Porous Titanium Cylinders Obtained by the Freeze-Casting Technique: Influence of Process Parameters on Porosity and Mechanical Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
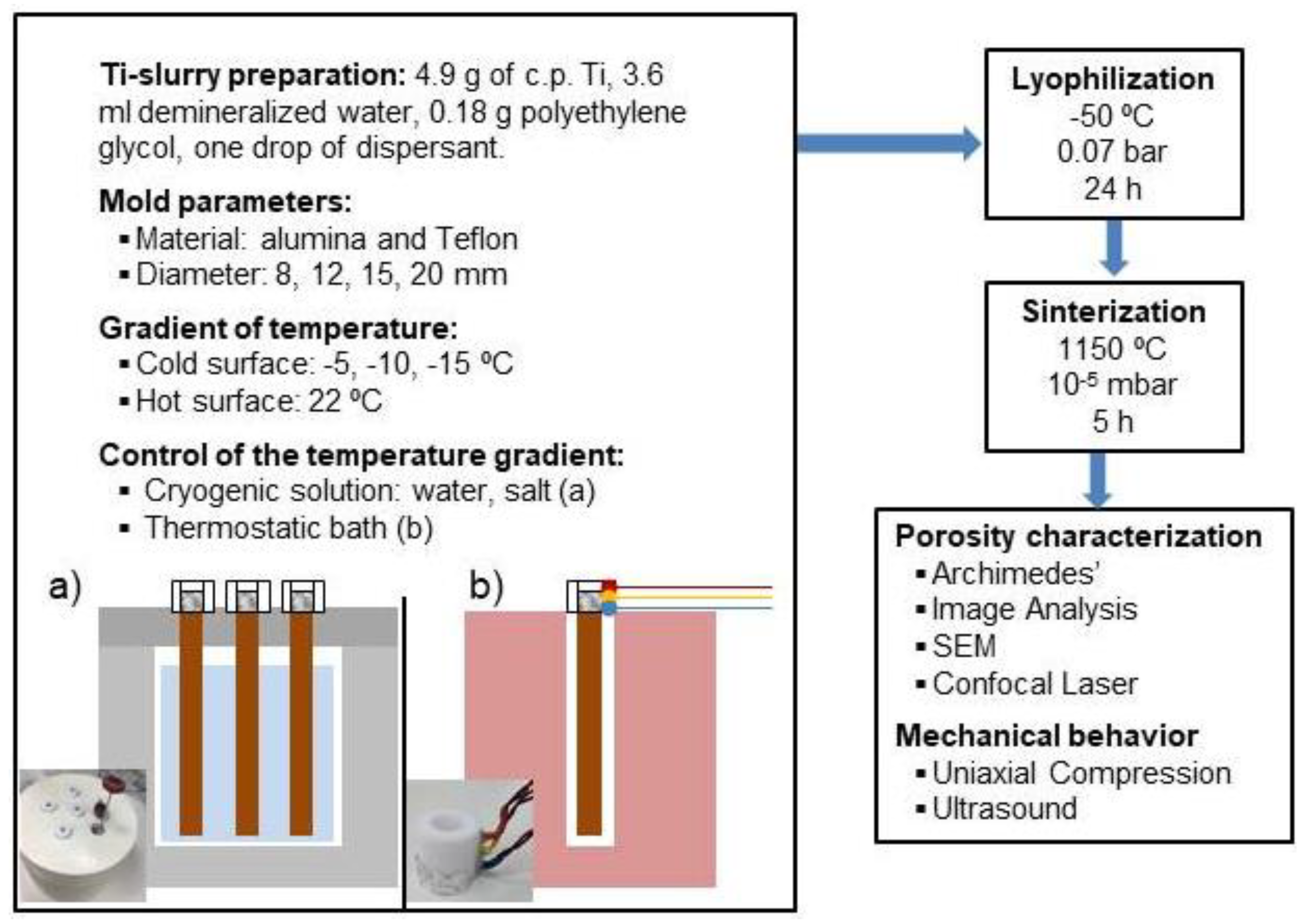
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
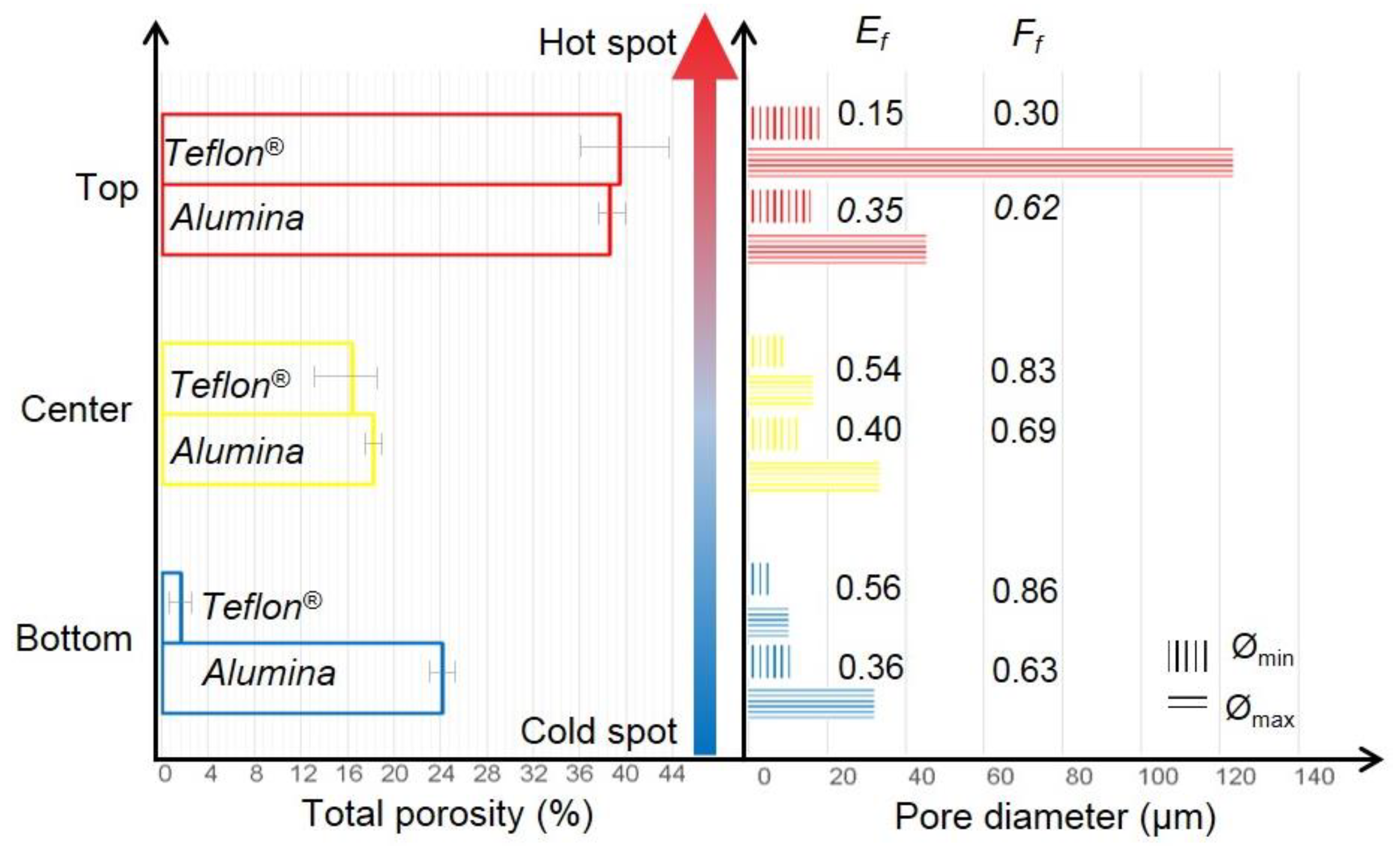
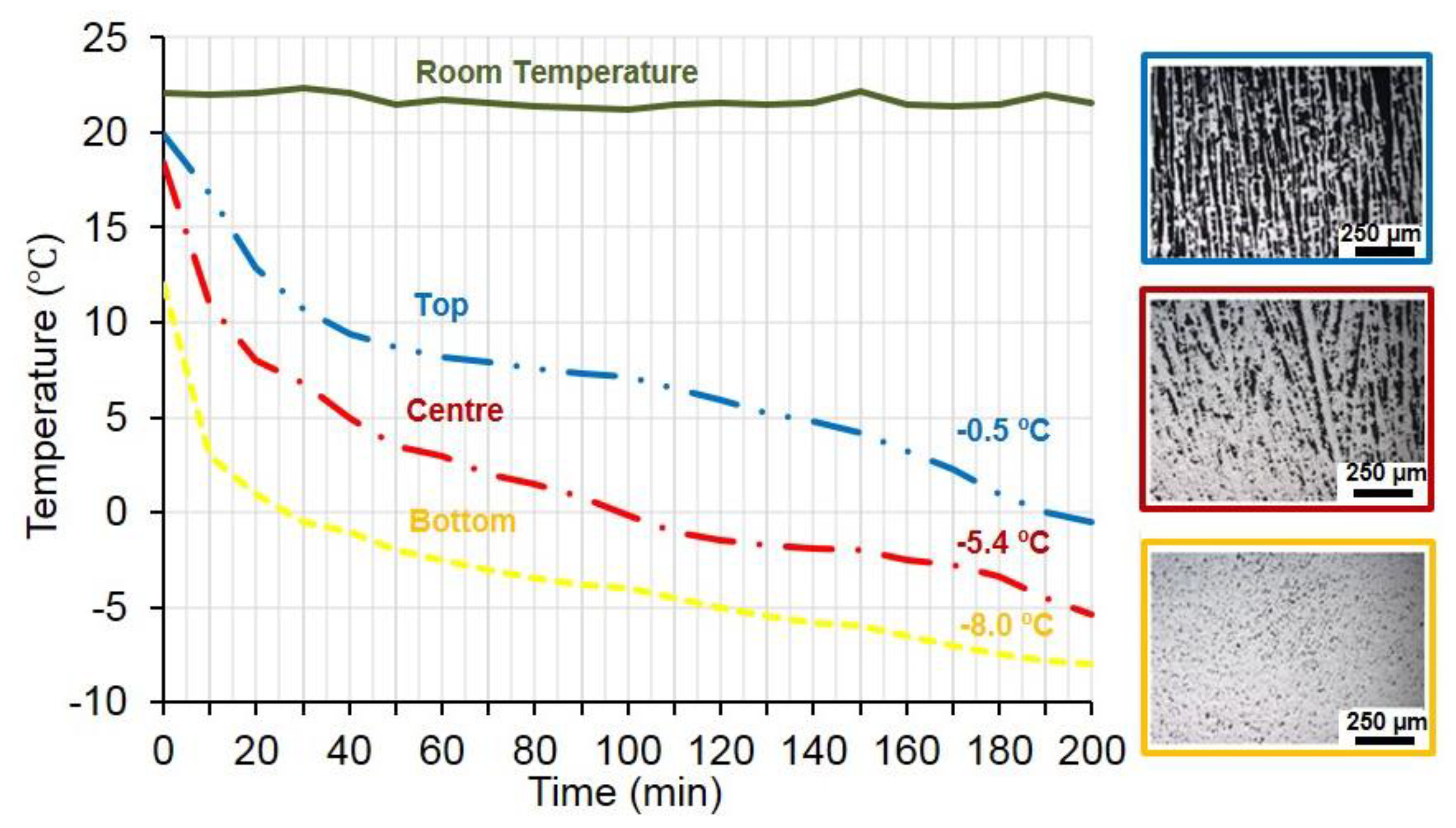
3.1. Fabrication of the Porous Titanium Substrates Using Cryogenic Solution and the Home-Made Device to Control Temperature Gradient
3.2. Fabrication of the Porous Substrates Using a Thermostatic Bath
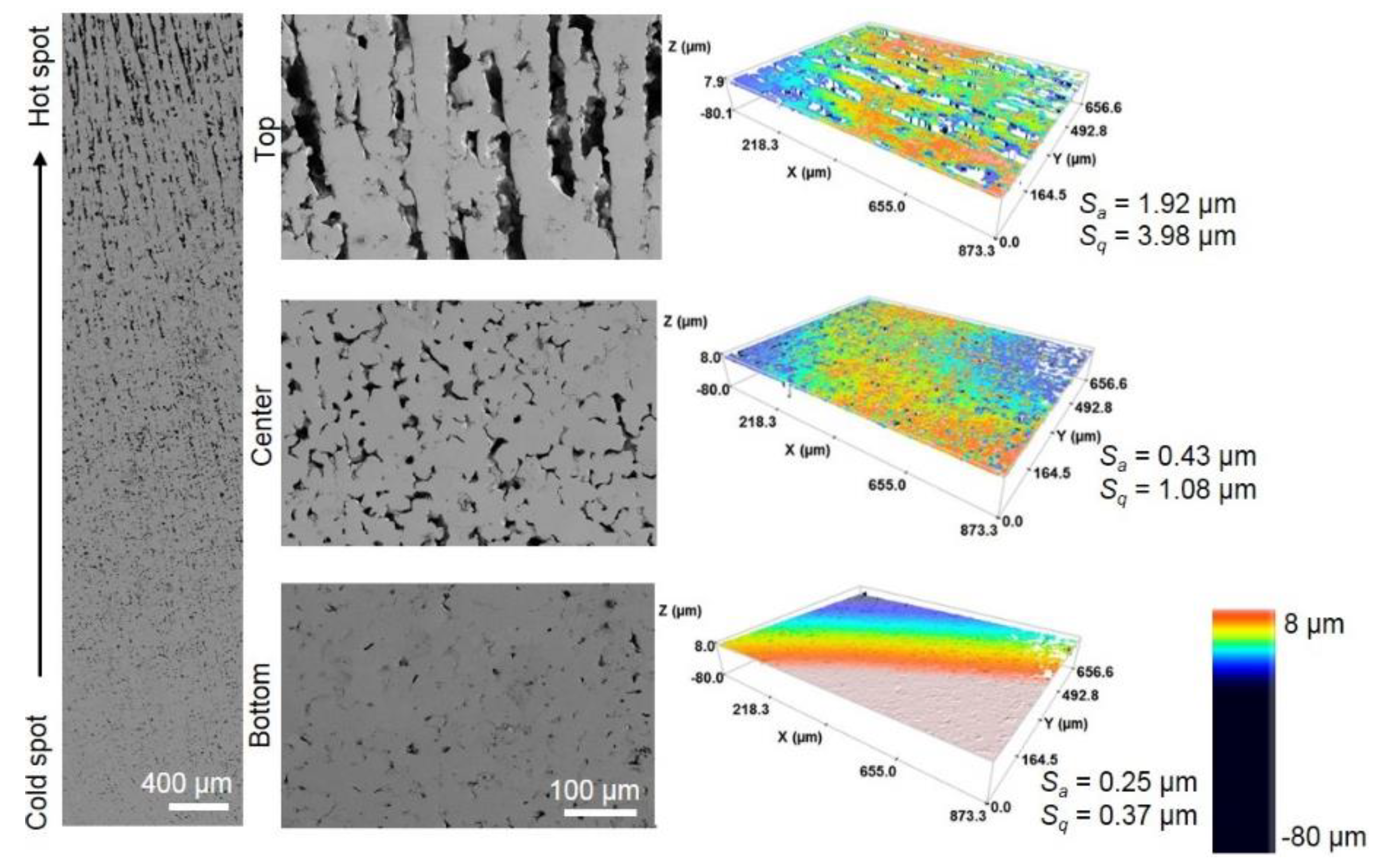
3.3. Mechanical Behavior of Porous Titanium Cylinders
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USA Arthritis Prevention, Treatment, and Rehabilitation. Hearing before the Subcommittee on Public Health and Environment of the Committee on Interstate and Foreign Commerce House of Representative; U.S. Government Printing Office Washington: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; pp. 93–102.
- Norowski, P.A.; Bumgardner, J.D. Biomaterial and antibiotic strategies for peri-implantitis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 88, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Zhou, L.; Tan, G. Fourth-generation biomedical materials. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, A.M.; Goldberg, M.; Doeven, E.H.; Littlefair, G. Titanium in Biomedical Applications-Properties and Fabrication: A Review. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2015, 5, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengvall, P.; Elwing, H.; Sjöqvist, L.; Lundström, I.; Bjursten, L.M. Interaction between hydrogen peroxide and titanium: A possible role in the biocompatibility of titanium. Biomaterials 1989, 10, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, K. Review on titanium and titanium based alloys as biomaterials for orthopaedic applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 844–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, J.Y.; Ashman, R.B.; Turner, C.H. Young’s modulus of trabecular and cortical bone material: Ultrasonic and microtensile measurements. J. Biomech. 1993, 26, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgiou, V.; Kaplan, D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5474–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.M.; O’Brien, F.J. Understanding the effect of mean pore size on cell activity in collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2010, 4, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidinia, M.; Wang, L.; Tong, W.; Ajlouni, R.; Kovacevic, R. Fatigue properties of a dental implant produced by electron beam melting ® (EBM). J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 226, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin Yavari, S.; Ahmadi, S.M.; Wauthle, R.; Pouran, B.; Schrooten, J.; Weinans, H.; Zadpoor, A.A. Relationship between unit cell type and porosity and the fatigue behavior of selective laser melted meta-biomaterials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 43, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Huang, Y.; Ao, Y.; Han, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, Z. Effect of pore geometry on the fatigue properties and cell affinity of porous titanium scaffolds fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 88, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Li, S.J.; Wang, S.G.; Hou, W.T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.C.; Hao, Y.L.; Yang, R.; Misra, R.D.K.; Murr, L.E. Compressive and fatigue behavior of functionally graded Ti-6Al-4V meshes fabricated by electron beam melting. Acta Mater. 2018, 150, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Hou, W.; Hao, Y.; Jin, W.; Yang, R.; Misra, R.D.K.; Murr, L.E. Fatigue behavior of Ti-6Al-4V cellular structures fabricated by additive manufacturing technique. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueba, P. Desarrollo de titanio con porosidad gradiente radial y longitudinal para aplicaciones biomédicas. Ph.D Thesis, University of Seville, Sevilla, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chino, Y.; Dunand, D.C. Directionally freeze-cast titanium foam with aligned, elongated pores. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, W.A.; Gurnick, R.S.; Francisco, A.C. Preliminary investigation of the freeze-casting method for forming refractory powders. Natl. Advis. Comm. Aeronaut. 1954, RME53L21, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, H.M.; Gryte, C.C. Mechanism of lamellar spacing adjustment in directionally frozen agar gels. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1985, 263, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, H.M.; Noda, I.; Gryte, C.C. No CPS 768 Formation of anisotropic ice-agar composites by directional freezing. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1984, 262, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoof, H.; Apel, J.; Heschel, I.; Rau, G. Control of pore structure and size in freeze-dried collagen sponges. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 58, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deville, S. Freeze-casting of porous biomaterials: Structure, properties and opportunities. Materials 2010, 3, 1913–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deville, S. Freeze-casting of porous ceramics: A review of current achievements and issues. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xu, T.; Wang, C. A review of fabrication strategies and applications of porous ceramics prepared by freeze-casting method. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 2907–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Dunand, D.C. Mechanical properties of directionally freeze-cast titanium foams. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotti, K.L.; Dunand, D.C. Freeze casting—A review of processing, microstructure and properties via the open data repository, FreezeCasting. net. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 94, 243–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, P.T.; Bascón Suá, J.R.; Beltrán, A.M.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, J.A.; Hernández, Y.T.; Palacio, J.J.P.; Álvarez, E.A.; Dunand, D.C. A simple and economical device to process Ti cylinders with elongated porosity by freeze-casting techniques: Design and manufacturing. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 770, 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Lascano, S.; Arévalo, C.; Montealegre-Melendez, I.; Muñoz, S.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, J.A.; Trueba, P.; Torres, Y. Porous titanium for biomedical applications: Evaluation of the conventional powder metallurgy frontier and space-holder technique. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhao, H.; Qu, S.; Li, X.; Li, Y. New developments of ti-based alloys for biomedical applications. Materials 2014, 7, 1709–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Brinson, L.C. Finite element modeling of porous titanium. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2007, 44, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.F. On strength of porous material: Simple systems and densified systems. Mater. Struct. Constr. 1996, 31, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imwinkelried, T. Mechanical properties of open-pore titanium foam. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2007, 81, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.E.; Yamada, Y.; Shimojima, K.; Chino, Y.; Asahina, T.; Mabuchi, M. Processing and mechanical properties of autogenous titanium implants materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2002, 13, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, Y.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Arias, S.; Echeverry, M.; Robledo, S.; Amigo, V.; Pavón, J.J. Processing, characterization and biological testing of porous titanium obtained by space-holder technique. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 6565–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, S.; Pavón, J.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, J.A.; Civantos, A.; Allain, J.P.; Torres, Y. On the influence of space holder in the development of porous titanium implants: Mechanical, computational and biological evaluation. Mater. Charact. 2015, 108, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Trujillo, C.; Beltrán, A.M.; Garvi, M.D.; Salazar-Moya, A.; Lebrato, J.; Hickey, D.J.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, J.A.; Kamm, P.H.; Lebrato, C.; García-Moreno, F.; et al. Bacterial behavior on coated porous titanium substrates for biomedical applications. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2019, 357, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civantos, A.; Domínguez, C.; Pino, R.J.; Setti, G.; Pavón, J.J.; Martínez-Campos, E.; Garcia Garcia, F.J.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Allain, J.P.; Torres, Y. Designing bioactive porous titanium interfaces to balance mechanical properties and in vitro cells behavior towards increased osseointegration. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2019, 368, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, Y.; Pavón, J.J.; Nieto, I.; Rodríguez, J.A. Conventional powder metallurgy process and characterization of porous titanium for biomedical applications. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2011, 42, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.M.; Muñoz, S.; Trueba, P.; Eduardo, D.; Torres, Y. Influence of the Compaction Pressure and Sintering temperature on the mechanical properties of porous titanium for biomedical applications. Metals 2019, 9, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, C.; Oppenheimer, S.M.; Dunand, D.C. High strength, low stiffness, porous NiTi with superelastic properties. Acta Biomater. 2005, 1, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Area of the Sample | Pi (%) | PT (%) | Ff | Ultrasound Technique | Uniaxial Compression Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Archimedes’ | IA | Test | Estimated Dynamic Young’s Modulus, Ed, (GPa) | Test | σy (MPa) Estimated by Equation (3) | |||||
| Equation (1) | Equation (2) | Ec (GPa) | σy (MPa) | |||||||
| Top | 18.3 | 38.5 | 39.5 | 0.30 | 35.3 | 46.5 | 20.86 | 19 | 396 | 312 |
| Center | 16.4 | 0.83 | 75.9 | 74.36 | 514 | |||||
| Bottom | 1.7 | 0.86 | 103.0 | 105.97 | 644 | |||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trueba, P.; Beltrán, A.M.; Bayo, J.M.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, J.A.; Larios, D.F.; Alonso, E.; Dunand, D.C.; Torres, Y. Porous Titanium Cylinders Obtained by the Freeze-Casting Technique: Influence of Process Parameters on Porosity and Mechanical Behavior. Metals 2020, 10, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020188
Trueba P, Beltrán AM, Bayo JM, Rodríguez-Ortiz JA, Larios DF, Alonso E, Dunand DC, Torres Y. Porous Titanium Cylinders Obtained by the Freeze-Casting Technique: Influence of Process Parameters on Porosity and Mechanical Behavior. Metals. 2020; 10(2):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020188
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrueba, Paloma, Ana M. Beltrán, José Manuel Bayo, José Antonio Rodríguez-Ortiz, Diego F. Larios, Esteban Alonso, David C. Dunand, and Yadir Torres. 2020. "Porous Titanium Cylinders Obtained by the Freeze-Casting Technique: Influence of Process Parameters on Porosity and Mechanical Behavior" Metals 10, no. 2: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020188
APA StyleTrueba, P., Beltrán, A. M., Bayo, J. M., Rodríguez-Ortiz, J. A., Larios, D. F., Alonso, E., Dunand, D. C., & Torres, Y. (2020). Porous Titanium Cylinders Obtained by the Freeze-Casting Technique: Influence of Process Parameters on Porosity and Mechanical Behavior. Metals, 10(2), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020188









