Differential Balance Enhancements Associated with Conventional Balance Training and Portable Slackline Board Training: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
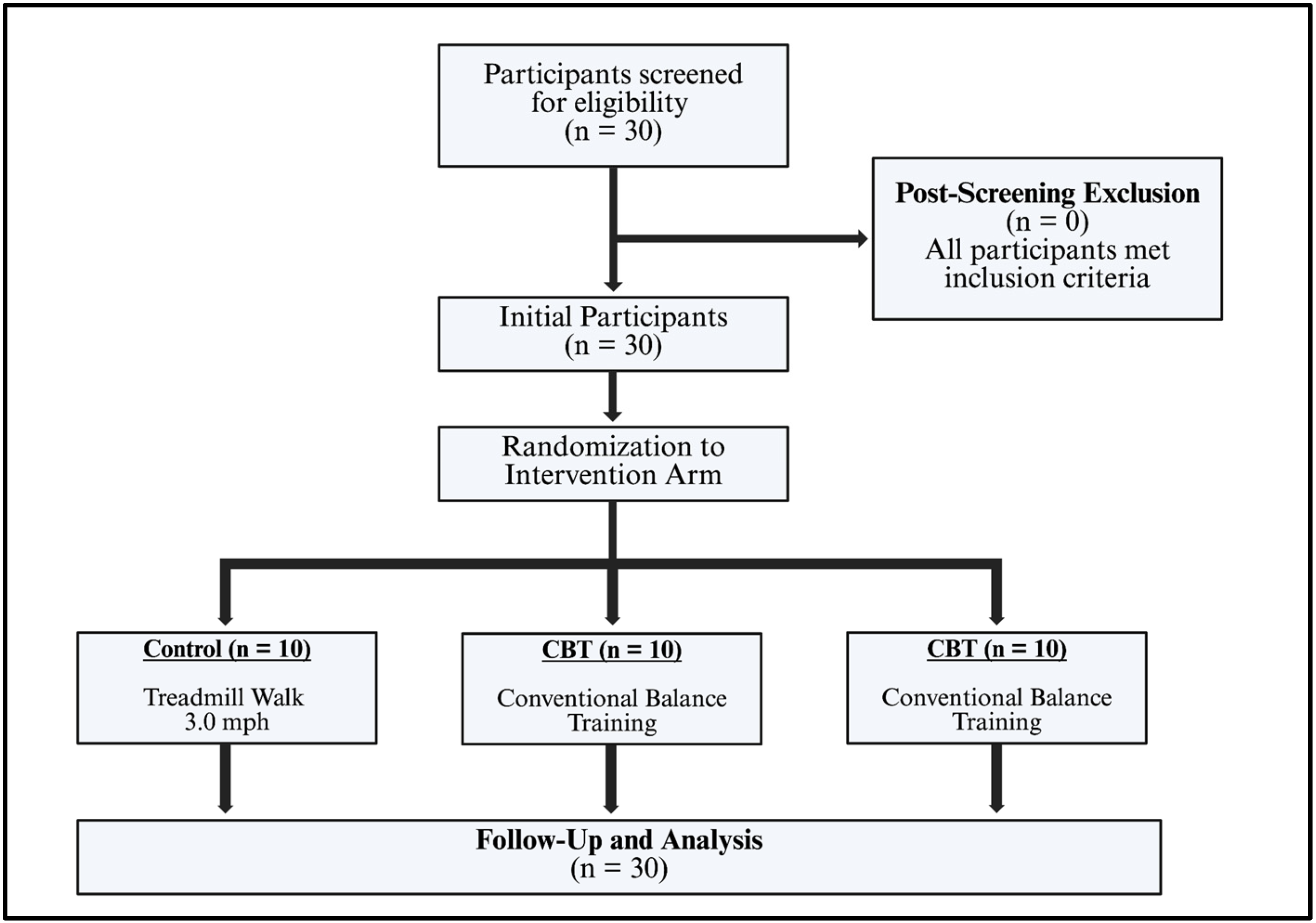
2.2. Participants
2.3. Conventional Balance Training (CBT) and Slackline Balance Training (SBT) Equipment
2.4. Supervised 8-Week Progression-Based Balance Training Program
2.5. Testing Procedures
2.5.1. Anthropometrics
2.5.2. Assessment of Balance Performance
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anthropometric Characterization
3.2. Static Balance
3.3. Dynamic Balance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SLT | Slackline Balance Training |
| CON | Control |
| CBT | Conventional Balance Training |
| mSEBT | Modified Star Excursion Balance Test |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
References
- DiStefano, L.J.; Clark, M.A.; Padua, D.A. Evidence Supporting Balance Training in Healthy Individuals: A Systemic Review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 2718–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrijević, S.; Moskovljević, L.; Dabović, M. The influence of proprioceptive training on young rhythmic gymnasts balance. Facta Univ. 2016, 14, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Eisen, T.C.; Danoff, J.V.; Leone, J.E.; Miller, T.A. The Effects of Multiaxial and Uniaxial Unstable Surface Balance Training in College Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Franco, N.; Martínez-López, E.; Lomas-Vega, R.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Martínez-Amat, A. Effects of Proprioceptive Training Program on Core Stability and Center of Gravity Control in Sprinters. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannicandro, I.; Cofano, G.; Rosa, R.A.; Piccinno, A. Balance training exercises decrease lower-limb strength asymmetry in young tennis players. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2014, 13, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Brachman, A.; Kamieniarz, A.; Michalska, J.; Pawłowski, M.; Słomka, K.J.; Juras, G. Balance Training Programs in Athletes—A Systematic Review. J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 58, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghavi Asl, A.; Shojaedin, S.S.; Hadadnezhad, M. Comparison of effect of wobble board training with and without cognitive intervention on balance, ankle proprioception and jump landing kinetic parameters of men with chronic ankle instability: A randomized control trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linens, S.W.; Ross, S.E.; Arnold, B.L. Wobble Board Rehabilitation for Improving Balance in Ankles with Chronic Instability. Clin. J. Sport. Med. 2016, 26, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, M.G.; Rutbil, H.; Akpinar, E.; Yildirim, A.; Karakaya, İ.Ç. Effect of ankle proprioceptive training on static body balance. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.J.; Linens, S.W.; Cain, M.S. A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Rehabilitation Efficacy in Chronic Ankle Instability. J. Sport Rehabil. 2017, 26, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguish, B.; Sandrey, M.A. Two 4-Week Balance-Training Programs for Chronic Ankle Instability. J. Athl. Train. 2018, 53, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, A.; Klahn, P.; Hoeft, J.; Zu Eulenburg, C.; Steib, S. Time course and dimensions of postural control changes following neuromuscular training in youth field hockey athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benis, R.; Bonato, M.; Torre, A.L. Elite Female Basketball Players’ Body-Weight Neuromuscular Training and Performance on the Y-Balance Test. J. Athl. Train. 2016, 51, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pau, M.; Loi, A.; Pezzotta, M.C. Does sensorimotor training improve the static balance of young volleyball players? Sports Biomech. 2012, 11, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trecroci, A.; Cavaggioni, L.; Lastella, M.; Broggi, M.; Perri, E.; Iaia, F.M.; Alberti, G. Effects of traditional balance and slackline training on physical performance and perceived enjoyment in young soccer players. Res. Sports Med. 2018, 26, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfusterschmied, J.; Stöggl, T.; Buchecker, M.; Lindinger, S.; Wagner, H.; Müller, E. Effects of 4-week slackline training on lower limb joint motion and muscle activation. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2013, 16, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, L.; Roth, R.; Zahner, L.; Faude, O. Slackline Training (Balancing Over Narrow Nylon Ribbons) and Balance Performance: A Meta-Analytical Review. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Rio, J.; Santos, L.; Fernández-García, B.; Robles, R.; Casquero, I.; Paredes, R. Effects of Slackline Training on Acceleration, Agility, Jump Performance and Postural Control in Youth Soccer Players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2019, 67, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Fernández-Río, J.; Fernández-García, B.; Jakobsen, M.D.; González-Gómez, L.; Suman, O.E. Effects of Slackline Training on Postural Control, Jump Performance, and Myoelectrical Activity in Female Basketball Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordevic, M.; Hökelmann, A.; Müller, P.; Rehfeld, K.; Müller, N.G. Improvements in Orientation and Balancing Abilities in Response to One Month of Intensive Slackline-Training. A Randomized Controlled Feasibility Study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbitt, R.D. Semicircular canal biomechanics in health and disease. J. Neurophysiol. 2019, 121, 732–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.J.; Lehr, M.E.; Fink, M.L.; Kiesel, K.B.; Plisky, P.J. Dynamic Balance Performance and Noncontact Lower Extremity Injury in College Football Players: An Initial Study. Sports Health Multidiscip. Approach 2013, 5, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyward, V. ASEP methods recommendation: Body composition assessment. J. Exerc. Physiol. Online 2001, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, A.; Kim, J.; Jo, S.; Jee, J.; Heymsfield, S.; Bhagat, Y.; Kim, I.; Cho, J. Smartphone-Based Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Devices for Daily Obesity Management. Sensors 2015, 15, 22151–22166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Lieshout, R.; Reijneveld, E.A.E.; van den Berg, S.M.; Haerkens, G.M.; Koenders, N.H.; de Leeuw, A.J.; Van Oorsouw, R.G.; Paap, D.; Scheffer, E.; Weterings, S.; et al. Reproducibility of the Modified Star Excursion Balance Test Composite and Specific Reach Direction Scores. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2016, 11, 356–365. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, M.; Lichtenstein, E.; Roth, R.; Faude, O. Balance Training Under Fatigue: A Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effect of Fatigue on Adaptations to Balance Training. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2024, 38, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertel, J.; Braham, R.A.; Hale, S.A.; Olmsted-Kramer, L.C. Simplifying the star excursion balance test: Analyses of subjects with and without chronic ankle instability. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2006, 36, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picot, B.; Terrier, R.; Forestier, N.; Fourchet, F.; McKeon, P.O. The Star Excursion Balance Test: An Update Review and Practical Guidelines. Int. J. Athl. Ther. Train. 2021, 26, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haanappel, C.P.; Voor In ‘THolt, A.F. Using the interquartile range in infection prevention and control research. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2024, 6, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Su, M.K. Biostatistics and Epidemiology for the Toxicologist: Measures of Central Tendency and Variability—Where Is the “Middle?” and What Is the “Spread?”. J. Med. Toxicol. 2022, 18, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfusterschmied, J.; Buchecker, M.; Keller, M.; Wagner, H.; Taube, W.; Müller, E. Supervised slackline training improves postural stability. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2013, 13, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, L.; Roth, R.; Rueegge, A.; Groppa, M.; Zahner, L.; Faude, O. Effects of Slackline Training on Balance, Jump Performance & Muscle Activity in Young Children. Int. J. Sports Med. 2013, 34, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giboin, L.-S.; Gruber, M.; Kramer, A. Three months of slackline training elicit only task-specific improvements in balance performance. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, L.; Roth, R.; Zahner, L.; Faude, O. Slackline training and neuromuscular performance in seniors: A randomized controlled trial. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glänzel, M.H.; Carpes, F.P.; Ourique, L.D.; de Noronha, M.; Geremia, J.M. Slackline training and postural control in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2022, 30, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giboin, L.-S.; Loewe, K.; Hassa, T.; Kramer, A.; Dettmers, C.; Spiteri, S.; Gruber, M.; Schoenfeld, M.A. Cortical, subcortical and spinal neural correlates of slackline training-induced balance performance improvements. NeuroImage 2019, 202, 116061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.; Pfusterschmied, J.; Buchecker, M.; Müller, E.; Taube, W. Improved postural control after slackline training is accompanied by reduced H-reflexes. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2012, 22, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.; Mau-Moeller, A.; Wassermann, F.; Plewka, A.; Bader, R.; Bruhn, S. Repetitive jumping and sprinting until exhaustion alters hamstring reflex responses and tibial translation in males and females. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, M.; Gollhofer, A. Submaximal fatigue of the hamstrings impairs specific reflex components and knee stability. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2007, 15, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Luna, M.A.; Cortell-Tormo, J.M.; García-Jaén, M.; Ortega-Navarro, M.; Tortosa-Martínez, J. Acute Effects of ACL Injury-Prevention Warm-Up and Soccer-Specific Fatigue Protocol on Dynamic Knee Valgus in Youth Male Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, D.; Melnyk, M.; Gollhofer, A. Gender and fatigue have influence on knee joint control strategies during landing. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, D.C.; Ellefsen, S.; Baar, K. Adaptations to Endurance and Strength Training. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a029769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelman, R.; Berg, M.; Ilan, Y. A Subject-Tailored Variability-Based Platform for Overcoming the Plateau Effect in Sports Training: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowski, S.; Wrzeciono, A.; Czech, O.; Rutkowska, A.; Szczegielniak, J. Effects of a Short-Term Slackline Training Program on Energy Expenditure and Balance in Healthy Young Adults: A Preliminary Report of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PAGAC. 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee Scientific Report; USA Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Luedke, L.E.; Geisthardt, T.W.; Rauh, M.J. Y-Balance Test Performance Does Not Determine Non-Contact Lower Quadrant Injury in Collegiate American Football Players. Sports 2020, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.P.; Tyler, T.F.; Mirabella, M.R.; Mullaney, M.J.; Nicholas, S.J. The Effectiveness of a Balance Training Intervention in Reducing the Incidence of Noncontact Ankle Sprains in High School Football Players. Am. J. Sports Med. 2007, 35, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Conventional Balance Training (CBT) Regimen | Slackboard Balance Training (SLT) Regimen |
|---|---|
Bosu Ball (flat side downwards): Squat (2 sets of 10 reps), static balance with double-leg stance (3 sets of 30 s) Cushion Disc: Seated single-leg lift with arms crossed (3 sets of 30 s hold per leg), Standing double-leg balance with eyes open |
Reverse lunge (3 sets of 10): non-slackline knee soft touch floor Squat (3 sets of 10): non-slackline foot shoulder-width stance, lift leg off floor to knee-bend |
Bosu Ball (flat side downwards): Squat with medicine ball toss (2 sets of 10 reps), step on/off with alternating legs (2 sets of 10 reps per leg) Cushion Disc: Standing single-leg hold with head rotations to the left and right (2 sets of 5 rotations per direction on each leg), lateral lunges on/off with alternating legs |
Walk across (3 sets of 10): forward and reverse Reverse lung crossover (3 sets of 10): after knee touch leg crossover board to pike |
Bosu Ball (flat side downwards): Lateral jumps onto Bosu Ball (2 sets of 8 reps per side), Cushion Disc: Tandem stance with light resistance band arm pulls (2 sets of 8 reps per arm), Clock reach on single-leg stance with reaches in 3 different directions |
Reverse lunge (3 sets of 10): non-slackline knee soft touch floor with eyes closed Squat (3 sets of 10): non-slackline foot shoulder-width stance, lift leg off floor to knee-bend with one eye closed |
Bosu Ball (flat side upwards): Squat (2 sets of 6 reps), alternating step-ups with knee drive (3 sets of 6 reps per leg) Cushion Disc: Single-leg hop to disc and hold (3 sets of 10 s hold per leg), double-leg stance with eyes closed while balancing and experiencing light perturbations |
Walk across (3 sets of 10): forward and reverse reacting to called out direction Side shuffle (3 sets of 10): keep torso rigid, bend at hips reacting to called out direction |
| CON | CBT | SLT | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Post- Training | p-Value | Baseline | Post- Training | p-Value | Baseline | Post- Training | p-Value | |
| Body Mass | 86.6 (8.5) | 88.6 (9.1) | 0.009 * | 86.3 (8.9) | 87.8 (8.5) | 0.009 * | 85.9 (8.5) | 88.1 (10.2) | 0.009 * |
| Sway Path Length (mm) Firm Surface | 779 (34.3) | 794 (41.3) | 0.330 | 788 (35.3) | 727 (52.3) | 0.011 * | 778.0 (51.0) | 687.0 (84.8) | 0.007 * |
| Sway Path Length (mm) Wobble Board | 914 (168.5) | 904 (151.8) | 0.570 | 971 (33.5) | 883 (48.5) | 0.007 * | 988 (66.5) | 799 (43.0) | 0.009 * |
| Sway Path Length (mm) Soft Mat | 879 (87.0) | 878 (102.5) | 0.111 | 845 (53.5) | 789 (48.5) | 0.009 * | 829 (87.3) | 745 (76.8) | 0.007 * |
| mSEBT (%) Anterior | 60 (3.3) | 61 (1.3) | 0.590 | 60 (3.4) | 64 (3.6) | 0.007 * | 61 (1.1) | 68 (1.4) | 0.007 * |
| mSEBT (%) Posterolateral | 82 (5.8) | 82 (2.7) | 0.883 | 83.0 (5.0) | 87 (4.6) | 0.007 * | 84 (6.7) | 90 (1.9) | 0.009 * |
| mSEBT (%) Posteromedial | 97 (4.3) | 97 (5.0) | 0.579 | 99 (5.1) | 101 (4.8) | 0.009 * | 99 (4.0) | 107 (3.8) | 0.009 * |
| mSEBT (%) Composite | 80 (3.9) | 80 (3.0) | 0.910 | 80 (3.1) | 83 (3.1) | 0.009 * | 80 (3.1) | 89 (1.0) | 0.007 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamamoto, T.; Kidwell, J.A.; Shatagopam, V.; Hetherton, K.J.; Neufeld, E.V.; Dolezal, B.A. Differential Balance Enhancements Associated with Conventional Balance Training and Portable Slackline Board Training: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sports 2025, 13, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13120457
Yamamoto T, Kidwell JA, Shatagopam V, Hetherton KJ, Neufeld EV, Dolezal BA. Differential Balance Enhancements Associated with Conventional Balance Training and Portable Slackline Board Training: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sports. 2025; 13(12):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13120457
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamamoto, Trent, Joshua A. Kidwell, Vishruth Shatagopam, Kyle J. Hetherton, Eric V. Neufeld, and Brett A. Dolezal. 2025. "Differential Balance Enhancements Associated with Conventional Balance Training and Portable Slackline Board Training: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Sports 13, no. 12: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13120457
APA StyleYamamoto, T., Kidwell, J. A., Shatagopam, V., Hetherton, K. J., Neufeld, E. V., & Dolezal, B. A. (2025). Differential Balance Enhancements Associated with Conventional Balance Training and Portable Slackline Board Training: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sports, 13(12), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13120457







