Awareness, Perceived Importance and Implementation of Sports Vision Training
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Instrument
- Sociodemographic and professional data: This section gathered information on participants’ age, gender, region of professional activity, sport modality, and athlete categories coached (e.g., youth, senior, elite). These variables allowed contextualizing the responses and stratifying analyses by demographic and sport-related characteristics. For clarity, definitions of all sport modalities included in the study are provided in Appendix A (Glossary of Sport Modalities).
- Awareness of Sports Vision Training: This part included items to determine whether participants had heard of sports vision training, their self-reported level of understanding, and whether they could define the concept. The aim was to assess baseline familiarity with the topic.
- Perceived importance of visual skills: Participants evaluated the importance of improving ten specific visual skills, hand–eye/body coordination, reaction time, anticipation, peripheral vision, visual memory, visual concentration, depth perception, recognition speed, contrast sensitivity, and moving-object recognition, for optimizing their athletes’ performance. Ratings were provided using a 5-point Likert scale, where 1 corresponded to very important and 5 to not important. This scale allowed quantifying the perceived relevance of each skill and facilitated statistical comparison between groups. As each Likert-scale item was intended to measure the perceived importance of a different visual skill, no factor analysis or internal consistency (e.g., Cronbach’s alpha) was conducted.
- Incorporation of visual training into practice plans: This section contained a dichotomous (yes/no) question regarding whether coaches currently integrate specific exercises to develop visual skills into their training sessions. Additional questions explored interest in receiving further information and whether their club or organization would be willing to invest in such training programs.
2.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
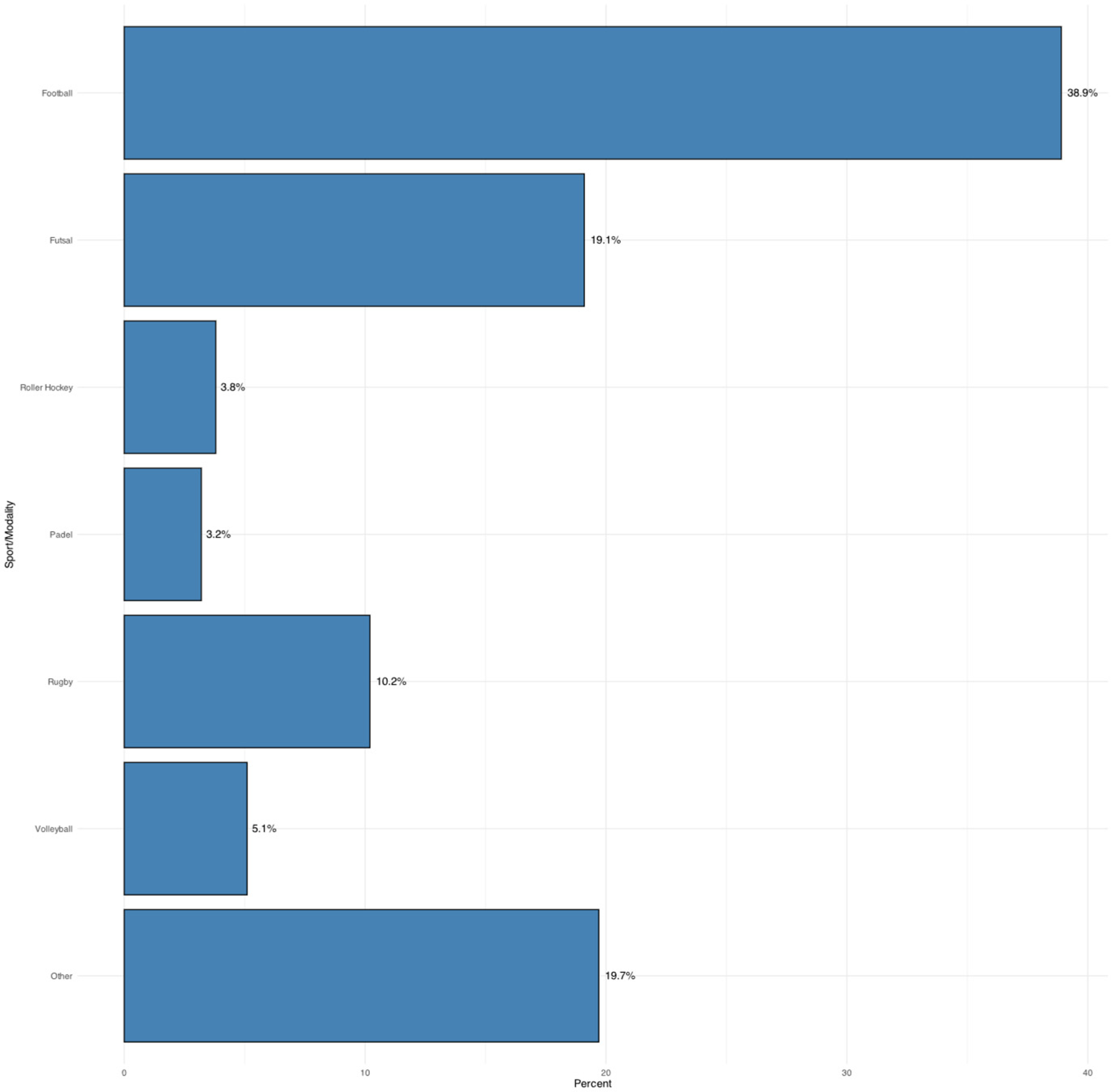
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Stratified Comparisons (Sex, Age, Modality)
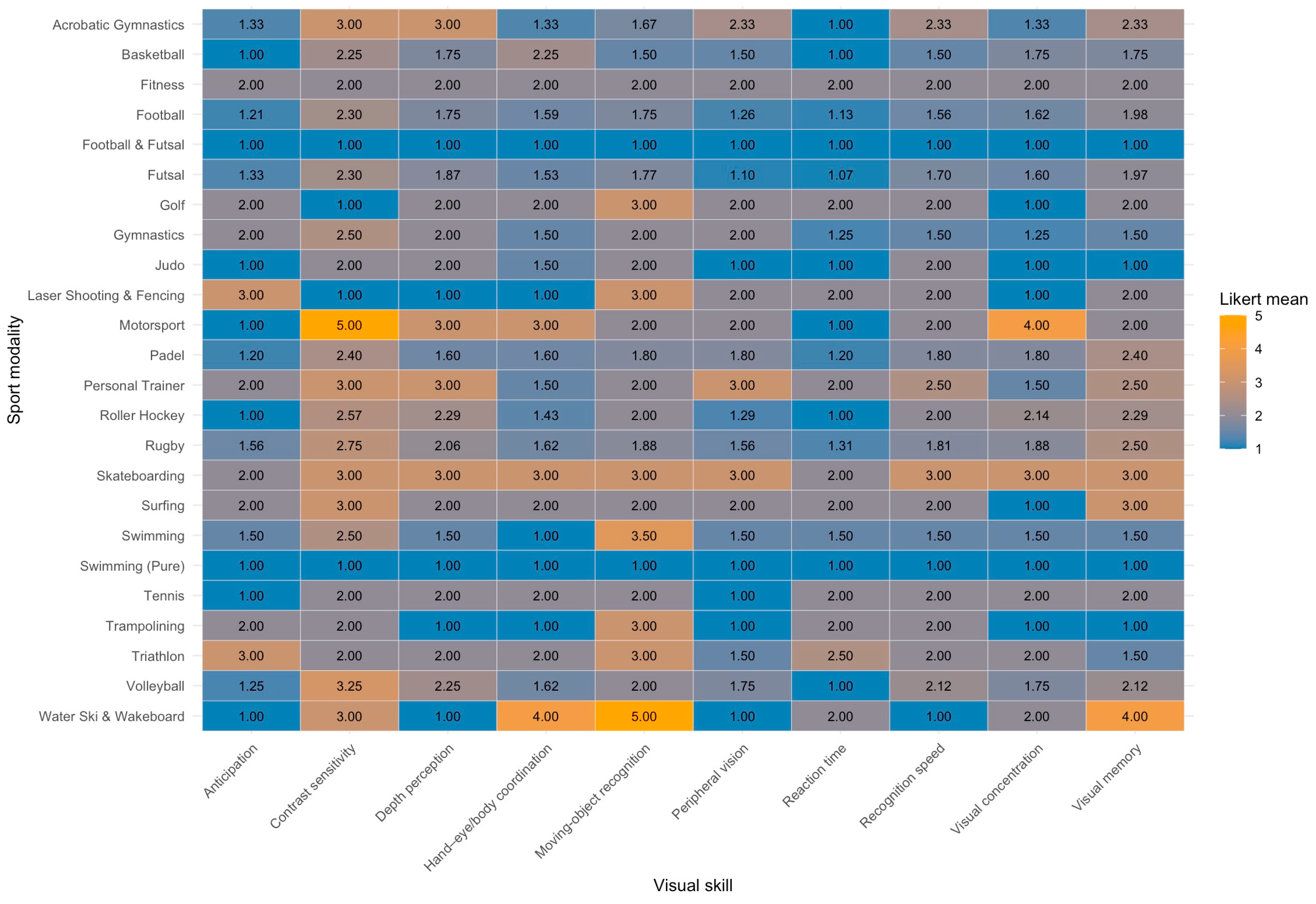
3.2.1. Visual Skills
3.2.2. Visual Processing and Memory
3.2.3. Spatial Perception and Visual Discrimination
3.2.4. Incorporation of Visual Training into Practice Plans
3.3. Multivariable Logistic Regression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Glossary of Sport Modalities
- Acrobatic Gymnastics: A gymnastics discipline combining tumbling, balance, and partner acrobatics.
- Basketball: A team sport played on a court with the objective of scoring points by shooting a ball through a hoop.
- Fitness: General training activities focused on strength, endurance, or conditioning, rather than a single competitive sport.
- Football (Soccer): The world’s most widely played team sport, in which two teams of 11 players attempt to score by moving a ball into the opponent’s goal.
- Football & Futsal: Combined category including traditional football and futsal.
- Futsal: A variant of soccer played indoors on a smaller court with five players per team.
- Golf: An individual sport in which players hit a ball into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible.
- Gymnastics: Competitive artistic gymnastics, involving apparatus such as floor, vault, bars, and beam.
- Judo: A martial art and Olympic combat sport emphasizing throws, holds, and grappling techniques.
- Laser Shooting & Fencing: Precision sports involving either aiming with laser pistols or combat with fencing blades.
- Motorsport: Competitive racing of motor vehicles, such as cars or motorcycles.
- Padel: A racket sport similar to tennis, typically played in doubles on an enclosed court with glass walls.
- Personal Trainer: Professional-led training sessions focusing on physical fitness and individualized conditioning.
- Roller Hockey (Rink Hockey): A team sport played on roller skates, using sticks to hit a ball (or puck) into the opponent’s goal.
- Rugby: A contact team sport played with an oval ball, involving carrying, passing, kicking, and tackling.
- Skateboarding: An action sport involving riding and performing tricks using a skateboard.
- Surfing: A water sport where the athlete rides waves on a surfboard.
- Swimming: Competitive swimming across various strokes (freestyle, backstroke, breaststroke, butterfly).
- Swimming (Pure): Subcategory indicating non-competitive or recreational swimming in pure form.
- Tennis: A racket sport played individually or in pairs, where players hit a ball over a net into the opponent’s court.
- Trampolining: A gymnastics discipline involving aerial acrobatics performed on a trampoline.
- Triathlon: A multisport event combining swimming, cycling, and running in immediate succession.
- Volleyball: A team sport where two teams of six players attempt to ground a ball on the opponent’s court over a net.
- Water Ski & Wakeboard: Water sports involving being towed by a boat while gliding on skis or a board, often with acrobatics or jumps.
References
- Nascimento, H.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Alvarez-Peregrina, C.; Sánchez-Tena, M.Á. Citations Network Analysis of Vision and Sport. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbaum, L.G.; Erickson, G. Sports Vision Training: A Review of the State-of-the-Art in Digital Training Techniques. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2018, 11, 160–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.; Betz, B.; Borders, L.; Kuehn-Himmler, A.; Hasselfeld, K.; Divine, J. Vision Training and Reaction Training for Improving Performance and Reducing Injury Risk in Athletes: Sports Vision Training. J. Sports Perform. Vis. 2020, 2, e8–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presta, V.; Vitale, C.; Ambrosini, L.; Gobbi, G. Stereopsis in Sports: Visual Skills and Visuomotor Integration Models in Professional and Non-Professional Athletes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscemi, A.; Mondelli, F.; Biagini, I.; Gueli, S.; D’Agostino, A.; Coco, M. Role of Sport Vision in Performance: Systematic Review. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, H.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Alvarez-Peregrina, C.; Sánchez-Tena, M.Á. Reply to Laby, D.M.; Appelbaum, L.G. Comment on “Nascimento et al. Citations Network Analysis of Vision and Sport. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7574”. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welford, A.T. Fundamentals of Skill; Methuen: London, UK, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Habekost, T.; Ovesen, J.; Madsen, J.B. Cognition in Elite Soccer Players: A General Model. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1477262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, G.B. Review: Visual Performance Assessments for Sport. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2021, 98, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonato, M.; Gatti, C.; Rossi, C.; Merati, G.; La Torre, A. Effects of Visual Training in Tennis Performance in Male Junior Tennis Players: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2019, 60, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, P.E.; Campher, J.; Smit, C.E. The Role of Visual Skills and Its Impact on Skill Performance of Cricket Players. Afr. J. Phys. Health Educ. Recreat. Danc. 2009, 15, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wilkins, L.; Appelbaum, L.G. An Early Review of Stroboscopic Visual Training: Insights, Challenges and Accomplishments to Guide Future Studies. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2020, 13, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasaheb, T.; Maman, P.; Sandhu, J.S. The Impact of Visual Skills Training Program on Batting Performance in Cricketers. Serb. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 2, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Ferris, L.M.; Hilbig, S.; Asamoa, E.; LaRue, J.L.; Lyon, D.; Connolly, K.; Port, N.; Appelbaum, L.G. Dynamic Vision Training Transfers Positively to Batting Practice Performance among Collegiate Baseball Batters. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2020, 51, 101759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltavski, D.; Biberdorf, D.; Praus Poltavski, C. Which Comes First in Sports Vision Training: The Software or the Hardware Update? Utility of Electrophysiological Measures in Monitoring Specialized Visual Training in Youth Athletes. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 732303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelbaum, L.G.; Lu, Y.; Khanna, R.; Detwiler, K.R. The Effects of Sports Vision Training on Sensorimotor Abilities in Collegiate Softball Athletes. Athl. Train. Sports Health Care 2016, 8, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthis, J.S.; Yates, J.L.; Hayhoe, M.M. Gaze and the Control of Foot Placement When Walking in Natural Terrain. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 1224–1233.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmis, M.A.; Pardhan, S. Patients with Central Visual Field Loss Adopt a Cautious Gait Strategy during Tasks That Present a High Risk of Falling. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 4120–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpham, J.A.; Mihalik, J.P.; Littleton, A.C.; Frank, B.S.; Guskiewicz, K.M. The Effect of Visual and Sensory Performance on Head Impact Biomechanics in College Football Players. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.F.; Ellis, J.K.; Bench, J.; Khoury, J.; Graman, P. High-Performance Vision Training Improves Batting Statistics for University of Cincinnati Baseball Players. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obërtinca, R.; Meyer, T.; aus der Fünten, K. Injury Prevention in Youth Football (Soccer): A Comprehensive Description of the Development Process of the “FUNBALL” Programme. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2024, 10, e002260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, J.; Jiménez, R.; Cárdenas, D.; Redondo, B.; García, J.A. Visual Function, Performance, and Processing of Basketball Players vs. Sedentary Individuals. J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grooms, D.; Appelbaum, G.; Onate, J. Neuroplasticity Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury: A Framework for Visual-Motor Training Approaches in Rehabilitation. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 45, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, G.B. Sports Vision: Vision Care for the Enhancement of Sports Performance, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R. Important Visual Skills in Sports and Introduction to Sports Vision. J. Optom. Ophthalmol. 2021, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephson, J.E.; Caffery, B.E. Contact Lens Considerations in Surface and Subsurface Aqueous Environments. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1991, 68, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, J.; Vuu, K.; Bergenske, P.; Burnham, K.; Smythe, J.; Caroline, P. Bacterial Populations on Silicone Hydrogel and Hydrogel Contact Lenses after Swimming in a Chlorinated Pool. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2005, 82, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.S.; Siegel, I.M. Cornea-Contact Lens Interaction in the Aquatic Environment. CLAO J. 1997, 23, 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Cairns, J. Health Psychology. A Textbook. Prim. Health Care 2004, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, G.O.; Neilands, T.B.; Frongillo, E.A.; Melgar-Quiñonez, H.R.; Young, S.L. Best Practices for Developing and Validating Scales for Health, Social, and Behavioral Research: A Primer. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVellis, R.F.; Thorpe, C.T. Scale Development: Theory and Applications, 5th ed.; Applied Social Research Methods; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2021; ISBN 9781544379326. [Google Scholar]
- Dass, S.; Dogra, P.; Singh, D. Awareness of Sports Vision among the Coaches of Cricket and Badminton. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2025, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukahara, Y.; Kamada, H.; Torii, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Yamasawa, F. Awareness and Knowledge of Medical Issues Related to Female Athletes Among Track and Field Coaches. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2023, 14, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legault, I.; Faubert, J. Gender Comparison of Perceptual-Cognitive Learning in Young Athletes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.; Cathcart, J.; Kerr, D.; Moore, I.; Hislop, M.; Wilson, I. An Investigation of Coaches’ Awareness of Injury in Elite Adolescent Rugby Union in Northern Irish Schools—A Qualitative Study. Phys. Ther. Sport 2022, 57, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coetzee, D.; de Waal, E. An Exploratory Investigation of the Effect of a Sports Vision Program on Grade 4 and 5 Female Netball Players’ Visual Skills. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.; Williams, A.; Ward, P.; Janelle, C. Perceptual-Cognitive Expertise in Sport: A Meta-Analysis. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2007, 29, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Lim, J.J.J.; Moh, F.K.C.; Siddiqi, A.; Zachar, J.; Zafar, S. Parental and Training Coaches’ Knowledge and Attitude towards Dental Trauma Management of Children. Aust. Dent. J. 2022, 67, S31–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoye, A.; Heuzé, J.-P.; Larsen, T.; Sarrazin, P. Comparison of Coaches’ Perceptions and Officials Guidance towards Health Promotion in French Sport Clubs: A Mixed Method Study. Health Educ. Res. 2016, 31, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, D.; Duca, M.; Trecroci, A.; Ansaldi, L.; Bonfanti, L.; Alberti, G.; Iodice, P. Perceptual Vision Training in Non-Sport-Specific Context: Effect on Performance Skills and Cognition in Young Females. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, S.M.; Suksreephaisan, T.K.; Perry, B.G.; Palmer, B.R.; Page, R.A. The Effects of Anticipation and Visual and Sensory Performance on Concussion Risk in Sport: A Review. Sports Med. Open 2020, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sport | Sex | Anticipation | Contrast Sensitivity | Depth Perception | Hand–Eye/Body Coordination | Moving-Object Recognition | Peripheral Vision | Reaction Time | Recognition Speed | Visual Concentration | Visual Memory |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Football | Female | 1.00 ± NA | 3.00 ± NA | 2.00 ± NA | 1.00 ± NA | 2.00 ± NA | 1.00 ± NA | 1.00 ± NA | 3.00 ± NA | 2.00 ± NA | 3.00 ± NA |
| Football | Male | 1.22 ± 0.42 | 2.28 ± 0.87 | 1.75 ± 0.68 | 1.60 ± 0.62 | 1.75 ± 0.79 | 1.27 ± 0.52 | 1.13 ± 0.34 | 1.53 ± 0.65 | 1.62 ± 0.58 | 1.97 ± 0.76 |
| Futsal | Female | 1.20 ± 0.45 | 2.00 ± 0.71 | 2.00 ± 0.71 | 1.40 ± 0.55 | 1.20 ± 0.45 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 2.00 ± 0.71 | 1.40 ± 0.55 | 2.20 ± 0.84 |
| Futsal | Male | 1.36 ± 0.49 | 2.36 ± 0.76 | 1.84 ± 0.62 | 1.56 ± 0.77 | 1.88 ± 0.83 | 1.12 ± 0.33 | 1.08 ± 0.28 | 1.64 ± 0.57 | 1.64 ± 0.57 | 1.92 ± 0.76 |
| Padel | Male | 1.20 ± 0.45 | 2.40 ± 0.89 | 1.60 ± 0.55 | 1.60 ± 0.55 | 1.80 ± 0.45 | 1.80 ± 0.45 | 1.20 ± 0.45 | 1.80 ± 0.45 | 1.80 ± 0.45 | 2.40 ± 0.55 |
| Roller Hockey | Female | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 2.50 ± 0.71 | 2.50 ± 0.71 | 1.50 ± 0.71 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.50 ± 0.71 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 2.50 ± 0.71 |
| Roller Hockey | Male | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 2.75 ± 1.26 | 2.25 ± 1.26 | 1.50 ± 0.58 | 2.25 ± 1.26 | 1.50 ± 0.58 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 2.50 ± 1.29 | 2.50 ± 1.29 | 2.25 ± 1.50 |
| Rugby | Male | 1.56 ± 0.63 | 2.75 ± 1.06 | 2.06 ± 1.00 | 1.62 ± 0.81 | 1.88 ± 1.02 | 1.56 ± 0.96 | 1.31 ± 0.48 | 1.81 ± 0.66 | 1.88 ± 0.81 | 2.50 ± 1.15 |
| Volleyball | Female | 1.33 ± 0.58 | 3.00 ± 0.00 | 2.33 ± 0.58 | 2.00 ± 1.00 | 2.00 ± 1.00 | 1.67 ± 0.58 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 2.33 ± 0.58 | 1.33 ± 0.58 | 1.67 ± 0.58 |
| Volleyball | Male | 1.20 ± 0.45 | 3.40 ± 0.55 | 2.20 ± 0.45 | 1.40 ± 0.55 | 2.00 ± 1.00 | 1.80 ± 0.45 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 2.00 ± 1.00 | 2.00 ± 0.71 | 2.40 ± 0.55 |
| Other | Female | 1.14 ± 0.38 | 2.00 ± 1.00 | 2.00 ± 1.15 | 1.57 ± 1.13 | 1.57 ± 0.79 | 1.71 ± 0.76 | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 1.57 ± 0.79 | 1.29 ± 0.49 | 1.71 ± 0.76 |
| Other | Male | 1.75 ± 0.79 | 2.46 ± 1.10 | 2.00 ± 0.78 | 1.79 ± 0.83 | 2.38 ± 1.01 | 1.75 ± 0.74 | 1.62 ± 0.71 | 1.88 ± 0.68 | 1.62 ± 0.77 | 1.92 ± 0.78 |
| Predictor * | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% CI (Lower–Upper) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 13.59 | 1.00–237.83 | 0.0595 |
| Age (per year) | 1.05 | 1.01–1.09 | 0.0551 |
| Male (vs. Female) | 2.04 | 0.45–8.66 | 0.3376 |
| Futsal (vs. Football) | 0.67 | 0.21–2.15 | 0.4953 |
| Rugby (vs. Football) | 0.51 | 0.12–2.21 | 0.3628 |
| Volleyball (vs. Football) | 2.45 | 1.09–5.48 | 0.031 |
| Other sports (vs. Football) | 1.74 | 0.54–5.91 | 0.36 |
| Eye–hand coordination | 0.84 | 0.45–1.57 | 0.5916 |
| Reaction time | 0.35 | 0.10–1.09 | 0.0778 |
| Anticipation | 1.46 | 0.52–4.42 | 0.4838 |
| Visual memory | 1.41 | 0.60–3.42 | 0.4375 |
| Visual attention | 0.8 | 0.43–1.52 | 0.4895 |
| Visual concentration | 0.54 | 0.32–0.89 | 0.0226 |
| Peripheral vision | 1.2 | 0.53–2.72 | 0.6629 |
| Visual reaction speed | 0.71 | 0.33–1.53 | 0.3829 |
| Visual acuity | 0.81 | 0.42–1.55 | 0.5246 |
| Visual tracking | 0.9 | 0.49–1.67 | 0.7397 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinez-Perez, C.; Nascimento, H.; Roque, A.; on behalf of the Sports Vision High-Performance Research Group. Awareness, Perceived Importance and Implementation of Sports Vision Training. Sports 2025, 13, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13100353
Martinez-Perez C, Nascimento H, Roque A, on behalf of the Sports Vision High-Performance Research Group. Awareness, Perceived Importance and Implementation of Sports Vision Training. Sports. 2025; 13(10):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13100353
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinez-Perez, Clara, Henrique Nascimento, Ana Roque, and on behalf of the Sports Vision High-Performance Research Group. 2025. "Awareness, Perceived Importance and Implementation of Sports Vision Training" Sports 13, no. 10: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13100353
APA StyleMartinez-Perez, C., Nascimento, H., Roque, A., & on behalf of the Sports Vision High-Performance Research Group. (2025). Awareness, Perceived Importance and Implementation of Sports Vision Training. Sports, 13(10), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13100353







