Kinematic and Kinetic Analyses of the Vertical Jump with and without Header as Performed by Para-Footballers with Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Test Battery
2.4. Data Extraction
2.4.1. Kinematic Analyses
2.4.2. Kinetic Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M.; Damiano, D.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. Suppl. 2007, 109, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanger, T.D.; Delgado, M.R.; Gaebler-Spira, D.; Hallett, M.; Mink, J.W. Classification and definition of disorders causing hypertonia in childhood. Pediatrics 2003, 111, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woollacott, M.H.; Shumway-Cook, A. Postural dysfunction during standing and walking in children with cerebral palsy: What are the underlying problems and what new therapies might improve balance? Neural Plast. 2005, 12, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Ribés, A. Aplicación de la toxina botulínica tipo A en la parálisis cerebral infantil espástica. Bol. Soc. Vasco-Navar. Pediatr. 2004, 37, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Damiano, D.L.; Vaughan, C.L.; Abel, M.F. Muscle response to heavy resistance exercise in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1995, 37, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Paralympic Committee, International Standard for Eligible Impairments. September 2016. Available online: https://www.paralympic.org/sites/default/files/document/161004145727129_2016_10_04_International_Standard_for_Eligible_Impairments_1.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2019).
- Blanchard, Y.; Gannotti, M.E.; Romney, W. Health-related fitness for children and adults with cerebral palsy. ACSM Sports Med. Basics 2016. Available online: https://digitalcommons.sacredheart.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1264&context=pthms_fac (accessed on 7 June 2019).
- Reina, R. Evidence-based classification in Paralympic sport: Application to football-7-a-side. Eur. J. Hum. Mov. 2014, 32, 161–185. [Google Scholar]
- Tweedy, S.M.; Vanlandewijck, Y.C. International Paralympic Committee position stand—background and scientific principles of classification in Paralympic sport. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Paralympic Committee, IPC Athlete Classification Code. November 2015. Available online: https://www.paralympic.org/sites/default/files/document/170704160235698_2015_12_17%2BClassification%2BCode_FINAL2_0.pdf (accessed on 7 June 2019).
- Tweedy, S.M.; Beckman, E.M.; Connick, M.J. Paralympic classification: Conceptual basis, current methods, and research update. PM&R 2014, 6, S11–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, R.; Iturricastillo, A.; Sabido, R.; Campayo-Piernas, M.; Yanci, J. Vertical and horizontal jump capacity in international cerebral palsy football players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cámara, J.; Grande, I.; Mejuto, G.; Los-Arcos, A.; Yanci, J. Jump landing characteristics in elite soccer players with cerebral palsy. Biol. Sport 2013, 30, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanci, J.; Arcos, A.; Mendiguchia, J.; Brughelli, M. Relationships between sprinting, agility, one- and two-leg vertical and horizontal. Kinesiology 2014, 46, 194–201. [Google Scholar]
- Yanci, J.; Castagna, C.; Los Arcos, A.; Santalla, A.; Grande, I.; Figueroa, J.; Cámara, J. Muscle strength and anaerobic performance in football players with cerebral palsy. Disabil. Health J. 2016, 9, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadaba, M.P.; Ramakrishnan, H.K.; Wootten, M.E. Measurement of lower extremity kinematics during level walking. J. Orthop. Res. 1990, 8, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanci, J.; Cámara, J. Bilateral and unilateral vertical ground reaction forces and leg asymmetries in soccer players. Biol. Sport 2016, 33, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linthorne, N.P. Analysis of standing vertical jumps using a force platform. Am. J. Phys. 2001, 69, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for meta-Analysis; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge Academic: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, W.; Marshall, S.; Batterham, A.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harry, J.R.; Barker, L.A.; James, R.; Dufek, J.S. Performance differences among skilled soccer players of different playing positions during vertical jumping and landing. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loturco, I.; Jeffreys, I.; Abad, C.C.C.; Kobal, R.; Zanetti, V.; Pereira, L.A.; Nimphius, S. Change-of-direction, speed and jump performance in soccer players: A comparison across different age-categories. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.; Tilp, M.; Von Duvillard, S.P.; Mueller, E. Kinematic analysis of volleyball spike jump. Int. J. Sports Med. 2009, 30, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.C.; Izquierdo, M.; Marinho, D.A.; Barbosa, T.M.; Ferraz, R.; González-Badillo, J.J. Association between force-time curve characteristics and vertical jump performance in trained athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 2045–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbert, M.F.; Casius, L.J. Is the effect of a countermovement on jump height due to active state development? Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stackhouse, S.K.; Binder-Macleod, S.A.; Lee, S.C. Voluntary muscle activation, contractile properties, and fatigability in children with and without cerebral palsy. Muscle Nerve Off. J. Am. Assoc. Electrodiagn. Med. 2005, 31, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiano, D.L.; Martellotta, T.L.; Sullivan, D.J.; Granata, K.P.; Abel, M.F. Muscle force production and functional performance in spastic cerebral palsy: Relationship of cocontraction. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2000, 81, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reina, R.; Sarabia, J.M.; Yanci, J.; García-Vaquero, M.P.; Campayo-Piernas, M. Change of direction ability performance in cerebral palsy football players according to functional profiles. Front. Physiol. 2016, 6, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reina, R.; Sarabia, J.M.; Caballero, C.; Yanci, J. How does the ball influence the performance of change of direction and sprint tests in para-footballers with brain impairments? Implications for evidence-based classification in CP-Football. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanci, J.; Los Arcos, A.; Grande, I.; Santalla, A.; Figueroa, J.; Gil, E.; Cámara, J. Capacidad de salto en futbolistas con parálisis cerebral. Int. J. Med. Sci. Phys. Act. Sport 2014, 14, 199–211. [Google Scholar]
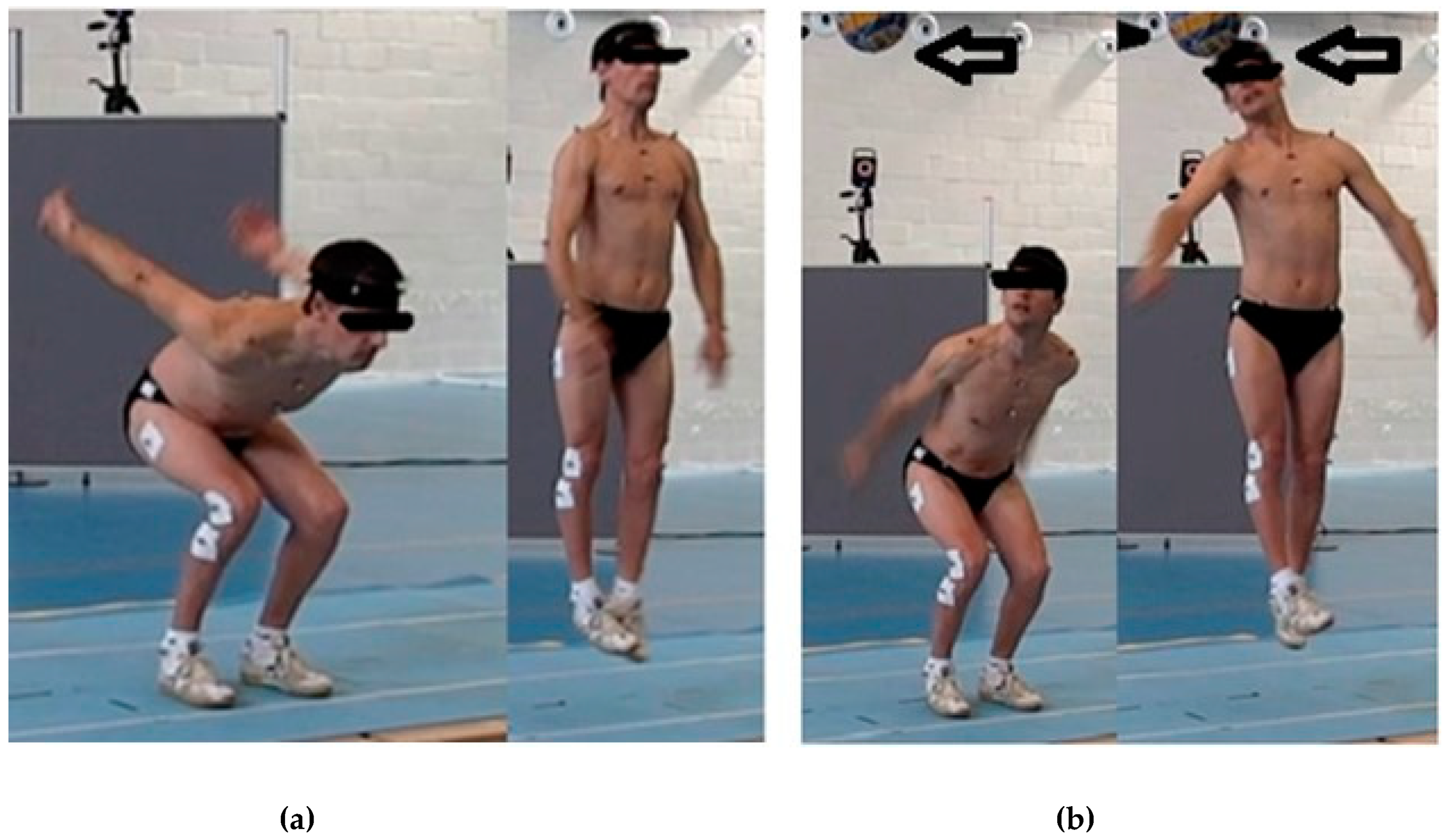
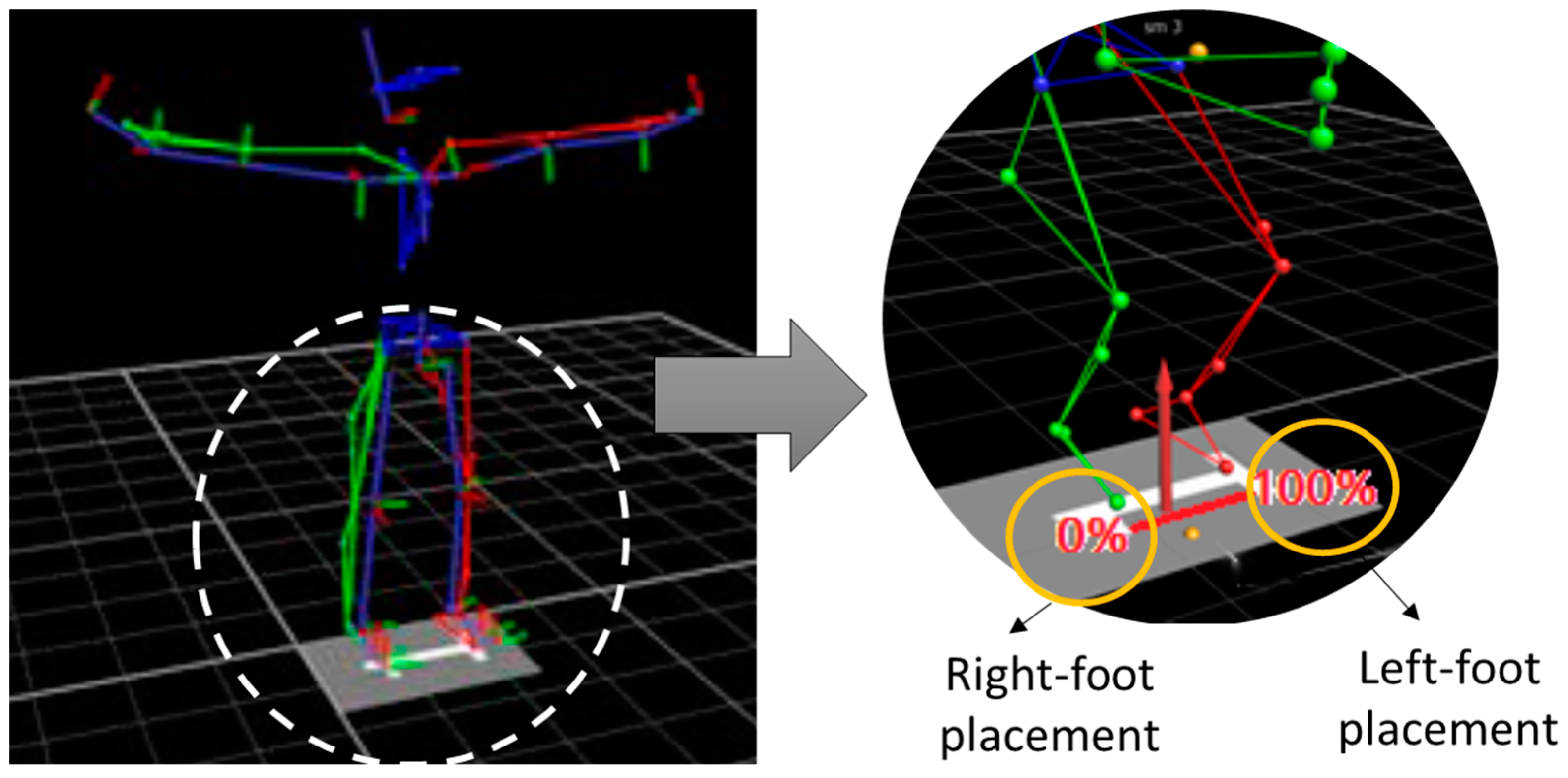
| Impairment Profile | N | Age (year) | Body Mass (kg) | Height (cm) | BMI (kg/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diplegia | 3 (2L-1R) | 27.0 ± 4.4 | 66.5 ± 11.6 | 169.6 ± 1.5 | 23.1 ± 3.3 |
| Ataxia/Athetosis | 3 (1L-2R) | 21.0 ± 1.7 | 62.6 ± 4.1 | 170.6 ± 9.3 | 21.5 ± 1.1 |
| Hemiplegia | 5 (2L-3R) | 27.8 ± 4.6 | 74.6 ± 9.1 | 178.2 ± 10.1 | 23.7 ± 3.4 |
| Minimal Impairment | 2 (2R) | 35.2 ± 1.4 | 72.2 ± 11.5 | 176.0 ± 7.1 | 23.1 ± 1.8 |
| Overall | 13 (5L-8R) | 27.7 ± 5.7 | 68.9 ± 5.4 | 173.6 ± 4.2 | 22.8 ± 0.9 |
| CMJAS Kinematics | without a Header | with a Header | t | p | dg | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | ± | SD | M | ± | SD | |||||
| Dominant Side (Ds) | Hip (°) (1) | 90.0 | ± | 16.9 | 76.3 | ± | 17.1 | 3.30 | 0.007 ** | 0.75 |
| Knee (°) (1) | 92.1 | ± | 13.7 | 76.8 | ± | 21.0 | 2.85 | 0.016 * | 1.04 | |
| Ankle Flexion (°) (1) | 34.9 | ± | 7.7 | 36.0 | ± | 12.4 | −0.33 | 0.746 | −0.13 | |
| Ankle Extension (°) (2) | 20.6 | ± | 6.7 | 25.7 | ± | 9.6 | −2.89 | 0.015 * | −0.71 | |
| Shoulder Extension (°) (1) | −39.8 | ± | 19.4 | -32.1 | ± | 19.6 | −1.60 | 0.139 | −0.37 | |
| Shoulder Flexion (°) (2) | 53.6 | ± | 17.3 | 54.1 | ± | 19.6 | −0.14 | 0.893 | −0.03 | |
| Shoulder ROM (°) | 87.1 | ± | 31.1 | 77.9 | ± | 40.6 | 0.96 | 0.357 | 0.28 | |
| Non-Dominant Side (NDs) | Hip (°) (1) | 93.0 | ± | 22.9 | 73.5 | ± | 17.6 | 3.48 | 0.005 ** | 0.79 |
| Knee (°) (1) | 92.9 | ± | 10.2 | 80.3 | ± | 21.2 | 1.95 | 0.076 | 1.15 | |
| Ankle Flexion (°) (1) | 31.9 | ± | 8.3 | 28.4 | ± | 8.1 | 1.87 | 0.089 | 0.39 | |
| Ankle Extension (°) (2) | 18.9 | ± | 6.2 | 17.7 | ± | 7.6 | 1.28 | 0.228 | 0.18 | |
| Shoulder Extension (°) (1) | −28.4 | ± | 19.8 | −26.3 | ± | 20.4 | −0.55 | 0.597 | −0.10 | |
| Shoulder Flexion (°) (2) | 50.5 | ± | 16.7 | 49.7 | ± | 15.1 | 0.16 | 0.877 | 0.05 | |
| Shoulder ROM (°) | 74.6 | ± | 25.2 | 68.9 | ± | 38.3 | 0.76 | 0.466 | 0.21 | |
| Asymmetry (Ds – NDs) | Hip (°) (1) | −2.9 | ± | 12.8 | 2.8 | ± | 9.5 | −1.34 | 0.207 | −0.41 |
| Knee (°) (1) | −0.8 | ± | 6.2 | −3.5 | ± | 16.7 | 0.71 | 0.495 | 0.41 | |
| Ankle Flexion (°) (1) | 3.0 | ± | 8.9 | 7.6 | ± | 13.8 | −1.34 | 0.208 | −0.48 | |
| Ankle Extension (°) (2) | 1.6 | ± | 5.6 | 8.0 | ± | 11.7 | −3.07 | 0.011 * | −1.06 | |
| Shoulder Extension (°) (1) | −11.5 | ± | 15.6 | −5.8 | ± | 13.6 | −1.34 | 0.207 | −0.34 | |
| Shoulder Flexion (°) (2) | 3.1 | ± | 13.9 | 4.4 | ± | 20.4 | −0.24 | 0.815 | −0.09 | |
| Shoulder ROM (°) | 12.5 | ± | 27.7 | 9.0 | ± | 24.2 | 0.62 | 0.546 | 0.12 | |
| CMJAS Kinetics | without a Header | with a Header | t | p | dg | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | ± | SD | M | ± | SD | |||||
| Height (cm) | 38.4 | ± | 11.5 | 30.9 | ± | 6.3 | 2.11 | 0.058 | 0.61 | |
| maxF (N) | 2.4 | ± | 0.5 | 2.7 | ± | 0.3 | −1.62 | 0.134 | −0.56 | |
| RFD (N/s) | 30.9 | ± | 15.9 | 52.1 | ± | 47.4 | −2.24 | 0.047 | * | −1.24 |
| CMJ Kinematics | without a Header | with a Header | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rho Spearman ± 90% CL | Rho Spearman ± 90% CL | ||
| Dominant Side (Ds) | Hip (°) (1) | NS | NS |
| Knee (°) (1) | NS | 0.80 ± 0.20** | |
| Ankle Flexion (°) (1) | NS | NS | |
| Ankle Extension (°) (2) | NS | NS | |
| Shoulder Extension (°) (1) | NS | NS | |
| Shoulder Flexion (°) (2) | 0.79 ± 0.21** | NS | |
| Shoulder ROM (°) | NS | NS | |
| Non-Dominant Side (NDs) | Hip (°) (1) | NS | NS |
| Knee (°) (1) | NS | 0.58 ± 0.34* | |
| Ankle Flexion (°) (1) | NS | 0.78 ± 0.22** | |
| Ankle Extension (°) (2) | NS | NS | |
| Shoulder Extension (°) (1) | NS | NS | |
| Shoulder Flexion (°) (2) | NS | NS | |
| Shoulder ROM (°) | NS | NS | |
| Asymmetry (Ds – NDs) | Hip (°) (1) | NS | NS |
| Knee (°) (1) | NS | NS | |
| Ankle Flexion (°) (1) | NS | NS | |
| Ankle Extension (°) (2) | NS | NS | |
| Shoulder Extension (°) (1) | NS | NS | |
| Shoulder Flexion (°) (2) | NS | NS | |
| Shoulder ROM (°) | NS | NS | |
| Height (cm) | NS | NS | |
| maxF (N) | NS | NS | |
| RFD (N/s) | NS | NS | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reina, R.; Elvira, J.L.L.; Valverde, M.; Roldán, A.; Yanci, J. Kinematic and Kinetic Analyses of the Vertical Jump with and without Header as Performed by Para-Footballers with Cerebral Palsy. Sports 2019, 7, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7090209
Reina R, Elvira JLL, Valverde M, Roldán A, Yanci J. Kinematic and Kinetic Analyses of the Vertical Jump with and without Header as Performed by Para-Footballers with Cerebral Palsy. Sports. 2019; 7(9):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7090209
Chicago/Turabian StyleReina, Raúl, José L.L. Elvira, Manuel Valverde, Alba Roldán, and Javier Yanci. 2019. "Kinematic and Kinetic Analyses of the Vertical Jump with and without Header as Performed by Para-Footballers with Cerebral Palsy" Sports 7, no. 9: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7090209
APA StyleReina, R., Elvira, J. L. L., Valverde, M., Roldán, A., & Yanci, J. (2019). Kinematic and Kinetic Analyses of the Vertical Jump with and without Header as Performed by Para-Footballers with Cerebral Palsy. Sports, 7(9), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7090209







