m6A RNA Methylation in Psychiatric Disorders: An Emerging Epitranscriptomic Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
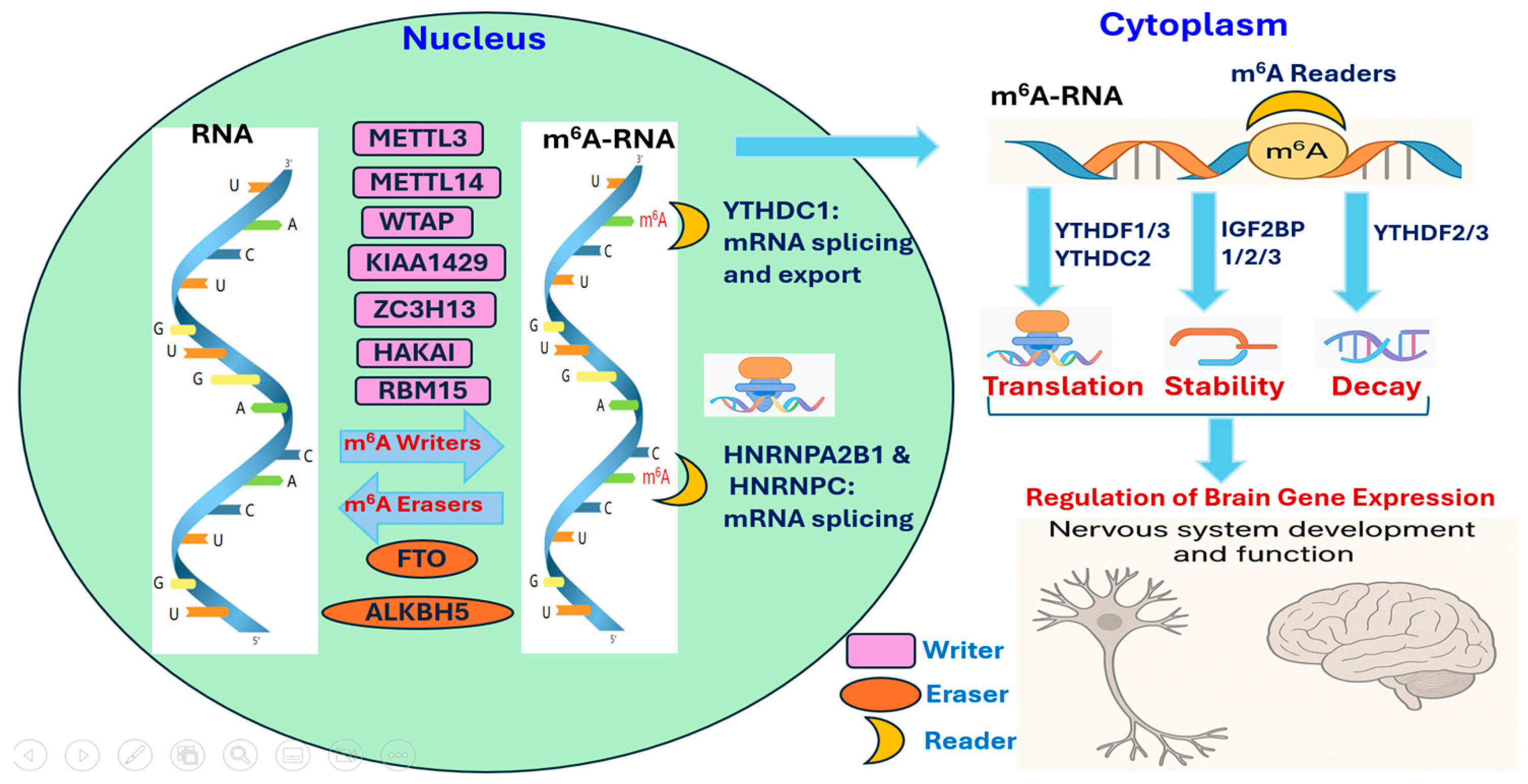
2. Mechanisms of RNA Methylation
2.1. Overview of m6A Machinery
2.2. RNA Methylation in mRNA Regulation
2.3. m6A: A Central Epitranscriptomic Mark in the Nervous System
2.4. m1A: A Marker of Neuronal Stress Adaptation
2.5. m5C: Developmental Regulation in the Brain
2.6. Genetic and Environmental Influences on m6A and Disease Susceptibility
3. m6A Methylation in Brain Development and Function
4. m6A Methylation and Learning and Memory
4.1. Mechanisms of m6A in Cognitive Function
4.2. Studies on Memory Formation and Retrieval
4.3. Therapeutic Implications for Memory Improvement
5. m6A Methylation and Psychiatric Disorders
5.1. m6A Methylation and Depression
5.2. m6A Methylation and Anxiety Disorders
5.3. m6A Methylation and Schizophrenia
5.4. m6A Methylation and Bipolar Disorder
6. Future Directions and Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Lv, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, D. Decoding m6A RNA methylation in kidney disorders: From molecular insights to therapeutic strategies. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, H.; Kim, G.W.; Siddiqui, A. Epitranscriptomic(N6-methyladenosine) Modification of Viral RNA and Virus-Host Interactions. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 584283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, Z. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification: Emerging regulators in plant-virus interactions. Virology 2025, 603, 110373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cheng, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. N6-Methyladenosine methylation modification in breast cancer: Current insights. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loedige, I.; Baranovskii, A.; Mendonsa, S.; Dantsuji, S.; Popitsch, N.; Breimann, L.; Zerna, N.; Cherepanov, V.; Milek, M.; Ameres, S.; et al. mRNA stability and m6A are major determinants of subcellular mRNA localization in neurons. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 2709–2725.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; She, Y.; Ji, S.J. m6A Modification in Mammalian Nervous System Development, Functions, Disorders, and Injuries. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 679662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabtree, G.W.; Gogos, J.A. Synaptic plasticity, neural circuits, and the emerging role of altered short-term information processing in schizophrenia. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2014, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, M.; Khan, Y.; Arab, M.M.; Alshammari, S.O.; Hussain, M.S.; Almufarriji, F.M. m6A methylation: A new frontier in epilepsy research and therapeutics. EXCLI J. 2025, 24, 578–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhao, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, D.; Hong, S.; Yang, Y.; Shu, Q.; Li, X. m6A Modification Involves in Enriched Environment-Induced Neurogenesis and Cognition Enhancement. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 903179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.P.; Pickering, B.F.; Jaffrey, S.R. Reading m6A in the Transcriptome: m6A-Binding Proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Zha, X.; Li, M.; Xia, X.; Wang, S. Insights into the m6A demethylases FTO and ALKBH5: Structural, biological function, and inhibitor development. Cell Biosci. 2024, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoumi, M.; Munir, M. Evolutionary conservation of the DRACH signatures of potential N6-methyladenosine (m6A) sites among influenza A viruses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, B.; Grozhik, A.V.; Olarerin-George, A.O.; Meydan, C.; Mason, C.E.; Jaffrey, S.R. Single-nucleotide-resolution mapping of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, P.; Dong, W.; Zuo, Y. METTL3 regulates m6A in endometrioid epithelial ovarian cancer independently of METTl14 and WTAP. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 2524–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, X.L.; Sun, B.F.; Wang, L.; Xiao, W.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.J.; Adhikari, S.; Shi, Y.; Lv, Y.; Chen, Y.S.; et al. Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; He, C. The YTHDF proteins display distinct cellular functions on m6A-modified RNA. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2024, 49, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Gao, Y.; Xu, S.; Yuan, J.; Wang, M.; Li, T.; Gong, J. N6-methyladenosine reader YTHDF family in biological processes: Structures, roles, and mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1162607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larivera, S.; Meister, G. Domain confusion 2: m6A-independent role of YTHDC2. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 1608–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.S.; Batista, P.J.; Gold, R.S.; Chen, Y.G.; de Rooij, D.G.; Chang, H.Y.; Fuller, M.T. The conserved RNA helicase YTHDC2 regulates the transition from proliferation to differentiation in the germline. eLife 2017, 6, e26116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.L.; Wachter, K.; Muhleck, B.; Pazaitis, N.; Kohn, M.; Lederer, M.; Huttelmaier, S. Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs): Post-transcriptional drivers of cancer progression? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 2657–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Weng, H.; Sun, W.; Qin, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, H.; Zhao, B.S.; Mesquita, A.; Liu, C.; Yuan, C.L.; et al. Recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon, C.R.; Goodarzi, H.; Lee, H.; Liu, X.; Tavazoie, S.; Tavazoie, S.F. HNRNPA2B1 Is a Mediator of m6A-Dependent Nuclear RNA Processing Events. Cell 2015, 162, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Lu, T.Z.; Wang, T.; Yan, W.H.; Zhong, F.Y.; Qu, X.H.; Gong, X.C.; Li, J.G.; Tou, F.F.; Jiang, L.P.; et al. The m6A reader HNRNPC promotes glioma progression by enhancing the stability of IRAK1 mRNA through the MAPK pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Wang, P.; Wei, L.; Qin, K.; Pei, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wang, J. Unraveling the independent role of METTL3 in m6A modification and tumor progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Yi, C.; Lindahl, T.; Pan, T.; Yang, Y.G.; et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, Z.; Qing, Y.; Yang, F.; Ji, F.; Zhang, L.; Sau, L.; Chen, J.; et al. FTO degrader impairs ribosome biogenesis and protein translation in acute myeloid leukemia. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadv7648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Dahl, J.A.; Niu, Y.; Fedorcsak, P.; Huang, C.M.; Li, C.J.; Vagbo, C.B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, W.L.; Song, S.H.; et al. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roundtree, I.A.; Evans, M.E.; Pan, T.; He, C. Dynamic RNA Modifications in Gene Expression Regulation. Cell 2017, 169, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Corovic, M.; Hoch-Kraft, P.; Meiser, N.; Mesitov, M.; Kortel, N.; Back, H.; Naarmann-de Vries, I.S.; Katti, K.; Obrdlik, A.; et al. m6A sites in the coding region trigger translation-dependent mRNA decay. Mol. Cell 2024, 84, 4576–4593.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamand, M.N.; Meyer, K.D. m6A and YTHDF proteins contribute to the localization of select neuronal mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 4464–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, H.; Li, P.; Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, M.; Lyu, H.; et al. m6A methyltransferase METTL3 participated in sympathetic neural remodeling post-MI via the TRAF6/NF-kappaB pathway and ROS production. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2022, 170, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Sun, W.; Xia, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, S. The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes LPS-induced microglia inflammation through TRAF6/NF-kappaB pathway. Neuroreport 2022, 33, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jian, H.; Hou, M.; Lou, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wang, W.; Lv, Y.; Shang, S.; Wang, C.; et al. N1-Methyladenosine modification of mRNA regulates neuronal gene expression and oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation induction. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yi, X.; Hou, M.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Lu, L.; Qi, E.; Wu, M.; Qi, L.; Jian, H.; et al. The landscape of m1A modification and its posttranscriptional regulatory functions in primary neurons. eLife 2023, 12, e85324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, Z.; Xu, X.; Lin, Y.; Xie, H. Dynamics of RNA m5C modification during brain development. Genomics 2023, 115, 110604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, B.; Nie, Z.; Duan, L.; Xiong, Q.; Jin, Z.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y. The role of m6A modification in the biological functions and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Lv, J.; Yu, H.; Han, J.; Yang, X.; Feng, D.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, B.; Lu, Q.; Yang, H. Mechanism of RNA modification N6-methyladenosine in human cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Frazier, K.; Zhang, J.; Gan, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhong, X. Emerging role of m6A RNA methylation in nutritional physiology and metabolism. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e12942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Guilherme, M.; Tsoutsouli, T.; Todorov, H.; Teifel, S.; Nguyen, V.T.T.; Gerber, S.; Endres, K. N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Chronic Stress Response Due to Social Hierarchy Positioning of Mice. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 705986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.; Malchow, B.; Hasan, A.; Falkai, P. The impact of environmental factors in severe psychiatric disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegstein, A.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. The glial nature of embryonic and adult neural stem cells. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 32, 149–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegowski, M.; Meyer, K.D. Studying m6A in the brain: A perspective on current methods, challenges, and future directions. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2024, 17, 1393973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.J.; Ringeling, F.R.; Vissers, C.; Jacob, F.; Pokrass, M.; Jimenez-Cyrus, D.; Su, Y.; Kim, N.S.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, L.; et al. Temporal Control of Mammalian Cortical Neurogenesis by m6A Methylation. Cell 2017, 171, 877–889.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Han, P.; Zhang, J.; She, Y.; Yang, L.; Yu, J.; Zhuang, M.; Tang, K.; Shi, Y.; Yang, B.; et al. The m6A reader YTHDF2 is a negative regulator for dendrite development and maintenance of retinal ganglion cells. elife 2022, 11, e75827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Cheng, J. The role and regulatory mechanism of m6A methylation in the nervous system. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 962774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez De La Cruz, B.; Markus, R.; Malla, S.; Haig, M.I.; Gell, C.; Sang, F.; Bellows, E.; Sherif, M.A.; McLean, D.; Lourdusamy, A.; et al. Modifying the m6A brain methylome by ALKBH5-mediated demethylation: A new contender for synaptic tagging. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 7141–7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chokkalla, A.K.; Mehta, S.L.; Vemuganti, R. Epitranscriptomic regulation by m6A RNA methylation in brain development and diseases. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 40, 2331–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhong, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Xiao, X.; Zu, X.; Liu, J. The expression of m6A enzymes in the hippocampus of diabetic cognitive impairment mice and the possible improvement of YTHDF1. Brain Res. 2022, 1777, 147766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonetti, A.M.; Chu, M.Y.; Ramnaraign, F.O.; Holm, S.; Walters, B.J. An Emerging Role of m6A in Memory: A Case for Translational Priming. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.M.; Galluzzo, I.R.; McLean, T.A.D.; Stefanelli, G.; Ramnaraign, F.; Holm, S.; Winston, S.M.; Reeves, I.L.; Brimble, M.A.; Walters, B.J. The role of the m6A/m demethylase FTO in memory is both task and sex-dependent in mice. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2024, 210, 107903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, L.; Ott, S.; Joseph, B.; Park, E.S.; Dai, W.; Kleiner, R.E.; Claridge-Chang, A.; Lai, E.C. A neural m6A/Ythdf pathway is required for learning and memory in Drosophila. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Huang, C.; Liu, Z.; Ai, S.; Wang, H.L. Decreased expression of Chrna4 by METTL3-mediated m6A modification participates in BPA-induced spatial memory deficit. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Guo, F.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, B.; Wang, C.; Huang, L.; Jiang, S.; Ma, X.; Ren, H.; et al. Effects of m6A methylation of MAT2A mRNA regulated by METTL16 on learning and memory, hippocampal synaptic plasticity and Aβ1–42 in 5 × FAD mice. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2025, 17, 1572976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, M.; Du, Z.; Li, H.; Fan, C.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Bi, X. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification and its clinical relevance in cognitive dysfunctions. Aging 2021, 13, 20716–20737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Hernandez, R.; Berulava, T.; Metelova, M.; Epple, R.; Pena Centeno, T.; Richter, J.; Kaurani, L.; Pradhan, R.; Sakib, M.S.; Burkhardt, S.; et al. Conserved reduction of m6A RNA modifications during aging and neurodegeneration is linked to changes in synaptic transcripts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2204933120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, X.; Qi, Z.; Sang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B.; Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Deng, Y. The role of mRNA m6A methylation in the nervous system. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhashi, H.; Lin, R.; Chawla, A.; Mechawar, N.; Nagy, C.; Turecki, G. Altered m6A RNA methylation profiles in depression implicate the dysregulation of discrete cellular functions in males and females. iScience 2024, 27, 111316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xiu, J.; Zhu, C.; Meng, K.; Li, C.; Han, R.; Du, T.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, R.; et al. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein regulates RNA methylation associated with depression-like behavior in mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Lv, X.; Chen, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, M. m6A methylation: Critical roles in aging and neurological diseases. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1102147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanarik, M.; Liiver, K.; Norden, M.; Teino, I.; Org, T.; Laugus, K.; Shimmo, R.; Karelson, M.; Saarma, M.; Harro, J. RNA m6A methyltransferase activator affects anxiety-related behaviours, monoamines and striatal gene expression in the rat. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2024, 37, e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuhashi, H.; Nagy, C. Potential Roles of m6A and FTO in Synaptic Connectivity and Major Depressive Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelin, M.; Gopinath, P.; Raghavan, V.; Thara, R.; Ahmad, F.; Munirajan, A.K.; Sudesh, R. Global DNA and RNA Methylation Signature in Response to Antipsychotic Treatment in First-Episode Schizophrenia Patients. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2024, 20, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.J.; Shi, H.; Zhu, A.C.; Lu, Z.; Miller, N.; Edens, B.M.; Ma, Y.C.; He, C. The RNA-binding protein FMRP facilitates the nuclear export of N6-methyladenosine-containing mRNAs. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 19889–19895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Kang, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, T.; Yang, W.; Song, H.; Wu, H.; Shu, Q.; Jin, P. Fragile X mental retardation protein modulates the stability of its m6A-marked messenger RNA targets. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 3936–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie-Claire, C.; Lejeune, F.X.; Mundwiller, E.; Ulveling, D.; Moszer, I.; Bellivier, F.; Etain, B. A DNA methylation signature discriminates between excellent and non-response to lithium in patients with bipolar disorder type 1. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Chen, T.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Maes, M. FTO (fat-mass and obesity-associated protein) deficiency aggravates age-dependent depression-like behaviors and cognitive impairment. Behav. Brain Funct. 2025, 21, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, K.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, E.; Yu, X.; Meng, P.; Xiu, J. The RNA Demethyltransferase FTO Regulates Ferroptosis in Major Depressive Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Dwivedi, Y. M6A RNA epitranscriptome dynamics linked to major depressive disorder and suicide risk. Neuropsychopharmacology 2025, 50, 1524–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, M.; Eggert, C.; Kaplick, P.M.; Eder, M.; Roh, S.; Tietze, L.; Namendorf, C.; Arloth, J.; Weber, P.; Rex-Haffner, M.; et al. The Role of m6A/m-RNA Methylation in Stress Response Regulation. Neuron 2018, 99, 389–403.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Li, X.; Hou, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Sukegawa, M.; Hong, W.; Oomoto, I.; Ito, H.; Joshi, K.; Fan, R.; et al. Schizophrenia and autism associated mutations and disrupted m6A signal by YTHDF1 cause defects in microtubule function and neurodevelopment. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, M.H. m6A mRNA methylation: A new circadian pacesetter. Cell 2013, 155, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| Psychiatric Disorders | m6A Methylation/ m6A Regulators | Human/ Animal | Research Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression | FTO | Human | Polymorphisms linked to depression risk/protection | [56] |
| FTO; ALKBH5 | Human, mouse | Reduced hippocampal FTO leads to depression-like behaviors; Reduced VTA FTO leads to higher stress susceptibility; circSTAG1 overexpression inhibits ALKBH5 translocation, resulting in reduced depressive-like behaviors | [45] | |
| Global m6A | Human | Sex-specific m6A changes: microtubule movement in | [57] | |
| vmPFC | males; neuronal projection in females | |||
| FTO | Human | Decreased hippocampal FTO leads to MDD | [58] | |
| FTO | Mouse | Hippocampal Fto KD/KO leads to depression-like | [58] | |
| behaviors; Fto overexpression rescues; ADRB2 stimulation rescues | ||||
| ALKBH5 | Human | Decreased peripheral blood ALKBH5 leads to MDD | [58] | |
| Global m6A | Human & Animal | Altered brain m6A linked to depression | [59] | |
| METTL3; METTL14 | Rat | Antidepressant-like effects; regulated depression/stress genes | [60] | |
| Anxiety | FTO | Mouse | FTO deficiency reduced anxiety- and depression-like behaviors | [45] |
| disorders | METTL3 | Mouse | Loss of METTL3 increases fear generalization | [45] |
| FTO | Mouse VTA | FTO loss increases stress; overexpression protective | [45] | |
| FTO, global m6A | Mouse PFC | FTO knockdown increases cued fear memory | [45] | |
| FTO, ALKBH5, global m6A | Mouse | Stress alters m6A regionally | [61] | |
| FTO | Mouse | Reduced FTO in anterior cingulate cortex increases anxiety | [61] | |
| FTO (global KO) | Mouse | FTO (global KO) leads to anxiety | [61] | |
| METTL3; METTL14 | Rat | METTL3/14 activation reduces anxiety-like behavior | [60] | |
| Schizophrenia | ZC3H13 | Human | Polymorphism associated with schizophrenia | [56] |
| Global m6A | Human | m6A level unchanged; slightly up in non-responders (not significant) | [62] | |
| FMRP (m6A reader) | Mouse | FMRP loss leads to nuclear retention of m6A RNAs | [63] | |
| FMRP (m6A reader); | Mouse | FMRP stabilizes m6A-marked RNAs; | [64] | |
| YTHDF2 | FMRP loss leads to YTHDF2-driven decay | |||
| Bipolar | m6A | Human | DMR—EIF2B5/VWA5B2 (TTS) related to lithium response | [65] |
| disorder | m6A | Human | DMR—RALGAPA1 (promoter/TSS) related to lithium response | [65] |
| m6A | Human | DMR—C2orf81 (exon) related to lithium response | [65] | |
| m6A | Human | DMR—LINC01237 (intron) related to lithium response | [65] | |
| m6A | Human | DMR—Intergenic sites related to lithium response | [65] | |
| METTL3/METTL14 activator compound CHMA1004 | Rat | CHMA1004 elicits anxiolytic-like effects | [60] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ngo, A.L.; Nguyen, L.; Gharavi Alkhansari, N.; Zhang, H. m6A RNA Methylation in Psychiatric Disorders: An Emerging Epitranscriptomic Axis. Epigenomes 2025, 9, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9030036
Ngo AL, Nguyen L, Gharavi Alkhansari N, Zhang H. m6A RNA Methylation in Psychiatric Disorders: An Emerging Epitranscriptomic Axis. Epigenomes. 2025; 9(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleNgo, Ambrose Loc, Linda Nguyen, Niki Gharavi Alkhansari, and Huiping Zhang. 2025. "m6A RNA Methylation in Psychiatric Disorders: An Emerging Epitranscriptomic Axis" Epigenomes 9, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9030036
APA StyleNgo, A. L., Nguyen, L., Gharavi Alkhansari, N., & Zhang, H. (2025). m6A RNA Methylation in Psychiatric Disorders: An Emerging Epitranscriptomic Axis. Epigenomes, 9(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9030036







