Hydration Status and Fluid Needs of Division I Female Collegiate Athletes Exercising Indoors and Outdoors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Approach
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Fluid and Food Intake
2.2.2. Urine Collection and Body Weight Difference
2.2.3. Urine Specific Gravity and Urine Color
2.2.4. Heart Rate, Breathing Rate and Activity
2.2.5. Temperature, Humidity, and Wet Bulb Globe Temperature
2.3. Calculations
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Training Conditions
3.2. Acute Changes in Hydration Status
3.2.1. Body Weight Difference (kg and %)
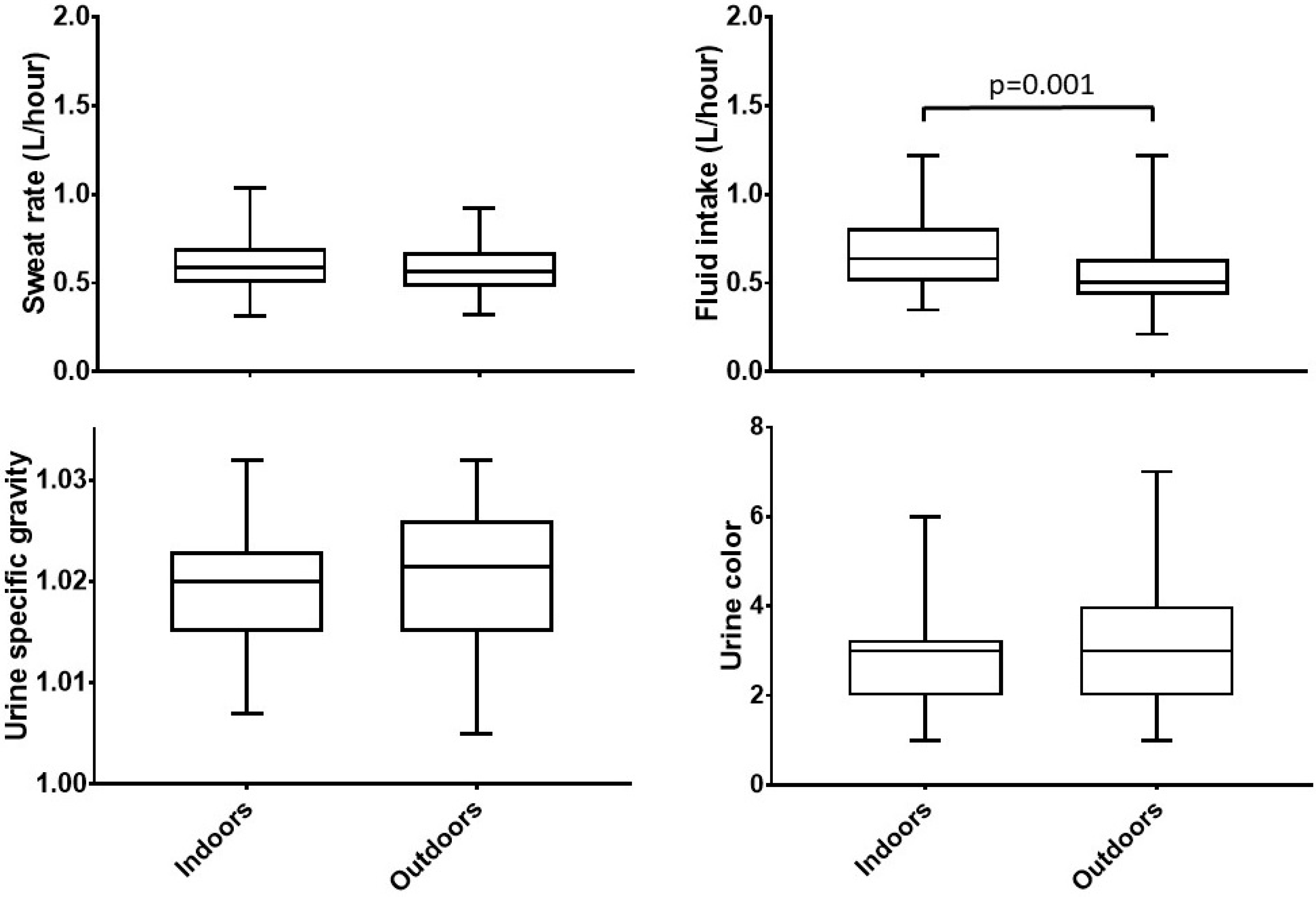
3.2.2. Fluid Intake and Urine Output
3.2.3. Sweat Rate
3.3. Chronic Hydration Status
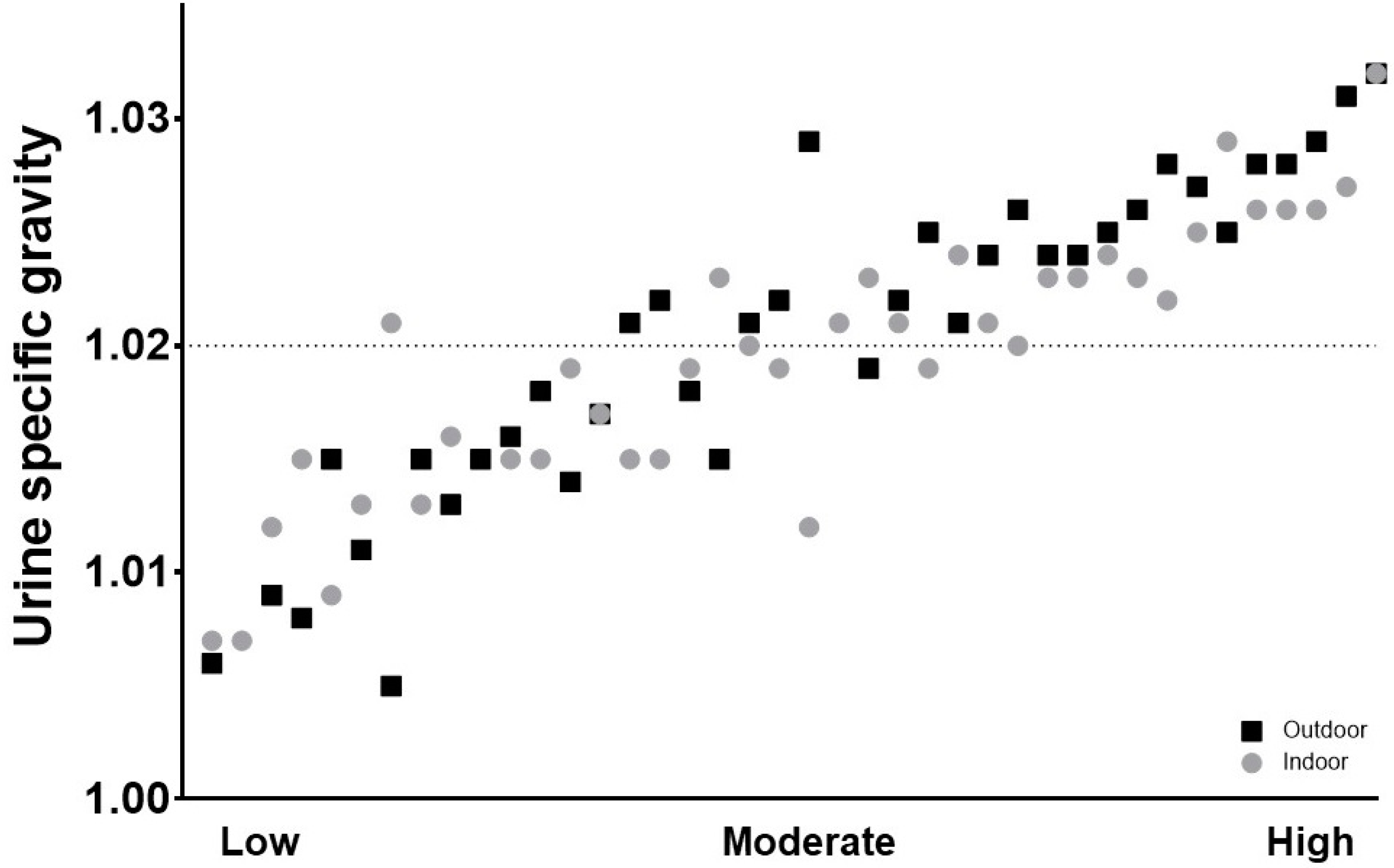
3.3.1. Urine Specific Gravity
3.3.2. Urine Color
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDermott, B.P.; Anderson, S.A.; Armstrong, L.E.; Casa, D.J.; Cheuvront, S.N.; Cooper, L.; Kenney, W.L.; O’Connor, F.G.; Roberts, W.O. National Athletic Trainers’ Association Position Statement: Fluid Replacement for the Physically Active. J. Athl. Train. 2017, 52, 877–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavouras, S.A. Hydration, dehydration, underhydration, optimal hydration: are we barking up the wrong tree? Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawka, M.N.; Montain, S.J. Fluid and electrolyte supplementation for exercise heat stress. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 564S–572S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardis, C.N.; Kavouras, S.A.; Arnaoutis, G.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Sidossis, L.S. Mild Dehydration and Cycling Performance During 5-Kilometer Hill Climbing. J. Athl. Train. 2013, 48, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan-Sprenger, H.M.; Heigenhauser, G.J.F.; Killian, K.J.; Spriet, L.L. Effects of Dehydration during Cycling on Skeletal Muscle Metabolism in Females. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utter, A.C.; McAnulty, S.R.; Riha, B.F.; A Pratt, B.; Grose, J.M. The Validity of Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Measures to Detect Changes in the Hydration Status of Wrestlers During Acute Dehydration and Rehydration. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Elias, V.E.; Martínez-Abellán, A.; López-Gullón, J.M.; Morán-Navarro, R.; Pallarés, J.G.; De La Cruz-Sánchez, E.; Mora-Rodriguez, R. Validity of Hydration Non-Invasive Indices during the Weightcutting and Official Weigh-In for Olympic Combat Sports. PLOS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thigpen, L.K.; Green, J.M.; O’Neal, E.K. Hydration profile and sweat loss perception of male and female division II basketball players during prcatice. J. Strengh Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 3425–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.T.; Erdman, K.A.; Burke, L.M. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and Athletic Performance. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 501–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segar, W.E.; Moore, W.W. The regulation of antidiuretic hormone release in man. J. Clin. Investig. 1968, 47, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, M.A.; Hetzler, R.K.; Wasson, D.; Wages, J.J.; Stickley, C. Hydration behaviors before and after an education and prescribed hydration intervention in adolescent athletes. J. Sport Sci. Med. 2014, 14, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulet, E.D.B. Effect of exercise-induced dehydration on endurance performance: evaluating the impact of exercise protocols on outcomes using a meta-analytic procedure. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curry, F.-R.E.; Curry, F.-R.E. Atrial natriuretic peptide: An essential physiological regulator of transvascular fluid, protein transport, and plasma volume. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1458–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broad, E.M.; Cox, G.R.; Heeley, P.; Riley, M.; Burke, L.M. Body Weight Changes and Voluntary Fluid Intakes during Training and Competition Sessions in Team Sports. Int. J. Sport Nutr. 1996, 6, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, L.E. Assessing hydration status: the elusive gold standard. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 575S–584S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawka, M.N.; Burke, L.M.; Eichner, E.R.; Maughan, R.J.; Montain, S.J.; Stachenfeld, N.S. Exercise and fluid replacement. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casa, D.J.; Armstrong, L.E.; Hillman, S.K.; Montain, S.J.; Reiff, R.V.; Rich, B.S.E.; Roberts, W.O.; Stone, J.A. National Athletic Trainers’ Association Position Statement: Fluid Replacement for Athletes. J. Athl. Train. 2000, 35, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ungaro, C.T.; Reimel, A.J.; Nuccio, R.P.; Barnes, K.A.; Pahnke, M.D.; Baker, L.B. Non-invasive estimation of hydration status changes through tear fluid osmolarity during exercise and post-exercise rehydration. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 115, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, L.B.; Lang, J.A.; Kenney, W.L. Change in body mass accurately and reliably predicts change in body water after endurance exercise. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 105, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaoutis, G.; Kavouras, S.A.; Angelopoulou, A.; Skoulariki, C.; Bismpikou, S.; Mourtakos, S.; Sidossis, L.S. Fluid Balance During Training in Elite Young Athltes of Different Sports HHS Public Access. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 3447–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.E.; Pumerantz, A.C.; Fiala, K.A.; Roti, M.W.; Kavouras, S.A.; Casa, D.J.; Maresh, C.M. Human Hydration Indices: Acute and Longitudinal Reference Values. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2010, 20, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, C.H.; Slater, G.; Nair, G.; Miller, M. Relationship between Changes in Upon-Waking Urinary Indices of Hydration Status and Body Mass in Adolescent Singaporean Athletes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2010, 20, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavouras, S.A.; Johnson, E.C.; Bougatsas, D.; Arnaoutis, G.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Perrier, E.; Klein, A. Validation of a urine color scale for assessment of urine osmolality in healthy children. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Average Annual Temperature for Each US State. Current Results Publishing. Available online: https://www.currentresults.com/Weather/US/average-annual-state-temperatures.php (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Brandenburg, J.P.; Gaetz, M. Fluid Balance of Elite Female Basketball Players before and during Game Play. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2012, 22, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCAA. NCAA Weight Management Program. 2016. Available online: https://www.ncaa.org/sites/default/files/2018DIMWR_Weight_Management_Program_Information_20180108.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Climate Phoenix-Arizona. U.S. Data. Available online: https://www.usclimatedata.com/climate/phoenix/arizona/united-states/usaz0166 (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Edwards, A.M.; E Mann, M.; Marfell-Jones, M.J.; Rankin, D.M.; Noakes, T.D.; Shillington, D.P. Influence of moderate dehydration on soccer performance: Physiological responses to 45 min of outdoor match-play and the immediate subsequent performance of sport-specific and mental concentration tests. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, E.R.; Goff, D.C.; Isom, S.; Blackwell, C.; Whitt-Glover, M.C.; Katula, J.A. Relationship of weekly activity minutes to metabolic syndrome in prediabetes: the healthy living partnerships to prevent diabetes. J. Phys. Act Health 2013, 10, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- National Academy of Sciences. Dietary Reference Intakes; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. Available online: https://www.nal.usda.gov/sites/default/files/fnic_uploads/energy_full_report.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2019). [CrossRef]
- Sommerfield, L.M.; McAnulty, S.R.; McBride, J.M.; Zwetsloot, J.J.; Austin, M.D.; Mehlhorn, J.D.; Calhoun, M.C.; Young, J.O.; Haines, T.L.; Utter, A.C. Validity of urine specific gravity when compared with plasma osmolality as a measure of hydration status in male and female NCAA collegiate athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 30, 2219–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, L.M. Fluid balance during team sports. J. Sports Sci. 1997, 15, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beis, L.Y.; Wright-Whyte, M.; Fudge, B.; Noakes, T.; Pitsiladis, Y.P. Drinking Behaviors of Elite Male Runners During Marathon Competition. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2012, 22, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Idárraga, A.; Aragón-Vargas, L.F. Postexercise rehydration: potassium-rich drinks versus water and a sports drink. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 39, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, L.M.; Loucks, A.B.; Broad, N. Energy and carbohydrate for training and recovery. J. Sports Sci. 2006, 24, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, A.M.; McCormack, J.M.; Magee, P.J. High Prevalence of Dehydration and Inadequate Nutritional Knowledge Among University and Club Level Athletes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2017, 27, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Sepúlveda, M.; Astudillo, S.; Álvarez, C.; Zapata-Lamana, R.; Zbinden-Foncea, H.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Jorquera, C. Prevalencia de deshidratación en futbolistas profesionales Chilenos antes del entrenamiento. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (n = 40) | Soccer (n = 10) | Lacrosse (n = 19) | Triathlon (n = 11) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y | 19.9 ± 1.4 | 19.8 ± 1.2 | 18.8 ± 0.76 | 20.0 ± 1.6 | 0.055 |
| Height, cm | 167.7 ± 7.1 | 171.6 ± 6.0 | 167.9 ± 4.6 | 163.7 ± 9.6 | 0.083 |
| Weight, kg | 62.6 ± 5.8 | 64.0 ± 7.2 | 63.5 ± 4.2 | 59.6 ± 6.3 | 0.247 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.3 ± 2.0 | 21.7 ± 1.6 | 22.6 ± 1.3 | 22.4 ± 3.2 | 0.765 |
| Total | Sports | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soccer | Lacrosse | Triathlon | p-Value | ||||
| Ambient temp (°C) | Indoor | 23.3 (20.4, 24.7) | 19.4 ab | 23.3 ac | 24.7 bc | <0.001 | |
| Outdoor | 20.5 (17.4, 23.3) | 16.4 ab | 23.3 ac | 20.5 bc | <0.001 | ||
| p-value | <0.001 | 0.02 | 1.000 | 0.001 | |||
| Relative humidity (%) | Indoor | 35.3 (29.8, 57.0) | 28.0 ab | 35.3 ac | 57.0 bc | <0.001 | |
| Outdoor | 38.0 (34.3, 38.4) | 33.0 ab | 38.4 ac | 38.0 bc | <0.001 | ||
| p-value | 0.732 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |||
| WBGT (°C) | Indoor | 18.0 (14.1, 25.6) | 12.8 ab | 25.6 ac | 18.0 bc | <0.001 | |
| Outdoor | 17.5 (14.6, 30.8) | 13.6 ab | 30.8 ac | 17.5 bc | <0.001 | ||
| p-value | <0.001 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | |||
| Heart rate (bpm) | Indoor | 137 (129, 150) | 156 (140, 165) ab | 131 (122, 137) a | 137 (134, 139) b | 0.008 | |
| Outdoor | 142 (130, 158) | 163 (156, 170) ab | 130 (120, 140) a | 135 (132, 145) b | <0.001 | ||
| p-value | 0.199 | 0.114 | 0.265 | 0.683 | |||
| METs | Indoor | 5.1 (4.2, 6.0) | 7.8 (6.0, 7.9) ab | 5.2 (4.7, 5.4) ac | 4.1 (4.1, 4.2) bc | <0.001 | |
| Outdoor | 5.2 (4.4, 7.5) | 8.0 (7.5, 8.4) ab | 5.3 (4.8, 5.5) ac | 4.1 (4.0, 4.4) bc | <0.001 | ||
| p-value | 0.157 | 0.173 | 0.166 | 0.681 | |||
| Energy expenditure estimated (EEe, kcal/h) | Indoor | 318 (269, 389) | 509 (459, 552) ab | 318 (318, 338) ac | 242 (219, 265) bc | <0.001 | |
| Outdoor | 305 (272, 425) | 492 (473, 585) ab | 305 (305, 340) ac | 236 (209, 279) bc | <0.001 | ||
| p-value | 0.183 | 0.445 | 0.012 | 0.534 | |||
| Total | Sports | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soccer | Lacrosse | Triathlon | p-Value | ||||
| Body weight difference (kg) | Indoor | −0.05 (−0.38, 0.18) | 0.10 (−0.15, 0.20) | −0.10 (−0.40, 0.00) | −0.10 (−0.50, 0.30) | 0.284 | |
| Outdoor | −0.20 (−0.48, −0.10) | −0.20 (−0.35, −0.10) | −0.20 (−0.50, 0.00) | −0.10 (−0.50, 0.00) | 0.930 | ||
| p-value | 0.004 | 0.059 | 0.022 | 0.384 | |||
| Percentage weight change | Indoor | −0.07 (−0.59, 0.25) | 0.18 (−0.22, 0.31) | −0.15 (−0.63, 0.00) | −0.18 (−0.72, 0.52) | 0.209 | |
| Outdoor | −0.32 (−0.75, −0.15) | −0.29 (−0.55, −0.17) | −0.34 (−0.78, 0.00) | −0.18 (−0.84, 0.00) | 0.986 | ||
| p-value | 0.003 | 0.047 | 0.022 | 0.386 | |||
| Sweat rate (L/h) | Indoor | 0.59 (0.50, 0.70) | 0.69 (0.43, 0.86) | 0.57 (0.51, 0.67) | 0.58 (0.50, 0.94) | 0.428 | |
| Outdoor | 0.56 (0.48, 0.68) | 0.61 (0.51, 0.86) | 0.57 (0.49, 0.68) | 0.54 (0.42, 0.63) | 0.274 | ||
| p-value | 0.168 | 0.541 | 0.920 | 0.110 | |||
| Fluid intake (L/h) | Indoor | 0.64 (0.50, 0.83) | 0.76 (0.53, 0.94) a | 0.58 (0.45, 0.66) ac | 0.84 (0.60, 0.89) c | 0.043 | |
| Outdoor | 0.51 (0.43, 0.63) | 0.49 (0.42, 0.67) | 0.54 (0.46, 0.66) | 0.50 (0.37, 0.63) | 0.854 | ||
| p-value | 0.001 | 0.059 | 0.376 | 0.004 | |||
| Urine output (L) | Indoor | 0.08 (0.03, 0.21) | 0.03 (0.02, 0.12) b | 0.08 (0.03, 0.13) c | 0.14 (0.08, 0.33) cb | 0.020 | |
| Outdoor | 0.11 (0.06, 0.15) | 0.03 (0.03, 0.06) ab | 0.11 (0.09, 0.15) a | 0.14 (0.13, 0.31) b | <0.001 | ||
| p-value | 0.317 | 0.838 | 0.064 | 0.859 | |||
| USG pre-practice | Indoor | 1.018 (1.008, 1.023) | 1.025 (1.023, 1.028) ab | 1.011 (1.006, 1.021) a | 1.013 (1.008, 1.020) b | <0.001 | |
| Outdoor | 1.022 (1.012, 1.026) | 1.023 (1.017, 1.028) | 1.023 (1.011, 1.027) | 1.017 (1.006, 1.024) | 0.288 | ||
| p-value | 0.058 | 0.386 | 0.017 | 0.236 | |||
| USG day after | Indoor | 1.020 (1.015, 1.023) | 1.022 (1.018, 1.026) | 1.021 (1.017, 1.023) | 1.015 (1.012, 1.021) | 0.063 | |
| Outdoor | 1.022 (1.015, 1.026) | 1.023 (1.015, 1.028) | 1.022 (1.017, 1.026) | 1.017 (1.009, 1.025) | 0.246 | ||
| p-value | 0.230 | 0.440 | 0.233 | 0.838 | |||
| Urine color day after (Uc) | Indoor | 3.0 (2.0, 3.3) | 2.5 (2.0, 3.0) | 3.0 (2.0, 5.0) c | 2.0 (1.8, 2.3) c | 0.040 | |
| Outdoor | 3.0 (2.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (2.0, 4.0) | 3.0 (3.0, 4.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.3) | 0.114 | ||
| p-value | 1.000 | 0.589 | 0.904 | 0.414 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olzinski, S.; Beaumont, J.; Toledo, M.; Yudell, A.; Johnston, C.S.; Wardenaar, F.C. Hydration Status and Fluid Needs of Division I Female Collegiate Athletes Exercising Indoors and Outdoors. Sports 2019, 7, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7070155
Olzinski S, Beaumont J, Toledo M, Yudell A, Johnston CS, Wardenaar FC. Hydration Status and Fluid Needs of Division I Female Collegiate Athletes Exercising Indoors and Outdoors. Sports. 2019; 7(7):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7070155
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlzinski, Stephanie, Joshua Beaumont, Meynard Toledo, Amber Yudell, Carol S. Johnston, and Floris C. Wardenaar. 2019. "Hydration Status and Fluid Needs of Division I Female Collegiate Athletes Exercising Indoors and Outdoors" Sports 7, no. 7: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7070155
APA StyleOlzinski, S., Beaumont, J., Toledo, M., Yudell, A., Johnston, C. S., & Wardenaar, F. C. (2019). Hydration Status and Fluid Needs of Division I Female Collegiate Athletes Exercising Indoors and Outdoors. Sports, 7(7), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7070155







