Relationships between Bat Swing Speed and Muscle Thickness and Asymmetry in Collegiate Baseball Players
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeRenne, C.; Hetzler, R.K.; Buxton, B.P.; Ho, K.W. Effects of training frequency on strength maintenance in pubescent baseball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 1996, 10, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski, D.J.; DeRenne, C.; Spaniol, F.J. Contributing factors for increased bat swing velocity. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaguchi, K.; Demura, S. Relationship between upper-body strength and bat swing speed in high-school baseball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymanski, D.J.; Szymanski, J.M.; Schade, R.L.; Bradford, T.J.; McIntyre, J.S.; DeRenne, C.; Madsen, N.H. The relation between anthropometric and physiological variables and bat velocity of high-school baseball players before and after 12 weeks of training. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 2933–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, G.F.; Dolny, D. Acute effects of various weighted bat warm-up protocols on bat velocity. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 2114–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, T.; Miyatani, M.; Tachi, M.; Kouzaki, M.; Kawakami, Y.; Kanehisa, H. Muscle volume is a major determinant of joint torque in humans. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2001, 172, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshikawa, Y.; Muramatsu, M.; Iida, T.; Uchiyama, A.; Nakajima, Y.; Kanehisa, H.; Fukunaga, T. Influence of the Psoas Major and Thigh Muscularity on 100-m Times in Junior Sprinters. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 2138–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyatani, M.; Kanehisa, H.; Ito, M.; Kawakami, Y.; Fukunaga, T. The accuracy of volume estimates using ultrasound muscle thickness measurements in different muscle groups. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 91, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takai, Y.; Katsumata, Y.; Kawakami, Y.; Kanehisa, H.; Fukunaga, T. Ultrasound method for estimating the cross-sectional area of the psoas major muscle. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 2000–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, C.M.; Banks, S.A.; Cook, F.F.; Draovitch, P. Hitting a baseball: A biomechanical description. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 1995, 22, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.K.; Richardson, C.A.; Jull, G.A. Electromyographic Amplitude and Frequency Changes in the Iliocostalis Lumborum and Multifidus Muscles During a Trunk Holding Test. Phys. Ther. 1997, 77, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugaya, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Nakazawa, R.; Wada, N. Relationship between spinal range of motion and trunk muscle activity during trunk rotation. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, B.; Jobe, F.W.; Pink, M.; Perry, J. Baseball Batting: An Electromyographic Study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1993, 292, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski, D.J.; Szymanski, J.M.; Bradford, T.J.; Schage, R.L.; Pascoe, D.D. Effect of twelve weeks of medicine ball training on high school baseball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, B.; Fleisig, G.S. Kinematic comparison of baseball batting off of a tee among various competition levels. Sports Biomech. 2016, 15, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchis-Moysi, J.; Idoate, F.; Izquierdo, M.; Calbet, J.A.; Dorado, C. The hypertrophy of the lateral abdominal wall and quadratus lumborum is sport-specific: An MRI segmental study in professional tennis and soccer players. Sports Biomech. 2013, 12, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, T.; Nagami, T.; Mizuguchi, N.; Anderson, T. The acute and chronic effects of isometric contraction conditioning on baseball bat velocity. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugaya, T.; Abe, Y.; Sakamoto, M. Ultrasound Evaluation of Muscle Thickness Changes in the External Oblique, Internal Oblique, and Transversus Abdominis Muscles Considering the Influence of Posture and Muscle Contraction. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2014, 26, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hides, J.A.; Stanton, W.R.; McMahon, S.; Sims, K.; Richardson, C.A. Effect of stabilization training on multifidus muscle cross-sectional area among young elite cricketers with low back pain. J. Orthop. Sprot. Phys. 2008, 38, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, K.; Kearns, C.F.; Midorikawa, T.; Abe, T. Prediction and validation of total and regional skeletal muscle mass by ultrasound in Japanese adults. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 96, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachi, M.; Suga, T.; Higuchi, T.; Misaki, J.; Tsuchikane, R.; Tanaka, D.; Miyake, Y.; Isaka, T. Applicability of ultrasonography for evaluating trunk muscle size: A pilot study. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, S.S.; Lyons, B.C.; Mayo, J.J. Effect of grip strength and grip strengthening exercises on instantaneous bat velocity of collegiate baseball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2004, 18, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urquhart, D.M.; Hodges, P.W. Differential activity of regions of transversus abdominis during trunk rotation. Eur. Spine J. 2005, 14, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, E.A.; Grundström, H.; Thorstensson, A. Diverging intramuscular activity patterns in back and abdominal muscles during trunk rotation. Spine 2002, 27, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.A.; Moseley, G.L.; Hodges, P.W. The lumbar multifidus: Does the evidence support clinical beliefs? Man Ther. 2006, 11, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Demura, S.; Takahashi, K.; Demura, G.; Mori, Y. Differences in muscle power between the dominant and nondominant upper limbs of baseball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hides, J.A.; Stanton, W.R.; Freke, M.; Wilson, S.; McMahon, S.; Richardson, C.A. MRI study of the size, symmetry and function of the trunk muscles among elite cricketers with and without low back pain. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 42, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.J.; Swanik, C.B.; Higginson, J.S.; Kaminski, T.W.; Swanik, K.A.; Kelly, J.D.; Nazarian, L.N. Neuromuscular and stiffness adaptations in division I collegiate baseball players. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2013, 23, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Muscle | Dominant (mm) | Non-Dominant (mm) | Asymmetry (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trunk muscles | |||
| Upper abdominal rectus | 16.2 ± 2.4 | 16.2 ± 2.4 | 0.0 ± 6.0 |
| Central abdominal rectus | 17.4 ± 2.5 | 17.2 ± 2.6 | +1.9 ± 7.0 |
| Lower abdominal rectus | 19.5 ± 3.3 | 19.8 ± 3.5 | −0.6 ± 9.9 |
| Abdominal wall | 30.9 ± 5.2 | 33.7 ± 5.9 ∗ | −7.5 ± 8.6 |
| Multifidus lumborum | 27.3 ± 3.5 | 27.9 ± 3.1 ∗ | −2.2 ± 4.5 |
| Upper limb muscles | |||
| Elbow flexors | 32.3 ± 2.9 | 32.1 ± 2.9 | +1.0 ± 6.1 |
| Elbow extensors | 35.1 ± 5.5 | 35.3 ± 5.6 | +0.1 ± 11.2 |
| Forearm flexors | 24.5 ± 2.7 | 24.5 ± 2.5 | +0.6 ± 10.1 |
| Lower limb muscles | |||
| Knee extensors | 61.7 ± 5.2 | 60.2 ± 5.4 | +2.7 ± 5.9 |
| Knee flexors | 76.6 ± 6.6 | 76.6 ± 5.9 | +0.1 ± 3.3 |
| Dorsiflexors | 29.5 ± 2.3 | 29.2 ± 2.3 | +1.3 ± 4.0 |
| Plantar flexors | 69.4 ± 4.9 | 69.6 ± 4.5 | −0.3 ± 4.5 |
| Muscle | Dominant | Non-dominant | % Asymmetry | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p Values | r | p Values | r | p Values | |
| Trunk | ||||||
| Upper abdominal rectus | 0.229 | 0.283 | 0.151 | 0.480 | 0.160 | 0.456 |
| Central abdominal rectus | 0.236 | 0.267 | 0.184 | 0.390 | 0.077 | 0.722 |
| Lower abdominal rectus | 0.097 | 0.651 | 0.098 | 0.650 | 0.006 | 0.978 |
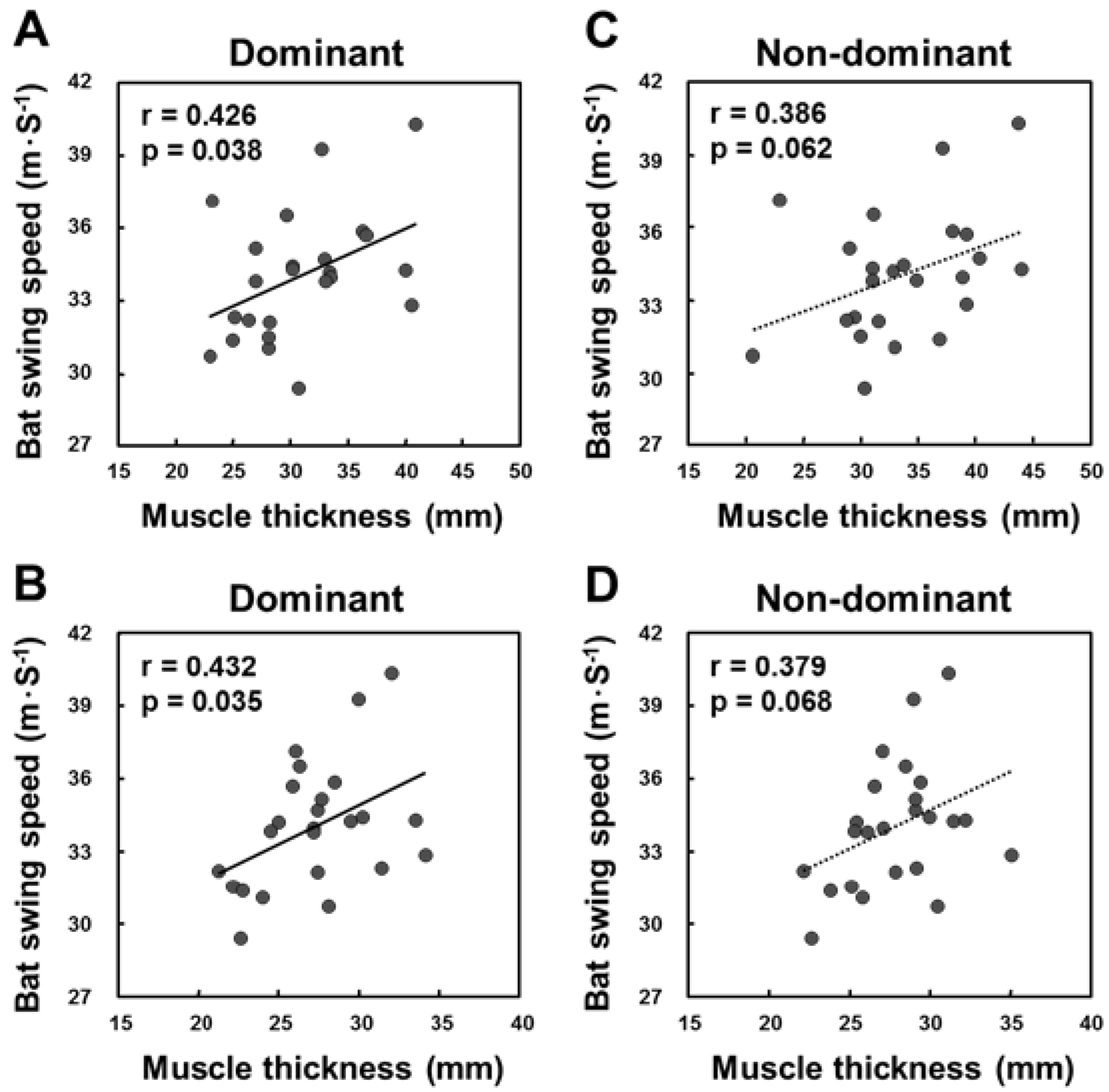
| Abdominal wall | 0.426 | 0.038 | 0.386 | 0.062 | 0.008 | 0.972 |
| Multifidus lumborum | 0.432 | 0.035 | 0.379 | 0.068 | 0.261 | 0.218 |
| Upper limb | ||||||
| Elbow flexors | 0.378 | 0.069 | 0.223 | 0.295 | 0.183 | 0.393 |
| Elbow extensors | −0.149 | 0.487 | −0.015 | 0.945 | −0.201 | 0.346 |
| Forearm flexors | 0.003 | 0.989 | −0.143 | 0.505 | 0.167 | 0.436 |
| Lower limb | ||||||
| Knee extensors | 0.194 | 0.364 | 0.245 | 0.249 | −0.105 | 0.624 |
| Knee flexors | 0.081 | 0.706 | 0.028 | 0.898 | 0.136 | 0.528 |
| Dorsiflexors | −0.110 | 0.609 | 0.005 | 0.980 | −0.237 | 0.265 |
| Plantar flexors | −0.044 | 0.837 | 0.152 | 0.478 | −0.286 | 0.176 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsuchikane, R.; Higuchi, T.; Suga, T.; Wachi, M.; Misaki, J.; Tanaka, D.; Miyake, Y.; Isaka, T. Relationships between Bat Swing Speed and Muscle Thickness and Asymmetry in Collegiate Baseball Players. Sports 2017, 5, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports5020033
Tsuchikane R, Higuchi T, Suga T, Wachi M, Misaki J, Tanaka D, Miyake Y, Isaka T. Relationships between Bat Swing Speed and Muscle Thickness and Asymmetry in Collegiate Baseball Players. Sports. 2017; 5(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports5020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsuchikane, Ryo, Takatoshi Higuchi, Tadashi Suga, Michio Wachi, Jun Misaki, Daichi Tanaka, Yuto Miyake, and Tadao Isaka. 2017. "Relationships between Bat Swing Speed and Muscle Thickness and Asymmetry in Collegiate Baseball Players" Sports 5, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports5020033
APA StyleTsuchikane, R., Higuchi, T., Suga, T., Wachi, M., Misaki, J., Tanaka, D., Miyake, Y., & Isaka, T. (2017). Relationships between Bat Swing Speed and Muscle Thickness and Asymmetry in Collegiate Baseball Players. Sports, 5(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports5020033





