Effect of Physical Activity on Metabolic Syndrome Markers in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Types of Studies Included
2.2. Data Sources and Search Strategy
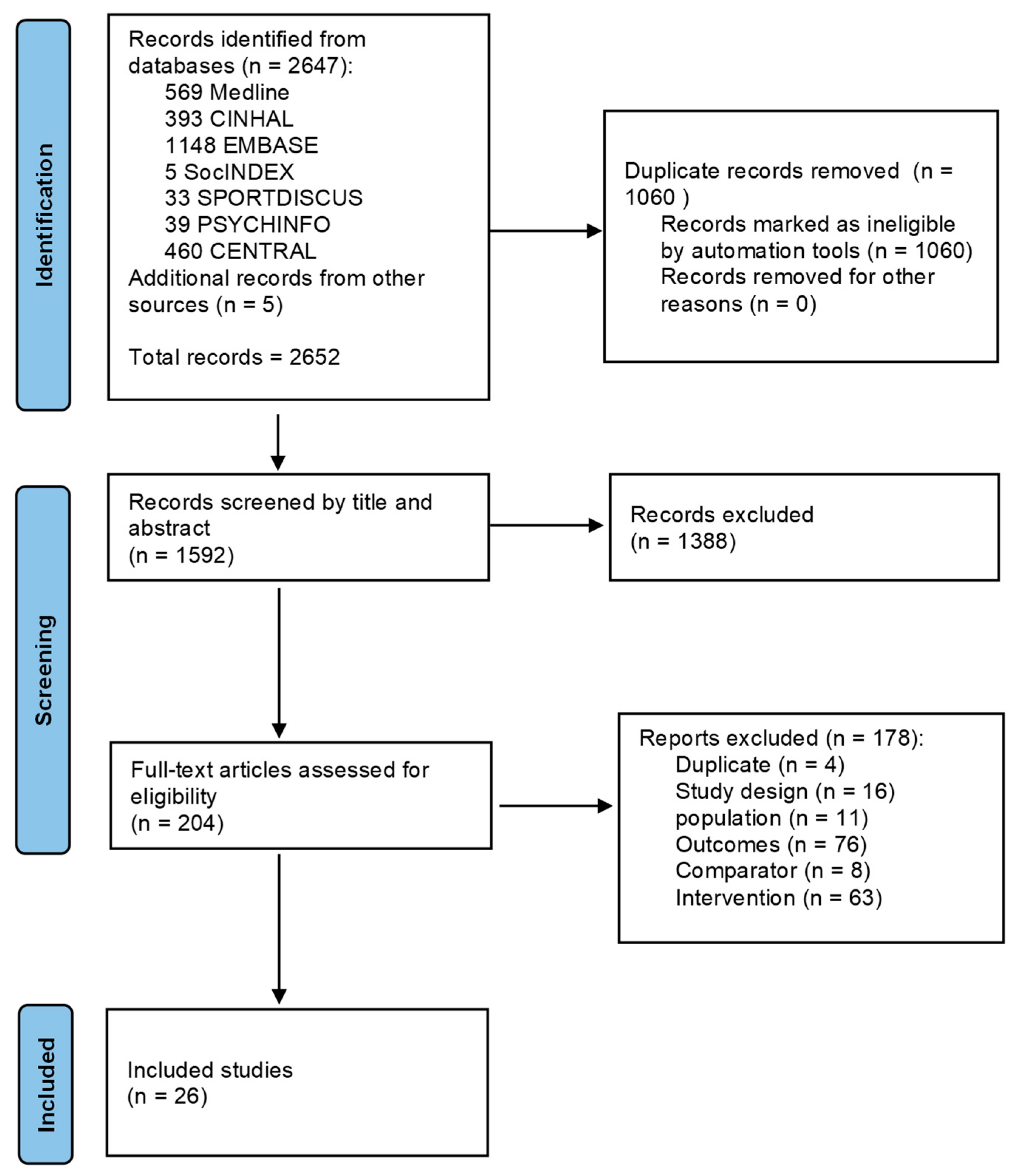
2.3. Data Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.6. Data Synthesis Strategy
3. Results
3.1. Interventions
3.2. Method Quality
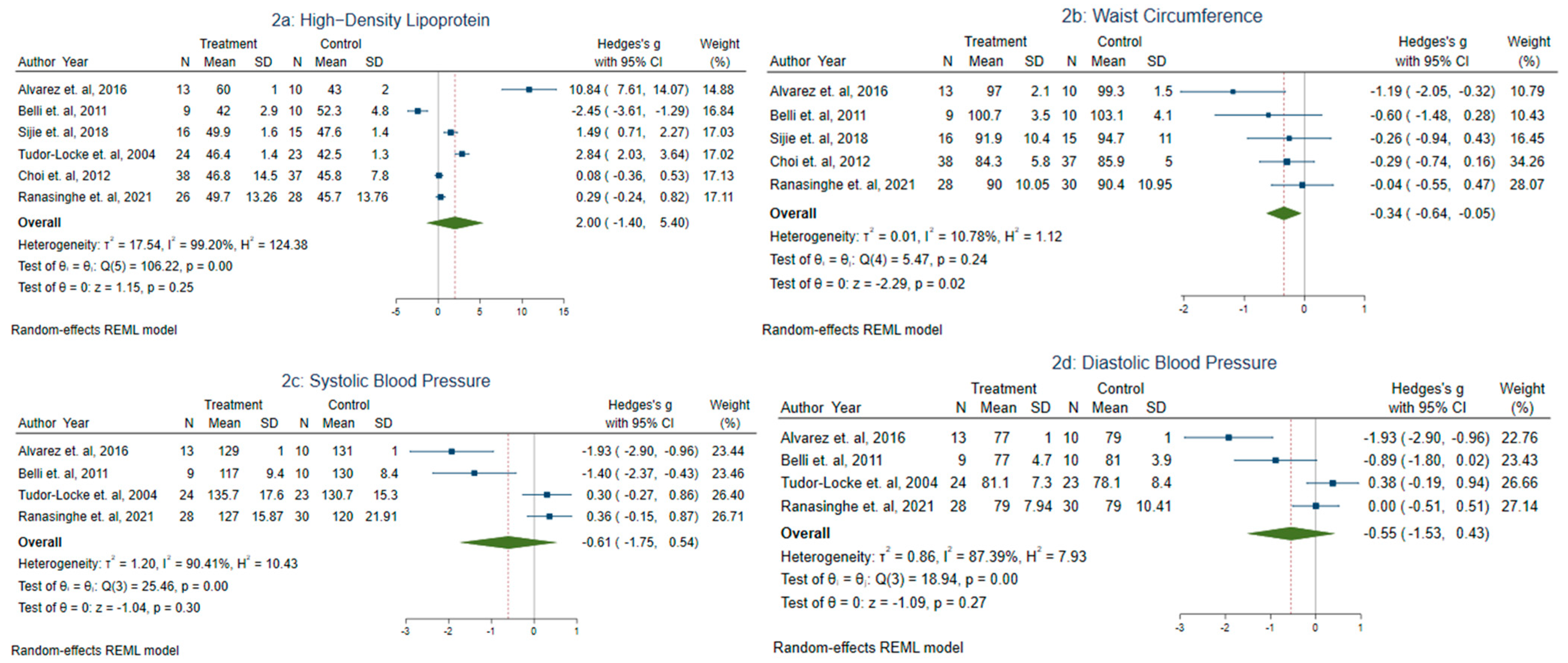
3.3. Meta-Analysis
3.3.1. Effect of Aerobic Training on Metabolic Syndrome Markers
3.3.2. Effect of Resistance Training on Metabolic Syndrome Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IDF IDF DIABETES ATLAS, Eighth Edition 2017. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/resources/2017-atlas.html (accessed on 2 October 2019).
- Ogurtsova, K.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Makaroff, L.E. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayfron-Benjamin, C.; van den Born, B.J.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H.; Amoah, A.G.B.; Meeks, K.A.C.; Klipstein-Grobusch, K.; Bahendeka, S.; Spranger, J.; Danquah, I.; Mockenhaupt, F.; et al. Microvascular and macrovascular complications in type 2 diabetes Ghanaian residents in Ghana and Europe: The RODAM study. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2019, 33, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ma, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Mo, Y.; Ying, L.; Lu, W.; Zhu, W.; Bao, Y.; Vigersky, R.A.; et al. Association of Time in Range, as Assessed by Continuous Glucose Monitoring, With Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2370–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Sun, F.; Zhan, S. The associations of metabolic syndrome with incident hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease: A cohort study. Endocrine 2018, 60, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, A.M.; Rasyid, H.; Bakri, S.; Patellongi, I.J. The Association Between Parents History of Type 2 Diabetes with Metabolic Syndrome Component and Insulin Resistance in Non-Diabetic Young Adult Male. Acta Med. Indones. 2018, 50, 309–313. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, S.-M.; Shih, H.-M.; Chien, M.-N.; Liu, S.-C.; Wang, C.-H.; Lee, C.-C. Risk factors in metabolic syndrome predict the progression of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 153, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M. Metabolic Syndrome; Agreement between Metabolic Syndrome Diagnostic Criteria among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Prof. Med. J. 2017, 24, 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Slagter, S.N.; van Vliet-Ostaptchouk, J.V.; van Beek, A.P.; Keers, J.C.; Lutgers, H.L.; van der Klauw, M.M.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H.R. Health-Related quality of life in relation to obesity grade, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome and inflammation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cholesterol Education Program (US). Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation 2002, 106, 3143–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biadgo, B.; Melak, T.; Ambachew, S.; Baynes, H.W.; Limenih, M.A.; Jaleta, K.N.; Tachebele, B.; Melku, M.; Abebe, M. The Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients at a Tertiary Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2018, 28, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, M.A.; Hammad, K.; Bagdadi, K. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and its components among type 2 diabetic mellitus Syrian patients according to NCEP-ATP III and IDF diagnostic criteria. Anthropol. Rev. 2019, 82, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bilbeisi, A.H.; Hosseini, S.; Djafarian, K. The association between physical activity and the metabolic syndrome among type 2 diabetes patients in Gaza Strip, Palestine. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2017, 27, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyemang-Yeboah, F.; Eghan, B.A.J.; Annani-Akollor, M.E.; Togbe, E.; Donkor, S.; Oppong Afranie, B. Evaluation of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Associated Risk Factors in Type 2 Diabetes: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study at the Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital, Kumasi, Ghana. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4562904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missud, D.C.; Parot-Schinkel, E.; Connan, L.; Vielle, B.; Huez, J.F. Physical activity prescription for general practice patients with cardiovascular risk factors-the PEPPER randomised controlled trial protocol. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-L. The Effectiveness of a Lifestyle-Based Intervention on Physical Activity, Blood Pressure, and Health-Related Quality of Life in Older Adults with Hypertension. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of North Carolina at Greensboro, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Balducci, S.; Conti, F.; Cardelli, P.; Vitale, M.; Bollanti, L.; Pugliese, G.; Haxhi, J.; Rapisarda, G.; D’Errico, V.; Sacchetti, M.; et al. Study to Weigh the Effect of Exercise Training on BONE quality and strength (SWEET BONE) in type 2 diabetes: Study protocol for a randomised clinical trial. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashino, Y.; Jackson, J.L.; Fukumori, N.; Nakamura, F.; Fukuhara, S. Effects of supervised exercise on lipid profiles and blood pressure control in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 98, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bauman, A.E.; Reis, R.S.; Sallis, J.F.; Wells, J.C.; Loos, R.J.F.; Martin, B.W. Correlates of physical activity: Why are some people physically active and others not? Lancet 2012, 380, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The EndNote Team. EndNote X9; Clarivate Analytics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, C.G.; Sherrington, C.; Herbert, R.D.; Moseley, A.M.; Elkins, M. Reliability of the PEDro Scale for Rating Quality of Randomized Controlled Trials. Phys. Ther. 2003, 83, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huedo-Medina, T.B.; Sánchez-Meca, J.; Marín-Martínez, F.; Botella, J. Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I2 index? Psychol. Methods 2006, 11, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.; Arora, E.; Jaspal, S. Effects of progressive resistance training and aerobic exercise on type 2 diabetics in Indian population. Int. J. Diabetes Metab. 2009, 17, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Fang, H.; Xia, Q.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, P.; Yan, Y.; Yao, B.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Health literacy and exercise-focused interventions on clinical measurements in Chinese diabetes patients: A cluster randomized controlled trial. EClinicalMedicine 2019, 17, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotnikoff, R.C.; Eves, N.; Jung, M.; Sigal, R.J.; Padwal, R.; Karunamuni, N. Multicomponent, home-based resistance training for obese adults with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudor-Locke, C.; Bell, R.C.; Myers, A.M.; Harris, S.B.; Ecclestone, N.A.; Lauzon, N.; Rodger, N.W. Controlled outcome evaluation of the First Step Program: A daily physical activity intervention for individuals with type II diabetes. Int. J. Obes. 2004, 28, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.M.; Han, K.A.; Ahn, H.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Hong, H.C.; Choi, H.Y.; Yang, S.J.; Yoo, H.J.; Baik, S.H.; Choi, D.S.; et al. Effects of exercise on sRAGE levels and cardiometabolic risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3751–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.; Dennis, S.M.; Diamond, T.H.; Zwar, N. Improving glycaemic and BP control in type 2 diabetes. The effectiveness of tai chi. Aust. Fam. Physician 2008, 37, 884–887. [Google Scholar]
- Sigal, R.J.; Kenny, G.P.; Boulé, N.G.; Wells, G.A.; Prud’homme, D.; Fortier, M.; Reid, R.D.; Tulloch, H.; Coyle, D.; Phillips, P.; et al. Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 147, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agurs-Collins, T.D.; Kumanyika, S.K.; Ten Have, T.R.; Adams-Campbell, L.L. A randomized controlled trial of weight reduction and exercise for diabetes management in older African-American subjects. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, C.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Martinez-Salazar, C.; Mancilla, R.; Flores-Opazo, M.; Cano-Montoya, J.; Ciolac, E.G. Low-Volume High-Intensity Interval Training as a Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Sport. Med. 2016, 37, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huimin, Y.; Prista, A.; Ranadive, S.M.; Damasceno, A.; Caupers, P.; Kanaley, J.A.; Fernhall, B. Effect of Aerobic Training on Glucose Control and Blood Pressure in T2DDM East African Males. ISRN Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 864897. [Google Scholar]
- Emerenziani, G.P.; Gallotta, M.C.; Meucci, M.; Di Luigi, L.; Migliaccio, S.; Donini, L.M.; Strollo, F.; Guidetti, L. Effects of aerobic exercise based upon heart rate at aerobic threshold in obese elderly subjects with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 695297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balducci, S.; Zanuso, S.; Nicolucci, A.; de Feo, P.; Cavallo, S.; Cardelli, P.; Fallucca, S.; Alessi, E.; Fallucca, F.; Pugliese, G. Effect of an intensive exercise intervention strategy on modifiable cardiovascular risk factors in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial: The Italian Diabetes and Exercise Study (IDES). Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 1794–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, S.; van Laethem, C.; van Acker, K.; Calders, P. Influence of combined exercise training on indices of obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes patients. Clin. Rehabil. 2008, 22, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, A.; Najafipoor, F.; Aliasgarzadeh, A.; Niafar, M.; Mobasseri, M. Effect of Aerobic Exercise, Resistance Training or Combined Training on Glycaemic Control and Cardio-Vascular Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Biol. Sport 2012, 29, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Du, P.; Zhao, W.; Pang, J.; Wang, J. Exercise Training at Maximal Fat Oxidation Intensity for Older Women with Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Sport. Med. 2018, 39, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantakumari, N.; Sequeira, S.; El Deeb, R. Effects of a yoga intervention on lipid profiles of diabetes patients with dyslipidemia. Indian Heart J. 2013, 65, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, C.; Devage, S.; Constantine, G.R.; Katulanda, P.; Hills, A.P.; King, N.A. Glycemic and cardiometabolic effects of exercise in South Asian Sri Lankans with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial Sri Lanka diabetes aerobic and resistance training study (SL-DARTS). Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2021, 15, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.L.; Tseng, C.H.; Tseng, Y.J.; Yang, W.S. Resistance Training Improves Muscle Function and Cardiometabolic Risks But Not Quality of Life in Older People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2018, 41, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangping, Z.; Xiaona, Q.; Qi, Z.; Qingchun, L.; Na, Y.; Lijin, J.; Siying, L.; Shuo, Z.; Xiaoming, Z.; Xiaoxia, L.; et al. The impact on glycemic control through progressive resistance training with bioDensityTM in Chinese elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: The PReTTy2 (Progressive Resistance Training in Type 2 Diabetes) Trial. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 150, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancea, D.M.M.; Vancea, J.N.; Pires, M.I.F.; Reis, M.A.; Moura, R.B.; Dib, S.A. Effect of frequency of physical exercise on glycemic control and body composition in type 2 diabetic patients. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2009, 92, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, L.; Morrison, E.Y.; McGrowder, D.A.; Young, R.; Garwood, D.; Zamora, E.; Alexander-Lindo, R.L.; Irving, R.; Perez Sanz, E.C. Changes in clinical and metabolic parameters after exercise therapy in patents with type 2 diabetes. Arch. Med. Sci. 2008, 4, 427–437. [Google Scholar]
- Belli, T.; Ribeiro, L.F.; Ackermann, M.A.; Baldissera, V.; Gobatto, C.A.; Galdino da Silva, R. Effects of 12-week overground walking training at ventilatory threshold velocity in type 2 diabetic women. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 93, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bassi, D.; Mendes, R.G.; Arakelian, V.M.; Caruso, F.C.R.; Cabiddu, R.; Júnior, J.C.B.; Arena, R.; Borghi-Silva, A. Potential Effects on Cardiorespiratory and Metabolic Status After a Concurrent Strength and Endurance Training Program in Diabetes Patients - a Randomized Controlled Trial. Sport. Med. Open 2016, 2, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conners, R.T.; Coons, J.M.; Fuller, D.K.; Morgan, D.W.; Caputo, J.L. Effects of underwater treadmill walk training on glycemic and metabolic control in adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2017, 66, A608. [Google Scholar]
- Church, T.S.; Blair, S.N.; Cocreham, S.; Johannsen, N.; Johnson, W.; Kramer, K.; Mikus, C.R.; Myers, V.; Nauta, M.; Rodarte, R.Q.; et al. Effects of aerobic and resistance training on hemoglobin A1c levels in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2010, 304, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, C.; Layne, J.E.; Munoz-Orians, L.; Gordon, P.L.; Walsmith, J.; Foldvari, M.; Roubenoff, R.; Tucker, K.L.; Nelson, M.E. A randomized controlled trial of resistance exercise training to improve glycemic control in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 2335–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, C.; Hills, A.P.; Constantine, G.R.; Finlayson, G.; Katulanda, P.; King, N.A. Study protocol: A randomised controlled trial of supervised resistance training versus aerobic training in Sri Lankan adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: SL-DART study. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, L.A.; Morrison, E.Y.; McGrowder, D.A.; Young, R.; Fraser, Y.T.P.; Zamora, E.; Alexander-Lindo, R.L.; Irving, R.R. Effect of exercise therapy on lipid profile and oxidative stress indicators in patients with type 2 diabetes. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2008, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattyn, N.; Cornelissen, V.; Eshghi, S.; Vanhees, L. The Effect of Exercise on the Cardiovascular Risk Factors Constituting the Metabolic Syndrome. Sport. Med. 2013, 43, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.; Genest, J. Effect of Obesity on High-density Lipoprotein Metabolism. Obesity 2007, 15, 2875–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J. Updated review on the benefits of weight loss. Int. J. Obes. 2002, 26, S25–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattilo, A.M.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Effects of weight reduction on blood lipids and lipoproteins: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 56, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macmohan, S.; Cutler, J.; Brittain, E.; Higgins, M. Obesity and hypertension: Epidemiological and clinical issues. Eur. Heart J. 1987, 8 (Suppl. B), 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Leon, A.S.; Wilmore, J.H.; Skinner, J.S.; Rao, D.C.; Rankinen, T.; Bouchard, C. Targeting the metabolic syndrome with exercise: Evidence from the HERITAGE Family Study. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2003, 35, 1703–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doewes, R.I.; Gharibian, G.; Zaman, B.A.; Akhavan-Sigari, R. An updated systematic review on the effects of aerobic exercise on human blood lipid profile. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2022, 48, 101108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashin, A.G.; Lee, H.; Bagg, M.K.; O’Hagan, E.; Traeger, A.C.; Kamper, S.J.; Folly, T.; Jones, M.D.; Booth, J.; McAuley, J.H. A systematic review highlights the need to improve the quality and applicability of trials of physical therapy interventions for low back pain. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2020, 126, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Author, Year | Specified Eligibility Criteria | Random Allocation | Allocation Concealed | Groups Similar | Blinding of All Subjects | Therapist Blinding | Assessor Blinding | Point Estimate Reported | <15% Dropout Rate | Intention-to-Treat Analysis | Group Difference Reported | Total PEDro Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agurs-Collins et al., 1997 [1] | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | 5 |
| Alvarez et al., 2016 [2] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | 🗸 | 7 |
| Balducci et al., 2010 [3] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | 8 |
| Bassi et al., 2016 [4] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | 8 |
| Belli et al., 2011 [5] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | - | 🗸 | - | - | 🗸 | 6 |
| Castaneda et al., 2002 [6] | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 7 |
| Choi et al., 2012 [7] | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | 6 |
| Church et al., 2010 [8] | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 9 |
| Conners et al., 2017 [9] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 7 |
| Emerenziani et al., 2015 [10] | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | 6 |
| Gordon et al., 2008 [11] | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 7 |
| Hangping et al., 2019 [12] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | 8 |
| Hsieh et al., 2018 [13] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 9 |
| Huimin et al., 2014 [14] | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 7 |
| Lam et al., 2008 [15] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | 🗸 | 7 |
| Lambers et al., 2008 [16] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 8 |
| Plotnikoff et al., 2010 [17] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 8 |
| Ranasinghe et al., 2021 [18] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 8 |
| Shantakumari et al., 2013 [19] | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 6 |
| Shenoy et al., 2009 [20] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | 7 |
| Sigal et al., 2007 [21] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 8 |
| Sijie et al., 2018 [22] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | 7 |
| Tudor-Locke et al., 2004 [23] | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | - | - | - | 🗸 | - | - | 🗸 | 5 |
| Vancea et al., 2009 [24] | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | 🗸 | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 7 |
| Wang et al., 2019 [25] | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | - | - | - | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 6 |
| Yavari et al., 2012 [26] | 🗸 | 🗸 | - | - | - | - | - | 🗸 | - | - | 🗸 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin, M.; Kerr, D.; Atiase, Y.; Aldwikat, R.K.; Driscoll, A. Effect of Physical Activity on Metabolic Syndrome Markers in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports 2023, 11, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11050101
Amin M, Kerr D, Atiase Y, Aldwikat RK, Driscoll A. Effect of Physical Activity on Metabolic Syndrome Markers in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports. 2023; 11(5):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11050101
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin, Mohammed, Debra Kerr, Yacoba Atiase, Rami Kamel Aldwikat, and Andrea Driscoll. 2023. "Effect of Physical Activity on Metabolic Syndrome Markers in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Sports 11, no. 5: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11050101
APA StyleAmin, M., Kerr, D., Atiase, Y., Aldwikat, R. K., & Driscoll, A. (2023). Effect of Physical Activity on Metabolic Syndrome Markers in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports, 11(5), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11050101






