Comparison of Morphological Characteristics of Antennae and Antennal Sensilla Among Three Species of Gall Wasps (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Sample Collection
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
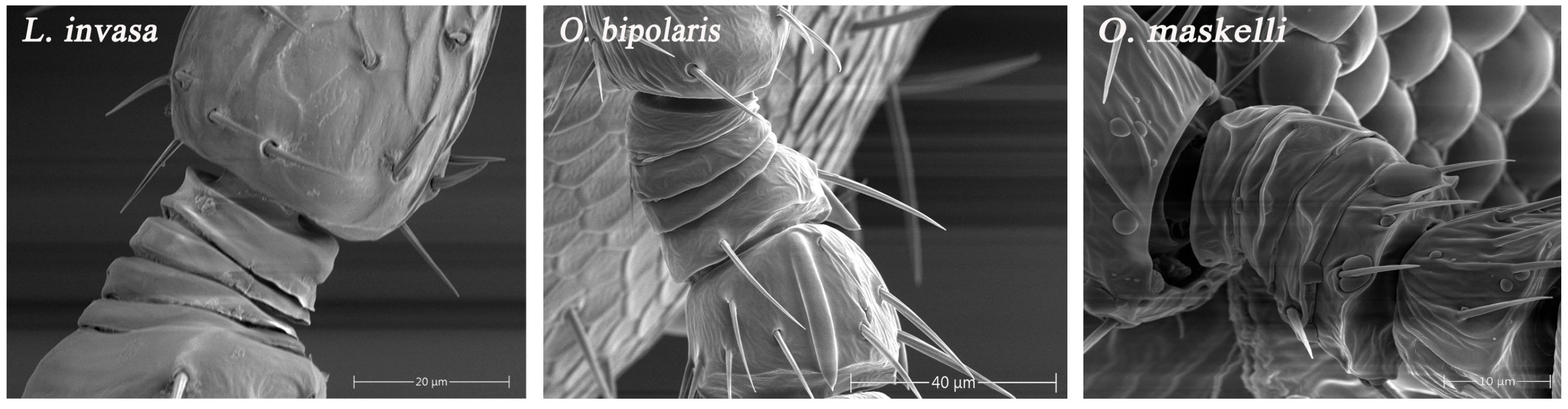
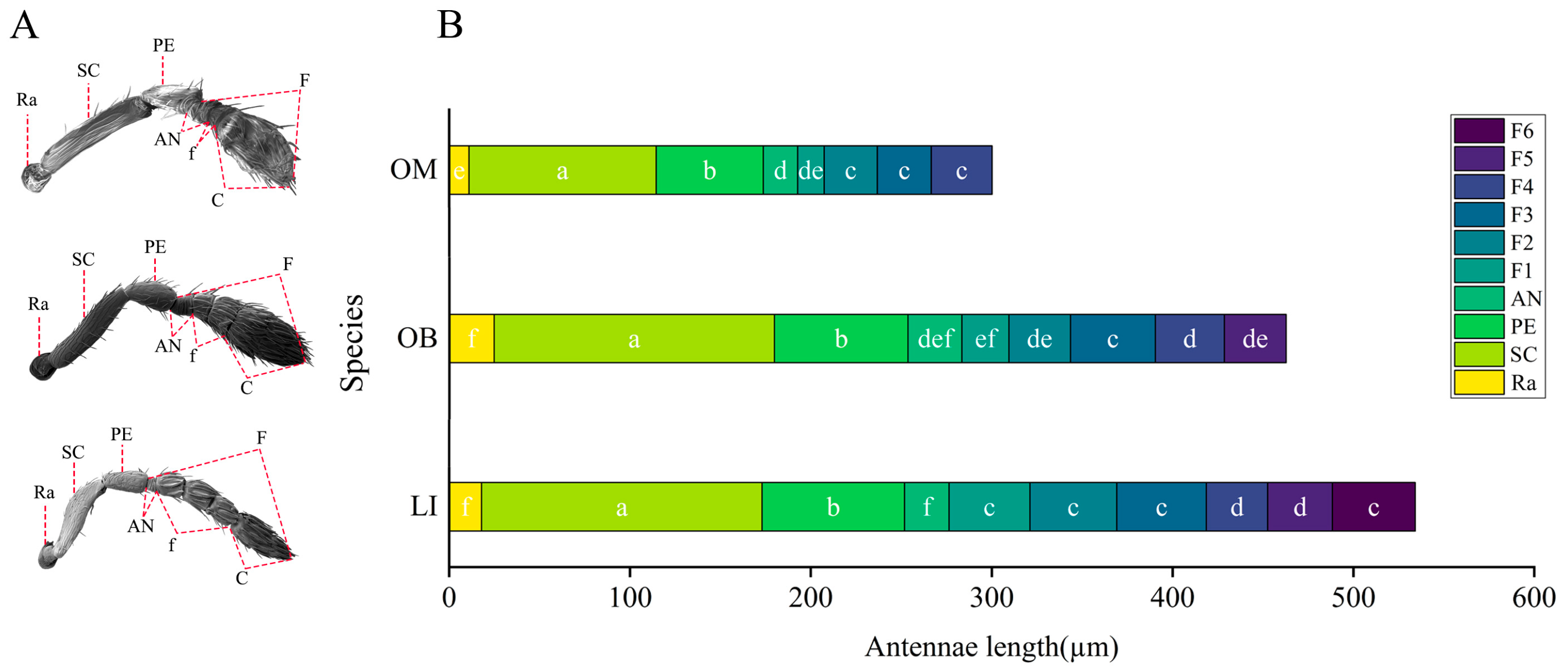
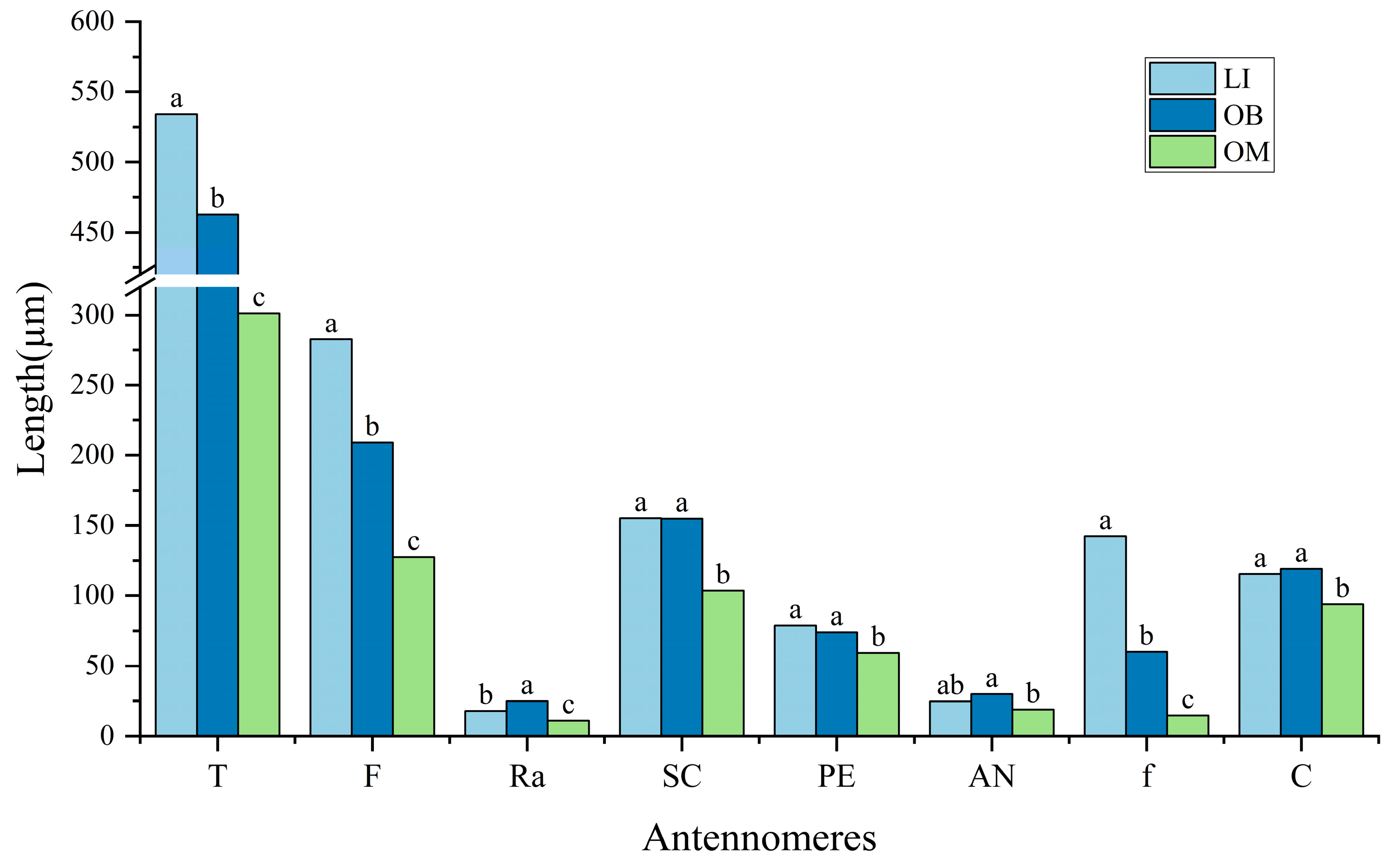
3.1. Overall Morphology of Antennae
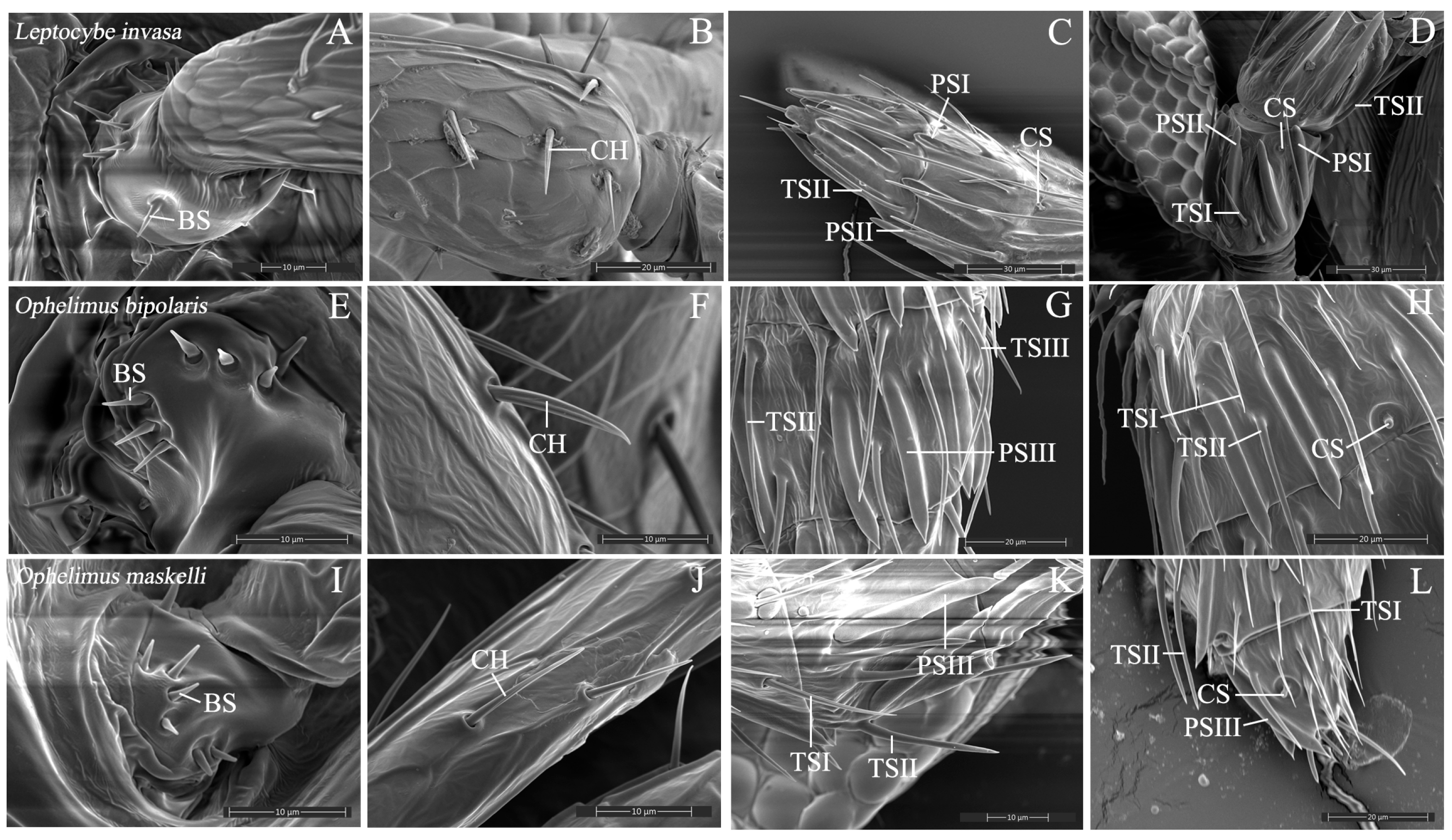
3.2. Antennal Sensilla
3.2.1. Böhm Sensilla
3.2.2. Chaetica Sensilla
3.2.3. Trichodea Sensilla
3.2.4. Placodea Sensilla
3.2.5. Campaniform Sensilla
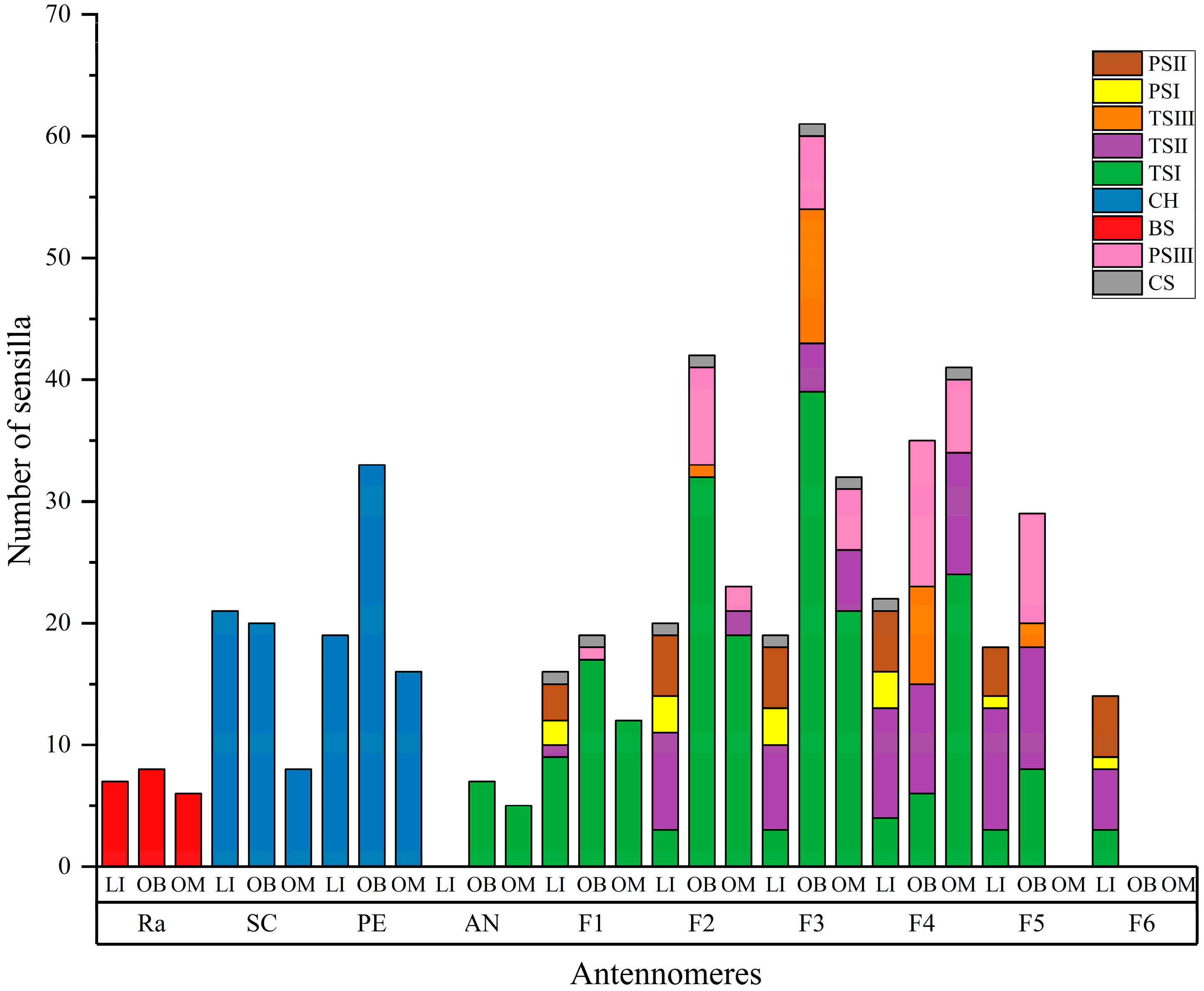
3.2.6. Number and Distribution of Sensilla
4. Discussions
4.1. Antennal Morphological Differentiation
4.2. Diversity and Functional Specialization of Sensilla
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Wechsler, S.P.; Bhandawat, V. Behavioral algorithms and neural mechanisms underlying odor-modulated locomotion in insects. J. Exp. Biol. 2023, 226, jeb200261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadenne, C.; Barrozo, R.B.; Anton, S. Plasticity in insect olfaction: To smell or not to smell? Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.N.; Xiang, S.S.; Zhu, H. Research progress on the types and functions of insect antennae sensilla. J. Environ. Entomol. 2023, 45, 1197–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Yokohari, F. The sensillum capitulum, an antennal hygro-and thermoreceptive sensillum of the cockroach, Periplaneta americana L. Cell Tissue Res. 1981, 216, 525–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D. Insect antennae. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1964, 9, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, O.; Barata, E.N.; Mustaparta, H.; Araújo, J. Fine structure of antennal sensilla basiconica and their detection of plant volatiles in the eucalyptus woodborer, Phoracantha semipunctata Fabricius (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2002, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, K.P.; Wilgenburg, E.V.; Macmillan, D.L.; Elgar, M.A. Density of antennal sensilla influences efficacy of communication in a social insect. Am. Nat. 2013, 182, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Guo, H.; Hou, C.; Wu, H.; Huang, L.Q.; Wang, C.Z. Olfactory perception and behavioral effects of sex pheromone gland components in Helicoverpa armigera and Helicoverpa assulta. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22998. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, M.J. Antennal sensilla of the weaver ant Oecophylla smaragdina (F.)-males and females sense differently? Indian J. Entomol. 2019, 81, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialho, M.D.Q.; Guss-Matiello, C.P.; Zanuncio, J.C.; Campos, L.A.O.; Serrao, J.E. A comparative study of the antennal sensilla in corbiculate bees. J. Apic. Res. 2014, 53, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.T.; Liu, G.T.; Wang, Q.K.; Yan, L.P.; Liu, X.H.; Li, X.Y.; Pape, T.; Zhang, D. Ultrastructure of antennal sensory organs in nine flesh flies (Diptera: Sarcophagidae): New insight into the definition of family Sarcophagidae. Insects 2022, 13, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidori, C.; Jorge, A.; Ornosa, C. Antennal morphology and sensillar equipment vary with pollen diet specialization in Andrena bees. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2020, 57, 100950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidori, C.; Jorge, G.A.; Nieves-Aldrey, J.L. Antennal sensillar equipment in closely related predatory wasp species (Hymenoptera: Philanthinae) hunting for different prey types. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2012, 335, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvani, G.L.; Gonzalez-Vaquero, R.A.; Guerra-Navarro, C.; Settembrini, B.P. Antennal sensilla of cleptoparasitic and non-parasitic bees in two subfamilies of Apidae. Apidologie 2017, 48, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wcislo, W.T. Sensilla numbers and antennal morphology of parasitic and non-parasitic bees (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). Int. J. Insect Morphol. Embryol. 1995, 24, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agren, L.; Hallberg, E. Flagellar sensilla of bumble bee males (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Bombus). Apidologie 1996, 27, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, H.S.; Preisler, H.D.; Kanter, P.M. DNA damage in AML cell exposed to adriamycin; correlations with clinical response to therapy. Leuk. Res. 1981, 5, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgar, M.A.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Q. Focus: Ecology and evolution: Insect antennal morphology: The evolution of diverse solutions to odorant perception. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2018, 91, 457. [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth, D.C.; Ammagarahalli, B.; Layne, J.E.; Rollmann, S.M. Evolution of coeloconic sensilla in the peripheral olfactory system of Drosophila mojavensis. J. Insect Physiol. 2018, 110, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, S.G.; Wingfield, M.J.; Hurley, B.P.; Slippers, B. Diversity in Eucalyptus susceptibility to the gall-forming wasp Leptocybe invasa. Agric. For. Entomol. 2012, 14, 419–427. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Li, J.; Lu, W.; Zheng, X.L.; Yang, Z.D. Parasitoids of the eucalyptus gall wasp Leptocybe spp.: A global review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 29983–29995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burks, R.A.; Mottern, J.L.; Pownall, N.G.; Paine, D.T. First record of Closterocerus chamaeleon, parasitoid of the Eucalyptus gall wasp Ophelimus maskelli (Hymenoptera, Chalcidoidea, Eulophidae), in the New World. ZooKeys 2015, 504, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, D.A.; Hernández, C.M.; Cuello, E.M.; Andorno, A.V.; Botto, E.N. Primera cita de la Argentina de Ophelimus maskelli (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera:Eulophidae) y su parasitoide, Closterocerus chamaeleon (Girault) (Hymenoptera:Eulophidae). Rev. Soc. Entomol. Argent. 2014, 73, 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Wondafrash, M.; Slippers, B.; Nambazimana, A.; Kayumba, I.; Nibouche, S. Distribution and genetic diversity of five invasive pests of Eucalyptus in sub-Saharan Africa. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 2205–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, J.; Pudjianto; Harahap, I.S. Current Infestation Status and Damage Severity of Eucalyptus Gall Wasps, Leptocybe invasa (Fisher & La Salle), and Ophelimus maskelli Ashmead (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), Infesting Eucalyptus Germplasms in Tanzania. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1208, 12010. [Google Scholar]
- Protasov, A.; Blumberg, D.; Brand, D.; La Salle, J.; Mendel, Z. Biological control of the gall wasp Ophelimus maskelli (Ashmead): Taxonomy and biology of the parasitoid species Closterocerus chamaeleon (Girault), with information on its establishment in Israel. Biol. Control 2007, 42, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, I. Descubiertas dos nuevas plagas del eucalipto en España. Quercus 2003, 214, 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, J.T.; Mendel, Z.; Protasov, A.; La Salle, J. Two New Species of Stethynium (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae), Australian Larval Parasitoids of Ophelimus maskelli (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) on Eucalyptus. J. Nat. Hist. 2006, 40, 1909–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuela, B.; Conceicao, B.; Nicolas, D.; Carlos, F.J.; Zvi, M. Presence of the Eucalyptus gall wasp Ophelimus maskelli and its parasitoid Closterocerus chamaeleon in Portugal: First record, geographic distribution and host preference. Phytoparasitica 2009, 37, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Tang, R.T.; Huang, T.W.; Zheng, L.X. Ultrastructure and sense organs of ovipositors in the phytophagous gall-maker pest Ophelimus maskelli (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) and its parasitoid, Closterocerus chamaeleon (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2025, 28, 102424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Yao, J.M.; Huang, S.B.; Pang, H. Ophelimus bipolaris sp. n. (Hymenoptera, Eulophidae), a new invasive Eucalyptus pest and its host plants in China. Insects 2021, 12, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.X.; Zhang, Z.N. Scanning electron microscopy observation of antennae receptors of Microplitis mediator. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2006, 6, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.X.; Wan, F.H. Scanning electron microscopy observation of antennae of the Campoletis chlorideae sensilla. Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2007, 23, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Diakova, A.V.; Makarova, A.A.; Polilov, A.A. Between extreme simplification and ideal optimization: Antennal sensilla morphology of miniaturized Megaphragma wasps (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). PeerJ 2018, 6, e6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Q.C.; Chen, S.Z.; Li, C.W. Observation of Tetrastichus septentrionalis antenna with scanning electron microscope. Plant Prot. 2016, 42, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Onagbola, E.O.; Fadamiro, H.Y. Scanning electron microscopy studies of antennal sensilla of Pteromalus cerealellae (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Micron 2008, 39, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Hong, J.; Hu, C. Ultrastructural studies on the antennal sensilla of Pteromalus puparum (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. 2000, 26, 394–398. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yang, P.; Peng, Y.; Yang, D. Ultrastructure of antennal sensilla of female Ceratosolen solmsi marchali (Hymenoptera:Chalcidoidea:Agaonidae: Agaoninae). Can. Entomol. 2009, 141, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.Y.; Zhang, L.S.; Chen, H.Y. Scanning electron microscopic observation on sensilla of the antenna in female Diglyphus isaea. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2009, 46, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Liang, Q.C.; Wu, W.J.; Huang, J. Ultrastructural Studies on Sensilla of Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) Adult. J. South Chin. Agric. Univ. 2007, 28, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.Y.; Xu, M.; Lin, L.L.; Liao, R.F.; Wu, Y. Ultrastructure of sensilla of Leptocybe invasa. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2010, 47, 752–758. [Google Scholar]
- Loo, J.X.; Ong, Y.C.; Tee, S.C.; Wong, L.W. Morphometric analysis of antennae of three female Brachymeria species (Hymenoptera: Chalcididae), parasitoids from the oil palm bagworm, Metisa plana Walker (Lepidoptera: Psychidae). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2025, 45, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, P.; Cristina, M.; Michele, M.; Chiara, S.; Milvia, C. Morphological characterization of the antenna of Torymus sinensis (Hymenoptera: Torymidae) and a comparison within the superfamily Chalcidoidea. Arthropod Str. Dev. 2024, 78, 101325. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, E.I.; Gostin, N.I. A New Species of Megastigmus and First Record of the Genus and Megastigmidae Family from the Paradise of the Maldives Archipelago. Insects 2023, 14, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovici, O.; Bin, F.; Masner, L.; Popovici, M.; Notton, D. Triteleia peyerimhoffi comb. n., a remarkably variable circum-Mediterranean scelionid (Hymenoptera, Platygastroidea). ZooKeys 2011, 140, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z. A Comparative Morphological Study of the Ultrastructure of Antennal Sensilla in Sclerodermus guani (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae). Insects 2025, 16, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, X.; Wang, H.; Shen, G.; Zhang, H. Antennal morphology and sensilla ultrastructure of the web-spinning sawfly Acantholyda posticalis Matsumura (Hymenoptera: Pamphiliidae). Micron 2013, 50, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Huang, X.; Ullah, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Xu, H.; Wen, Q.; Tian, X.; Tan, J. Comparative SEM Study of Sensilla and Tyloid Structures in the Antennae of Vespinae (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Insects 2024, 15, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharuk, R.Y. Antennae and sensilla. Comp. Insect Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1985, 6, 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, W.N.; Vinson, S.B. Antennal sensilla of three parasitic Hymenoptera. Int. J. Insect Morphol. Embryol. 1974, 3, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.H.; Zheng, L.X.; Liao, Y.L.; Wu, W.J. Sexual dimorphism in antennal morphology and sensilla ultrastructure of a pupal endoparasitoid Tetrastichus howardi (Olliff) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2016, 79, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.C.; Loo, J.X.; Tee, S.C.; Wong, W.L. Distribution and morphometric studies on antennal sensilla of female and male Pediobius imbreus (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Zoomorphology 2024, 143, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.W.; Siang, C.T.; Chuan, A.P.O.; Lim, W.W. Sexual dimorphism of antennal and ovipositor sensilla of Tetrastichus sp. (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2021, 24, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar]
- Mankin, R.W.; Mayer, M.S. The insect antenna is not a molecular sieve. Experientia 1984, 40, 1251–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, A.; Houston, T.F.; Ball, A.D.; Goral, T.; Barclay, M.V.; Cox, J.P. Towards an understanding of molecule capture by the antennae of male beetles belonging to the genus Rhipicera (Coleoptera, Rhipiceridae). Anat. Rec. 2015, 298, 1519–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.C.; Gao, S.S.; Wang, J.S.; Zhang, K.P. Ultramorphology of Female Andricus moriokae (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae). Sci. Silvae Sin. 2021, 57, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.H.; Zhang, M.; Shi, J.N.; Li, K.; Zhang, D. Ultrastructure of antennal sensilla of a parasitoid fly, Pales pavida Meigen (Diptera: Tachinidae). Micron 2013, 54, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.J.; Chen, D.; Fan, X.J.; LIu, L.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, C.H.; Ren, G.W.; Liu, X.D. Antennal Ultrastructure of Aphidius gifuensis and the Effect of Cold Storage on Antennae. Sci. Agri. Sin. 2014, 47, 4637–4647. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, D. The sense of smell in insects. Sci. Am. 1964, 210, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Slifer, E.H. Structure of insect sensilla. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1970, 15, 121–142. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Yang, Z.D.; Lu, W.; Zheng, L.X. Ultrastructure of female antennal sensilla of an endoparasitoid wasp, Quadrastichus mendeli Kim and La Salle (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae: Tetrastichinae). Microsc. Microanal. 2018, 24, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, Z.B.; Yang, D.R.; Peng, Y.Q.; Finn, K. Comparison of the antennal sensilla of females of four fig-wasps associated with Ficus auriculata. Acta Oecol. 2018, 90, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.L.; Zong, S.X.; Luo, Y.Q. Sensilla on the antennae and ovipositor of the sea buckthorn carpenter moth, Holcocerus hippophaecolus Hua et al. (Lepidoptera: Cossidae). Neotrop. Entomol. 2015, 44, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.C.; Meng, Z.J.; Peng, L.; Liu, D. Antennal sensilla of the pine weevil Pissodes nitidus Roel. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2011, 74, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keil, T.A. Morphology and Development of the Peripheral Olfactory Organs. In Insect Olfaction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 5–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Luo, L.Z.; Hammond, A. Antennal morphology, structure and sensilla distribution in Microplitis pallidipes (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Micron 2007, 38, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, B.J.; Boivin, G.; Bourdais, D.; Roux, O.E. Antennal sensilla of hymenopteran parasitic wasps: Variations linked to host exploitation behavior. Mod. Res. Educ. Top. Microsc. 2007, 1, 345–352. [Google Scholar]
- Shiota, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Daimon, T.; Mitsuno, H.; Fujii, T.; Matsuyama, S.; Sezutsu, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Kanzaki, R. In vivo functional characterization of pheromone binding protein-1 in the silkmoth Bombyx mori. Sci. Rep. 2018, 1, 13529. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Chang, H.; Liu, W.; Cui, W.C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Ren, B.Z.; Wang, G.R. Essential role for SNMP1 in detection of sex pheromones in Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 127, 103485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochieng, S.A.; Park, K.C.; Zhu, J.W.; Baker, T.C. Functional morphology of antennal chemoreceptors of the parasitoid Microplitis croceipes (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2000, 29, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, A.; Compton, S. Repeated evolution of elongate multiporous plate sensilla in female fig wasps (Hymenoptera: Agaonidae: Agaoninae). Proc. K. Ned. Akad. Wet. 1992, 95, 275–292. [Google Scholar]
- Aldworth, Z.N.; Stopfer, M. Olfactory coding: Tagging and tuning odor-activated synapses for memor. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R227–R229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Proffit, M.; Schatz, B.; Borges, R.M.; Hossaert-Mckey, M. Chemical mediation and niche partitioning in non-pollinating fig-wasp communities. J. Anim. Ecol. 2007, 76, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segar, S.T.; Dunn, D.W.; Darwell, C.T.; Cook, J.M. How to be a fig wasp, down under: The diversity and structure of an Australian fig wasp community. Acta Oecologica 2014, 57, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Castes and Types | Length | Width | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LI | OB | OM | LI | OB | OM | |
| BS | 5.78 ± 0.39 Af | 3.13 ± 0.22 Be | 3.03 ± 0.31 Bd | 1.20 ± 0.08 Ad | 1.26 ± 0.05 Acd | 0.71 ± 0.04 Bd |
| CH | 12.25 ± 0.44 Be | 14.66 ± 0.45 Ad | 13.19 ± 0.71 ABc | 1.12 ± 0.02 Ad | 1.10 ± 0.01 Ad | 0.98 ± 0.02 Bc |
| TSI | 21.30 ± 0.75 Ad | 16.97 ± 0.16 Bc | 13.69 ± 0.12 Cc | 1.24 ± 0.09 ABcd | 1.36 ± 0.07 Ac | 0.97 ± 0.07 Bc |
| TSII | 50.84 ± 0.97 Aa | 35.57 ± 0.18 Ba | 25.02 ± 0.86 Cb | 1.62 ± 0.15 Ac | 2.00 ± 0.04 Ab | 1.98 ± 0.05 Ab |
| TSIII | - | 33.86 ± 0.50 b | - | - | 1.87 ± 0.06 b | - |
| PSI | 32.73 ± 0.17 c | - | - | 5.12 ± 0.13 a | - | - |
| PSII | 36.26 ± 0.14 b | - | - | 2.59 ± 0.07 b | - | - |
| PSIII | - | 34.24 ± 0.12 Ab | 27.42 ± 0.73 Ba | - | 3.47 ± 0.06 Aa | 2.49 ± 0.09 Ba |
| CS | 2.77 ± 0.06 Ag | 2.51 ± 0.33 Ae | 2.69 ± 0.09 Ad | 1.25 ± 0.10 Acd | 1.37 ± 0.08 Ac | 1.15 ± 0.04 Ac |
| Castes and Types | Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LI | OB | OM | |
| BS | 7.33 ± 0.88 Ad | 8.67 ± 0.88 Ae | 6.67 ± 1.20 Ad |
| CH | 40.67 ± 1.45 Ba | 53.33 ± 1.20 Ab | 24.00 ± 1.15 Cb |
| TSI | 25.67 ± 1.20 Cb | 109.33 ± 0.88 Aa | 81.00 ± 1.53 Ba |
| TSII | 40.00 ± 1.15 Aa | 23.00 ± 0.58 Bd | 17.67 ± 0.88 Cc |
| TSIII | - | 22.67 ± 1.15 d | - |
| PSI | 13.33 ± 1.20 c | - | - |
| PSII | 27.67 ± 0.88 b | - | - |
| PSIII | - | 36.67 ± 0.88 Ac | 13.66 ± 1.20 Bc |
| CS | 4.00 ± 0.58 Ad | 3.00 ± 0.58 Af | 1.66 ± 0.67 Ad |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Xu, X.; Yang, Z. Comparison of Morphological Characteristics of Antennae and Antennal Sensilla Among Three Species of Gall Wasps (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Insects 2025, 16, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090976
Xie J, Liu Y, Li J, Zhou L, Xu X, Yang Z. Comparison of Morphological Characteristics of Antennae and Antennal Sensilla Among Three Species of Gall Wasps (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Insects. 2025; 16(9):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090976
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Jinting, Yi Liu, Junjue Li, Leming Zhou, Xiu Xu, and Zhende Yang. 2025. "Comparison of Morphological Characteristics of Antennae and Antennal Sensilla Among Three Species of Gall Wasps (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae)" Insects 16, no. 9: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090976
APA StyleXie, J., Liu, Y., Li, J., Zhou, L., Xu, X., & Yang, Z. (2025). Comparison of Morphological Characteristics of Antennae and Antennal Sensilla Among Three Species of Gall Wasps (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Insects, 16(9), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090976






