The Association of Childhood Allergic Diseases with Prenatal Exposure to Pollen Grains Through At-Birth DNA Methylation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Descriptive Statistics
2.2. Pollen Grain Exposure in Pregnancy Is Associated with DNA Methylation at Birth
2.3. Relationship of Prenatal Pollen Grain-Associated CpGs with Childhood Asthma
2.4. Relationship of Prenatal Pollen Grain-Associated CpGs with Childhood Allergic Rhinitis
3. Discussion
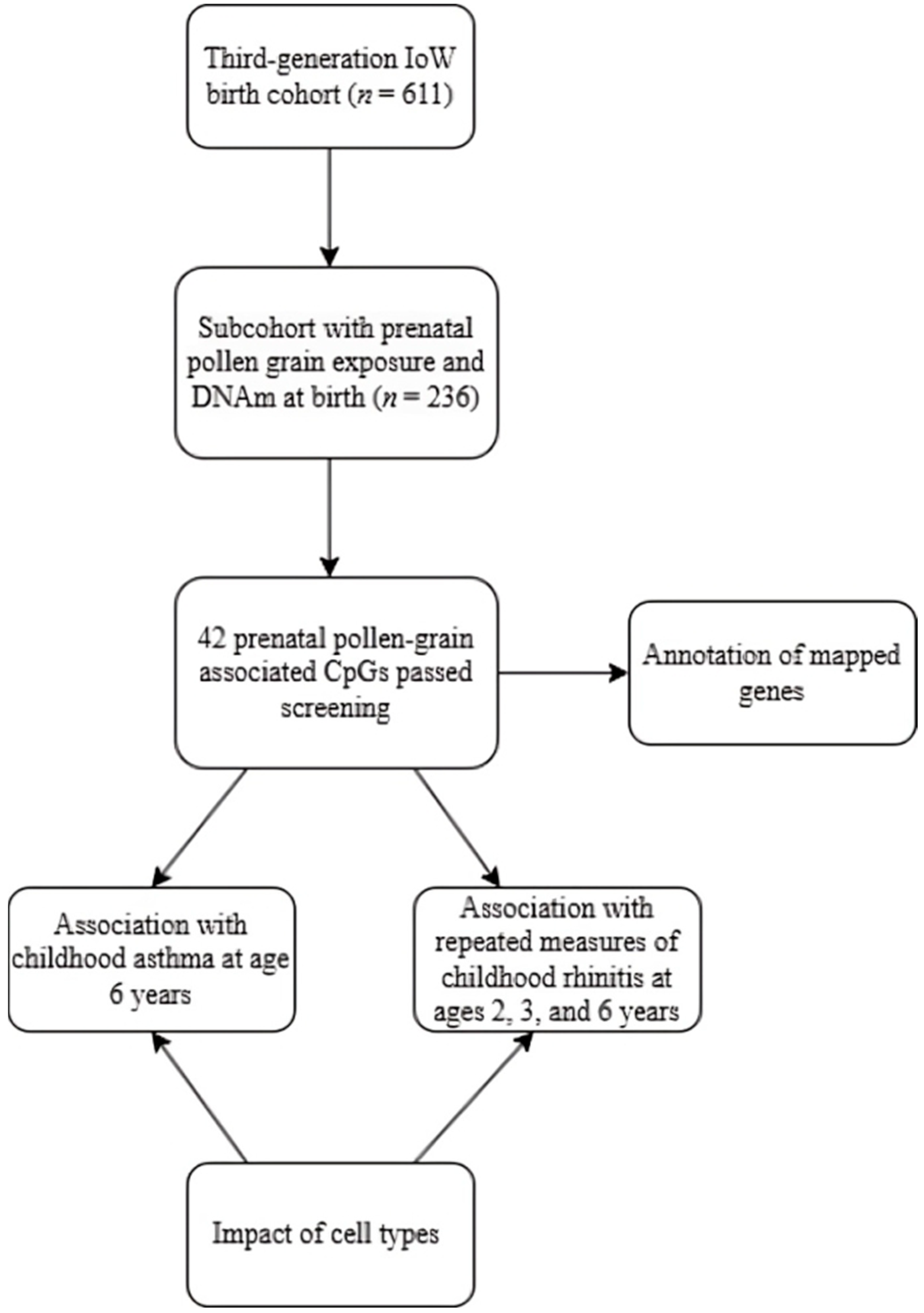
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Isle of Wight Third Generation Birth Cohort (IOWTBC)
4.2. Outcome Variables
4.3. Exposure Variable
4.4. DNA Methylation
4.5. Cell Type Composition Correction
4.6. Descriptive Analyses
4.7. Screening of CpG Sites
4.8. Association of Prenatal Pollen Grain Exposure and DNAm at Birth (First Arm)
4.9. Association of Prenatal Pollen Grain Exposure-Related DNAm at Birth and Childhood Allergic Diseases (Second Arm)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | confidence interval |
| CpG | cytosine-phosphate-guanine |
| DNAm | DNA methylation |
| IoW | Isle of Wight |
| IOWTBC | The Isle of Wight third-generation birth cohort |
| ISAAC | International Study of Asthma and Allergy in Childhood |
| NK | natural killer |
| NRES | National Research Ethics Service |
| OR | odds ratio |
| PFAS | pollen–food allergy syndrome |
| PPG | prenatal pollen grain |
| SES | socioeconomic status |
References
- Baloh, C.H.; Mathias, R.A. Recent Progress in the Genetic and Epigenetic Underpinnings of Atopy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.J.; Kong, X.M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Guo, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Cheng, Z.H. Global, Regional and National Epidemiology of Allergic Disorders in Children from 1990 to 2019: Findings From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e080612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annesi-Maesano, I.; Cecchi, L.; Biagioni, B.; Chung, K.F.; Clot, B.; Collaud Coen, M.; D’Amato, G.; Damialis, A.; Dominguez-Ortega, J.; Galan, C.; et al. Is Exposure to Pollen a Risk Factor for Moderate and Severe Asthma Exacerbations? Allergy 2023, 78, 2121–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.B.; Mims, J.W.; Clinger, J.D. The Burden of Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis: Epidemiology and Health Care Costs. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 57, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.T.; Scotland, G.S.; Cotton, S.; Turner, S.W. Direct and Indirect Costs of Paediatric Asthma in the UK: A Cost Analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2024, 109, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M.; Cunningham, S.; Bhuia, M.R.; Lo, T.M.; Been, J.V.; Sheikh, A. Asthma in Paediatric Intensive Care in England Residents: Observational Study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Zhu, D.; Sha, J.; Zhao, B.; Jin, P.; Meng, C. Decoding the Role of DNA Methylation in Allergic Diseases: From Pathogenesis to Therapy. Cell Biosci. 2024, 14, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketomi, E.A.; Sopelete, M.C.; de Sousa Moreira, P.F.; de Assis Machado Vieira, F. Pollen Allergic disease: Pollens and its Major Allergens. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 72, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, B.H.; Alsante, A.N.; Brooks, S.D. Pollen Emissions of Subpollen Particles and Ice Nucleating Particles. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2023, 7, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guryanova, S.V.; Finkina, E.I.; Melnikova, D.N.; Bogdanov, I.V.; Bohle, B.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. How Do Pollen Allergens Sensitize? Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 900533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mozo, H. Poaceae Pollen as the Leading Aeroallergen Worldwide: A review. Allergy 2017, 72, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pablos, I.; Wildner, S.; Asam, C.; Wallner, M.; Gadermaier, G. Pollen Allergens for Molecular Diagnosis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabina, M.; Peltre, G.; Van Ree, R.; Moingeon, P. Grass Pollen Allergens. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 8, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzler, L.; Panetta, V.; Lau, S.; Wagner, P.; Bergmann, R.L.; Illi, S.; Bergmann, K.E.; Keil, T.; Hofmaier, S.; Rohrbach, A.; et al. Molecular Spreading and Predictive Value of Preclinical IgE Response to Phleum pratense in Children With Hay Fever. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2012, 130, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, G.; Cecchi, L.; Bonini, S.; Nunes, C.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Behrendt, H.; Liccardi, G.; Popov, T.; van Cauwenberge, P. Allergenic Pollen and Pollen Allergy in Europe. Allergy 2007, 62, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, G.; Murrieta-Aguttes, M.; D’Amato, M.; Ansotegui, I.J. Pollen Respiratory Allergy: Is it Really Seasonal? World Allergy Organ. J. 2023, 16, 100799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiteneder, H.; Kraft, D. The History and Science of the Major Birch Pollen Allergen Bet v 1. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Fujieda, S. Comprehensive Review of Pollen-Food Allergy Syndrome: Pathogenesis, Epidemiology, and Treatment Approaches. Allergol. Int. 2025, 74, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, T.; Takei, M.; Saito, Y.; Rumi, F.; Zheng, J.; Lu, X.; Chafey, P.; Broussard, C.; Guilloux-Assalet, L.; Charpin, D.; et al. Gibberellin-Regulated Protein Sensitization in Japanese Cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) Pollen Allergic Japanese Cohorts. Allergy 2021, 76, 2297–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skypala, I.J. Can Patients With Oral Allergy Ayndrome be at Risk of Anaphylaxis? Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 20, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbas, B.; Lowe, A.J.; Lodge, C.J.; Matheson, M.C.; Hosking, C.S.; Hill, D.J.; Vicendese, D.; Allen, K.J.; Abramson, M.J.; Dharmage, S.C. Persistent Pollen Exposure during Infancy is Associated With Increased Risk of Subsequent Childhood Asthma and Hayfever. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, S.; Sherrill, D.L.; Cottini, M.; Michetti, G.; Allegra, L. On the Association Between Date of Birth and Pollen Sensitization: Is Age an Effect Modifier? Allergy Asthma Proc. 2002, 23, 303–310. [Google Scholar]
- Kihlstrom, A.; Lilja, G.; Pershagen, G.; Hedlin, G. Exposure to High Doses of Birch Pollen during Pregnancy, and Risk of Sensitization and Atopic Disease in the Child. Allergy 2003, 58, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, N.J.; Alcock, I.; Wheeler, B.W.; Hajat, S.; Sarran, C.; Clewlow, Y.; McInnes, R.N.; Hemming, D.; White, M.; Vardoulakis, S.; et al. Pollen Exposure and Hospitalization due to Asthma Exacerbations: Daily Time Series in a European City. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 1837–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaram, R.; Adefisoye, J.; Warden, D.; Potter, S.; Arshad, H.; Zhang, H. Pollen Exposures in Pregnancy and Early Life are Associated With Childhood Asthma Incidence. World Allergy Organ. J. 2024, 17, 100976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.D.; Le, T.; Fan, G. DNA Methylation and its Basic Function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, F.; Viallon, V.; Ambatipudi, S.; Ghantous, A.; Cuenin, C.; Hernandez-Vargas, H.; Chajes, V.; Baglietto, L.; Matejcic, M.; Moreno-Macias, H.; et al. Association of Leukocyte DNA Methylation Changes With Dietary Folate and Alcohol Intake in the EPIC Study. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, M.L.; Jones, M.J.; MacIsaac, J.L.; Morin, A.M.; Steacy, L.M.; Gregor, A.; Kobor, M.S.; Ellis, A.K. Blood and Nasal Epigenetics Correlate With Allergic Rhinitis Symptom Development in the Environmental Exposure Unit. Allergy 2018, 73, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wen, P.; Chen, J.; Kang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Ding, S.; Gao, L.; Tong, X.; Guo, A. DNA Methylation Regulatory Patterns and Underlying Pathways Behind the Co-Pathogenesis of Allergic Rhinitis and Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1053558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadalayil, L.; Alam, M.Z.; White, C.H.; Ghantous, A.; Walton, E.; Gruzieva, O.; Merid, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Roy, R.P.; Solomon, O.; et al. Analysis of DNA Methylation at Birth and in Childhood Reveals Changes Associated With Season of Birth and Latitude. Clin. Epigenetics 2023, 15, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockett, G.A.; Soto-Ramirez, N.; Ray, M.A.; Everson, T.M.; Xu, C.J.; Patil, V.K.; Terry, W.; Kaushal, A.; Rezwan, F.I.; Ewart, S.L.; et al. Association of Season of Birth With DNA Methylation and Allergic Disease. Allergy 2016, 71, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanninen, R.; Murtomaki, A.; Svard, F.; Dietz, A.; Torkki, P.; Haukka, J.; Nuutinen, M.; Toppila-Salmi, S. Being Born in Autumn or Winter is Associated With Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis in Finland. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2024, 14, e12383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Lu, W.; He, S.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; et al. Discovery of Novel Variants on the CHD7 Gene: A Case Series of CHARGE Syndrome. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 852429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.; Campbell, M.; Harbinson, M.; Bell, D. Protective Effects of Intermedin on Cardiovascular, Pulmonary and Renal Diseases: Comparison With Adrenomedullin and CGRP. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2013, 14, 294–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrison, L.B.; Brandt, E.B.; Myers, J.B.; Hershey, G.K.K. Environmental Exposures and Mechanisms in Allergy and Asthma Development. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunas, A.S.; Iunusbaev, B.B.; Fedorova, I.; Gimalova, G.F.; Ramazanova, N.N.; Gur’eva, L.L.; Mukhtarova, L.A.; Zagidullin Sh, Z.; Etkina, E.I.; Khusnutdinova, E.K. Genome-Wide Association Study of Bronchial Asthma in the Volga-Ural Region of Russia. Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanescu, C.; Talarico, R.; Weichenthal, S.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Smargiassi, A.; Stieb, D.M.; To, T.; Hebbern, C.; Crighton, E.; Lavigne, E. Early Life Exposure to Pollens and Increased Risks of Childhood Asthma: A Prospective Cohort Study in Ontario Children. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 63, 2301568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Yao, Z.; Xu, X.; Wu, Q.; Xu, F. LncRNA HCG11 Promotes Proliferation and Migration in Gastric Cancer via Targeting miR-1276/CTNNB1 and Activating Wnt Signaling Pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.; Kou, X.; Che, L.; Zhou, X.; Chen, G.; Zhao, J. Long Non-coding RNA HCG11 Suppresses the Growth of Glioma by Cooperating With the miR-4425/MTA3 Axis. J. Gene Med. 2019, 21, e3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Bai, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Li, S. LncRNA HCG11 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis via Sponging miR-224-3p in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 6553–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, H.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Ming, L.; Lu, X. LncRNA HCG11 Facilitates Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Progression Through Regulating miRNA-490-3p/MAP3K9 Axis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 872033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Teschendorff, A.E. Cell-Type Heterogeneity: Why We Should Adjust for it in Epigenome and Biomarker Studies. Clin. Epigenetics 2022, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Ancestral Informative Marker Selection and Population Structure Visualization using Sparse Laplacian Eigenfunctions. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, M.W.; Smith, A.K.; Wolf, E.J.; Maniates, H.; Stone, A.; Schichman, S.A.; McGlinchey, R.E.; Milberg, W.; Miller, M.W. The Correlation of Methylation Levels Measured using Illumina 450K and EPIC BeadChips in Blood Samples. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, S.H.; Holloway, J.W.; Karmaus, W.; Zhang, H.; Ewart, S.; Mansfield, L.; Matthews, S.; Hodgekiss, C.; Roberts, G.; Kurukulaaratchy, R. Cohort Profile: The Isle Of Wight Whole Population Birth Cohort (IOWBC). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 1043–1044i. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, S.H.; Patil, V.; Mitchell, F.; Potter, S.; Zhang, H.; Ewart, S.; Mansfield, L.; Venter, C.; Holloway, J.W.; Karmaus, W.J. Cohort Profile Update: The Isle of Wight Whole Population Birth Cohort (IOWBC). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 1083–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Ramirez, N.; Ziyab, A.H.; Karmaus, W.; Zhang, H.; Kurukulaaratchy, R.J.; Ewart, S.; Arshad, S.H. Epidemiologic Methods of Assessing Asthma and Wheezing Episodes in Longitudinal Studies: Measures of Change and Stability. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Ewart, S.; Holloway, J.W.; Arshad, H.; Karmaus, W. Intergenerational Association of DNA Methylation Between Parents and Offspring. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Zhang, X.; Huang, C.C.; Jafari, N.; Kibbe, W.A.; Hou, L.; Lin, S.M. Comparison of Beta-Value and M-Value Methods for Quantifying Methylation Levels by Microarray Analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.E.; Li, C.; Rabinovic, A. Adjusting Batch Effects in Microarray Expression Data using Empirical Bayes Methods. Biostatistics 2007, 8, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakulski, K.M.; Feinberg, J.I.; Andrews, S.V.; Yang, J.; Brown, S.; LMcKenney, S.; Witter, F.; Walston, J.; Feinberg, A.P.; Fallin, M.D. DNA Methylation of Cord Blood Cell Types: Applications for Mixed Cell Birth Studies. Epigenetics 2016, 11, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houseman, E.A.; Accomando, W.P.; Koestler, D.C.; Christensen, B.C.; Marsit, C.J.; Nelson, H.H.; Wiencke, J.K.; Kelsey, K.T. DNA Methylation Arrays as Surrogate Measures of Cell Mixture Distribution. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbin, K.K.; Simon, R.M. Optimally Splitting Cases for Training and Testing High Dimensional Classifiers. BMC Med. Genom. 2011, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubach, Z.M.; Perng, W.; Cardenas, A.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Oken, E.; DeMeo, D.; Litonjua, A.A.; Duca, R.C.; Godderis, L.; Baccarelli, A.; et al. Socioeconomic Status and DNA Methylation From Birth Through Mid-Childhood: A Prospective Study in Project Viva. Epigenomics 2019, 11, 1413–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, R.C.; Simpkin, A.J.; Woodward, G.; Gaunt, T.R.; Lyttleton, O.; McArdle, W.L.; Ring, S.M.; Smith, A.D.; Timpson, N.J.; Tilling, K.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Maternal Smoking and Offspring DNA Methylation across the Lifecourse: Findings From the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 2201–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbuanu, I.U.; Karmaus, W.J.; Zhang, H.; Sabo-Attwood, T.; Ewart, S.; Roberts, G.; Arshad, S.H. Birth Order Modifies the Effect of IL13 gene Polymorphisms on Serum IgE at Age 10 and Skin Prick Test at Ages 4, 10 and 18: A Prospective Birth Cohort Study. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
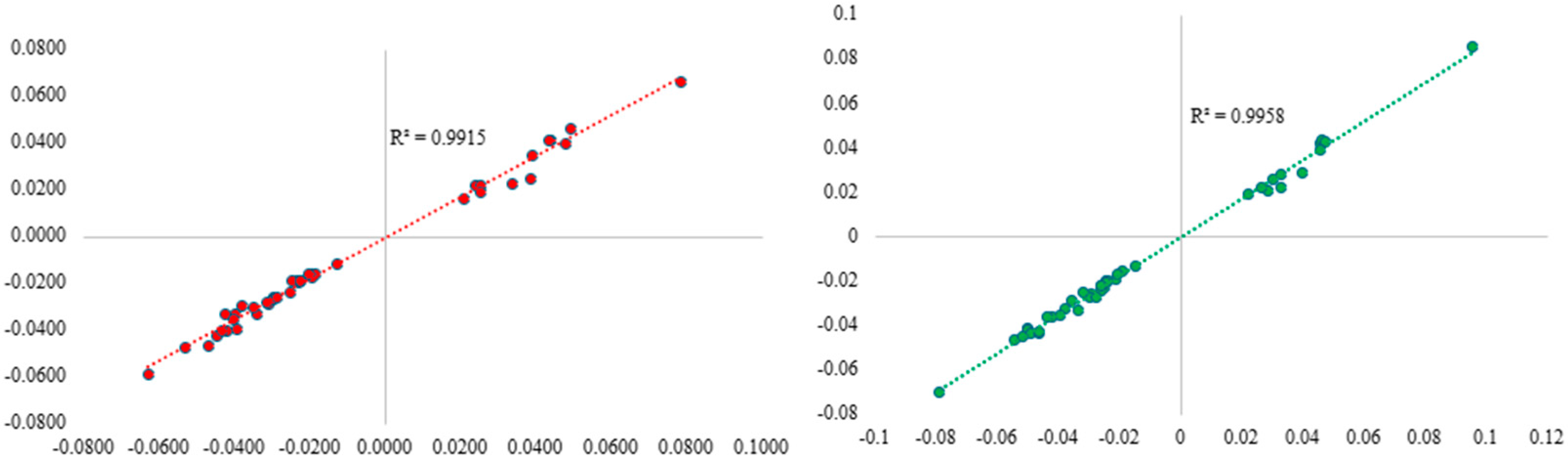
| Variables * (N) | Complete Cohort n (n/N; %) | Subcohort n (%) | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal smoking (Yes) | 178 (178/560; 31.79) | 75 (32.75) | 0.7548 |
| Maternal asthma or wheeze (Yes) | 79 (79/490; 16.12) | 33 (16.02) | 0.9687 |
| Maternal rhinitis (Yes) | 217 (217/492; 44.11) | 97 (42.73) | 0.6757 |
| SES 1 (lowest) 2 3 4 5 (highest) | 77 (77/400; 19.25) 97 (97/400; 24.25) 114 (114/400; 28.50) 61 (61/400; 15.25) 51 (51/400; 12.75) | 30 (12.93) 67 (28.88) 72 (31.03) 40 (17.24) 23 (9.91) | 0.0507 |
| Sex (Male) | 336 (336/600; 56.00) | 122 (51.69) | 0.1827 |
| Passive smoke in the first year (Yes) | 58 (58/354; 16.38) | 24 (14.37) | 0.4830 |
| Childhood asthma status at age 6 (Yes) | 44 (44/611; 7.20) | 32 (13.56) | 0.0002 |
| Childhood allergic rhinitis at age 2 (Yes) | 42 (42/287; 14.63) | 24 (15.79) | 0.6859 |
| age 3 (Yes) | 40 (40/271; 14.76) | 24 (14.72) | 0.9896 |
| age 6 (Yes) | 38 (38/181; 20.99) | 24 (19.51) | 0.6873 |
| CpG | Estimate/p-Value * | Gene | Gene Location | Biological Functions ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cg01375976 | 0.0327 (0.0001) | ZNF3 | TSS1500 | Negative regulation of transcription Nucleic acid binding Identical protein binding |
| cg13814708 | 0.0283 (0.0001) | CAND2 | TSS200 | TBP-class protein binding activity SCF complex assembly Positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription Protein ubiquitination |
| cg22654601 | −0.0154 (0.0001) | ATP6V1H | TSS200; TSS1500 | Mediates acidification of intracellular organelles |
| cg15150215 | −0.0225 (0.001) | TBL3 | TSS1500 | RNA binding snoRNA binding |
| cg07046197 | −0.0252 (0.0002) | CDC27 | TSS1500 | Controls progression through mitosis Protein phosphatase binding |
| cg10571824 | 0.0391 (0.0002) | MAD1L1 | Body | Cell cycle control and tumor suppression |
| cg26202797 | 0.0272 (0.0002) | -- | -- | -- |
| cg26525457 | 0.0388 (0.0002) | CYTH1 | Body | Lipid binding Guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity Membrane trafficking |
| cg19056515 | 0.0297 (0.0002) | #LOC404266; HOXB5 | Body; TSS200 | DNA-binding transcription factor activity DNA-binding transcription activator activity |
| cg25644556 | −0.0525 (0.0003) | ##FAM38B | TSS1500 | Monoatomic cation channel activity Mechanosensitive monoatomic cation channel activity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melaram, R.; Zhang, H.; Adefisoye, J.; Arshad, H. The Association of Childhood Allergic Diseases with Prenatal Exposure to Pollen Grains Through At-Birth DNA Methylation. Epigenomes 2025, 9, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9010009
Melaram R, Zhang H, Adefisoye J, Arshad H. The Association of Childhood Allergic Diseases with Prenatal Exposure to Pollen Grains Through At-Birth DNA Methylation. Epigenomes. 2025; 9(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelaram, Rajesh, Hongmei Zhang, James Adefisoye, and Hasan Arshad. 2025. "The Association of Childhood Allergic Diseases with Prenatal Exposure to Pollen Grains Through At-Birth DNA Methylation" Epigenomes 9, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9010009
APA StyleMelaram, R., Zhang, H., Adefisoye, J., & Arshad, H. (2025). The Association of Childhood Allergic Diseases with Prenatal Exposure to Pollen Grains Through At-Birth DNA Methylation. Epigenomes, 9(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes9010009






