Injury and Illness Surveillance in Para-Cycling: A Single-Centre One-Season Prospective Longitudinal Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Conduct prospective surveillance of all self-reported and medical attention injuries and illnesses among professional Para cyclists using the OSTRC framework.
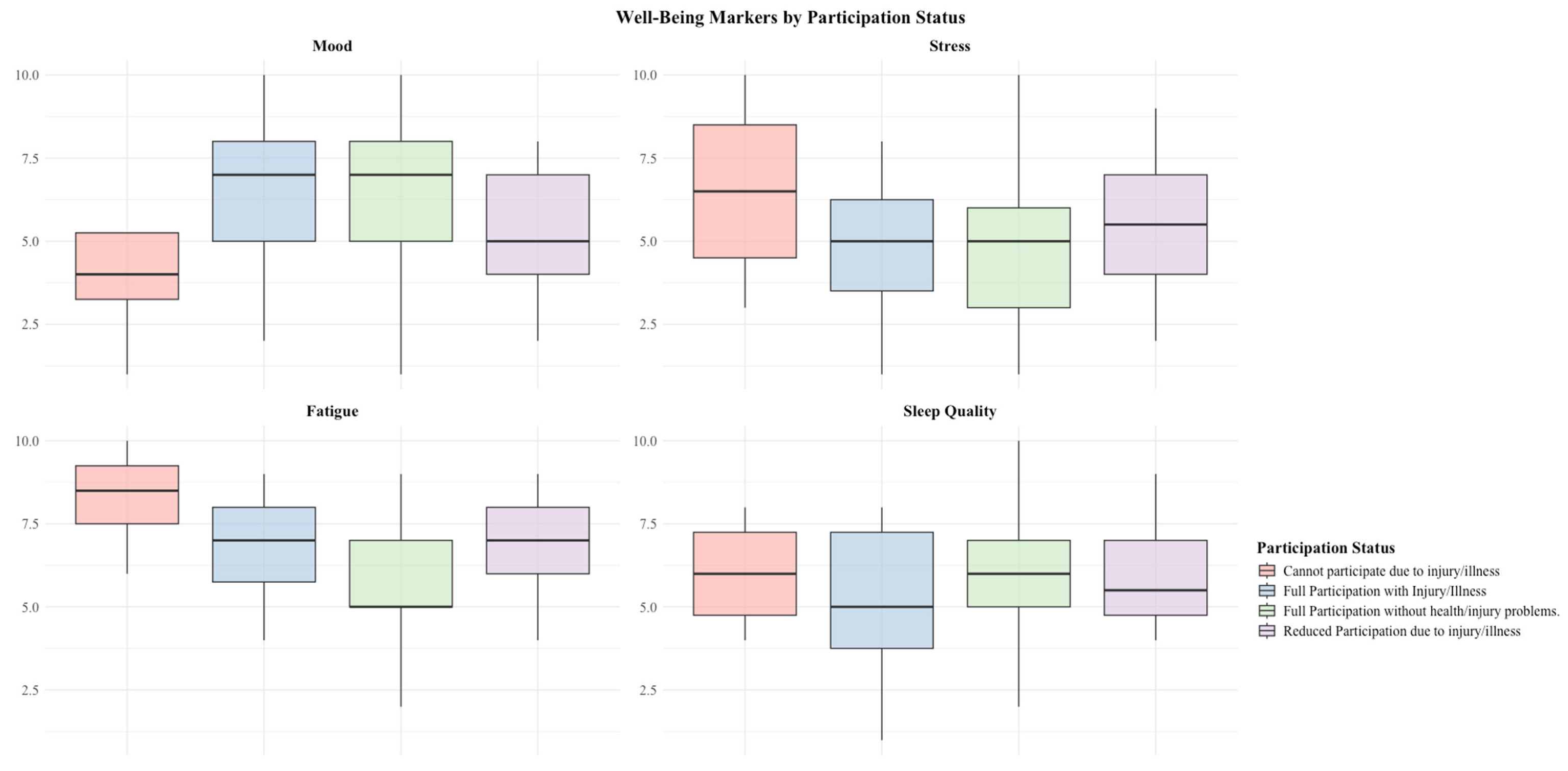
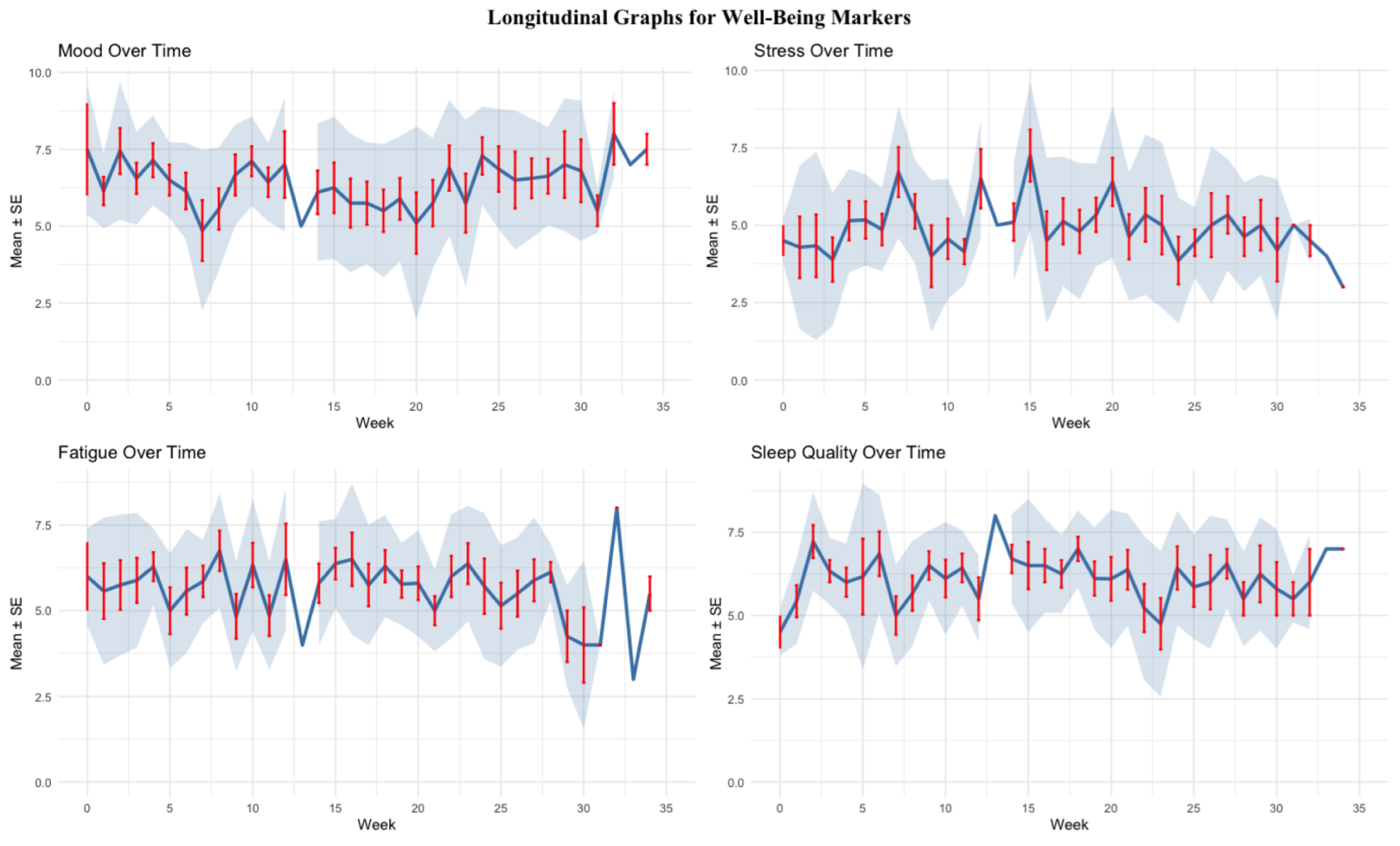
- Evaluate how health problems affect subjective athlete-reported outcomes, including fatigue, stress, mood, sleep, and training volume/intensity.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Injury and Illness Definitions
- Injuries were defined as “tissue damage or other derangement of normal physical function due to participation in sports, resulting from rapid or repetitive transfer of kinetic energy requiring medical attention”.
- Illness was “a complaint or disorder experienced by an athlete, not related to injury. Illnesses include health-related problems in physical (e.g., influenza), mental (e.g., depression) or social well-being, or removal or loss of vital elements (e.g., air, water, warmth) requiring medical attention.”
2.3. Survey Design and Data Collection
2.4. Descriptive and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Types and Locations of Injuries
3.2. Illness
4. Discussion
- The overall injury rate was 1.94 (95% CI: 1.23–2.93) per 365 athlete days, while the overall illness rate was 3.60 (95% CI: 2.29–5.10) per 365 athlete days.
- Males had a higher injury rate (2.44, 95% CI: 1.53–3.67) compared to females (1.51, 95% CI: 0.68–2.95), with an injury risk ratio (females vs. males) of 0.62 (95% CI: 0.19–1.93).
- Females reported a significantly higher number of illnesses compared to males, resulting in an illness rate of 5.40 (95% CI: 3.00–8.11) per 365 athlete days for females and 1.80 (95% CI: 0.60–3.30) for males, with an illness risk ratio (females vs. males) of 3.66 (95% CI 0.71–6.61, p ≤ 0.05).
- The shoulder region had the highest injury rate of 0.60 per 365 days (95% CI: 0.15–1.20).
- Respiratory illnesses had a significantly higher incidence in females (1.65 per 365 athlete days, 95% CI: 0.75–2.70) compared to males (0.45 per 365 athlete days, 95% CI: 0.012–1.05), resulting in an incidence rate ratio (IRR) of 3.66 (95% CI: 0.71–6.61, p < 0.05).
4.1. Injury Rates
4.2. Subjective Markers
4.3. Injury Locations and Types
4.4. Illness
4.5. Limitations
4.6. Clinical Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fallon, T.; Heron, N. A systematic review protocol of injuries and illness across all the competitive cycling disciplines, including track cycling, mountain biking, road cycling, time trial, cyclocross, gravel cycling, BMX freestyle, BMX racing, e-sport, para-cycling and artistic cycling. Front. Sports Act. Living 2024, 6, 1385832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, C.F.; Bahr, R.; Drezner, J.A.; Dvorak, J.; Engebretsen, L.; Hewett, T.; Junge, A.; Khan, K.M.; MacAuley, D.; Matheson, G.O.; et al. Towards the reduction of injury and illness in athletes: Defining our research priorities. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Union Cycliste Internationale. Agenda 2030. Available online: https://assets.ctfassets.net/761l7gh5x5an/6RrOHtU0QlyN80MDJ7vJm3/cf54c913960a66a71baaac379ef12b88/2022_UCI_AGENDA2030_web_EN.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2023).
- van Mechelen, W.; Hlobil, H.; Kemper, H.C. Incidence, Severity, Aetiology and Prevention of Sports Injuries. Sports Med. 1992, 14, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, C. A new framework for research leading to sports injury prevention. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2006, 9, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahr, R.; Clarsen, B.; Derman, W.; Dvorak, J.; Emery, C.A.; Finch, C.F.; Hägglund, M.; Junge, A.; Kemp, S.; Khan, K.M.; et al. International Olympic Committee consensus statement: Methods for recording and reporting of epidemiological data on injury and illness in sport 2020 (including STROBEExtension for Sport Injury and Illness Surveillance (STROBE-SIIS)). Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 372–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarsen, B.; Pluim, B.M.; Moreno-Pérez, V.; Bigard, X.; Blauwet, C.; Del Coso, J.; Courel-Ibáñez, J.; Grimm, K.; Jones, N.; Kolman, N.; et al. Methods for epidemiological studies in competitive cycling: An extension of the IOC consensus statement on methods for recording and reporting of epidemiological data on injury and illness in sport 2020. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derman, W.; Badenhorst, M.; Blauwet, C.; Emery, C.A.; Fagher, K.; Lee, Y.H.; Kissick, J.; Lexell, J.; Miller, I.S.; Pluim, B.M.; et al. Para sport translation of the IOC consensus on recording and reporting of data for injury and illness in sport. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarsen, B.; Myklebust, G.; Bahr, R. Development and validation of a new method for the registration of overuse injuries in sports injury epidemiology: The Oslo Sports Trauma Research Centre (OSTRC) overuse injury questionnaire. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarsen, B.; Bahr, R.; Myklebust, G.; Andersson, S.H.; Docking, S.I.; Drew, M.; Finch, C.F.; Fortington, L.V.; Harøy, J.; Khan, K.M.; et al. Improved reporting of overuse injuries and health problems in sport: An update of the Oslo Sport Trauma Research Center questionnaires. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschmüller, A.; Fassbender, K.; Kubosch, J.; Leonhart, R.; Steffen, K. Injury and Illness Surveillance in Elite Para Athletes. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 100, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubosch, E.J.; Fassbender, K.; Steffen, K.; Kubosch, D.; Südkamp, N.; Hirschmüller, A. Implementation eines Injury and Illness Surveillance Systems im paralympischen Leistungssport—Machbarkeitsstudie am Beispiel des Nationalkaders Radsport. Sports Orthop. Traumatol. 2017, 33, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwellnus, M.; Derman, W.; Jordaan, E.; Blauwet, C.; Emery, C.A.; Lee, Y.H.; Kissick, J.; Lexell, J.; Miller, I.S.; Pluim, B.M.; et al. Factors associated with illness in athletes participating in the London 2012 Paralympic Games: A prospective cohort study involving 49 910 athlete-days. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derman, W.; Schwellnus, M.P.; Jordaan, E.; Runciman, P.; Blauwet, C.; Webborn, N.; Lexell, J.; Van de Vliet, P.; Tuakli-Wosornu, Y.; Kissick, J.; et al. Sport, sex and age increase risk of illness at the Rio 2016 Summer Paralympic Games: Aprospective cohort study of 51 198 athlete days. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derman, W.; Runciman, P.; Eken, M.; Boer, P.H.; Blauwet, C.; Bogdos, M.; Idrisova, G.; Jordaan, E.; Kissick, J.; LeVan, P.; et al. Incidence and burden of illness at the Tokyo 2020 Paralympic Games held during the COVID-19 pandemic: Aprospective cohort study of 66 045 athlete days. Br. J. Sports Med. 2023, 57, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derman, W.; Runciman, P.; Schwellnus, M.; Jordaan, E.; Blauwet, C.; Webborn, N.; Lexell, J.; van de Vliet, P.; Tuakli-Wosornu, Y.; Kissick, J.; et al. High precompetition injury rate dominates the injury profile at the Rio 2016 Summer Paralympic Games: A prospective cohort study of 51 198 athlete days. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, F.; Derman, W.; Schwellnus, M.; Boer, P.-H.; Jordaan, E.; Runciman, P. Injury incidence according to athlete impairment type during the 2012 and 2016 Summer Paralympic Games: A combined analysis of 101 108 athlete days. Br. J. Sports Med. 2024, 58, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willick, S.E.; Webborn, N.; Emery, C.; Blauwet, C.A.; Pit-Grosheide, P.; Stomphorst, J.; Van de Vliet, P.; Patino Marques, N.A.; Martinez-Ferrer, J.O.; Jordaan, E.; et al. The epidemiology of injuries at the London 2012 Paralympic Games. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, R.; Van Mechelen, W.; Fuller, C.; Verhagen, E. Sport Injuries Sustained by Athletes with Disability: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, L.S.P.; Ocarino, J.M.; Madaleno, F.O.; Verhagen, E.; de Mello, M.T.; Albuquerque, M.R.; Andrade, A.G.P.; da Mata, C.P.; Pinto, R.Z.; Silva, A.; et al. Prevalence and incidence of injuries in para athletes: Asystematic review with meta-analysis and GRADE recommendations. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottesen, T.; Mashkovskiy, E.; Gentry, M.; Jensen, D.; Webborn, N.; Tuakli-Wosornu, Y. Acute and chronic musculoskeletal injury in para-sport: A systematic review. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 61, e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagher, K.; Dahlström, Ö.; Jacobsson, J.; Timpka, T.; Lexell, J. Prevalence of Sports-Related Injuries and Illnesses in Paralympic Athletes. PMR 2020, 12, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanief, Y.N.; Umar, F. The characteristics of Indonesian para-cycling athletes’ injuries. Adv. Rehabil. 2020, 34, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagher, K.; Dahlström, Ö.; Jacobsson, J.; Timpka, T.; Lexell, J. Injuries and illnesses in Swedish Paralympic athletes—A 52-week prospective study of incidence and risk factors. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2020, 30, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentzen, M.; Kenttä, G.; Derman, W.; Halvorsen Wik, E.; Havela, J.; Karls, T.; Stenman, A.; Fagher, K. Mental distress is associated with injury and illness in elite Para athletes: A 44-week prospective study over 13 860 athlete days. BMJ Open Sport. Exerc. Med. 2025, 11, e002267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, K.; Clarsen, B.; Gjelsvik, H.; Haugvad, L.; Koivisto-Mørk, A.; Bahr, R.; Berge, H.M. Illness and injury among Norwegian Para athletes over five consecutive Paralympic Summer and Winter Games cycles: Prevailing high illness burden on the road from 2012 to 2020. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 56, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, A.; Kubosch, E.J.; Leonhart, R.; Meidl, V.; Bretthauer, B.; Dallmann, P.; Steffen, K.; Hirschmueller, A. Health problems in elite Para athletes—A prospective cohort study of 53,739 athlete days. J. Sci. Med. Sport, 2025; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, L.; Silva, A.; Oliveira Madaleno, F.; Verhagen, E.; de Mello, M.T.; Melo Ocarino, J.; Alves Resende, R. Prevalence and incidence of health problems and their characteristics in Brazilian para athletes: A one-season single-center prospective pilot study. Disabil. Health J. 2024, 17, 101511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braybrook, P.J.; Tohira, H.; Birnie, T.; Brink, D.; Finn, J.; Buzzacott, P. Types and anatomical locations of injuries among mountain bikers and hikers: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholtz, K.; Lambert, M.; Corten, L.; Burgess, T.L. Incidence of Injuries, Illness and Related Risk Factors in Cross-Country Marathon Mountain Biking Events: A Systematic Search and Review. Sports Med. Open 2021, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, D.; Sarriegui, I.; Heron, N. ‘As easy as riding a bike’: A systematic review of injuries and illness in road cycling. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2020, 6, e000840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarsen, B.; Steffen, K.; Moseby Berge, H.; Bendiksen, F.; Fossan, B.; Fredriksen, H.; Gjelsvik, H.; Haugvad, L.; Kjelsberg, M.; Ronsen, O.; et al. Methods, challenges and benefits of a health monitoring programme for Norwegian Olympic and Paralympic athletes: The road from London 2012 to Tokyo 2020. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentzen, M.; Kenttä, G.; Karls, T.; Fagher, K. Monitoring mental distress in Para athletes in preparation, during and after the Beijing Paralympic Games 2022: A 22 week prospective mixed-method study. Front. Sports Act. Living 2022, 4, 945073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma-Brymer, V.; Brymer, E. Flourishing and Eudaimonic Well-Being; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Fagher, K.; Dahlström, Ö.; Jacobsson, J.; Timpka, T.; Lexell, J. Athlete health monitoring in paralympic athletes: A 52-week prospective study. Br. Assoc. Sport Exerc. Med. 2021, 55, A31.2–A32. [Google Scholar]
- Luijten, S.C.M.; Te Loo, L.M.; Nauta, J.; Janssen, T.W.J.; Holla, J.F.M.; Otten, R.H.J.; Vriend, I.; Verhagen, E. Sports-Related Health Problems in Para-Sports: A Systematic Review with Quality Assessment. Sports Health 2024, 16, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goalscape. Available online: https://goalscape.com/ (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Bache-Mathiesen, L.K.; Andersen, T.E.; Clarsen, B.; Fagerland, M.W. Handling and reporting missing data in training load and injury risk research. Sci. Med. Footb. 2022, 6, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarsen, B.; Berge, H.M.; Bendiksen, F.; Fossan, B.; Fredriksen, H.; Haugvad, L.; Kjelsberg, M.; Ronsen, O.; Steffen, K.; Torgalsen, T.; et al. Injury and illness among Norwegian Olympic athletes during preparation for five consecutive Summer and Winter Games. Br. J. Sports Med. 2024, 58, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heron, N.; Sarriegui, I.; Jones, N.; Nolan, R. International consensus statement on injury and illness reporting in professional road cycling. Physician Sportsmed. 2021, 49, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, D.; Florida-James, G.; Ball, C. Enduro World Series (EWS) Mountain Biking Injuries: A 2-year Prospective Study of 2010 Riders. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanturali, S.; Canacik, O.; Karsli, E.; Suner, S. Injury and illness among athletes during a multi-day elite cycling road race. Phys. Sport. 2015, 43, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roi, G.S.; Tinti, R. Requests for medical assistance during an amateur road cycling race. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2014, 73, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soligard, T.; Palmer, D.; Steffen, K.; Lopes, A.D.; Grek, N.; Onishi, K.; Shimakawa, T.; Grant, M.E.; Mountjoy, M.; Budgett, R.; et al. New sports, COVID-19 and the heat: Sports injuries and illnesses in the Tokyo 2020 Summer Olympics. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edler, C.; Droste, J.N.; Anemüller, R.; Pietsch, A.; Gebhardt, M.; Riepenhof, H. Injuries in elite road cyclists during competition in one UCI WorldTour season: A prospective epidemiological study of incidence and injury burden. Physician Sportsmed. 2023, 51, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwe, B.; Wahl, I.; Rose, M.; Spitzer, C.; Glaesmer, H.; Wingenfeld, K.; Schneider, A.; Brähler, E. A 4-item measure of depression and anxiety: Validation and standardization of the Patient Health Questionnaire-4 (PHQ-4) in the general population. J. Affect. Disord. 2010, 122, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidl, V.; Dallmann, P.; Steffen, K.; Bretthauer, B.; Busch, A.; Kubosch, E.J.; Leonhart, R.; Hirschmueller, A. Mental health surveillance in elite Para athletes: Early identification and follow-up of athletes at risk of mental health problems. Br. J. Sports Med. 2024, 58, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.A.; Hume, P.A.; Hind, K.; Clark, T.N.; Hardaker, N. The Incidence, Cost, and Burden of Concussion in Women’s Rugby League and Rugby Union: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.W.; Starling, L.; Kemp, S.; Williams, S.; Cross, M.; Taylor, A.; Brooks, J.H.M.; Stokes, K.A. Trends in match injury risk in professional male rugby union: A 16-season review of 10 851 match injuries in the English Premiership (2002–2019): The Professional Rugby Injury Surveillance Project. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeomans, C.; Kenny, I.C.; Cahalan, R.; Warrington, G.D.; Harrison, A.J.; Hayes, K.; Lyons, M.; Campbell, M.J.; Comyns, T.M. The Incidence of Injury in Amateur Male Rugby Union: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLarnon, M.; Boyce, S.; Heron, N. A call to action: The need for concussion assessment and diagnostic protocols for use in the different elite cycling disciplines, including paracyclists. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2023, 9, e001654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, R.; Blauwet, C.; Clarke, D.; Dalton, K.; Derman, W.; Fagher, K.; Gouttebarge, V.; Kissick, J.; Lee, K.; Lexell, J.; et al. Concussion in para sport: The first position statement of the Concussion in Para Sport (CIPS) Group. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, E.G.; Anderson, T.; Samson, O.; Triplett, A.N.; Gidley, A.D.; Isono, S.S.; Watters, J.; Donaldson, A.T.; Finnoff, J.T.; Adams, W.M. High rates of respiratory illnesses upon arrival: Lessons from Team USA at the Santiago 2023 Pan American and Parapan American Games. Br. J. Sports Med. 2024, 58, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagher, K. Sports-related injuries and illnesses in Paralympic athletes (PhD Academy Award). Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse Van Rensburg, D.C.; Schwellnus, M.; Derman, W.; Webborn, N. Illness Among Paralympic Athletes. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 29, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.M.; Griffiths, P.C.; Mellalieu, S.D. Training Load and Fatigue Marker Associations with Injury and Illness: A Systematic Review of Longitudinal Studies. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 943–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwellnus, M.; Adami, P.E.; Bougault, V.; Budgett, R.; Clemm, H.H.; Derman, W.; Erdener, U.; Fitch, K.; Hull, J.H.; McIntosh, C.; et al. International Olympic Committee (IOC) consensus statement on acute respiratory illness in athletes part 1: Acute respiratory infections. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 56, 1066–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwellnus, M.; Adami, P.E.; Bougault, V.; Budgett, R.; Clemm, H.H.; Derman, W.; Erdener, U.; Fitch, K.; Hull, J.H.; McIntosh, C.; et al. International Olympic Committee (IOC) consensus statement on acute respiratory illness in athletes part 2: Non-infective acute respiratory illness. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 56, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannion, P.; Toparlar, Y.; Blocken, B.; Clifford, E.; Andrianne, T.; Hajdukiewicz, M. Aerodynamic drag in competitive tandem para-cycling: Road race versus time-trial positions. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 179, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, Y.; Adami, P.E.; Stephenson, B.T.; Blauwet, C.; Bermon, S.; Webborn, N.; Racinais, S.; Derman, W. Goosey-Tolfrey VL Prehospital management of exertional heat stroke at sports competitions for Paralympic athletes. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 56, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Equipment Classification Category | Impairment Types | n (M/F) |
|---|---|---|
| Bicycle (C division, C1–C5) | Impaired passive range of motion | 1 (1/-) |
| Hypertonia/ataxia/athetosis | 2 (1/1) | |
| Handcycle (H division, H1–H5) | Impaired muscle power | 1 (1/-) |
| Tandem Bicycle (B division) | - | 6 (2/4) |
| Sex | Total Injuries | Total Illnesses | Athlete Days | Injury Rate 365 (95% CI) | Illness Rate 365 (95% CI) | Injury Rate 1000 h (95% CI) | Illness Rate 1000 h (95% CI) | Injury Severity (95% CI) | Injury Burden per 365 Days (95% CI) | Injury Burden per 1000 h (95% CI) | Illness Severity (95% CI) | Illness Burden per 365 Days (95% CI) | Illness Burden per 1000 h (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 8 | 6 | 1215 | 2.44 (1.53–3.67) | 1.80 (0.60, 3.30) | 3.72 (1.39–6.51) | 3.25 (0.93–6.04) | 10.2 (7.40,13.0) | 7.66 (5.57–9.75) | 12.2 (9.34–15.06) | 2.43 (1.27, 3.59) | 0.85 (0.61–1.09) | 4.08 (2.82–5.34) |
| Female | 5 | 18 | 1215 | 1.51 (0.68–2.95) | 5.407 (3.00, 8.11) | 2.48 (0.50–4.96) | 7.44 (3.97–11.41) | 14.2 (10.6, 17.8) | 8.56 (6.30–10.82) | 13.7 (10.5–16.9) | 2.94 (2.15, 3.73) | 2.65 (2.28–3.02) | 12.7 (10.5–14.9) |
| Total | 13 | 24 | 2430 | 1.94 (1.23–2.93) | 3.60 (2.29–5.10) | 3.12 (1.44–5.04) | 5.28 (3.12–7.68) | 12.0 (9.74,14.26) | 16.2 (13.18–19.22) | 25.9 (21.25–30.55) | 2.80 (2.14, 3.46) | 3.50 (2.94–4.06) | 16.8 (14.2–19.4) |
| Location | Concussion/Brain Injury (n) | Cartilage Injury (n) [95% CI] | Fracture (n) [95% CI] | Abrasion (n) [95% CI] | Joint Sprain (n) [95% CI] | Muscle Injury (n) [95% CI] | Bone Contusion (n) [95% CI] | Burden per 1000 h [95% CI] | Severity [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder | - | - | 1000% (2) | - | - | 50% (1) | 100% (1) | 10.80 [9.25–12.36] | 11.25 [9.48– 13.02] |
| Knee | - | 66.7% (2) | - | - | 100% (1) | - | - | 2.40 [1.00–3.80] | 5.00 [2.50– 7.50] |
| Head, eyes, ears, teeth | 100% (2) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 9.84 [8.10–11.58] | 20.50 [14.23–26.77] |
| Hand | - | 33% (1) | - | - | - | - | - | 0.00 [0.00–0.00] | 0.00 [0.00–0.00] |
| Elbow and forearm | - | - | - | 100% (1) | - | - | - | 0.48 [0.15–0.81] | 2.00 [0.00–4.00] |
| Lower Lumbar Region | - | - | - | - | - | 50% (1) | - | 2.40 [1.00–3.80] | 10.00 [3.80–16.20] |
| Burden Per 1000 h | 9.84 [6.83–12.85] | 1.68 [0.22–2.92] | 10.08 [7.03–13.12] | 0.48 [0.19–1.14] | 0.72 [0.09–1.53] | 2.40 [0.91–3.89] | 1.98 [0.22–3.32] | ||
| Severity | 20.50 [14.23–26.77] | 3.50 [0.91–6.09] | 21.00 [14.65–27.35] | 2.00 [0.77–4.77] | 1.50 [0.200 3.20] | 5.00 [1.90–8.10] | 3.80 [0.91–6.59] |
| System | Percentage (n) | Rate per 365 Days [95% CI] | Burden per 365 Days [95% CI] | Severity per Injury [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Respiratory | 56.0% (14) | 2.10 [1.05–3.30] | 6.46 [2.51–4.65] | 3.58 [2.51–4.65] |
| Thermoregulatory | 12.0% (3) | 0.45 [0.00–1.05] | 0.30 [−0.26–1.59] | 0.67 [−0.26–1.59] |
| Gastrointestinal | 8.0% (2) | 0.30 [0.00–0.75] | 1.92 [0.29–1.62] | 4.00 [1.23–6.77] |
| Ophthalmological | 8.0% (2) | 0.30 [0.00–0.75] | 0.48 [−0.09–0.57] | 1.00 [−0.39–2.39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fallon, T.; Carragher, P.; Heron, N. Injury and Illness Surveillance in Para-Cycling: A Single-Centre One-Season Prospective Longitudinal Study. Sports 2025, 13, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13060158
Fallon T, Carragher P, Heron N. Injury and Illness Surveillance in Para-Cycling: A Single-Centre One-Season Prospective Longitudinal Study. Sports. 2025; 13(6):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13060158
Chicago/Turabian StyleFallon, Thomas, Paul Carragher, and Neil Heron. 2025. "Injury and Illness Surveillance in Para-Cycling: A Single-Centre One-Season Prospective Longitudinal Study" Sports 13, no. 6: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13060158
APA StyleFallon, T., Carragher, P., & Heron, N. (2025). Injury and Illness Surveillance in Para-Cycling: A Single-Centre One-Season Prospective Longitudinal Study. Sports, 13(6), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13060158






