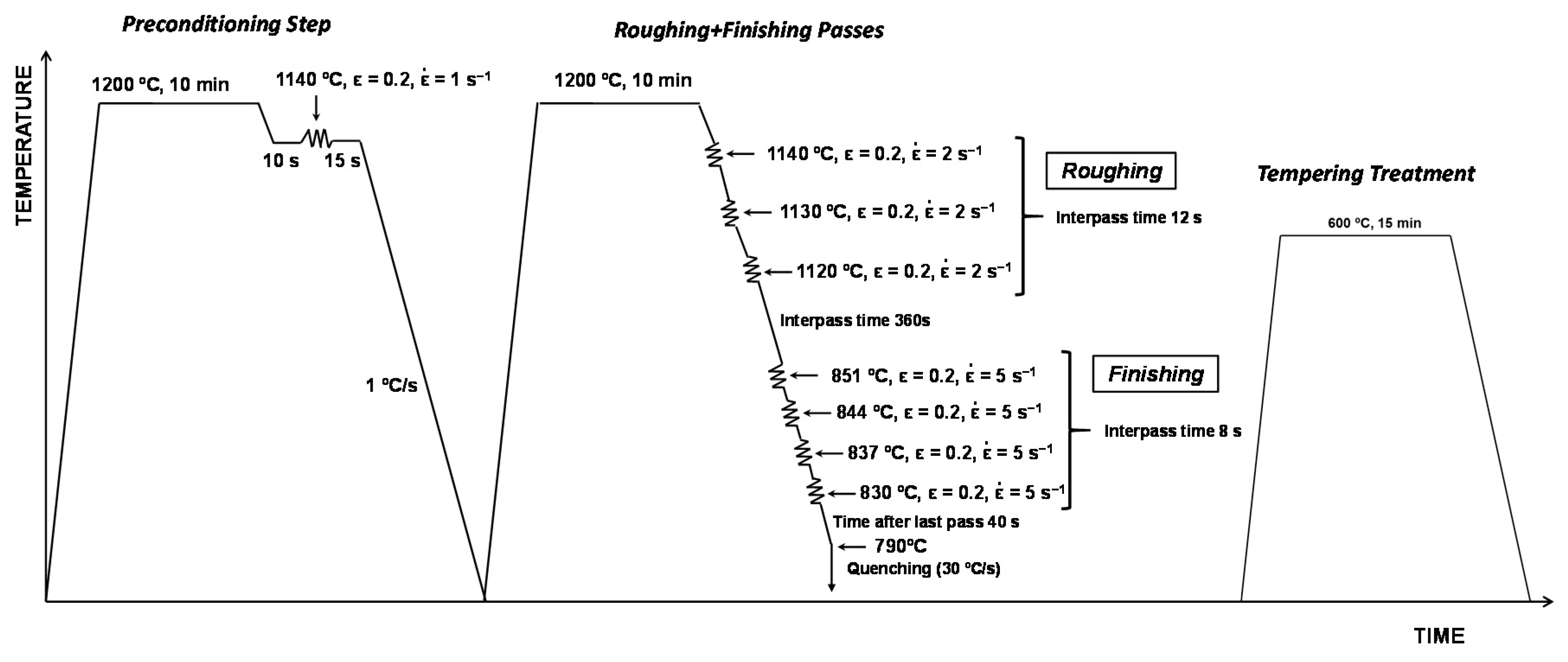
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mechanical Behaviour
3.2. Microstructural Characterization
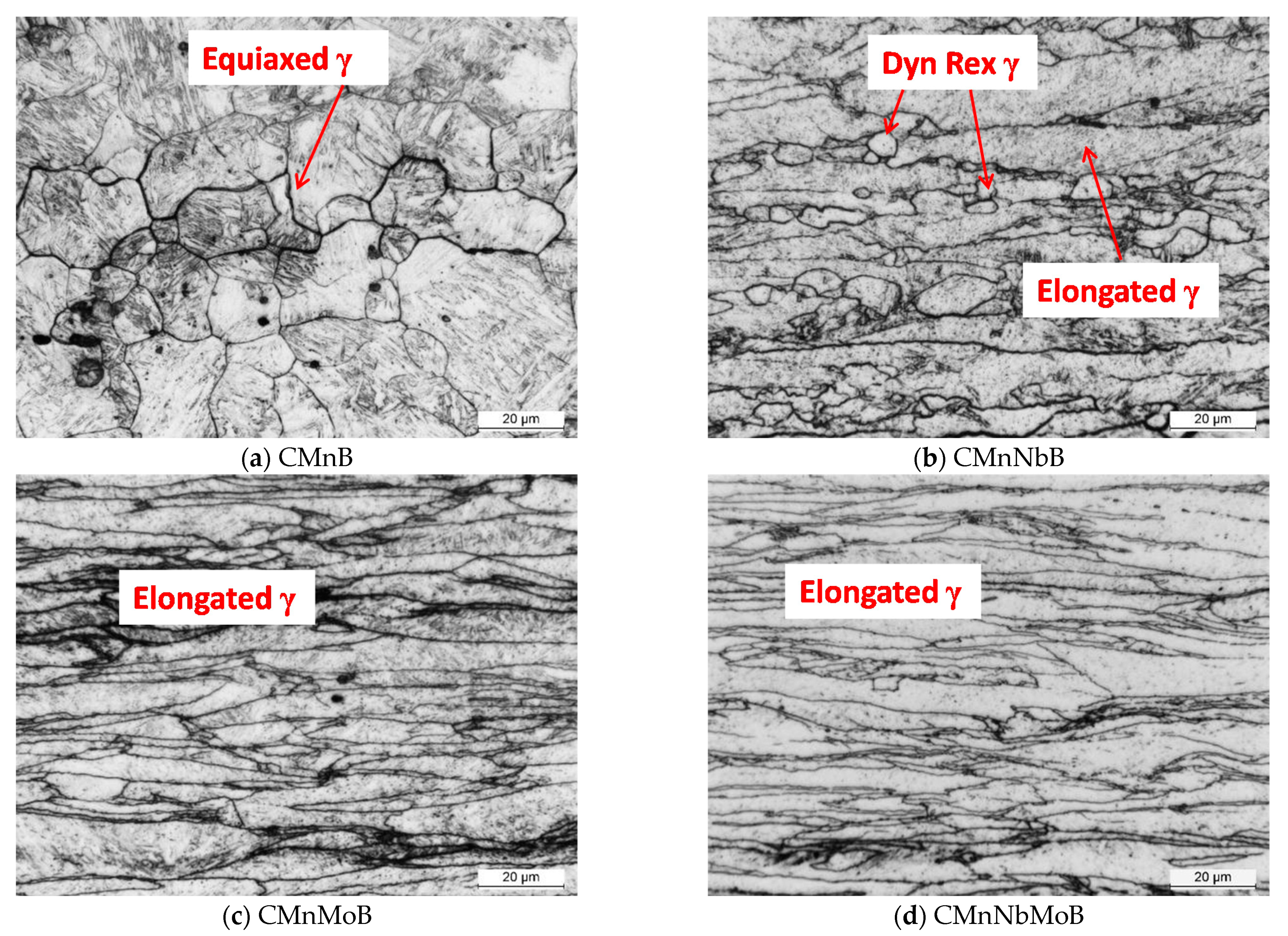
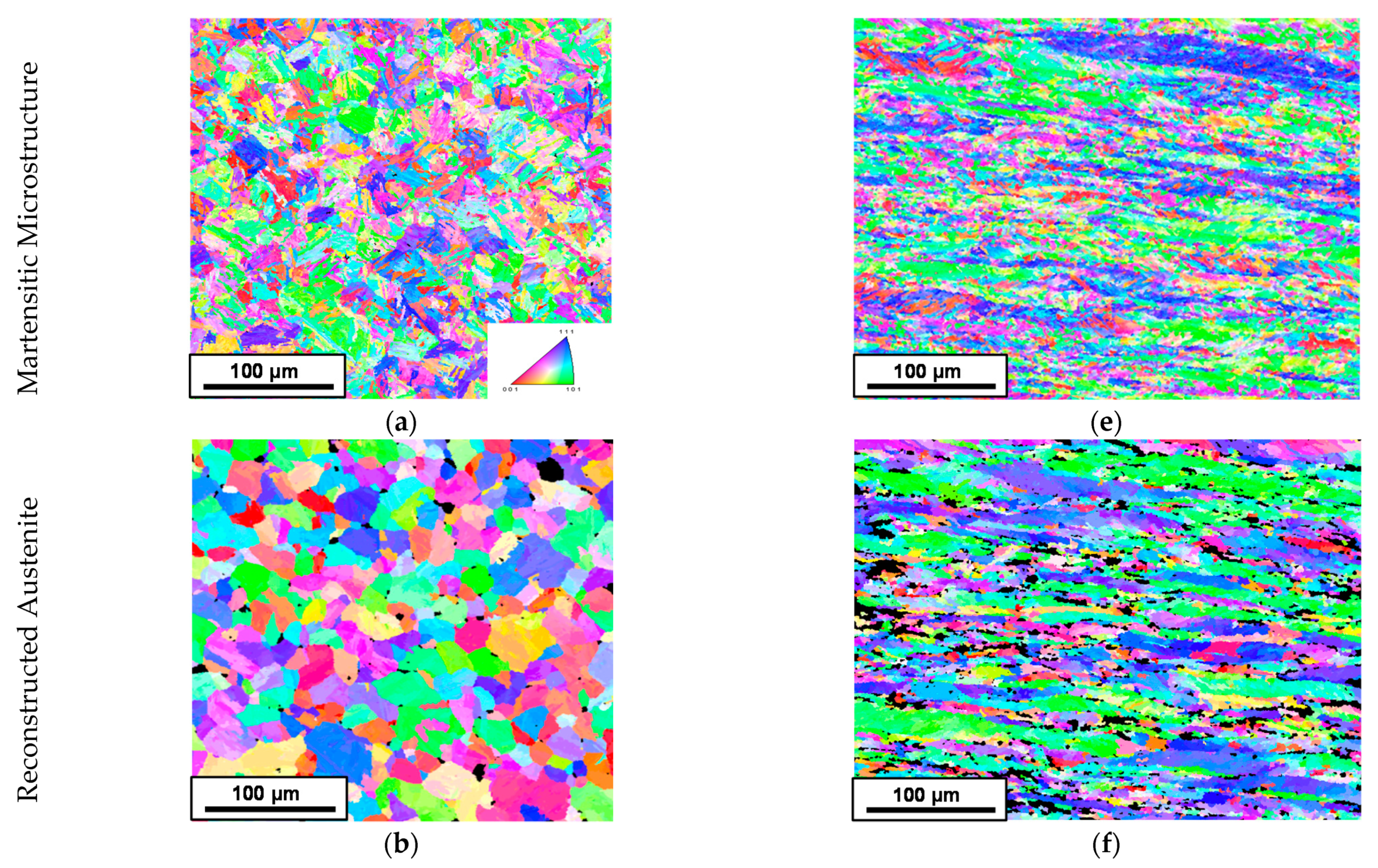
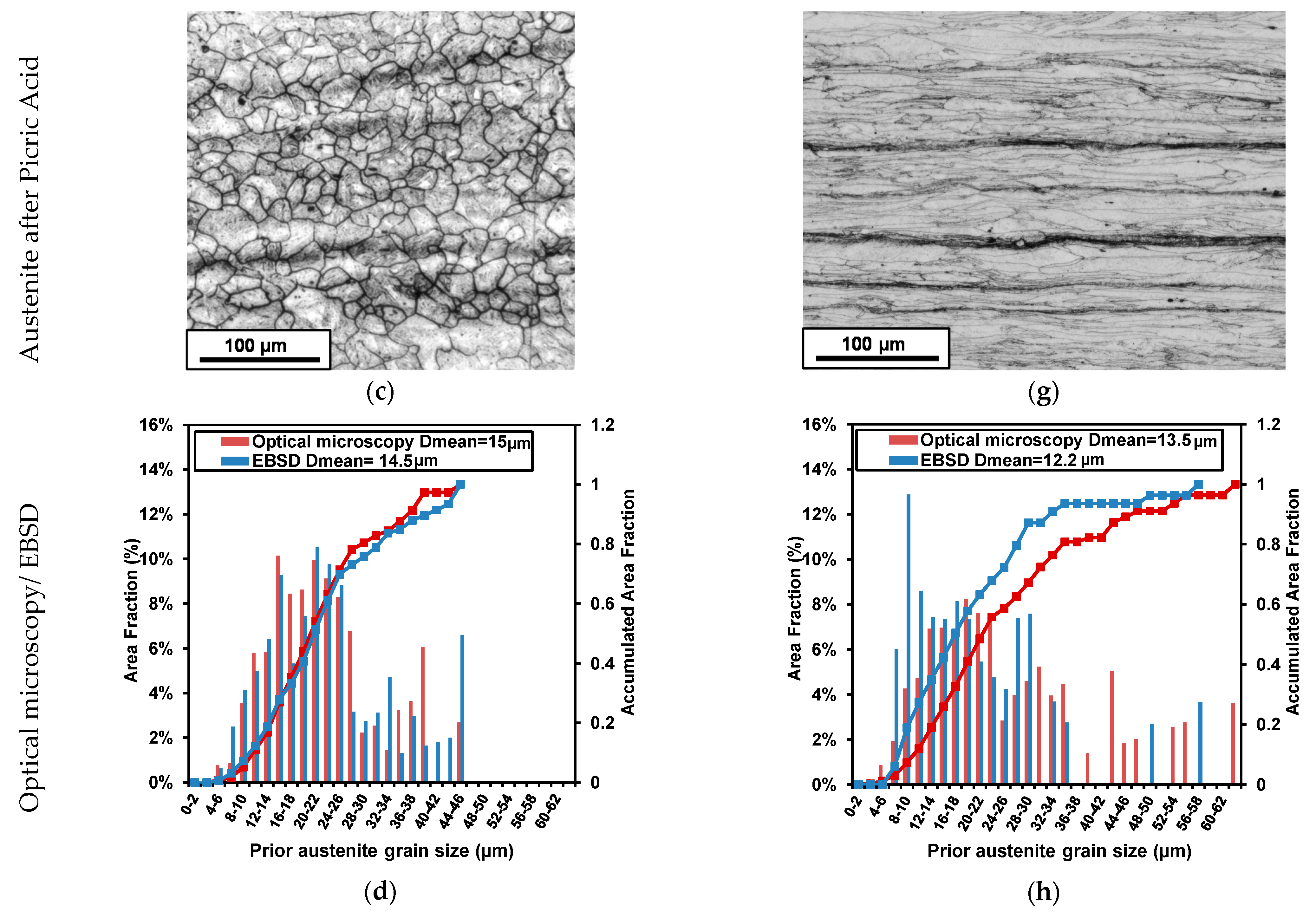
3.2.1. Analysis of the Prior Austenitic Structure
3.2.2. Quantification of Mean unit Sizes and Microstructural Homogeneity
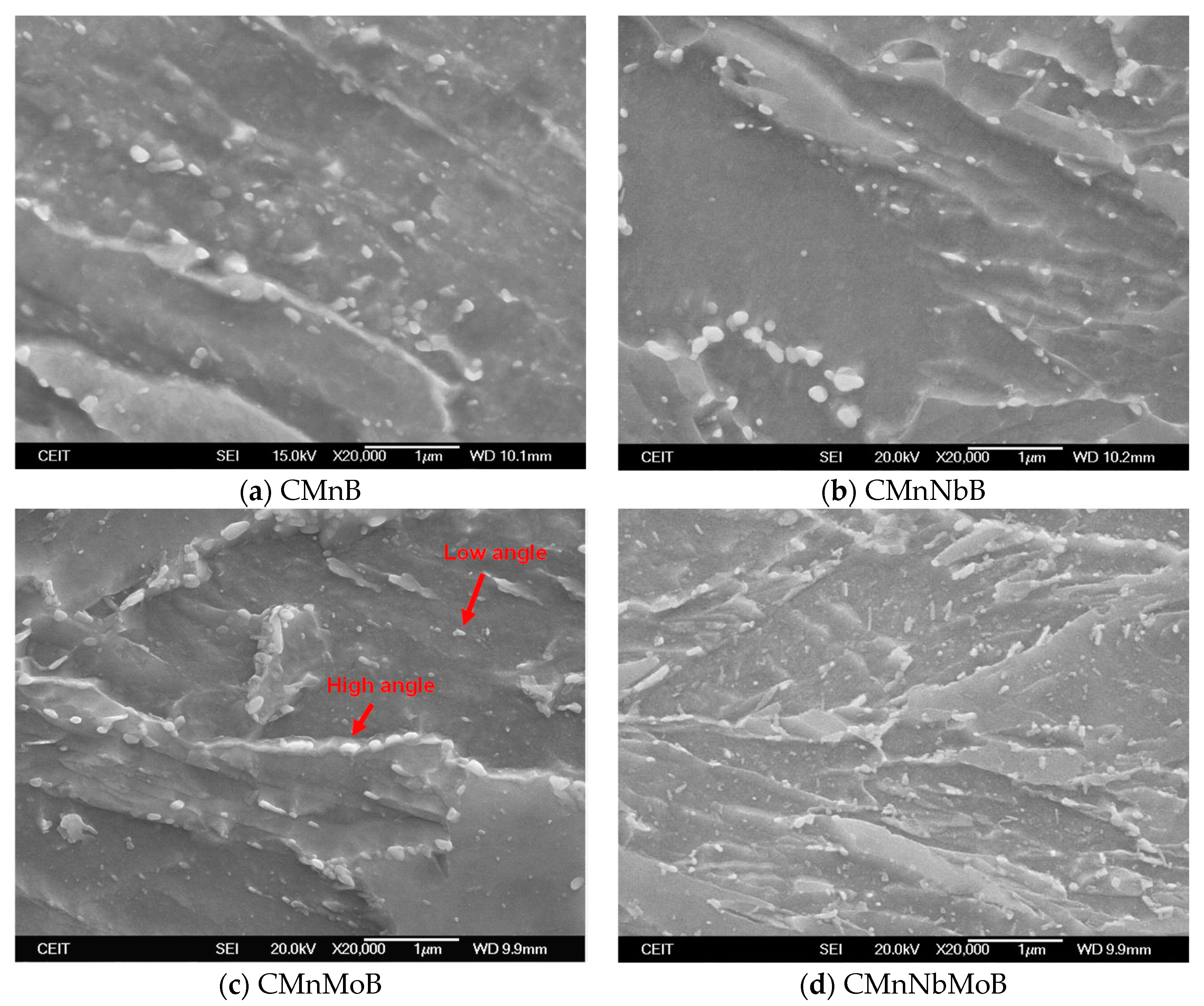
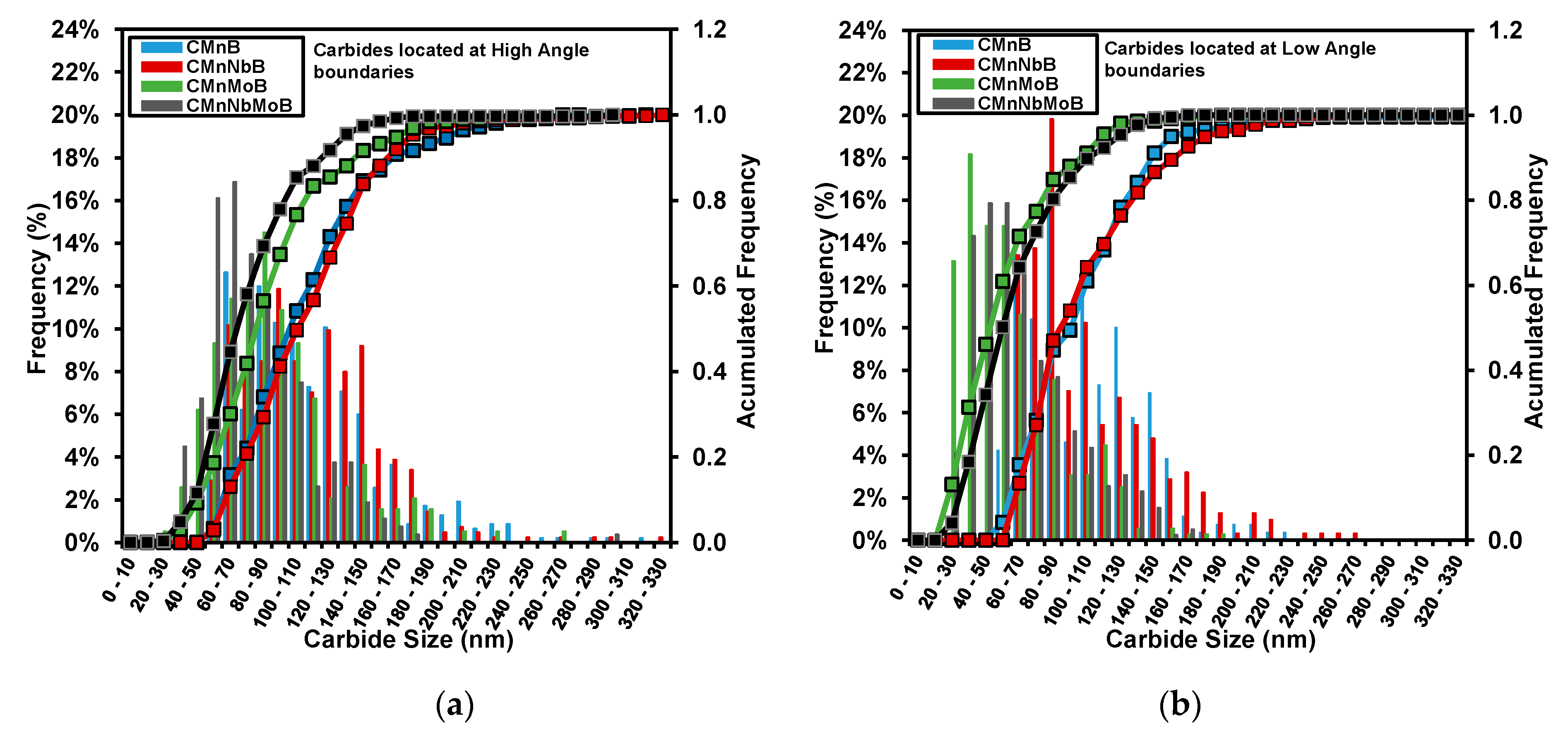
3.2.3. Quantification of Carbide Size and Area Fraction
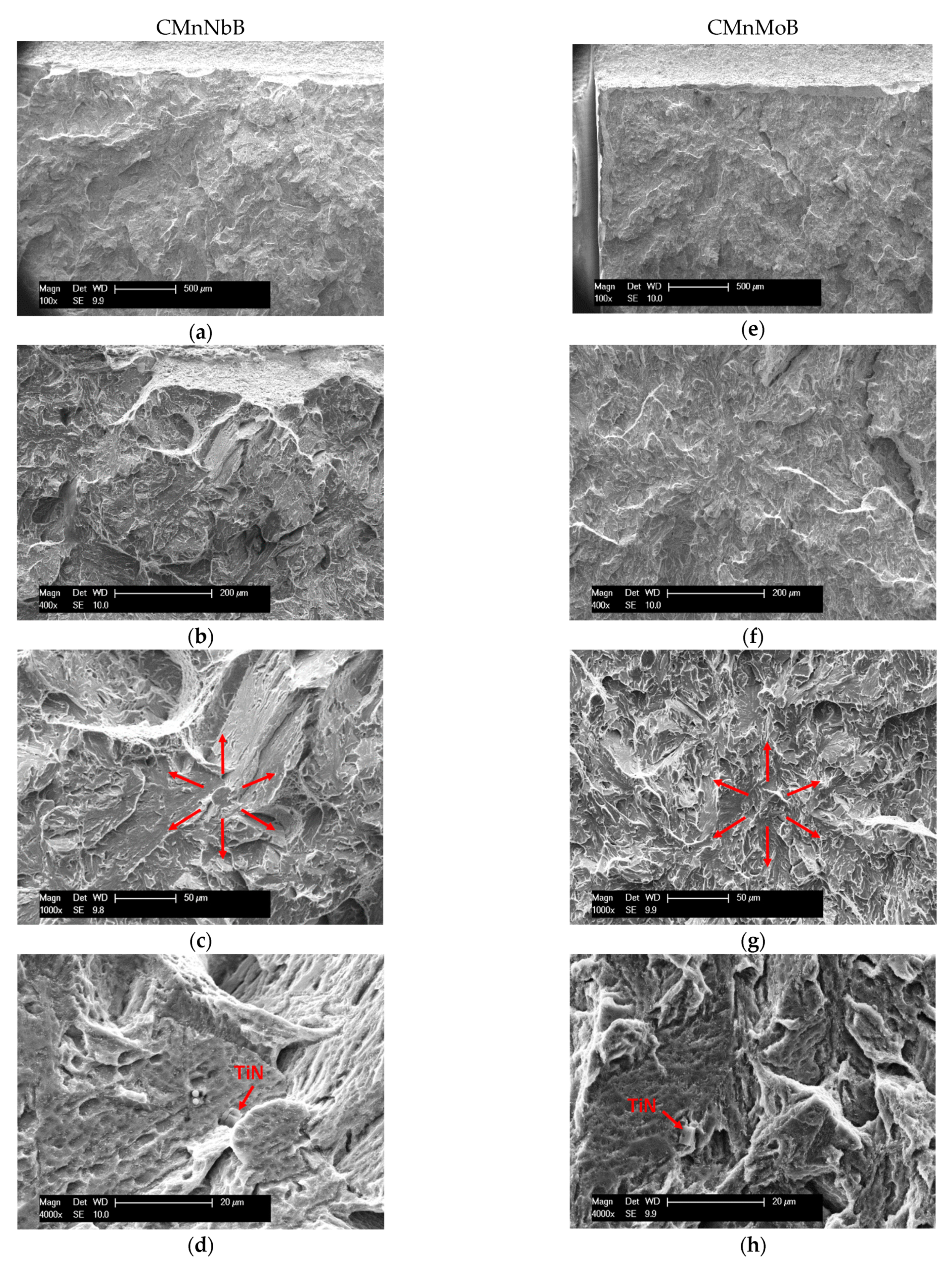
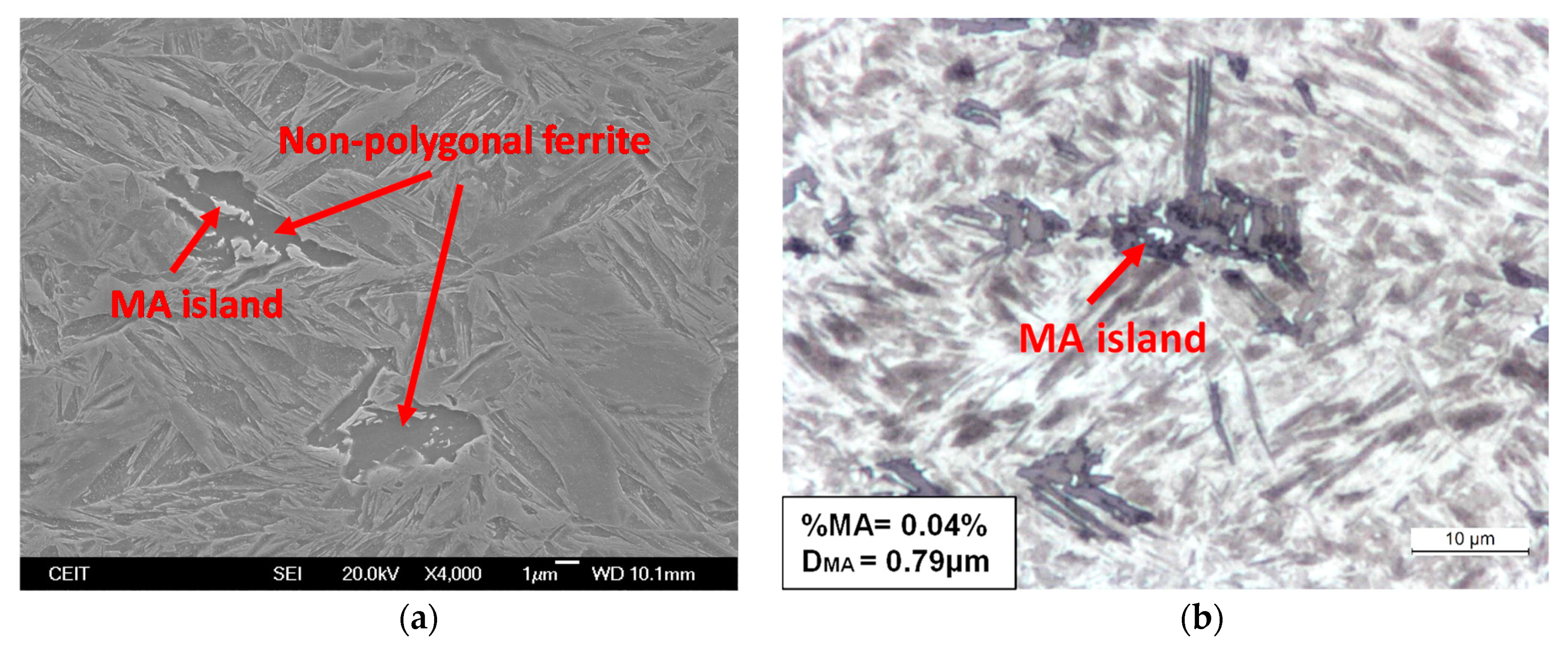
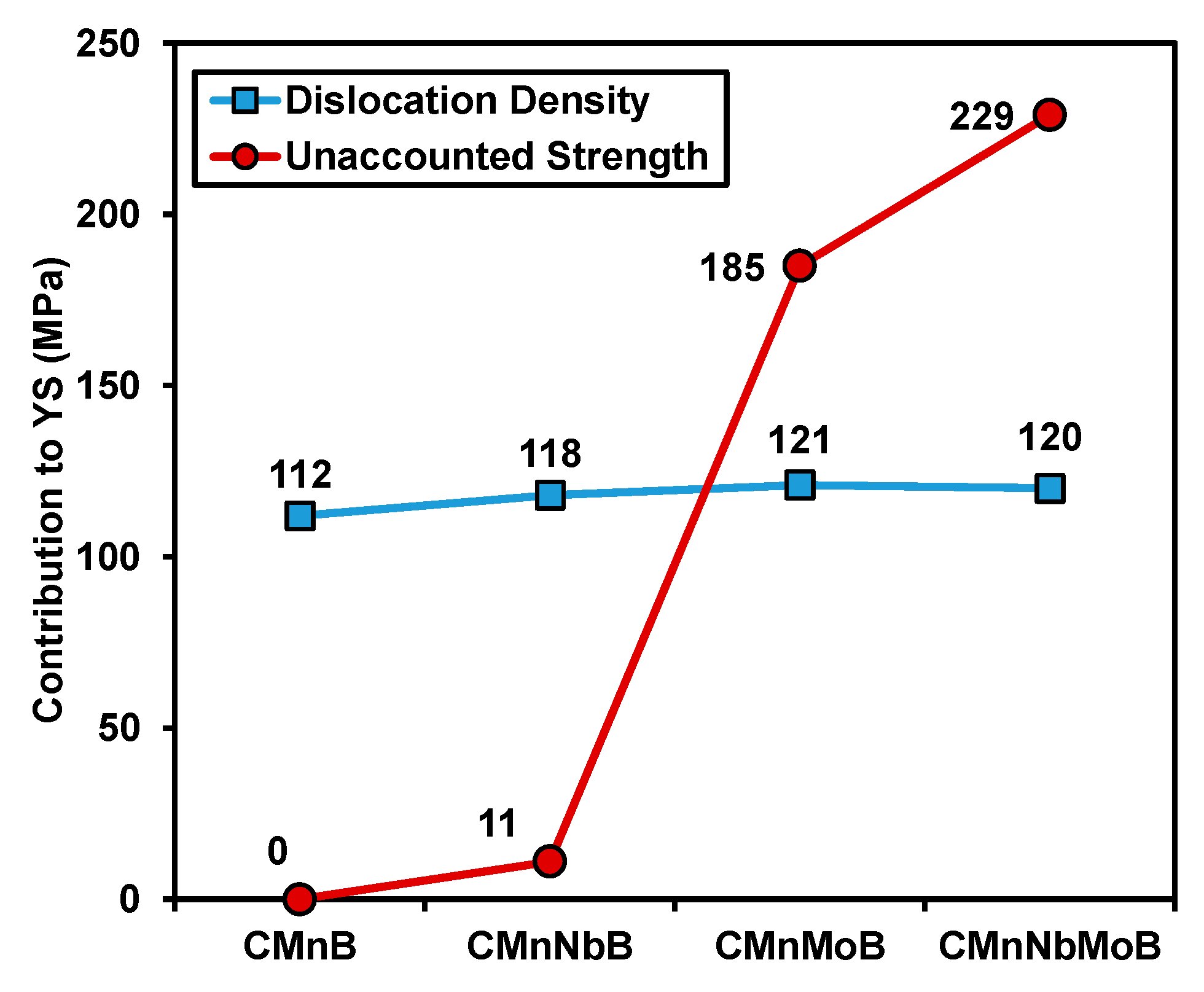
3.2.4. Additional Contributions to Toughness
- (1)
- Presence of hard secondary phases
- (2)
- Hardening due to dislocation density, fine precipitation and carbon in solid solution
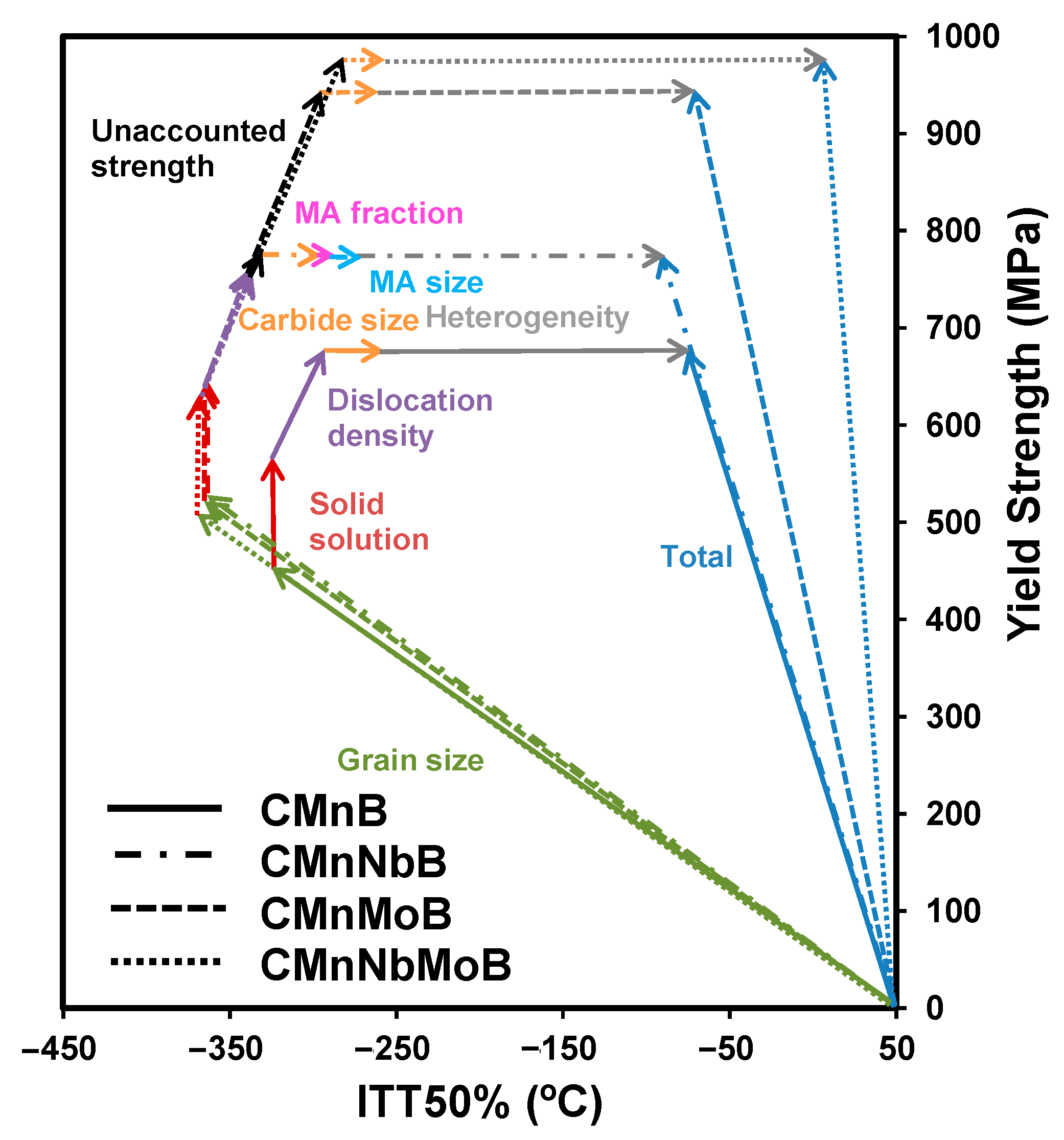
3.3. Quantitative Relationship between Microstructure and Transition Temperature
3.4. Comparative Evaluation of Strengthening versus Transition Temperature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berns, H. On Toughness of Quenched and Tempered Steels. Z. Werkstofftech 1978, 9, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohrbacher, H. Property Optimization in As-Quenched Martensitic Steel by Molybdenum and Niobium Alloying. Metals 2018, 8, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohrbacher, H. Synergies of niobium and boron microalloying in molybdenum based bainitic and martensitic steel. Fundam. Appl. Mo Nb Alloy. High Perform. Steels 2014, 1, 83–108. [Google Scholar]
- Larrañaga-Otegui, A.; Pereda, B.; Jorge-Badiola, D.; Gutierrez, I. Austenite Static Recrystallization Kinetics in Microalloyed B Steels. Metall. Trans. A 2016, 47, 3150–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.L.; Djahazi, M.; Jonas, J.J.; Jackman, J. The non-equilibrium segregation of boron during the recrystalization of Nb-treated HSLA steels. Acta Met. Mater. 1991, 39, 2295–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulka, K.; Kern, A.; Schriever, U. Application of Niobium in Quenched and Tempered High-Strength Steels. Mater. Sci. Forum 2005, 500–501, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Ortlepp, I.; Bleck, W. Boron in Heat-Treatable Steels: A Review. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1900133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla, C.; López, B.; Rodriguez-Ibabe, J.M. Carbide Size Refinement by Controlling the Heating Rate during Induction in a Low Alloy Steel. Mater. Des. 2014, 62, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, G. Martensite in steel: Strength and structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 273, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linaza, M.A.; Rodriguez-Ibabe, J.M.; Urcola, J.J. Determination of the energetic parameters controlling cleavage fracture initiation in steels. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 1997, 20, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, T.; Tsuzaki, K.; Tamura, I. The morphology of the strengthening of lath martensite in steels. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1980, 20, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannula, J.; Kömi, J.; Porter, D.A. Effect of boron on the strength and toughness of direct-quenched low-carbon niobium bearing ultra-high-strength martensitic steel. Metall. Mat. Trans. A 2017, 48, 5344–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawoto, Y.; Jasmawati, N.; Sumeru, K. Effect of prior austenite grain size on the morphology and mechanical properties of martensite in medium carbon steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhara, T.; Kikumoto, K.; Saito, H.; Sekine, T.; Ogata, T.; Morino, S. Phase transformation from fine-grained austenite. ISIJ Int. 2008, 48, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani Sanij, M.H.; Ghasemi Banadkouki, S.S.; Mashreghi, A.R.; Moshrefifar, M. The effect of single and double quenching and tempering heat treatments on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI 4140 steel. Mater. Des. 2012, 42, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laasraoui, A.; Jonas, J.J. Recrystallization of Austenite after Deformation at High Temperatures and Strain Rates-Analysis and Modeling. Metall. Trans. A 1991, 22, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, C.R.; Zurob, H.S.; Sinclair, C.W.; Brechet, Y.J.M. The comparative effectiveness of Nb solute and NbC precipitates at impeding grain-boundary motion in Nb steels. Scripta Mater. 2008, 59, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isasti, N.; Jorge-Badiola, D.; Taheri, M.L.; Uranga, P. Microstructural and precipitation characterization in Nb-Mo microalloyed steels, estimation of the contributions to the strength. Met. Mater. Int. 2014, 20, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, L.; López, B.; Pereda, B. Characterization of Austenite Microstructure from Quenched Martensite Using Conventional Metallographic Techniques and a Crystallographic Reconstruction Procedure. Metals 2018, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, L.; Pereda, B.; López, B. Validation and Analysis of the Parameters for Reconstructing the Austenite Phase from Martensite Electron Backscatter Diffraction Data. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 5258–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, L.; Gey, N.; Mercier, R.; Blaineau, P.; Humbert, M. An advanced approach to reconstructing parent orientation maps in the case of approximate orientation relations: Application to steels. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 4551–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaijalainen, A.; Pallaspuro, S.; Porter, D.A. Tempering of direct quenched low-alloy ultra-high-strength steel, Part I—Microstructure. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 922, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallaspuro, S.; Kaijalainen, A.; Limnell, T.; Porter, D. Tempering of Direct Quenched Low-Alloy Ultra-High-Strength Steel, Part II—Mechanical Properties. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 922, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, A.; Kaijalainen, A.; Porter, D.; Suikkanen, P.; Yang, J.-R.; Tsai, Y.-T. The effect of finish rolling temperature and tempering on the microstructure, mechanical properties and dislocation density of direct-quenched steel. Mater. Charact. 2018, 139, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannula, J.; Kaijalainen, A.; Porter, D.; Somani, M.; Kömi, J. Evaluation of Mechanical Properties and Microstructures of Direct-Quenched and Direct Quenched and Tempered Microalloyed Ultrahigh-Strength Steels. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 2000451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isasti, N.; Badiola, D.J.; Taheri, M.L.; Uranga, P. Microstructural features controlling mechanical properties in Nb-Mo microalloyed steels. Part II: Impact toughness. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 4972–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, K.J.; Pickering, F.B.; Gladman, T. Grain-refined C-Mn steels. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1967, 205, 161–182. [Google Scholar]
- Mintz, B.; Peterson, G.; Nassar, A. Structure-property relationships in ferrite-pearlite steels. Ironmak. Steelmak. 1994, 21, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Mintz, B.; Morrison, W.B.; Jones, A. Influence of carbide thickness on impact transition temperature of ferritic steels. Met. Technol. 1979, 6, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, I. Effect of microstructure on the impact toughness of Nb-microalloyed steel: Generalisation of existing relations from ferrite-pearlite to high strength microstructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 571, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, F.B.; Gladman, T. Metallurgical Developments in Carbon Steels. ISI Spec. Rep. 1963, 81, 42. [Google Scholar]
- From, A.; Sandstrom, R. Influence of mixed grain size distributions on the toughness in high and extra high strength steels. Mater. Charact. 1999, 42, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanamura, T.; Yin, F.; Nagai, K. Ductile-brittle transition temperature of ultrafine ferrite/cementite microstructure in a low carbon steel controlled by effective grain size. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larzabal, G.; Isasti, N.; Rodríguez-Ibabe, J.M.; Uranga, P. Evaluating Strengthening and Impact Toughness Mechanisms for Ferritic and Bainitic Microstructures in Nb, Nb-Mo and Ti-Mo Microalloyed Steels. Metals 2017, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurutuza, I.; Isasti, N.; Detemple, E.; Schwinn, V.; Mohrbacher, H.; Uranga, P. Effect of Nb and Mo Additions in the Microstructure/Tensile Property Relationship in High Strength Quenched and Quenched and Tempered Boron Steels. Metals 2021, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranga, P.; Gutierrez, I.; Lopez, B. Determination of recrystallization kinetics from plane strain compression tests. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2013, 578, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, K. Modified Tank Fitting Algorithm Charpy Impact Data; Research Seminar on Economical and Safe Application of Modern Steels for Pressure Vessels: Aachen, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Schambron, T.; Dehghan-Manshadi, A.; Chen, L.; Gooch, T.; Killmore, C.; Pereloma, E. Effect of Mo on Dynamic Recrystallization and Microstructure Development of Microalloyed Steels. Met. Mater. Int. 2017, 23, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereda, B.; Fernández, A.I.; López, B.; Rodriguez-Ibabe, J.M. Effect of Mo on Dynamic recrystallization behavior of Nb-Mo microalloyed steels. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.F.; Hernandez, C.A. General expression of the Zener-Hollomon parameter as a function of the chemical composition of low alloy and microalloyed steels. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.B.; Hong, S.G.; Park, C.G.; Park, S.H. Carbide precipitation and high-temperature strength of hot-rolled high strength, low alloy steels containing Nb and Mo. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, I.; Salas-Reyes, A.E.; Bedolla-Jacuinde, A.; Calvo, J.; Cabrera, J.M. Effect of Nb and Mo on the hot ductility behavior of a high-manganese austenitic Fe-21Mn-1.3Al-1.5Si-0.5C TWIP steel. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 616, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larzabal, G.; Isasti, N.; Rodriguez-Ibabe, J.M.; Uranga, P. Effect of Microstructure on Post-Rolling Induction Treatment in a Low C Ti-Mo Microalloyed Steel. Metals 2018, 8, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagnotto, M.; Ponge, D.; Demir, E.; Raabe, D. Orientation gradients and geometrically necessary dislocations in ultrafine grained dual-phase steels studied by 2D and 3D EBSD. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 257, 2738–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranga, P.; Shang, C.-J.; Senuma, T.; Yang, J.-R.; Guo, A.-M.; Mohrbacher, H. Molybdenum alloying in high-performance flat-rolled steel grades. Adv. Manuf. 2020, 8, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djahazi, M.; He, X.L.; Jonas, J.J.; Sun, W.P. Nb(C, N) Precipitation and Austenite Recrystallization in Boron-Containing High-Strength Low-Alloy Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1992, 23, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohrbacher, H. Mo and Nb alloying in plate steels for high-performance applications. Proc. International Symposium on the Recent Developments in Plate Steels. Int. Symp. Recent Dev. Plate Steels 2011, 169–179. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Hardy_Mohrbacher/publication/333661101_Mo_and_Nb_Alloying_in_Plate_Steels_for_High-Performance_Applications/links/5cfb6da24585157d159b1ad7/Mo-and-Nb-Alloying-in-Plate-Steels-for-High-Performance-Applications.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Kim, Y.M.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Hwang, B.; Lee, S.; Kim, N.J. Effects of molybdenum and vanadium addition on tensile and charpy impact properties of API X70 linepipe steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, P.; Solberg, J.K.; Karlsen, M.; Akselsen, O.M.; Østby, E. Cleavage fracture initiation at M-A constituents in intercritically coarse-grained heat-affected zone of a HSLA steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LePera, F.S. Improved etching technique for the determination of percent martensite in high-strength dual-phase steels. Metallography 1979, 12, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, F.B. The optimization of microstructures in steel and their relationship to mechanical properties. In Hardenability Concepts with Applications to Steel; Doane, D.V., Kirkaldy, J.S., Eds.; AIME: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 179–228. [Google Scholar]
- Gladman, T. The Physical Metallurgy of Microalloyed Steels, 2nd ed.; The Institute of Materials: London, UK, 1997; pp. 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Tobie, T.; Hippenstiel, F.; Mohrbacher, H. Optimizing Gear Performance by Alloy Modification of Carburizing Steels. Metals 2017, 7, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Steel | C | Si | Mn | Mo | Nb | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMnB | 0.15 | 0.32 | 1.05 | - | - | 0.0022 |
| CMnNbB | 0.16 | 0.29 | 1.05 | - | 0.026 | 0.0019 |
| CMnMoB | 0.16 | 0.28 | 1.07 | 0.5 | - | 0.0022 |
| CMnNbMoB | 0.16 | 0.31 | 1.07 | 0.5 | 0.026 | 0.0018 |
| Steel | US (J) | ITT 27 J (°C) | ITT 50% (°C) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMnB | 108 | −63 | −66 | 617 | 700 |
| CMnNbB | 112 | −59 | −75 | 757 | 818 |
| CMnMoB | 97 | −80 | −84 | 943 | 991 |
| CMnNbMoB | 82 | −1 | −10 | 977 | 1034 |
| Steel | Sv (µm−1) | Austenite Thickness (µm) | D2° (µm) | D15° (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMnB | 0.13 | 12.9 ± 0.8 | 1.26 ± 0.03 | 1.85 ± 0.1 |
| CMnNbB | 0.24 | 5.5 ± 0.2 | 0.92 ± 0.01 | 1.45 ± 0.05 |
| CMnMoB | 0.30 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 0.86 ± 0.1 | 1.44 ± 0.05 |
| CMnNbMoB | 0.23 | 6.9 ± 0.4 | 0.85 ± 0.01 | 1.43 ± 0.06 |
| Steel | Carbide Size (nm) (Total Carbide Population) | Area Fraction (%) (Total Carbide Population) |
|---|---|---|
| CMnB | 110.1 ± 3 | 0.54 |
| CMnNbB | 111.3 ± 2.9 | 0.60 |
| CMnMoB | 70.6 ± 3 | 1.46 |
| CMnNbMoB | 72.3 ± 2.4 | 1.72 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zurutuza, I.; Isasti, N.; Detemple, E.; Schwinn, V.; Mohrbacher, H.; Uranga, P. Toughness Property Control by Nb and Mo Additions in High-Strength Quenched and Tempered Boron Steels. Metals 2021, 11, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010095
Zurutuza I, Isasti N, Detemple E, Schwinn V, Mohrbacher H, Uranga P. Toughness Property Control by Nb and Mo Additions in High-Strength Quenched and Tempered Boron Steels. Metals. 2021; 11(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010095
Chicago/Turabian StyleZurutuza, Irati, Nerea Isasti, Eric Detemple, Volker Schwinn, Hardy Mohrbacher, and Pello Uranga. 2021. "Toughness Property Control by Nb and Mo Additions in High-Strength Quenched and Tempered Boron Steels" Metals 11, no. 1: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010095
APA StyleZurutuza, I., Isasti, N., Detemple, E., Schwinn, V., Mohrbacher, H., & Uranga, P. (2021). Toughness Property Control by Nb and Mo Additions in High-Strength Quenched and Tempered Boron Steels. Metals, 11(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010095







