RETRACTED: The Effects of Acute Caffeine Supplementation on Performance in Trained CrossFit Athletes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Measures and Procedures
2.3. Analysis
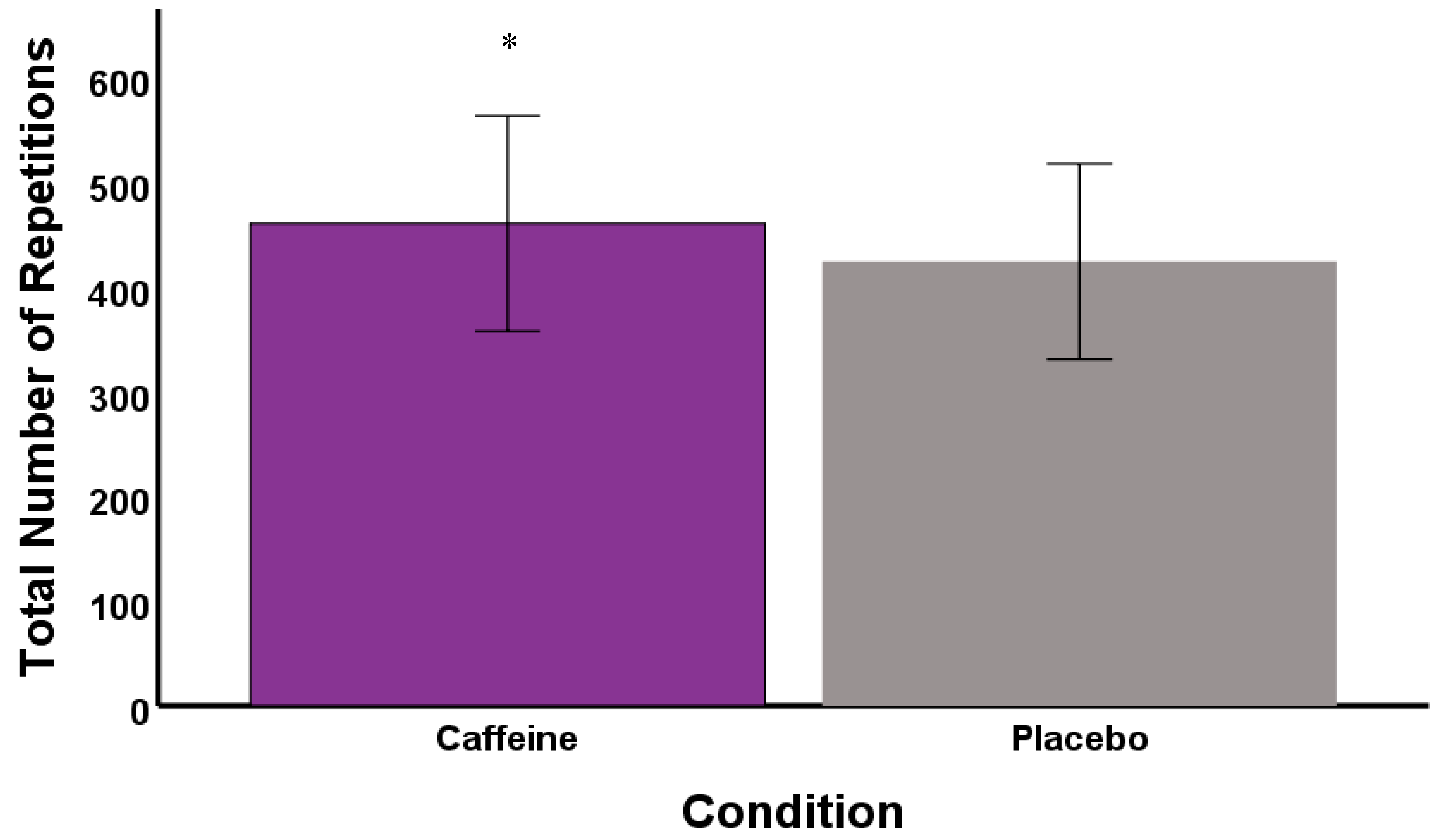
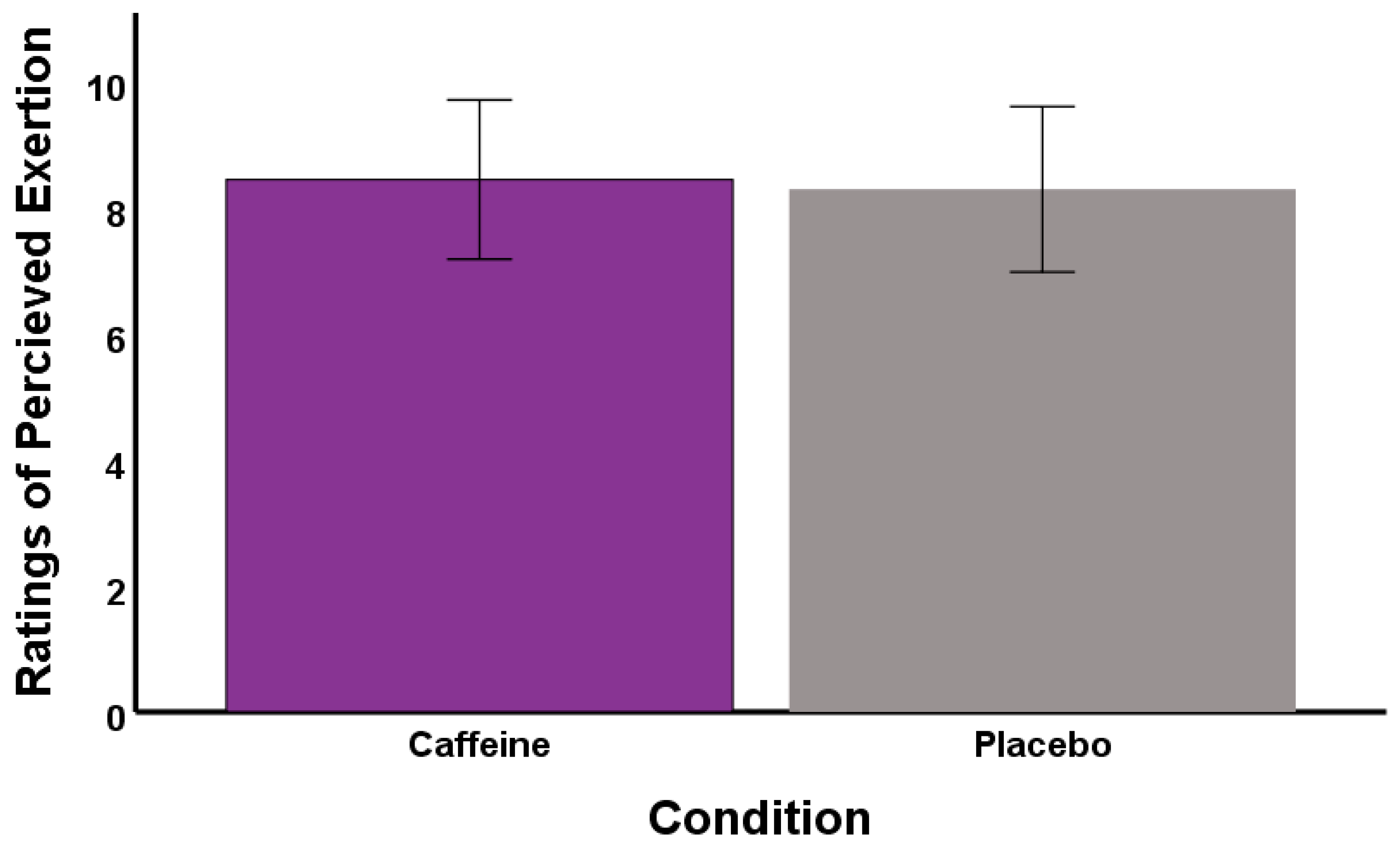
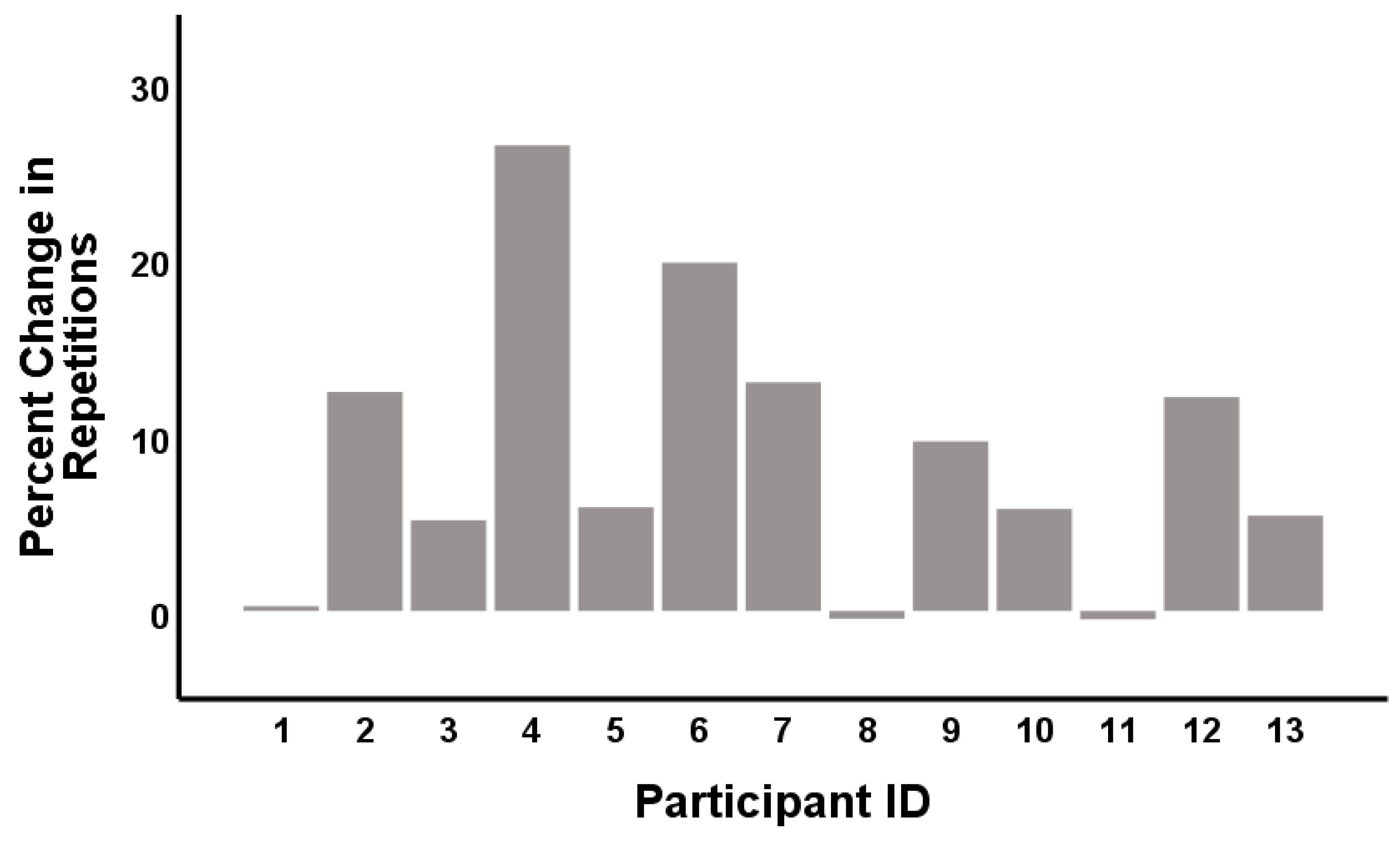
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Del Coso, J.; Muñoz, G.; Muñoz-Guerra, J. Prevalence of caffeine use in elite athletes following its removal from the World Anti-Doping Agency list of banned substances. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 36, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maughan, R.J.; Burke, L.M.; Dvorak, J.; Larson-Meyer, D.E.; Peeling, P.; Phillips, S.M. IOC consensus statement: Dietary supplements and the high-performance athlete. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 104–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, J.; Mikulic, P.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Bishop, D.J.; Pedisic, Z. The Influence of Caffeine Supplementation on Resistance Exercise: A Review. Sport Med. 2018, 49, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, G.L.; Park, N.D.; Maresca, R.D.; McKibans, K.I.; Millard-Stafford, M.L. Effect of Caffeine Ingestion on Muscular Strength and Endurance: A Meta-Analysis. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2010, 42, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerksick, C.M.; Wilborn, C.D.; Roberts, M.D.; Smith-Ryan, A.; Kleiner, S.M.; Jäger, R.; Greenwood, M. ISSN exercise & sports nutrition review update: research & recommendations. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.; Tierney, P.; Gray, N.; Hawe, G.; Macken, M.; Egan, B. Acute Ingestion of Caffeinated Chewing Gum Improves Repeated Sprint Performance of Team Sport Athletes with Low Habitual Caffeine Consumption. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyer, K.L.; Pivarnik, J.M.; Eisenmann, J.C.; Vorkapich, M. Physiological Characteristics of National Collegiate Athletic Association Division I Ice Hockey Players and Their Relation to Game Performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, T.E. Caffeine and Exercise Metabolism, Endurance and Performance. Sport Med. 2001, 31, 785–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, A.; Daniel, W. Efficacy of caffeine ingestion for short-term high-intensity performance: A systematic review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 257–265. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, D.J.; Girard, O. Determinants of team-sport performance: implications for altitude training by team-sport athletes. Br J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Calleja-Gonzalez, J.; Del Coso, J.; Urdampilleta, A.; León-Guereño, P.; Fernández-Lázaro, D. Caffeine Supplementation and Physical Performance, Muscle Damage and Perception of Fatigue in Soccer Players: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinero, J.J.; Lara, B.; Del Coso, J. Effects of acute ingestion of caffeine on team sports performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Res. Sport Med. 2018, 27, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, M.D.; Souza, D.B.; Casonatto, J.; Farinatti, P. Acute effect of caffeine consumption on isotonic muscular strength and endurance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Sports 2016, 31, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astorino, T.A.; Rohmann, R.L.; Firth, K. Effect of caffeine ingestion on one-repetition maximum muscular strength. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 102, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astorino, T.A.; Marcos, S. Minimal Effect of Acute Caffeine Ingestion on Intense Resistance Training Performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, M.; Oxford, S. The Effect of Caffeine Ingestion on Mood State and Bench Press Performance to Failure. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 25, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, G.; Green, J.M.; Bishop, P.; Richardson, M. Effects of Caffeine and Aspirin on Light Resistance Training Performance, Perceived Exertion, and Pain Perception. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 1950–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feito, Y.; Heinrich, K.; Butcher, S.; Poston, W. High-Intensity Functional Training (HIFT): Definition and Research Implications for Improved Fitness. Sports 2018, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, A.G.; Feito, Y.; Petruzzello, S.; Mangine, G. Mood State Changes Accompanying the Crossfit Open TM Competition in Healthy Adults. Sports 2018, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagim, A.; Rader, O.; Jones, M.; Oliver, J. The physical demands of multi-modal training competitions and their relationship to measures of performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 31, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, S.J.; Judd, T.B.; Benko, C.R.; Horvey, K.J.; Pshyk, A.D. Relative intensity of two types of Crossfit exercise: acute circuit and high-intensity interval exercise. J. Fit. Res. 2015, 4, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Fernández, J.; Sabido-solana, R.; Moya, D.; Sarabia, J.M.; Moya, M. Acute physiological responses during crossfit® workouts. Eur. J. Hum. Mov. 2015, 35, 114–124. [Google Scholar]
- Butcher, S.J.; Neyedly, T.J.; Horvey, K.J.; Benko, C.R. Do physiological measures predict selected CrossFit ® benchmark performance? J. Sports Med. 2015, 6, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, D.A.; Drake, N.B.; Carper, M.J.; Deblauw, J.; Heinrich, K.M. Are Changes in Physical Work Capacity Induced by High-Intensity Functional Training Related to Changes in Associated Physiologic Measures? Sports 2018, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rountree, J.A.; Krings, B.M.; Peterson, T.J.; Thigpen, A.G.; Mcallister, M.J.; Holmes, M.E. Efficacy of Carbohydrate Ingestion on CrossFit Exercise Performance. Sports 2017, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southward, K.; Rutherfurd-Markwick, K.J.; Ali, A. The Effect of Acute Caffeine Ingestion on Endurance Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sport Med. 2018, 48, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, C.; Kiely, J. What Should We Do About Habitual Caffeine Use in Athletes? Sport Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.M. Caffeine and sports performance. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 33, 1319–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliszczewicz, B.; Snarr, L.; Esco, M. Metabolic and Cardiovascular Response to The CrossFit Workout ‘Cindy’: A Pilot Study. J. Sport Hum. Perform. 2014, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Borg, G. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Schneiker, K.T.; Bishop, D.; Dawson, B.; Hackett, L.P. Effects of Caffeine on Prolonged Intermittent-Sprint Ability in Team-Sport Athletes. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2006, 38, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.; Messias, F.; Zanchi, N.; Gerlinger-Romero, F.; Duncan, M.; Guimaraes-Ferreira, L. Effects of acute caffeine ingestion on resistance training performance and perceptual responses during repeated sets to failure Effects of acute caffeine ingestion on resistance training performance and perceptual responses during repeated sets. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2015, 55, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lane, S.C.; Hawley, J.A.; Desbrow, B.; Jones, A.M.; Blackwell, J.R.; Ross, M.L. Single and combined effects of beetroot juice and caffeine supplementation on cycling time trial performance. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 39, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, D.; Nicholas, D.; Carper, M.; DeBlauw, J.; Heinrich, K. Validity, Reliability, and Application of the Session-RPE Method for Quantifying Training Loads during High Intensity Functional Training. Sports 2018, 6, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Womack, C.J.; Saunders, M.J.; Bechtel, M.K.; Bolton, D.J.; Martin, M.; Luden, N.D. The influence of a CYP1A2 polymorphism on the ergogenic effects of caffeine. J. Int. Soc. Sport Nutr. 2012, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Donnell, J.O.; Foskett, A.; Rutherfurd-Markwick, K. The influence of caffeine ingestion on strength and power performance in female team-sport players. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2016, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, B.C.; Scorniaenchi, J.; Kerr, N.L.; Eisenmann, J.C.; Feltz, D.L. Aerobic exercise is promoted when individual performance affects the group: A test of the kohler motivation gain effect. Ann. Behav. Med. 2012, 44, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brupbacher, G.; Harder, J.; Faude, O.; Zahner, L.; Donath, L. Music in CrossFit®—Influence on Performance, Physiological, and Psychological Parameters. Sports 2014, 2, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, R.H. Deception by manipulating the clock calibration influences cycle ergometer endurance time in males. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2009, 12, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stein, J.A.; Ramirez, M.; Heinrich, K.M. RETRACTED: The Effects of Acute Caffeine Supplementation on Performance in Trained CrossFit Athletes. Sports 2019, 7, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7040095
Stein JA, Ramirez M, Heinrich KM. RETRACTED: The Effects of Acute Caffeine Supplementation on Performance in Trained CrossFit Athletes. Sports. 2019; 7(4):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7040095
Chicago/Turabian StyleStein, Jesse A., Melitza Ramirez, and Katie M. Heinrich. 2019. "RETRACTED: The Effects of Acute Caffeine Supplementation on Performance in Trained CrossFit Athletes" Sports 7, no. 4: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7040095
APA StyleStein, J. A., Ramirez, M., & Heinrich, K. M. (2019). RETRACTED: The Effects of Acute Caffeine Supplementation on Performance in Trained CrossFit Athletes. Sports, 7(4), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7040095





