Air Pollution and Its Impact on Health and Performance in Football Players
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search
3. Literature Review
3.1. Mechanisms of Air Pollution Impact on Human Health and Performance
3.2. Impact of Air Pollution on Health and Exercise-Related Traits
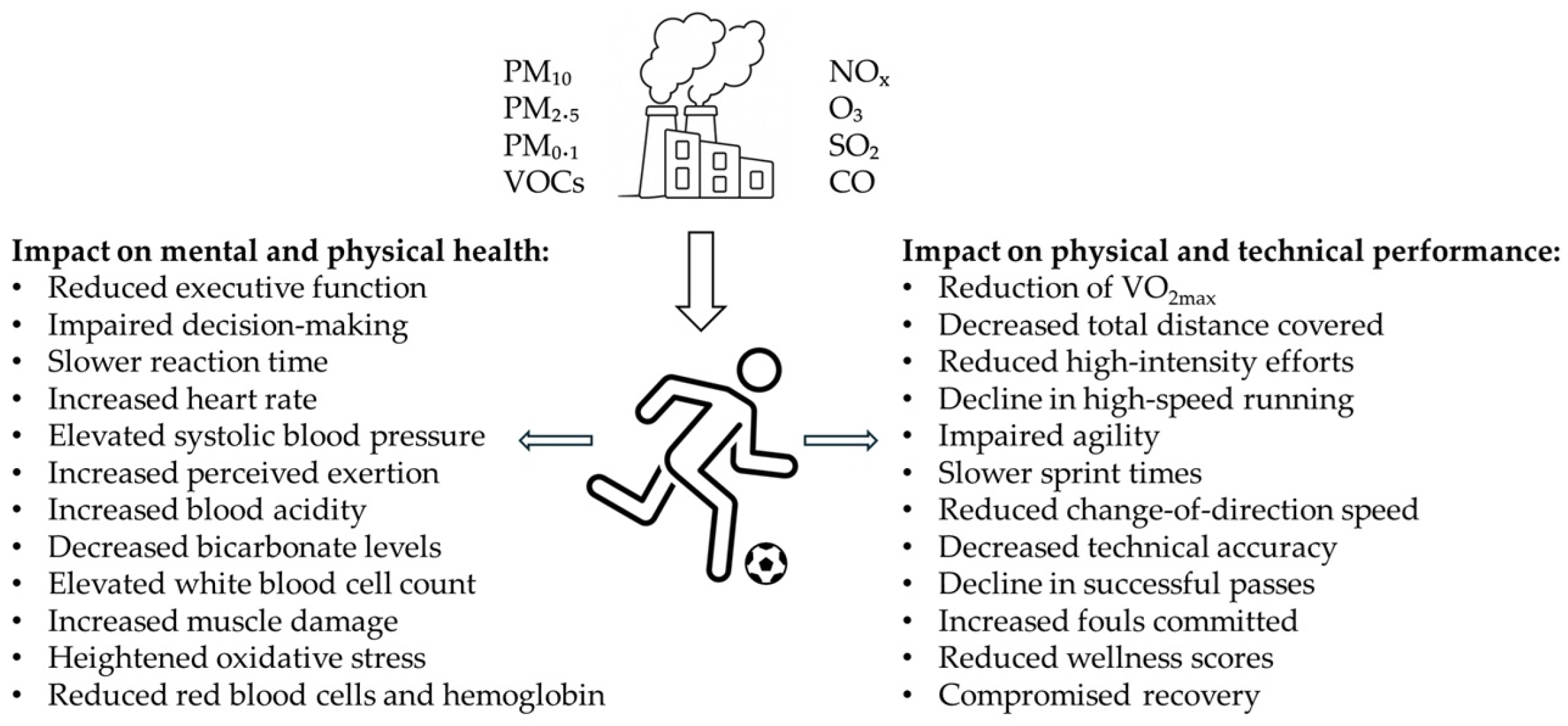
3.3. Air Pollution and Its Impact on Health, Performance, and Recovery in Football Players
3.4. Sex- and Genotype-Dependent Variability in the Health Effects of Air Pollution
3.5. Mitigation Strategies for Football Players in Response to Air Pollution
3.5.1. Temporal and Spatial Avoidance of Pollution Peaks
3.5.2. Monitoring and Forecasting Pollution Levels
3.5.3. Acclimation Protocols and Pre-Exposure Conditioning
3.5.4. Face Masks and Protective Equipment
3.5.5. Antioxidant Supplementation
3.5.6. Indoor Air Quality Management
3.5.7. Policy and Infrastructure Interventions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.R.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Basu, N.N.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; et al. The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. Lancet 2018, 391, 462–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Pope, C.A., 3rd; Brook, J.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Holguin, F.; Hong, Y.; Luepker, R.V.; Mittleman, M.A.; et al. Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: An update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 121, 2331–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraufnagel, D.E.; Balmes, J.R.; Cowl, C.T.; De Matteis, S.; Jung, S.H.; Mortimer, K.; Perez-Padilla, R.; Rice, M.B.; Riojas-Rodriguez, H.; Sood, A.; et al. Air Pollution and Noncommunicable Diseases: A Review by the Forum of International Respiratory Societies’ Environmental Committee, Part 1: The Damaging Effects of Air Pollution. Chest 2019, 155, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, S.; Tang, R.; Qiu, H.; Huang, Q.; Mason, T.G.; Tian, L. Major air pollutants and risk of COPD exacerbations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2016, 11, 3079–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Int Panis, L.; Provost, E.B.; Cox, B.; Louwies, T.; Laeremans, M.; Standaert, A.; Dons, E.; Holmstock, L.; Nawrot, T.; De Boever, P. Short-term air pollution exposure decreases lung function: A repeated measures study in healthy adults. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.; Rice, M.B.; Gold, D.R. Air pollution and lung function in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardt, C.M.; Wu, H. Environmental Exposures and Lung Aging: Molecular Mechanisms and Implications for Improving Respiratory Health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2021, 8, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Atkinson, R.W.; Andersen, Z.J.; Oftedal, B.; Stafoggia, M.; Lim, Y.H.; Bekkevold, T.; Krog, N.H.; Renzi, M.; Zhang, J.; et al. Long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and risk of lung cancer—A comparative analysis of incidence and mortality in four administrative cohorts in the ELAPSE study. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, S.; Al-Kindi, S.G.; Brook, R.D. Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2054–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Liu, X.Y.; Sheng, Y.H.; Li, S.Q.; Zhang, D.; Chen, B.; Yu, P.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, S.; Xu, R.B. Ambient Air Pollution and the Risk of Cancer: Evidence from Global Cohort Studies and Epigenetic-Related Causal Inference. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 489, 137619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrel, J.; Dong, M.; Rosario, M.A.; Cotter, D.L.; Bottenhorn, K.L.; Herting, M.M. A systematic review of air pollution exposure and brain structure and function during development. Environ. Res. 2025, 275, 121368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weuve, J.; Puett, R.C.; Schwartz, J.; Yanosky, J.D.; Laden, F.; Grodstein, F. Exposure to particulate air pollution and cognitive decline in older women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, F.; Forastiere, A.; Michelozzi, P.; Forastiere, F.; Stafoggia, M. Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Incidence of Mental Disorders: A Large Longitudinal Cohort Study of Adults within an Urban Area. Environ. Int. 2023, 181, 108302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkó, M.; Mattsson, M.O. Interactions between Nanosized Materials and the Brain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 4200–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, M.E.; Hale, L.; Johnson, D.A. Physical and Social Environment Relationship with Sleep Health and Disorders. Chest 2020, 157, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.L.; Haskin, O.; Younger, J.W. Association between Chronic Pain and Fatigue Severity with Weather and Air Pollution among Females with Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araneda, O.F.; Kosche-Cárcamo, F.; Verdugo-Marchese, H.; Tuesta, M. Pulmonary Effects Due to Physical Exercise in Polluted Air: Evidence from Studies Conducted on Healthy Humans. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, H.; Salthammer, T.; Morawska, L. Human Exposure to Air Contaminants in Sports Environments. Indoor Air 2020, 30, 1109–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, W. Physical Exercise in the Context of Air Pollution: An Emerging Research Topic. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 784705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bai, L.; Wang, X.; Huo, M.; Gao, W.; Jiang, L.; Jin, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, D. Exposure Assessment of Benzotriazole Ultraviolet Absorbers in Plastic Sports Field Dust and Indoor Dust: Are Plastic Sports Fields High Exposure Scenarios? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 17419–17428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morici, G.; Cibella, F.; Cogo, A.; Palange, P.; Bonsignore, M.R. Respiratory Effects of Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollutants during Exercise. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 575137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, W.E.; Covert, D.S.; Koenig, J.Q.; Namekata, T.; Kim, Y.S. Implications of Air Pollution Effects on Athletic Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1986, 18, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.; Nelson, H.; Koehle, M.S. The Acute Effects of Exercising in Air Pollution: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B.; Tian, H. Effects of Physical Exercise on Cardio-Respiratory Health of Young Adults during Short-Term Exposure to Varying Air Pollution Levels. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavan, A.; Härtel, S.; Spielmann, J.; Koehle, M. Air Pollution, a Worthy Opponent? How Pollution Levels Impair Athlete Performance across Physical, Technical, and Cognitive Domains. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sioutas, C.; Cho, A.; Schmitz, D.; Misra, C.; Sempf, J.; Wang, M.; Oberley, T.; Froines, J.; Nel, A. Ultrafine particulate pollutants induce oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M.T. Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, Z.; Wei, Y. Advances in understanding mechanisms underlying mitochondrial structure and function damage by ozone. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rider, C.F.; Carlsten, C. Air pollution and DNA methylation: Effects of exposure in humans. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averill-Bates, D. Reactive oxygen species and cell signaling. Review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2024, 1871, 119573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, R.G.; Hicks, L.L.; Thompson, D.L. The Effects of Passive Inhalation of Cigarette Smoke on Exercise Performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1985, 54, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, M. Pollution at Schools and Children’s Aerobic Capacity. Health Econ. 2021, 30, 3016–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougault, V.; Carlsten, C.; Adami, P.E.; Sewry, N.; Schobersberger, W.; Soligard, T.; Engebretsen, L.; Budgett, R.; Schwellnus, M.; Fitch, K. Air Quality, Respiratory Health and Performance in Athletes: A Summary of the IOC Consensus Subgroup Narrative Review on ‘Acute Respiratory Illness in Athletes’. Br. J. Sports Med. 2025, 59, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jang, J.; So, B.; Lee, K.; Yeom, D.; Zhang, Z.; Shin, W.S.; Kang, C. Effects of Particulate Matter Inhalation during Exercise on Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Function in Mouse Skeletal Muscle. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayalar, Ö.; Rajabi, H.; Konyalilar, N.; Mortazavi, D.; Aksoy, G.T.; Wang, J.; Bayram, H. Impact of Particulate Air Pollution on Airway Injury and Epithelial Plasticity; Underlying Mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1324552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mölter, A.; Agius, R.M.; de Vocht, F.; Lindley, S.; Gerrard, W.; Lowe, L.; Belgrave, D.; Custovic, A.; Simpson, A. Long-Term Exposure to PM10 and NO2 in Association with Lung Volume and Airway Resistance in the MAAS Birth Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareba, W.; Nomura, A.; Couderc, J.P. Cardiovascular Effects of Air Pollution: What to Measure in ECG? Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109 (Suppl. S4), 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantrakool, S.; Sriwichai, M.; Shaengkhamnang, B.; Leetrakool, N.; Niprapan, P.; Kawichai, S.; Wannakul, S.; Panyasit, N.; Tuntivate, P.; Wongtagan, O.; et al. The Effects of Ambient Particulate Matter Air Pollution on Platelets and Hemostasis. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1410406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, J.M. Anthropogenic Emissions of Carbon Monoxide. Rev. Environ. Health 2000, 15, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panni, T.; Mehta, A.J.; Schwartz, J.D.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Just, A.C.; Wolf, K.; Wahl, S.; Cyrys, J.; Kunze, S.; Strauch, K.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of DNA Methylation and Fine Particulate Matter Air Pollution in Three Study Populations: KORA F3, KORA F4, and the Normative Aging Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plusquin, M.; Guida, F.; Polidoro, S.; Vermeulen, R.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Campanella, G.; Hoek, G.; Kyrtopoulos, S.A.; Georgiadis, P.; Naccarati, A.; et al. DNA methylation and exposure to ambient air pollution in two prospective cohorts. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Karlsson, O.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Lin, X.; Zemplenyi, M.; Sanchez-Guerra, M.; Trevisi, L.; Urch, B.; et al. B vitamins attenuate the epigenetic effects of ambient fine particles in a pilot human intervention trial. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3503–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, J.W.; Savarimuthu Francis, S.; Fong, K.M.; Yang, I.A. Genomics and the Respiratory Effects of Air Pollution Exposure. Respirology 2012, 17, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Rundblad, A.; Marques, I.F.; Soares, A.G.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Vrijheid, M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Verlouw, J.; Matthews, J.; Holven, K.B.; et al. Air Pollution Exposure Is Associated with Gene Expression in Children. Environ. Epigenet. 2024, 10, dvae025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Moreno-Vinasco, L.; Huang, Y.; Lang, G.D.; Linares, J.D.; Goonewardena, S.N.; Grabavoy, A.; Samet, J.M.; Geyh, A.S.; Breysse, P.N.; et al. Murine Lung Responses to Ambient Particulate Matter: Genomic Analysis and Influence on Airway Hyperresponsiveness. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, N.; Lei, R.; Deng, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Li, H.; Luo, P. Large-Scale Genome-Wide Association Studies Reveal the Genetic Causal Etiology between Air Pollutants and Autoimmune Diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, T.; Si, X.; Liang, J.; Yan, X.; Zhang, J.; Pang, B.; Luo, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; et al. Multi-Omic Characterization of Air Pollution Effects: Applications of AirSigOmniTWP Hub. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 284, 116939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookherjee, N.; Ryu, M.H.; Hemshekhar, M.; Orach, J.; Spicer, V.; Carlsten, C. Defining the Effects of Traffic-Related Air Pollution on the Human Plasma Proteome Using an Aptamer Proteomic Array: A Dose-Dependent Increase in Atherosclerosis-Related Proteins. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, A.S.; Zhang, K.; Murthy, V.L.; Choi, B.; Zhao, S.; Gajjar, P.; Colangelo, L.A.; Hou, L.; Rice, M.B.; Carr, J.J.; et al. Proteomics, Human Environmental Exposure, and Cardiometabolic Risk. Circ. Res. 2024, 135, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Qi, X.; Yang, X.; Cheng, B.; Cheng, S.; Liu, L.; Meng, P.; He, D.; Wei, W.; Hui, J.; et al. Large-Scale Plasma Proteomics Uncovers Novel Targets Linking Ambient Air Pollution and Depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cai, J.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Z.; Ying, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Hao, K.; Kinney, P.L.; Chen, H.; et al. Particulate Matter Exposure and Stress Hormone Levels: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Trial of Air Purification. Circulation 2017, 136, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Tang, Z.; Diver, W.R.; Sarnat, J.A.; Chow, S.S.; Cheng, H.; Deubler, E.L.; Tan, Y.; Eick, S.M.; Jerrett, M.; et al. Metabolomics Signatures of Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution: A Large-Scale Metabolome-Wide Association Study in the Cancer Prevention Study-II Nutrition Cohort. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, B.; Ran, S.; Qian, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Tabet, M.; Howard, S.W.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, F.; Lin, H. Air Pollution Metabolomic Signatures and Chronic Respiratory Diseases Risk: A Longitudinal Study. Chest 2024, 166, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellano, P.; Reynoso, J.; Quaranta, N.; Bardach, A.; Ciapponi, A. Short-Term Exposure to Particulate Matter (PM10 and PM2.5), Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2), and Ozone (O3) and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bont, J.; Jaganathan, S.; Dahlquist, M.; Persson, Å.; Stafoggia, M.; Ljungman, P. Ambient Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Diseases: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 779–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Foley, C.N.; Zuber, V. Inferring Causal Relationships Between Risk Factors and Outcomes from Genome-Wide Association Study Data. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2018, 19, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmetov, I.I.; John, G.; Semenova, E.A.; Hall, E.C.R. Genomic predictors of physical activity and athletic performance. Adv. Genet. 2024, 111, 311–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Small, D.S.; Thompson, S.G. A Review of Instrumental Variable Estimators for Mendelian Randomization. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2017, 26, 2333–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ou, X.; Ou, Q.; Pan, D. Air Pollution and Risk of Sarcopenia: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomized Study. Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Pei, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, C.; Hua, J.; He, B. Impact of Particulate-Matter Air Pollution on 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels: A Mendelian Randomisation Study. Public Health 2024, 230, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, S.; Jiang, N.; Xu, F.; Liu, H.; Jia, X. Causal Effects of Air Pollutants on Lung Function and Chronic Respiratory Diseases: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1438974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Qu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Luo, F.; Mou, S. Association between Air Pollution and Bone Mineral Density: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Arch. Med. Sci. 2024, 20, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Yan, Y.; Xiong, J.; Mi, J. Integrative Genetic Analysis to Decode the Causal Effect of Air Pollution on Accelerated Aging. QJM 2025, hcaf093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Si, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, F.; Lu, X.; Li, X.; Sun, D.; Wang, Z. The Relationship between PM2.5 and Eight Common Lung Diseases: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Toxics 2024, 12, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.X.; Peng, Z.X.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Ni, H.G. Big Picture Thinking of Global PM2.5-Related COPD: Spatiotemporal Trend, Driving Force, Minimal Burden and Economic Loss. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gan, Q.; Su, X.; Zhang, S.; Ding, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, N.; Wu, K. Genetic Evidence for the Causal Effects of Air Pollution on the Risk of Respiratory Diseases. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 290, 117602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Tong, T.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Ni, K. Causal Relationship between Air Pollution and Infections: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1409640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Causal Effects of Noise and Air Pollution on Multiple Diseases Highlight the Dual Role of Inflammatory Factors in Ambient Exposures. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.Q.; Han, X.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhao, N.; Ma, J. A Causal Relationship between Particulate Matter 2.5 and Obesity and Its Related Indicators: A Mendelian Randomization Study of European Ancestry. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1366838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W. Causal Relationship between Air Pollution, Lung Function, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Univariate and Multivariate Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1368483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Hu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, L.; He, T. Genetic Evidence Supports the Causal Effects of Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution on Autoimmune Eye Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.; Liu, F.; Deng, T.; Jia, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, F.; Gong, M.; Li, Y.; Yin, Y. Association between Air Pollution and Osteoporosis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Medicine 2025, 104, e41490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mu, A.; Jing, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cao, X.; Guo, J.; Xi, Y.; Guo, Q. Cross Ethnic Mendelian Randomization Analysis Reveals Causal Relationship between Air Pollution and Risk of Kidney Stones. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, G. Mendelian Randomization Study Supports the Causal Effects of Air Pollution on Longevity via Multiple Age-Related Diseases. NPJ Aging 2023, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Peng, Z.; Li, Z.; Qi, Z.; Wu, Q.; Ding, B. A Novel Concern from Two Sample Mendelian Randomization Study: The Effects of Air Pollution Exposure on the Cardiovascular, Respiratory, and Nervous System. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 284, 116871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Li, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Hu, X. Causal Associations of Environmental Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Glob. Heart 2024, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Li, J.; Dou, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Ma, X. Linking Ambient Air Pollution to Mental Health: Evidence Based on the Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Study. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; He, G.; Sun, S.; Feng, Y.; Huang, Y. Causal Associations of Ambient Particulate Matter 10 and Alzheimer’s Disease: Result from a Two-Sample Multivariable Mendelian Randomization Study. Arch. Med. Sci. 2024, 20, 1604–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, Z.; Ling, Y.; Teng, W.; Cui, J.; Yan, Z.; Hou, X.; Cen, W.; Long, N.; Li, W.; et al. Causal Effect of Air Pollution on the Risk of Brain Health and Potential Mediation by Gut Microbiota. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Li, Q.Y.; Shi, A.Y.; Li, J.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, X. Association of Air Pollutants with Psychiatric Disorders: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X. Role of Air Pollution Exposure in the Alteration of Brain Cortical Structure: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 297, 118221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wen, J.; Wu, W.; Dai, Z.; Liang, X.; Zhang, N.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, H. Causal Relationship and Shared Genes between Air Pollutants and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Large-Scale Genetic Analysis. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, P.; Guo, X.; Qu, Q.; Li, R. Exploring the Association between Air Pollution and Parkinson’s Disease or Alzheimer’s Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 123939–123947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; Xie, J.; Fu, X. Causal Relationships between Air Pollutants and Upper Respiratory Tract Infections: A Two-Sample, Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yu, K. Air Pollution and Oral Health: An Overall Insight from Genetic Causality. Int. Dent. J. 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Wu, Y. Causal Relationships between Air Pollution and Common Autoimmune Diseases: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tong, K.; Deng, J.; Wu, J.; Guo, C. Causal Effects of Various Particulate Matter on Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Its Subtypes: Insights from Mendelian Randomization. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2025, 69, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Z. Mendelian Randomization Analysis of Environmental Pollution Factors and Head and Neck Cancer Risk: A Causal Inference Study Integrating Autophagy-Related Genes. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Wang, J.; Hou, W. Air Pollution and Breast Cancer Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; An, Y.; Han, H.; Chen, R.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. The Association between Ambient Air Pollution and Colorectal Cancer: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2025, 35, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, W. Causal Effects of Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution on Cancer Risk: Insights from Genetic Evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, L.V.; Koehle, M.S. The Health Effects of Exercising in Air Pollution. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussetta, N.; Abedelmalek, S.; Aloui, K.; Souissi, N. The Effect of Air Pollution on Diurnal Variation of Performance in Anaerobic Tests, Cardiovascular and Hematological Parameters, and Blood Gases on Soccer Players Following the Yo-Yo Intermittent Recovery Test Level-1. Chronobiol. Int. 2017, 34, 903–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussetta, N.; Abedelmalek, S.; Khouloud, A.; Ben Anes, A.; Souissi, N. Does Red Orange Juice Supplementation Have a Protective Effect on Performance, Cardiovascular Parameters, Muscle Damage and Oxidative Stress Markers Following the Yo-Yo Intermittent Recovery Test Level-1 under Polluted Air? Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2020, 30, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharko, M.; Cichowicz, R.; Andrzejewski, M.; Chmura, P.; Kowalczuk, E.; Chmura, J.; Konefał, M. Air Pollutants Reduce the Physical Activity of Professional Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharko, M.; Cichowicz, R.; Depta, A.; Chmura, P.; Konefał, M. High Levels of PM10 Reduce the Physical Activity of Professional Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavan, A.; Härtel, S.; Spielmann, J.; Koehle, M. Air Pollution and Elite Adolescent Soccer Players’ Performance and Well-Being: An Observational Study. Environ. Int. 2023, 175, 107943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundell, K.W.; Caviston, R.; Hollenbach, A.M.; Murphy, K. Vehicular Air Pollution, Playgrounds, and Youth Athletic Fields. Inhal. Toxicol. 2006, 18, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wei, X.; Huang, X.; He, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Lin, T.; Shi, X.; Liu, Z.; Freeman, R.B. The Impact of Transient Air Pollution Exposure on Worker Performance in Chinese Soccer Players. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clougherty, J.E. A growing role for gender analysis in air pollution epidemiology. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward-Caviness, C.K. A Review of Gene-by-Air Pollution Interactions for Cardiovascular Disease, Risk Factors, and Biomarkers. Hum. Genet. 2019, 138, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunginger, J.W.; Reed, C.E.; O’Connell, E.J.; Melton, L.J., 3rd; O’Fallon, W.M.; Silverstein, M.D. A Community-Based Study of the Epidemiology of Asthma: Incidence Rates, 1964–1983. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1992, 146, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, H.; Heiss, G.; Rose, K.M.; Whitsel, E.; Lurmann, F.; London, S.J. Traffic Exposure and Lung Function in Adults: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Thorax 2007, 62, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.; Zeka, A.; Schwartz, J. Association between PM2.5 and All-Cause and Specific-Cause Mortality in 27 US Communities. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2007, 17, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, U.; Cyrys, J.; Sedlmeir, G.; Brunekreef, B.; Bellander, T.; Fischer, P.; Bauer, C.P.; Reinhardt, D.; Wichmann, H.E.; Heinrich, J. Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Respiratory Health during the First 2 Years of Life. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 19, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocks, J.; Henschen, M.; Hoo, A.F.; Costeloe, K.; Dezateux, C. Influence of Ethnicity and Gender on Airway Function in Preterm Infants. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oftedal, B.; Brunekreef, B.; Nystad, W.; Madsen, C.; Walker, S.E.; Nafstad, P. Residential Outdoor Air Pollution and Lung Function in Schoolchildren. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenlund, M.; Forastiere, F.; Porta, D.; De Sario, M.; Badaloni, C.; Perucci, C.A. Traffic-Related Air Pollution in Relation to Respiratory Symptoms, Allergic Sensitisation and Lung Function in Schoolchildren. Thorax 2009, 64, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.C.R.; John, G.; Ahmetov, I.I. Testing in Football: A Narrative Review. Sports 2024, 12, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, G.; AlNadwi, A.; Georges Abi Antoun, T.; Ahmetov, I.I. Injury Prevention Strategies in Female Football Players: Addressing Sex-Specific Risks. Sports 2025, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Tian, G.; Zhu, J.; Yang, F.; Zhang, R.; Li, H.; An, Z.; Li, J.; Song, J.; Jiang, J.; et al. Air Pollution Associated Acute Respiratory Inflammation and Modification by GSTM1 and GSTT1 Gene Polymorphisms: A Panel Study of Healthy Undergraduates. Environ. Health 2023, 22, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschard, H.; Lutz, S.; Maus, B.; Duell, E.J.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Chatterjee, N.; Kraft, P.; Van Steen, K. Challenges and Opportunities in Genome-Wide Environmental Interaction (GWEI) Studies. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 1591–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imboden, M.; Kumar, A.; Curjuric, I.; Adam, M.; Thun, G.A.; Haun, M.; Tsai, M.Y.; Pons, M.; Bettschart, R.; Turk, A.; et al. Modification of the Association between PM10 and Lung Function Decline by Cadherin 13 Polymorphisms in the SAPALDIA Cohort: A Genome-Wide Interaction Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulou, I.; Tsintzas, O.K.; Daganou, M.; Cokkinos, D.V.; Tzelepis, G.E. Contribution of Lung Function to Exercise Capacity in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Respiration 1999, 66, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Seo, Y.S.; Sung, J.; Chae, J.; Yun, J.M.; Kwon, H.; Cho, B.; Kim, J.I.; Park, J.H. A Genome-Wide by PM10 Interaction Study Identifies Novel Loci for Lung Function Near BICD1 and IL1RN-IL1F10 Genes in Korean Adults. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paco, A.; Catapano, G.A.; Vagheggini, G.; Mazzoleni, S.; Micheli, M.L.; Ambrosino, N. Ventilatory Response to Exercise of Elite Soccer Players. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2014, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Son, H.Y.; Park, P.; Yun, J.M.; Kwon, H.; Cho, B.; Kim, J.I.; Park, J.H. A Genome-Wide by PM10 Exposure Interaction Study for Blood Pressure in Korean Adults. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierodiakonou, D.; Coull, B.A.; Zanobetti, A.; Postma, D.S.; Boezen, H.M.; Vonk, J.M.; McKone, E.F.; Schildcrout, J.S.; Koppelman, G.H.; Croteau-Chonka, D.C.; et al. Pathway Analysis of a Genome-Wide Gene by Air Pollution Interaction Study in Asthmatic Children. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babb, T.G.; Long, K.A.; Rodarte, J.R. The relationship between maximal expiratory flow and increases of maximal exercise capacity with exercise training. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melbourne, C.A.; Erzurumluoglu, A.M.; Shrine, N.; Chen, J.; Tobin, M.D.; Hansell, A.L.; Wain, L.V. Genome-Wide Gene-Air Pollution Interaction Analysis of Lung Function in 300,000 Individuals. Environ. Int. 2022, 159, 107041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Fan, M.; Qin, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; et al. KCNQ1 rs2237892 Polymorphism Modifies the Association Between Short-Term Ambient Particulate Matter Exposure and Fasting Blood Glucose: A Family-Based Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, P.; Pan, C.; Qin, X.; Cai, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, W.; Cheng, S.; Yang, X.; Cheng, B.; Liu, L.; et al. A Genome-Wide Gene-Environmental Interaction Study Identified Novel Loci for the Relationship Between Ambient Air Pollution Exposure and Depression, Anxiety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, F.; Tang, L.; Khalid, S.; Tian, Y.; Xie, J. Independent and Combined Effects of Long-Term Air Pollution Exposure and Genetic Predisposition on COVID-19 Severity: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2421513122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska-Skrendo, A.; Sawczuk, M.; Cięszczyk, P.; Ahmetov, I.I. Genes and power athlete status. In Sports, Exercise, and Nutritional Genomics: Current Status and Future Directions; Barh, D., Ahmetov, I., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 41–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtagh, C.F.; Brownlee, T.E.; Rienzi, E.; Roquero, S.; Moreno, S.; Huertas, G.; Lugioratto, G.; Baumert, P.; Turner, D.C.; Lee, D.; et al. The genetic profile of elite youth soccer players and its association with power and speed depends on maturity status. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Fuku, N.; Miyamoto-Mikami, E.; Tanaka, M.; Miyachi, M.; Murakami, H.; Mitchell, B.; Morrison, E.; Ahmetov, I.I.; Sportgene Research Group; et al. Multi-Phase, Multi-Ethnic GWAS Uncovers Putative Loci in Predisposition to Elite Sprint and Power Performance, Health and Disease. Biol. Sport 2025, 42, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbasov, R.T.; Arkhipova, A.A.; Borisova, A.V.; Hakimullina, A.M.; Kuznetsova, A.V.; Williams, A.G.; Day, S.H.; Ahmetov, I.I. The HIF1A Gene Pro582Ser Polymorphism in Russian Strength Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 2055–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreland, E.; Borisov, O.V.; Semenova, E.A.; Larin, A.K.; Andryushchenko, O.N.; Andryushchenko, L.B.; Generozov, E.V.; Williams, A.G.; Ahmetov, I.I. Polygenic Profile of Elite Strength Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2022, 36, 2509–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmetov, I.I.; Astranenkova, I.V.; Rogozkin, V.A. Association of PPARD gene polymorphism with human physical performance. Mol. Biol. 2007, 41, 852–857. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmetov, I.I.; Hakimullina, A.M.; Popov, D.V.; Lyubaeva, E.V.; Missina, S.S.; Vinogradova, O.L.; Williams, A.G.; Rogozkin, V.A. Association of the VEGFR2 gene His472Gln polymorphism with endurance-related phenotypes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, E.A.; Miyamoto-Mikami, E.; Akimov, E.B.; Al-Khelaifi, F.; Murakami, H.; Zempo, H.; Kostryukova, E.S.; Kulemin, N.A.; Larin, A.K.; Borisov, O.V.; et al. The association of HFE gene H63D polymorphism with endurance athlete status and aerobic capacity: Novel findings and a meta-analysis. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, J.P.L.F.; Bosnyák, E.; Semenova, E.A.; Szmodis, M.; Griff, A.; Móra, Á.; Almási, G.; Trájer, E.; Udvardy, A.; Kostryukova, E.S.; et al. The MCT1 gene Glu490Asp polymorphism (rs1049434) is associated with endurance athlete status, lower blood lactate accumulation and higher maximum oxygen uptake. Biol. Sport 2021, 38, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulygina, E.A.; Borisov, O.V.; Valeeva, E.V.; Semenova, E.A.; Kostryukova, E.S.; Kulemin, N.A.; Larin, A.K.; Nabiullina, R.M.; Mavliev, F.A.; Akhatov, A.M.; et al. Whole genome sequencing of elite athletes. Biol. Sport 2020, 37, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, A.B.; Hughes, D.C.; Tsaprouni, L.G.; Varley, I.; Suraci, B.; Baker, J.; Herbert, A.J.; Kelly, A.L. Genetic Associations with Technical Capabilities in English Academy Football Players: A Preliminary Study. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2023, 63, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmetov, I.I.; Donnikov, A.E.; Trofimov, D.Y. Actn3 genotype is associated with testosterone levels of athletes. Biol. Sport 2014, 31, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, J.P.L.; Semenova, E.A.; Borisov, O.V.; Larin, A.K.; Moreland, E.; Generozov, E.V.; Ahmetov, I.I. Genomic predictors of testosterone levels are associated with muscle fiber size and strength. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 122, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.F.; Liu, Y.Z.; Yang, X.L.; Zhang, H.; Feng, G.J.; Wei, X.T.; Zhang, L. The genetic architecture of appendicular lean mass characterized by association analysis in the UK Biobank study. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, E.A.; Pranckevičienė, E.; Bondareva, E.A.; Gabdrakhmanova, L.J.; Ahmetov, I.I. Identification and Characterization of Genomic Predictors of Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity Using UK Biobank Data. Nutrients 2023, 15, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.C.R.; Baumert, P.; Larruskain, J.; Gil, S.M.; Lekue, J.A.; Rienzi, E.; Moreno, S.; Tannure, M.; Murtagh, C.F.; Ade, J.D.; et al. The genetic association with injury risk in male academy soccer players depends on maturity status. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2022, 32, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtagh, C.F.; Hall, E.C.R.; Brownlee, T.E.; Drust, B.; Williams, A.G.; Erskine, R.M. The Genetic Association with Athlete Status, Physical Performance, and Injury Risk in Soccer. Int. J. Sports Med. 2023, 44, 941–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.; Koch, S.; Bougault, V.; Gee, C.M.; Bertuzzi, R.; Elmore, M.; McCluskey, P.; Hidalgo, L.; Garcia-Aymerich, J.; Koehle, M.S. Personal Strategies to Mitigate the Effects of Air Pollution Exposure during Sport and Exercise: A Narrative Review and Position Statement by the Canadian Academy of Sport and Exercise Medicine and the Canadian Society for Exercise Physiology. Br. J. Sports Med. 2023, 57, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.P.; Tharp, P.A.; Kiley, K.; Koehle, M.S. Air Pollution and Its Effects on Sports and Exercise: A Narrative Review of Impacts and Mitigation Strategies. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2025, 24, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reche, C.; Viana, M.; van Drooge, B.L.; Fernández, F.J.; Escribano, M.; Castaño-Vinyals, G.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Adami, P.E.; Bermon, S. Athletes’ Exposure to Air Pollution during World Athletics Relays: A Pilot Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Lee, J.; Hong, A. Does Urban Greenway Design Affect Air Pollution Exposure? A Case Study of Seoul, South Korea. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 103038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Karatzas, K.; Arvanitis, A.; Reche, C.; Escribano, M.; Ibarrola-Ulzurrun, E.; Adami, P.E.; Garrandes, F.; Bermon, S. Air Quality Sensors Systems as Tools to Support Guidance in Athletics Stadia for Elite and Recreational Athletes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, J.T. Ambient Air Pollution and Human Performance: Contemporaneous and Acclimatization Effects of Ozone Exposure on Athletic Performance. Health Econ. 2018, 27, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, L.V.; Carlsten, C.; Koehle, M.S. The Effect of Pre-Exercise Diesel Exhaust Exposure on Cycling Performance and Cardio-Respiratory Variables. Inhal. Toxicol. 2012, 24, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, N.; Ryu, M.H.; Dhillon, S.; Schaeffer, M.R.; Ramsook, A.H.; Leung, J.M.; Ryerson, C.J.; Carlsten, C.; Guenette, J.A.; Canadian Respiratory Research Network. Effects of Traffic-Related Air Pollution on Exercise Endurance, Dyspnea, and Cardiorespiratory Responses in Health and COPD: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial. Chest 2022, 161, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laeremans, M.; Dons, E.; Avila-Palencia, I.; Carrasco-Turigas, G.; Orjuela-Mendoza, J.P.; Anaya-Boig, E.; Cole-Hunter, T.; de Nazelle, A.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Standaert, A.; et al. Black Carbon Reduces the Beneficial Effect of Physical Activity on Lung Function. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grievink, L.; Jansen, S.M.; van’t Veer, P.; Brunekreef, B. Acute Effects of Ozone on Pulmonary Function of Cyclists Receiving Antioxidant Supplements. Occup. Environ. Med. 1998, 55, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grievink, L.; Zijlstra, A.G.; Ke, X.; Brunekreef, B. Double-Blind Intervention Trial on Modulation of Ozone Effects on Pulmonary Function by Antioxidant Supplements. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 149, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Cai, W.; Luo, C.; Zhang, F. The Impact of Renovation on the Air Quality in the Stadium, and Prevention of Indoor Air Pollution. Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ge, X.; Sonya, C.; Ye, J.; Lei, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Q. Influence of Regional Emission Controls on the Chemical Composition, Sources, and Size Distributions of Submicron Aerosols: Insights from the 2014 Nanjing Youth Olympic Games. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Andrea, C.; Shi, J.; Chen, C.; Teng, Y.; Zeng, L. Evaluating Air Pollution Exposure among Cyclists: Real-Time Levels of PM2.5 and NO2 and POI Impact. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 173559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langrish, J.P.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Lee, M.M.; Barnes, G.D.; Miller, M.R.; Cassee, F.R.; Boon, N.A.; Donaldson, K.; Li, J.; et al. Reducing Personal Exposure to Particulate Air Pollution Improves Cardiovascular Health in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, H.; Frankland, T.B.; Chen, C.; Tartof, S.Y.; Mayeda, E.R.; Lee, G.S.; Northrop, A.J.; Torres, J.M.; Benmarhnia, T.; Casey, J.A. Wildfire Smoke Exposure and Incident Dementia. JAMA Neurol. 2025, 82, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mechanism | Biological Processes | Physiological Effects | Impact on Performance | Key Air Pollutants |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulmonary irritation [35] | Activation of airway sensory nerves (e.g., C-fibers); release of neuropeptides (substance P, CGRP); recruitment of immune cells | Airway inflammation; epithelial damage; mucus production; local edema | Coughing; chest tightness; elevated perceived exertion (RPE) | O3, SO2, NO2, PM2.5, PM10, formaldehyde, acrolein |
| Airway resistance [36] | Bronchoconstriction (via vagal reflexes); edema; mucus hypersecretion; particulate obstruction in small airways | Increased airway resistance; reduced airflow; impaired gas exchange | Dyspnea; lower ventilation efficiency; early fatigue | SO2, O3, NO2, PM2.5, PM10, formaldehyde, toluene |
| Systemic inflammation [24] | Spillover of cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α); circulating acute-phase proteins (e.g., CRP); endothelial dysfunction | Vascular inflammation; reduced NO-mediated vasodilation; arterial stiffness | Reduced oxygen delivery; decreased cardiovascular efficiency | PM2.5, NO2, O3, benzene, formaldehyde |
| Autonomic nervous system imbalance [37] | Altered heart rate variability; increased sympathetic tone; decreased vagal activity | Elevated heart rate; vasoconstriction; increased cardiac workload | Elevated RPE; risk of arrhythmias; reduced exercise capacity | PM2.5, O3, CO, NO2, benzene |
| Oxidative stress [26] | Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production; oxidative damage to membranes, proteins, and DNA; mitochondrial dysfunction | Inflammation and tissue injury; reduced metabolic efficiency | Increased muscle fatigue; impaired recovery | O3, PM2.5, NO2, SO2, acrolein, benzene |
| Blood coagulation changes [38] | Platelet activation; increased fibrinogen; vascular endothelial activation | Hypercoagulability; impaired microcirculation | Reduced muscle perfusion; risk of thrombotic events | PM2.5, NO2, O3, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| Reduced oxygen transport [39] | CO binds hemoglobin (COHb formation); decreased oxygen-binding capacity; hypoxemia | Reduced arterial oxygen content; lower VO2 delivery | Decreased VO2max; impaired endurance | CO |
| Pollutants | Affected Traits | References |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | Reduced appendicular lean mass, slow walking pace, and decreased hand grip strength | [59] |
| PM10, PM2.5–10, PM2.5 | Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) levels | [60] |
| PM2.5, PM10, NO2 | Reduced forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) and reduced forced vital capacity (FVC) | [61] |
| PM2.5, PM10, NOx | Decreased bone mineral density | [62] |
| PM2.5 | Frailty | [63] |
| PM2.5 | Asthma | [64] |
| PM2.5 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [65] |
| PM10 | Pneumonia and bronchiectasis | [66] |
| PM2.5, PM2.5–10, NOx | COVID-19 and bacterial pneumonia | [67] |
| PM10, PM2.5–10 | Type 2 diabetes | [68] |
| PM2.5 | Obesity, increased visceral adipose tissue volume, and increased abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue volume | [69] |
| PM2.5 | Gastroesophageal reflux disease | [70] |
| NO2 | Hypothyroidism | [46] |
| NO2, NOx, PM2.5 | Diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration | [71] |
| PM2.5, NOx | Osteoporosis | [72] |
| PM2.5 | Kidney stones | [73] |
| PM2.5 | Hypercholesterolemia | [74] |
| PM10, NO2 | Myocardial infarction and chronic heart failure | [68] |
| NOx | Stroke | [75] |
| PM10 | Hypertension and atrial fibrillation | [76] |
| PM2.5 | Heart failure | [76] |
| NO2, NOx, PM2.5 | Anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder | [77] |
| PM10 | Alzheimer’s disease | [78] |
| PM10 | Post-traumatic stress disorder and multiple sclerosis | [79] |
| NO2, NOx, PM2.5 | Major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and autism spectrum disorder | [80] |
| PM2.5, NO2 | Reduction in cortical surface area | [81] |
| NOx, PM2.5 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | [82] |
| NO2 | Parkinson’s disease | [83] |
| PM10 | Acute pharyngitis | [84] |
| NO2 | Chronic rhinitis, chronic nasopharyngitis, and chronic pharyngitis | [84] |
| PM2.5, PM2.5–10, NO2 | Oral leukoplakia, gingivitis, periodontitis, pulp diseases, periapical diseases, oral cavity diseases, salivary gland diseases, and jaw diseases | [85] |
| NOx | Rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren’s syndrome, and systemic lupus erythematosus | [86] |
| PM10 | Psoriasis | [86] |
| PM2.5 | Ulcerative colitis | [87] |
| NO2, NOx, PM2.5 | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | [88] |
| PM10, NOx | Breast cancer | [89] |
| NO2 | Colorectal cancer | [90] |
| NO2 | Endometrial cancer and ovarian cancer | [91] |
| Strategy | Description | Key Benefits | Limitations/Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal and spatial avoidance [142,144] | Schedule training in early morning when pollutant levels (e.g., TRAP, O3) are low; train in greenways or areas distant from traffic. | Reduces exposure to NO2, PM, and O3; leverages natural filtration in vegetated areas. | Requires access to pollution data and suitable training locations; may not be feasible in urban settings. |
| Monitoring and forecasting [145] | Use Air Quality Index (AQI) systems, stadium sensors, or wearable devices (e.g., silicone wristbands) to track pollutant exposure. | Enables personalized exposure management; identifies optimal training times and locations. | Fixed-site monitors may lack precision; wearable tech adoption is limited. |
| Acclimation protocols [146] | Repeated low-level O3 exposure may reduce performance decrements via cardiorespiratory adaptations. | Potential to mitigate O3-related performance losses. | Safety concerns; limited evidence for other pollutants (e.g., PM, NO2); not widely recommended. |
| Face masks [155] | Use high-filtration masks (e.g., N95, FFP2) during low-intensity activities, warm-ups, or travel. | Reduces inhaled pollutant load in non-competitive settings. | Uncomfortable during high-intensity exercise; limited evidence for efficacy in sports. |
| Antioxidant supplementation [94,150,151] | Supplement with vitamins C, E, or red orange juice to counter oxidative stress from pollutants. | May improve lung function and reduce oxidative stress/muscle damage. | Mixed results; requires medical guidance; pollutant-specific benefits unclear. |
| Indoor air quality (IAQ) management [152] | Monitor and improve IAQ in training facilities using filtration systems. | Protects athletes in indoor arenas; mitigates ambient pollutant infiltration. | Indoor pollutant levels often mirror outdoor conditions; requires infrastructure investment. |
| Policy and infrastructure interventions [153] | Implement emission controls and integrate air quality into sports facility design. | Long-term regional emission reductions improve air quality; enhances urban planning. | Short-term controls often ineffective due to meteorological factors; requires policy coordination. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
John, G.; Semenova, E.A.; Mohamed, D.A.; Georges Abi Antoun, T.; Yusupov, R.A.; Ahmetov, I.I. Air Pollution and Its Impact on Health and Performance in Football Players. Sports 2025, 13, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13060170
John G, Semenova EA, Mohamed DA, Georges Abi Antoun T, Yusupov RA, Ahmetov II. Air Pollution and Its Impact on Health and Performance in Football Players. Sports. 2025; 13(6):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13060170
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohn, George, Ekaterina A. Semenova, Dana Amr Mohamed, Tiffany Georges Abi Antoun, Rinat A. Yusupov, and Ildus I. Ahmetov. 2025. "Air Pollution and Its Impact on Health and Performance in Football Players" Sports 13, no. 6: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13060170
APA StyleJohn, G., Semenova, E. A., Mohamed, D. A., Georges Abi Antoun, T., Yusupov, R. A., & Ahmetov, I. I. (2025). Air Pollution and Its Impact on Health and Performance in Football Players. Sports, 13(6), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13060170








