Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructural Evolution of a Single Crystal High-Entropy Superalloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Single Crystal Casting
2.2. Heat Treatment
2.3. Thermal Analysis
2.4. Microstructural Observation
3. Results and Discussion
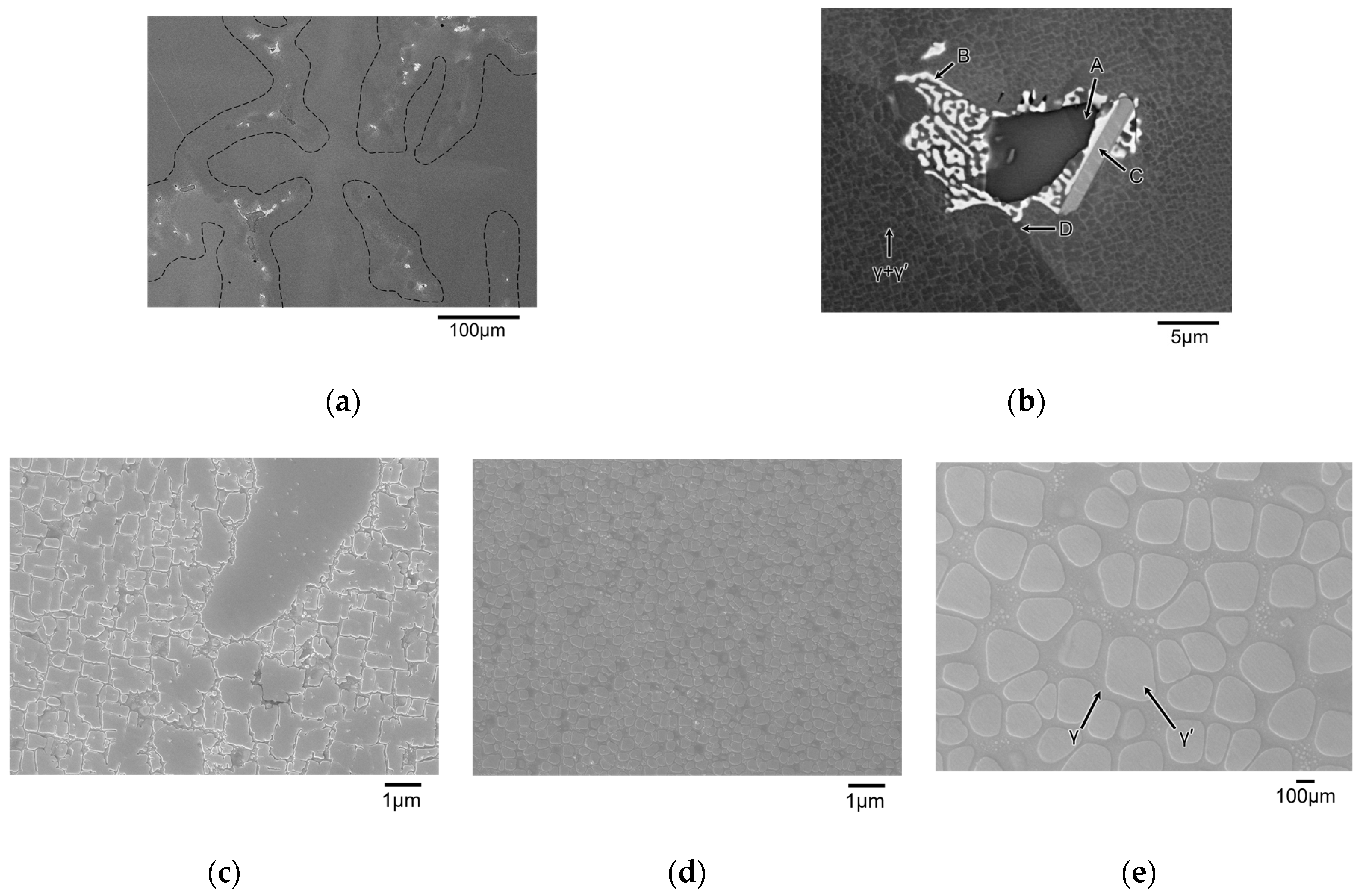
3.1. As-Cast Sample
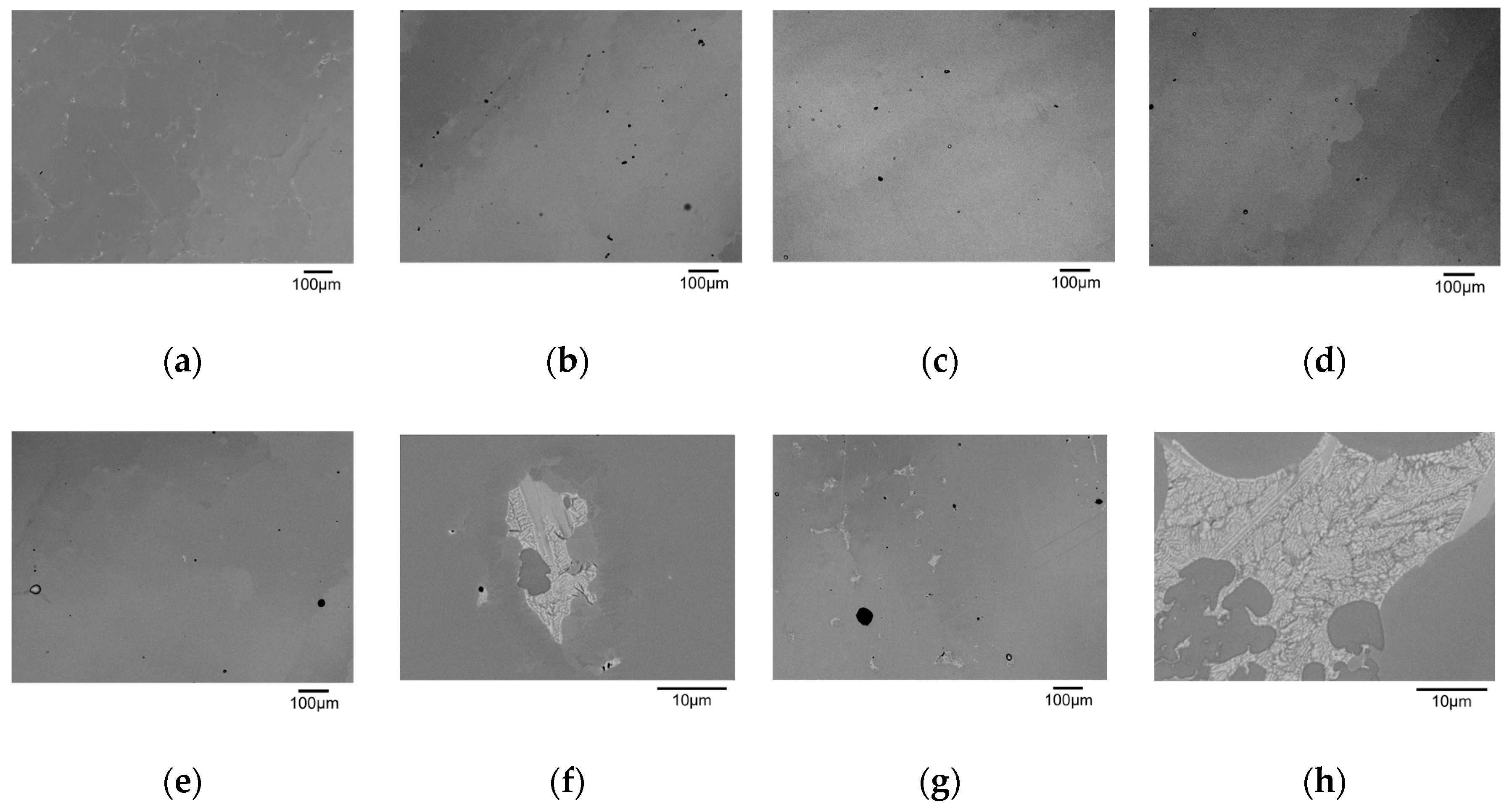
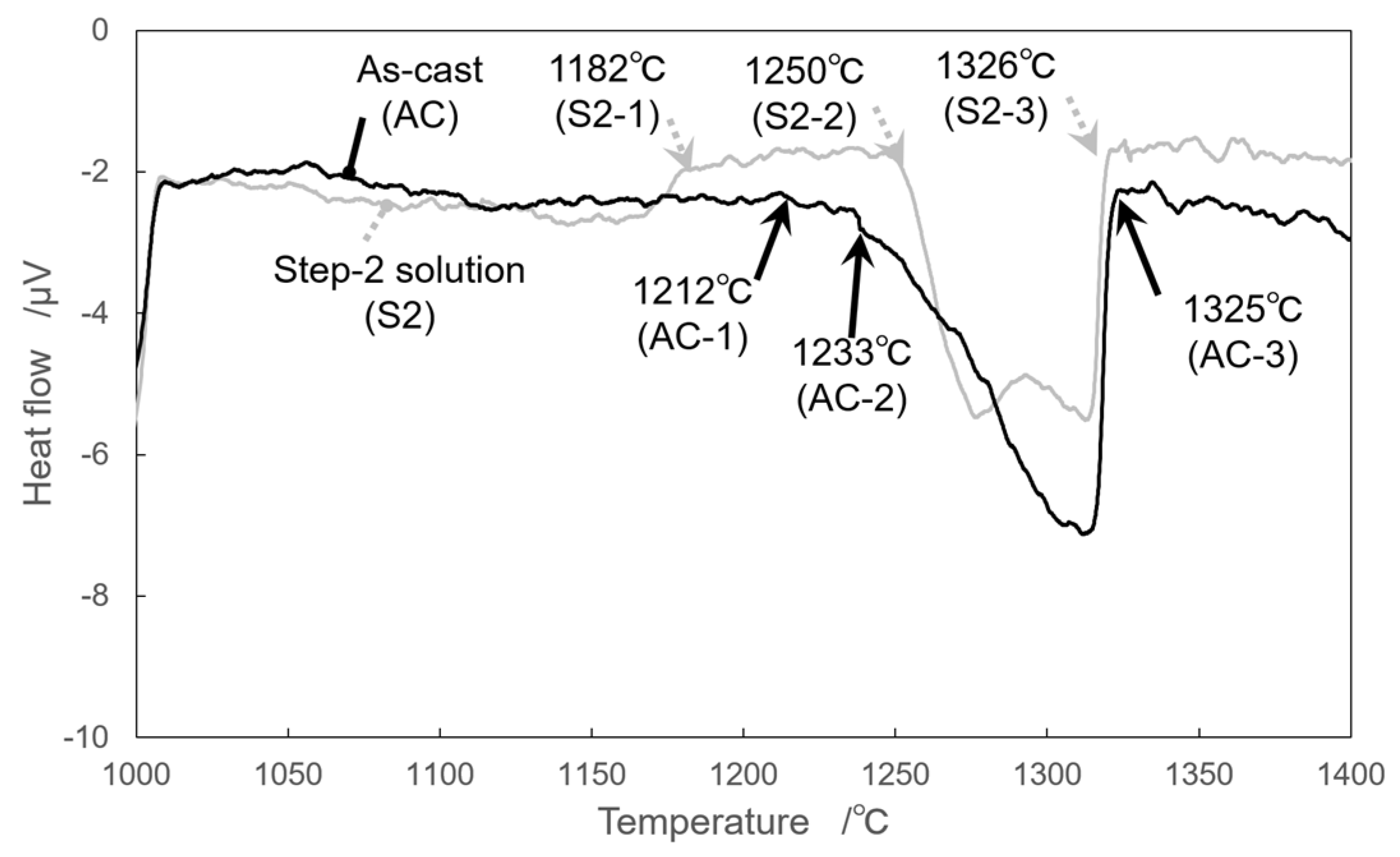
3.2. Solution Treatment
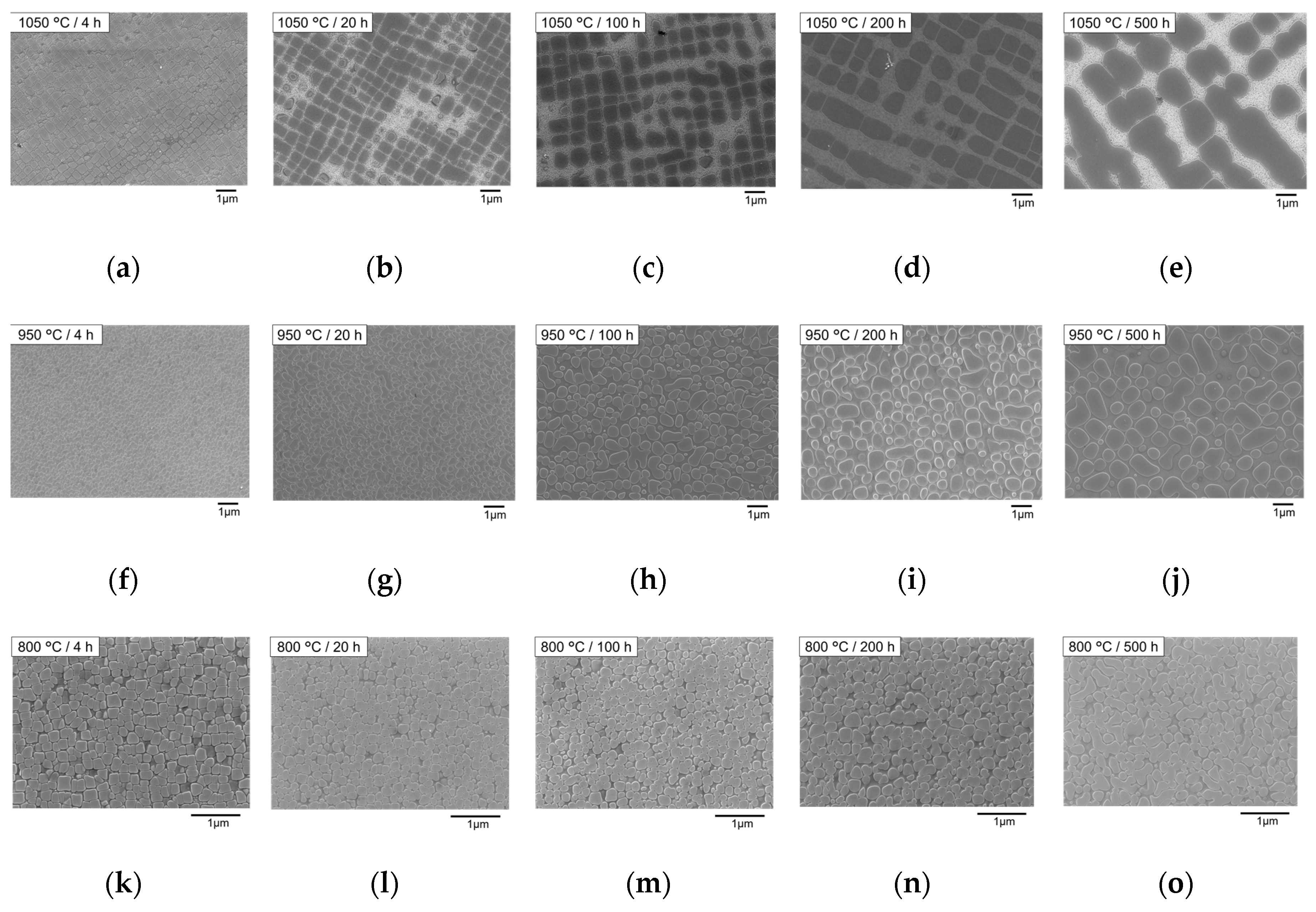
3.3. Primary Aging Treatment
3.3.1. Morphology of Primary γ′ Precipitates
3.3.2. Morphology of Secondary γ′ Precipitates
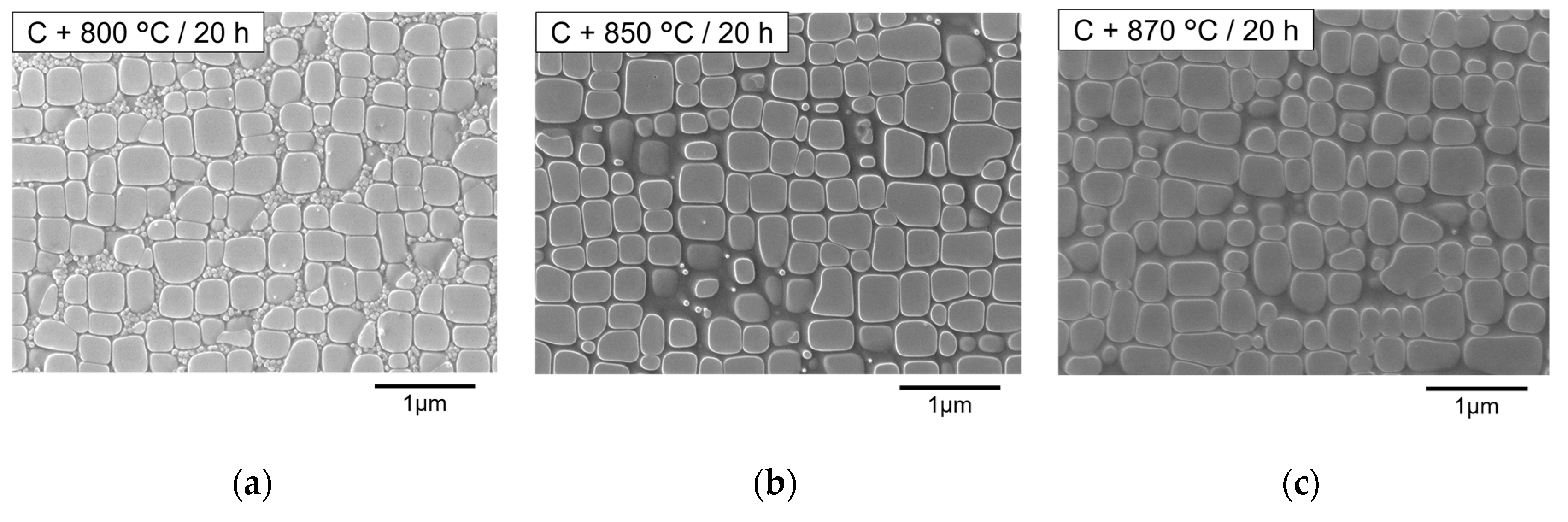
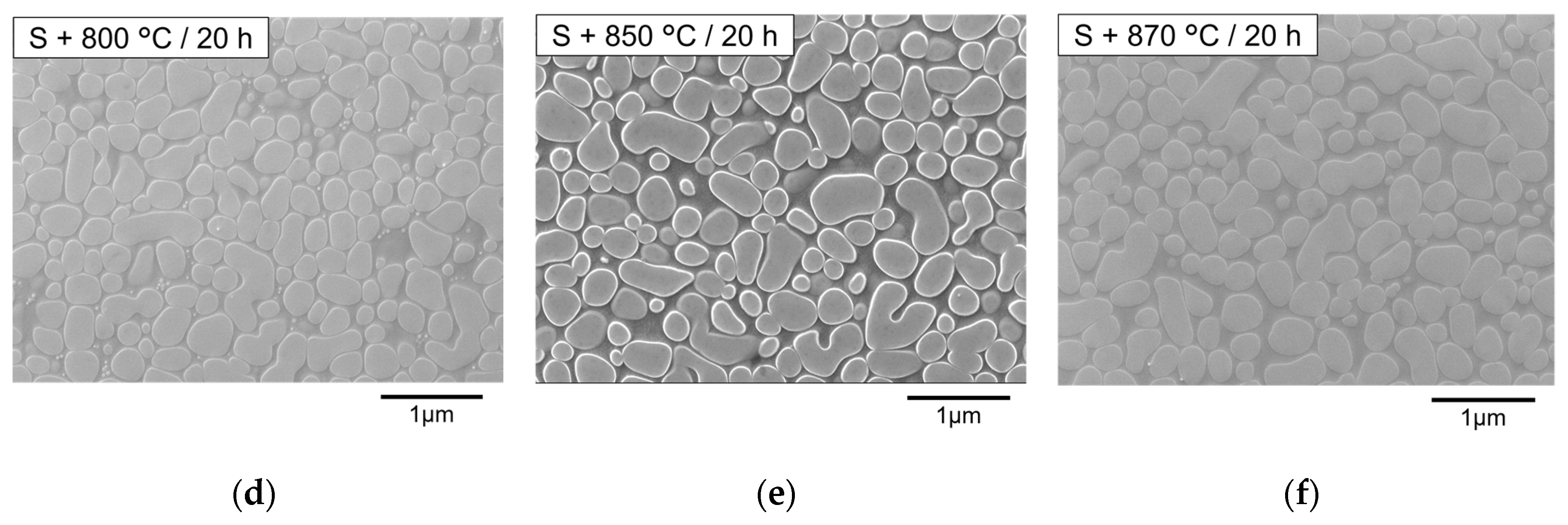
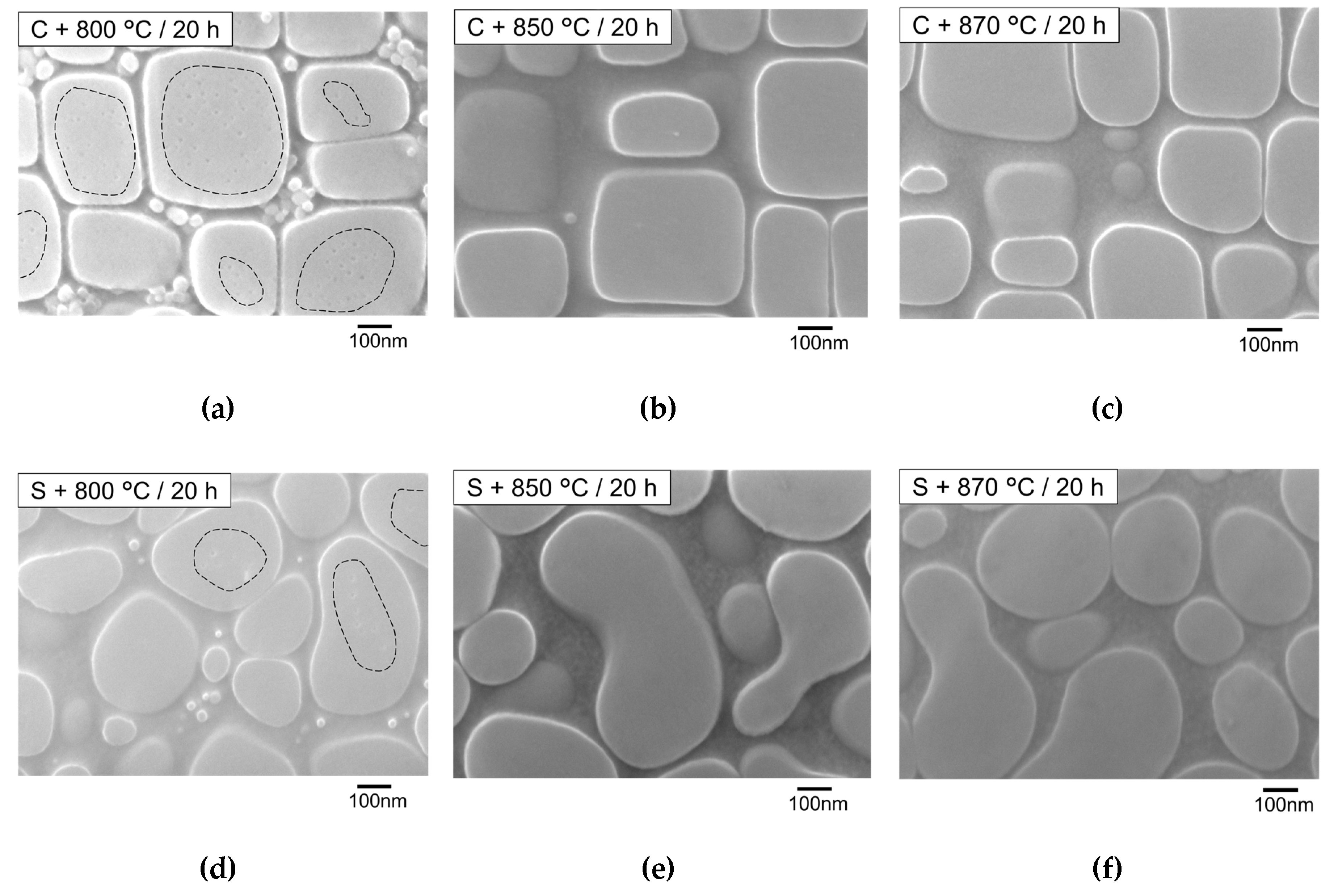
3.4. Secondary Aging Treatment
3.4.1. Morphology of Primary γ′ Precipitates
3.4.2. Morphology of Secondary γ′ Precipitates
3.4.3. Morphology of Nano γ Particles
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the as-cast stage, some extra phases were observed. Furthermore, coarsened γ′ precipitates at the interdendrite region were found due to the microsegregation of constituent elements.
- (2)
- Optimum solution treatment conditions to homogenize the microstructure by avoiding incipient melting was obtained. The solvus of γ′ phase, the solidus, and the liquidus of the HESA were experimentally determined and were found to be lower than those of conventional Ni-based single crystal superalloys, SRR99, CMSX-2, CMSX-4, and CMSX-10.
- (3)
- In the primary aging, the morphology of γ′ precipitates changed depending on the aging temperature. When aged below 950 °C, randomly distributed spherical γ′ precipitates formed, while at 1050 °C, aligned cubic γ′ precipitates formed. This indicates that the lattice misfit between γ and γ′ phases goes from near zero to negative when the temperature rises from 950 to 1050 °C.
- (4)
- At 800 °C for 20 h in secondary aging, coarsened secondary γ′ precipitates and nano γ particles inside primary γ′ precipitates were found. Coarsened secondary γ′ precipitates were formed during secondary aging at 800 °C from the finer secondary γ′ precipitates that formed during cooling from primary aging. After secondary aging at 850 and 870 °C for 20 h, much smaller secondary γ′ precipitates, which formed during cooling from secondary aging, were found instead of coarsened secondary γ′ precipitates.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bei, H.; Pharr, G.M.; George, E.P. Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of equiatomic solid solution alloys with face-centered cubic crystal structures. Acta Mater. 2014, 81, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Dlouhý, A.; Somsen, C.; Bei, H.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. The influence of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2013, 5743–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Catoor, D.; Chang, E.H.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 2014, 345, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ro, Y.; Koizumi, Y.; Harada, H. High temperature tensile properties of a series of nickel-base superalloys on a γ/γ′ tie line. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1997, 223, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakumo, T.; Koizumi, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Harada, H. Creep strength of Ni-base single-crystal superalloys on the γ/γ′ tie-line. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Symposium on Superaloys (Superalloys 2004), Champion, PA, USA, 19–23 September 2004; pp. 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.-C.; Chang, Y.-J.; Tsai, C.-W.; Wang, Y.-C.; Yeh, J.-W.; Kuo, C.-M. On the Solidification and Phase Stability of a Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Ti High-Entropy Alloy. Metall. Mat. Trans. A 2014, 45, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.H.; Tsai, M.H.; Wang, W.R.; Lin, S.J.; Yeh, J.W. Microstructure and wear behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeN1.5Tiy high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6308–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Yeh, J.W.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, S.K.; Shun, S.K.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Microstructure characterization of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Chang, Y.J.; Muraami, H.; Gorsse, S.; Yeh, A.C. Designing high entropy superalloys for elevated temperature application. Scr. Mater. 2020, 187, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W. Alloy design strategies and future trends in high-entropy alloys. JOM 2013, 6, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, T.-K.; Yeh, A.-C.; Kuo, C.-M.; Kakehi, K.; Murakami, H.; Yeh, J.-W.; Jian, S.-R. The High Temperature Tensile and Creep Behaviors of High Entropy Superalloy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Harada, H.; Zhang, J. Influence of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of 1st generation single-crystal superalloy. J. Japan Inst. Metals 2006, 70, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, P.; Khan, T. Improvement of Creep strength in a nickel-base single-crystal superalloy by heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1983, 61, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reppich, B.; Schepp, P.; Wehner, G. Some new aspects concerning particle hardening mechanisms in γ’ precipitating nickel-base alloys—II. Experiments. Acta Metall. 1982, 30, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reppich, B. Some new aspects concerning particle hardening mechanisms in γ′ precipitating Ni-base alloy- 1. Theoretical concept. Acta Metall. 1982, 1, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Shen, C.; Mills, M.J.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Modeling displacive–diffusional coupled dislocation shearing of γ′ precipitates in Ni-base superalloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 3484–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Lv, D.; Rhein, R.K.; Goiri, J.G.; Titus, M.S.; Van der Ven, A.; Pollock, T.M.; Wang, Y. Shearing of γ’ particles in Co-base and Co-Ni-base superalloys. Acta Mater. 2018, 161, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, T.-K.; Yeh, A.-C.; Yeh, J.-W.; Chiou, M.-S.; Kuo, C.-M.; Murakami, H.; Kakehi, K. High Temperature Properties of Advanced Directionally-Solidified High Entropy Superalloys. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Superalloys (Superalloys 2016), Champion, PA, USA, 11–15 September 2016; pp. 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Chang, Y.-J.; Murakami, H.; Sasaki, T.; Hono, K.; Li, C.-W.; Kakehi, K.; Yeh, J.-W.; Yeh, A.-C. Hierarchical microstructure strengthening in a single crystal high entropy superalloy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.R.; Kearsey, R.M.; Beddoes, J.C. Designing homogenization–solution heat treatments for single crystal superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 5528–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.T.; D’Souza, N.; Dong, H.; Stone, H.J.; Rae, C.M.F. Detailed Analysis of the Solution Heat Treatment of a Third-Generation Single-Crystal Nickel-Based Superalloy CMSX-10K®. Metall. Mat. Trans. A 2016, 47, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopgood, A.A.; Martin, J.W. Coarsening of γ′-precipitates in single-crystal superalloy SRR 99. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1986, 2, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.; Erickson, G.L.; Schwer, R.E. MAR M 247 derivations—CM 247 LC DS alloy CMSX single crystal alloys properties and performance. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Superalloys (Superalloys 1984), Champion, PA, USA, 7–11 October 1984; pp. 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.; Erickson, G.L.; Sikkenga, S.L.; Brentnall, W.D.; Aurrecoechea, J.M.; Kubarych, K.G. Development of the Rhenium Containing Superalloy CMSX-4 for Single Crystal Blade Applications in Advanced Turbine Engines. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Superalloys (Superalloys 1992), Champion, PA, USA, 20–24 September 1992; pp. 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, G.L. The development and application of CMSX-10. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Symposium on Superalloys (Superalloys 1996), Champion, PA, USA, 22–26 September 1996; pp. 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, M.; Miyazaki, T. The effect of elastic interaction energy on the shape. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Superalloys (Superalloys 1984), Champion, PA, USA, 7–11 October 1984; pp. 543–552. [Google Scholar]
- Nathal, M.V.; Mackay, R.A.; Garlick, R.G. Temperature dependence of γ-γ′ lattice mismatch in Nickel-base superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1985, 75, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.C.; Voorhees, P.W. Elastic interaction and stability of misfitting cuboidal inhomogeneities. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 61, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epishin, A.; Link, T.; Nolze, G. SEM investigation of interfacial dislocations in nickel-base superalloys. J. Microsc. 2007, 228, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Véron, M.; Bréchet, Y.; Louchet, F. Strain induced directional coarsening in Ni based superalloys. Scr. Mater. 1996, 34, 1883–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matan, N.; Cox, D.C.; Rae, C.M.F.; Reed, R.C. On the kinetics of rafting in CMSX-4 superalloy single crystals. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 2013–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, A.; Strudel, J.L. On the creep resistance of some nickel base single crystals. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Superalloys (Superalloys 1984), Champion, PA, USA, 7–11 October 1984; pp. 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Watanabe, R.; Yoshinari, A. Effect of aging heat-treatment condition on creep-rupture strength of Nickel-base single crystal superalloys. Tetsu-to-Hagané 1989, 75, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| HESA | Ni | Co | Cr | Fe | Mo | W | Ti | Al | Nb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal composition | 48.0 | 16.9 | 7.5 | 8.9 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 5.8 | 10.3 | 1.2 |
| ICP-OES | 48.5 | 17.1 | 7.1 | 8.9 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 5.8 | 10.0 | 1.2 |
| Analyzed Phase | Ni | Co | Cr | Fe | Mo | W | Ti | Al | Nb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 38.7 | 15.8 | 3.6 | 4.5 | 0.3 | <0.1 | 12.7 | 20.4 | 4.1 |
| B | 24.0 | 23.2 | 13.1 | 11.9 | 3.9 | 0.3 | 6.4 | 3.7 | 13.5 |
| C | 49.2 | 18.5 | 3.4 | 5.3 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 10.9 | 5.3 | 6.5 |
| D | 48.5 | 16.1 | 4.9 | 6.2 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 4.3 |
| Type | No. | Procedure | Incipient Melting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | 1 | R.T.→(2.5 h)→1100 °C→(2.5 h)→1160 °C→(17.5 h)→1230 °C→A.Q. | No |
| Step | 1 | R.T.→(2.0 h)→1150 °C/2 h→(0.5 h)→1210 °C/5 h→A.Q. | No |
| 2 | R.T.→(2.0 h)→1175 °C/2 h→(0.5 h)→1215 °C/5 h→A.Q. | No | |
| 3 | R.T.→(2.0 h)→1200 °C/2 h→(0.5 h)→1230 °C/5 h→A.Q. | Yes | |
| 4 | R.T.→(2.0 h)→1230 °C/2 h→(0.5 h)→1260 °C/5 h→A.Q. | Yes |
| Alloys | Method | Solution Conditions | Solvus of γ′ Phase /°C | Incipient Melting Temperature /°C | Solidus /°C | Liquidus /°C | Heat Treatment Window /°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HESA | DTA | As-cast | Unclear | 1212 | - | 1325 | - |
| DTA | Step-2 | 1182 | 1250 | 1250 | 1326 | 68 | |
| ThermoCalc (TCNI8) | - | 1173 | - | 1235 | 1313 | 62 | |
| ThermoCalc (TCHEA4) | - | 1161 | - | 1212 | 1309 | 51 | |
| SRR99 | ThermoCalc (TCNI8) | - | 1239 | - | 1325 | 1371 | 86 |
| CMSX-2 | ThermoCalc (TCNI8) | - | 1281 | - | 1341 | 1378 | 60 |
| CMSX-4 | ThermoCalc (TCNI8) | - | 1263 | - | 1342 | 1388 | 79 |
| CMSX-10 | ThermoCalc (TCNI8) | - | 1371 | - | 1385 | 1428 | 14 |
| Temperature/°C | Type of Phase | Time/h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 20 | 100 | 200 | 500 | ||
| 1050 | Primary γ′ precipitates | Cube/aligned | Directional cube/aligned | |||
| Secondary γ′ precipitates | Fine (approximately 40 nm in diameter) | |||||
| Nano γ particles | No | |||||
| 950 | Primary γ′ precipitates | Sphere/random | ||||
| Secondary γ′ precipitates | Fine (approximately 10 nm in diameter) | |||||
| Nano γ particles | No | |||||
| 800 | Primary γ′ precipitates | Cube/random | Transition/random | Sphere/random | ||
| Secondary γ′ precipitates | Coarsened | Coarsened + Fine (approximately 10 nm in diameter) | ||||
| Nano γ particles | No | |||||
| Primary Aging Condition | Type of Phase | Secondary Aging Condition | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 °C for 20 h | 850 °C for 20 h | 870 °C for 20 h | ||
| C condition (1050 °C for 4 h) | Primary γ′ precipitates | Cube/aligned | Transition/aligned | |
| Secondary γ′ precipitates | Coarsened | Cooling (approximately 10 nm in diameter) | ||
| Nano γ particles | Yes | No | ||
| S condition (950 °C for 20 h) | Primary γ′ precipitates | Sphere/random | ||
| Secondary γ′ precipitates | Coarsened | Cooling (approximately 10 nm in diameter) | ||
| Nano γ particles | Yes | No | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saito, T.; Chen, Y.-T.; Takata, Y.; Kawagishi, K.; Hsu, W.-C.; Yeh, A.-C.; Murakami, H. Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructural Evolution of a Single Crystal High-Entropy Superalloy. Metals 2020, 10, 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10121600
Saito T, Chen Y-T, Takata Y, Kawagishi K, Hsu W-C, Yeh A-C, Murakami H. Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructural Evolution of a Single Crystal High-Entropy Superalloy. Metals. 2020; 10(12):1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10121600
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaito, Takuma, Yung-Ta Chen, Yuji Takata, Kyoko Kawagishi, Wei-Che Hsu, An-Chou Yeh, and Hideyuki Murakami. 2020. "Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructural Evolution of a Single Crystal High-Entropy Superalloy" Metals 10, no. 12: 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10121600
APA StyleSaito, T., Chen, Y.-T., Takata, Y., Kawagishi, K., Hsu, W.-C., Yeh, A.-C., & Murakami, H. (2020). Effect of Heat Treatments on the Microstructural Evolution of a Single Crystal High-Entropy Superalloy. Metals, 10(12), 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10121600




