Short-Term L-Citrulline Supplementation Does Not Affect Blood Pressure, Pulse Wave Reflection, or Arterial Stiffness at Rest and during Isometric Exercise in Older Males
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Anthropometry
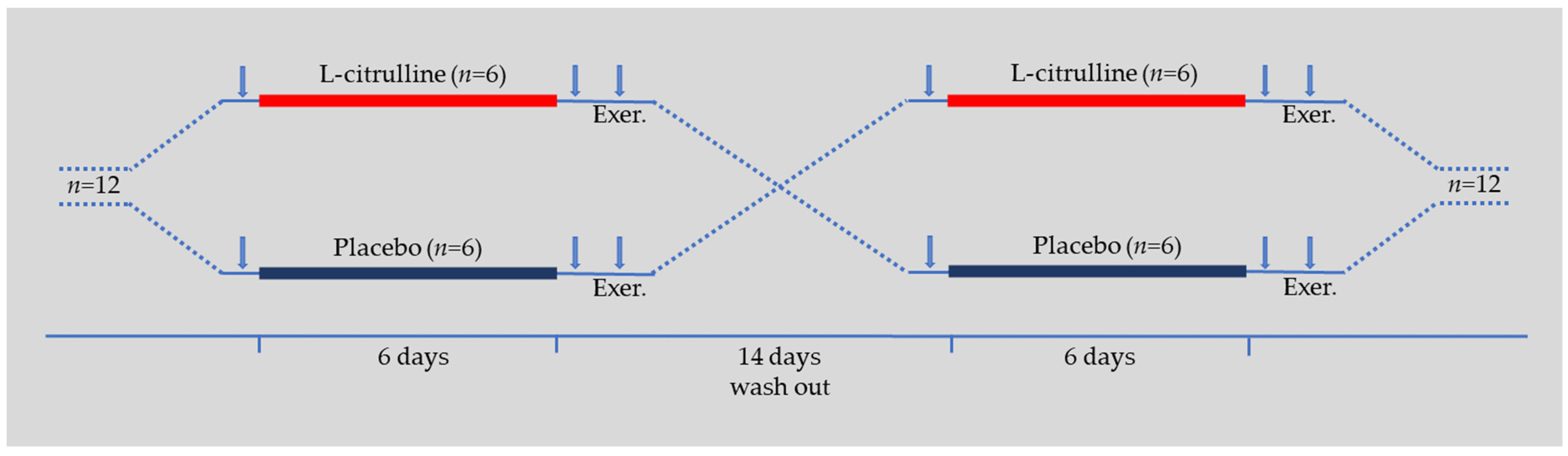
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Hemodynamics
2.5. Arterial Pressure Waveform Analysis and Pulse Wave Velocity
2.6. Isometric Knee Extensor Exercise
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
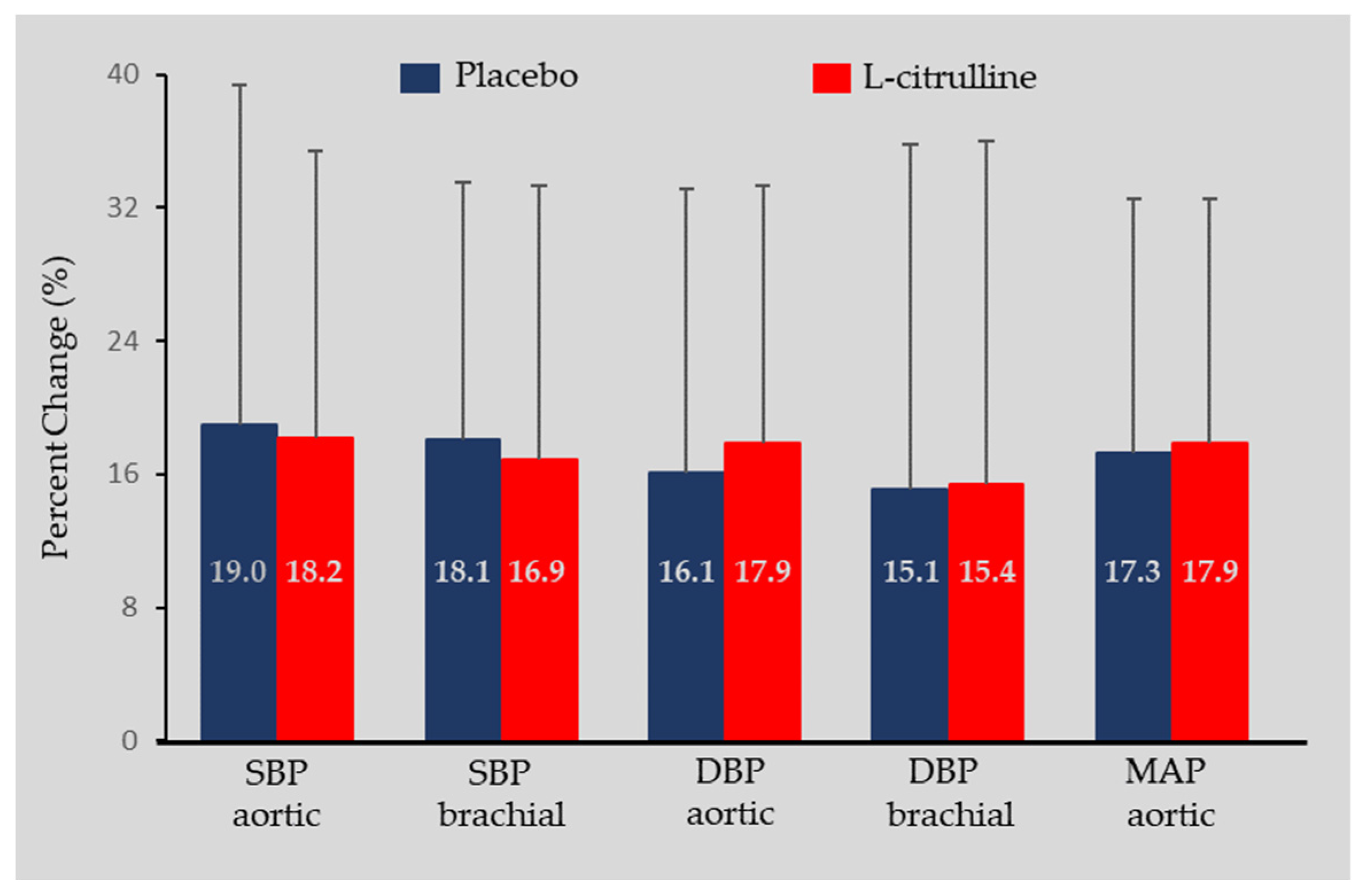
3.1. Hemodynamics
3.2. Arterial Pressure Waveform Analysis and Pulse Wave Velocity
4. Discussion
4.1. L-Citrulline and Blood Pressure
4.2. L-Citrulline and Arterial Stiffness
4.3. L-Citrulline and Aortic Pulse Wave Reflection
4.4. Limitations
4.5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaess, B.M.; Rong, J.; Larson, M.G.; Hamburg, N.M.; Vita, J.A.; Levy, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Vasan, R.S.; Mitchell, G.F. Aortic stiffness, blood pressure progression, and incident hypertension. JAMA 2012, 308, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.F. Arterial stiffness and hypertension: Chicken or egg? Hypertension 2014, 64, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safar, M.E.; Asmar, R.; Benetos, A.; Blacher, J.; Boutouyrie, P.; Lacolley, P.; Laurent, S.; London, G.; Pannier, B.; Protogerou, A.; et al. Interaction Between Hypertension and Arterial Stiffness. Hypertension 2018, 72, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancia, G.; Bombelli, M.; Facchetti, R.; Madotto, F.; Corrao, G.; Trevano, F.Q.; Grassi, G.; Sega, R. Long-term prognostic value of blood pressure variability in the general population: Results of the Pressioni Arteriose Monitorate e Loro Associazioni Study. Hypertension 2007, 49, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willum-Hansen, T.; Staessen, J.A.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Rasmussen, S.; Thijs, L.; Ibsen, H.; Jeppesen, J. Prognostic value of aortic pulse wave velocity as index of arterial stiffness in the general population. Circulation 2006, 113, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Nitric oxide signaling in health and disease. Cell 2022, 185, 2853–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousoulis, D.; Kampoli, A.M.; Tentolouris, C.; Papageorgiou, N.; Stefanadis, C. The role of nitric oxide on endothelial function. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 10, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamler, J.S.; Meissner, G. Physiology of nitric oxide in skeletal muscle. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzinikolaou, P.N.; Margaritelis, N.V.; Chatzinikolaou, A.N.; Paschalis, V.; Theodorou, A.A.; Vrabas, I.S.; Kyparos, A.; Nikolaidis, M.G. Oxygen Transport. A Redox O2dyssey. In Oxidative Eustress in Exercise Physiology; Cobley, J.N., Davison, G.W., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Margaritelis, N.V.; Paschalis, V.; Theodorou, A.A.; Kyparos, A.; Nikolaidis, M.G. Antioxidants in Personalized Nutrition and Exercise. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejero, J.; Shiva, S.; Gladwin, M.T. Sources of Vascular Nitric Oxide and Reactive Oxygen Species and Their Regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 311–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.M., Jr. Enzymes of arginine metabolism. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2743S–2747S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bescos, R.; Sureda, A.; Tur, J.A.; Pons, A. The effect of nitric-oxide-related supplements on human performance. Sports Med. 2012, 42, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerksick, C.M.; Wilborn, C.D.; Roberts, M.D.; Smith-Ryan, A.; Kleiner, S.M.; Jager, R.; Collins, R.; Cooke, M.; Davis, J.N.; Galvan, E.; et al. ISSN exercise & sports nutrition review update: Research & recommendations. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, H.; Zhang, J.; Yi, J.; Niu, Y.; Xi, H.; Peng, X.; Guo, L. Effect of inorganic nitrate supplementation on blood pressure in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nitric Oxide 2021, 113–114, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.K.; Patterson, A.J.; MacDonald-Wicks, L.K.; Oldmeadow, C.; McEvoy, M.A. The role of inorganic nitrate and nitrite in cardiovascular disease risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of human evidence. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 348–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allerton, T.D.; Proctor, D.N.; Stephens, J.M.; Dugas, T.R.; Spielmann, G.; Irving, B.A. l-Citrulline Supplementation: Impact on Cardiometabolic Health. Nutrients 2018, 10, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Poll, M.C.; Siroen, M.P.; van Leeuwen, P.A.; Soeters, P.B.; Melis, G.C.; Boelens, P.G.; Deutz, N.E.; Dejong, C.H. Interorgan amino acid exchange in humans: Consequences for arginine and citrulline metabolism. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwedhelm, E.; Maas, R.; Freese, R.; Jung, D.; Lukacs, Z.; Jambrecina, A.; Spickler, W.; Schulze, F.; Boger, R.H. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of oral L-citrulline and L-arginine: Impact on nitric oxide metabolism. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 65, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moinard, C.; Maccario, J.; Walrand, S.; Lasserre, V.; Marc, J.; Boirie, Y.; Cynober, L. Arginine behaviour after arginine or citrulline administration in older subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windmueller, H.G.; Spaeth, A.E. Source and fate of circulating citrulline. Am. J. Physiol. 1981, 241, E473–E480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguayo, E.; Martínez-Sánchez, A.; Fernández-Lobato, B.; Alacid, F. L-Citrulline: A Non-Essential Amino Acid with Important Roles in Human Health. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharaj, A.; Fischer, S.M.; Dillon, K.N.; Kang, Y.; Martinez, M.A.; Figueroa, A. Effects of L-Citrulline Supplementation on Endothelial Function and Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Postmenopausal Women. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Koutnik, A.P.; Ramirez, K.; Wong, A.; Figueroa, A. The effects of short term L-citrulline supplementation on wave reflection responses to cold exposure with concurrent isometric exercise. Am. J. Hypertens. 2013, 26, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.; Alvarez-Alvarado, S.; Jaime, S.J.; Kinsey, A.W.; Spicer, M.T.; Madzima, T.A.; Figueroa, A. Combined whole-body vibration training and l-citrulline supplementation improves pressure wave reflection in obese postmenopausal women. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Chernykh, O.; Figueroa, A. Chronic l-citrulline supplementation improves cardiac sympathovagal balance in obese postmenopausal women: A preliminary report. Auton. Neurosci. 2016, 198, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.H.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, W.G.; Figueroa, A.; Chen, L.H.; Qin, L.Q. Effect of oral L-citrulline on brachial and aortic blood pressure defined by resting status: Evidence from randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chant, B.; Bakali, M.; Hinton, T.; Burchell, A.E.; Nightingale, A.K.; Paton, J.F.R.; Hart, E.C. Antihypertensive Treatment Fails to Control Blood Pressure During Exercise. Hypertension 2018, 72, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.P.; Young, C.N.; Fadel, P.J. Autonomic adjustments to exercise in humans. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 475–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerome, L.S.; Milliken, L.A.; Blew, R.M.; Lohman, T. Body Composition Field Methods. In ACSM’s Body Composition Assessment; Lohman, T., Milliken, L., Eds.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2020; pp. 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Siri, W.E. Body composition from fluid spaces and density: Analysis of methods. 1961. Nutrition 1993, 9, 480–491. [Google Scholar]
- Butlin, M.; Qasem, A. Large Artery Stiffness Assessment Using SphygmoCor Technology. Pulse 2017, 4, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, A.W.; Thomas, M.W.; Bohannon, R.W. Normative values for isometric muscle force measurements obtained with hand-held dynamometers. Phys. Ther. 1996, 76, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilou, G.; Ladakis, I.; Mavroidi, C.; Kilintzis, V.; Mirachtsis, T.; Chouvarda, I.; Kouidi, E. The Effects of a Visual Stimuli Training Program on Reaction Time, Cognitive Function, and Fitness in Young Soccer Players. Sensors 2022, 22, 6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltzopoulos, V.; Gleeson, N.P. Skeletal muscle function. In Kinanthropometry and Exercise Physiology Laboratory Manual: Tests, Procedures and Data; Eston, R., Reilly, T., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 12–29. [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysant, S.G.; Chrysant, G.S. The age-related hemodynamic changes of blood pressure and their impact on the incidence of cardiovascular disease and stroke: New evidence. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2014, 16, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, E. Blood pressure and ageing. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, M.; Hayashi, T.; Morita, M.; Ina, K.; Maeda, M.; Watanabe, F.; Morishita, K. Short-term effects of L-citrulline supplementation on arterial stiffness in middle-aged men. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 155, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, A.A.; Chatzinikolaou, P.N.; Margaritelis, N.V.; Christodoulou, F.; Tsatalas, T.; Paschalis, V. Short-Term L-Citrulline Supplementation Does Not Affect Inspiratory Muscle Oxygenation and Respiratory Performance in Older Adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, A.A.; Zinelis, P.T.; Malliou, V.J.; Chatzinikolaou, P.N.; Margaritelis, N.V.; Mandalidis, D.; Geladas, N.D.; Paschalis, V. Acute L-Citrulline Supplementation Increases Nitric Oxide Bioavailability but Not Inspiratory Muscle Oxygenation and Respiratory Performance. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, D.; Kruger, M.; Wehland, M.; Infanger, M.; Grimm, D. The Effects of Oral l-Arginine and l-Citrulline Supplementation on Blood Pressure. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, A.; Alvarez-Alvarado, S.; Ormsbee, M.J.; Madzima, T.A.; Campbell, J.C.; Wong, A. Impact of L-citrulline supplementation and whole-body vibration training on arterial stiffness and leg muscle function in obese postmenopausal women with high blood pressure. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 63, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, A.; Trivino, J.A.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Vicil, F. Oral L-citrulline supplementation attenuates blood pressure response to cold pressor test in young men. Am. J. Hypertens. 2010, 23, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaime, S.J.; Nagel, J.; Maharaj, A.; Fischer, S.M.; Schwab, E.; Martinson, C.; Radtke, K.; Mikat, R.P.; Figueroa, A. L-Citrulline supplementation attenuates aortic pulse pressure and wave reflection responses to cold stress in older adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 159, 111685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, J.; Kim, Y.; Gonzales, J.U. Impact of l-citrulline supplementation on oxygen uptake kinetics during walking. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 43, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, S.; Ichihara, A. Late age at menopause positively associated with obesity-mediated hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2023, 46, 1163–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, A.; Alvarez-Alvarado, S.; Jaime, S.J.; Kalfon, R. l-Citrulline supplementation attenuates blood pressure, wave reflection and arterial stiffness responses to metaboreflex and cold stress in overweight men. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, E.J. The Influence of Obesity and Metabolic Health on Vascular Health. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.D.; Gona, P.; Larson, M.G.; Plehn, J.F.; Benjamin, E.J.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Wang, T.J. Exercise blood pressure and the risk of incident cardiovascular disease (from the Framingham Heart Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, J.U.; Raymond, A.; Ashley, J.; Kim, Y. Does l-citrulline supplementation improve exercise blood flow in older adults? Exp. Physiol. 2017, 102, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashina, A.; Tomiyama, H.; Arai, T.; Hirose, K.; Koji, Y.; Hirayama, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hori, S. Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity as a marker of atherosclerotic vascular damage and cardiovascular risk. Hypertens. Res. 2003, 26, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, A.; Wong, A.; Jaime, S.J.; Gonzales, J.U. Influence of L-citrulline and watermelon supplementation on vascular function and exercise performance. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, D.G.; Mastin, C.R.; Kenefick, R.W. Wave reflection and central aortic pressure are increased in response to static and dynamic muscle contraction at comparable workloads. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, J.M.; Chouramanis, N.V.; Chirinos, J.A.; Edwards, D.G. Dynamic and isometric handgrip exercise increases wave reflection in healthy young adults. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 129, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, P.J.; Currie, G.; Delles, C. Sex Differences in the Prevalence, Outcomes and Management of Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2022, 24, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reckelhoff, J.F. Mechanisms of sex and gender differences in hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2023, 37, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanhewicz, A.E.; Wenner, M.M.; Stachenfeld, N.S. Sex differences in endothelial function important to vascular health and overall cardiovascular disease risk across the lifespan. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H1569–H1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, A.; Maharaj, A.; Kang, Y.; Dillon, K.N.; Martinez, M.A.; Morita, M.; Nogimura, D.; Fischer, S.M. Combined Citrulline and Glutathione Supplementation Improves Endothelial Function and Blood Pressure Reactivity in Postmenopausal Women. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n = 12 | |
|---|---|
| Age (y) | 64.3 ± 5.1 |
| Height (cm) | 173.9 ± 4.2 |
| Weight (kg) | 78.4 ± 6.9 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.0 ± 2.7 |
| Body fat (%) | 26.8 ± 2.6 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 100 ± 5.6 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 105.8 ± 6.8 |
| Waist-to-hip ratio | 0.95 ± 0.02 |
| Post Supplementation | During Exercise | Interactions and Main Effects | Partial Eta-Squared | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | C × T | C | T | C × T | C | T | |||
| Heart rate (bpm) | |||||||||
| Placebo | 64.1 ± 6.3 | 64.0 ± 7.9 | 76.8 ± 11.5 | p = 0.631 | p = 0.963 | p < 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.126 |
| L-citrulline | 63.5 ± 5.9 | 63.7 ± 6.1 | 78.1 ± 9.0 | ||||||
| Aortic SBP (mmHg) | |||||||||
| Placebo | 121.9 ± 13.3 | 121.2 ± 12.7 | 142.5 ± 17.4 | p = 0.899 | p = 0.822 | p < 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.538 |
| L-citrulline | 120.0 ± 11.5 | 121.1 ± 11.3 | 141.8 ± 14.4 | ||||||
| Brachial SBP (mmHg) | |||||||||
| Placebo | 130.8 ± 13.2 | 129.4 ± 12.6 | 152.5 ± 21.6 | p = 0.553 | p = 0.788 | p < 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.563 |
| L-citrulline | 131.5 ± 12.6 | 130.1 ± 14.5 | 151.8 ± 23.8 | ||||||
| Aortic DBP (mmHg) | |||||||||
| Placebo | 83.3 ± 6.1 | 84.1 ± 6.5 | 97.5 ± 14.8 | p = 0.919 | p = 0.608 | p < 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.012 | 0.527 |
| L-citrulline | 82.1 ± 5.9 | 81.9 ± 7.2 | 96.3 ± 9.0 | ||||||
| Brachial DBP (mmHg) | |||||||||
| Placebo | 83.4 ± 6.0 | 84.2 ± 7.9 | 97.3 ± 21.5 | p = 0.808 | p = 0.652 | p < 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.009 | 0.379 |
| L-citrulline | 82.8 ± 7.6 | 82.1 ± 6.5 | 94.6 ± 17.1 | ||||||
| Aortic MAP (mmHg) | |||||||||
| Placebo | 99.2 ± 8.0 | 99.4 ± 8.2 | 116.0 ± 13.0 | p = 0.962 | p = 0.660 | p < 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.009 | 0.618 |
| L-citrulline | 97.7 ± 6.6 | 98.1 ± 7.2 | 115.1 ± 12.6 | ||||||
| Aortic PP (mmHg) | |||||||||
| Placebo | 38.6 ± 11.4 | 37.1 ± 10.7 | 45.01 ± 18.7 | p = 0.856 | p = 0.876 | p = 0.071 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.126 |
| L-citrulline | 37.9 ± 11.5 | 39.2 ± 11.4 | 45.5 ± 12.0 | ||||||
| Post Supplementation | During Exercise | Interactions and Main Effects | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | C × T | C | T | |||
| Augmented pressure (mmHg) | ||||||
| Placebo | 10.8 ± 4.4 | 11.0 ± 4.4 | 11.3 ± 5.7 | p = 0.537 | p = 0.730 | p = 0.286 |
| L-citrulline | 11.1 ± 4.4 | 11.2 ± 4.0 | 12.8 ± 6.8 | |||
| Augmentation index (%) | ||||||
| Placebo | 31.9 ± 20.3 | 32.9 ± 19.4 | 37.2 ± 16.2 | p = 0.729 | p = 0.965 | p = 0.796 |
| L-citrulline | 35.7 ± 17.5 | 31.6 ± 14.6 | 33.5 ± 17.6 | |||
| Augmentation index @75 (%) | ||||||
| Placebo | 26.7 ± 20.5 | 27.6 ± 20.8 | 38.0 ± 35.4 | p = 0.767 | p = 0.249 | p = 0.969 |
| L-citrulline | 30.2 ± 25.4 | 26.1 ± 14.6 | 35.0 ± 26.4 | |||
| Forward wave pressure (mmHg) | ||||||
| Placebo | 43.3 ± 5.6 | 31.9 ± 5.1 | 32.7 ± 4.8 | p = 0.896 | p = 0.816 | p = 0.503 |
| L-citrulline | 31.5 ± 4.5 | 31.6 ± 5.6 | 32.4 ± 6.1 | |||
| Backward wave pressure (mmHg) | ||||||
| Placebo | 17.2 ± 4.0 | 17.5 ± 4.2 | 17.8 ± 4.4 | p = 0.769 | p = 0.659 | p = 0.631 |
| L-citrulline | 16.8 ± 5.3 | 16.5 ± 3.2 | 17.0 ± 4.2 | |||
| C-f pulse wave velocity (m/s) | ||||||
| Placebo | 7.3 ± 1.7 | 7.1 ± 1.4 | p = 0.251 | p = 0.251 | p = 0.666 | |
| L-citrulline | 7.7 ± 1.8 | 7.7 ± 1.8 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tryfonos, A.; Christodoulou, F.; Pamboris, G.M.; Christodoulides, S.; Theodorou, A.A. Short-Term L-Citrulline Supplementation Does Not Affect Blood Pressure, Pulse Wave Reflection, or Arterial Stiffness at Rest and during Isometric Exercise in Older Males. Sports 2023, 11, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11090177
Tryfonos A, Christodoulou F, Pamboris GM, Christodoulides S, Theodorou AA. Short-Term L-Citrulline Supplementation Does Not Affect Blood Pressure, Pulse Wave Reflection, or Arterial Stiffness at Rest and during Isometric Exercise in Older Males. Sports. 2023; 11(9):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11090177
Chicago/Turabian StyleTryfonos, Andrea, Filippos Christodoulou, George M. Pamboris, Stephanos Christodoulides, and Anastasios A. Theodorou. 2023. "Short-Term L-Citrulline Supplementation Does Not Affect Blood Pressure, Pulse Wave Reflection, or Arterial Stiffness at Rest and during Isometric Exercise in Older Males" Sports 11, no. 9: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11090177
APA StyleTryfonos, A., Christodoulou, F., Pamboris, G. M., Christodoulides, S., & Theodorou, A. A. (2023). Short-Term L-Citrulline Supplementation Does Not Affect Blood Pressure, Pulse Wave Reflection, or Arterial Stiffness at Rest and during Isometric Exercise in Older Males. Sports, 11(9), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11090177









