The Role of Generative AI in Enhancing Audience Participation in Journalism: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- RQ.1: Which theoretical and empirical approaches are currently used to examine generative AI in journalism and its impact on audience participation?
- RQ.2: Which are the target sectors and areas of focus in recent studies on generative AI in journalism?
- RQ.3: How is generative AI used by media organizations to enhance audience participation and engagement with the news?
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Audience Participation in Journalism in the Digital Age
2.2. Redefining Journalism Practices and Audience Participation in News Making Through Automation and Artificial Intelligence
2.3. The Integration of Generative AI Tools in Media Organizations
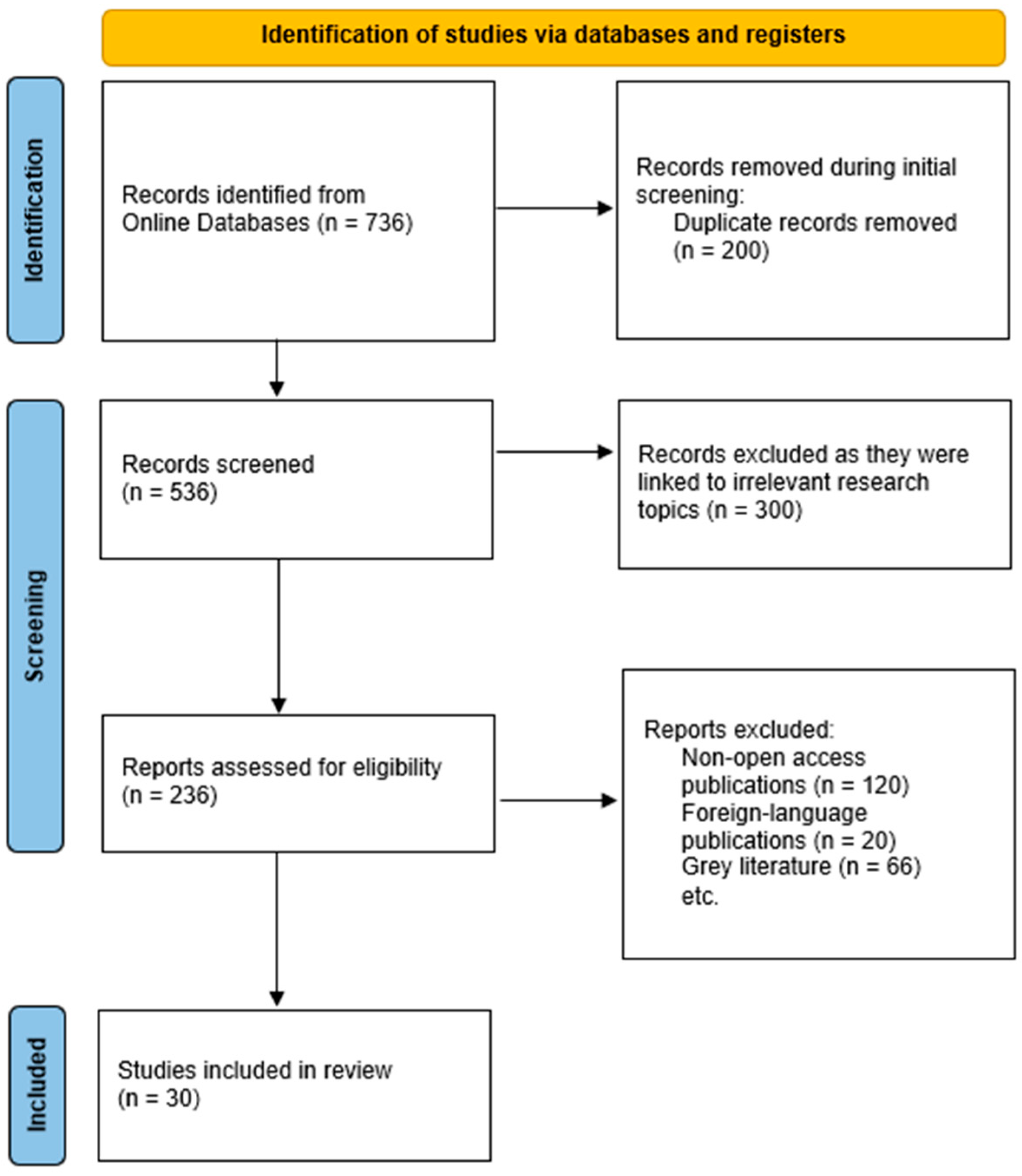
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Theoretical and Empirical Approaches to AI and Generative AI in Journalism
4.2. Target Sectors and Areas of Focus on Generative AI in Journalism
4.3. Use of Generative AI by Media Organizations for Enhancing Audience Participation and Engagement
- Experimental uses and working examples of news products and publishing workflows similar to LLMs and generative AI
- AI tools for video automation services
- AI-generated news anchors and robot news readers
- AI-driven systems for news recommendations and content personalization
- Transcription robots for real time news
- AI-tools for interactive and dynamic storytelling
- AI-tools for immersive news experiences
- AI-driven meta data tagging
- Generative-AI in journalism education
5. Discussion
6. Limitations and Future Research
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewis, C.S.; Guzman, L.A.; Schmidt, R.T. Automation, Journalism, and Human–Machine Communication: Rethinking Roles and Relationships of Humans and Machines in News. Digit. J. 2019, 7, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siapera, E.; Dimitrakopoulou, D. Internet and Journalism: Traditional and alternatives forms. Commun. Issues 2012, 14–15, 30–46. [Google Scholar]
- Siapera, E.; Veglis, A. Introduction: The Evolution of Online Journalism. In The Handbook of Global Online Journalism, 1st ed.; Siapera, E., Veglis, A., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, D. Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Journalism: A Comprehensive Review of AI in Journalism. J. Commun. Manag. 2024, 3, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, B.G.; Hermida, A.; Domingo, D.; Heinonen, A.; Paulussen, S.; Quandt, Τ.; Reich, Ζ.; Vujnovic, Μ. Participatory Journalism: Guarding Open Gates at Online Newspapers, 1st ed.; Swayze, Ε., Morse, Μ., Helenius, Ε., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–227. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, S.C. The tension between professional control and open participation: Journalism and its boundaries. Inf. Commun. Soc. 2012, 15, 836–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.; Witschge, T. From grand narratives of democracy to small expectations of participation. J. Pract. 2015, 9, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, N.; Lewis, C.S.; Kunert, J. Algorithms, Automation, and News. Digit. J. 2019, 7, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veglis, A. Moderation Techniques for Social Media Content. In Social Computing and Social Media—SCSM 2014, Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2014, 8531, Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Social Computing and Social Media, Heraclion, Crete, Greece, 22–27 June 2014; Meiselwitz, G., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Caswell, D. AI and Journalism: What’s Next? Reuters Institute. About the Reuters Institute|Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism. Available online: https://reutersinstitute.politics.ox.ac.uk//news/ai-and-journalism-whats-next (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Newman, N.; Fletcher, R.; Eddy, K.; Robertson, C.T.; Nielsen, K.R. Digital News Report 2023; Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism: Oxford, UK, 2023; pp. 5–158. [Google Scholar]
- Cools, H.; Diakopoulos, N. Uses of Generative AI in the Newsroom: Mapping Journalists’ Perceptions of Perils and Possibilities. J. Pract. 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, L.A.; Lewis, C.S. What Generative AI Means for the Media Industries, and why it Matters to Study the Collective Consequences for Advertising, Journalism, and Public Relations. Emerg. Media 2024, 2, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioscote, F.; Gonçalves, A.; Quadros, C. Artificial Intelligence in Journalism: A Ten-Year Retrospective of Scientific Articles (2014–2023). J. Media 2024, 5, 873–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, L. How Generative AI Is Transforming Journalism: Development, Application and Ethics. J. Media 2024, 5, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, C. How journalism adapted the Internet in Germany: Results of six newsroom surveys (1997–2014). Journalism 2024, 25, 1070–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermida, A. Mechanisms of Participation: How audience options shape the conversation. In Participatory Journalism: Guarding Open Gates at Online Newspapers, 1st ed.; Swayze, Ε., Morse, Μ., Helenius, Ε., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 14–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bruns, A. The active audience: Transforming journalism from gatekeeping to gatewatching. In Making Online News: The Ethnography of New Media Production; Paterson, C., Domingo, D., Eds.; Peter Lang: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Saridou, T.; Panagiotidis, K.; Tsipas, Ν.; Veglis, A. Towards a semantic-oriented model of participatory journalism management: Perceptions of user-generated content. J. Educ. Innov. Commun. 2019, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, S.; Willis, C. We Media: How Audiences are Reshaping the Future of News and Information; The Media Press at the American Press Institute: Reston, VA, USA, 2003; pp. 7–64. [Google Scholar]
- Saridou, T.; Veglis, A. Participatory journalism policies in newspapers’ websites in Greece. J. Greek Media Cult. 2016, 2, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saridou, T.; Veglis, A. Exploring participatory journalism through the integration of user-generated content in media organizations. In Encyclopedia of Information Science and Technology, 5th ed.; Khosrow-Pour, M., Ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porlezza, C. From participatory culture to participatory fatigue: The problem with the public. Soc. Media Soc. 2019, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, M. Clarifying Journalism’s Quantitative Turn: A typology for evaluating data journalism, computational journalism, and computer-assisted reporting. Digit. J. 2015, 3, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siitonen, Μ.; Laajalahti, A.; Venäläinen, P. Mapping Automation in Journalism Studies 2010–2019: A Literature Review. J. Stud. 2019, 25, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindén, G.C. Algorithms for journalism: The future of news work. J. Media Innov. 2017, 4, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEleny, C. What CNN Has Learnt After Six Months of Chatbot Experimentation. The Drum. Available online: https://www.thedrum.com/news/2016/11/16/what-cnn-has-learnt-after-six-months-chatbot-experimentation (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Saridou, T.; Panagiotidis, K.; Tsipas, Ν.; Veglis, A. Semantic tools for participatory journalism. J. Media Crit. 2018, 4, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushahidi. Huffington Post First-Hand: A Citizen Journalism Platform Built to Crowdsource Personal Accounts of Privation and Triumph During the Great Recession. Available online: https://www.ushahidi.com/in-action/huffington-post-first-hand/ (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Diaz Ruiz, C.; Nilsson, T. Disinformation and Echo Chambers: How Disinformation Circulates on Social Media Through Identity-Driven Controversies. J. Public Policy Mark. 2022, 42, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, L. The old-new epistemology of digital journalism: How algorithms and filter bubbles are (re)creating modern metanarratives. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, Ν.; Fletcher, R.; Robertson, C.T.; Arguedas, A.R.; Nielsen, K.R. Digital News Report 2024; Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism: Oxford, UK, 2024; pp. 4–167. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, M.F. AI in the News: Retooling, Rationalizing, and Reshaping Journalism and the Public Arena; Tow Center for Digital Journalism: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Beckett, C.; Yaseen, M. Generating Change: A Global Survey of What News Organizations Are Doing with AI; The London School of Economics and Political Science: London, UK, 2023; pp. 1–87. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlik, V.J. Collaborating with ChatGPT: Considering the Implications of Generative Artificial Intelligence for Journalism and Media Education. J. Mass Commun. Educ. 2023, 78, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Associated Press. AP Expands UGC on Video Hub with Spectee Collaboration. Available online: https://www.ap.org/media-center/press-releases/2017/ap-expands-ugc-on-video-hub-with-spectee-collaboration/ (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- The New York Times. How The New York Times Uses A.I. for Journalism. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2024/10/07/reader-center/how-new-york-times-uses-ai-journalism.html (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Viner, K.; Bateson, A. The Guardian’s Approach to Generative AI. The Guardian. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/help/insideguardian/2023/jun/16/the-guardians-approach-to-generative-ai (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Boavida, Ν.; Candeias, Μ. Recent Automation Trends in Portugal: Implications on Industrial Productivity and Employment in Automotive Sector. Societies 2021, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouros, T.; Papa, V. Digital Mirrors: AI Companions and the Self. Societies 2024, 14, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Meri, A.; Doménech-Fabregat, H.; Marcos-García, S. Digital Competencies in Verifying Fake News: Assessing the Knowledge and Abilities of Journalism Students. Societies 2024, 14, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Gil, V.; Ramon-Vegas, Χ.; Rodríguez-Martínez, R.; Mauri-Ríos, Μ. Explanatory Journalism within European Fact Checking Platforms: An Ally against Disinformation in the Post-COVID-19 Era. Societies 2023, 13, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphaln, K.K.; Regoeczi, W.; Masotya, M.; Vazquez-Westphaln, B.; Lounsbury, K.; McDavid, L.; Lee, H.; Johnson, J.; Ronis, D.C. From Arksey and O’Malley and Beyond: Customizations to enhance a team-based, mixed approach to scoping review methodology. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, D.J.M.; Godfrey, M.C.; Khalil, H.; McInerney, P.; Parker, D.; Soares, B.D. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int. J. Evid.-Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelke, K.M. Online Participatory Journalism: A Systematic Literature Review. Media Commun. 2019, 7, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, M.V. Factors Influencing the Rejection of Automated Journalism: A Systematic Literature Review. Nord. J. Media Manag. 2021, 2, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedman, U.; Djerf-Pierre, M. THE SOCIAL JOURNALIST: Embracing the social media life or creating a new digital divide? Digit. J. 2013, 1, 368–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrichsen, J.R. Breaking through the ambivalence: Journalistic responses to information security technologies. Digit. J. 2019, 8, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsvairo, B.; Borges-Rey, E.; Bebawi, S.; Márquez-Ramírez, M.; Mellado, C.; Mabweazara, H.M.; Demeter, M.; Głowacki, M.; Badr, H.; Thussu, D. Ontologies of Journalism in the Global South. J. Mass Commun. Q. 2021, 98, 996–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westlund, O. News consumption in an age of mobile media: Patterns, people, place, and participation. Mob. Media Commun. 2015, 3, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayani, M. Digital Journalism, Social Media Platforms, and Audience Engagement: The Case of AJ+. Digit. J. 2020, 9, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, D. Audiences, automation, and AI: From structured news to language models. AI Mag. 2024, 45, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Impact of AI Virtual Anchors on Traditional News Anchors. Int. J. Knowl. Manag. (IJKM) 2025, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongbo, N. From Human Anchors to AI Anchors: A Review of Technology, Ethics, and Audience Response in Audiovisual Media Transformation. Int. Theory Pract. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2025, 2, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heise, N.; Loosen, W.; Reimer, J.; Schmidt, J.H. Including the audience. J. Stud. 2014, 15, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.; St. John, B., III. Interacting with the Audience through News Comment Sections. In Personalized News Communication and Media Trust in the Modern Era; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 113–132. [Google Scholar]
| Criterion | Application in Study Selection |
|---|---|
| English-language publications | Accurate data examination, as authors are proficient in English, ensuring the presentation of comprehensible results |
| Peer-reviewed journals | Expert evaluation, ensuring accuracy and credibility of each scholarly work, similar to Engelke’s corresponding criterion [46] |
| Open-access publications, open access and hybrid open access publishing model | All types of open-access publications (e.g., research articles, commentaries, review papers etc.) included in journals with both open access and hybrid open access publishing model, enriching the results with diverse contributions and supporting transparency with publicly accessible information |
| Keyword relevance | Publications whose titles, abstracts, and keywords matched the search terms |
| Topic relevance | Publications whose topics were relevant to the review’s aims, providing insights into how media outlets are using generative AI in enhancing audience participation and engagement with the news |
| Number of Publications | n = 30 |
|---|---|
| Type of Publication | |
| Articles | 23 |
| Colloquiums/Commentaries | 2 |
| Reports | 1 |
| Reviews | 1 |
| Experimental Studies | 1 |
| Technical Papers | 1 |
| Position Papers | 1 |
| Journal Publishing Model | |
| Open-access | 10 |
| Hybrid open-access | 5 |
| Type of Approach | |
| Interdisciplinary approach | 9 |
| Disciplinary approach | 6 |
| Publisher | |
| Sage | 2 |
| MDPI | 1 |
| Routledge | 1 |
| Taylor & Francis | 1 |
| Springer | 2 |
| Oxbridge Publishing House | 1 |
| Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) | 1 |
| Elsevier | 2 |
| Adham Center for Television and Digital Journalism—American University in Cairo | 1 |
| The Royal Institution of Naval Architects | 1 |
| Faculty of Information and Audiovisual Media—University of Barcelona | 1 |
| Review of Communication Research (RCR) | 1 |
| Publication Year | |
| 2024 | 25 |
| 2023 | 4 |
| 2022 | 1 |
| Research Design | Method Type | Number of Publications |
|---|---|---|
| Single-method studies | Literature reviews | 6 |
| Interviews | 6 | |
| Case study | 2 | |
| Content analysis | 2 | |
| Benchmarking analysis | 1 | |
| Archival research | 1 | |
| Focus groups | 1 | |
| Numerical data analysis | 2 | |
| Experiments | 2 | |
| Multi-method studies | Mixed data analysis | 2 |
| Convergent parallel design (CPD) | 2 | |
| Exploratory sequential design (ESD) | 1 | |
| Systematic review | 1 | |
| Bibliometric and content analysis | 1 |
| Study Type | Target Sector |
|---|---|
| Single method |
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Multi method |
|
| |
| |
| |
|
| Study Type | Areas of Focus |
|---|---|
| Single method |
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Multi method |
|
| |
| |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chalikiopoulou, E.; Saridou, T.; Veglis, A. The Role of Generative AI in Enhancing Audience Participation in Journalism: A Scoping Review. Societies 2025, 15, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc15120358
Chalikiopoulou E, Saridou T, Veglis A. The Role of Generative AI in Enhancing Audience Participation in Journalism: A Scoping Review. Societies. 2025; 15(12):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc15120358
Chicago/Turabian StyleChalikiopoulou, Eleni, Theodora Saridou, and Andreas Veglis. 2025. "The Role of Generative AI in Enhancing Audience Participation in Journalism: A Scoping Review" Societies 15, no. 12: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc15120358
APA StyleChalikiopoulou, E., Saridou, T., & Veglis, A. (2025). The Role of Generative AI in Enhancing Audience Participation in Journalism: A Scoping Review. Societies, 15(12), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc15120358








