Single-Bout Strength: Acute Mental Health Responses to Resistance Training in Active Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
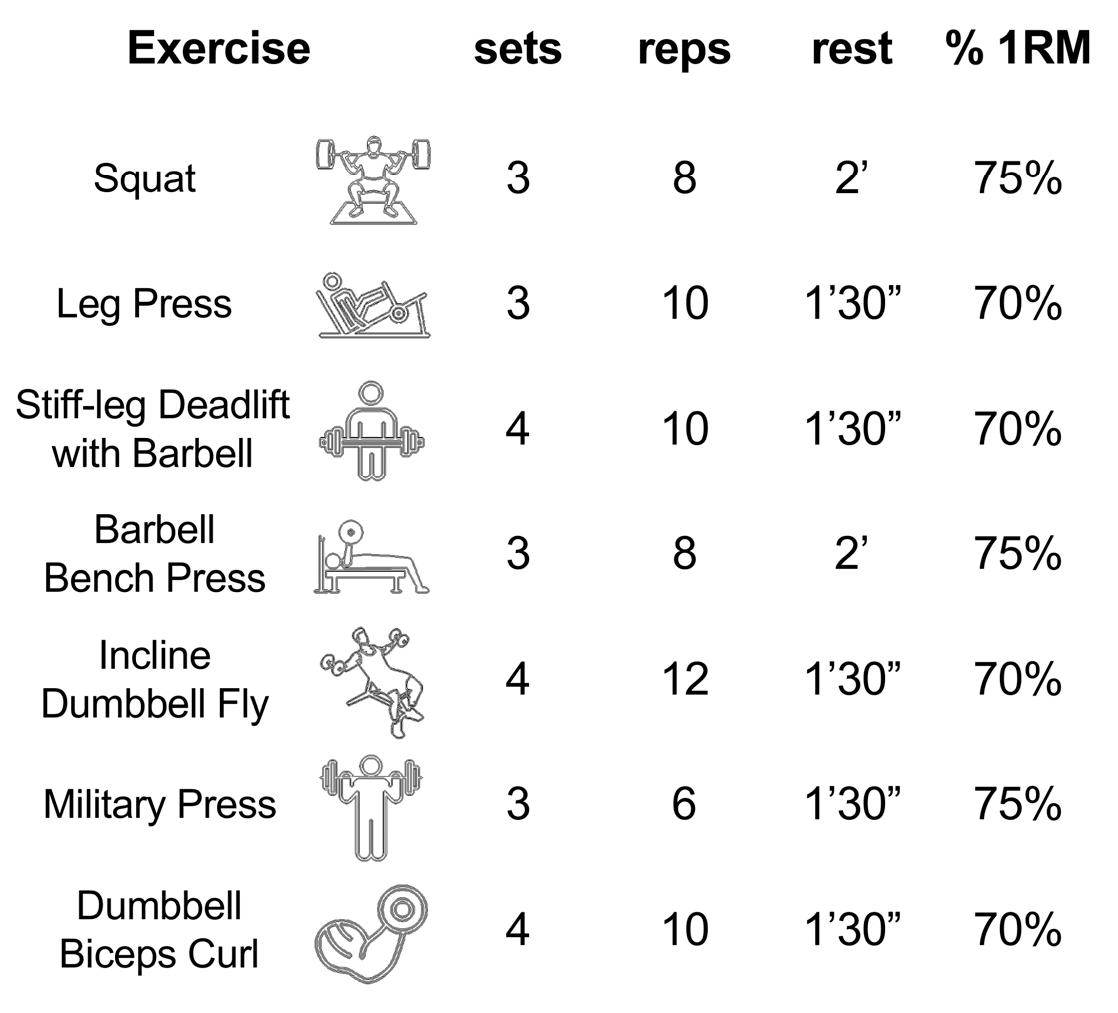
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Group C
2.4. Psychological Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eather, N.; Wade, L.; Pankowiak, A.; Eime, R. The impact of sports participation on mental health and social outcomes in adults: A systematic review and the ‘Mental Health through Sport’ conceptual model. Syst. Rev. 2023, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsen, E.W. Physical activity in the prevention and treatment of anxiety and depression. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2008, 62 (Suppl. S47), 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensari, I.; Greenlee, T.A.; Motl, R.W.; Petruzzello, S.J. META-ANALYSIS of ACUTE EXERCISE EFFECTS on STATE ANXIETY: AN UPDATE of RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIALS over the PAST 25 YEARS. Depress. Anxiety 2015, 32, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosburner, A.; Cramer, H.; Bilc, M.; Triana, J.; Anheyer, D. Yoga for Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Depress. Anxiety 2024, 2024, 6071055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.M.; Purcell, R.; De Silva, S.; Mawren, D.; McGorry, P.D.; Parker, A.G. The Mental Health of Elite Athletes: A Narrative Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 1333–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, C.L.; Hainline, B.; Aron, C.M.; Baron, D.; Baum, A.L.; Bindra, A.; Budgett, R.; Campriani, N.; Castaldelli-Maia, J.M.; Currie, A.; et al. Mental health in elite athletes: International Olympic Committee consensus statement (2019). Br. J. Sports Med. 2019, 53, 667–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzzello, S.J.; Landers, D.M.; Hatfield, B.D.; Kubitz, K.A.; Salazar, W. A Meta-Analysis on the Anxiety-Reducing Effects of Acute and Chronic Exercise Outcomes and Mechanisms. Sports Med. 1991, 11, 143–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Calderon, J.; Casuso-Holgado, M.J.; Muñoz-Fernandez, M.J.; Garcia-Muñoz, C.; Heredia-Rizo, A.M. Yoga-based interventions may reduce anxiety symptoms in anxiety disorders and depression symptoms in depressive disorders: A systematic review with meta-analysis and meta-regression. Br. J. Sports Med. 2023, 57, 1442–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, K.M.; Herring, M.P. The effects of pilates on mental health outcomes: A meta-analysis of controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2018, 37, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follador, L.; Alves, R.C.; Ferreira, S.D.S.; Silva, A.C.; da Silva, S.G. Perceived Exertion and Affect From Tai Chi, Yoga, and Stretching Classes for Elderly Women. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2019, 126, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szuhany, K.L.; Bugatti, M.; Otto, M.W. A meta-analytic review of the effects of exercise on brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 60, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekkekakis, P.; Parfitt, G.; Petruzzello, S.J. The Pleasure and Displeasure People Feel When they Exercise at Different Intensities Decennial Update and Progress towards a Tripartite Rationale for Exercise Intensity Prescription. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 641–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, J.C.; Smith, M.A. The anxiolytic effects of resistance exercise. Front. Res. Found. 2014, 5, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisler, J.M.; Crombie, K.M.; Adams, T.G. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences 67 Exercise and Mental Health; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Herring, M.P.; Meyer, J.D. Resistance exercise for anxiety and depression: Efficacy and plausible mechanisms. Trends Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crewther, B.; Keogh, J.; Cronin, J.; Cook, C. Possible Stimuli for Strength and Power Adaptation Acute Hormonal Responses. Sports Med. 2006, 36, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faelli, E.; Bisio, A.; Codella, R.; Ferrando, V.; Perasso, L.; Panascì, M.; Saverino, D.; Ruggeri, P. Acute and chronic catabolic responses to crossfit® and resistance training in young males. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernárdez-Vázquez, R.; Raya-González, J.; Castillo, D.; Beato, M. Resistance Training Variables for Optimization of Muscle Hypertrophy: An Umbrella Review. Front. Sports Act. Living 2022, 4, 949021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgente, V.; Agudo-Ortega, A.; Lopez-Hernandez, A.; Del Cerro, J.S.; Minciacchi, D.; Ravé, J.M.G. Relationship between Maximum Force–Velocity Exertion and Swimming Performances among Four Strokes over Medium and Short Distances: The Stronger on Dry Land, the Faster in Water? J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiou, N.; Bogdanis, G.C.; Mastorakos, G. Endocrine responses of the stress system to different types of exercise. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, E.E. Exercise and circulating cortisol levels: The intensity threshold effect 587. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2008, 31, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeusen, R.; De Meirleir, K. Exercise and Brain Neurotransmission. Sports Med. 1995, 20, 160–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, K.J.; Newton, M.J.; Brown, B.M.; Rainey-Smith, S.R.; Bird, S.; Martins, R.N.; Peiffer, J.J. Intense resistance exercise increases peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolucci, E.M.; Loukov, D.; Bowdish, D.M.E.; Heisz, J.J. Exercise reduces depression and inflammation but intensity matters. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 133, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, B.R.; McDowell, C.P.; Lyons, M.; Herring, M.P. The Effects of Resistance Exercise Training on Anxiety: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 2521–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, P.M.; Werneck, A.O.; Dos Santos, L.; Oliveira, M.D.; Zou, L.; Schuch, F.B.; Cyrino, E.S. Can resistance training improve mental health outcomes in older adults? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Psychiatry Res. 2024, 333, 115746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Rave, J.M.; Sorgente, V.; Agudo-Ortega, A.; Rodrigo-Carranza, V.; Psycharakis, S.; Turner, A.P. Countermovement-Jump and Pull-Up Performance Before and After a Swimming Race in Preparatory and Competitive Phases of a Swimming Season. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2024, 19, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, R.; Parker, A.G.; Levinger, I.; Bourke, M.; Patten, R.; Woessner, M.N. Resistance training and combined resistance and aerobic training as a treatment of depression and anxiety symptoms in young people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2024, 18, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibeau, W.S.; Moore, J.B.; Mitchell, N.G.; Vargas-Tonsing, T.; Bartholomew, J.B. Effects Of Acute Resistance Training Of Different Intensities And Rest Periods On Anxiety And Affect. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavarretta, D.J.; Hall, E.E.; Bixby, W.R. The acute effects of resistance exercise on affect, anxiety, and mood–practical implications for designing resistance training programs. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2018, 12, 295–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snaith, P. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes The Hospital Anxiety And Depression Scale. 2003. Available online: http://www.hqlo.com/content/1/1/29 (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Bjelland, I.; Dahl, A.A.; Haug, T.; Neckelmann, D. The validity of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale An updated literature review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 52, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, C. Review international experiences with the hospital anxiety and depression scale-a review of validation data and clinical results. J. Psychosom. Res. 1997, 42, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, R.R. The acute effects of exercise on mood state. J. Psychosom. Res. 1996, 40, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quade, D. Rank Analysis of Covariance. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1967, 62, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudielka, B.M.; Kirschbaum, C. Sex differences in HPA axis responses to stress: A review. Biol. Psychol. 2005, 69, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, P.R. Why is depression more prevalent in women? J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2015, 40, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartholomew, J.B.; Morrison, D.; Ciccolo, J.T. Effects of acute exercise on mood and well-being in patients with major depressive disorder. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 2032–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, T.E.; Fleshner, M. Neuroplasticity of dopamine circuits after exercise: Implications for central fatigue. NeuroMolecular Med. 2008, 10, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, C.; Yin, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Mu, R.; Liang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ye, C. Unlocking the full potential of resistance training: A comparative analysis of low- and high-intensity effects on neurotrophic growth factors and homocysteine. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, M.; Bishop, N.C.; Stensel, D.J.; Lindley, M.R.; Mastana, S.S.; Nimmo, M.A. The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: Mechanisms and implications for the prevention and treatment of disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.E.; VanDerwerker, C.J.; Saladin, M.E.; Gregory, C.M. The role of exercise in the treatment of depression: Biological underpinnings and clinical outcomes. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 298–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleber, B.; Sitges, C.; Brattico, E.; Vuust, P.; Zamorano, A.M. Association Between Interoceptive Accuracy and Pain Perception: Insights From Trained Musicians and Athletes. Eur. J. Pain 2025, 29, e70012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’connor, P.J.; Herring, M.P.; Caravalho, A. Mental Health Benefits of Strength Training in Adults. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2010, 4, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amore, M.; Minciacchi, D.; Panconi, G.; Guarducci, S.; Bravi, R.; Sorgente, V. Impact of Sled-Integrated Resisted Sprint Training on Sprint and Vertical Jump Performance in Young U-14 Male Football Players. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorgente, V.; Lopez-Hernandez, A.; Minciacchi, D.; Ravé, J.M.G. Diving into Recovery. The Effects of Different Post-Competition Protocols for Enhancing Physio-Psychological Parameters in National Level Youth Swimmers. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2023, 22, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz de la Cruz, V.; Agudo-Ortega, A.; Sorgente, V.; Turner, A.P.; González-Ravé, J.M. The effectiveness of adjusting resistance training loads through velocity-based techniques in experienced sprinters: A case series study. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1241459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Lo, Y.H.; Li, R.H.; Hung, C.S.; Cheng, Y.T.; Chen, F.T.; Chang, Y.K. Acute effects of resistance exercise intensity and repetition at a predetermined volume on inhibitory control: A randomized controlled trial. Front. Sports Act. Living 2025, 7, 1551624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanin, Y.L. Emotions in Sport: Current Issues and Perspectives. In Handbook of Sport Psychology, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rupprecht, A.G.O.; Tran, U.S.; Gröpel, P. The effectiveness of pre-performance routines in sports: A meta-analysis. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2024, 17, 39–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
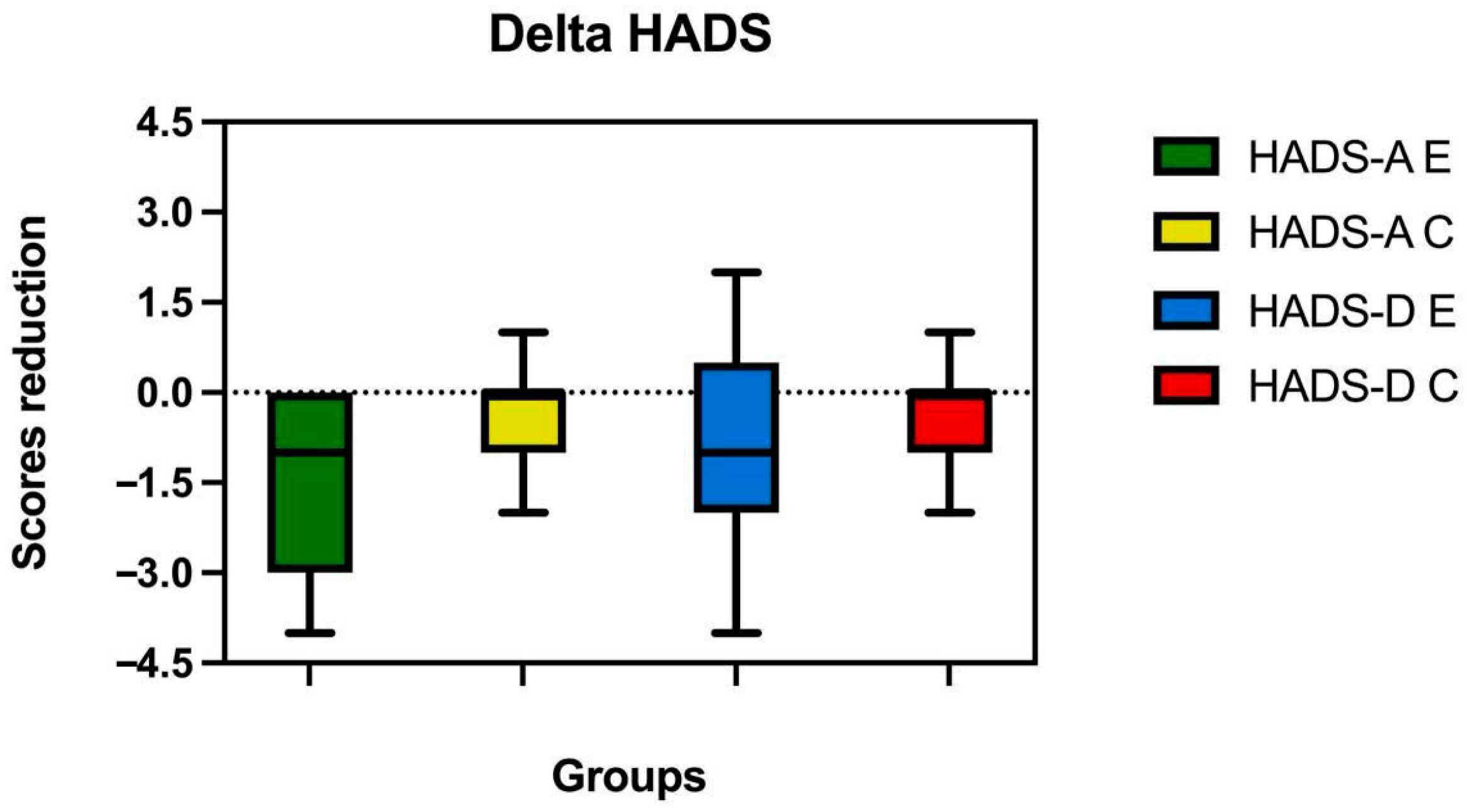
| Group | Status | Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HADS-A | ||||||
| mean ± s.d. | median | Z | p | r | ||
| E (n = 30) | Pre | 6.37 ± 3.00 | 6 | −3.3 | <0.001 | −0.7 |
| Post | 4.67 ± 3.02 | 4 | ||||
| C (n = 26) | Pre | 5.69 ± 2.11 | 6 | −1.5 | 0.139 | −0.4 |
| Post | 5.15 ± 1.91 | 5 | ||||
| HADS-D | ||||||
| mean ± s.d. | median | Z | p | r | ||
| E (n = 30) | Pre | 4.43 ± 2.30 | 4.5 | −2.8 | <0.005 | −0.6 |
| Post | 3.37± 2.41 | 3.5 | ||||
| C (n = 26) | Pre | 4.58 ± 2.16 | 5.5 | −1.5 | 0.135 | −0.4 |
| Post | 4.04 ± 1.84 | 4 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amore, M.; Alfarano, A.; Sorgente, V.; Panconi, G.; Guarducci, S.; Bravi, R.; Minciacchi, D. Single-Bout Strength: Acute Mental Health Responses to Resistance Training in Active Adults. Sports 2025, 13, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13070221
Amore M, Alfarano A, Sorgente V, Panconi G, Guarducci S, Bravi R, Minciacchi D. Single-Bout Strength: Acute Mental Health Responses to Resistance Training in Active Adults. Sports. 2025; 13(7):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13070221
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmore, Manuel, Adolfo Alfarano, Vincenzo Sorgente, Giulia Panconi, Sara Guarducci, Riccardo Bravi, and Diego Minciacchi. 2025. "Single-Bout Strength: Acute Mental Health Responses to Resistance Training in Active Adults" Sports 13, no. 7: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13070221
APA StyleAmore, M., Alfarano, A., Sorgente, V., Panconi, G., Guarducci, S., Bravi, R., & Minciacchi, D. (2025). Single-Bout Strength: Acute Mental Health Responses to Resistance Training in Active Adults. Sports, 13(7), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13070221






