Effectiveness of Specific Professional Training in Male Elite Adolescent Team Handball Players
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
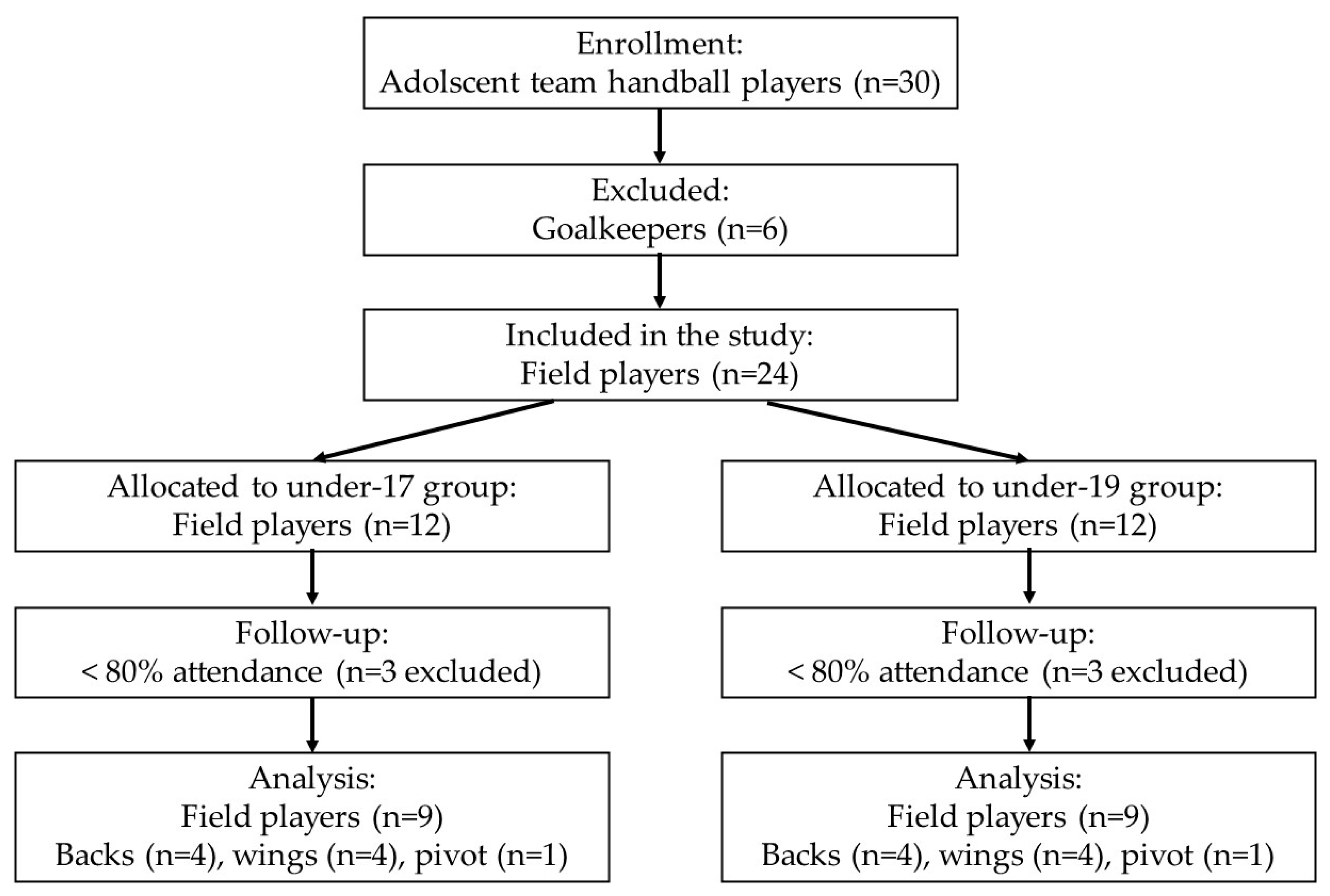
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
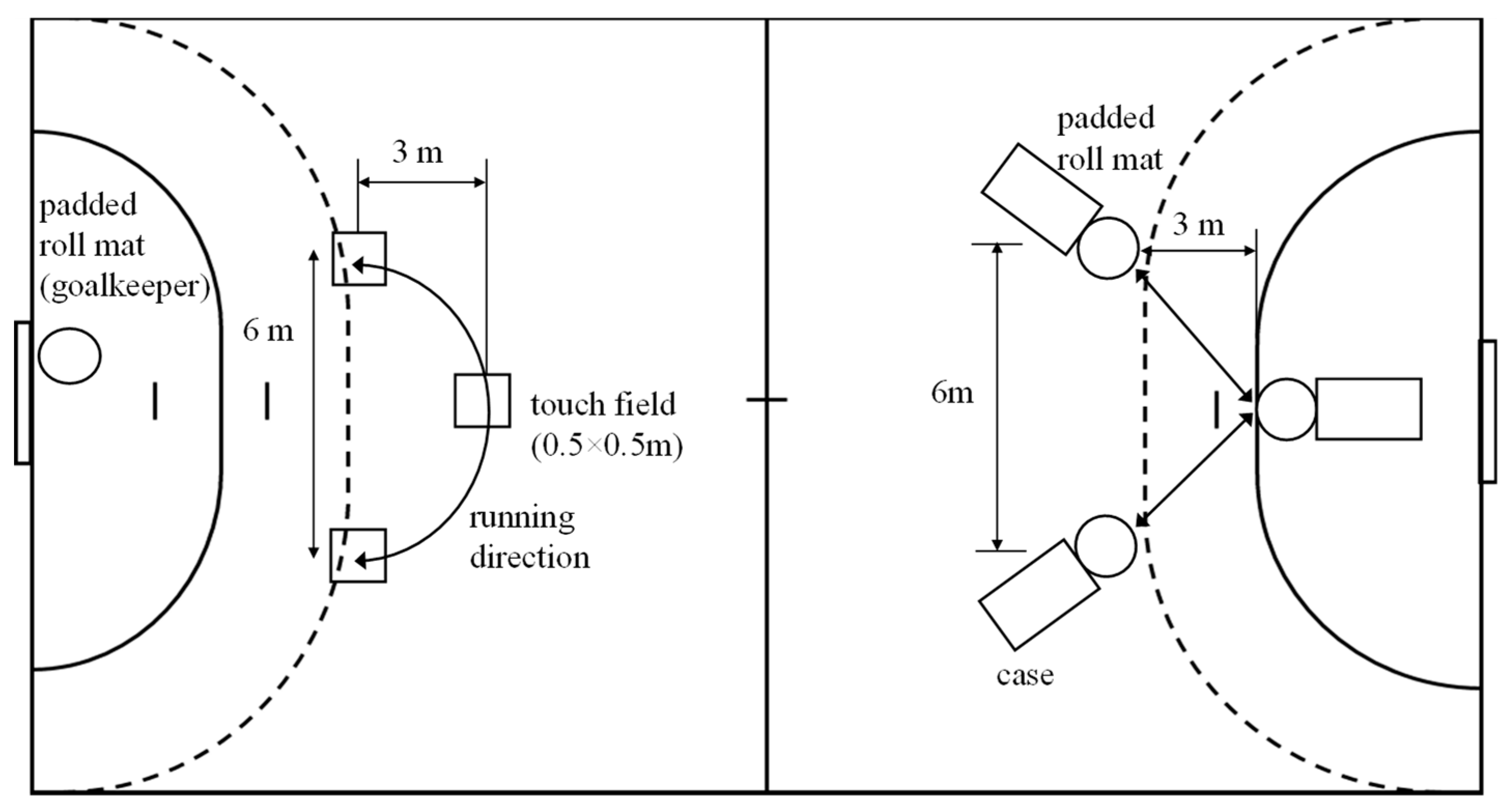
2.3. Team Handball Game-Based Performance Test (GBPT)
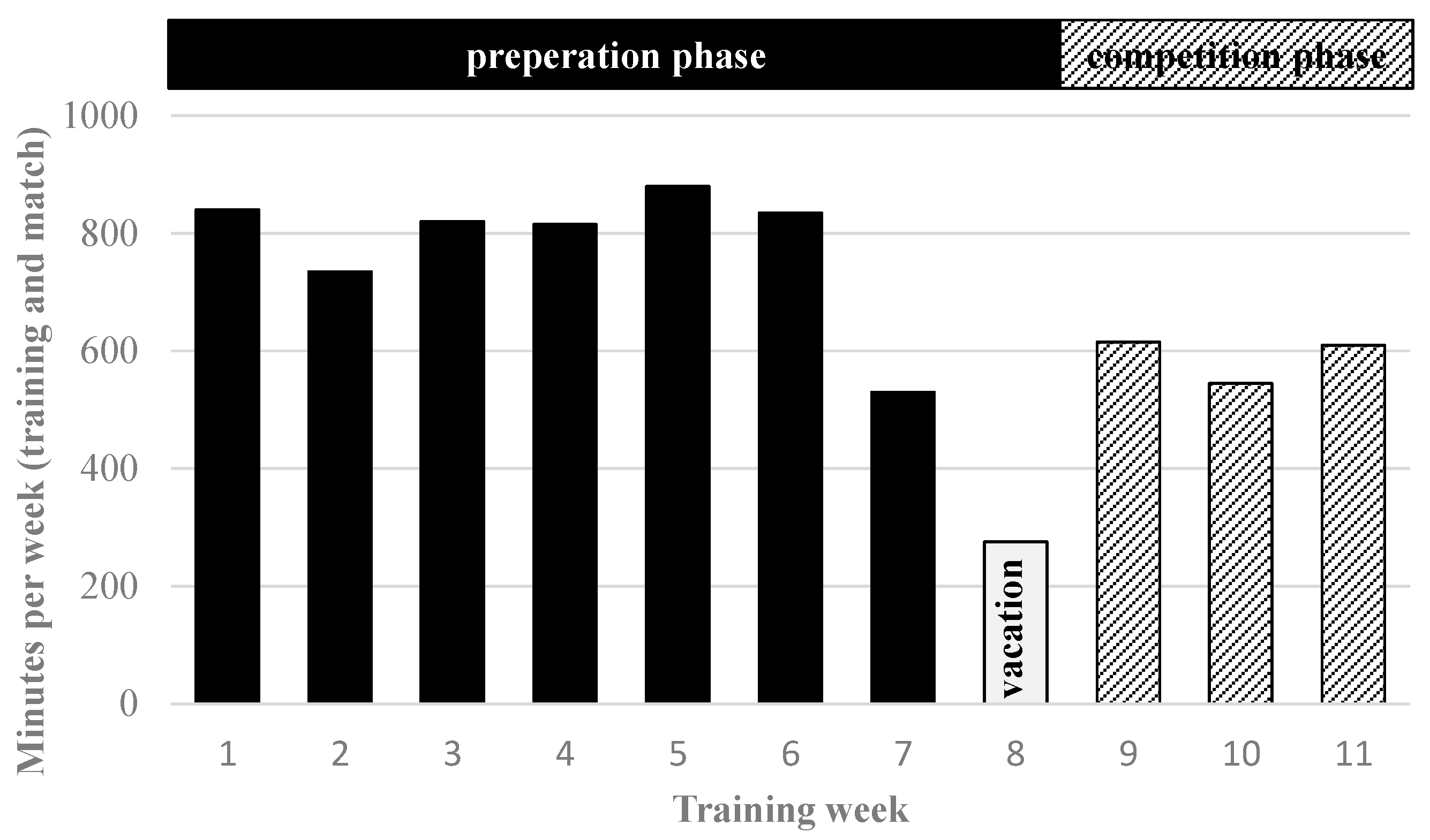
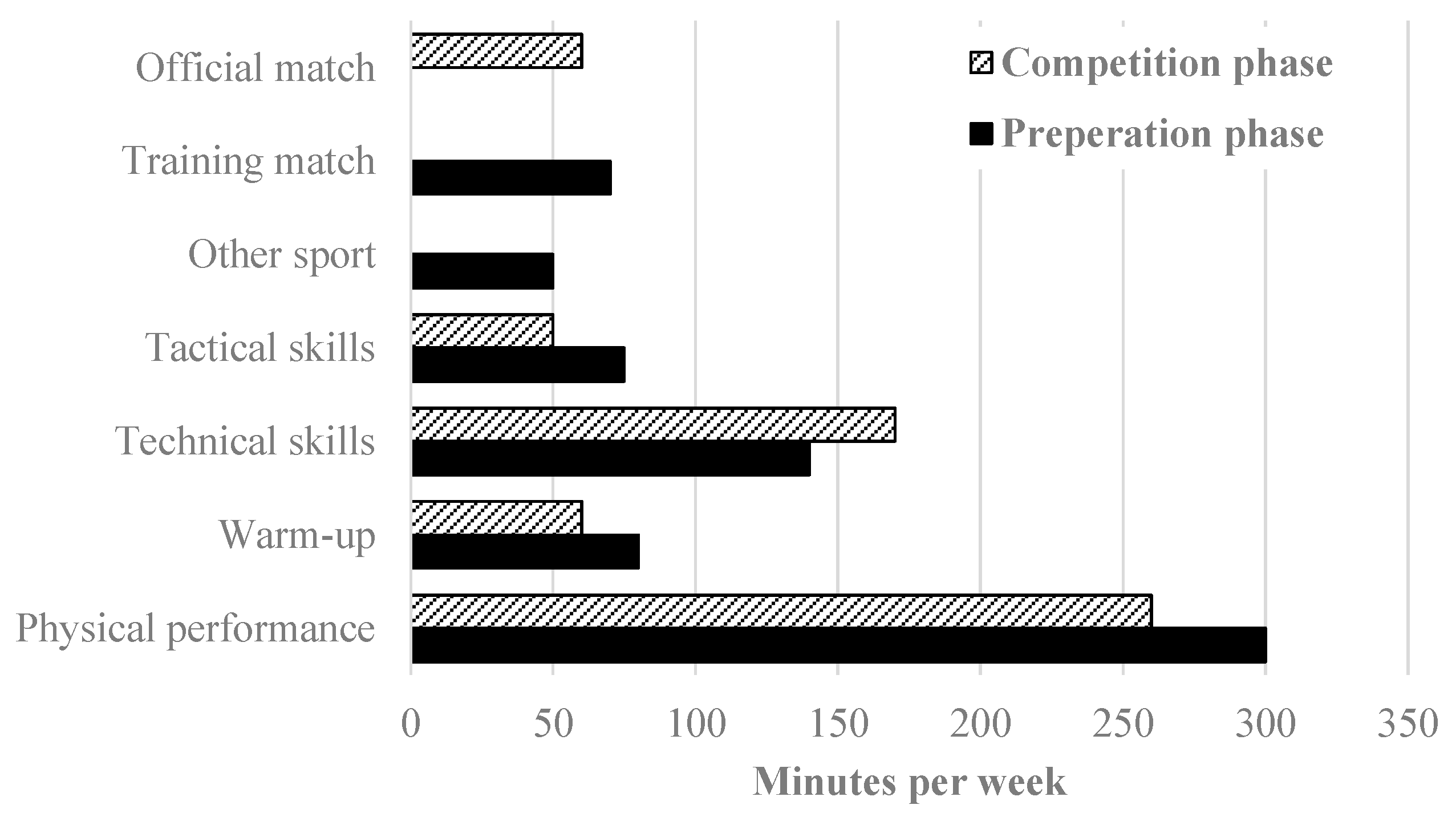
2.4. Training Program
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Practical Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VO2max | Maximal oxygen uptake |
| EHF | European Handball Federation |
| GBPT | Game-based performance test |
| HRpeak | Peak heart rate |
| VO2peak | Peak oxygen uptake |
| IHF | International Handball Federation |
References
- Michalsik, L.B.; Madsen, K.; Aagaard, P. Technical match characteristics and influence of body anthropometry on playing performance in male elite team handball. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalsik, L.B.; Madsen, K.; Aagaard, P. Physiological capacity and physical testing in male elite team handball. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2015, 55, 415–429. [Google Scholar]
- Michalsik, L.B.; Aagaard, P. Physical demands in elite team handball: Comparisons between male and female players. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2015, 55, 878–891. [Google Scholar]
- Michalsik, L.B.; Aagaard, P.; Madsen, K. Locomotion characteristics and match-induced impairments in physical performance in male elite team handball players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2013, 34, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchado, C.; Pueo, B.; Chirosa-Rios, L.J.; Tortosa-Martínez, J. Time-Motion Analysis by Playing Positions of Male Handball Players during the European Championship 2020. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchado, C.; Martínez, J.T.; Pueo, B.; Tormo, J.M.C.; Vila, H.; Ferragut, C.; Sánchez, F.S.; Busquier, S.; Amat, S.; Ríos, L.J.C. High-Performance Handball Player’s Time-Motion Analysis by Playing Positions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalsik, L.B.; Aagaard, P.; Madsen, K. Technical activity profile and influence of body anthropometry on playing performance in female elite team handball. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1126–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieseler, G.; Hermassi, S.; Hoffmeyer, B.; Schulze, S.; Irlenbusch, L.; Bartels, T.; Delank, K.-S.; Laudner, K.G.; Schwesig, R. Differences in anthropometric characteristics in relation to throwing velocity and competitive level in professional male team handball: A tool for talent profiling. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2017, 57, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, K.; Pilat, C.; Ückert, K.; Frech, T.; Mooren, F.C. Physical performance profile of handball players is related to playing position and playing class. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthys, S.P.J.; Fransen, J.; Vaeyens, R.; Lenoir, M.; Philippaerts, R. Differences in biological maturation, anthropometry and physical performance between playing positions in youth team handball. J. Sports Sci. 2013, 31, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohoric, U.; Abazovic, E.; Paravlic, A.H. Morphological and Physical Performance-Related Characteristics of Elite Male Handball Players: The Influence of Age and Playing Position. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, M.; Hermassi, S.; Gaamouri, N.; Aloui, G.; Comfort, P.; Shephard, R.J.; Chelly, M.S. Field Tests of Performance and Their Relationship to Age and Anthropometric Parameters in Adolescent Handball Players. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingebrigtsen, J.; Jeffreys, I.; Rodahl, S. Physical characteristics and abilities of junior elite male and female handball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidor, R.; Falk, B.; Arnon, M.; Cohen, Y.; Segal, G.; Lander, Y. Measurement of talent in team handball: The questionable use of motor and physical tests. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthys, S.P.J.; Vaeyens, R.; Fransen, J.; Deprez, D.; Pion, J.; Vandendriessche, J.; Vandorpe, B.; Lenoir, M.; Philippaerts, R. A longitudinal study of multidimensional performance characteristics related to physical capacities in youth handball. J. Sports Sci. 2013, 31, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthys, S.P.J.; Vaeyens, R.; Vandendriessche, J.; Vandorpe, B.; Pion, J.; Coutts, A.J.; Lenoir, M.; Philippaerts, R.M. A multidisciplinary identification model for youth handball. Eur. J. Sport. Sci. 2011, 11, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousanoglou, E.N.; Noutsos, K.S.; Bayios, I.A. Playing level and playing position differences of anthropometric and physical fitness characteristics in elite junior handball players. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2014, 54, 611–621. [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra, J.M.; Kristjánsdóttir, H.; Einarsson, I.Þ.; Guðmundsdóttir, M.L.; Þorgeirsson, S.; Stefansson, A. Anthropometric characteristics, physical fitness and the prediction of throwing velocity in young men handball players. Kinesiology 2019, 51, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visnapuu, M.; Juerimae, T. Relations of Anthropometric Parameters with Scores on Basic and Specific Motor Tasks in Young Handball Players. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2009, 108, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.; Fuchs, P.; Michalsik, L.B. On-court game-based testing in world-class, top-elite, and elite adult female team handball players. Transl. Sports Med. 2020, 3, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.; Orwat, M.; Hinz, M.; Pfusterschmied, J.; Bacharach, D.W.; Von Duvillard, S.P.; Müller, E. Testing game based performance in team-handball. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 2794–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, H.; Hinz, M.; Fuchs, P.; Bell, J.W.; von Duvillard, S.P. Specific Game-Based Performance in Elite Male Adolescent Team Handball Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2022, 17, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, H.; Gierlinger, M.; Adzamija, N.; Ajayi, S.; Bacharach, D.W.; Von Duvillard, S.P. Specific physical training in male team handball. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 3083–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, H.; Hinz, M. The Relationship between Specific Game-Based and General Performance in Young Adult Elite Male Team Handball Players. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.; Sperl, B.; Bell, J.W.; von Duvillard, S.P. Testing Specific Physical Performance in Male Team Handball Players and the Relationship to General Tests in Team Sports. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, M.; Laursen, P.B.; Kuhnle, J.; Ruch, D.; Renaud, C.; Ahmaidi, S. Game-based Training in Young Elite Handball Players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2009, 30, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.; Radic, V. Handball TAKT: Moderne Methoden für spielnahes Training; Meyer & Meyer: Aachen, Germany, 2022; 294p. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge Academic: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 2, 567p. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, J.; Wegner, M.; Wagner, H. Physical performance in female handball players according to playing position. Ger. J. Exerc. Sport. Res. 2018, 48, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, P.X.; Fuchs, P.; von Duvillard, S.P.; Wagner, H.; Shiang, T.Y. Critical assessment of a wide-spread method for estimating energy expenditure during accelerated running based on positioning tracking systems. J. Sport. Health Sci. 2022, 11, 641–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalsik, L.B.; Fuchs, P.; Wagner, H. The Team Handball Game-Based Performance Test Is Better than the Yo-Yo Intermittent Recovery Test to Measure Match-Related Activities in Female Adult Top-Elite Field Team Handball Players. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkinson, G.R. Global changes in anaerobic fitness test performance of children and adolescents (1958–2003). Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2007, 17, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkinson, G.R.; Olds, T.S.; Borms, J. Who are the Eurofittest? Med. Sport. Sci. 2007, 50, 104–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
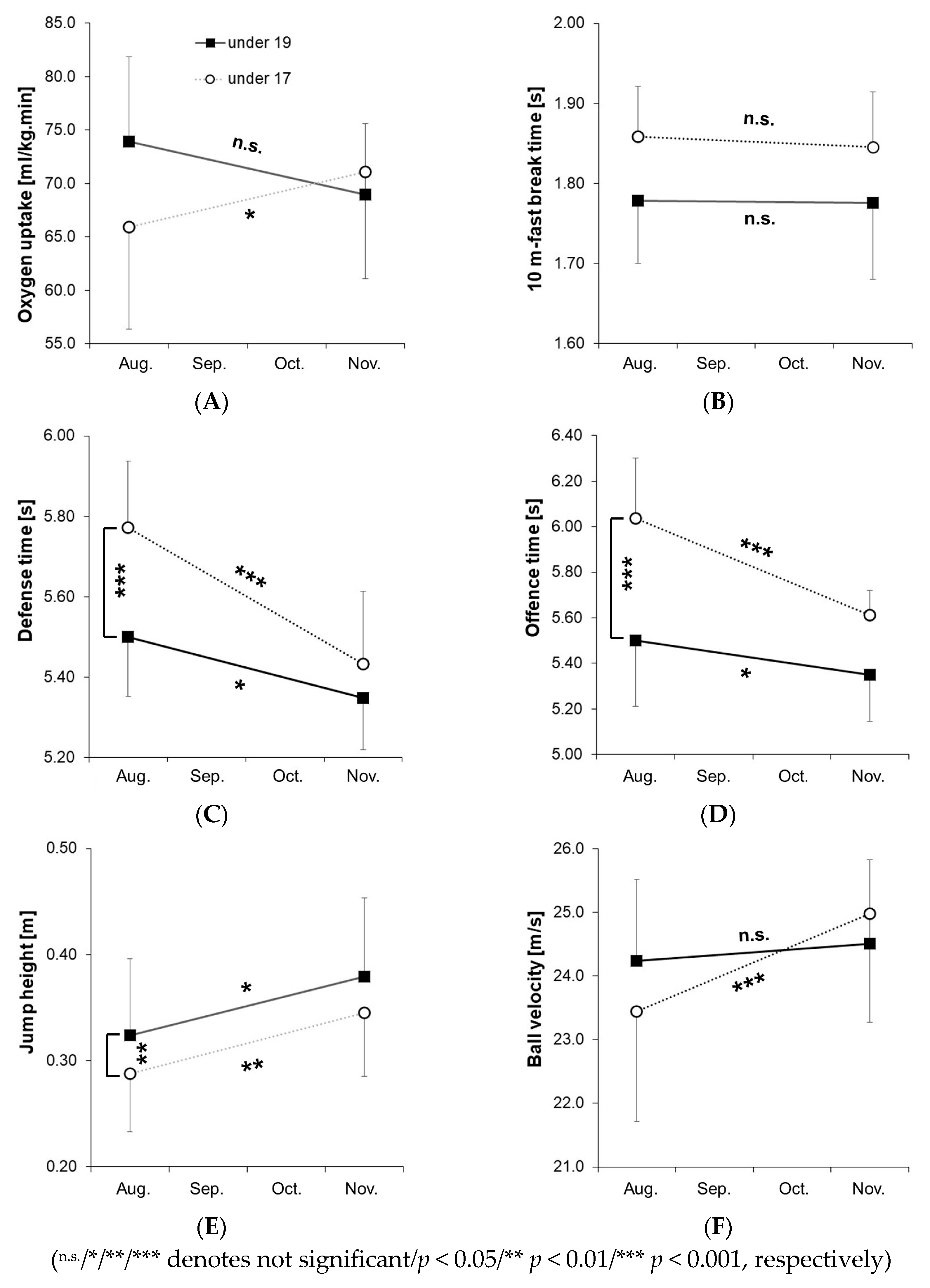
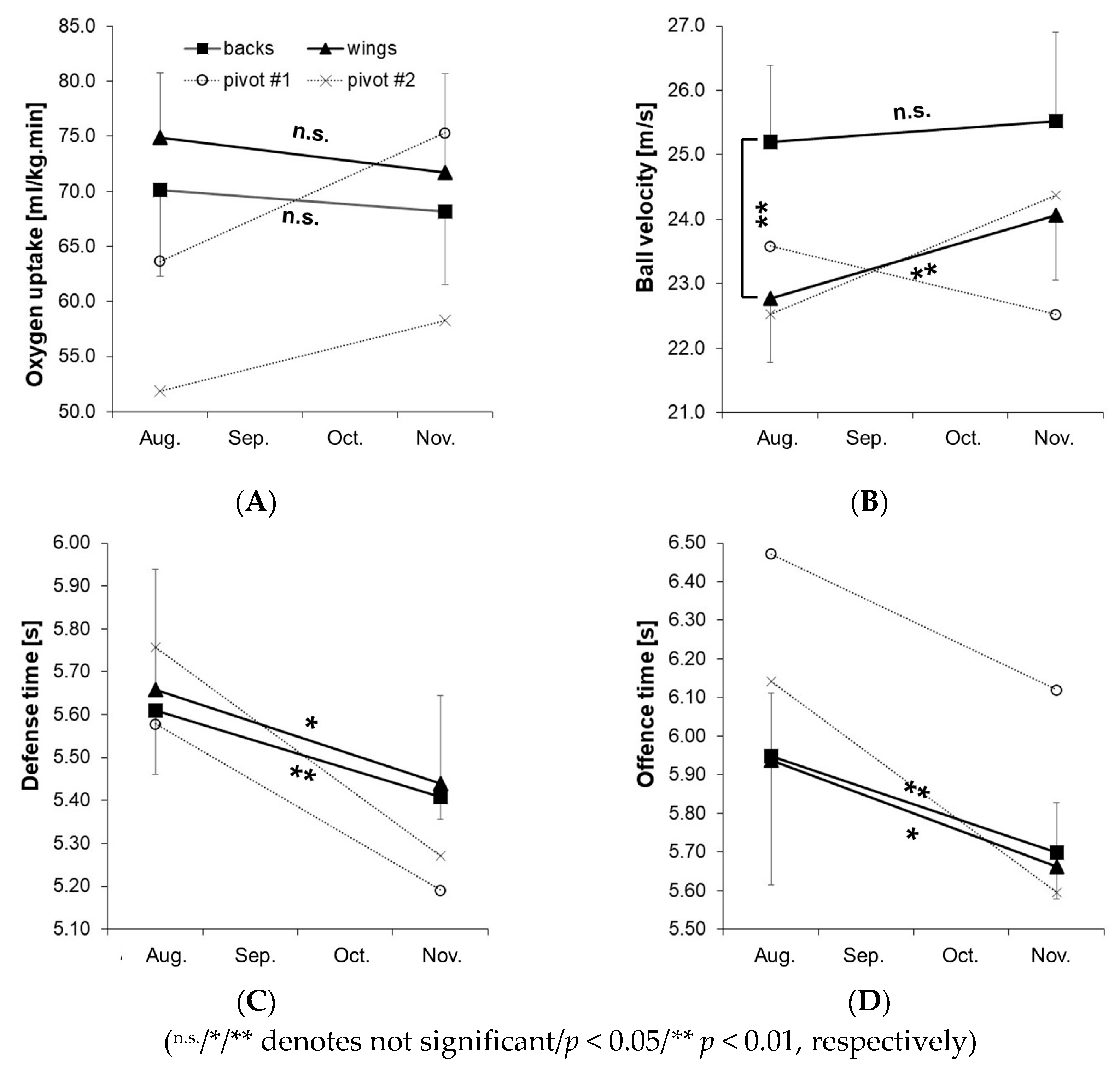
| Under-19 Player | Under-17 Players | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Test Mean ± SD (95% CI) | Post-Test Mean ± SD (95% CI) | Pre-Test Mean ± SD (95% CI) | Post-Test mean ± SD (95% CI) | Team F-, p-Value Effect Size | Time F-, p-Value Effect Size | Team × Time F-, p-Value Effect Size | |
| VO2peak (mL/kg.min) | 73.9 ± 7.9 (68.1–79.8) | 69.0 ± 6.6 (63.1–74.8) | 65.9 ± 9.6 (60.1–71.8) | 71.1 ± 10.0 (65.2–77.0) | 1.03, 0.32 0.03 | 0.01, 0.98 0.00 | 3.13, 0.09 0.09 |
| HRpeak (bpm) | 192 ± 5 (189–196) | 192 ± 9 (187–197) | 193 ± 6 (188–198) | 193 ± 7 (188–197) | 0.21, 0.65 0.01 | 0.00, 0.98 0.00 | 0.05, 0.83 0.00 |
| 10 m-fast break time (s) | 1.78 ± 0.08 (1.73–1.83) | 1.78 ± 0.10 (1.72–1.83) | 1.86 ± 0.06 (1.81–1.91) | 1.85 ± 0.07 (1.79–1.90) | 7.75, <0.01 ** 0.19 | 0.21, 0.65 0.01 | 0.10, 0.75 0.00 |
| 20 m-fast break time (s) | 1.75 ± 0.10 (1.68–1.93) | 1.79 ± 0.12 (1.71–1.86) | 1.86 ± 0.10 (1.78–1.94) | 1.72 ± 0.14 (1.66–1.81) | 0.68, 0.41 0.02 | 1.26, 0.27 0.04 | 4.03, 0.05 0.11 |
| Defense time (s) | 5.50 ± 0.15 (5.40–5.60) | 5.35 ± 0.13 (5.25–5.46) | 5.77 ± 0.16 (5.67–5.88) | 5.43 ± 0.18 (5.30–5.51) | 10.41, <0.001 *** 0.25 | 25.31, <0.001 *** 0.44 | 4.49, 0.04 * 0.12 |
| Offence time (s) | 5.92 ± 0.29 (5.76–6.07) | 5.76 ± 0.20 (5.60–5.91) | 6.04 ± 0.27 (5.88–6.19) | 5.61 ± 0.11 (5.45–5.76) | 0.03, 0.87 0.00 | 15.37, <0.001 *** 0.32 | 3.17, 0.08 0.09 |
| Jump height (m) | 0.32 ± 0.07 (0.28–0.37) | 0.38 ± 0.07 (0.34–0.42) | 0.29 ± 0.05 (0.24–0.33) | 0.34 ± 0.06 (0.31–0.40) | 2.14, 0.15 0.06 | 7.97, <0.01 ** 0.20 | 0.07, 0.80 0.00 |
| Ball velocity (m/s) | 24.2 ± 1.3 (23.2–25.2) | 24.5 ± 1.3 (23.5–25.5) | 23.4 ± 1.7 (22.4–24.5) | 25.0 ± 1.7 (23.8–25.8) | 0.25, 0.62 0.01 | 2.79, 0.10 0.08 | 1.22, 0.28 0.04 |
| Body mass (kg) | 78 ± 6 (70–82) | 80 ± 7 (72–87) | 72 ± 14 (64–79) | 78 ± 15 (67–82) | 2.21, 0.15 0.06 | 0.47, 0.50 0.01 | 0.04, 0.83 0.00 |
| Body height (m) | 1.82 ± 0.04 (1.79–1.86) | 1.83 ± 0.04 (1.80–1.86) | 1.82 ± 0.06 (1.78–1.85) | 1.82 ± 0.07 (1.78–1.85) | 0.51, 0.48 0.02 | 0.06, 0.81 0.00 | 0.02, 0.89 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herbert, W.; Vanja, R.; Matthias, H. Effectiveness of Specific Professional Training in Male Elite Adolescent Team Handball Players. Sports 2025, 13, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13060193
Herbert W, Vanja R, Matthias H. Effectiveness of Specific Professional Training in Male Elite Adolescent Team Handball Players. Sports. 2025; 13(6):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13060193
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerbert, Wagner, Radic Vanja, and Hinz Matthias. 2025. "Effectiveness of Specific Professional Training in Male Elite Adolescent Team Handball Players" Sports 13, no. 6: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13060193
APA StyleHerbert, W., Vanja, R., & Matthias, H. (2025). Effectiveness of Specific Professional Training in Male Elite Adolescent Team Handball Players. Sports, 13(6), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13060193







