Distribution of Larval Habitats and Efficiency of Various Trap Settings to Monitor Sympatric Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti in La Reunion
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Traps
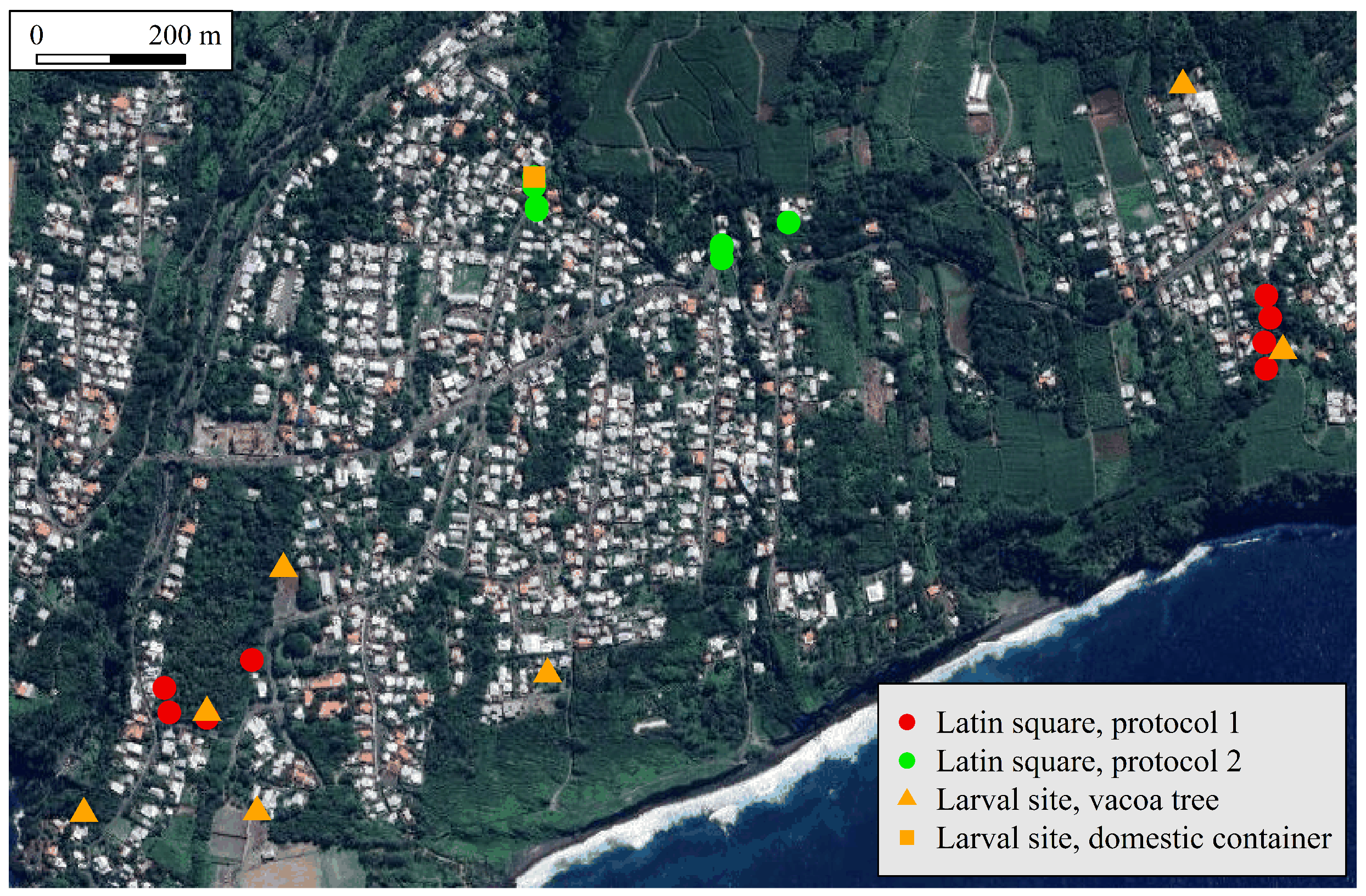
2.2. Design
- Protocol 1: A ravine located in the eastern part of the study site, and an orchard located in its western part;
- Protocol 2: Two close sets located in an urban area located in the northern part of the study site.
- Protocol 1: Every 24 h for BGS traps and ovi-sticky traps;
- Protocol 2: Every week, with BGS traps left in place for 48 h, and ovi-sticky traps for one week.
2.3. Larval Habitat
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
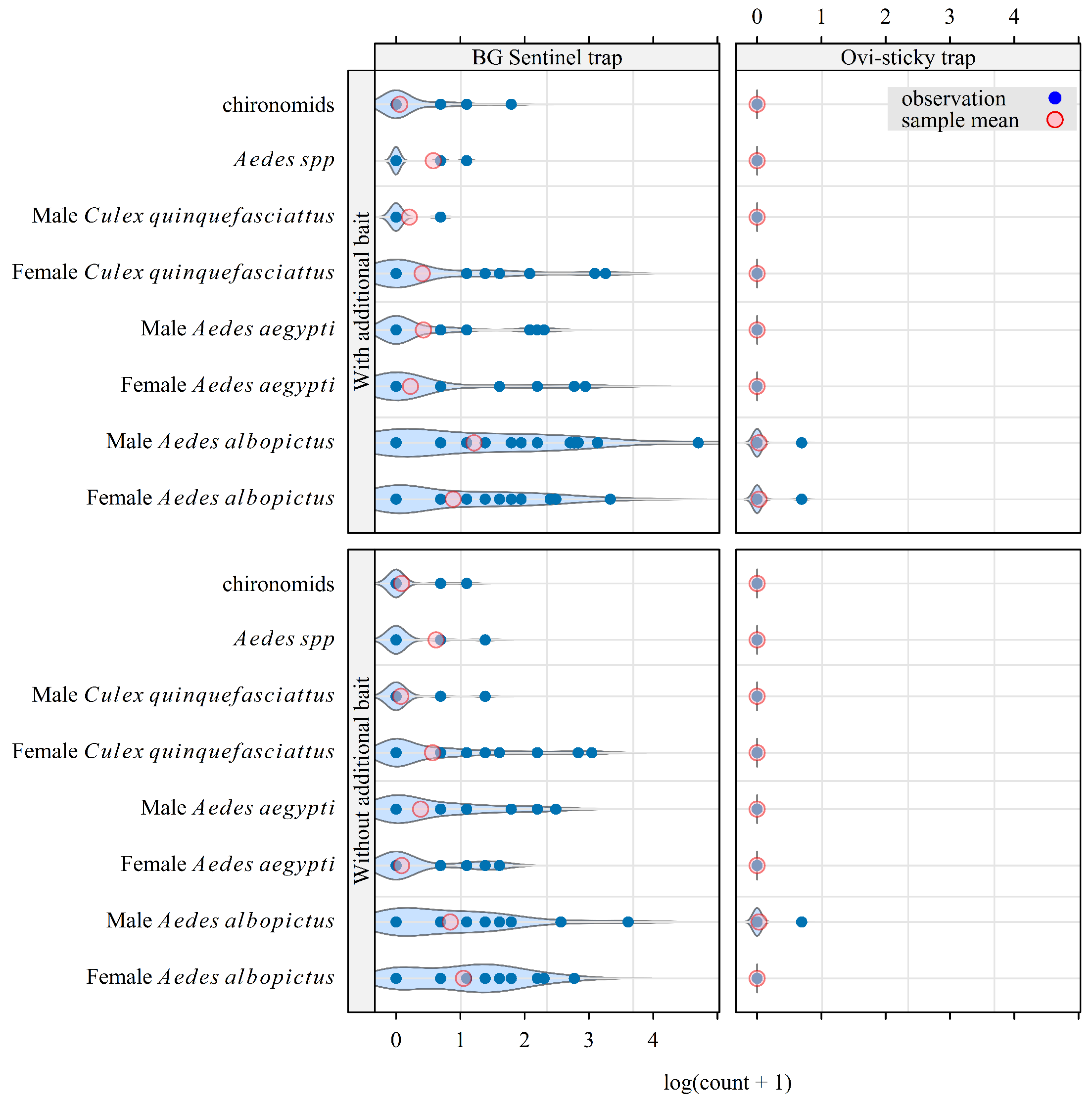
3.1. Insect Catches
3.2. Effect of Lure on CO2-Baited Traps’ Attractiveness
- Without lure, the attractiveness of the CO2-baited trap was the same for the females and the males of both species.
- With lure, the attractiveness of the CO2-baited trap was unchanged for the females of both species, as well as for male Ae. aegypti. In contrast, it was 4.3 times higher for male than for female Ae. albopictus: relative attractiveness , 95% credible interval [2.2; 7.6].
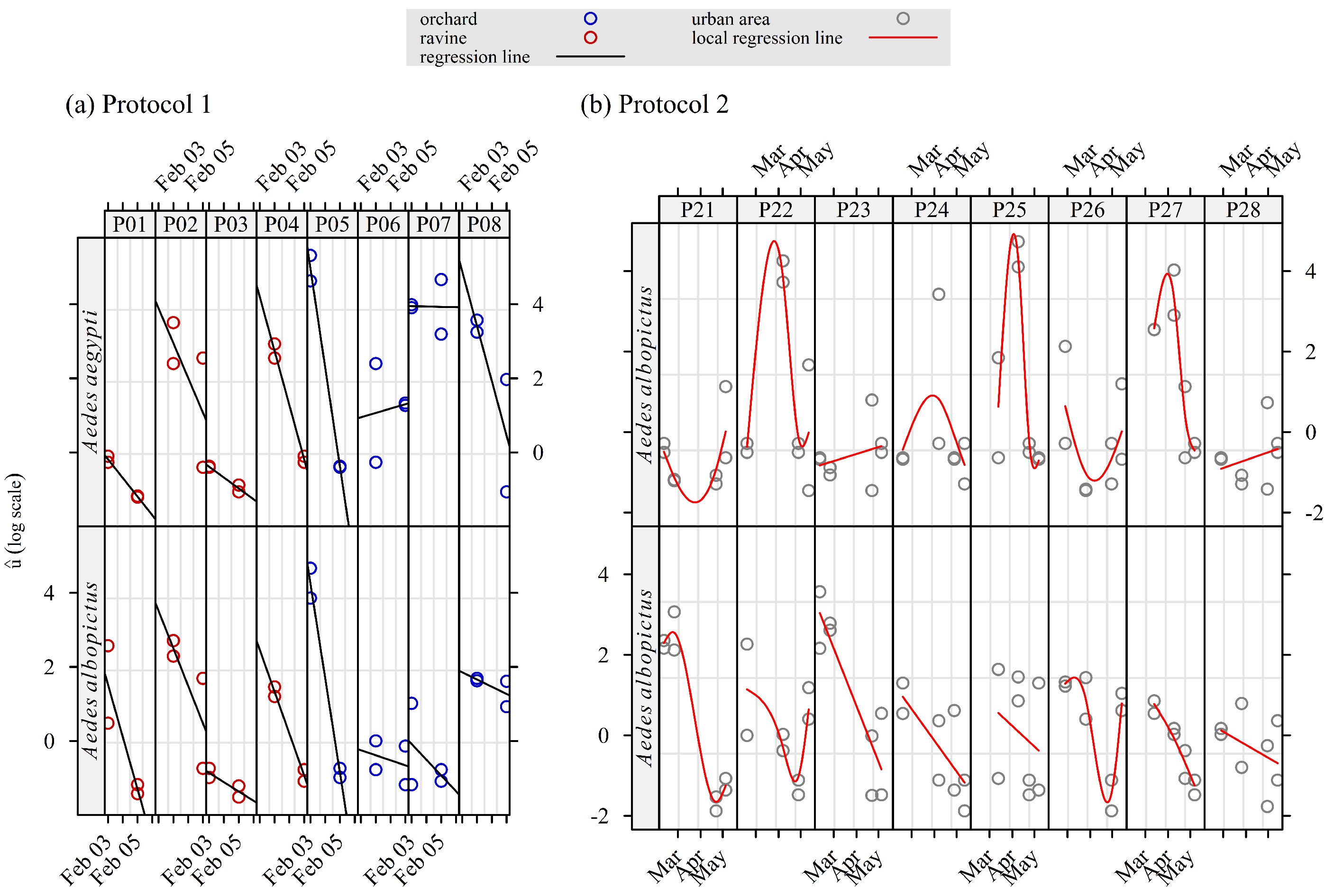
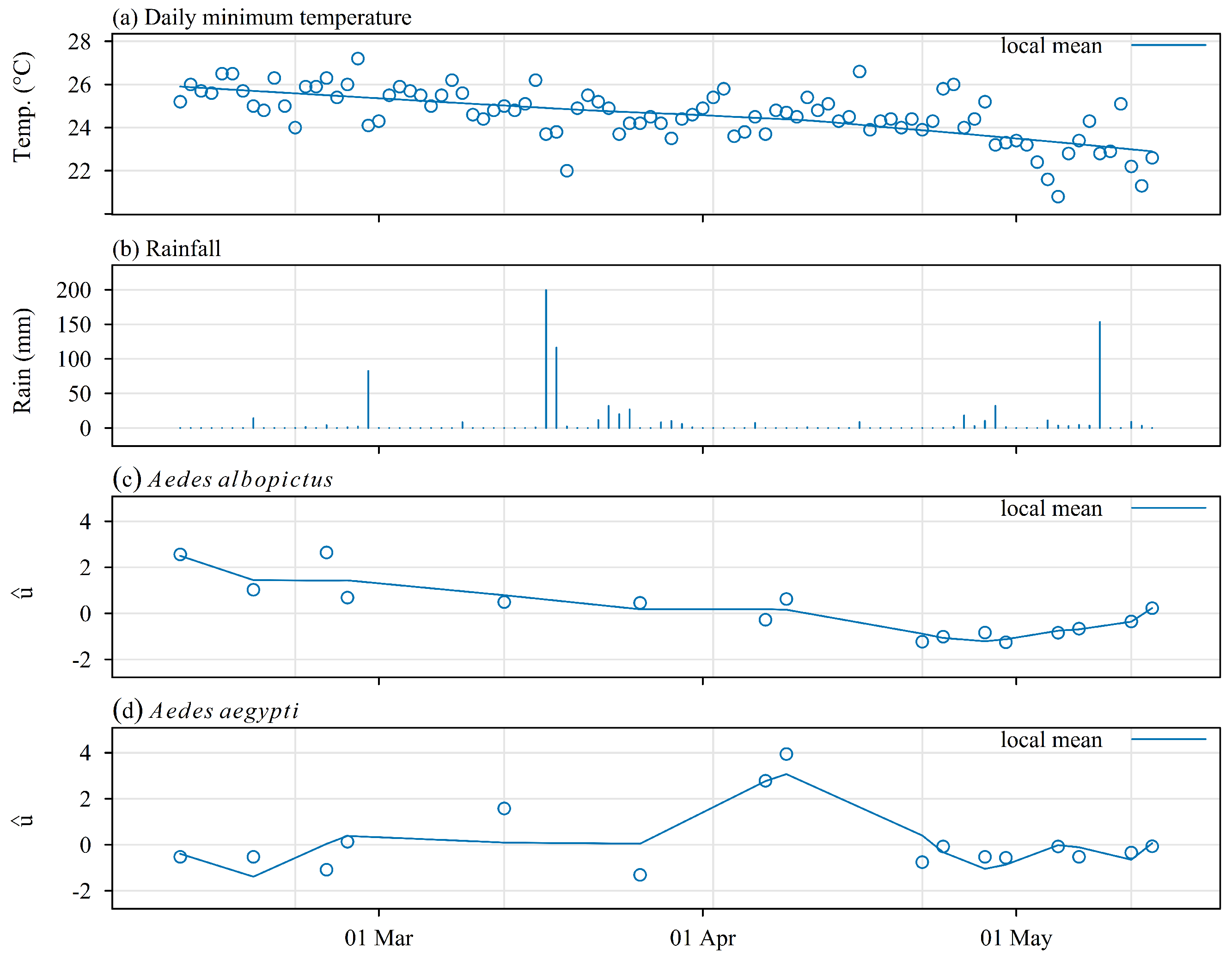
3.3. Variations in Space and Time
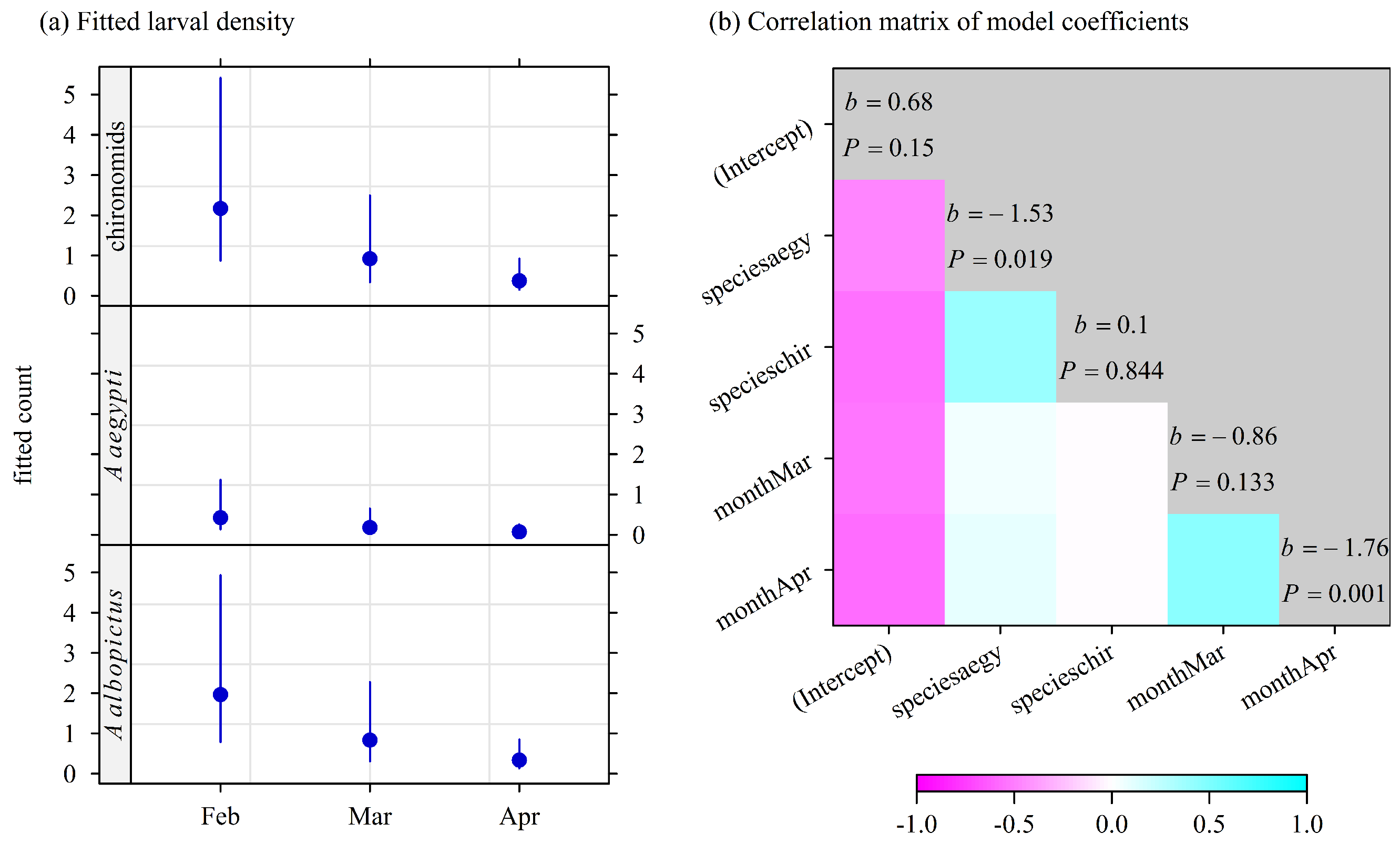
3.4. Larvae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ae. aegypti | Aedes aegypti |
| Ae. albopictus | Aedes albopictus |
| BG | Biogents, Germany |
| BGS | Biogents Sentinel, Germany |
| CO2 | carbon dioxide |
| FEDER | Fonds Européen de Développement Régional |
| OpTIS | Opérationalisation de la technique de l’insecte stérile |
| SIT | Sterile Insect Technique |
References
- Hafsia, S.; Haramboure, M.; Wilkinson, D.A.; Baldet, T.; Yemadje-Menudier, L.; Vincent, M.; Tran, A.; Atyame, C.; Mavingui, P. Overview of dengue outbreaks in the southwestern Indian Ocean and analysis of factors involved in the shift toward endemicity in Reunion Island: A systematic review. PLoS Neglected Trop Dis. 2022, 16, e0010547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumahoro, M.K.; Boelle, P.Y.; Gaüzere, B.A.; Atsou, K.; Pelat, C.; Lambert, B.; La Ruche, G.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, M.; Renault, P.; Sarazin, M.; et al. The Chikungunya epidemic on La Réunion Island in 2005–2006: A cost-of-illness study. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrieu, S.; Balleydier, E.; Renault, P.; Baville, M.; Filleul, L. Epidemiological surveillance of chikungunya virus in Reunion Island from 2005 to 2011. Med. Trop. 2012, 72, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Salvan, M.; Mouchet, J. Aedes albopictus et Aedes aegypti à l’Ile de La Réunion [Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti at Ile de la Réunion]. Ann. Soc. Belg. Med. Trop. 1994, 74, 323–326. [Google Scholar]
- Delatte, H.; Dehecq, J.S.; Thiria, J.; Domerg, C.; Paupy, C.; Fontenille, D. Geographic Distribution and Developmental Sites of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) During a Chikungunya Epidemic Event. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2008, 8, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagny, L.; Delatte, H.; Quilici, S.; Fontenille, D. Progressive Decrease in Aedes aegypti Distribution in Reunion Island Since the 1900s. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, M.; Larrieu, S.; Vilain, P.; Etienne, A.; Solet, J.L.; François, C.; Roquebert, B.; Bandjee, M.C.J.; Filleul, L.; Menudier, L. From the threat to the large outbreak: Dengue on Reunion Island, 2015 to 2018. Euro Surveill. 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, M.; Paty, M.C.; Gerardin, P.; Balleydier, E.; Etienne, A.; Daoudi, J.; Thouillot, F.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.C.; Menudier, L. From dengue outbreaks to endemicity: Reunion Island, France, 2018 to 2021. Euro Surveill. 2023, 28, 2200769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumence, E.; Piorkowski, G.; Traversier, N.; Amaral, R.; Vincent, M.; Mercier, A.; Ayhan, N.; Souply, L.; Pezzi, L.; Lier, C.; et al. Genomic insights into the re-emergence of chikungunya virus on Réunion Island, France, 2024 to 2025. Euro Surveill. Bull. Eur. Sur Les Mal. Transm. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2025, 30, 2500344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, J. Current status of the sterile insect technique for the suppression of mosquito populations on a global scale. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2024, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, M.S.; Craig, G.B.; Despommier, D.D. The protein nature of the substance inducing female monogamy in Aedes aegypti. J. Insect Physiol. 1969, 15, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, C.F.; Damiens, D.; Vreysen, M.J.B.; Lemperière, G.; Gilles, J. Reproductive Strategies of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) and Implications for the Sterile Insect Technique. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyaloo, D.P.; Bouyer, J.; Facknath, S.; Bheecarry, A. Pilot Suppression trial of Aedes albopictus mosquitoes through an Integrated Vector Management strategy including the Sterile Insect Technique in Mauritius. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouagna, L.C.; Damiens, D.; Oliva, C.F.; Boyer, S.; Le Goff, G.; Brengues, C.; Dehecq, J.S.; Raude, J.; Simard, F.; Fontenille, D. Strategic approach, advances, and challenges in the development and application of the sit for area-wide control of Aedes albopictus mosquitoes in Reunion Island. Insects 2020, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquereau, L.; Derepas, B.; Leclercq, A.; Gouagna, L.C. Standardization of irradiation process of Aedes albopictus males under mass-rearing conditions in support of SIT program in La Reunion Island. In Proceedings of the Mosquito Irradiation, Sterilization and Quality Control. Report of the First Research Coordination Meeting of an FAO/IAEA Coordinated Research Project, Vienna, Austria, 31 May–4 June 2021; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Marquereau, L.; Yamada, H.; Damiens, D.; Leclercq, A.; Derepas, B.; Brengues, C.; Dain, B.W.; Lejarre, Q.; Proudhon, M.; Bouyer, J.; et al. Upscaling irradiation protocols of Aedes albopictus pupae within an SIT Programme in Reunion Island. Sci. Rep. 2024, 2024, 12117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, J.; Lefrançois, T. Boosting the sterile insect technique to control mosquitoes. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupraz, M.; Lancelot, R.; Diouf, G.; Malfacini, M.; Marquereau, L.; Gouagna, L.C.; Rossignol, M.; Chandre, F.; Baldet, T.; Bouyer, J. Comparison of the standard and boosted sterile insect techniques for the suppression of Aedes albopictus populations under semi-field conditions. Parasites 2025, 32, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, J.; Almenar Gil, D.; Pla Mora, I.; Dalmau Sorli, V.; Maïga, H.; Mamai, W.; Claudel, I.; Brouazin, R.; Yamada, H.; Gouagna, L.C.; et al. Suppression of Aedes mosquito populations with the boosted sterile insect technique in tropical and Mediterranean urban areas. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 17648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudel, I.; Brouazin, R.; Lancelot, R.; Gouagna, L.C.; Dupraz, M.; Baldet, T.; Bouyer, J. Optimization of adult mosquito trap settings to monitor populations of Aedes and Culex mosquitoes, vectors of arboviruses in La Reunion. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.; Chong, C.S.; Yap, G.; Lee, C.; Abdul Razak, M.A.; Chiang, S.; Ng, L.C. Gravitrap deployment for adult Aedes aegypti surveillance and its impact on dengue cases. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.H.; Lim, J.T.; Ong, J.; Hapuarachchi, H.C.; Sim, S.; Ng, L.C. Singapore’s 5 decades of dengue prevention and control-Implications for global dengue control. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.; Lim, J.T.; Chong, C.S.; Dickens, B.; Ng, Y.; Deng, L.; Lee, C.; Tan, L.Y.; Kakani, E.G.; Yoong, Y.; et al. Effectiveness of Wolbachia-mediated sterility coupled with sterile insect technique to suppress adult Aedes aegypti populations in Singapore: A synthetic control study. Lancet Planet. Health 2024, 8, e617–e628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouazin, R.; Claudel, I.; Lancelot, R.; Dupuy, G.; Gouagna, L.C.; Dupraz, M.; Baldet, T.; Bouyer, J. Optimization of oviposition trap settings to monitor populations of Aedes mosquitoes, vectors of arboviruses in La Reunion. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARS Réunion. Clé d’Identification des Moustiques de La Réunion aux Stades Adulte et Larvaires; Technical Report; ARS Réunion: Saint Denis, France, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, X.A. Using observation-level random effects to model overdispersion in count data in ecology and evolution. PeerJ 2014, 2, e616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rue, H.; Riebler, A.I.; Sørbye, S.H.; Illian, J.B.; Simpson, D.P.; Lindgren, F.K. Bayesian computing with INLA: A review. Annu. Rev. Stat. Its Appl. 2017, 4, 395–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Barclay, H.J. Modelling the effects of population aggregation on the efficiency of insect pest control. Res. Popul. Ecol. 1992, 34, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinde, J.; Demétrio, C.G.B. Overdispersion: Models and estimation. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 1998, 27, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullagh, P.; Nelder, J.A. Generalized Linear Models, 2nd ed.; Monographs on statistics and applied probability; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1989; Volume 37, p. 532. [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, K.; Anderson, D. Kullback-Leibler information as a basis for strong inference in ecological studies. Wildl. Res. 2001, 28, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delatte, H.; Toty, C.; Boyer, S.; Bouetard, A.; Bastien, F.; Fontenille, D. Evidence of habitat structuring Aedes albopictus populations in Réunion Island. PLoS Neglected Trop Dis. 2013, 7, e2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latreille, A.C.; Milesi, P.; Magalon, H.; Mavingui, P.; Atyame, C.M. High genetic diversity but no geographical structure of Aedes albopictus populations in Réunion Island. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsakiozi, P.; Evans, B.R.; Gloria-Soria, A.; Kamgang, B.; Mayanja, M.; Lutwama, J.; Goff, G.L.; Ayala, D.; Paupy, C.; Badolo, A.; et al. Population structure of a vector of human diseases: Aedes aegypti in its ancestral range, Africa. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 7835–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soghigian, J.; Gloria-Soria, A.; Robert, V.; Goff, G.L.; Failloux, A.B.; Powell, J.R. Genetic evidence for the origin of Aedes aegypti, the yellow fever mosquito, in the southwestern Indian Ocean. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 3593–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, A.B.B.; Carvajal, A.; Medina, J.; Anderson, M.; Nieves, V.J.; Ramirez, M.; Vasquez, C.; Petrie, W.; Cardenas, G.; Beier, J.C. Assessment of the effectiveness of BG-Sentinel traps baited with CO2 and BG-Lure for the surveillance of vector mosquitoes in Miami-Dade County, Florida. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, E.; Bernard, C.; Lecollinet, S.; Rakotoharinome, V.; Ravaomanana, J.; Roger, M.; Olive, M.; Meenowa, D.; Jaumally, M.; Melanie, J.; et al. West Nile virus infection in horses, Indian Ocean. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 53, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomard, Y.; Lebon, C.; Mavingui, P.; Atyame, C.M. Contrasted transmission efficiency of Zika virus strains by mosquito species Aedes aegypti, Aedes albopictus and Culex quinquefasciatus from Reunion Island. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, J.; Iyaloo, D.; Baldet, T. Preventing the establishment of invasive exotic mosquitoes. Trends Parasitol. 2025, 41, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidlingmayer, W.L. A comparison of trapping methods for adult mosquitoes: Species response and environmental influence. J. Med. Entomol. 1967, 4, 200–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARS Réunion. Intervention de l’ARS, Démoustication. 2025. Available online: https://www.lareunion.ars.sante.fr/intervention-de-lars-demoustication (accessed on 11 August 2025).

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vitry, C.; Brouazin, R.; Herbin, A.; Whiteside, M.; Brengues, C.; Baldet, T.; Lancelot, R.; Bouyer, J. Distribution of Larval Habitats and Efficiency of Various Trap Settings to Monitor Sympatric Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti in La Reunion. Insects 2025, 16, 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090932
Vitry C, Brouazin R, Herbin A, Whiteside M, Brengues C, Baldet T, Lancelot R, Bouyer J. Distribution of Larval Habitats and Efficiency of Various Trap Settings to Monitor Sympatric Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti in La Reunion. Insects. 2025; 16(9):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090932
Chicago/Turabian StyleVitry, Caroline, Ronan Brouazin, Anthony Herbin, Mathieu Whiteside, Cécile Brengues, Thierry Baldet, Renaud Lancelot, and Jérémy Bouyer. 2025. "Distribution of Larval Habitats and Efficiency of Various Trap Settings to Monitor Sympatric Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti in La Reunion" Insects 16, no. 9: 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090932
APA StyleVitry, C., Brouazin, R., Herbin, A., Whiteside, M., Brengues, C., Baldet, T., Lancelot, R., & Bouyer, J. (2025). Distribution of Larval Habitats and Efficiency of Various Trap Settings to Monitor Sympatric Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti in La Reunion. Insects, 16(9), 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16090932





